Availability-oriented Routing Algorithm for Planning Multi-level Power Service Based on Link-failure Model
-
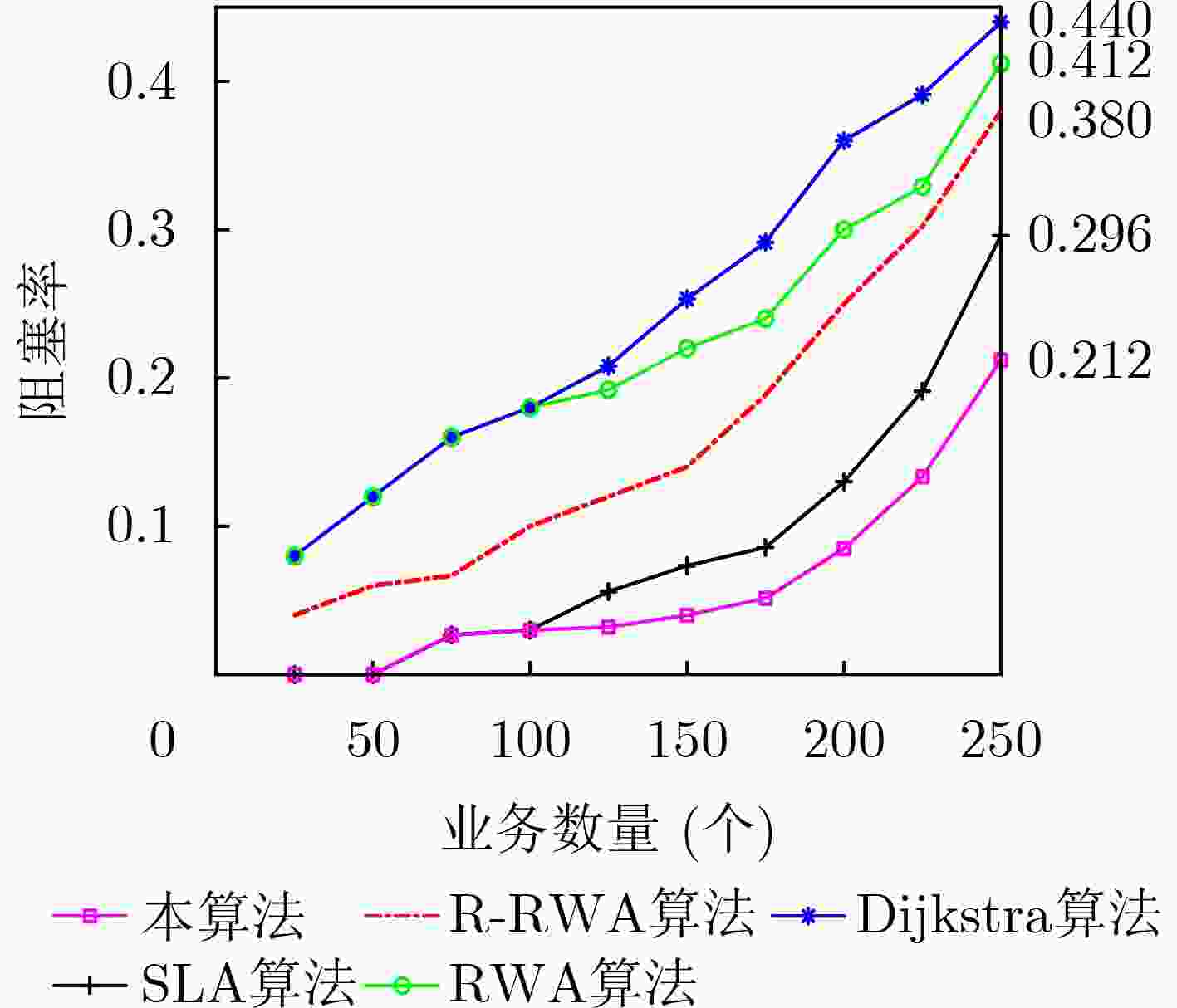
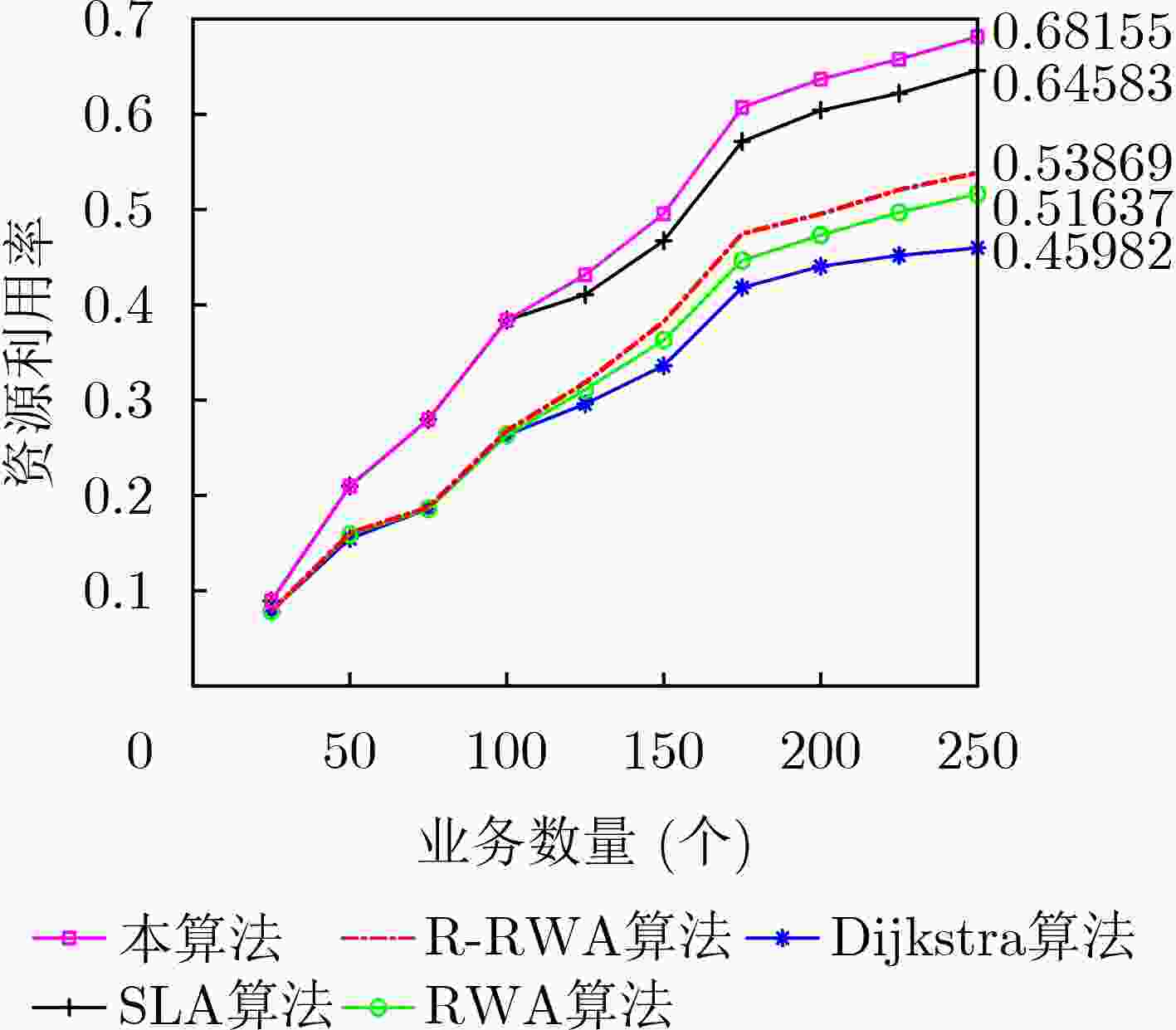
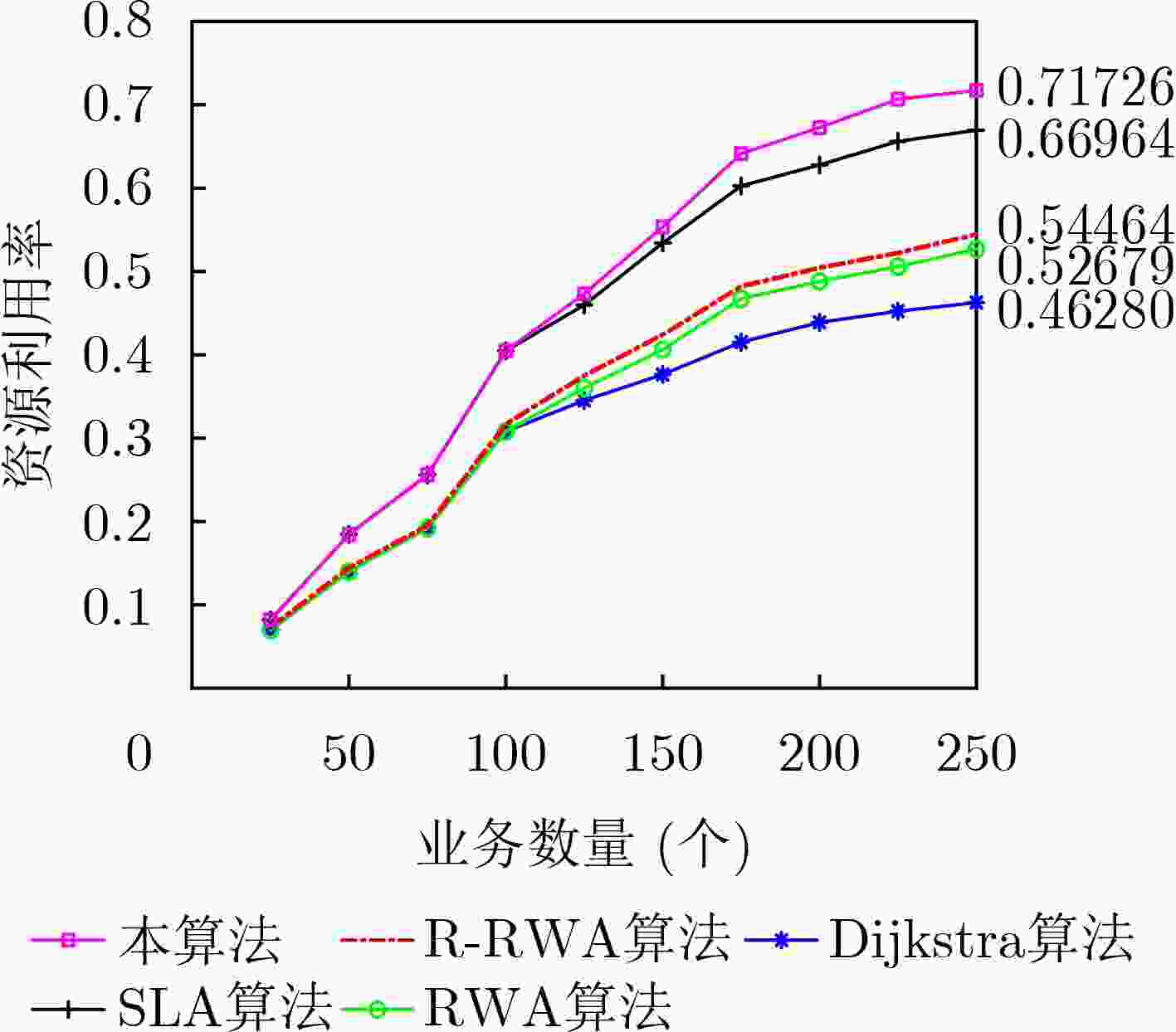
摘要: 该文从智能电网中电力业务多样性的角度出发,分析不同类型业务对网络的可靠性需求。建立链路失效函数模型,并基于该模型设计面向可靠性的路由规划方法。以网络阻塞率和资源利用率为指标,通过与传统链路失效路由算法的比较分析来验证所提出方法的有效性。传统链路失效路由规划算法忽略了电力业务多样性,对接入网络的业务请求无差别处理,路由规划约束条件相对单一,导致网络阻塞率较高。该文所提路由算法充分考虑了不同业务对网络需求的多样性,依据业务等级调整目标函数并分别进行路由分配,从而降低网络阻塞率,提升网络可靠性和资源利用率。Abstract: Considering the diversity of power services in smart grid, the reliability requirements of different levels of services are analyzed. A link-failure model is built, and an availability-oriented routing planning algorithm is designed based on the built model. The feasibility of the proposed algorithm, in terms of the network blocking rate and resource utilization, is validated by comparing with the classical link-failure routing algorithms. The classical link-failure routing algorithms ignore the diversity of power services, and process all service requests of the access network indiscriminately. The classical routing planning constraints are relatively simple, which leads to the high blocking rate. Regarding to the different requirements on the network availability from kinds of services, the routing algorithm proposed in this paper adjusts properly the target function and allocates the resource according to the incoming service. Thus, the network blocking rate is significantly reduced. Meanwhile, the network availability and resource utilization are greatly improved.
-
Key words:
- Smart grid /
- Availability /
- Link-failure model /
- Routing planning
-
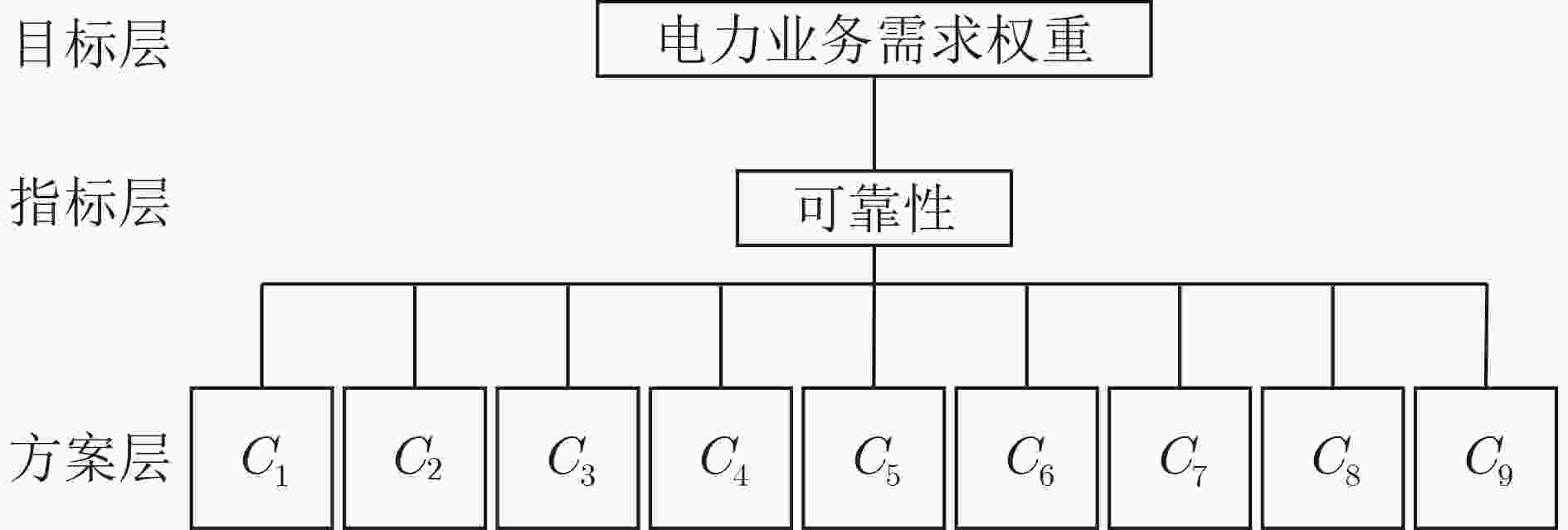
表 1 各电力业务的实时性与可靠性要求
业务编号 业务名称 业务类型 可靠性要求 C1 线路保护(继电保护) 数据业务 极高 C2 保护管理系统 数据业务 极高 C3 调度电话 语音、多媒体 极高 C4 调度自动化 数据业务 高 C5 视频会议 语音、多媒体 极高 C6 会议电视 语音、多媒体 较高 C7 行政电话 语音、多媒体 高 C8 配电自动化 数据业务 一般 C9 SG-ERP业务 数据业务 高 表 2 电力业务重要度赋值方法
重要性等级 重要性标度 i与j同样重要 1 i比j稍微重要 3 i比j明显重要 5 i比j强烈重要 7 i比j极端重要 9 i比j稍微不重要 1/3 i比j明显不重要 1/5 i比j强烈不重要 1/7 i比j极端不重要 1/9 表 3 判断矩阵构造方法
C1 C2 ··· Cn C1 C11 C12 ··· C1n C2 C21 C22 ··· C2n $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots$ $ \ddots$ $\vdots $ Cn Cn1 Cn2 ··· Cnn 表 4 具体电力业务可靠性需求的判断矩阵
C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C1 1 1 1 3 1 5 3 7 3 C2 1 1 1 3 1 5 3 7 3 C3 1 1 1 3 1 5 3 7 3 C4 1/3 1/3 1/3 1 1/3 3 1 5 1 C5 1 1 1 3 1 5 3 7 3 C6 1/5 1/5 1/5 1/3 1/5 1 1/3 3 1/3 C7 1/3 1/3 1/3 1 1/3 3 1 5 1 C8 1/7 1/7 1/7 1/5 1/7 1/3 1/5 1 1/5 C9 1/3 1/3 1/3 1 1/3 3 1 5 1 表 5 可靠性需求权重赋值结果
C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 可靠性需求权重值 0.1824 0.1824 0.1824 0.0720 0.1824 0.0345 0.0720 0.0198 0.0720 -
[1] 孟凡超, 高志强, 王春璞. 智能电网关键技术及其与传统电网的比较[J]. 河北电力技术, 2009, 28(S1): 4–5,12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9898.2009.z1.002MENG Fanchao, GAO Zhiqiang, and WANG Chunpu. Smart grid key technologies and comparing with traditional grid[J]. Hebei Electric Power, 2009, 28(S1): 4–5,12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9898.2009.z1.002 [2] 周光楠. 大容量OTN技术在骨干网上的应用研究[J]. 通讯世界, 2019, 26(11): 62–63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4222.2019.11.041ZHOU Guangnan. Research on the application of high-capacity OTN technology in backbone network[J]. Telecom World, 2019, 26(11): 62–63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4222.2019.11.041 [3] WANG Qiong and GAO Ying. OTN for the future transmission network[C]. 2012 Symposium on Photonics and Optoelectronics, Shanghai, China, 2012: 1–4. [4] 刘林, 祁兵, 李彬, 等. 面向电力物联网新业务的电力通信网需求及发展趋势[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44(8): 3114–3128. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2020.0013LIU Lin, QI Bing, LI Bin, et al. Requirements and developing trends of electric power communication network for new services in electric internet of things[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44(8): 3114–3128. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2020.0013 [5] 赵子岩, 张大伟. 国家电网公司“十二五”电力通信业务需求分析[J]. 电力系统通信, 2011, 32(5): 56–60.ZHAO Ziyan and ZHANG Dawei. Analysis on the requirement of SGCC on telecommunication services in the"12th five-year plan" Period[J] Telecommunications for Electric Power System, 2011, 32(5): 56–60. [6] 许超, 喻洪辉, 顾海林, 等. 智能电网通信业务的研究与分析[J]. 电气应用, 2013, 32(S1): 340–342.XU Chao, YU Honghui, GU Hailin, et al. Research and analysis of smart grid communication service[J]. Electrotechnical Application, 2013, 32(S1): 340–342. [7] 高超, 孙颖, 周静, 等. 电力通信业务预测分析方法研究[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2016, 14(7): 108–112. doi: 10.16543/j.2095-641x.electric.power.ict.2016.07.021GAO Chao, SUN Ying, ZHOU Jing, et al. Research on forecasting and analysis method of electric power communication service[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2016, 14(7): 108–112. doi: 10.16543/j.2095-641x.electric.power.ict.2016.07.021 [8] 董武, 彭迪栎, 汤玮, 等. 基于OSNR的OTN路由优化算法[J]. 自动化技术与应用, 2019, 38(10): 85–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7241.2019.10.020DONG Wu, PENG Dili, TANG Wei, et al. OTN network routing optimization algorithm based on OSNR[J]. Techniques of Automation and Applications, 2019, 38(10): 85–88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7241.2019.10.020 [9] 丁慧霞, 高会生, 王法宁. 链路失效的电力OTN业务风险分析[J]. 光通信技术, 2015, 39(8): 40–43. doi: 10.13921/j.cnki.issn1002-5561.2015.08.012DING Huixia, GAO Huisheng, and WANG Faning. Service risk analysis for electric power OTN by considering link failure[J]. Optical Communication Technology, 2015, 39(8): 40–43. doi: 10.13921/j.cnki.issn1002-5561.2015.08.012 [10] 茹予波. 智能电网背景下的继电保护新技术分析[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2020(31): 150–151.RU Yubo. Analysis of new relay protection technology under the background of smart grid[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2020(31): 150–151. [11] 蒋康明, 曾瑛, 邓博仁, 等. 基于业务的电力通信网风险评价方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2013, 41(24): 101–106. doi: 10.7667/j.issn.1674-3415.2013.24.016JIANG Kangming, ZENG Ying, DENG Boren, et al. Risk evaluation method of electric power communication network based on services[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2013, 41(24): 101–106. doi: 10.7667/j.issn.1674-3415.2013.24.016 [12] LI Wenzheng, LIU Junjun, and YAO Shunli. An improved dijkstra's algorithm for shortest path planning on 2D grid maps[C]. 2019 IEEE 9th International Conference on Electronics Information and Emergency Communication (ICEIEC), Beijing, China, 2019: 438–441. [13] 高立坡, 康伟, 郝军魁, 等. 基于OTN技术的电力通信网络业务路由优化算法[J]. 自动化技术与应用, 2021, 40(11): 75–79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7241.2021.11.017GAO Lipo, KANG Wei, HAO Junkui, et al. Service routing optimization algorithm of power communication network based on OTN technology[J]. Techniques of Automation and Applications, 2021, 40(11): 75–79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7241.2021.11.017 [14] 刘钰, 熊兰, 肖丹, 等. 基于业务重要度的电力通信路由系统可靠性分析[J]. 电测与仪表, 2017, 54(12): 34–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1390.2017.12.006LIU Yu, XIONG Lan, XIAO Dan, et al. Analysis on the reliability of communication routing system based on importance level of service[J]. Electrical Measurement &Instrumentation, 2017, 54(12): 34–41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1390.2017.12.006 [15] 高会生, 王法宁. 一种基于网络风险的路由波长分配算法[J]. 光通信研究, 2015(5): 12–14,18. doi: 10.13756/j.gtxyj.2015.05.004GAO Huisheng and WANG Faning. Considerations of a network risk-based RWA algorithm[J]. Study on Optical Communications, 2015(5): 12–14,18. doi: 10.13756/j.gtxyj.2015.05.004 [16] 郭振宇. 基于网状光网络中P圈启发式算法的研究[D]. [硕士论文], 南京邮电大学, 2017.GUO Zhenyu. Research on P-cycle heuristic algorithm in mesh optical network[D]. [Master dissertation], Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2017. [17] 李彬, 贾滨诚, 马永红, 等. 考虑链路失效概率的电力业务保护策略[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44(2): 725–732. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2018.1650LI Bin, JIA Bincheng, MA Yonghong, et al. Power business protection strategy considering link failure probability[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44(2): 725–732. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2018.1650 -





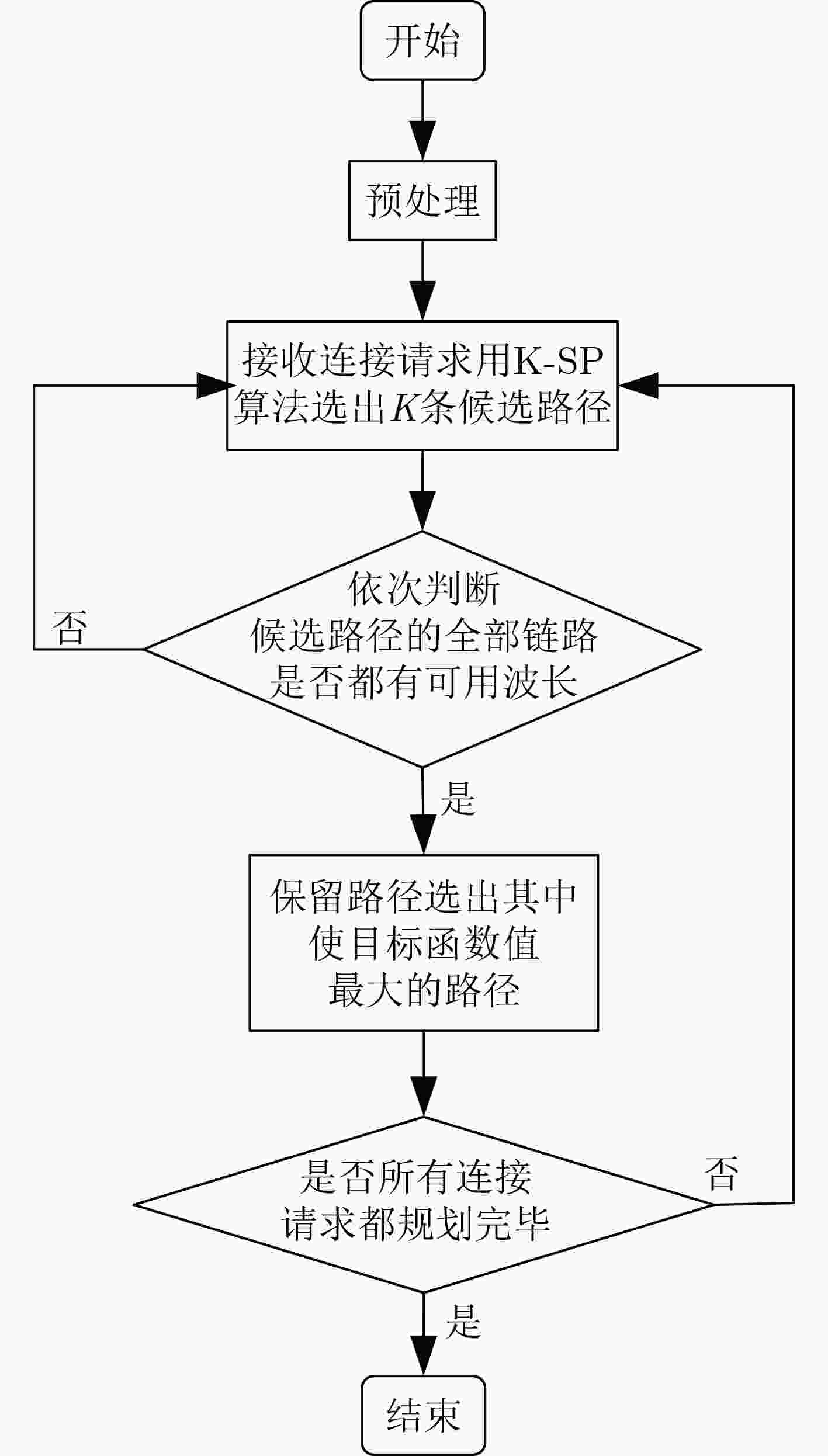
 下载:
下载:
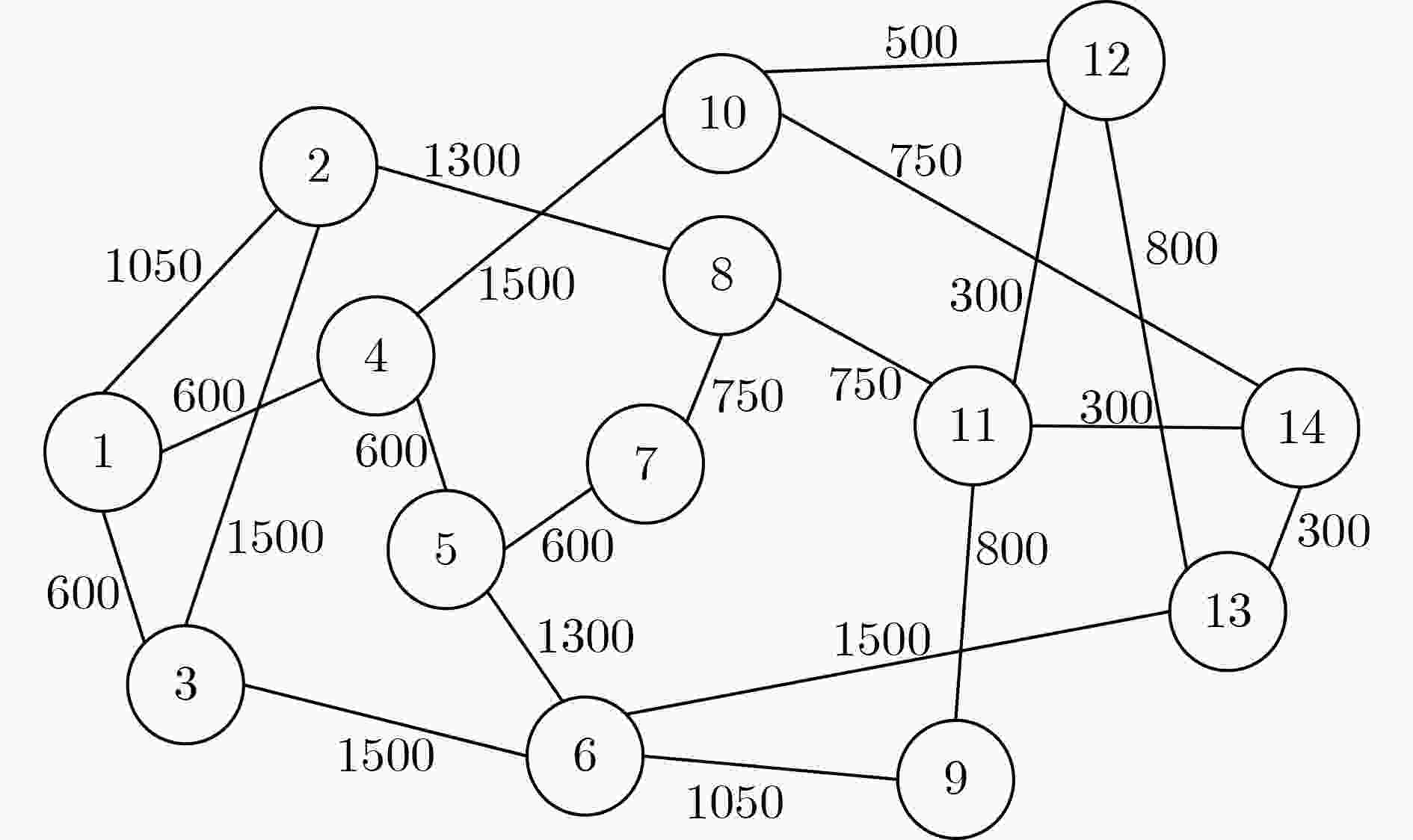
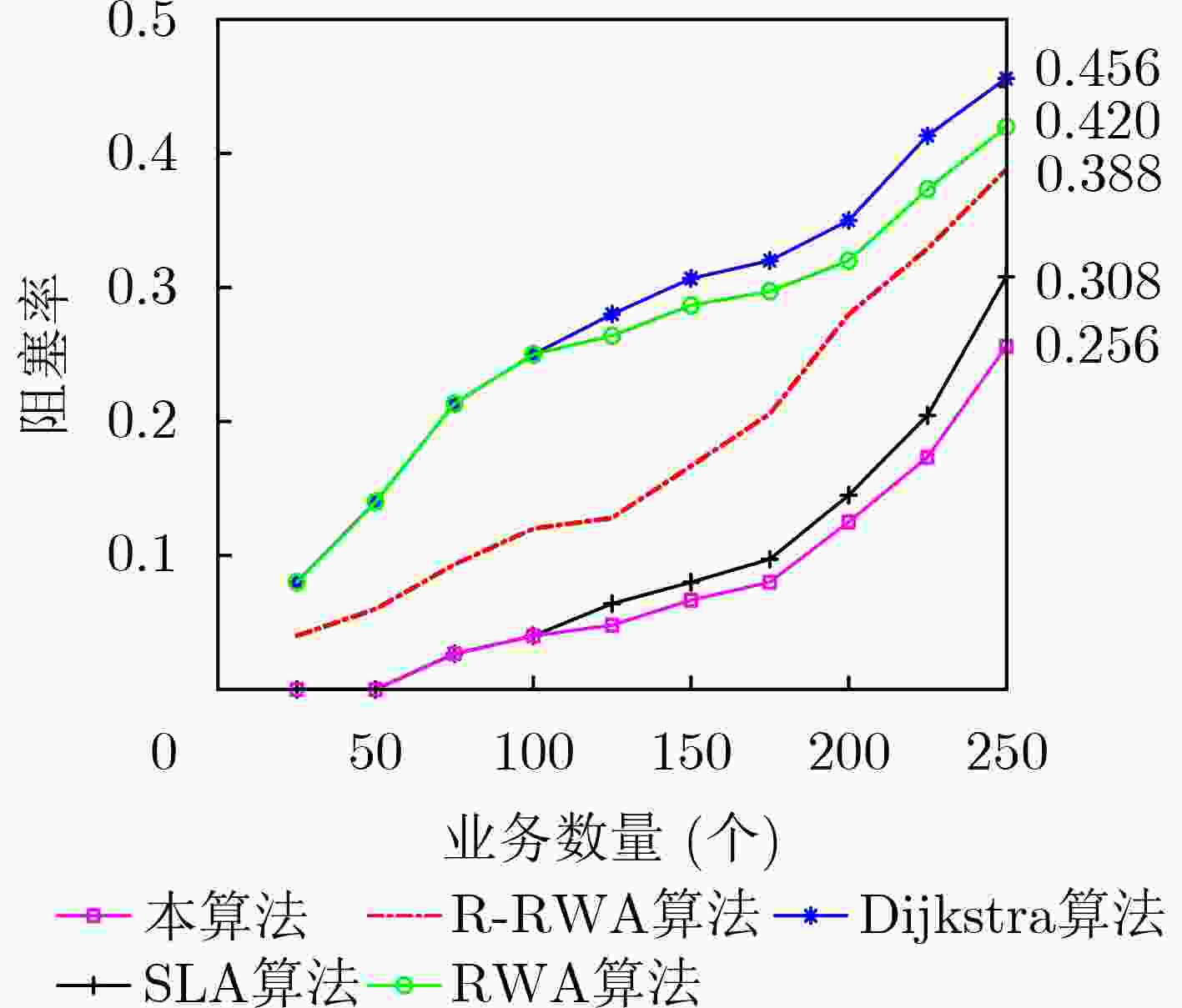


 下载:
下载:
