Marine Boat Lights Detection Method Based on Sparse Representation for Low Light Remote Sensing Images During Night
-
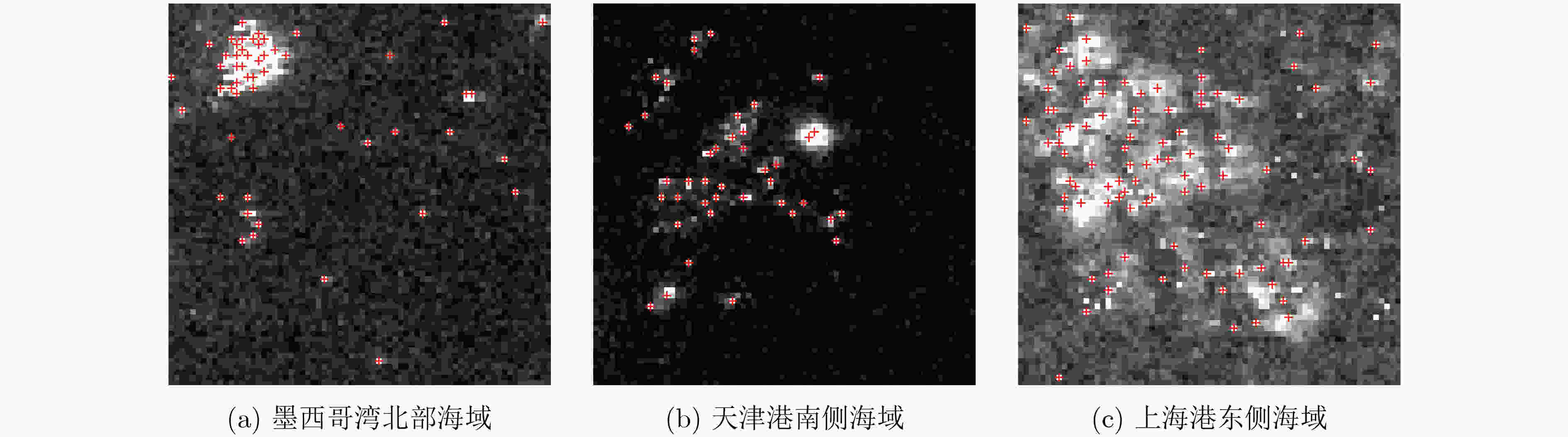
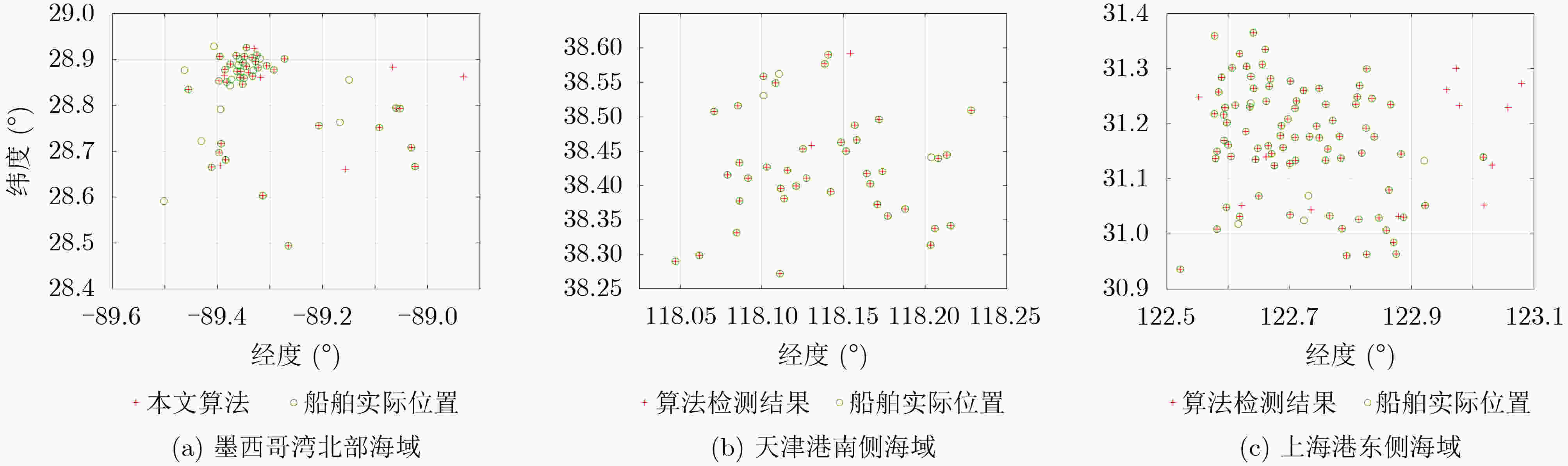
摘要: 针对目前基于低照度遥感影像对夜间海上船舶检测存在的目标特征挖掘不足的问题,该文设计了一种可使船舶目标样本和背景噪声样本最小错分的稀疏度指标,提出一种基于稀疏编码算法和字典学习算法的低照度遥感影像夜间船舶灯光检测算法,并将其应用于墨西哥湾北部海域、天津港南侧海域和上海港东侧海域,检测精确度分别为96.36%, 95.12%, 86.26%,召回率分别为96.36%, 92.86%, 94.19%,调和平均值分别为96.36%, 93.98%, 90.05%;进一步地,该文将此算法与3种典型低照度遥感影像夜间海上船舶检测算法进行了对比分析,结果表明该文算法更具有优越性能,可为夜间海上船舶的检测提供新的思路。Abstract: To address the problem of insufficient target feature mining in nighttime marine boat detection based on low light remote sensing images, a new sparsity index is designed to minimize the misclassification of boat lights samples and background noises samples, and a detection algorithm for boat lights based on sparse coding and dictionary learning is proposed in this paper. The proposed algorithm is applied to the northern sea area of the Gulf of Mexico, the sea area south of Tianjin Port, and the sea area east of Shanghai Port, and the detection precision is 96.36%, 95.12%, 86.26%, recall rate is 96.36%, 92.86%, 94.19%, and the harmonic mean is 96.36%, 93.98%, 90.05% respectively. Furthermore, the proposed algorithm is compared with three typical marine boat lights detection method for low light remote sensing images during night, demonstrating that the proposed algorithm has a superior performance and provides a new idea for marine boat detection during night.
-
Key words:
- Low light remote sensing /
- Target detection /
- Boat detection /
- Sparse representation
-
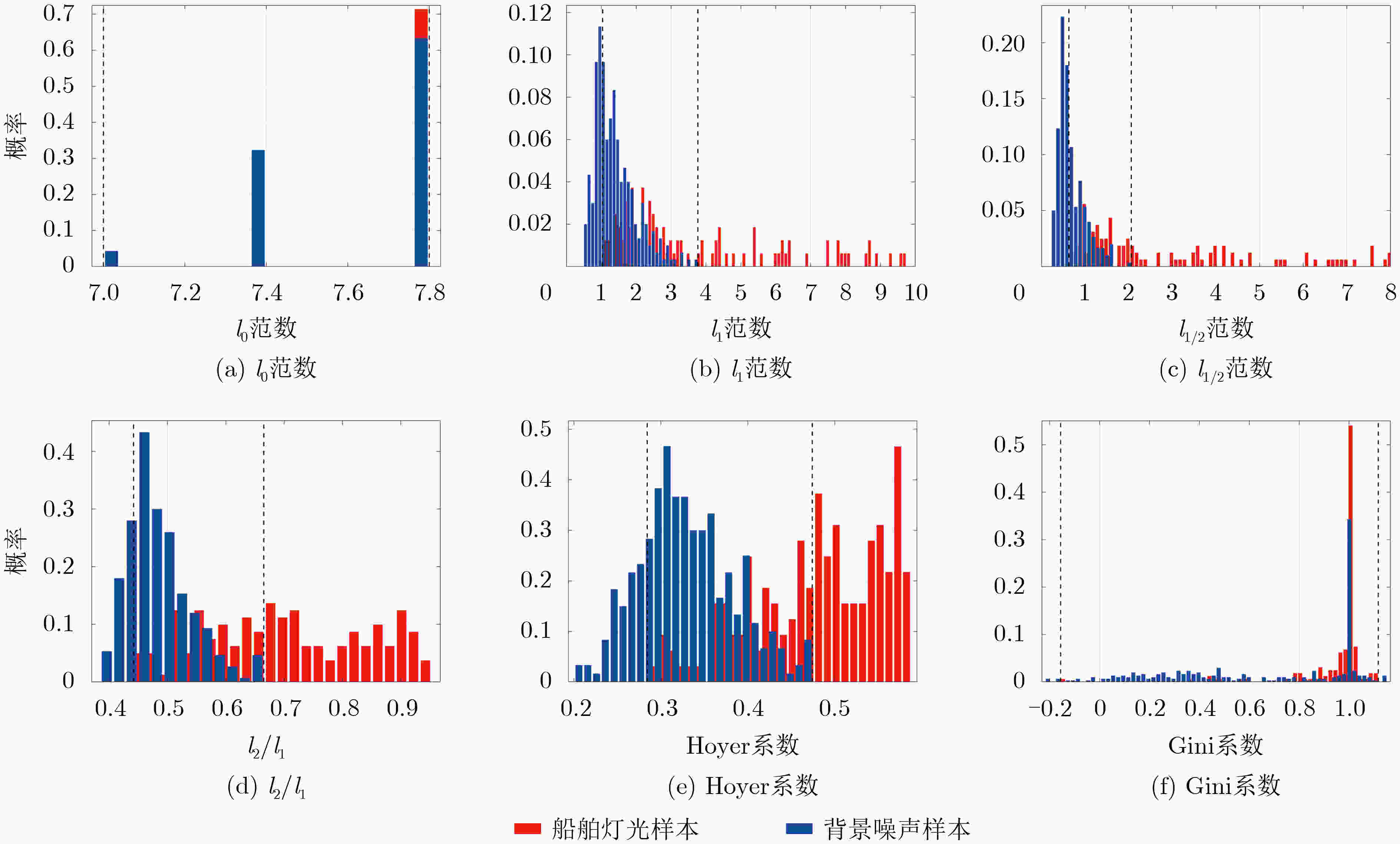
表 1 常用的稀疏度指标及其计算公式
稀疏度指标 计算公式 $ {l_p} $范数 $ {l_p} = {\left( {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {{{\left| {{x_i}} \right|}^p}} } \right)^{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 p}} \right. } p}}},0 < p \le 1 $ (4) $ {l_2} $范数与$ {l_1} $范数之比 $ {{{l_2}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{l_2}} {{l_1}}}} \right. } {{l_1}}} = {{\sqrt {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {x_i^2} } } \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\sqrt {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {x_i^2} } } {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {\left| {{x_i}} \right|} }}} \right. } {\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N {\left| {{x_i}} \right|} }} $ (5) Hoyer系数 ${\rm{Hoyer} } = { {\left( {\sqrt N - \dfrac{ { {l_1} } }{ { {l_2} } } } \right)} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom { {\left( {\sqrt N - \frac{ { {l_1} } }{ { {l_2} } } } \right)} {\left( {\sqrt N - 1} \right)} } } \right. } {\left( {\sqrt N - 1} \right)} }$ (6) Gini系数 ${\rm{Gini} } = 1 - \dfrac{2}{ { {l_1} } }\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^N { {x_i} } \frac{ {N - i + 1/2} }{N},|{x_1}| \le |{x_2}| \le \cdots \le \left| { {x_N} } \right|$ (7) 表 2 各稀疏度指标对船舶灯光和背景噪声的区分度
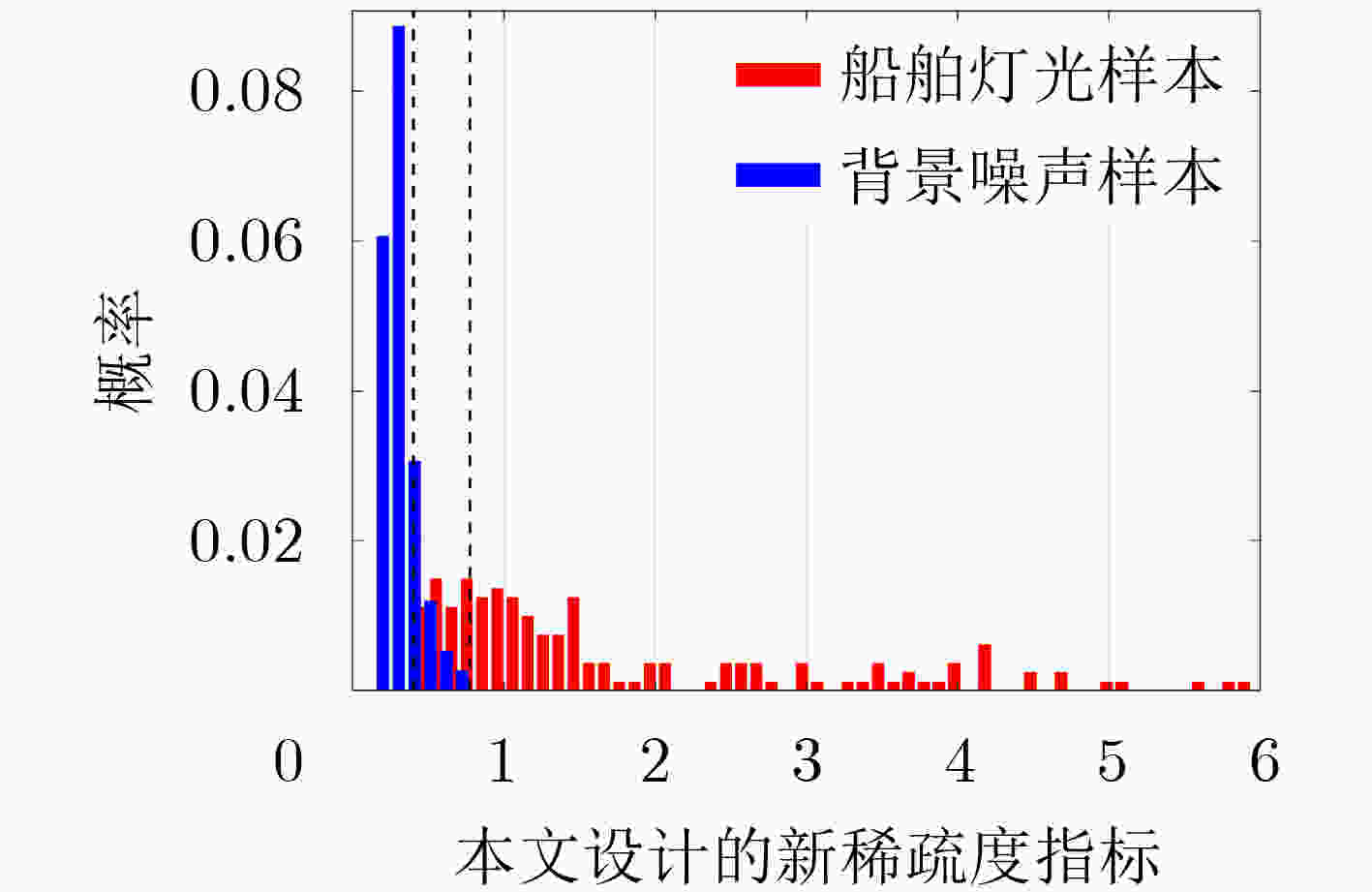
稀疏度指标 $ {\rho _{{\text{target}}}} $ ${\rho _{ {{\rm{noise}}} } }$ $ {J_{\min }} $ $ {l_0} $范数 1.00 1.00 48.00 $ {l_1} $范数 0.39 0.66 32.43 $ {l_{{1 \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {1 2}} \right. } 2}}} $范数 0.34 0.43 12.01 $ {{{l_2}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{l_2}} {{l_1}}}} \right. } {{l_1}}} $ 0.40 0.80 2.76 Hoyer系数 0.40 0.80 7.72 Gini系数 0.98 1.00 4.57 表 3 本文算法在3个不同海域的检测性能评价指标值
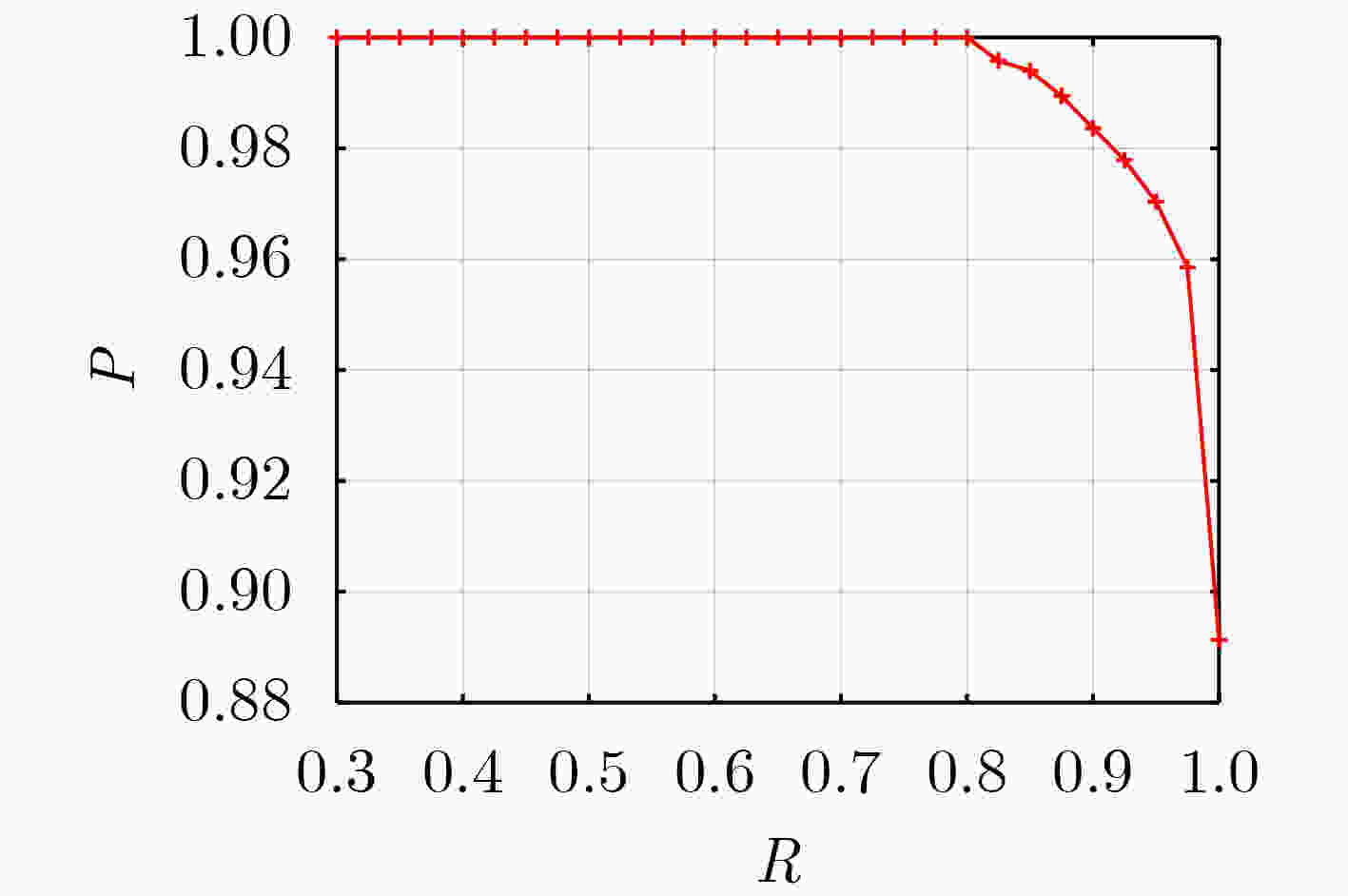
研究区域 $ P $ $ R $ ${\rm{F} }1$ 墨西哥湾北部海域 0.9636 0.9636 0.9636 天津港南侧海域 0.9512 0.9286 0.9398 上海港东侧海域 0.8626 0.9419 0.9005 表 4 已有的低照度遥感影像夜间海上船舶灯光检测算法和本文算法在验证集和测试集上的检测性能评价指标值
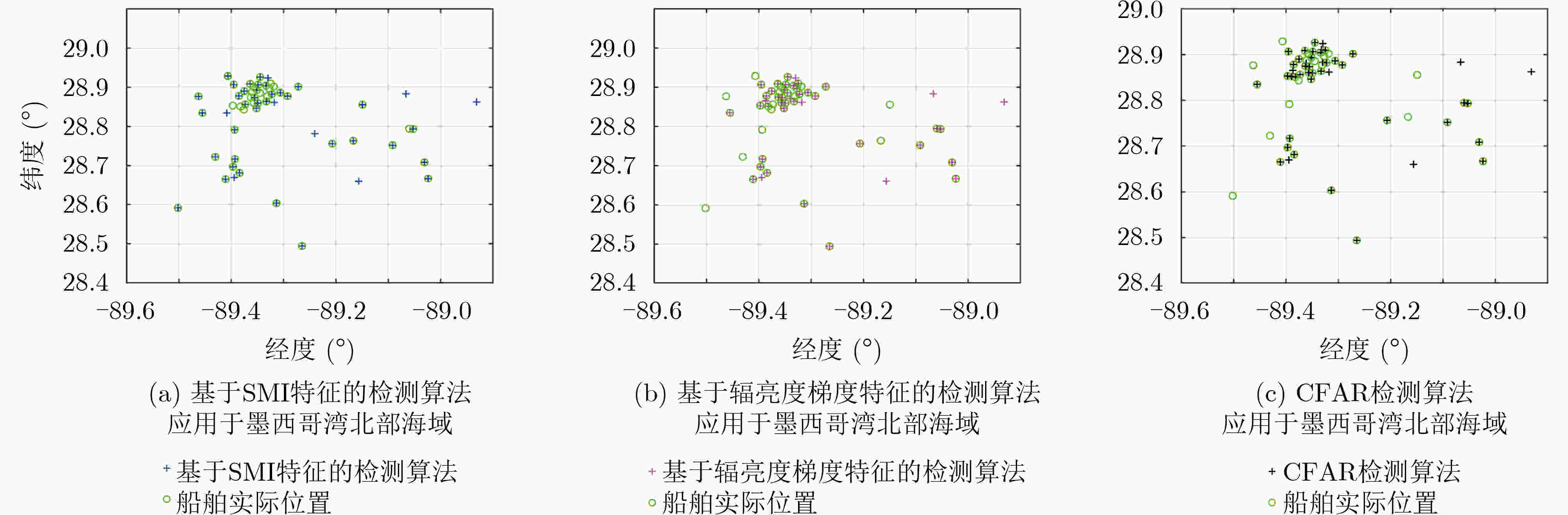
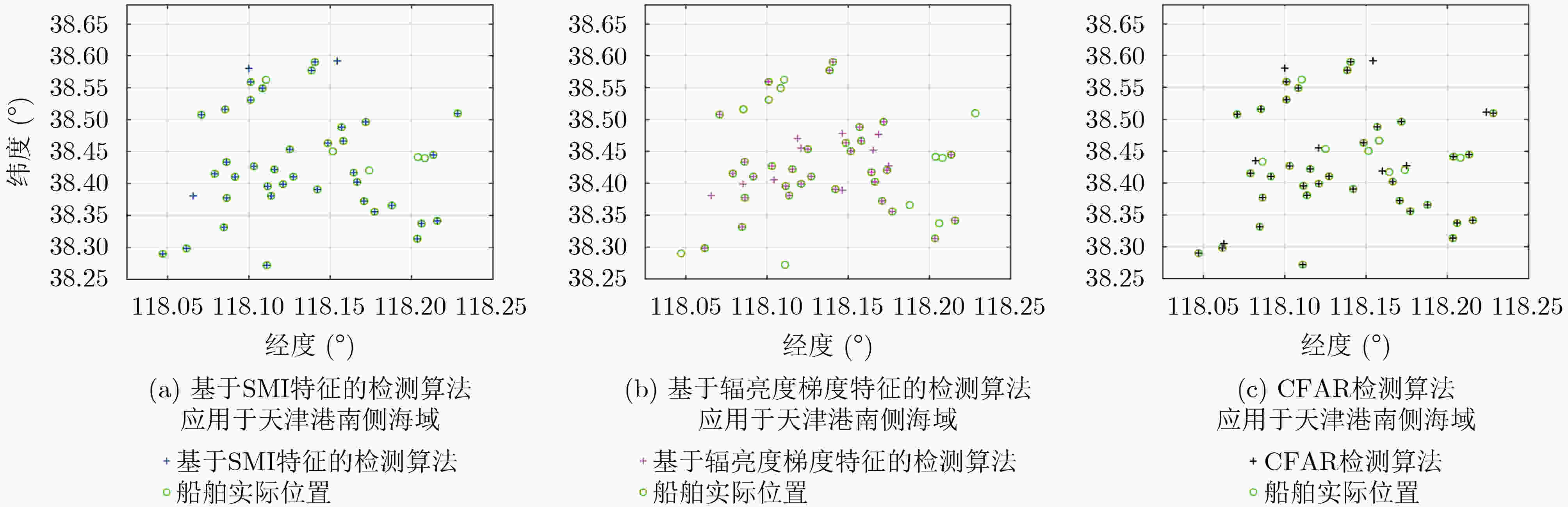
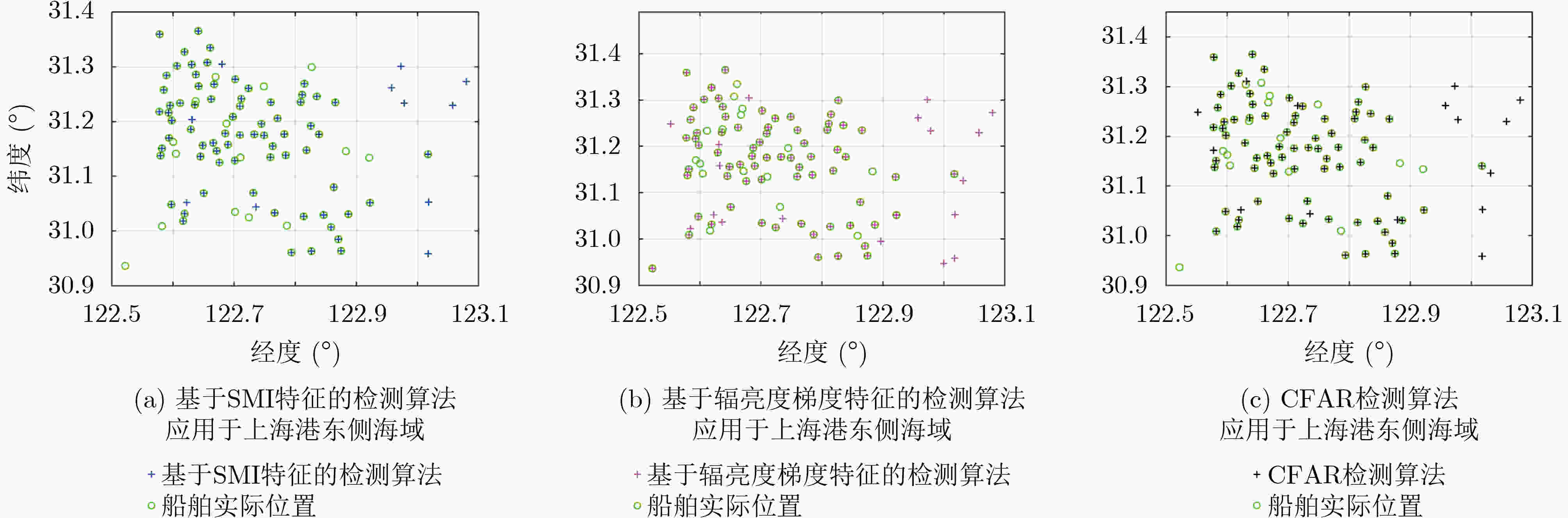
算法 验证集 测试集 $ P $ $ R $ ${\rm{F}}1$ $ P $ $ R $ $ {\rm{F}}1 $ 基于SMI特征的检测算法 0.9327 0.9000 0.9161 0.8951 0.9026 0.8988 基于辐亮度梯度特征的检测算法 0.9342 0.9150 0.9245 0.9048 0.9013 0.9030 CFAR检测算法 0.9119 0.8750 0.8931 0.8699 0.8764 0.8731 本文算法 0.9585 0.9750 0.9667 0.9731 0.9476 0.9602 表 5 已有的低照度遥感影像夜间海上船舶灯光检测算法在3个不同海域的检测性能评价指标值
算法 墨西哥湾北部海域 天津港南侧海域 上海港东侧海域 $ P $ $ R $ $ {\rm{F}}1 $ $ P $ $ R $ $ {\rm{F}}1 $ $ P $ $ R $ $ {\rm{F}}1 $ 基于SMI特征的检测算法 0.8364 0.9200 0.8762 0.9250 0.8810 0.9025 0.8659 0.8256 0.8453 基于辐亮度梯度特征的检测算法 0.7391 0.6800 0.7083 0.7209 0.7381 0.7294 0.7955 0.8140 0.8046 CFAR检测算法 0.7727 0.6800 0.7234 0.8095 0.8095 0.8095 0.8256 0.8256 0.8256 -
[1] CROFT T A. Nighttime images of the earth from space[J]. Scientific American, 1978, 239(1): 86–98. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0778-86 [2] ELVIDGE C D, CINZANO P, PETTIT D R, et al. The Nightsat mission concept[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2007, 28(12): 2645–2670. doi: 10.1080/01431160600981525 [3] ELVIDGE C D, BAUGH K E, ZHIZHIN M, et al. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights[J]. Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Advanced Network, 2013, 35: 62–69. doi: 10.7125/APAN.35.7 [4] SCHUELER C F, LEE T F, and MILLER S D. VIIRS constant spatial-resolution advantages[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 2013, 34(16): 5761–5777. doi: 10.1080/01431161.2013.796102 [5] MILLER S D, MILLS S P, ELVIDGE C D, et al. Suomi satellite brings to light a unique frontier of nighttime environmental sensing capabilities[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2012, 109(39): 15706–15711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1207034109 [6] MAN D C, TSUBASA H, and FUKUI H. Normalization of VIIRS DNB images for improved estimation of socioeconomic indicators[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2021, 14(5): 540–554. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2020.1849438 [7] RYBNIKOVA N. Everynight accounting: Nighttime lights as a proxy for economic performance of regions[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(4): 825. doi: 10.3390/rs14040825 [8] SUDALAYANDI R S, SRINIVASAN E, and KASARAGOD G R. Urban growth analysis of Tamil Nadu state, India using VIIRS DNB night data during 2012 and 2016[J]. Remote Sensing Applications:Society and Environment, 2021, 23: 100559. doi: 10.1016/j.rsase.2021.100559 [9] RUAN Yuling, ZOU Yanhong, CHEN Minghui, et al. Monitoring the spatiotemporal trajectory of urban area hotspots using the SVM regression method based on NPP-VIIRS imagery[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2021, 10(6): 415. doi: 10.3390/ijgi10060415 [10] ZHOU Meng, WANG Jun, CHEN Xi, et al. Nighttime smoke aerosol optical depth over U. S. rural areas: First retrieval from VIIRS moonlight observations[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2021, 267: 112717. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112717 [11] KOCIFAJ M and BARÁ S. Diffuse light around cities: New perspectives in satellite remote sensing of nighttime aerosols[J]. Atmospheric Research, 2022, 266: 105969. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105969 [12] LI Jiajun, CAI Yancong, ZHANG Peng, et al. Satellite observation of a newly developed light-fishing “hotspot” in the open South China Sea[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2021, 256: 112312. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112312 [13] TIAN Hao, LIU Yang, TIAN Yongjun, et al. A comprehensive monitoring and assessment system for multiple fisheries resources in the Northwest Pacific based on satellite remote sensing technology[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2022, 9: 808282. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.808282 [14] LIU Yang, SAITOH S I, and HIRAWAKE T. Detection of squid and pacific saury fishing vessels around Japan using VIIRS Day/Night Band image[J]. Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Advanced Network, 2015, 39: 28–39. doi: 10.7125/apan.39.3 [15] STRAKA III W C, SEAMAN C J, BAUGH K, et al. Utilization of the Suomi national polar-orbiting partnership (NPP) visible infrared imaging radiometer suite (VIIRS) day/night band for arctic ship tracking and fisheries management[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(1): 971–989. doi: 10.3390/rs70100971 [16] ELVIDGE C D, ZHIZHIN M, BAUGH K, et al. Automatic boat identification system for VIIRS low light imaging data[J]. Remote Sensing, 2015, 7(3): 3020–3036. doi: 10.3390/rs70303020 [17] COZZOLINO E and LASTA C A. Use of VIIRS DNB satellite images to detect jigger ships involved in the Illex argentinus fishery[J]. Remote Sensing Applications:Society and Environment, 2016, 4: 167–178. doi: 10.1016/j.rsase.2016.09.002 [18] LEBONA B, KLEYNHANS W, CELIK T, et al. Ship detection using VIIRS sensor specific data[C]. 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Beijing, China, 2016: 1245–1247. [19] 郭刚刚, 樊伟, 薛嘉伦, 等. 基于NPP/VIIRS夜光遥感影像的作业灯光围网渔船识别[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(10): 245–251. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.10.032GUO Ganggang, FAN Wei, XUE Jialun, et al. Identification for operating pelagic light-fishing vessels based on NPP/VIIRS low light imaging data[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(10): 245–251. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.10.032 [20] 黄明晶, 王雪梅, 蹇渊, 等. 基于海天线提取和混合灰度差的船舶检测方法[J]. 红外, 2021, 42(6): 29–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8785.2021.06.006HUANG Mingjing, WANG Xuemei, JIAN Yuan, et al. Ship detection method based on sea-sky line extraction and mixed gray difference[J]. Infrared, 2021, 42(6): 29–33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8785.2021.06.006 [21] QI Shengxiang, MA Jie, LIN Jin, et al. Unsupervised ship detection based on saliency and S-HOG descriptor from optical satellite images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12(7): 1451–1455. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2408355 [22] ZHANG Xiangrong, WANG Guanchun, ZHU Peng, et al. GRS-Det: An anchor-free rotation ship detector based on Gaussian-mask in remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(4): 3518–3531. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3018106 [23] SCHWEGMANN C P, KLEYNHANS W, and SALMON B P. Synthetic aperture radar ship detection using Haar-like features[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(2): 154–158. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2631638 [24] CORBANE C, MARRE F, and PETIT M. Using SPOT-5 HRG data in panchromatic mode for operational detection of small ships in tropical area[J]. Sensors, 2008, 8(5): 2959–2973. doi: 10.3390/s8052959 [25] JIANG Mingzhe, YANG Xuezhi, DONG Zhanyu, et al. Ship classification based on superstructure scattering features in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(5): 616–620. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2514482 [26] XU Fang, LIU Jinghong, DONG Chao, et al. Ship detection in optical remote sensing images based on wavelet transform and multi-level false alarm identification[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(10): 985. doi: 10.3390/rs9100985 [27] AI Jiaqiu, MAO Yuxiang, LUO Qiwu, et al. Robust CFAR ship detector based on bilateral-trimmed-statistics of complex ocean scenes in SAR imagery: A closed-form solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(3): 1872–1890. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3050654 [28] AI Jiaqiu, LUO Qiwu, YANG Xuezhi, et al. Outliers-robust CFAR detector of Gaussian clutter based on the truncated-maximum-likelihood-estimator in SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2020, 21(5): 2039–2049. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2019.2911692 [29] JIAO Jiao, ZHANG Yue, SUN Hao, et al. A densely connected end-to-end neural network for multiscale and multiscene SAR ship detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 20881–20892. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2825376 [30] TANG Jiexiong, DENG Chenwei, HUANG Guangbin, et al. Compressed-domain ship detection on spaceborne optical image using deep neural network and extreme learning machine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(3): 1174–1185. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2335751 [31] LIU Qiangwei, XIANG Xiuqiao, YANG Zhou, et al. Arbitrary direction ship detection in remote-sensing images based on multitask learning and multiregion feature fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(2): 1553–1564. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3002850 [32] AI Jiaqiu, TIAN Ruitian, LUO Qiwu, et al. Multi-scale rotation-invariant Haar-like feature integrated CNN-based ship detection algorithm of multiple-target environment in SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 10070–10087. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2931308 [33] AHARON M, ELAD M, and BRUCKSTEIN A. K-SVD: An algorithm for designing overcomplete dictionaries for sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(11): 4311–4322. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.881199 [34] LI Jin, PENG Yiqun, TANG Jingtian, et al. Denoising of magnetotelluric data using K‐SVD dictionary training[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2021, 69(2): 448–473. doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.13058 [35] FENG Deshan, LIU Shuo, YANG Jun, et al. The noise attenuation and stochastic clutter removal of ground penetrating radar based on the K-SVD dictionary learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 74879–74890. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3081349 [36] CANDÈS E J, WAKIN M B, and BOYD S P. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted ℓ1 minimization[J]. Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 2008, 14(5): 877–905. doi: 10.1007/s00041-008-9045-x [37] O'GRADY P D, PEARLMUTTER B A, and RICKARD S T. Survey of sparse and non‐sparse methods in source separation[J]. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 2005, 15(1): 18–33. doi: 10.1002/ima.20035 [38] HURLEY N and RICKARD S. Comparing measures of sparsity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(10): 4723–4741. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2009.2027527 [39] KARVANEN J and CICHOCKI A. Measuring sparseness of noisy signals[C]. 4th International Symposium on Independent Component Analysis and Blind Signal Separation, Nara, Japan, 2003: 125–130. [40] ELVIDGE C D, GHOSH T, BAUGH K, et al. Rating the effectiveness of fishery closures with visible infrared imaging radiometer suite boat detection data[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2018, 5: 132. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00132 -





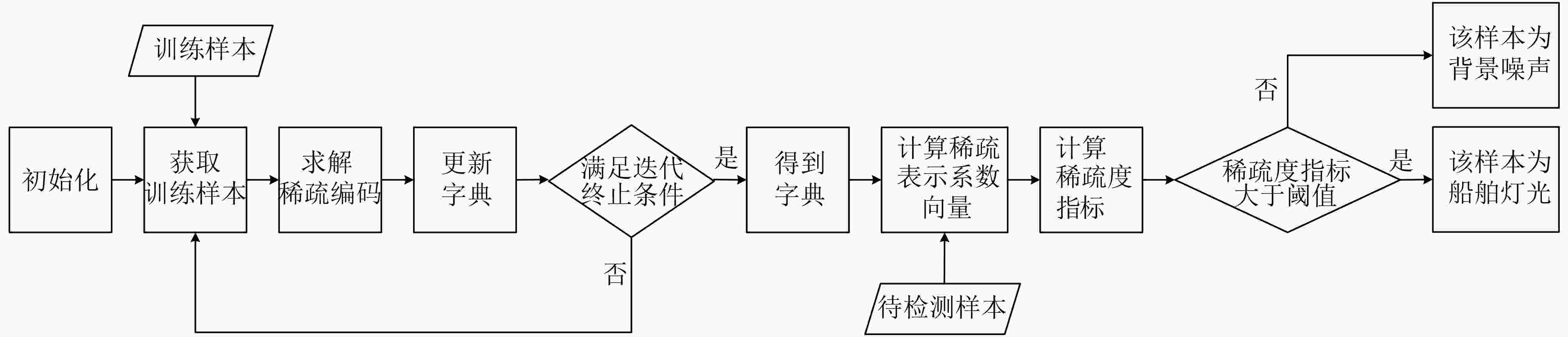
 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
