A Survey on File Architecture in DNA Storage
-
摘要: DNA存储因具有密度大、保存时间长及维护成本低等优点,为解决海量数据的存储和应用难题提供了“破局”可能。面对大规模数据应用场景,DNA存储必须要解决如何组织、访问和操作数据文件等问题—即文件系统设计问题。该文首先结合计算机文件系统模型,给出了未来DNA存储文件系统模型及具备的特点;然后,系统性综述了DNA存储文件系统研究进展;最后,对未来DNA存储文件系统研究进行了展望。Abstract: DNA storage technology provides a new way to tackle the problems of massive data storage and application, due to its high density, long durability, and low maintenance cost. To face massive data storage demand, DNA storage has to overcome the problem on how to organize, access and manipulate data files, that is, the design of file system. In this paper, future DNA storage file system model and its characteristics are studied according to computer file system model. Then, the research progress of file system of DNA storage is systematically reviewed. Finally, the perspectives on research direction of future DNA storage file system are discussed.
-
Key words:
- DNA Storage /
- File system /
- Random access /
- Error corrections
-
表 1 5种特异性PCR扩增引物设计方法性能比较
表 2 物理排列DNA分子存储方法比较
表 3 分子特异性杂交方法性能比较
表 4 代表性数据纠错方法性能比较
表 5 DNA存储数据加密方法性能比较
参考文献 技术特点 生物困难 鲁棒性 加密数据规模 密钥空间 Yang 等人[57] 一次一密+DNA链置换异或操纵 DNA链置换异或操纵 无 小 $C_{{{\text{4}}^{{\text{25}}}} \times {\text{1000}}}^{{\text{2000}}}$ Zakeri等人[58] 一代测序、色谱分析、数据隐藏 DNA分子数据隐藏 无 小 9.1×1061 Zhang 等人[8] DNA折纸 DNA分子自组装 无 小 2702 Grass 等人[60] AES加密+STR密钥编码 个体识别STR密钥 是 中 2132 Peng 等人[59] 混沌序列+DNA动态编码+DNA分子接头设计 DNA分子接头设计 无 中 33×564×2247 -
[1] ZHIRNOV V, ZADEGAN R M, SANDHU G S, et al. Nucleic acid memory[J]. Nature Materials, 2016, 15(4): 366–370. doi: 10.1038/nmat4594 [2] 沈鹏, 李颢, 孙清江, 等. DNA存储技术[J]. 生命科学仪器, 2020, 18(2): 3–13,39. doi: 10.11967/2020180401SHEN Peng, LI Hao, SUN Qingjiang, et al. Advance of data storage using DNA[J]. Life Science Instruments, 2020, 18(2): 3–13,39. doi: 10.11967/2020180401 [3] PANDA D, MOLLA K A, BAIG M J, et al. DNA as a digital information storage device: Hope or hype?[J]. 3 Biotech, 2018, 8(5): 239. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1246-7 [4] 许鹏, 方刚, 石晓龙, 等. DNA存储及其研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1326–1331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190863XU Peng, FANG Gang, SHI Xiaolong, et al. DNA storage and its research progress[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1326–1331. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190863 [5] CEZE L, NIVALA J, and STRAUSS K. Molecular digital data storage using DNA[J]. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2019, 20(8): 456–466. doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0125-3 [6] CHURCH G M, GAO Yuan, and KOSURI S. Next-generation digital information storage in DNA[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6102): 1628. doi: 10.1126/science.1226355 [7] ORGANICK L, ANG S D, CHEN Y J, et al. Random access in large-scale DNA data storage[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2018, 36(3): 242–248. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4079 [8] ZHANG Yinan, WANG Fei, CHAO Jie, et al. DNA origami cryptography for secure communication[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 5469. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13517-3 [9] SONG Xin, SHAH S, and REIF J. Multidimensional data organization and random access in large-scale DNA storage systems[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2021, 894: 190–202. doi: 10.1016/j.tcs.2021.09.021 [10] TOMEK K J, VOLKEL K, SIMPSON A, et al. Driving the scalability of DNA-based information storage systems[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2019, 8(6): 1241–1248. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.9b00100 [11] WINSTON C, ORGANICK L, WARD D, et al. Combinatorial PCR method for efficient, selective oligo retrieval from complex oligo pools[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2022, 11(5): 1727–1734. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.1c00482 [12] YAZDI S M H T, YUAN Yongbo, MA Jian, et al. A rewritable, random-access DNA-based storage system[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1): 14138. doi: 10.1038/srep14138 [13] YAZDI S M H T, GABRYS R, and MILENKOVIC O. Portable and error-free DNA-based data storage[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 5011. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05188-1 [14] 陈为刚, 黄刚, 李炳志, 等. 音视频文件的DNA信息存储[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2020, 50(1): 81–85. doi: 10.1360/ssv-2019-0211CHEN Weigang, HUANG Gang, LI Bingzhi, et al. DNA information storage for audio and video files[J]. Scientia Sinica Vitae, 2020, 50(1): 81–85. doi: 10.1360/ssv-2019-0211 [15] NEWMAN S, STEPHENSON A P, WILLSEY M, et al. High density DNA data storage library via dehydration with digital microfluidic retrieval[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 1706. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09517-y [16] ANTKOWIAK P L, KOCH J, NGUYEN B H, et al. Integrating DNA encapsulates and digital microfluidics for automated data storage in DNA[J]. Small, 2022, 18(15): 2107381. doi: 10.1002/smll.202107381 [17] BANAL J L, SHEPHERD T R, BERLEANT J, et al. Random access DNA memory using Boolean search in an archival file storage system[J]. Nature Materials, 2021, 20(9): 1272–1280. doi: 10.1038/s41563-021-01021-3 [18] YAMAMOTO M, KASHIWAMURA S, OHUCHI A, et al. Large-scale DNA memory based on the nested PCR[J]. Natural Computing, 2008, 7(3): 335–346. doi: 10.1007/s11047-008-9076-x [19] LIN K N, VOLKEL K, TUCK J M, et al. Dynamic and scalable DNA-based information storage[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 2981. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16797-2 [20] BEE C, CHEN Y J, QUEEN M, et al. Molecular-level similarity search brings computing to DNA data storage[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 4764. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24991-z [21] TOMEK K J, VOLKEL K, INDERMAUR E W, et al. Promiscuous molecules for smarter file operations in DNA-based data storage[J]. Nature Communications, 2021, 12(1): 3518. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23669-w [22] HAO Min, QIAO Hongyan, GAO Yanmin, et al. A mixed culture of bacterial cells enables an economic DNA storage on a large scale[J]. Communications Biology, 2020, 3: 416. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01141-7 [23] ZHANG Yi, KONG Linlin, WANG Fei, et al. Information stored in nanoscale: Encoding data in a single DNA strand with Base64[J]. Nano Today, 2020, 33: 100871. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100871 [24] LEE U J, HWANG S, KIM K E, et al. DNA data storage in Perl[J]. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, 2020, 25(4): 607–615. doi: 10.1007/s12257-020-0022-9 [25] SHIPMAN S L, NIVALA J, MACKLIS J D, et al. CRISPR–Cas encoding of a digital movie into the genomes of a population of living bacteria[J]. Nature, 2017, 547(7663): 345–349. doi: 10.1038/nature23017 [26] CHEN Y J, TAKAHASHI C N, ORGANICK L, et al. Quantifying molecular bias in DNA data storage[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 3264. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16958-3 [27] ERLICH Y and ZIELINSKI D. DNA Fountain enables a robust and efficient storage architecture[J]. Science, 2017, 355(6328): 950–954. doi: 10.1126/science.aaj2038 [28] GAO Yanmin, CHEN Xin, QIAO Hongyan, et al. Low-bias manipulation of DNA oligo pool for robust data storage[J]. ACS Synthetic Biology, 2020, 9(12): 3344–3352. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.0c00419 [29] CHEN Weigang, HAN Mingzhe, ZHOU Jianting, et al. An artificial chromosome for data storage[J]. National Science Review, 2021, 8(5): 62–70. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwab028 [30] 郜艳敏, 唐梦童, 刘倩, 等. DNA信息存储中关键生化方法的研究[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(3): 384–398. doi: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-085GAO Yanmin, TANG Mengtong, LIU Qian, et al. The pivotal biochemical methods in DNA data storage[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 384–398. doi: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-085 [31] MAKAROVA K S, GRISHIN N V, SHABALINA S A, et al. A putative RNA-interference-based immune system in prokaryotes: Computational analysis of the predicted enzymatic machinery, functional analogies with eukaryotic RNAi, and hypothetical mechanisms of action[J]. Biology Direct, 2006, 1: 7. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-1-7 [32] BRYKSIN A V and MATSUMURA I. Overlap extension PCR cloning: A simple and reliable way to create recombinant plasmids[J]. Biotechniques, 2010, 48(6): 463–464. doi: 10.2144/000113418 [33] SETLOW J K and SETLOW R B. Nature of the photoreactivable ultra-violet lesion in deoxyribonucleic acid[J]. Nature, 1963, 197(4867): 560–562. doi: 10.1038/197560a0 [34] OLIVIER M, AGGARWAL A, ALLEN J, et al. A high-resolution radiation hybrid map of the human genome draft sequence[J]. Science, 2001, 291(5507): 1298–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.1057437 [35] HEYROVSKA R. New insight into DNA damage by cisplatin at the atomic scale[J/OL]. Nature Precedings, 2012. [36] KIM J, BAE J H, BAYM M, et al. Metastable hybridization-based DNA information storage to allow rapid and permanent erasure[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5008. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18842-6 [37] 昝乡镇, 姚翔宇, 许鹏, 等. DNA存储中的纠错方法综述[J]. 广州大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 20(2): 13–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4229.2021.02.002ZAN Xiangzhen, YAO Xiangyu, XU Peng, et al. A survey on error correcting algorithms in DNA storage[J]. Journal of Guangzhou University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 20(2): 13–22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4229.2021.02.002 [38] HECKEL R, MIKUTIS G, and GRASS R N. A characterization of the DNA data storage channel[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 9: 9663. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45832-6 [39] BORNHOLT J, LOPEZ R, CARMEAN D M, et al. Toward a DNA-based archival storage system[J]. IEEE Micro, 2017, 37(3): 98–104. doi: 10.1109/MM.2017.70 [40] WANG Yixin, NOOR-A-RAHIM M, ZHANG Jingyun, et al. High capacity DNA data storage with variable-length Oligonucleotides using repeat accumulate code and hybrid mapping[J]. Journal of Biological Engineering, 2019, 13: 89. doi: 10.1186/s13036-019-0211-2 [41] MEISER L C, ANTKOWIAK P L, KOCH J, et al. Reading and writing digital data in DNA[J]. Nature Protocols, 2019, 15(1): 86–101. doi: 10.1038/s41596-019-0244-5 [42] GRASS R N, HECKEL R, PUDDU M, et al. Robust chemical preservation of digital information on DNA in silica with error‐correcting codes[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015, 54(8): 2552–2555. doi: 10.1002/anie.201411378 [43] GOLDMAN N, BERTONE P, CHEN Siyuan, et al. Towards practical, high-capacity, low-maintenance information storage in synthesized DNA[J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7435): 77–80. doi: 10.1038/nature11875 [44] ANTKOWIAK P L, LIETARD J, DARESTANI M Z, et al. Low cost DNA data storage using photolithographic synthesis and advanced information reconstruction and error correction[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11(1): 5345. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19148-3 [45] 陈为刚, 葛奇, 王盼盼, 等. 细胞内大片段DNA数据存储的多RS码交织编码[J]. 合成生物学, 2021, 2(3): 428–443. doi: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-023CHEN Weigang, GE Qi, WANG Panpan, et al. Multiple interleaved RS codes for data storage using up to Mb-scale synthetic DNA in living cells[J]. Synthetic Biology Journal, 2021, 2(3): 428–443. doi: 10.12211/2096-8280.2020-023 [46] ZHANG Shufang and PENG Kang. DNA information storage technology based on raptor code[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(15): 151701. doi: 10.3788/Lop57.151701 [47] CHEN Weigang, WANG Lixia, HAN Mingzhe, et al. Sequencing barcode construction and identification methods based on block error-correction codes[J]. Science China Life Sciences, 2020, 63(10): 1580–1592. doi: 10.1007/s11427-019-1651-3 [48] BLAWAT M, GAEDKE K, HÜTTER I, et al. Forward error correction for DNA data storage[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2016, 80: 1011–1022. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2016.05.398 [49] DENG Li, WANG Yixin, NOOR-A-RAHIM M, et al. Optimized code design for constrained DNA data storage with asymmetric errors[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 84107–84121. doi: 10.1109/Access.2019.2924827 [50] XUE Tianbo and LAU F C M. Notice of violation of IEEE publication principles: Construction of GC-balanced DNA with deletion/insertion/mutation error correction for DNA storage system[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 140972–140980. doi: 10.1109/Access.2020.3012688 [51] PRESS W H, HAWKINS J A, JONES S K JR, et al. HEDGES error-correcting code for DNA storage corrects indels and allows sequence constraints[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2020, 117(31): 18489–18496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2004821117 [52] SONG Lifu, GENG Feng, GONG Ziyi, et al. Super-robust data storage in DNA by de Bruijn graph-based decoding[Z]. bioRxiv, 2020. [53] LENZ A, MAAROUF I, WELTER L, et al. Concatenated codes for recovery from multiple reads of DNA sequences[C]. 2020 IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Riva del Garda, Italy, 2020. [54] DAVEY M C and MACKAY D J C. Reliable communication over channels with insertions, deletions, and substitutions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2001, 47(2): 687–698. doi: 10.1109/18.910582 [55] ZAN Xiangzhen, YAO Xiangyu, XU Peng, et al. A hierarchical error correction strategy for text DNA storage[J]. Interdisciplinary Sciences:Computational Life Sciences, 2022, 14(1): 141–150. doi: 10.1007/s12539-021-00476-x [56] ZAN Xiangzhen, XIE Ranze, YAO Xiangyu, et al. A robust and efficient DNA storage architecture based on modulation encoding and decoding[Z]. bioRxiv, 2022. [57] YANG Jing, MA Jingjing, LIU Shi, et al. A molecular cryptography model based on structures of DNA self-assembly[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(11): 1192–1198. doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0170-4 [58] ZAKERI B, CARR P A, and LU T K. Multiplexed sequence encoding: A framework for DNA communication[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(4): e0152774. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152774 [59] PENG Weiping, CUI Shuang, and SONG Cheng. One-time-pad cipher algorithm based on confusion mapping and DNA storage technology[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(1): e0245506. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245506 [60] GRASS R N, HECKEL R, DESSIMOZ C, et al. Genomic encryption of digital data stored in synthetic DNA[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2020, 59(22): 8476–8480. doi: 10.1002/anie.202001162 -





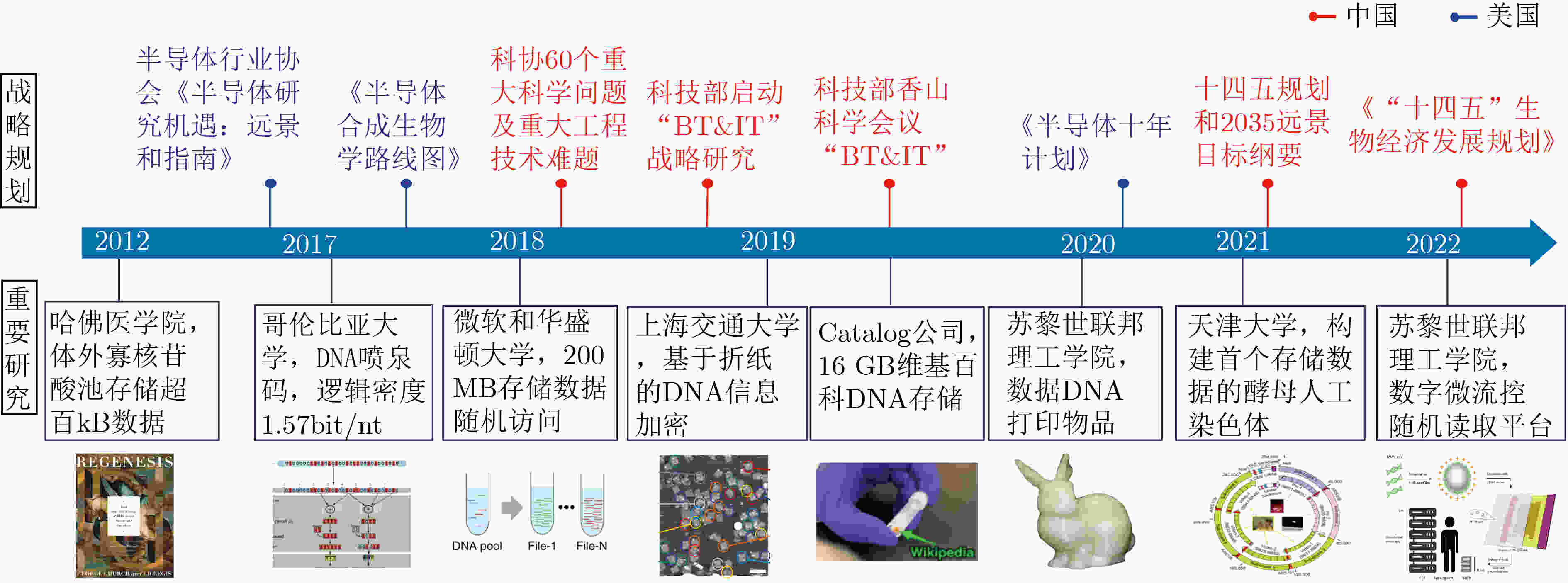
 下载:
下载:
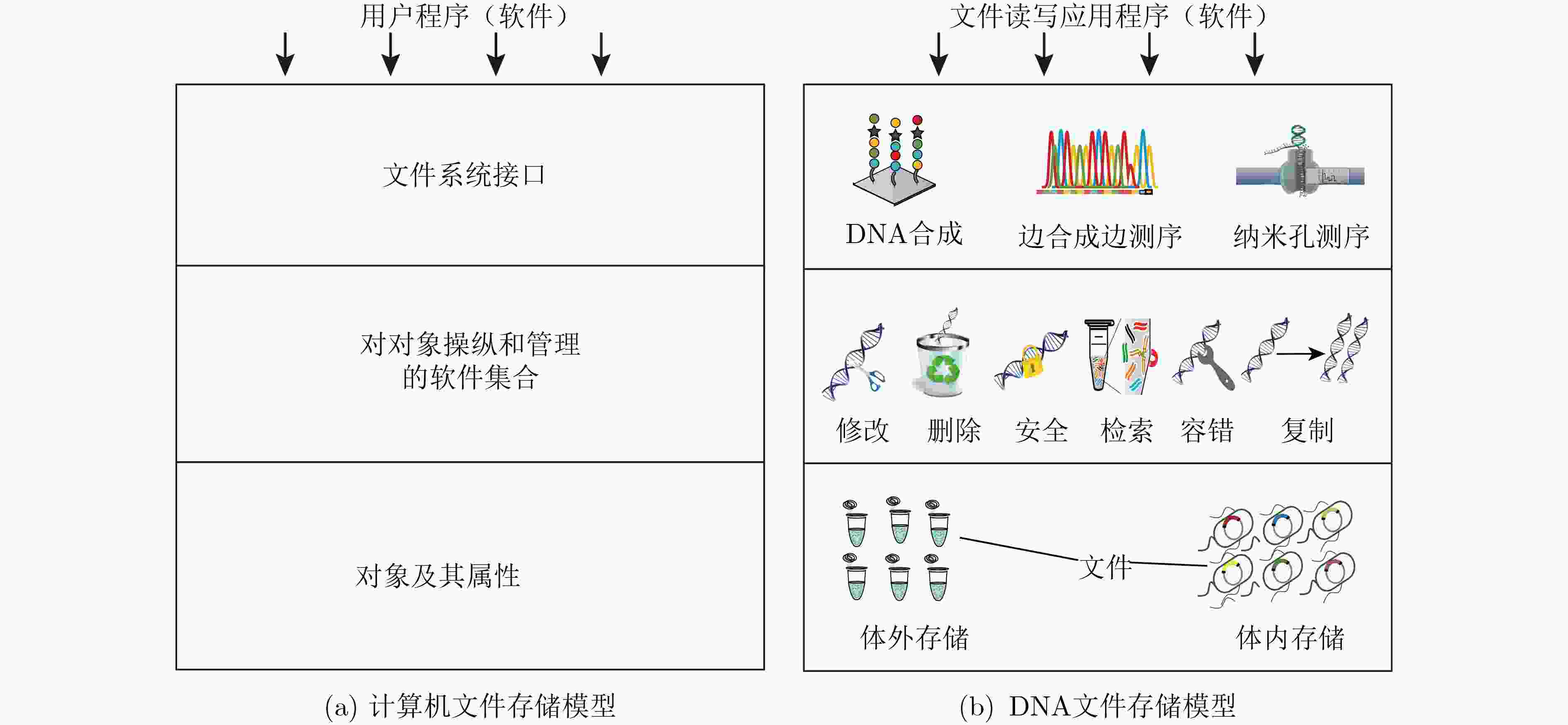
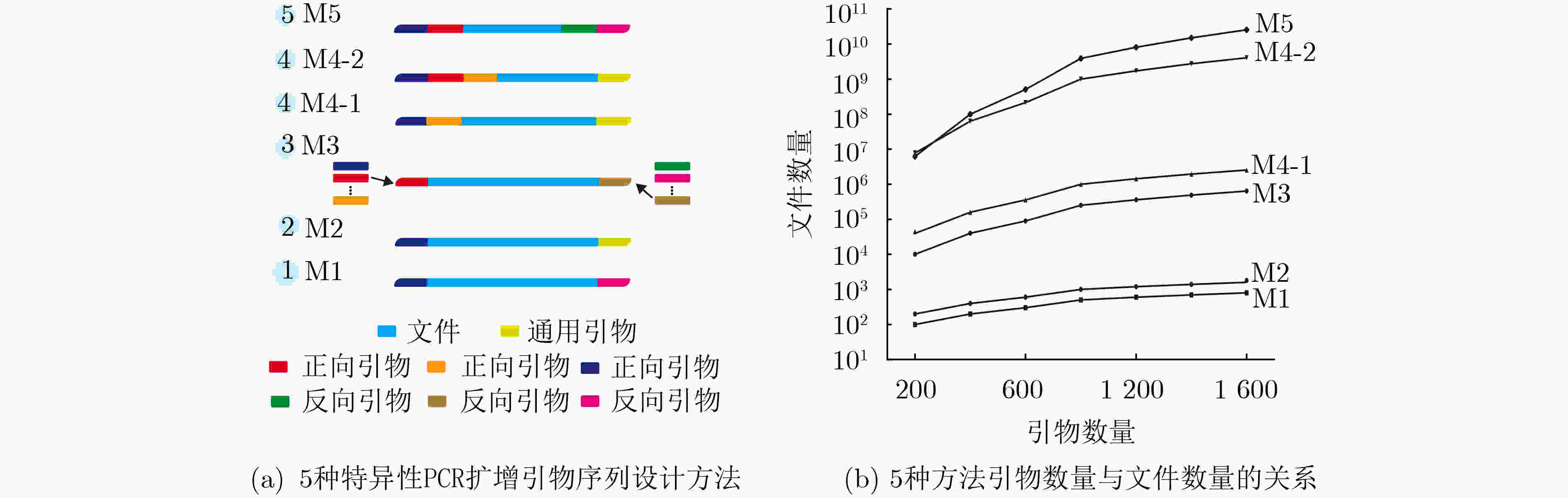
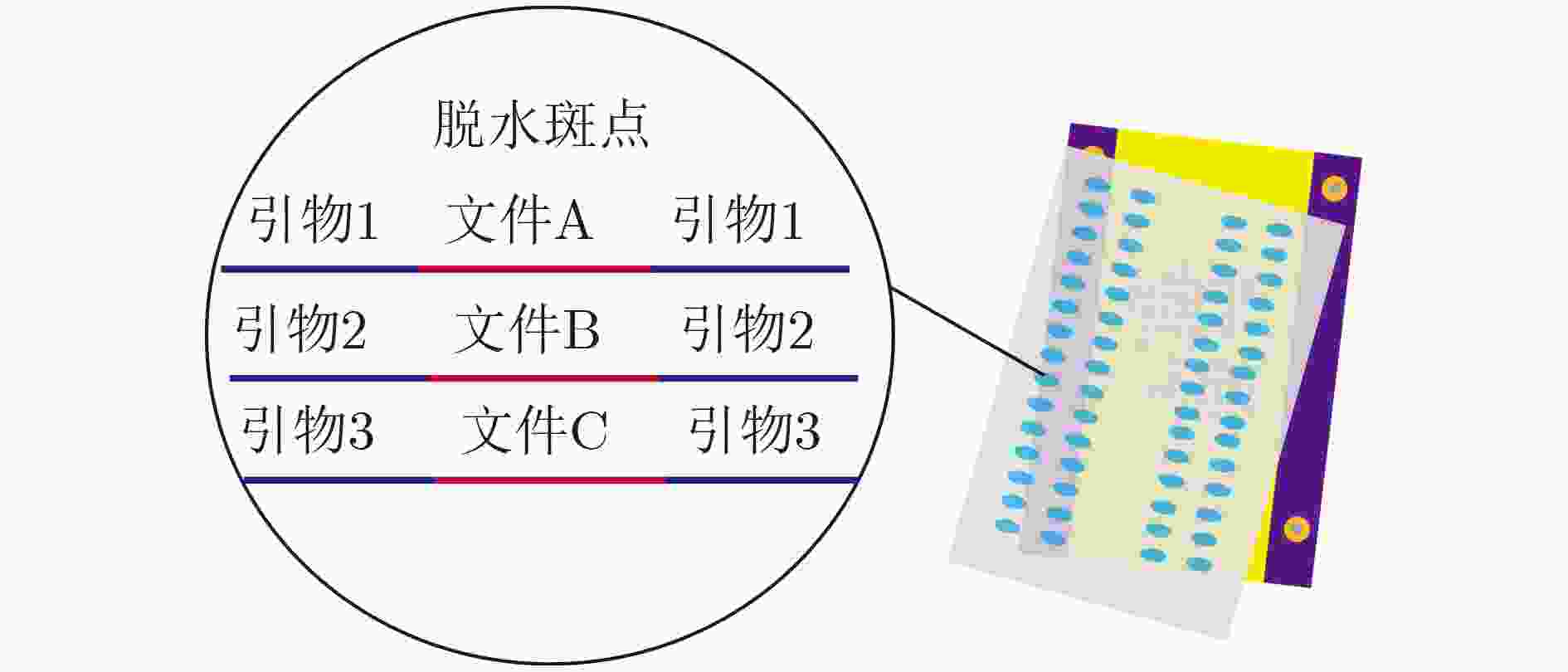
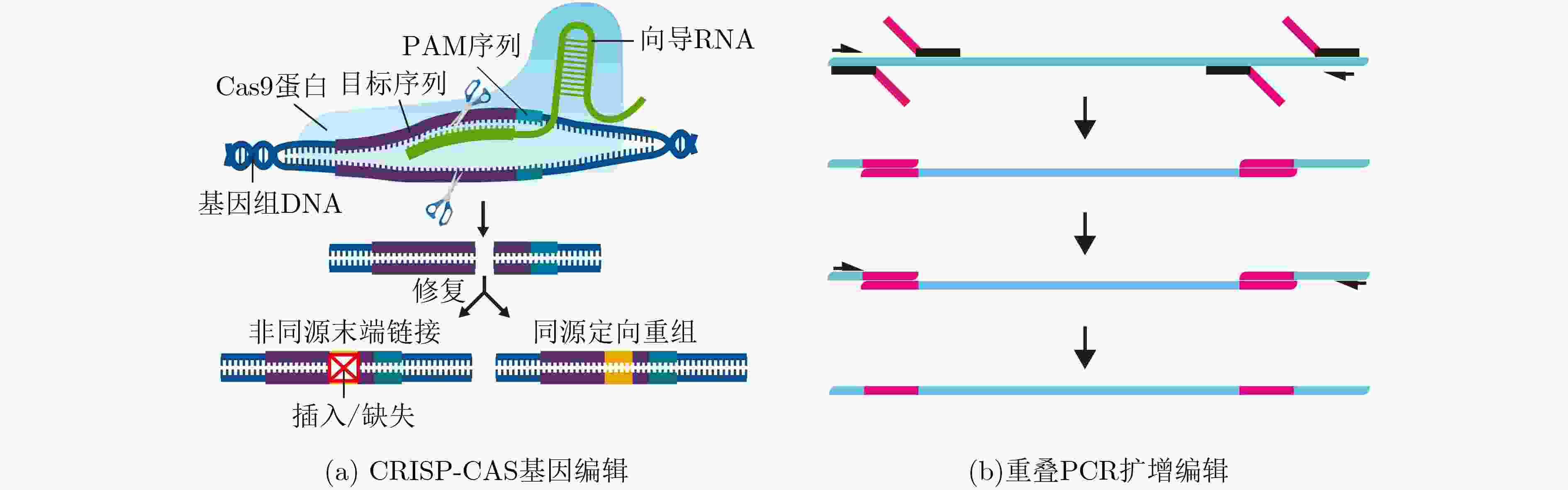


 下载:
下载:
