Semi-supervised Image Dehazing Algorithm Based on Multi-prior Constraint and Consistency Regularization
-
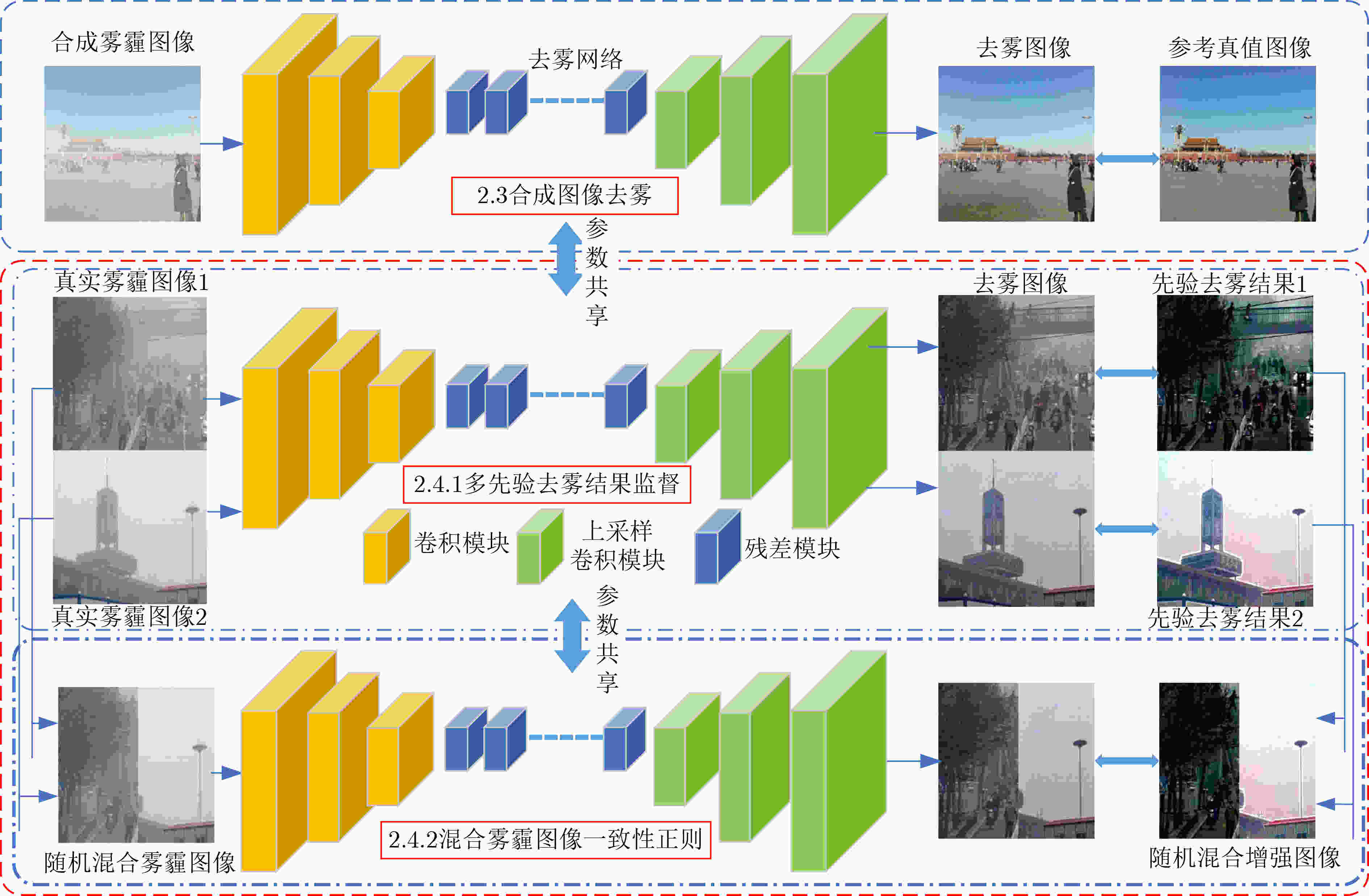
摘要: 针对合成雾霾图像训练的去雾模型在真实场景中去雾效果不佳、对高层视觉任务性能提升不明显等问题,该文提出一种基于多先验约束和一致性正则的半监督图像去雾算法。该方法采用编码器-解码器网络结构,同时在合成雾霾图像与真实雾霾图像上学习去雾映射,并利用多种统计先验去雾结果作为真实雾霾图像参考真值进行半监督学习,同时通过多张真实雾霾图像的随机混合进行一致性正则约束,以消除多种先验去雾结果差异以及噪声干扰,提高图像去雾结果的视觉质量。实验对比结果表明,所提算法可比现有方法获得更好的真实场景去雾结果,并且能够显著提升高层视觉任务性能。Abstract: Previous dehazing models trained on synthetic hazy images can not generalize well on real hazy scenes and improve the performance of high-level vision tasks significantly. To resolve this issue, a semi-supervised image dehazing based on multi-priors constrain and output consistency regularization is proposed. The algorithm adopts the encoder and decoder network to train on the synthetic and real hazy images by sharing the parameters. Multi prior-based dehazed images are adopted as pseudo labels to constrain the real scene hazy images. Furthermore, to reduce the divergence of different prior-based methods, the dehazing results of the random mix-up real hazy images are regularized to be consistent with the corresponding mix-up of the prior-based dehazed images. Finally, the experiment results demonstrate the performance of the proposed algorithm compared with the state-of-the-art methods.
-
Key words:
- Image dehazing /
- Semi-supervised learning /
- Multi-priors /
- Consistency regulation
-
表 1 本文图像去雾网络结构详细设计表(数字表示图像序号)
Conv1 Conv2 Conv3 Conv4 Res1-Res15 UpConv1 UpConv2 UpConv3 Conv5 输入 3 32 64 128 256 256 256 128 64 输出 32 64 128 256 256 128 64 32 3 卷积核大小 7 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 3 卷积步长 1 2 2 2 1 1 1 1 1 边界填充 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 表 2 图像去雾定量实验结果对比(红色表示第1,绿色表示第2,蓝色表示第3)
方法 数据集 SOTS(indoor) SOTS (outdoor) HAZERD IHAZE OHAZE BeDDE PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM VI RI BDCP 14.871 0.7425 17.459 0.8186 13.018 0.7802 15.893 0.8064 15.475 0.7288 0.8970 0.9650 NLD 17.328 0.805 18.115 0.870 14.571 0.8001 12.630 0.628 16.080 0.722 0.8592 0.9583 MSBDN 31.569 0.9825 30.255 0.9630 14.758 0.7956 16.547 0.8062 18.353 0.6999 0.8401 0.9655 SED 22.234 0.9200 25.295 0.9420 16.132 0.8389 15.854 0.7542 18.522 0.7414 0.8814 0.9674 DAAD 25.685 0.9529 25.38 0.9109 17.016 0.8165 17.369 0.8256 18.887 0.7781 0.8835 0.9652 PSD 12.496 0.7177 15.578 0.8049 14.212 0.7712 12.545 0.7364 12.513 0.7090 0.8392 0.9640 本文方法 25.239 0.9584 24.841 0.9394 16.459 0.8456 16.818 0.8130 17.603 0.7999 0.8972 0.9659 表 3 雾霾图像目标检测实验结果对比(红色表示第1,绿色表示第2,蓝色表示第3)
方法 目标类别 Person bicycle car motorbike bus All Gain AP AP AP AP AP mAP Hazy Image 81.76 65.76 75.06 63.13 37.59 64.46 – BDCP 82.23 63.92 72.99 58.41 43.38 64.19 –0.27 NLD 80.48 63.44 73.87 59.19 35.93 62.58 –1.88 MSBDN 83.00 65.47 75.66 61.55 38.48 64.83 +0.27 SED 82.43 65.59 75.81 61.92 38.99 64.94 +0.48 DAAD 81.45 64.27 76.34 61.87 40.74 64.93 +0.47 PSD 82.78 65.82 74.81 60.16 42.18 65.15 +0.69 本文方法 82.89 65.69 75.66 62.37 42.09 65.74 +1.28 表 4 消融实验结果对比
数据集 指标名称 基准方法 变体1 变体2 变体3 变体4 本文方法 BeDDE VI 0.8788 0.8812 0.8854 0.8903 0.8935 0.8972 RI 0.9552 0.9589 0.9603 0.9615 0.9632 0.9659 RTTS mAP (%) 64.7 64.6 63.9 65.2 65.4 65.7 表 5 5种去雾方法运行时间对比(s)
MSBDN SED DAAD PSD 本文方法 运行时间 0.075 0.012 0.049 0.043 0.028 -
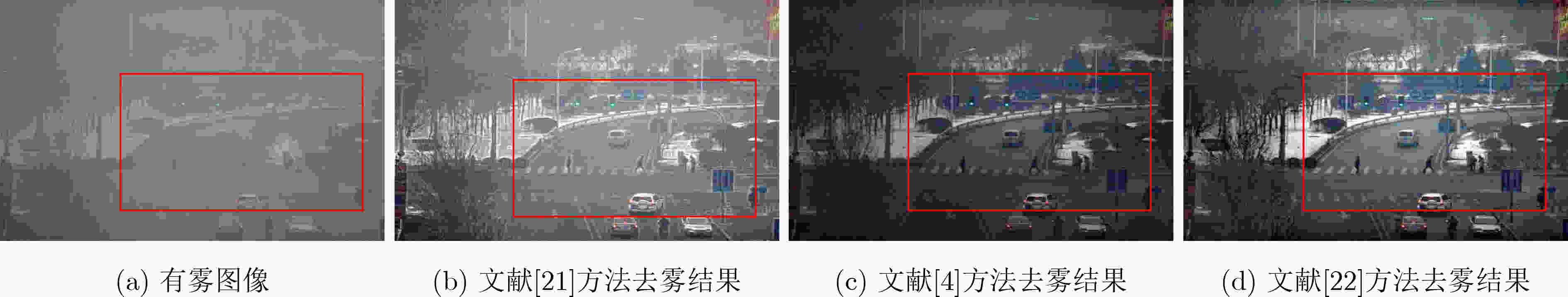
[1] 李红云, 施云, 高银. 基于显著性权重的多曝光融合的单幅雾天图像复原算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 261–270. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200931LI Hongyun, SHI Yun, and GAO Yin. Single image dehazing via saliency weighted multi-exposure fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 261–270. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200931 [2] YANG Wenhan, YUAN Ye, and REN Wenqi, et al. Advancing image understanding in poor visibility environments: A collective benchmark study[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 5737–5752. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2981922 [3] NAYAR S K and NARASIMHAN S G. Vision in bad weather[C]. Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 1999: 820–827. [4] HE Kaiming, SUN Jian, and TANG Xiaoou. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341–2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [5] ZHU Qingsong, MAI Jiaming, and SHAO Ling. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3522–3533. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2446191 [6] FATTAL R. Dehazing using color-lines[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2014, 34(1): 13. doi: 10.1145/2651362 [7] REN Wenqi, PAN Jinshan, ZHANG Hua, et al. Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks with holistic edges[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(1): 240–259. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01235-8 [8] CAI Bolun, XU Xiangmin, JIA Kui, et al. DehazeNet: An end-to-end system for single image haze removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(11): 5187–5198. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2598681 [9] ZHANG He and PATEL V M. Densely connected pyramid dehazing network[C]. The 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3194–3203. [10] LIU Xiaohong, MA Yongrui, SHI Zhihao, et al. GridDehazeNet: Attention-based multi-scale network for image dehazing[C]. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 7313–7322. [11] QIN Xu, WANG Zhilin, BAI Yuanchao, et al. FFA-Net: Feature fusion attention network for single image dehazing[C]. 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 11908–11915. [12] DONG Hang, PAN Jinshan, XIANG Lei, et al. Multi-scale boosted dehazing network with dense feature fusion[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 2154–2164. [13] SU Yanzhao, CUI Zhigao, HE Chuan, et al. Prior guided conditional generative adversarial network for single image dehazing[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 423: 620–638. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.10.061 [14] LI Lerenhan, DONG Yunlong, REN Wenqi, et al. Semi-supervised image dehazing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 2766–2779. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2952690 [15] SHAO Yuanjie, LI Lerenhan, REN Wenqi, et al. Domain adaptation for image dehazing[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 2805–2814. [16] CHEN Zeyuan, WANG Yangchao, YANG Yang, et al. PSD: Principled synthetic-to-real dehazing guided by physical priors[C]. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 7176–7185. [17] 张世辉, 路佳琪, 宋丹丹, 等. 基于多尺度特征结合细节恢复的单幅图像去雾方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 待发表.ZHANG Shihui, LU Jiaqi, SONG Dandan, et al. Single image dehazing method based on multi-scale features combined with detail recovery[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology. To be published, [18] WANG Nian, CUI Zhigao, SU Yanzhao, et al. Multiscale supervision-guided context aggregation network for single image dehazing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022, 29: 70–74. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3125272 [19] MEI Kangfu, JIANG Aiwen, LI Juncheng, et al. Progressive feature fusion network for realistic image dehazing[C]. 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2019: 203–215. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-20887-5_13. [20] ZHAO Hang, GALLO O, FROSIO I, et al. Loss functions for image restoration with neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2017, 3(1): 47–57. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2016.2644865 [21] 卢辉斌, 赵燕芳, 赵永杰, 等. 基于亮通道和暗通道结合的图像去雾[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(11): 1115004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.111500LU Huibin, ZHAO Yanfang, ZHAO Yongjie, et al. Image defogging based on combination of image bright and dark channels[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(11): 1115004. doi: 10.3788/AOS201838.111500 [22] BERMAN D, TREIBITZ T, and AVIDAN S. Non-local image dehazing[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1674–1682. [23] GHIASI G, ZOPH B, CUBUK E D, et al. Multi-task self-training for learning general representations[C]. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 8836–8845. [24] YUN S, HAN D, CHUN S, et al. CutMix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features[C]. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 6022–6031. [25] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2016.2577031 [26] LI Boyi, REN Wenqi, FU Dengpan, et al. Benchmarking single-image dehazing and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(1): 492–505. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2867951 [27] ZHANG Yanfu, DING Li, and SHARMA G. HazeRD: An outdoor scene dataset and benchmark for single image dehazing[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 2017: 3205–3209. [28] ANCUTI C, ANCUTI C O, TIMOFTE R, et al. I-HAZE: A dehazing benchmark with real hazy and haze-free indoor images[C]. The 19th International Conference on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, Poitiers, France, 2018: 620–631. [29] ANCUTI C O, ANCUTI C, TIMOFTE R, et al. O-HAZE: A dehazing benchmark with real hazy and haze-free outdoor images[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 867–875. [30] ZHAO Shiyu, ZHANG Lin, HUANG Shuaiyi, et al. Dehazing evaluation: Real-world benchmark datasets, criteria, and baselines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 6947–6962. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2995264 [31] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[EB/OL].https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1804.02767, 2018. [32] LI Chongyi, GUO Chunle, REN Wenqi, et al. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 4376–4389. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2955241 -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
