A Low Peak-to-average Ratio Secure Transmission Method Based on U Matrix Transformation in Orthogonal Time and Frequency Space System
-
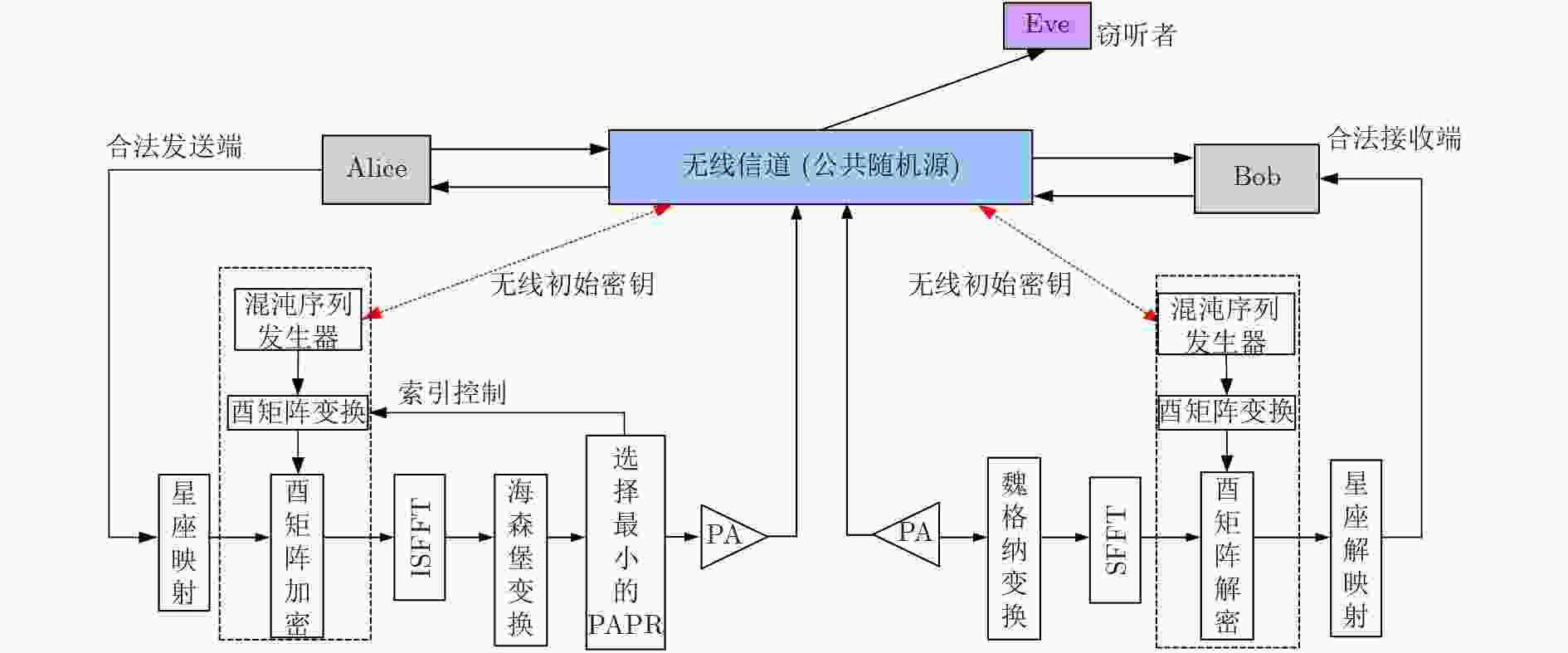
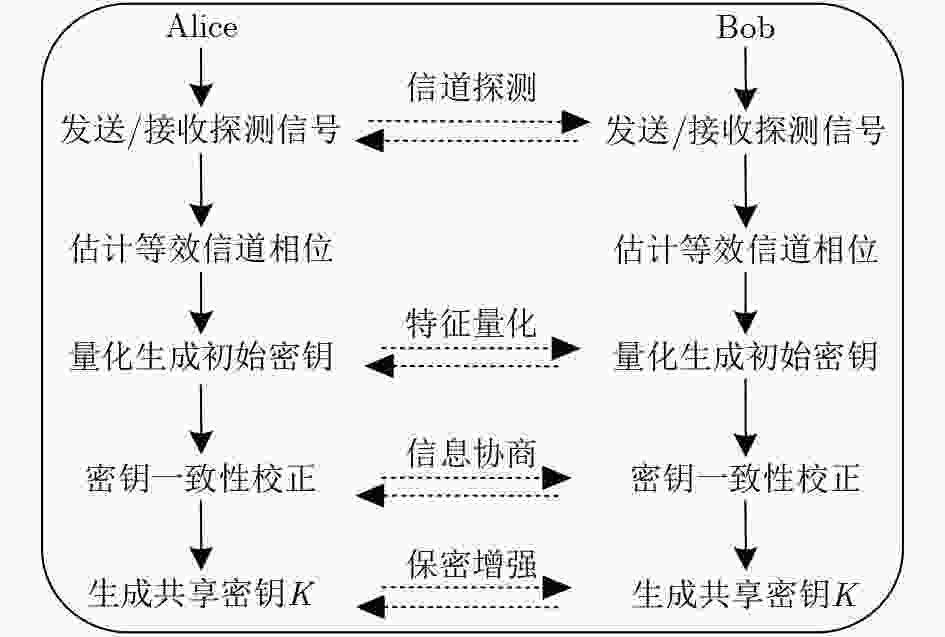
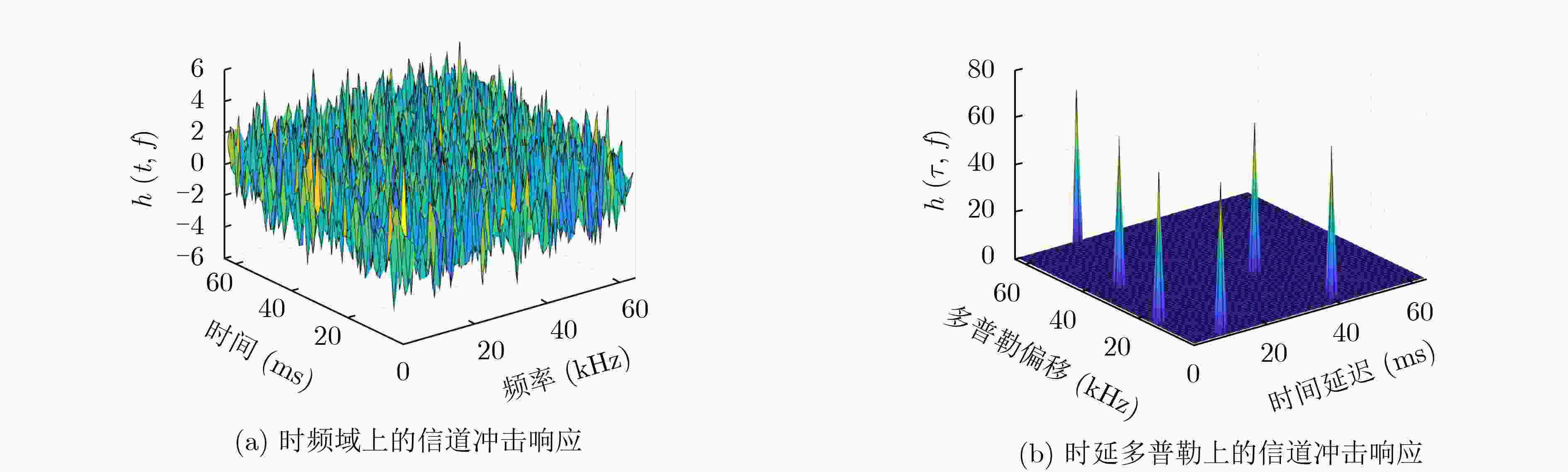
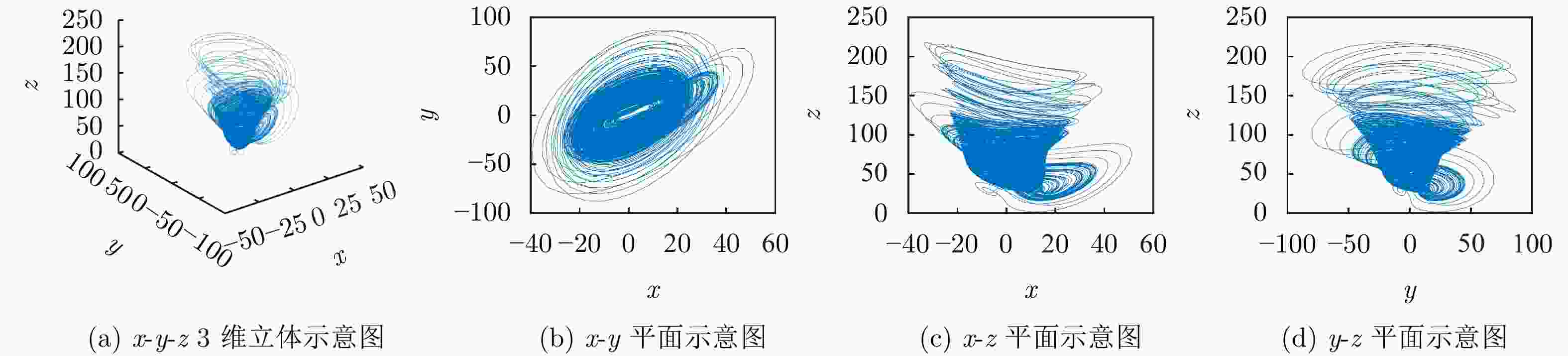
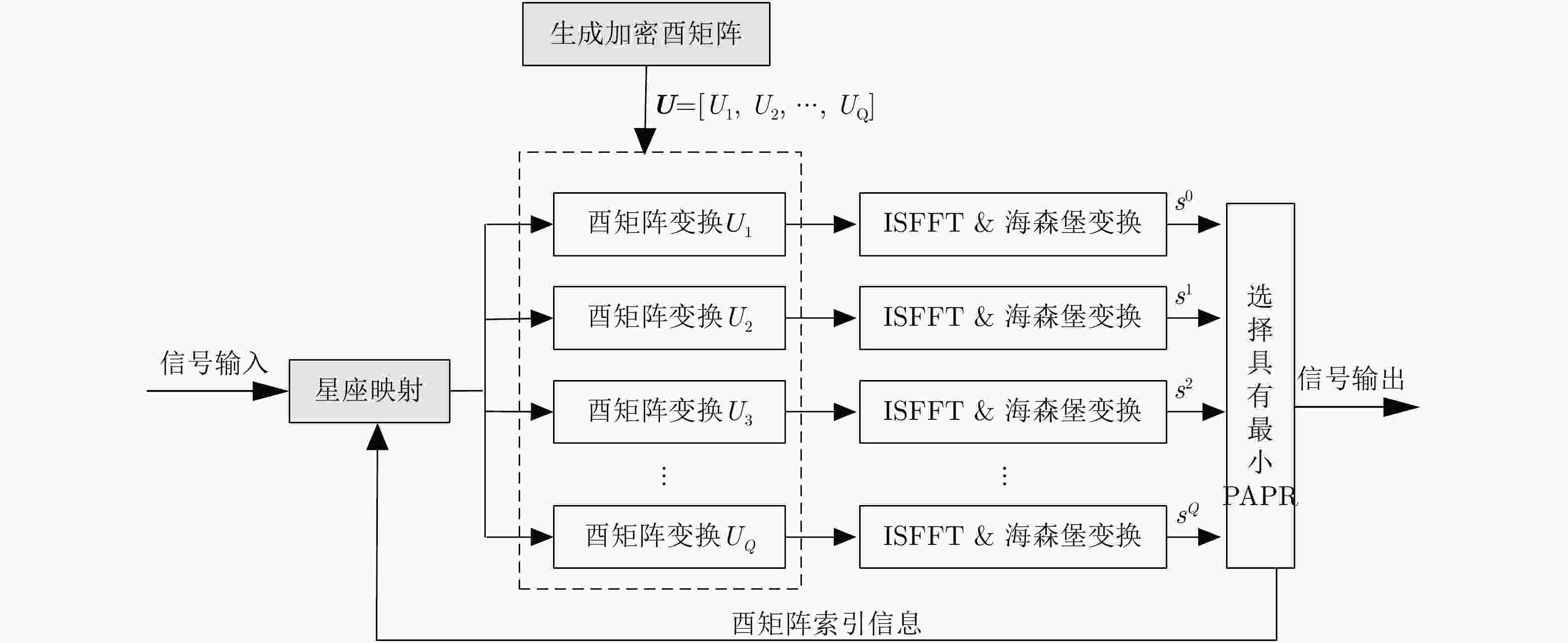
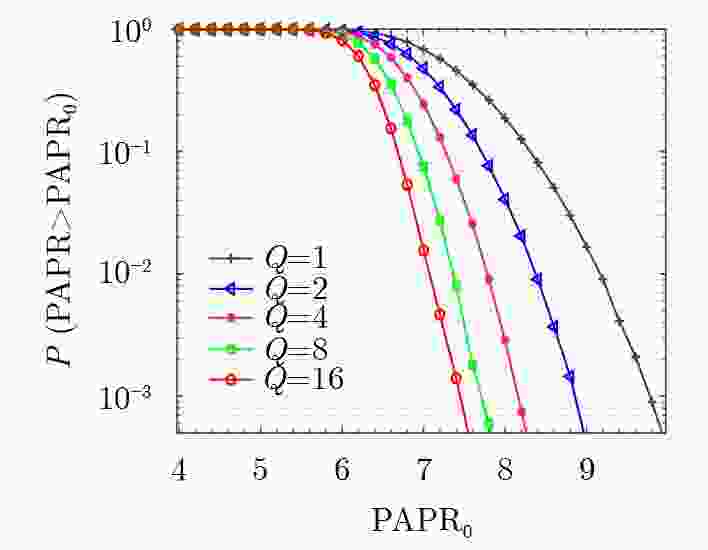
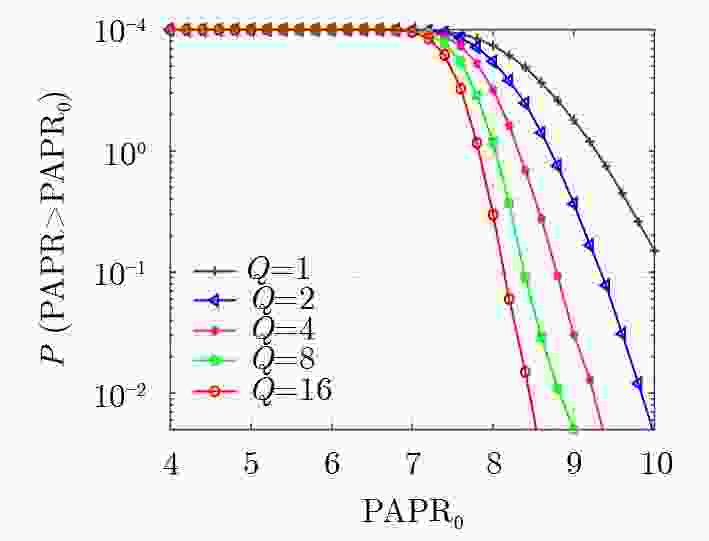
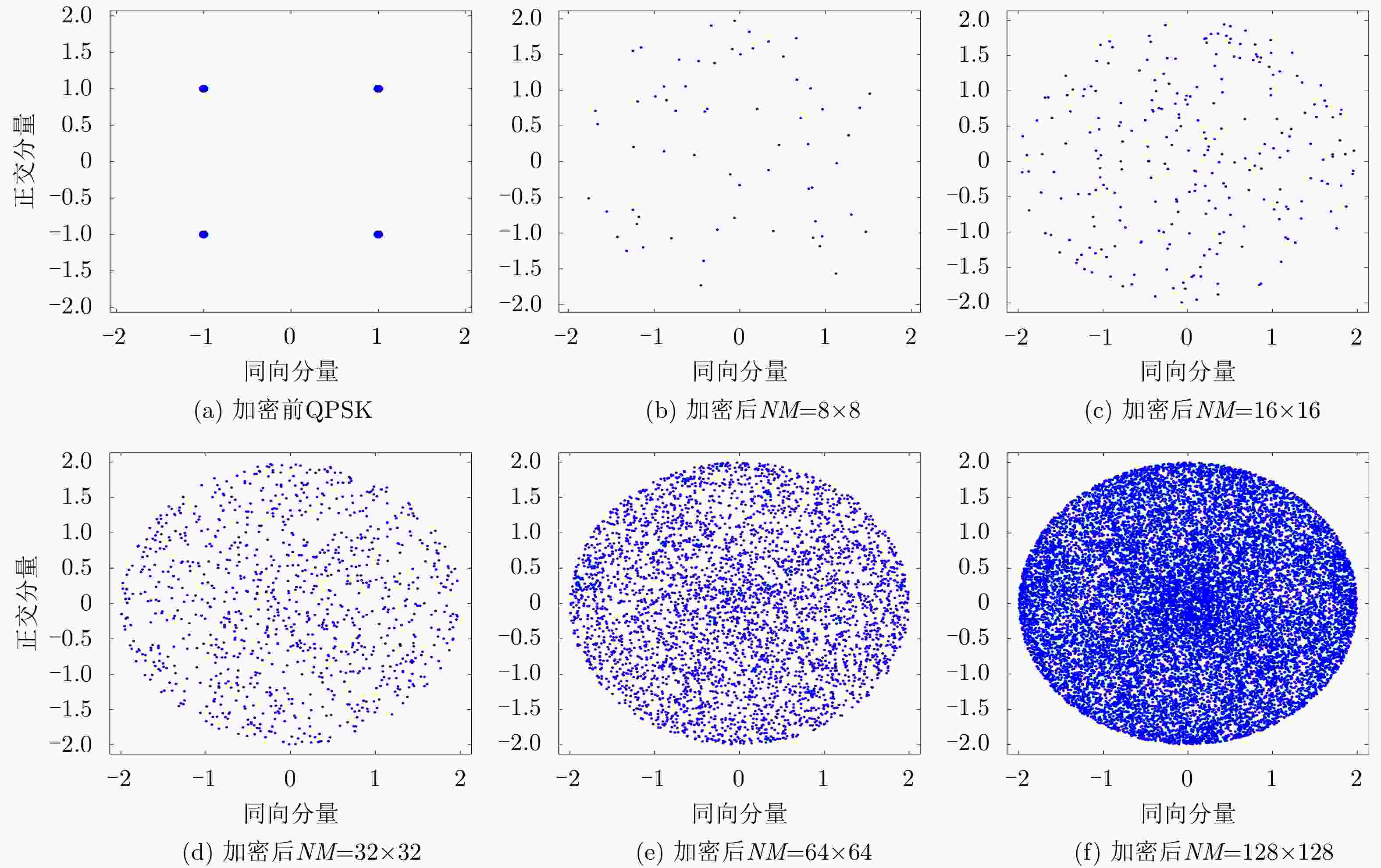
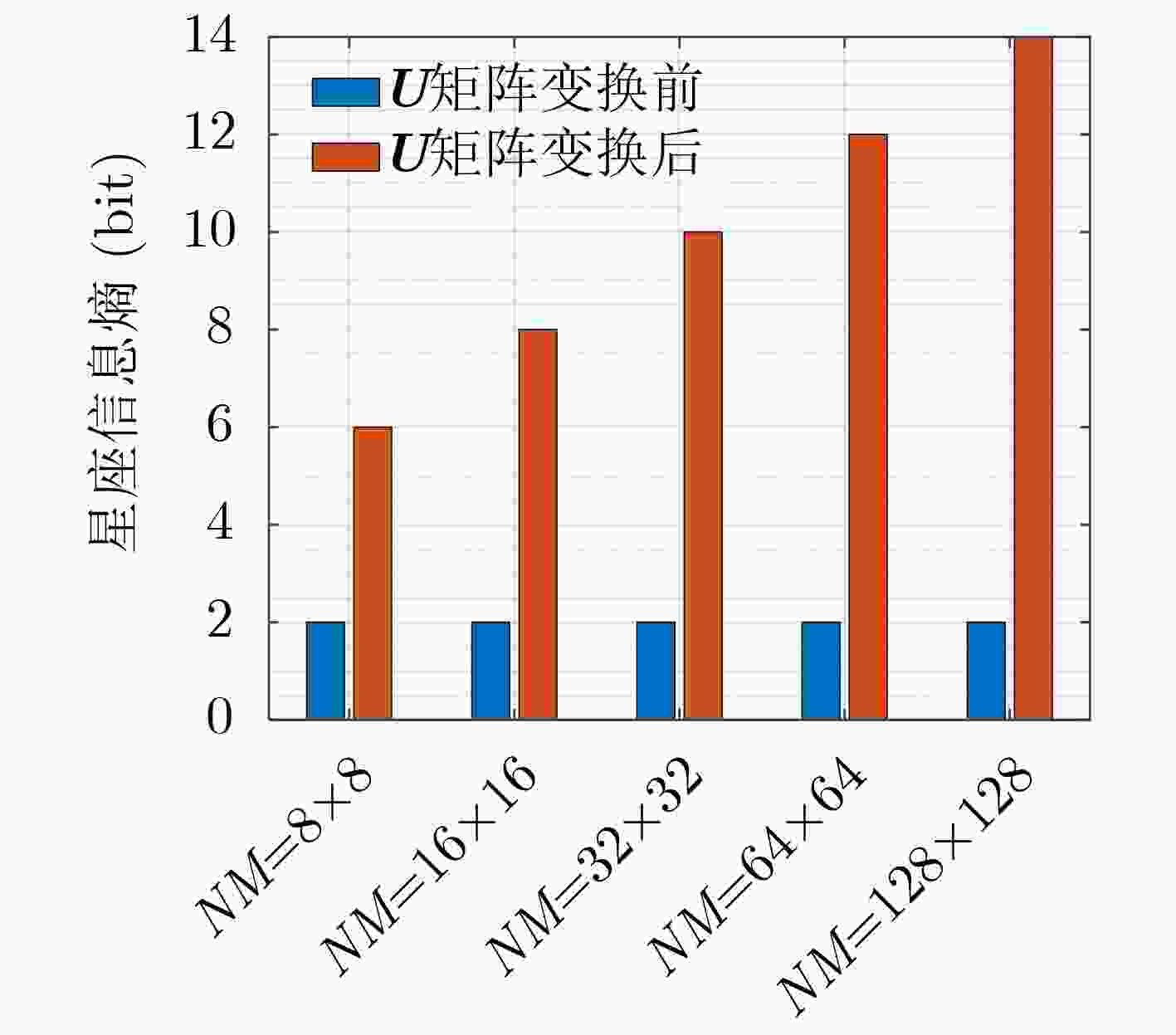
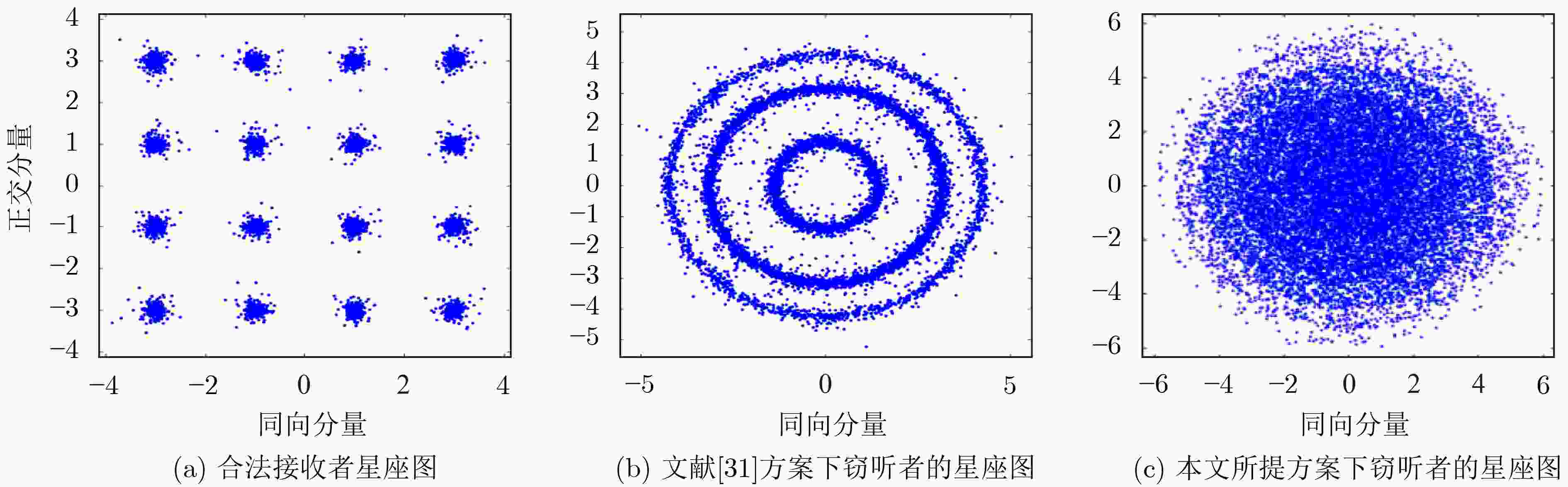
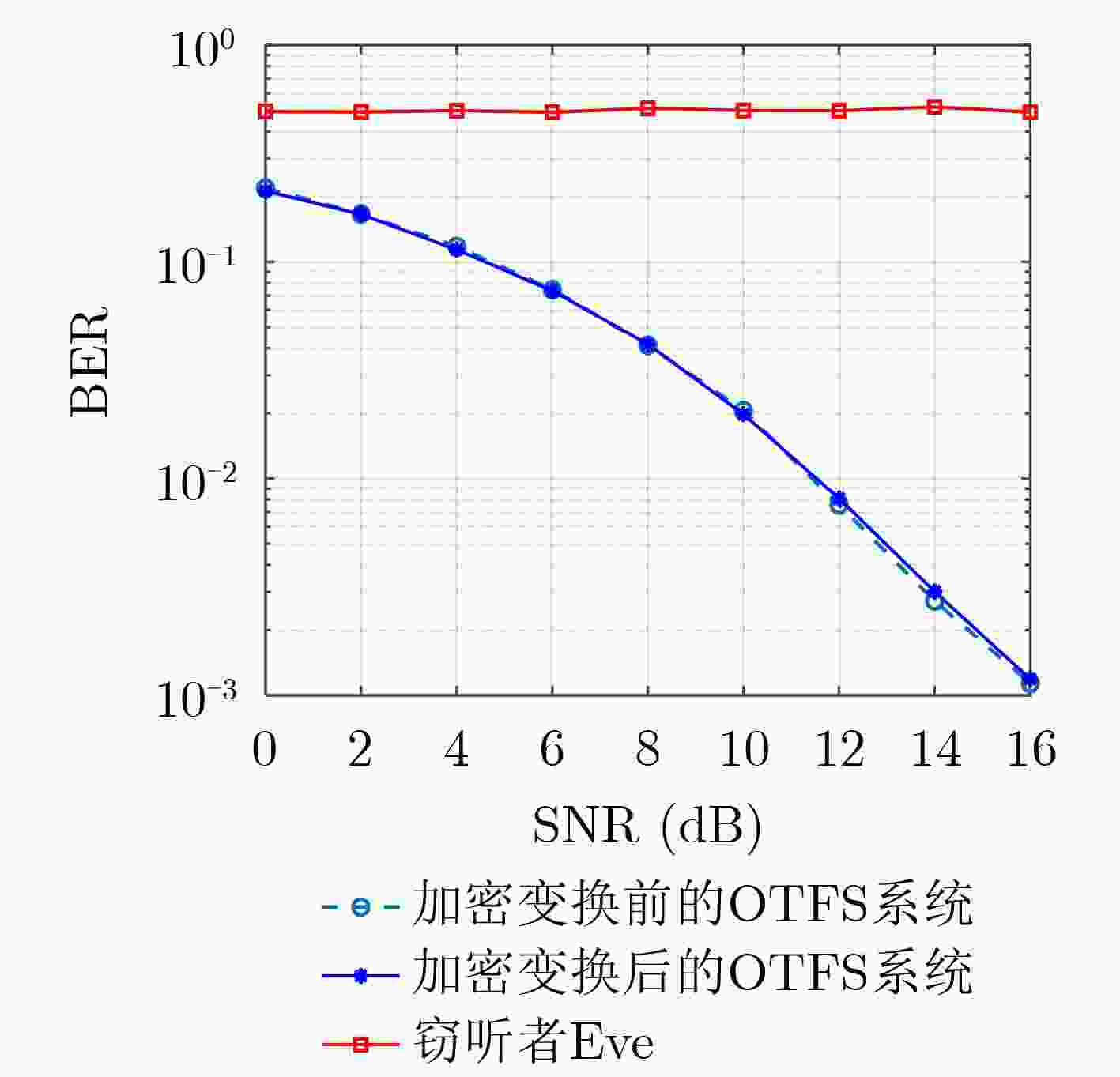
摘要: 为了降低正交时频空(OTFS)系统峰均比(PAPR)并且提升系统安全性,该文设计了一种基于酉矩阵变换的低峰均功率比OTFS安全传输方法。在该方法中,通过无线信道的时延多普勒(DD)域产生初始密钥,并将其作为混沌系统初始值进一步产生混沌序列。利用混沌序列进行酉矩阵设计,使得经过酉矩阵变换后的符号完全被混淆,具有类噪声的随机特性。此外通过索引控制酉矩阵选择,发射端将不同酉矩阵变换得到的OTFS时域信号进行排序并选择PAPR最低的信号进行发送。合法接收方获得索引值后可以正确解密和解调,而窃听者即使获得索引值信息,由于其没有相应的加密酉矩阵,为此无法正确解密。理论分析和仿真结果表明,所提方法在保证系统可靠性的前提下有效降低OTFS系统的PAPR。此外经过酉矩阵变换后的星座图呈现球状混乱,这使得调制方式和信息得以隐蔽,增大了窃听者的解密难度,系统的安全性得到保证。Abstract: In order to reduce the Peak-to-Average Power Ratio (PAPR) and improve the security of the Orthogonal Time and Frequency Space (OTFS) system, a low PAPR secure transmission method based on the U matrix transformation in OTFS system is proposed in this paper. In this method, the initial key is generated through the Delay-Doppler (DD) domain of wireless channel, which is used to generate further chaotic sequences. The U matrix is designed by the chaotic sequence, which makes the symbols after the U matrix transformation are completely confused and noise-like. Besides, the U matrix selections can be controlled by the index. The transmitter sortes the OTFS time domain signals obtained from different U matrix transformations and selectes the signal with the lowest PAPR for transmission. The encrypted signal can be correctly obtained by the legitimate receiver after obtaining the index value. However, the eavesdropper cannot decrypt the information even if he obtained the transmitted index value. The simulation results show that the proposed scheme can reduce the PAPR of OTFS system effectively while ensuring the system reliability. In addition, the constellation diagram the U matrix transformation becomes spherical chaos, which makes the modulation method and information hidden. The decryption difficulty of the eavesdropper is greatly increased, and the security of the system is effectively enhanced.
-
图 15 SNR=30 dB所提方案与文献[31]方案的窃听者星座图对比
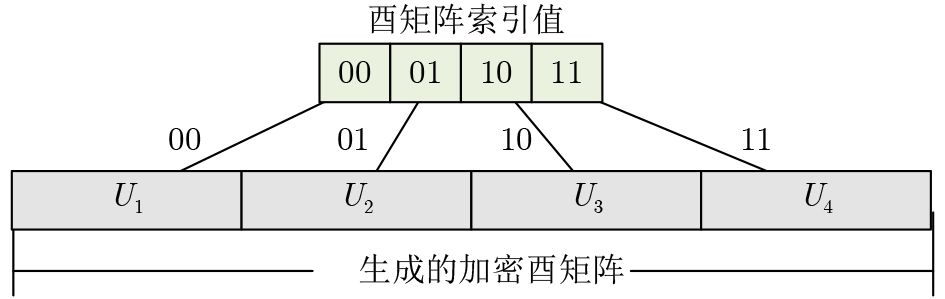
算法1 安全矩阵生成算法 输入:混沌序列$ {S_0} $; 输出:安全矩阵${{\boldsymbol{U}}}$; (1) 将$ {S_0} $分成$W$块序列${S_1},{S_2}, \cdots {S_i} \cdots {S_W}$; (2) 从$i = 1$到${W^2}$循环执行(3)~(5) (3) $S'_i = {\text{hash} }({S_i})$; (4) ${\theta _i} = 2{\pi }(S'_i\bmod \lambda )/\lambda$; (5) 结束循环 (6) 利用旋转矢量$ {\theta } $构建$ W \times W $的矩阵${ {{\boldsymbol{U}}}' }$; (7) 对${ {{\boldsymbol{U}}}'}$进行Gram正交化得到${{\boldsymbol{U}}}$ (8) 返回${{\boldsymbol{U}}}$。 -
[1] SOLDANI D, GUO Y J, BARANI B, et al. 5G for ultra-reliable low-latency communications[J]. IEEE Network, 2018, 32(2): 6–7. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.8329617 [2] MOUNTASER G, MAHMOODI T, and SIMEONE O. Reliable and low-latency Fronthaul for tactile internet applications[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(11): 2455–2463. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2872299 [3] JI Xingsheng, HUANG Kaizhi, JIN Liang, et al. Overview of 5G security technology[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2018, 61(8): 081301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-017-9426-4 [4] SHIU Y S, CHANG S Y, WU H C, et al. Physical layer security in wireless networks: A tutorial[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2011, 18(2): 66–74. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2011.5751298 [5] LU Xinjin, LEI Jing, and LI Wei. A physical layer encryption algorithm based on length-compatible polar codes[C]. 2020 IEEE 92nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Fall), Victoria, Canada, 2020: 1–7. [6] 彭建华, 张帅, 许晓明, 等. 物联网中一种抗大规模天线阵列窃听者的噪声注入方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(1): 67–73. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180342PENG Jianhua, ZHANG Shuai, XU Xiaoming, et al. A noise injection scheme resistant to massive MIMO eavesdropper in IoT[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(1): 67–73. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180342 [7] LU Xinjin, LEI Jing, SHI Yuxin, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface assisted secret key generation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 1036–1040. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3061301 [8] 鲁信金, 雷菁, 施育鑫. 基于旋转置乱的索引跳频抗干扰加密方法[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(12): 27–34. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021239LU Xinjin, LEI Jing, and SHI Yuxin. Index modulation aided frequency hopping anti-jamming and encryption method based on rotation scrambling[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(12): 27–34. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021239 [9] MATTHEWS R. On the derivation of a “chaotic” encryption algorithm[J]. Cryptologia, 1989, 13(1): 29–42. doi: 10.1080/0161-118991863745 [10] 李春彪, 赵云楠, 李雅宁, 等. 基于正弦反馈Logistic混沌映射的图像加密算法及其FPGA实现[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3766–3774. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200575LI Chunbiao, ZHAO Yunnan, LI Yaning, et al. An image encryption algorithm based on logistic chaotic mapping with sinusoidal feedback and its FPGA implementation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3766–3774. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200575 [11] LU Xinjin, SHI Yuxin, LI Wei, et al. A joint physical layer encryption and PAPR reduction scheme based on polar codes and chaotic sequences in OFDM system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 73036–73045. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2919598 [12] RAPPAPORT T S, 周文安, 付秀花, 王志辉, 等译. 无线通信原理与应用[M]. 2版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2006.RAPPAPORT T S, ZHOU Wenan, FU Xiuhua, WANG Zhihui, et al. translation. Wireless Communications Principles and Practice[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2006. [13] TUSHA A, DOĞAN S, and ARSLAN H. A hybrid downlink NOMA with OFDM and OFDM-IM for beyond 5G wireless networks[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 491–495. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2979059 [14] SHI Yuxin, LU Xinjin, GAO Kai, et al. Genetic algorithm aided OFDM with all index modulation[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(12): 2192–2195. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2942915 [15] RONNY H and SELIM R S. OTFS methods of data channel characterization and uses thereof[P]. US, 9444514-B2, 2016. [16] HADANI R, RAKIB S, TSATSANIS M, et al. Orthogonal time frequency space modulation[C]. 2017 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), San Francisco, USA, 2017: 1–6. [17] JIANG Tao and WU Yiyan. An overview: Peak-to-average power ratio reduction techniques for OFDM signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2008, 54(2): 257–268. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2008.915770 [18] SURABHI G D, AUGUSTINE R M, and CHOCKALINGAM A. Peak-to-average power ratio of OTFS modulation[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(6): 999–1002. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2914042 [19] GAO Shuang and ZHENG Jianping. Peak-to-average power ratio reduction in pilot-embedded OTFS modulation through iterative clipping and filtering[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(9): 2055–2059. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2993036 [20] LIU Mengxue, ZHAO Mingmin, LEI Ming, et al. Autoencoder based PAPR reduction for OTFS modulation[C]. 2021 IEEE 94th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2021-Fall), Norman, USA, 2021: 1–5. [21] NAVEEN C and SUDHA V. Peak-to-average power ratio reduction in OTFS modulation using companding technique[C]. 2020 5th International Conference on Devices, Circuits and Systems, Coimbatore, India, 2020: 140–143. [22] FRANCIS J K, AUGUSTINE R M, and CHOCKALINGAM A. Diversity and PAPR enhancement in OTFS using indexing[C]. 2021 IEEE 93rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2021-Spring), Helsinki, Finland, 2021: 1–6. [23] HU Junfan, SHI Jia, MA Shuai, et al. Secrecy analysis for orthogonal time frequency space scheme based uplink LEO satellite communication[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(8): 1623–1627. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3072902 [24] 杨欣, 邱彬, 谢坚, 等. 一种基于正交时频空方向调制安全通信方法[P]. 中国专利, 112398775A, 2021.YANG Xin, QIU Bin, XIE Jian, et al. Secure communication method based on orthogonal time-frequency-space direction modulation[P]. China Patent, 112398775A, 2021. [25] SUN Jinjing, WANG Zulin, and HUANG Qin. Secure Precoded orthogonal time frequency space modulation[C]. 2021 13th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), Changsha, China, 2021: 1–5. [26] WEI Yunchuan, ZENG Kai, and MOHAPATRA P. Adaptive wireless channel probing for shared key generation[C]. 2011 Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM, Shanghai, China, 2011: 2165–2173. [27] PENG Yuexing, WANG Peng, XIANG Wei, et al. Secret key generation based on estimated channel state information for TDD-OFDM systems over fading channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(8): 5176–5186. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2706657 [28] LÜ Jinhu and CHEN Guanrong. A new chaotic attractor coined[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2002, 12(3): 659–661. doi: 10.1142/S0218127402004620 [29] MORTARI D. On the rigid rotation concept in n-dimensional spaces[J]. The Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, 2001, 49(3): 401–420. doi: 10.1007/BF03546230 [30] 田鑫. 基于FPGA的SHA-3算法硬件实现优化与系统设计[D]. [硕士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020: 8–12.Tian Xin. Hardware implementation optimization and system design of SHA-3 algorithm based on FPGA[D]. [Master dissertation], Xidian University, 2020: 8–12. [31] SENGIJPTA S K. Fundamentals of statistical signal processing: Estimation theory[J]. Technometrics, 1995, 37(4): 465–466. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1995.10484391 -





 下载:
下载:
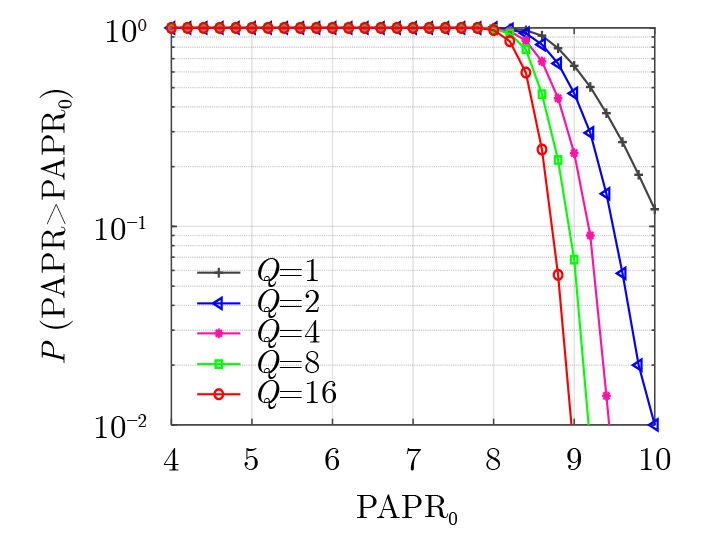
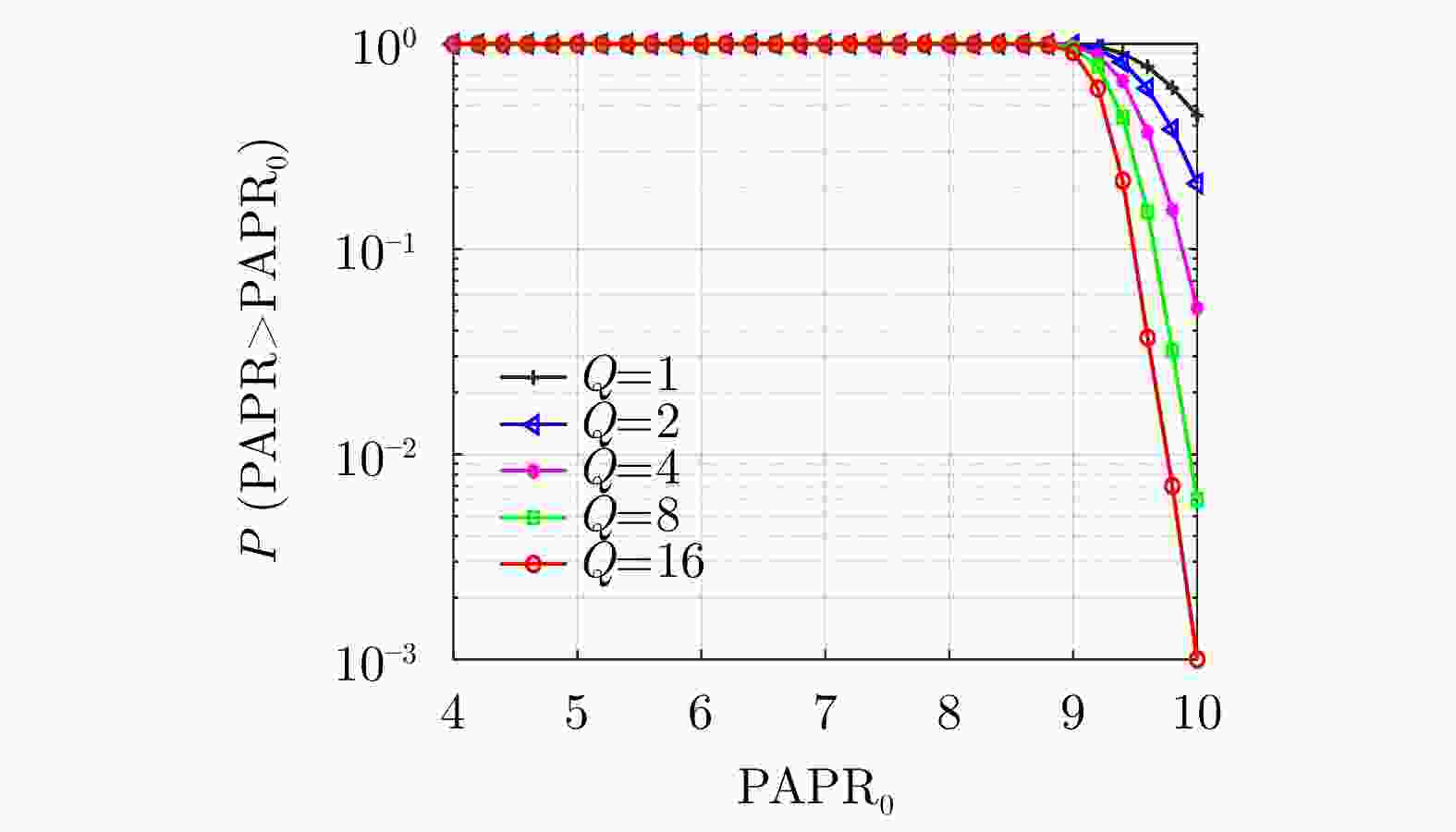
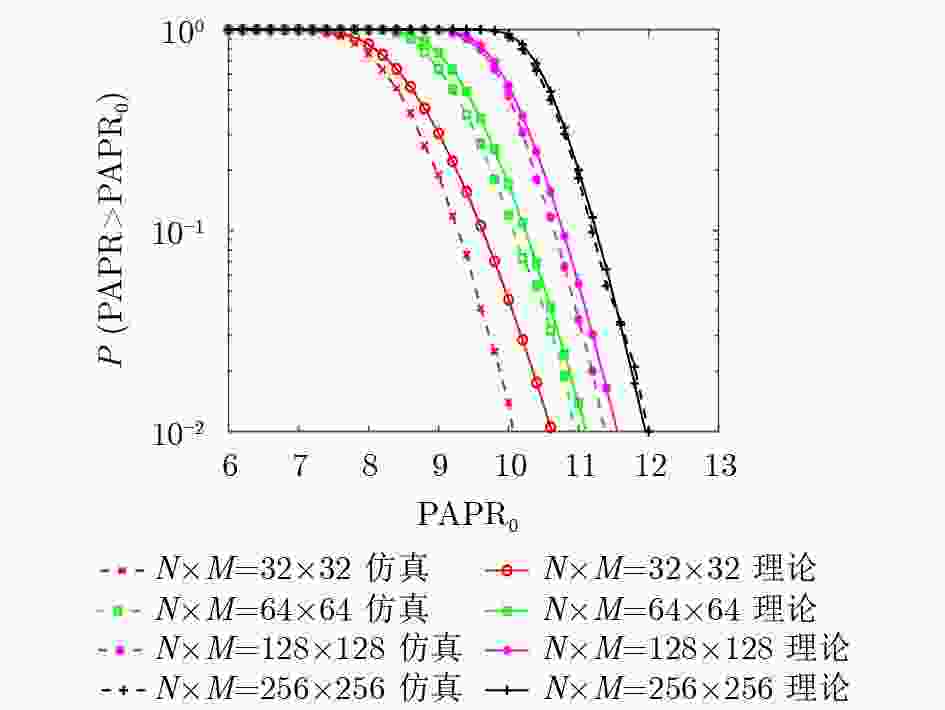
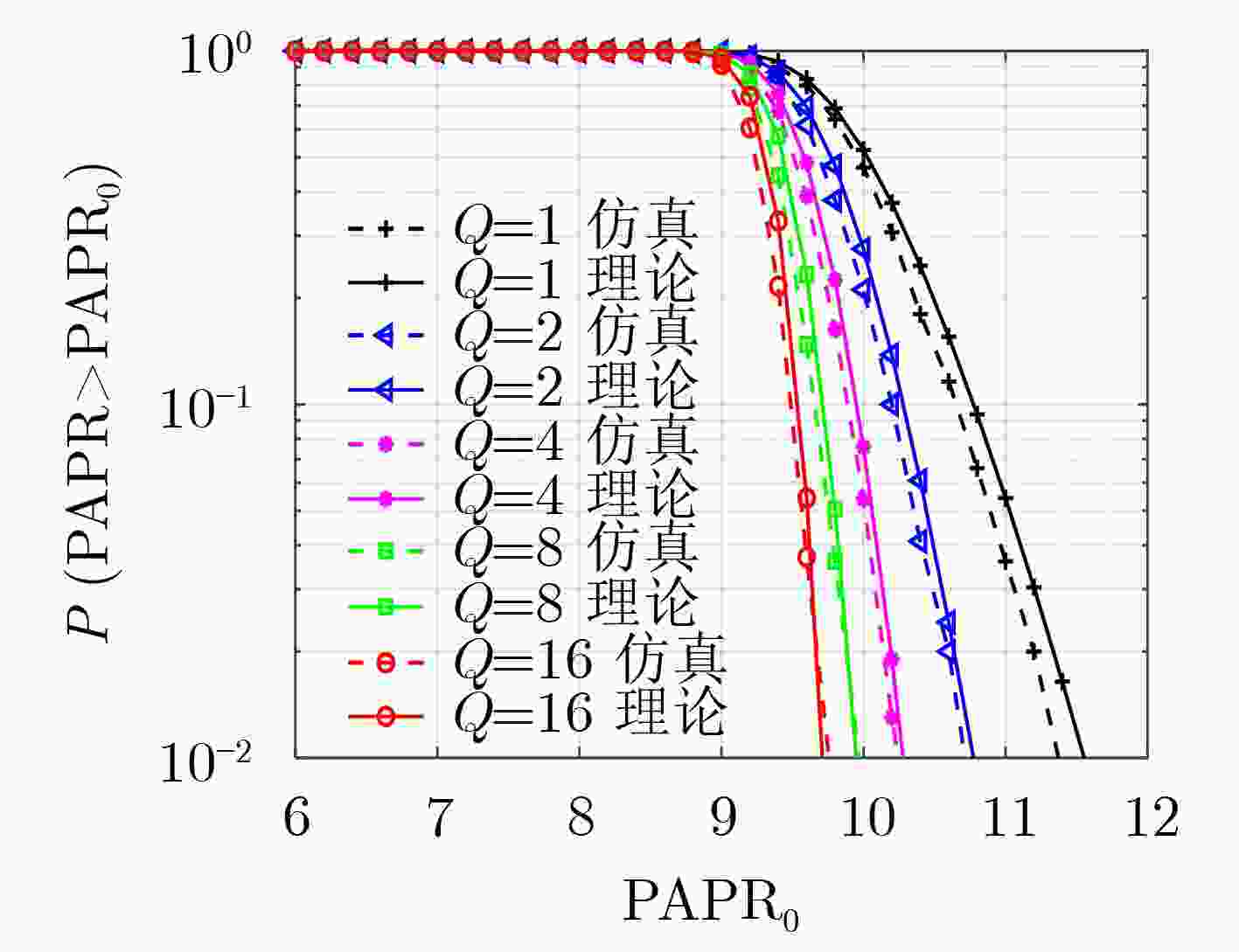


 下载:
下载:
