3D Wireless Secure Transmission under Random Frequency Diversity Array Assisted by Deep Learning
-
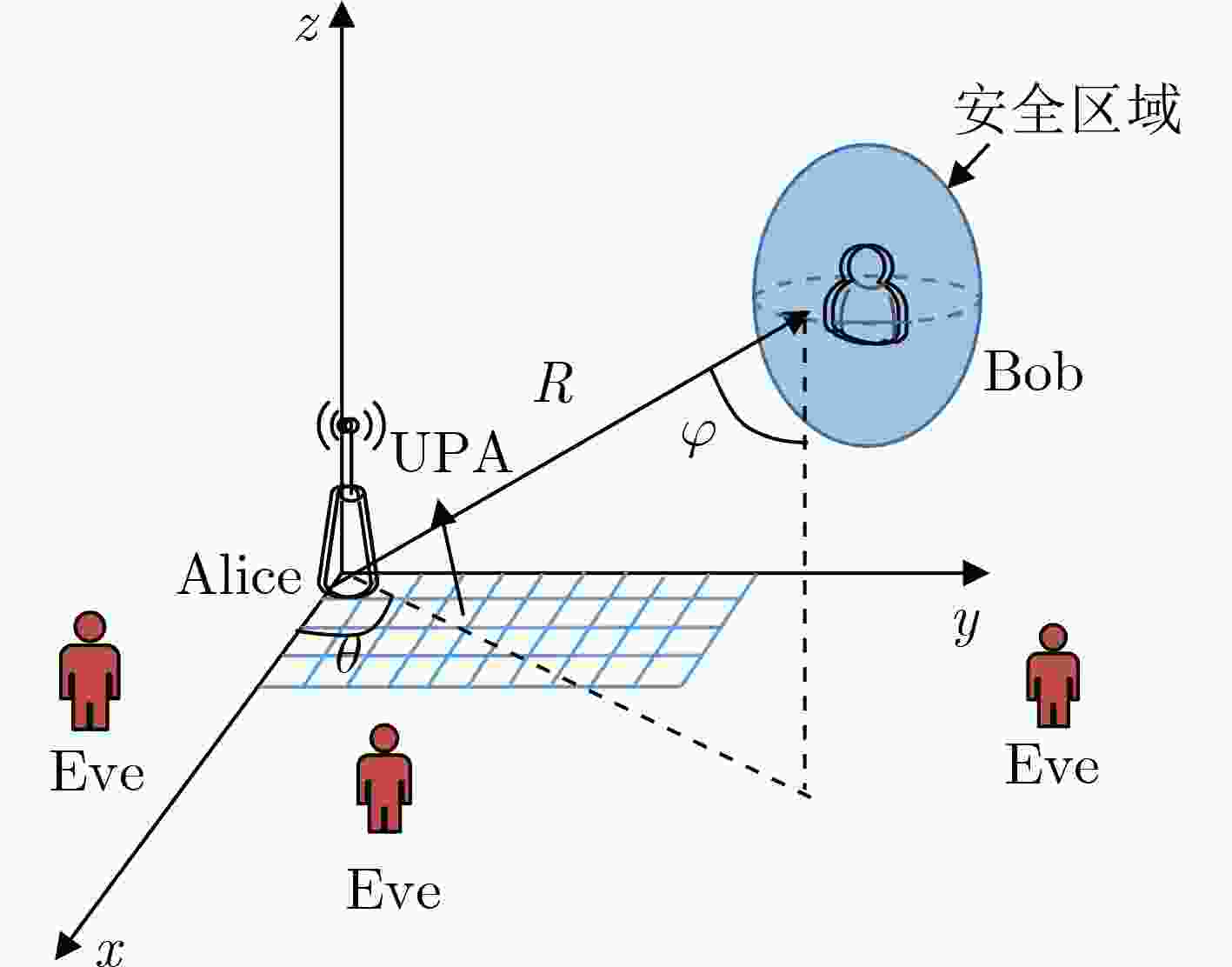
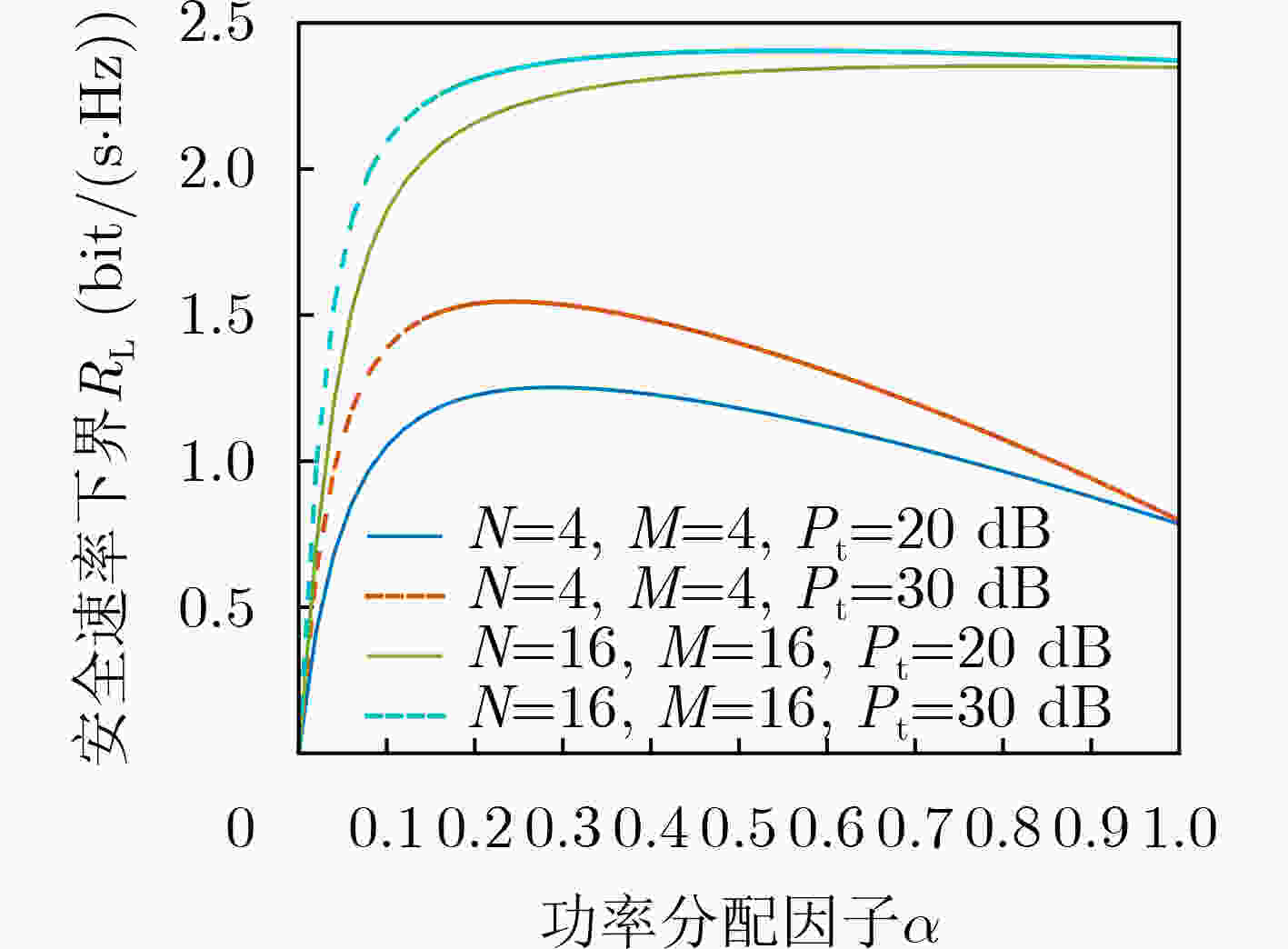
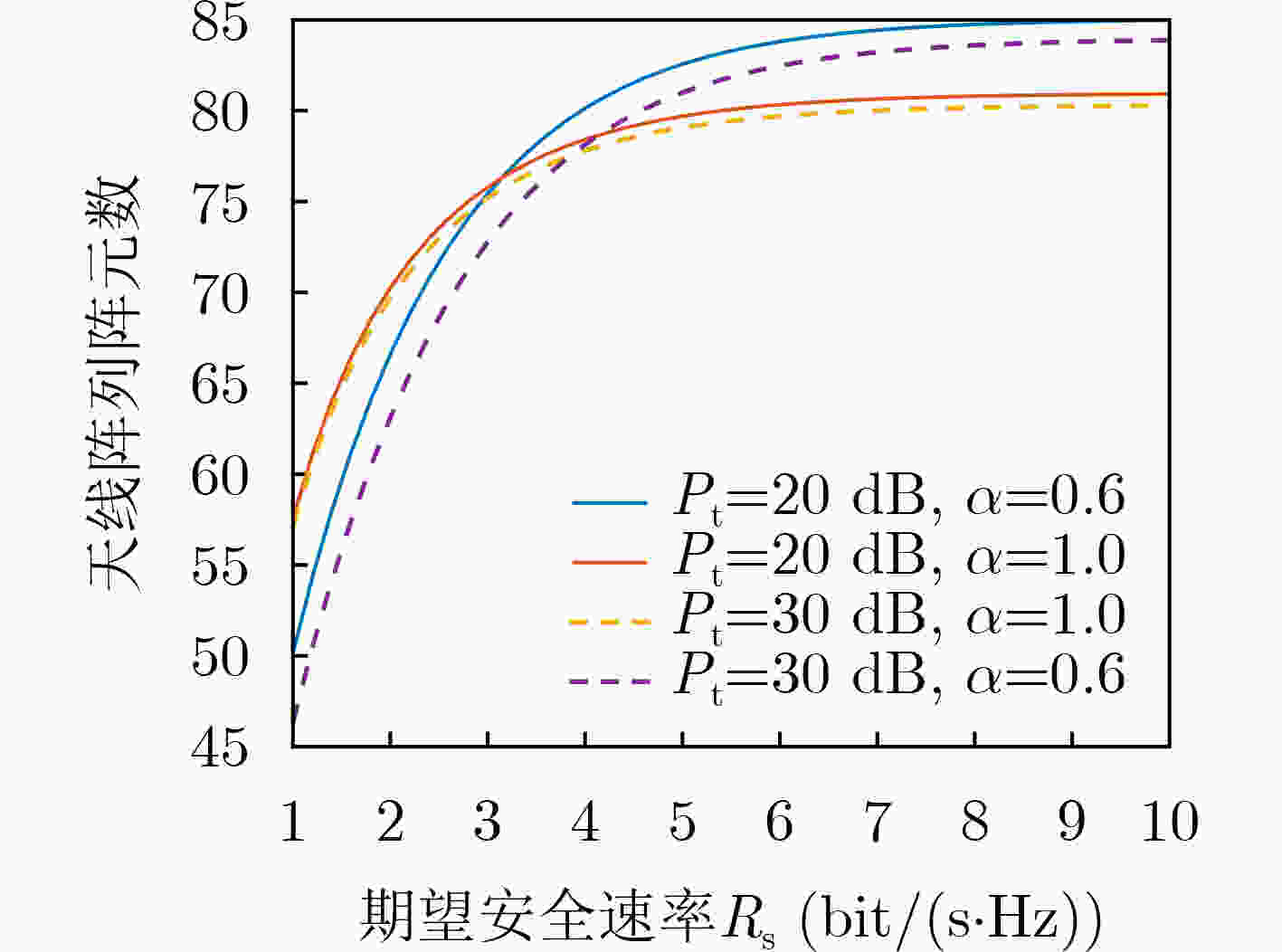
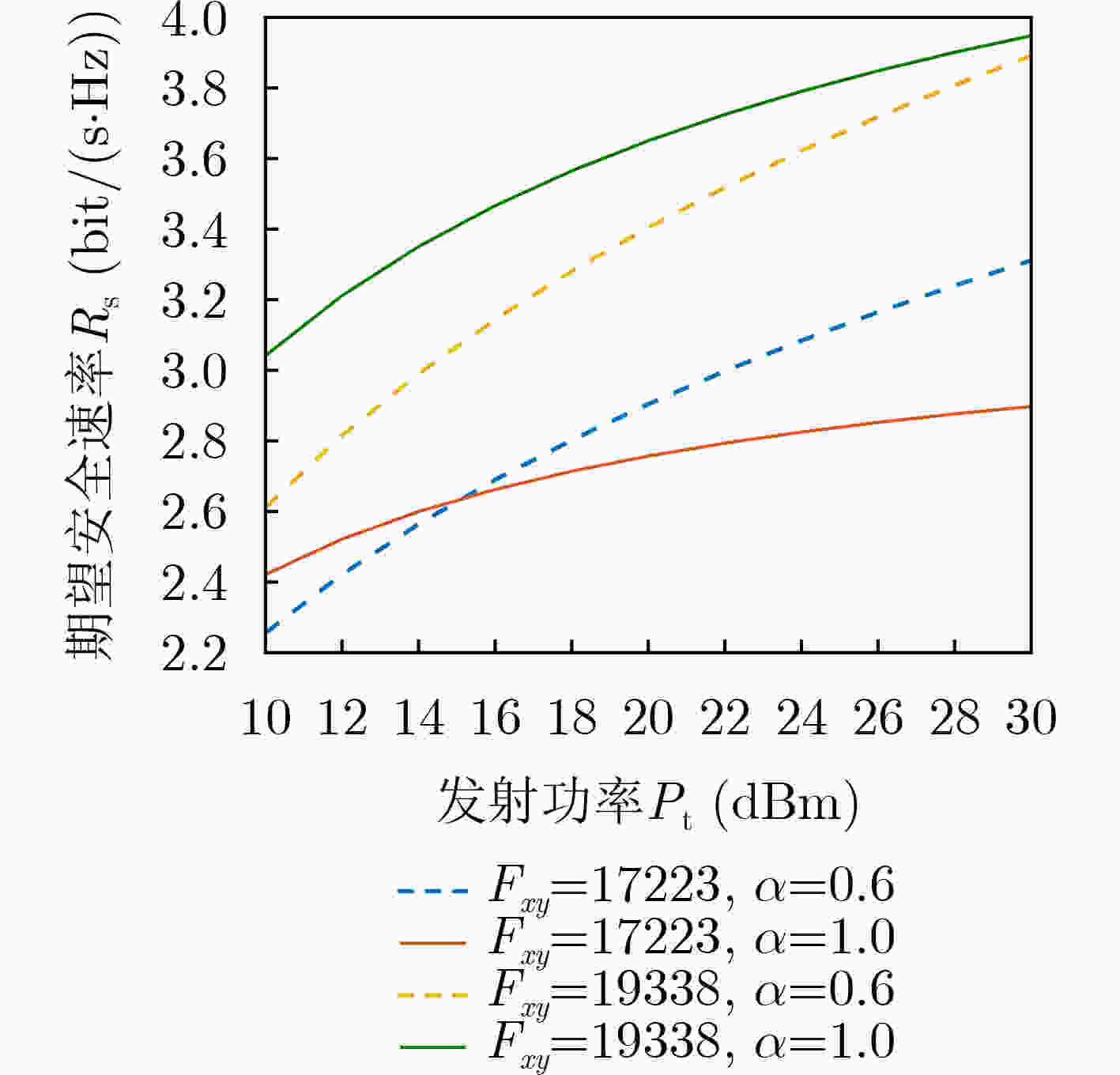
摘要: 针对相控阵列辅助的无线通信系统中发射波束只依赖角度特性而导致的安全隐患问题,以及传统的迭代算法所带来的高计算复杂度问题,该文提出由深度学习(DL)和随机频率分集阵列(RFDA)辅助带有3维安全区域的安全传输方案。首先,推导在3维空间中带有安全区域的期望用户实现安全通信的传输条件。在此基础上,构建系统安全速率下界最大化问题。随后,提出基于深度学习的神经网络方案来设计最优的波束成形矢量和人工噪声(AN)矢量来降低计算复杂度。仿真结果表明:即便是在窃听者位于安全区域边缘的最差情况下,所提方案仍能够在实现3维安全传输,能够保证安全区域内接收到的信息不被窃听。Abstract: To solve the potential security issue caused by the fact that the transmitted beam in the phased array-assisted wireless communication systems only depend on angle characteristics and high computational complexity caused by the traditional iteration algorithms. A secure transmission scheme with 3D secure region assisted by Random Frequency Diverse Array (RFDA) and Deep Learning (DL) is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the requirements for the secure communication with the desired user within 3D secure zone are derived. Based on it, an optimization problem is formulated to maximize the lower bound of the secure rate of the considered system. Then, an optimization scheme based on deep learning is proposed to design the beamforming vector and Artificial Noise (AN) vector, so as to reduce the computational complexity. Simulation results show that even when the eavesdropper is located at the edge of the desired user’s secure region, the proposed scheme can achieve the 3D secure transmission, and ensure the received confidential information in secure region.
-
表 1 所提神经网络模型参数
层名 输出维度 激活函数 输入层 $ 64 \times 2 $ 无 批量标准化层 $ 64 \times 2 $ 无 扁平层 $ 128 \times 1 $ 无 批量标准化层 $ 128 \times 1 $ 无 隐藏层1 $ 256 \times 1 $ ReLU 批量标准化层 $ 256 \times 1 $ 无 隐藏层2 $ 128 \times 1 $ ReLU 输出层 $ 128 \times 1 $ 无 自定层 $ 128 \times 1 $ 无 算法1 求解优化问题式(41)的鲁棒算法 输入:完美无线信道系数$ h $、非完美的信道状态信息$ \hat h $以及安全
传输条件$ \eta $;输出:输出训练完成的神经网络; (1) 初始化神经网络; (2) While $i \le T$ do (3) While 训练数据全部进入神经网络 do (4) 从训练数据从采样$ K $个数据; (5) 计算自定义损失函数并更新神经网络参数; (6) End While (7) 更新训练次数$ i = i + 1 $; (8) End While -
[1] YERRAPRAGADA A K, EISMAN T, and KELLEY B. Physical layer security for beyond 5G: Ultra secure low latency communications[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2021, 2: 2232–2242. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2021.3105185 [2] ARFAOUI M A, SOLTANI D M, TAVAKKOLNIA I, et al. Physical layer security for visible light communication systems: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(3): 1887–1908. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2020.2988615 [3] WEI Zhongxiang, MASOUROS C, and LIU Fan. Secure directional modulation with few-bit phase shifters: Optimal and iterative-closed-form designs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(1): 486–500. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3032459 [4] ZHANG Bo, LIU Wei, LI Qiang, et al. Directional modulation design under a given symbol-independent magnitude constraint for secure IoT networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(20): 15140–15147. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3040303 [5] HU Jinsong, SHU Feng, and LI Jun. Robust synthesis method for secure directional modulation with imperfect direction angle[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2016, 20(6): 1084–1087. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2550022 [6] SHU Feng, TENG Yin, LI Jiayu, et al. Enhanced secrecy rate maximization for directional modulation networks via IRS[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(12): 8388–8401. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3110598 [7] MA Yezi, WEI Ping, and ZHANG Huaguo. General focusing beamformer for FDA: Mathematical model and resolution analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2019, 67(5): 3089–3100. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2900400 [8] HU Jinsong, YAN Shihao, SHU Feng, et al. Artificial-noise-aided secure transmission with directional modulation based on random frequency diverse arrays[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 1658–1667. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2653182 [9] SHU Feng, WU Xiaomin, HU Jinsong, et al. Secure and precise wireless transmission for random-subcarrier-selection-based directional modulation transmit antenna array[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(4): 890–904. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2824231 [10] WANG Shuaiyu, YAN Shihao, ZHANG Jia, et al. Secrecy zone achieved by directional modulation with random frequency diverse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(2): 2001–2006. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3054803 [11] XIE Ning, LI Zhuoyuan, and TAN Haijun. A survey of physical-layer authentication in wireless communications[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(1): 282–310. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2020.3042188 [12] LIN Tian and ZHU Yu. Beamforming design for large-scale antenna arrays using deep learning[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(1): 103–107. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2943466 [13] HUANG Hongji, SONG Yiwei, YANG Jie, et al. Deep-learning-based millimeter-wave massive MIMO for hybrid precoding[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(3): 3027–3032. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2893928 [14] ZENG Jun, HE Zhengran, SUN Jinlong, et al. Deep transfer learning for 5G massive MIMO downlink CSI feedback[C]. 2021 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Nanjing, China, 2021. [15] HU Zhengyang, GUO Jianhua, LIU Guanzhang, et al. MRFNet: A deep learning-based CSI feedback approach of massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(10): 3310–3314. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3099841 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
