| [1] |
ALTINEL D and KURT G K. Modeling of hybrid energy harvesting communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2019, 3(2): 523–534. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2019.2908086
|
| [2] |
WANG Zhe, AGGARWAL V, and WANG Xiaodong. Iterative dynamic water-filling for fading multiple-access channels with energy harvesting[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2015, 33(3): 382–395. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2015.2391571
|
| [3] |
HO C K and ZHANG Rui. Optimal energy allocation for wireless communications with energy harvesting constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(9): 4808–4818. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2199984
|
| [4] |
BRACCIALE L and LORETI P. Lyapunov drift-plus-penalty optimization for queues with finite capacity[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(11): 2555–2558. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3013125
|
| [5] |
AMIRNAVAEI F and DONG Min. Online power control optimization for wireless transmission with energy harvesting and storage[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(7): 4888–4901. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2548459
|
| [6] |
LEI Weijia and LI Qin. Online power control based on Lyapunov optimization framework for decode-and-forward relay systems with energy harvesting[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 71335–71349. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2919968
|
| [7] |
MA Rui and ZHANG Wei. Adaptive MQAM for energy harvesting wireless communications with 1-Bit channel feedback[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(11): 6459–6470. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2455494
|
| [8] |
LI Mingyu, ZHAO Xiaohui, LIANG Hui, et al. Deep reinforcement learning optimal transmission policy for communication systems with energy harvesting and adaptive MQAM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(6): 5782–5793. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2911544
|
| [9] |
QIU Chengrun, HU Yang, CHEN Yan, et al. Lyapunov optimization for energy harvesting wireless sensor communications[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2018, 5(3): 1947–1956. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2817590
|
| [10] |
雷维嘉, 孙嘉琳, 谢显中, 等. 能量收集通信系统中功率和调制方式的在线联合优化策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 1024–1033. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210145LEI Weijia, SUN Jialin, XIE Xianzhong, et al. Online joint optimization of power and modulation in energy harvesting communication systems[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 1024–1033. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210145
|
| [11] |
王新梅, 肖国镇. 纠错码-原理与方法(修订版)[M]. 2版. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社, 2001: 73–174.WANG Xinmei and XIAO Guozhen. Error Correcting Code. Principle and Method (Revised Edition)[M]. 2nd ed. Xi’an: Xidian University Publishing House, 2001: 73–174.
|
| [12] |
KANG S M and LEBLEBICI Y. CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Analysis & Design[M]. 3rd ed. London: McGraw-Hill Education, 2002: 452–460.
|
| [13] |
SHAVIV D and ÖZGÜR A. Universally near optimal online power control for energy harvesting nodes[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2016, 34(12): 3620–3631. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2016.2612039
|
| [14] |
DENG Feng, YUE Xianghu, FAN Xinyu, et al. Multisource energy harvesting system for a wireless sensor network Node in the field environment[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(1): 918–927. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2865431
|
| [15] |
ZHANG Qiufang, HE Jinghan, XU Yin, et al. Average-value modeling of direct-driven PMSG-based wind energy conversion systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2022, 37(1): 264–273. doi: 10.1109/TEC.2021.3095486
|





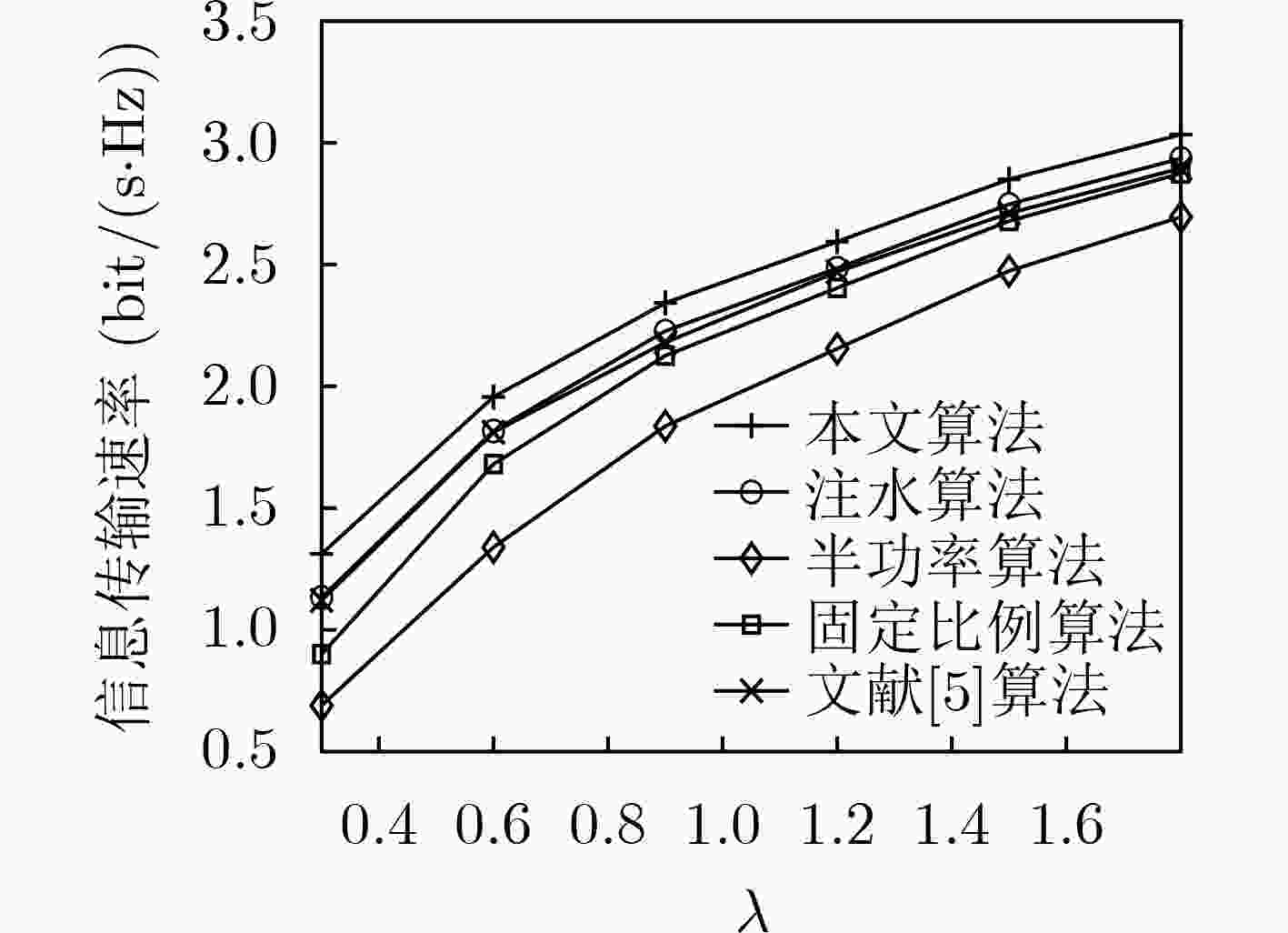
 下载:
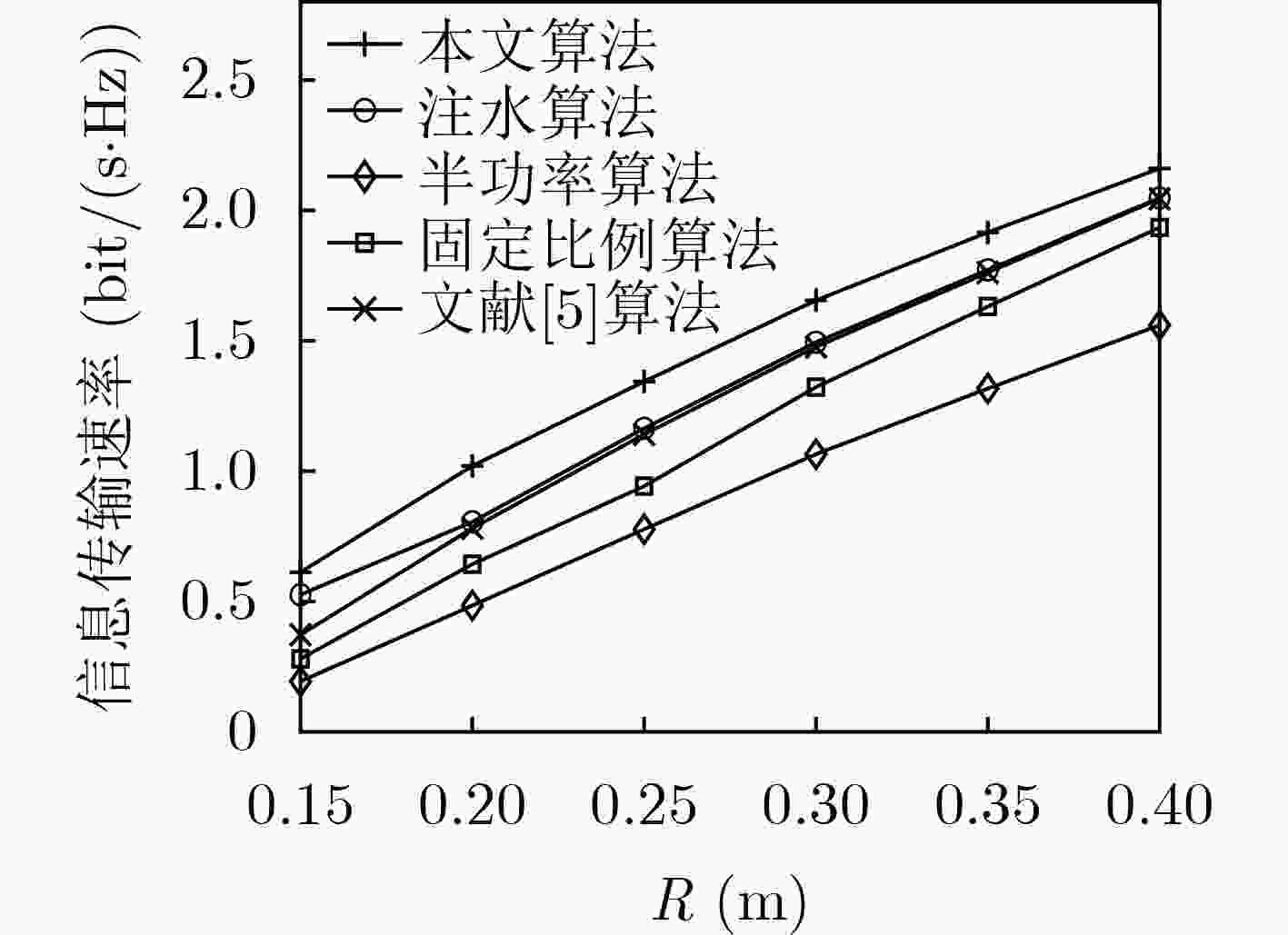
下载:

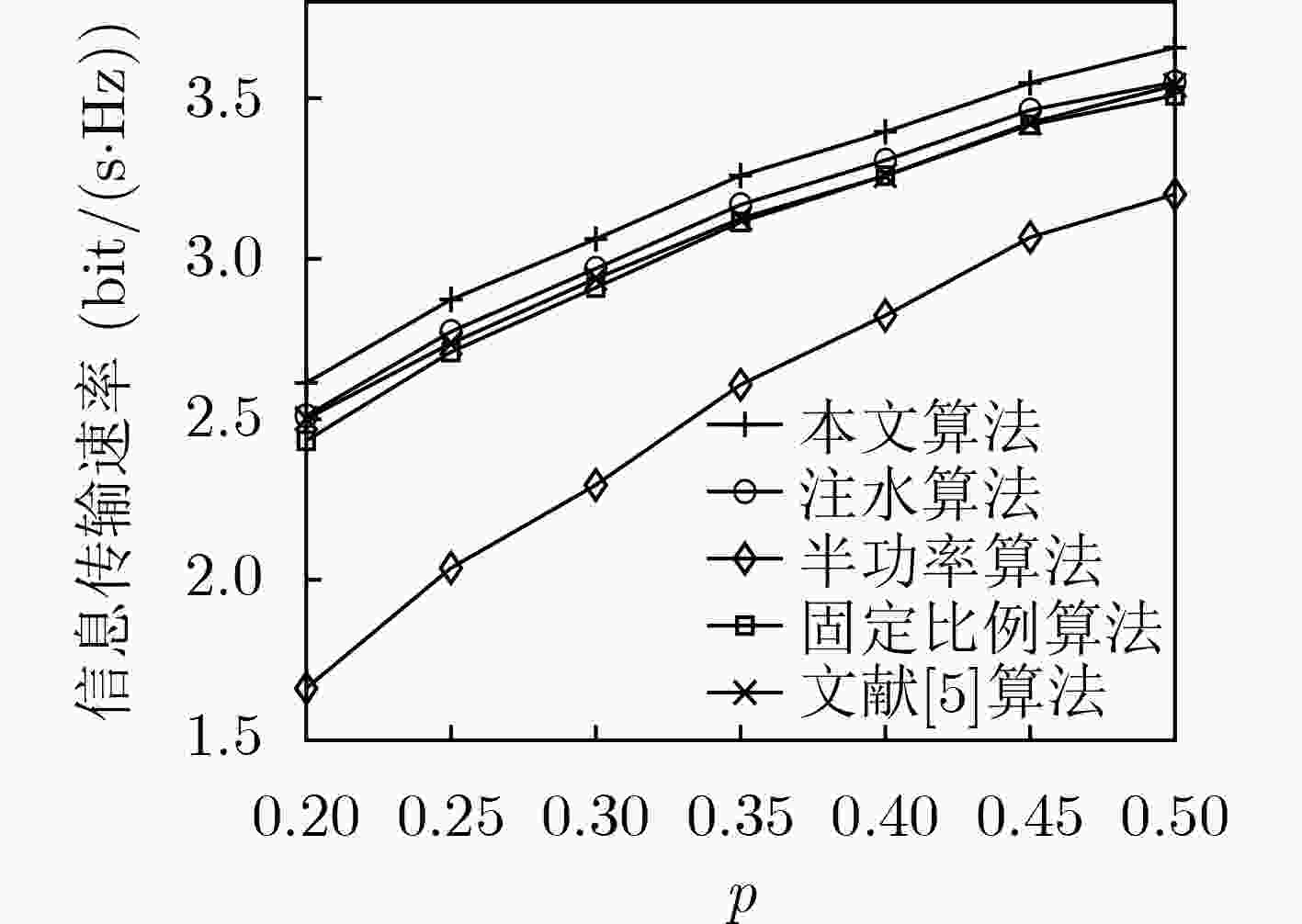


 下载:
下载:
