Design of Beamforming Algorithm for Ultra-reliable and Low-latency Communication in Heterogeneous Networks Based on IRS Assistance
-
摘要: 为了增强微小区内超可靠低时延通信(URLLC)业务在异构网络场景下的传输性能,该文提出一种基于智能超表面(IRS)辅助通信网络下最大化用户和速率的波束成形算法。异构网络中微小区采用短包通信技术,在保证宏小区用户通信质量的前提下,使用IRS提高微小区用户在一定解码错误概率下的短数据包传输性能,建立一个联合优化波束向量和IRS相移向量的微小区用户和速率最大化问题模型。通过交替固定优化变量的方式,将该非凸优化问题拆分为两个子问题,利用逐次凸逼近(SCA)的方法将原问题转换成凸优化问题,并利用交替优化算法对该问题进行求解。仿真结果表明,该算法通过部署IRS可以有效减弱异构场景下对于微小区用户的干扰,同时由于IRS的部署能够有效优化波束成形向量进而提高微小区用户的短包传输性能,并且IRS的通信增强效果与微小区用户的解码错误概率以及IRS反射单元的数量有直接关系。
-
关键词:
- 智能反射表面(IRS) /
- 异构网络 /
- 超可靠低时延通信
Abstract: In order to enhance the transmission performance of Ultra-Reliable and Low-Latency Communication (URLLC) services in small cell in heterogeneous network scenarios, this paper proposes a beamforming algorithm based on Intelligent Reflecting Surface (IRS) assisted communication network to maximize users sum rates. Small cells in heterogeneous networks adopt short packet communication technology. On the premise of ensuring the communication quality of macro cell users, IRS is used to improve the short packet transmission performance of micro cell users under a certain decoding error probability, and a joint optimization beamforming vector and IRS are established. A problem is modeled for jointly optimizing beamforming vector and IRS phase shift vector. The non-convex optimization problem is split into two sub-problems by alternately fixing the optimization variables. The original problem is transformed into a convex optimization problem by using the Successive Convex Approximation (SCA) method, and the problem is solved by the alternating optimization algorithm. The simulation results show that the algorithm can effectively reduce the interference to small cell users in heterogeneous scenarios by deploying IRS, because the deployment of IRS can effectively optimize the beamforming vector and improve the short-packet transmission performance of small cell users, and the communication of IRS is enhanced. The effect is directly related to the decoding error probability of small cell users and the number of IRS reflection units. -
表 1 基于SCA的迭代主动预编码波束向量算法设计(算法1)
初始化最大迭代次数$t_1^{\max }$,迭代序号为${t_1}$以及变量$ \{ {\mathbf{W}}_k^{{t_1}}\} $,固定
优化变量$ {\mathbf{u}} = {[{u_1},{u_2}, \cdots ,{u_N}]^{\text{H}}} $为常量;(1) ${\text{for }}i = 1,2, \cdots ,{\text{do}}$ (2) 在给定变量$ {\mathbf{W}}_k^{{t_1}} $,$ {\mathbf{u}} $的条件下,求解问题式(16),从而获取
$ {\mathbf{W}}_k^{{t_1} + 1} $;(3) 令${t_1} = {t_1} + 1$$ ; $ (4) 循环直到收敛或者${t_1} = t_1^{\max }$; (5) ${\text{end for}}$ 表 2 基于SCA迭代优化反射相移算法设计(算法2)
初始化最大迭代次数$t_2^{\max }$,迭代序号为${t_2} = 0$,在给定$ {\mathbf{W}}_k^{{t_1}} $,初
始化变量$ {{\mathbf{\bar U}}^{{t_2}}} $,(1) ${\text{for }}i = 1,2, \cdots ,{\text{do}}$ (2) 在给定$ {\mathbf{W}}_k^{{t_1}} $的情况下,通过求解问题(25),从而获取$ {{\mathbf{\bar U}}^{{t_2} + 1}} $ (3) 令${t_2} = {t_2} + 1$ (4) 循环直到收敛或者$ {t_2} = t_2^{\max } $ (5) ${\text{end for}}$ 表 3 基于交替迭代优化主动波束和反射相移算法设计(算法3)
初始化最大迭代次数$t_3^{\max }$,初始化迭代序列号${t_3} = 0$,变量
$ {\mathbf{W}}_k^{{t_3}} $以及$ {{\mathbf{\bar U}}^{{t_3}}} $(1) ${\text{for }}i = 1,2, \cdots ,{\text{do}}$ (2) 通过表1的算法在给定$ {\mathbf{W}}_k^{{t_3}} $以及$ {{\mathbf{\bar U}}^{{t_3}}} $的情况下获取$ {\mathbf{W}}_k^{{t_3} + 1} $ (3) 通过表2在给定$ {\mathbf{W}}_k^{{t_3} + 1} $的情况下获取$ {{\mathbf{\bar U}}^{{t_3} + 1}} $ (4) 令${t_3} = {t_3} + 1$ (5) 循环直到收敛或者$ {t_3} = t_3^{\max } $ (6) ${\text{end for}}$ -
[1] HUANG Chongwen, HU Sha, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Holographic MIMO surfaces for 6G wireless networks: Opportunities, challenges, and trends[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(5): 118–125. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.1900534 [2] NGUYEN H D and SUN Sumei. Massive MIMO versus small-cell systems: Spectral and energy efficiency comparison[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2016: 1–6. [3] SUTTON G J, ZENG Jie, LIU Renping, et al. Enabling technologies for ultra-reliable and low latency communications: From PHY and MAC layer perspectives[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2019, 21(3): 2488–2524. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2019.2897800 [4] SUER M T, THEIN C, TCHOUANKEM H, et al. Multi-connectivity as an enabler for reliable low latency communications—An overview[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(1): 156–169. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2019.2949750 [5] HUANG Chongwen, ZAPPONE A, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(8): 4157–4170. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922609 [6] WEI Li, HUANG Chongwen, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Channel estimation for RIS-empowered multi-user MISO wireless communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(6): 4144–4157. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3063236 [7] XIU Yue, ZHAO Jun, YUEN C, et al. Secure beamforming for multiple intelligent reflecting surfaces aided mmWave systems[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(2): 417–421. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3028135 [8] DAI Haibo, HUANG Wei, ZHANG Haiyang, et al. Achievable harvested energy region of IRS-assisted wireless power transfer system[C]. Proceedings of 2021 13th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, Changsha, China, 2021: 1–5. [9] GHANEM W R, JAMALI V, and SCHOBER R. Joint beamforming and phase shift optimization for multicell IRS-aided OFDMA-URLLC systems[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Nanjing, China, 2021. [10] XU Yongjun, GUI Guan, OHTSUKI T, et al. Robust resource allocation for two-tier HetNets: An interference-efficiency perspective[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2021, 5(3): 1514–1528. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2021.3090592 [11] 曹智禹. 智能反射表面增强的多用户通信系统的优化设计[D]. [硕士论文], 电子科技大学, 2021.CAO Zhiyu. Optimal design of reconfigurable intelligent surfaces enhanced multi-user communication systems[D]. [Master dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021. [12] WANG Jun, LIANG Yingchang, PEI Yiyang, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface for small cell network[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Madrid, Spain, 2021. [13] ZHENG Beixiong, YOU Changsheng, and ZHANG Rui. Fast channel estimation for IRS-assisted OFDM[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(3): 580–584. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3038434 [14] ZHANG Zijian and DAI Linglong. A joint precoding framework for wideband reconfigurable intelligent surface-aided Cell-Free network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 4085–4101. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3088755 [15] LO T K Y. Maximum ratio transmission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1999, 47(10): 1458–1461. doi: 10.1109/26.795811 [16] ERSEGHE T. Coding in the finite-blocklength regime: Bounds based on Laplace integrals and their asymptotic approximations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2016, 62(12): 6854–6883. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2016.2616900 [17] HE Shiwen, AN Zhenyu, ZHU Jianyue, et al. Beamforming design for multiuser uRLLC with finite blocklength transmission[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(12): 8096–8109. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3090197 [18] YU Xianghao, XU Dongfang, SUN Ying, et al. Robust and secure wireless communications via intelligent reflecting surfaces[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(11): 2637–2652. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3007043 [19] HU Shaokang, WEI Zhiqiang, CAI Yuanxin, et al. Sum-rate maximization for multiuser MISO downlink systems with self-sustainable IRS[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Taipei, China, 2020. [20] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Weighted sum power maximization for intelligent reflecting surface aided SWIPT[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(5): 586–590. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2961656 [21] NASIR A A, TUAN H D, NGUYEN H H, et al. Resource allocation and beamforming design in the short blocklength regime for URLLC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(2): 1321–1335. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3032729 [22] LI Zhendong, CHEN Wen, WU Qingqing, et al. Joint beamforming design and power splitting optimization in IRS-assisted SWIPT NOMA networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(3): 2019–2033. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3108901 [23] YU Yiding, WANG Taotao, and LIEW S C. Deep-reinforcement learning multiple access for heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(6): 1277–1290. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2904329 [24] ZHANG Yong, KANG Canping, TENG Yinglei, et al. Deep reinforcement learning framework for joint resource allocation in heterogeneous networks[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE 90th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall), Honolulu, USA, 2019. [25] HUANG Chongwen, MO Ronghong, and YUEN C. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multiuser MISO systems exploiting deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(8): 1839–1850. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3000835 [26] ZHANG Jing, ZHANG Haiyang, ZHANG Zhengming, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-empowered beamforming design for IRS-assisted MISO interference channels[C]. Proceedings of 2021 13th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, Changsha, China, 2021. -





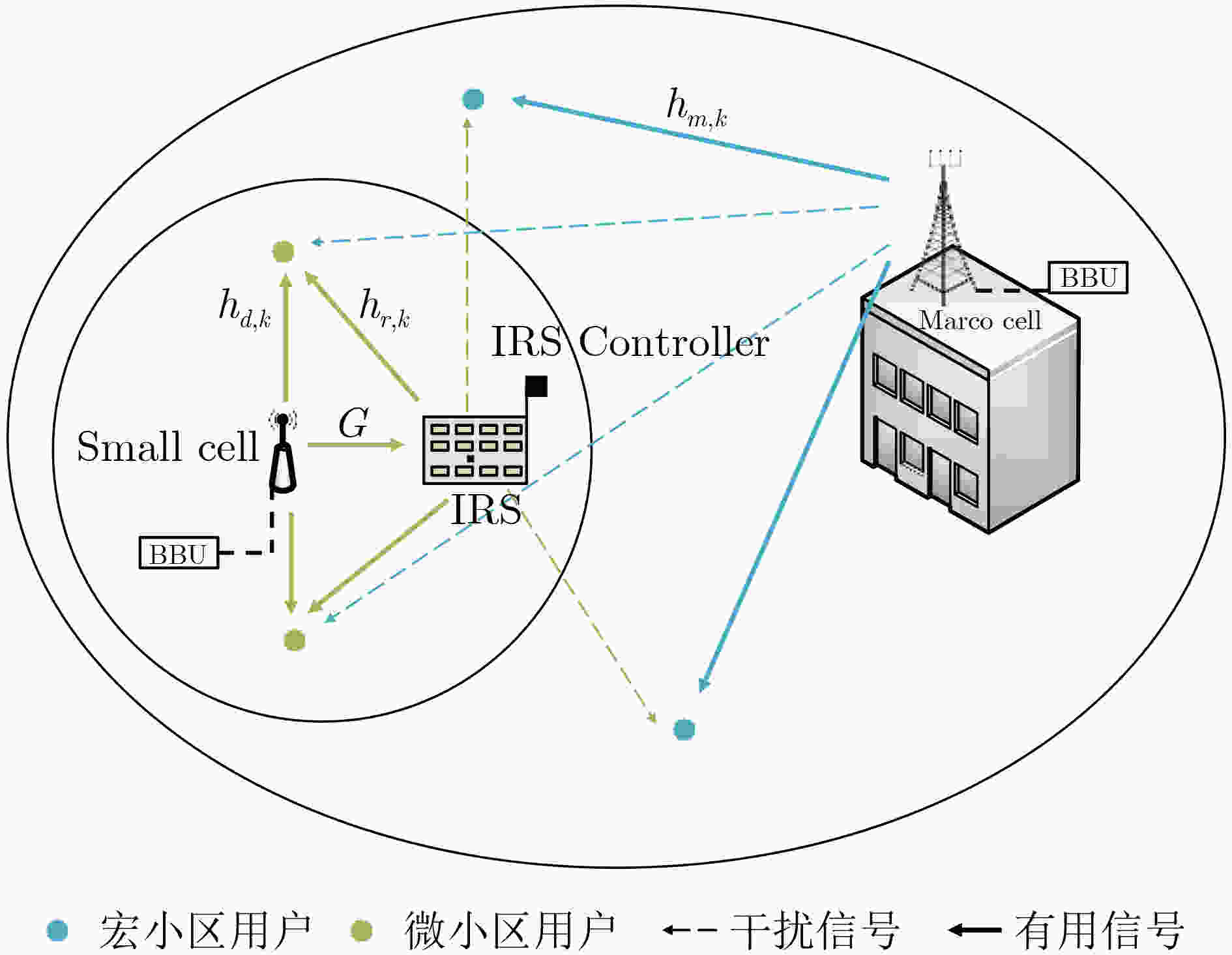
 下载:
下载:
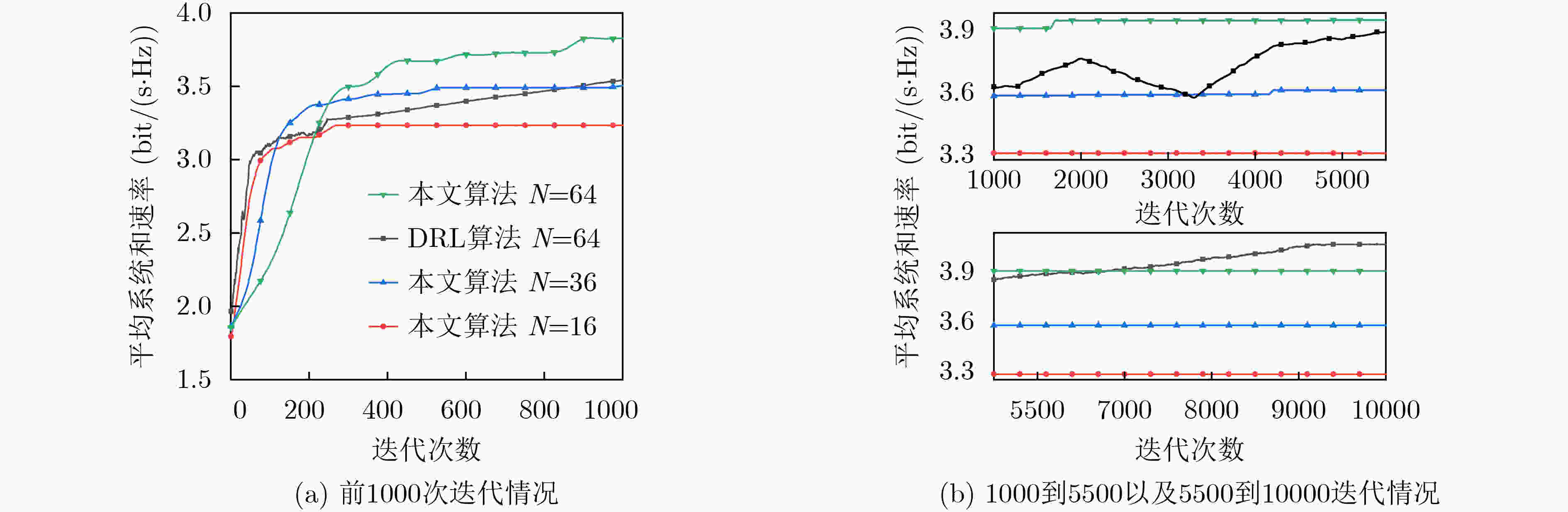


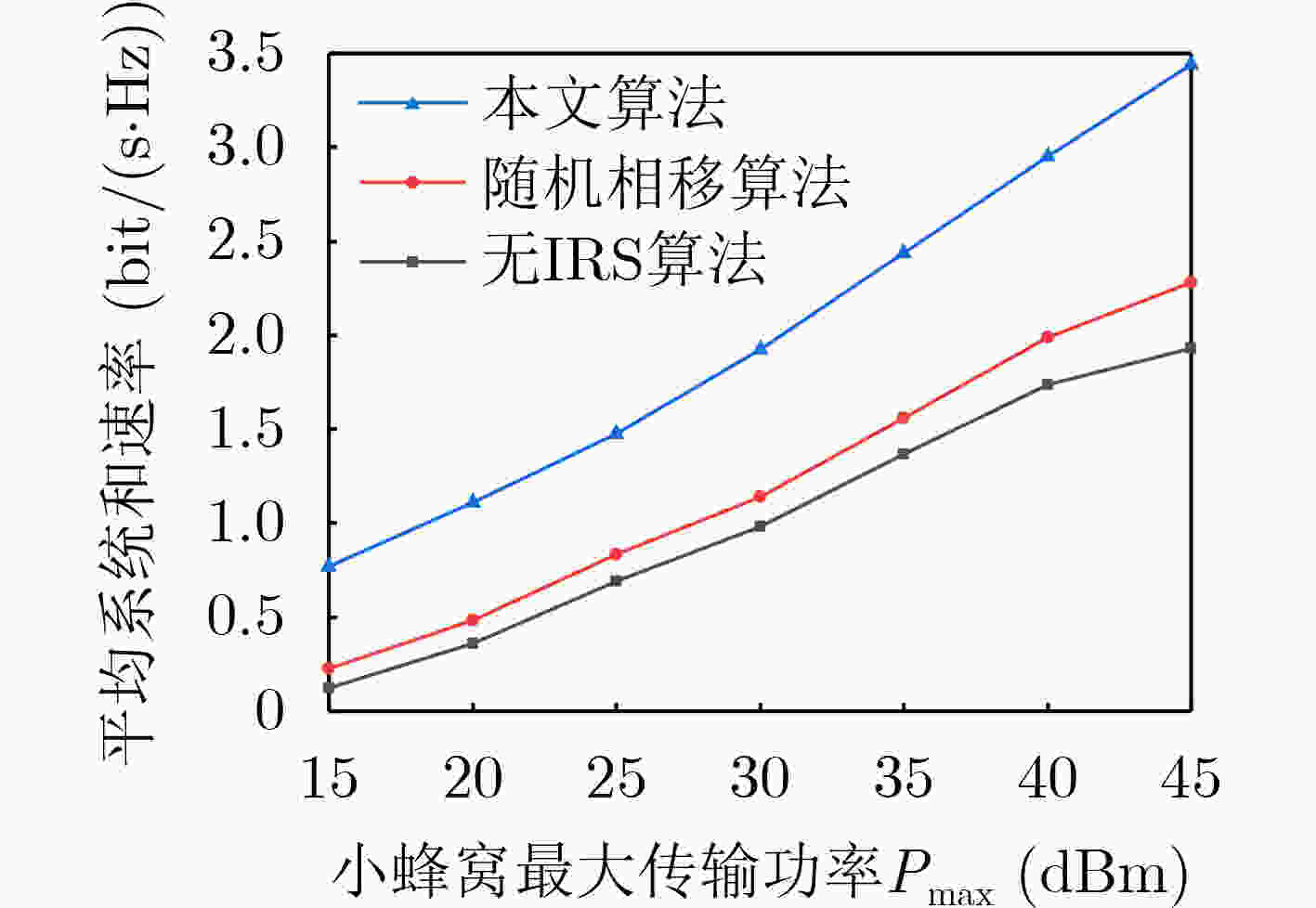


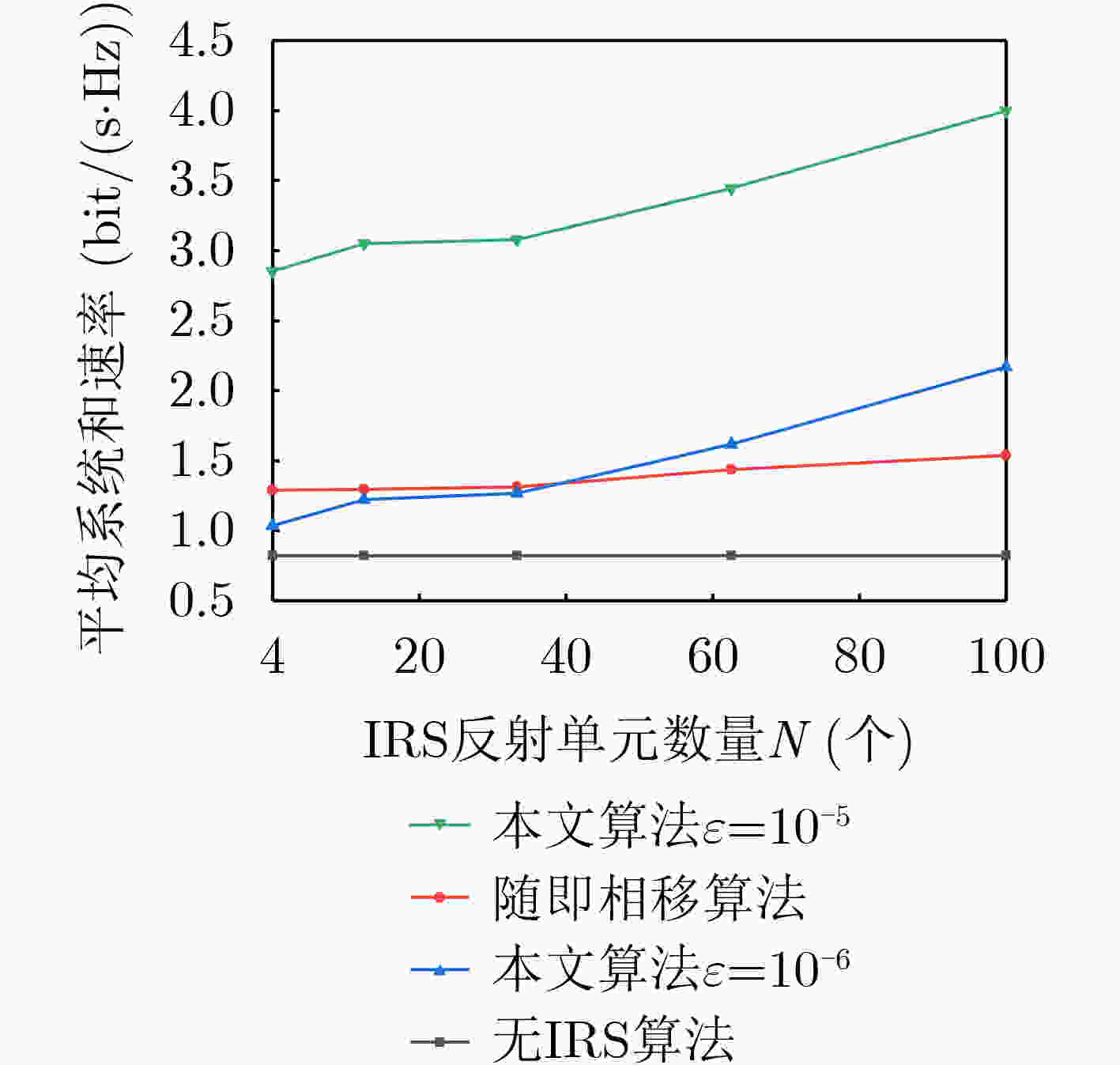


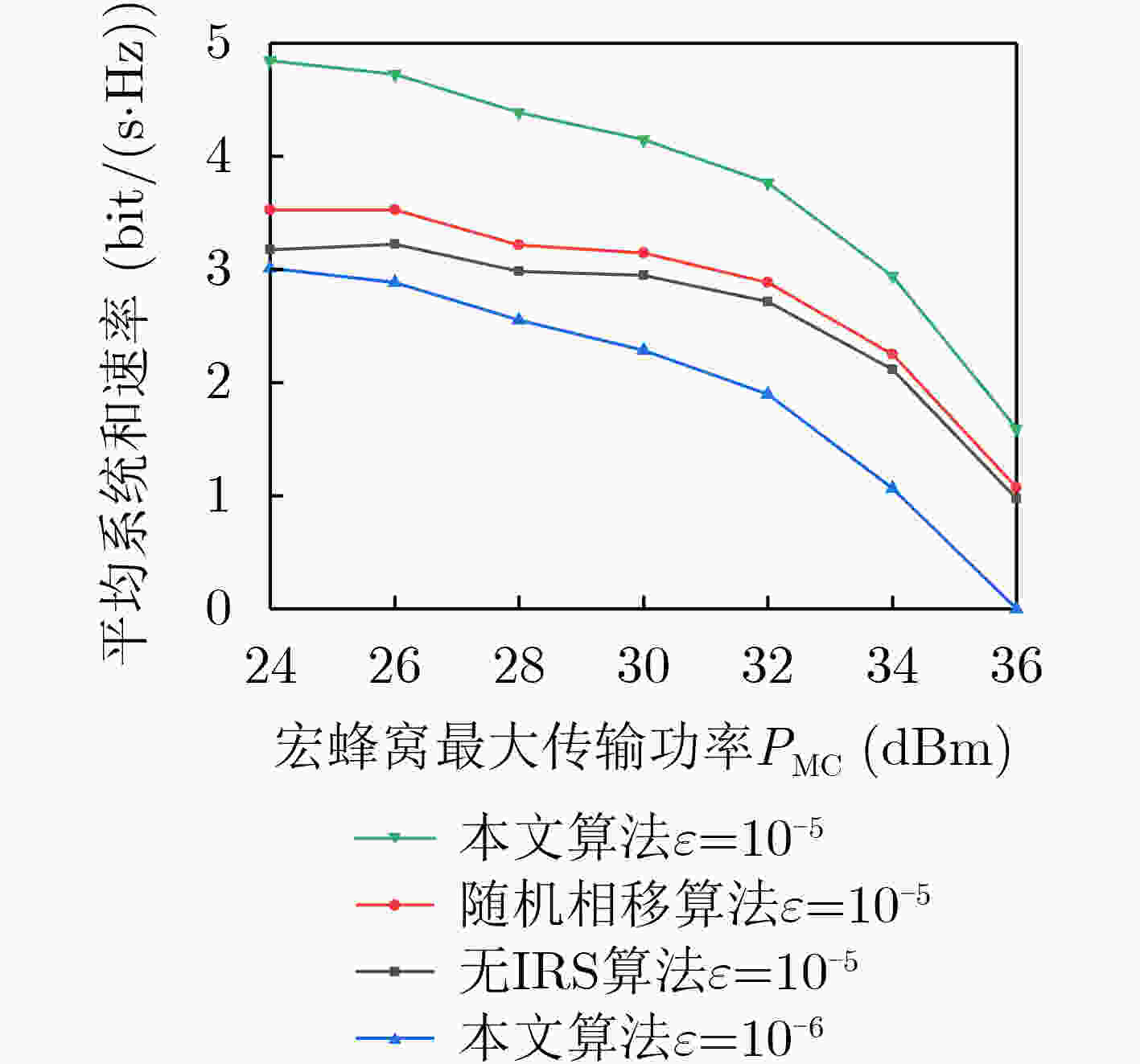


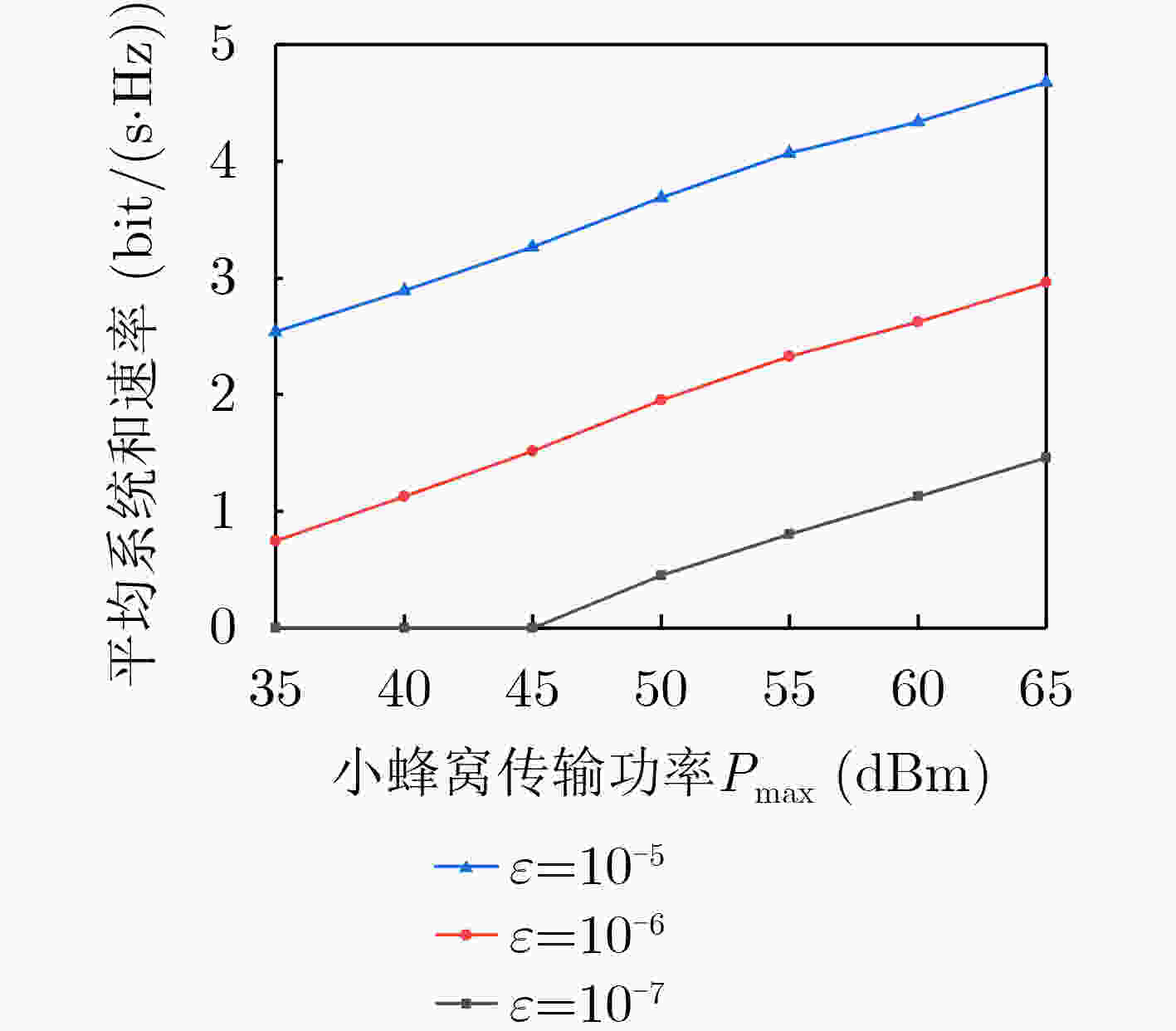


 下载:
下载:
