A Collaborative Mechanism for Smart Highway Edge Tasks Based on Location Prediction
-
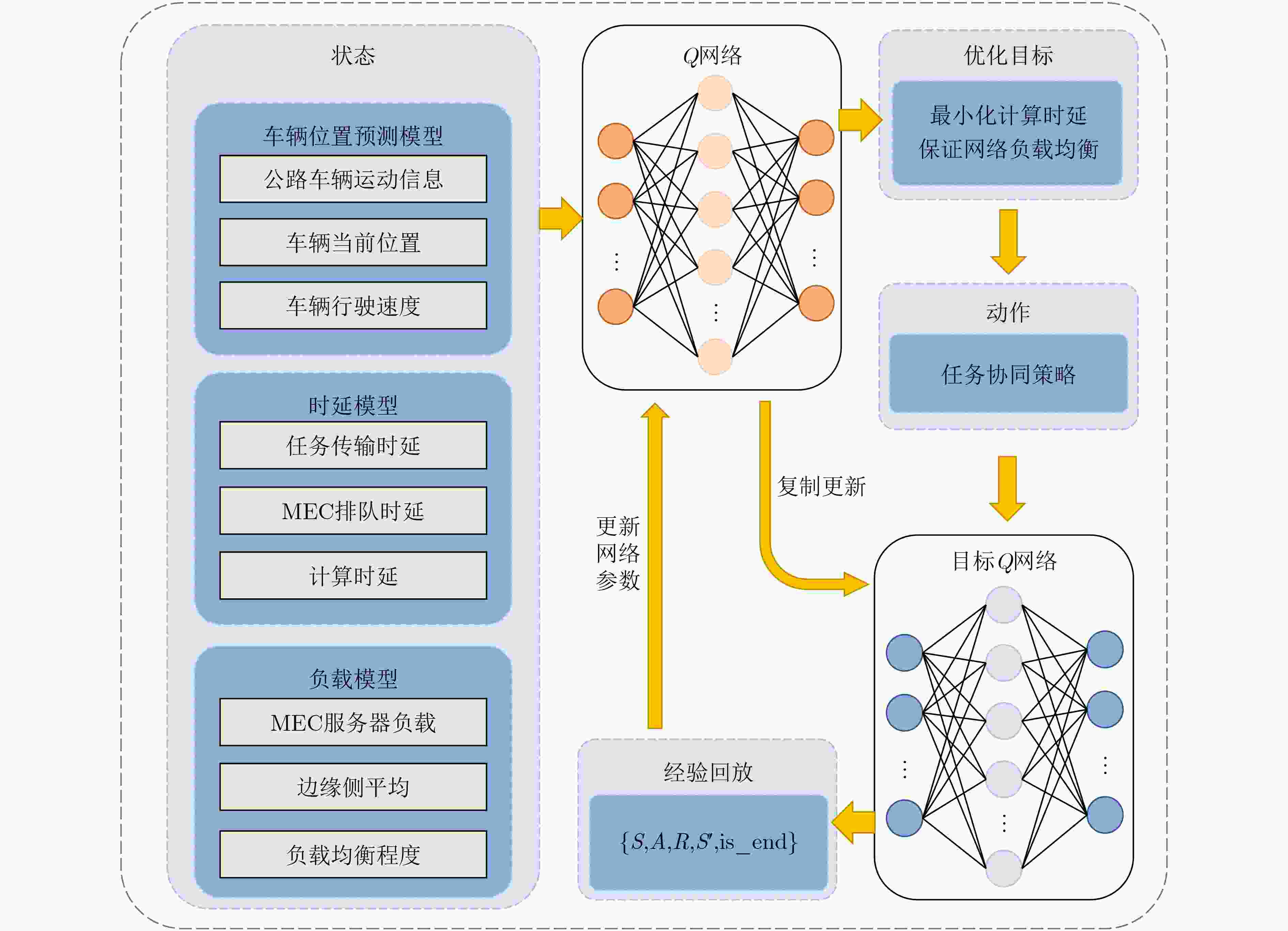
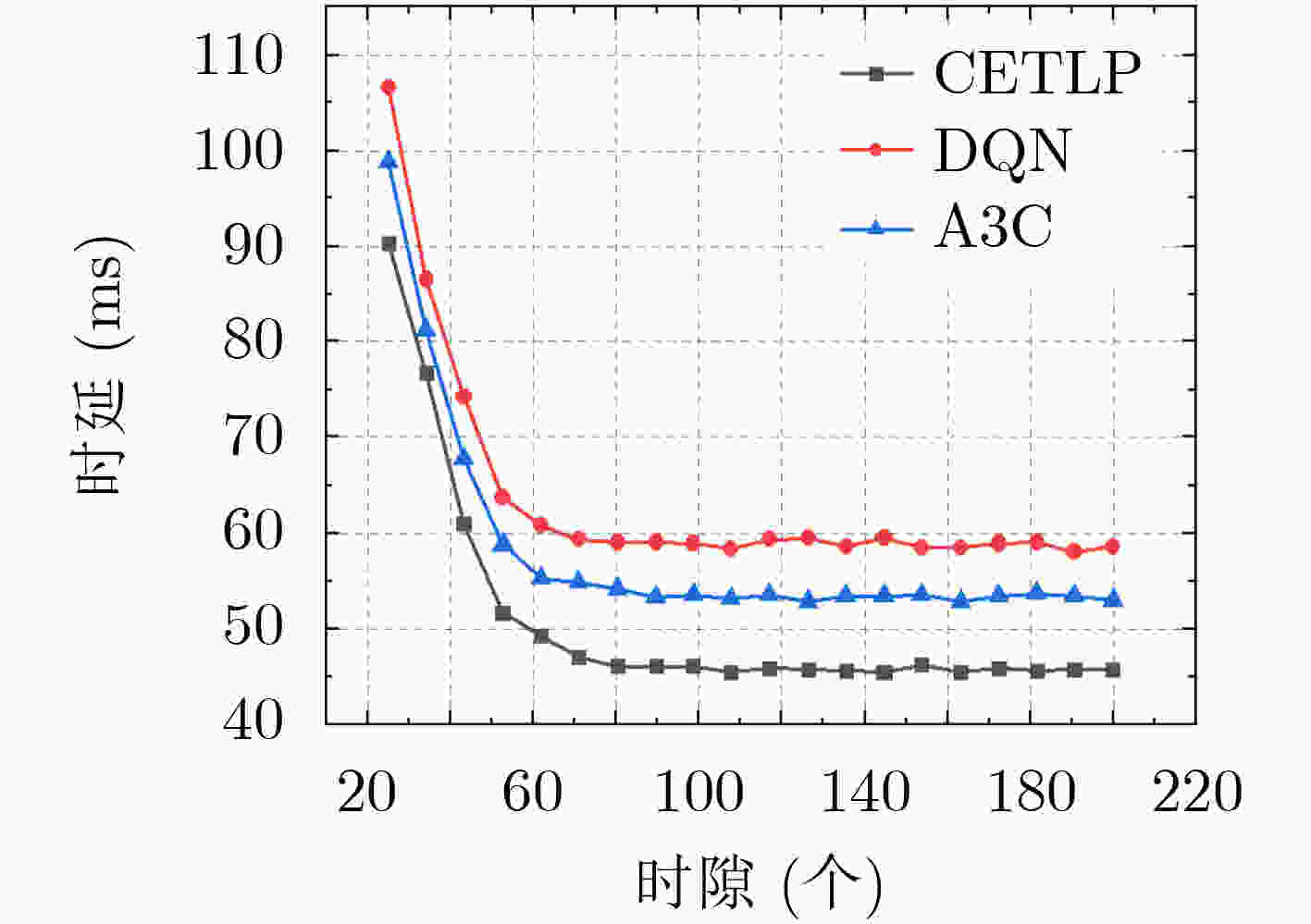
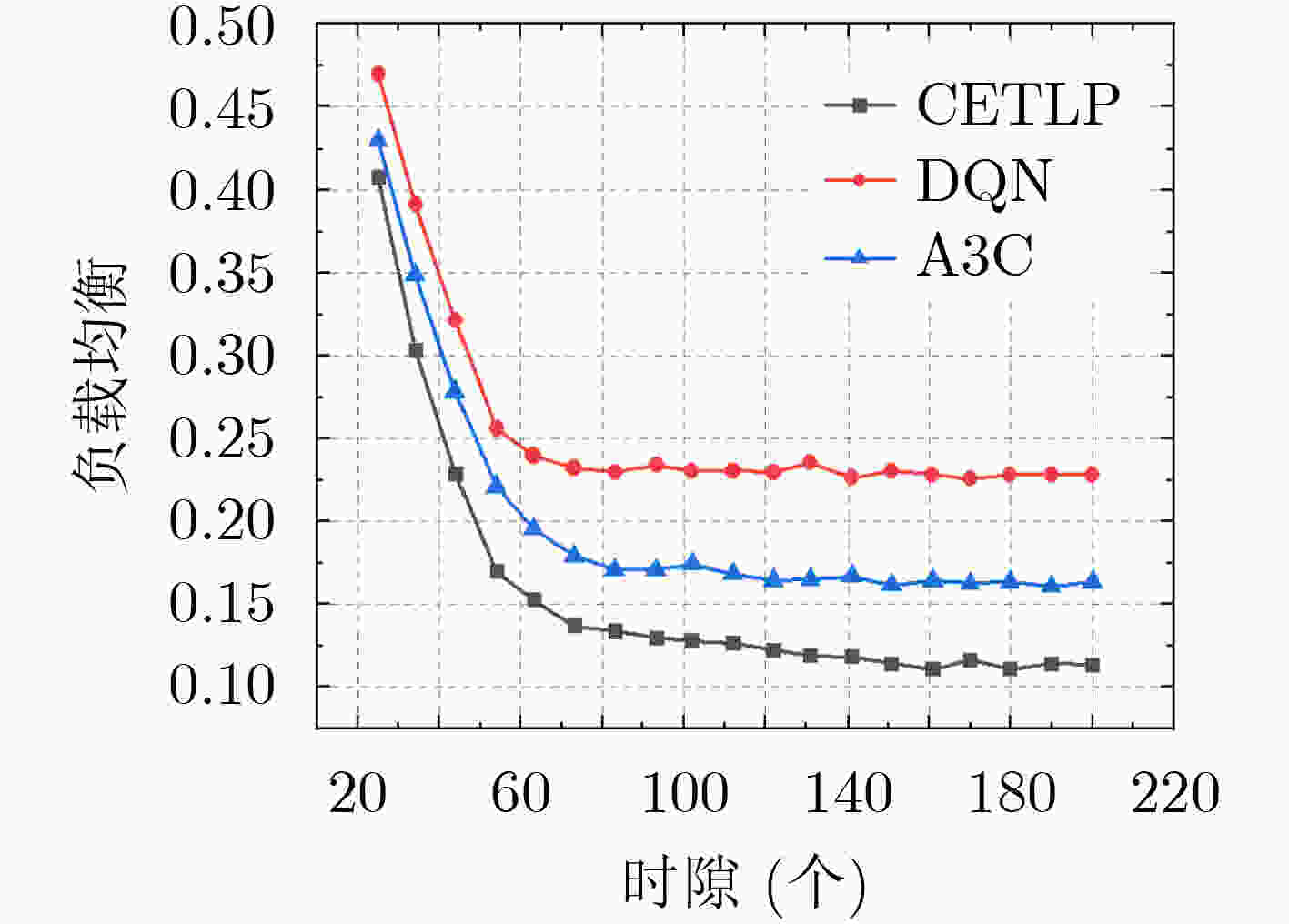
摘要: 近年来智慧公路为用户提供了道路监测、辅助驾驶等新型服务,但随之而来的是数据流量爆炸式的增长,这对网络的承载能力带来了极大的考验。随着5G和移动边缘计算技术的成熟,海量任务不必集中在云端处理,边缘侧的协同处理成为一种较好的选择。为了在车辆高速移动场景下为用户提供高效可靠的服务,该文提出一种基于位置预测的智慧公路边缘任务协同(CETLP)机制。首先,结合智慧公路场景下车辆运动特点,建立面向时延和负载均衡的边缘任务协同模型。进而,针对任务时延最小化以及网络负载均衡等目标,提出一种基于深度强化学习的边缘任务协同算法,对海量任务的协同策略进行求解。仿真结果表明,所提机制能够在保证网络负载均衡的情况下降低服务时延。Abstract: In recent years new services such as road monitoring and assisted driving in smart highways have been proposed, but the explosive growth of data traffic has also emerged, which has brought a great test to the carrying capacity of the network. With the maturity of 5G and mobile edge computing technology, massive tasks do not have to be processed centrally in the cloud, and edge-side co-processing becomes a better choice. In order to provide efficient and reliable services for users in the vehicle high-speed mobile scenario, a Collaboration of Edge Tasks based on Location Prediction (CETLP) is proposed in this paper. First, a delay and load balancing-oriented edge task collaboration model is established by combining the vehicle movement characteristics in the smart highway scenario. Then, a deep reinforcement learning-based edge task collaboration algorithm is proposed to solve the collaboration strategy for a large number of tasks with the objectives of task delay minimization and network load balancing. Simulation results show that the proposed mechanism can reduce the service delay while ensuring the network load balancing.
-
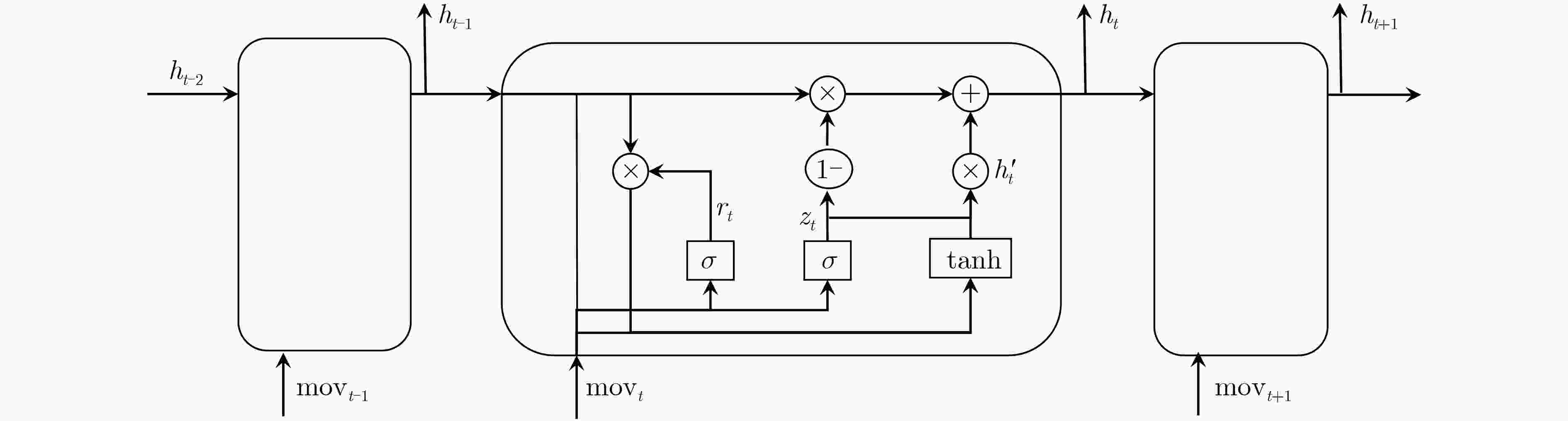
算法1 基于位置预测的边缘任务协同算法 输入:迭代轮数$ T $,状态特征维度$ n $,动作集$ A $,学习速率$ \alpha $,衰
减因子$ \gamma $,探索率$ \varepsilon $,当前$ Q $网络,目标$ Q $网络,批量梯度
下降样本数$ m $, 目标$ Q $网络更新频率$ C $输出:协同策略 初始化车辆和MECS,随机初始化系统状态,清空经验回放集合 FOR $i = 1,2, \cdots ,T$ DO 输入$ {S_i} $,得到网络中所有动作对应的$ Q $值输出,使用$ \varepsilon - $贪婪
法选择对应的动作$ {A_i} $;在状态$ {S_i} $执行当前动作$ {A_i} $,得到新状态$ {S_{i + 1}} $和对应奖励$ {R_i} $以
及是否是终止状态$ {\text{is\_end}} $;将集合$ \{ {S_i},{A_i},{R_i},{S_{i + 1}},{\text{is\_end}}\} $存入经验集合$ D $并更新车辆
位置以及车辆接入的服务器;$ {S_i} = {S_{i + 1}} $; 从经验回放集合$ D $中采样$ m $个样本
$ \{ {S_i},{A_i},{R_i},{S_{i + 1}},{\text{is\_end}}\} $;FOR $j = 1,2, \cdots ,m$ DO 根据式(25)计算当前目标$ Q $值$ {Y_t} $; 使用均方差损失函数式(26),更新$ Q $网络参数; END FOR IF $ i\% C = 1 $ THEN 更新目标$ Q $网络参数; END IF IF $ {\text{is\_end}} = {\text{true}} $ THEN BREAK END IF END FOR RETURN 卸载策略 表 1 网络参数
网络参数 取值 MECS计算能力(GHz) 10 RSU计算能力(GHz) 1 有线传输带宽(Gbit/s) 1 无限传输带宽(Mbit/s) 300 任务数据量(kbit) [50,100,150,200] 任务计算周期数 [3×106, 6×106, 9×106, 1.1×107] 任务比例 [0.3,0.3,0.2,0.2] -
[1] 崔雪薇. 车路协同创未来——智慧公路技术在车路协同中的应用探讨[J]. 中国交通信息化, 2018(12): 22–26. doi: 10.13439/j.cnki.itsc.2018.12.002CUI Xuewei. The future of vehicle-road collaboration: Application of intelligent highway technology in vehicle-road collaboration[J]. China ITS Journal, 2018(12): 22–26. doi: 10.13439/j.cnki.itsc.2018.12.002 [2] 田辉, 范绍帅, 吕昕晨, 等. 面向5G需求的移动边缘计算[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2017, 40(2): 1–10. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2017.02.001TIAN Hui, FAN Shaoshuai, LÜ Xinchen, et al. Mobile edge computing for 5G requirements[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2017, 40(2): 1–10. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2017.02.001 [3] 王寒松. 车联网中基于MEC的计算任务卸载策略研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2019.WANG Hansong. Research of computing offloading scheme for MEC-enabled vehicular networks[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019. [4] 尉志青, 马昊, 张奇勋, 等. 感知-通信-计算融合的智能车联网挑战与趋势[J]. 中兴通讯技术, 2020, 26(1): 45–49. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202001010WEI Zhiqing, MA Hao, ZHANG Qixun, et al. Challenge and trend of sensing, communication and computing integrated intelligent internet of vehicles[J]. ZTE Technology Journal, 2020, 26(1): 45–49. doi: 10.12142/ZTETJ.202001010 [5] YANG Xiaolong, FEI Zesong, ZHENG Jianchao, et al. Joint multi-user computation offloading and data caching for hybrid mobile cloud/edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(11): 11018–11030. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2942334 [6] ZHANG Ke, MAO Yuming, LENG Supeng, et al. Mobile-edge computing for vehicular networks: A promising network paradigm with predictive off-Loading[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2017, 12(2): 36–44. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2017.2668838 [7] ZHANG Ke, LENG Supeng, XIN Peng, et al. Artificial intelligence inspired transmission scheduling in cognitive vehicular communications and networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 1987–1997. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2872013 [8] LI Mushu, GAO Jie, ZHAO Lian, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for collaborative edge computing in vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2020, 6(4): 1122–1135. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2020.3003036 [9] ZENG Feng, CHEN Qiao, MENG Lin, et al. Volunteer assisted collaborative offloading and resource allocation in vehicular edge computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(6): 3247–3257. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.2980422 [10] LIU Jun, WANG Shoubin, WANG Jintao, et al. A task oriented computation offloading algorithm for intelligent vehicle network with mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 180491–180502. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2958883 [11] 张凤荔, 赵佳君, 刘东, 等. 基于深度强化学习的边云协同串行任务卸载算法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2021, 50(3): 398–404. doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021015ZHANG Fengli, ZHAO Jiajun, LIU Dong, et al. Edge cloud collaboration serial task offloading algorithm based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021, 50(3): 398–404. doi: 10.12178/1001-0548.2021015 [12] 詹文翰, 王瑾, 朱清新, 等. 移动边缘计算中基于深度强化学习的计算卸载调度方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2021, 38(1): 241–245,263. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2019.10.0594ZHAN Wenhan, WANG Jin, ZHU Qingxin, et al. Deep reinforcement learning based offloading scheduling in mobile edge computing[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2021, 38(1): 241–245,263. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2019.10.0594 [13] ZHANG Jie, GUO Hongzhi, and LIU Jiajia. Adaptive task offloading in vehicular edge computing networks: A reinforcement learning based scheme[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2020, 25(5): 1736–1745. doi: 10.1007/s11036-020-01584-6 [14] QI Qi, WANG Jingyu, MA Zhanyu, et al. Knowledge-driven service offloading decision for vehicular edge computing: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(5): 4192–4203. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2894437 -





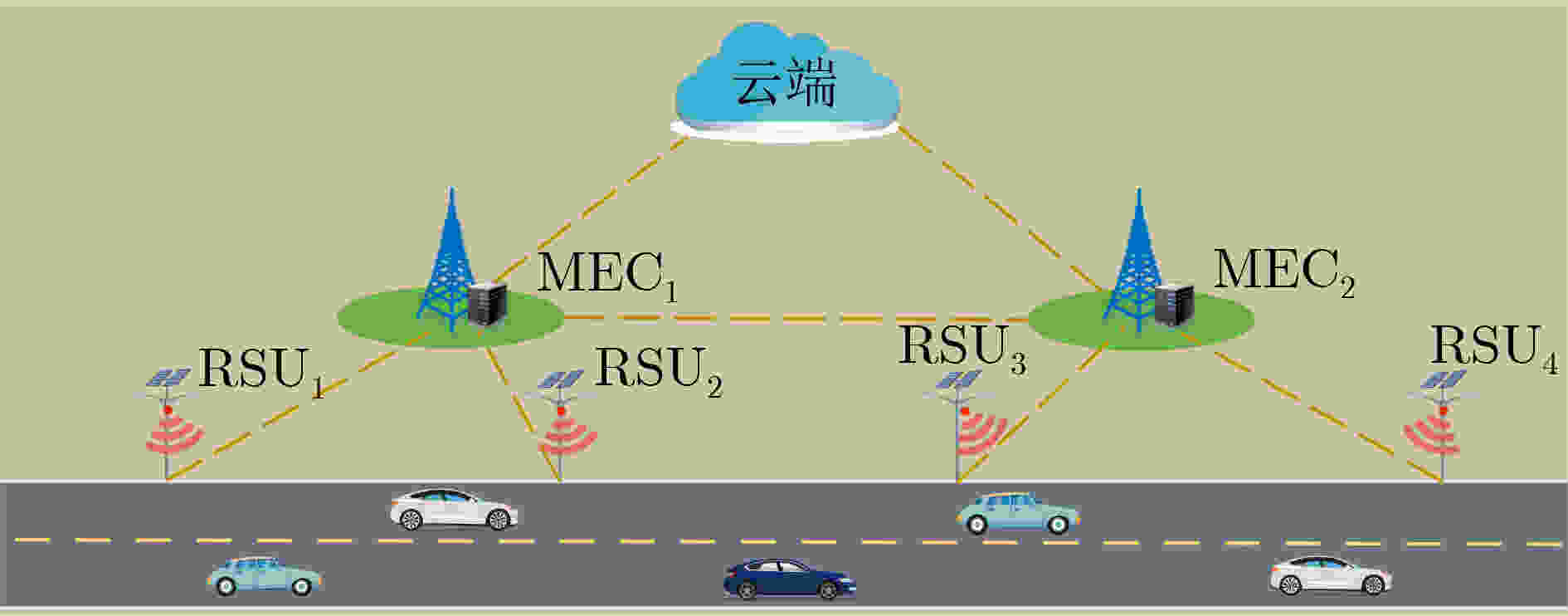
 下载:
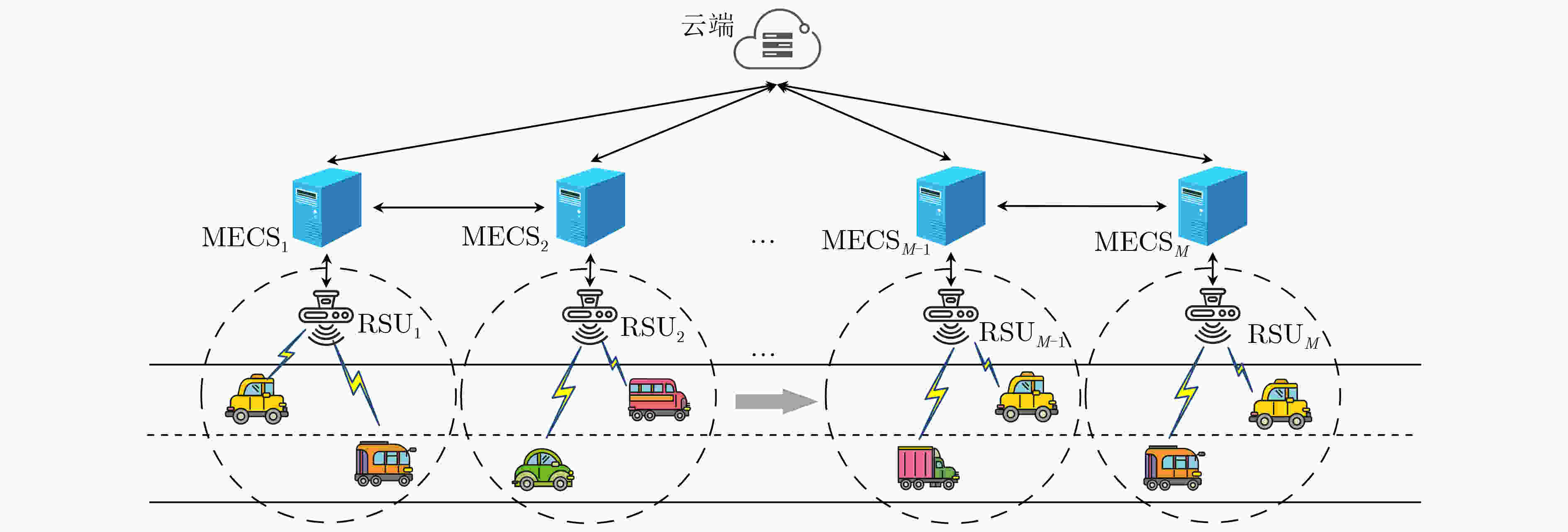
下载:
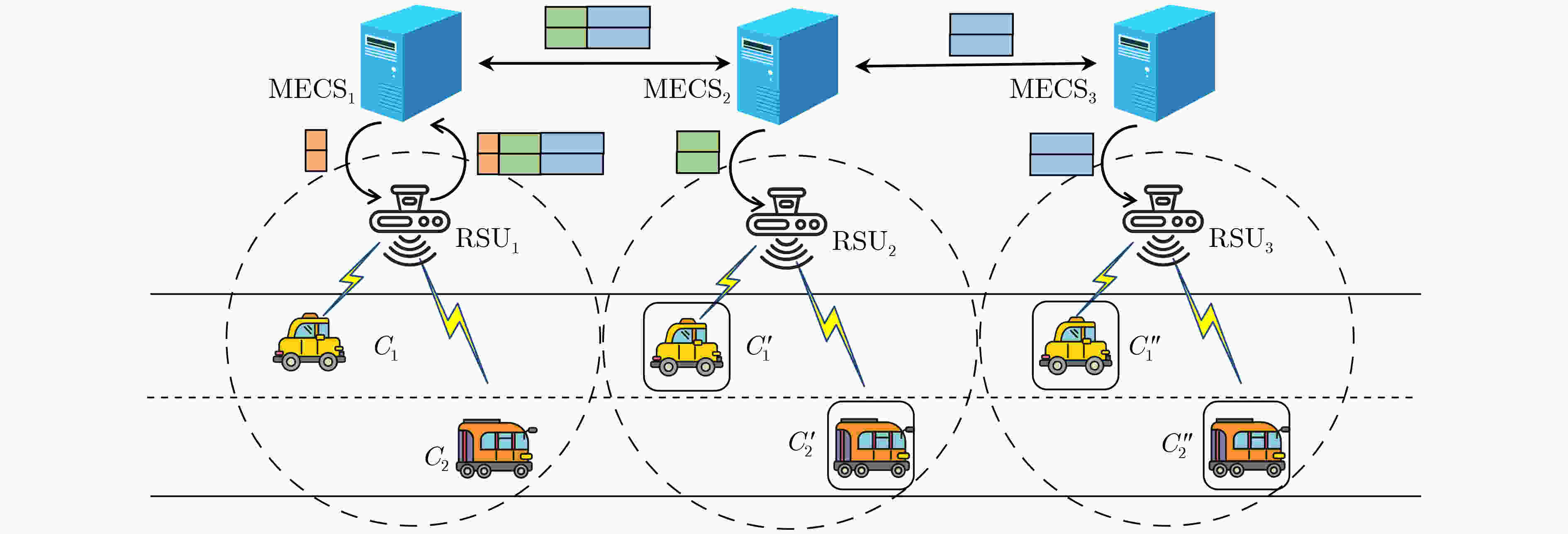
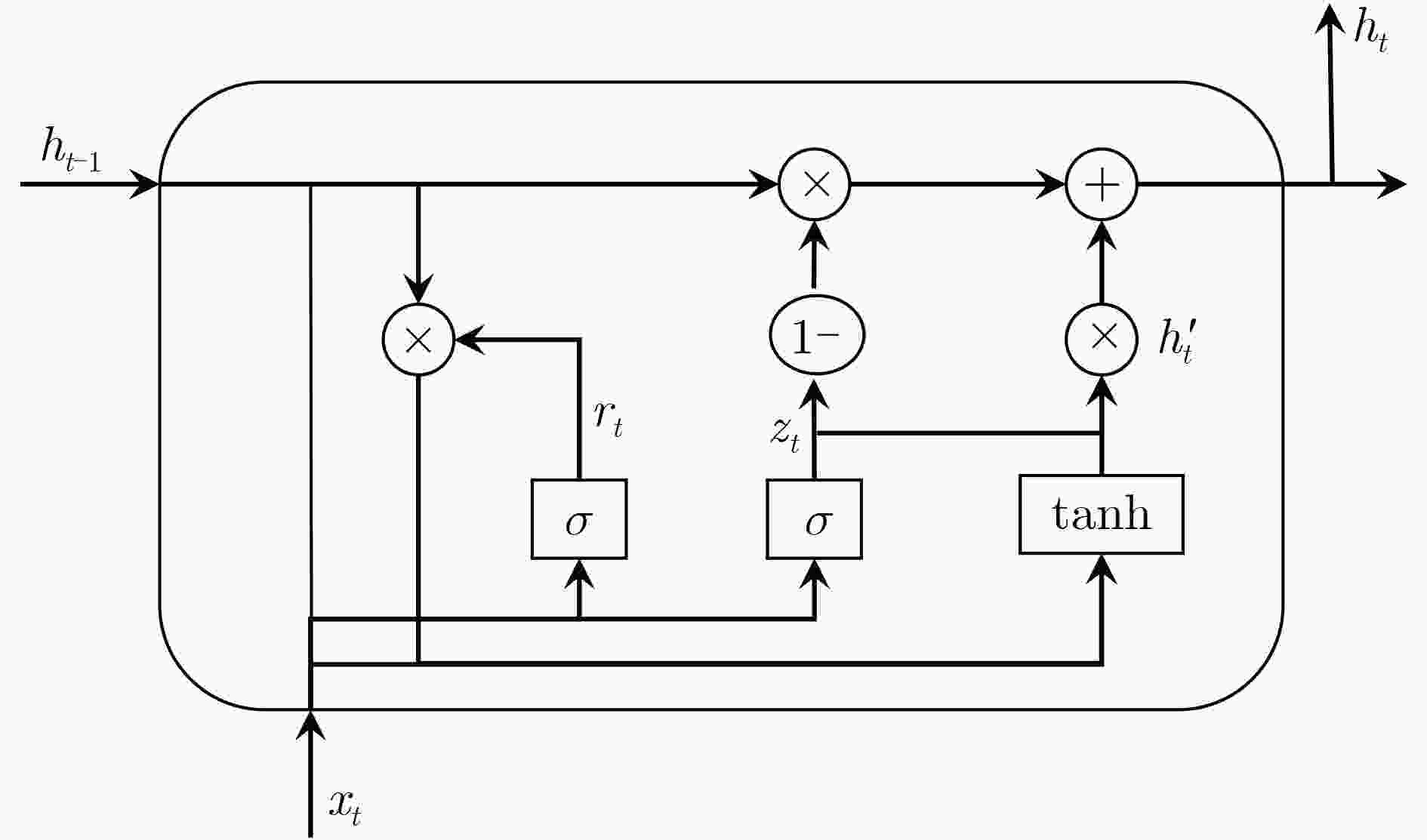
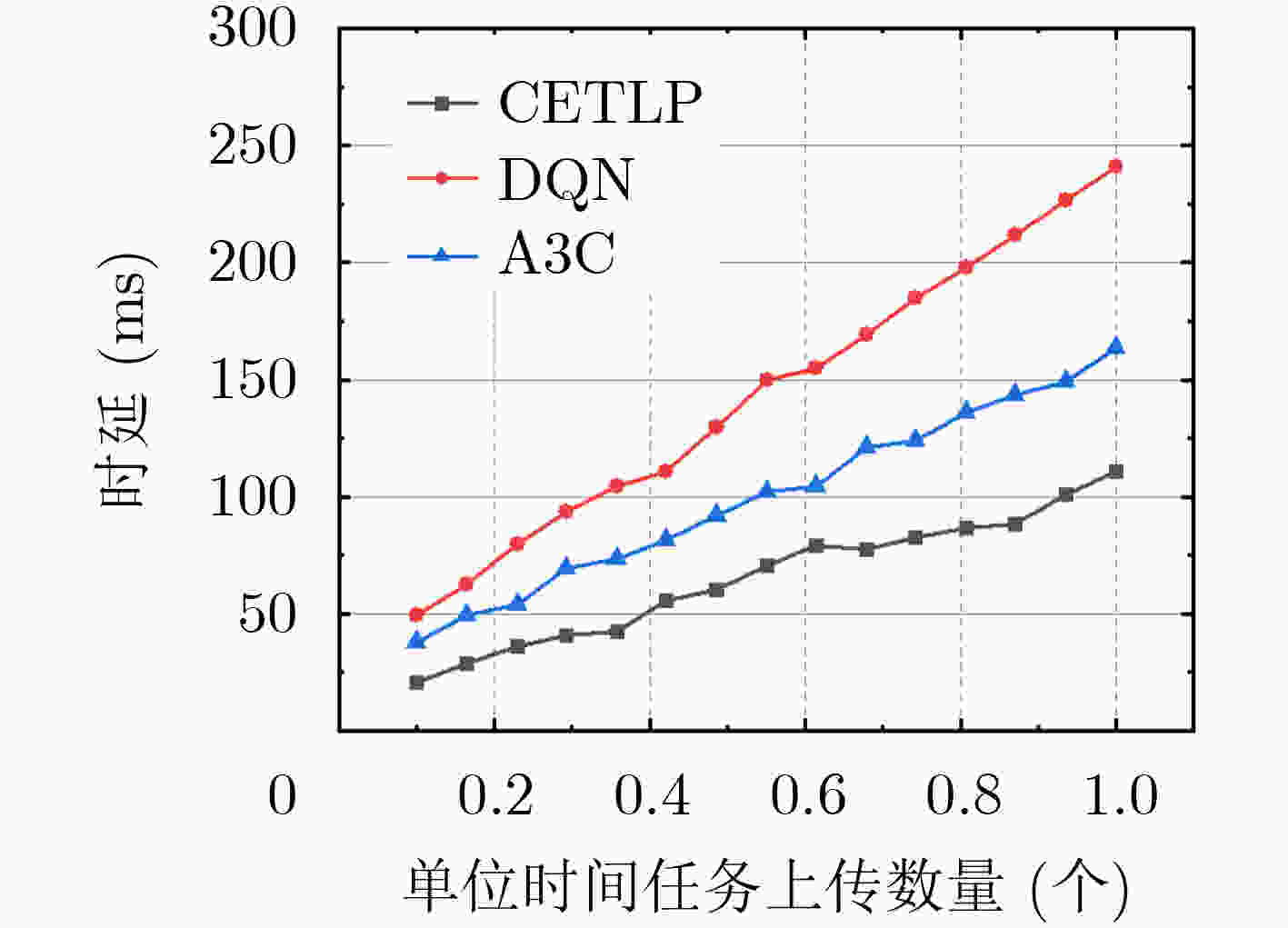
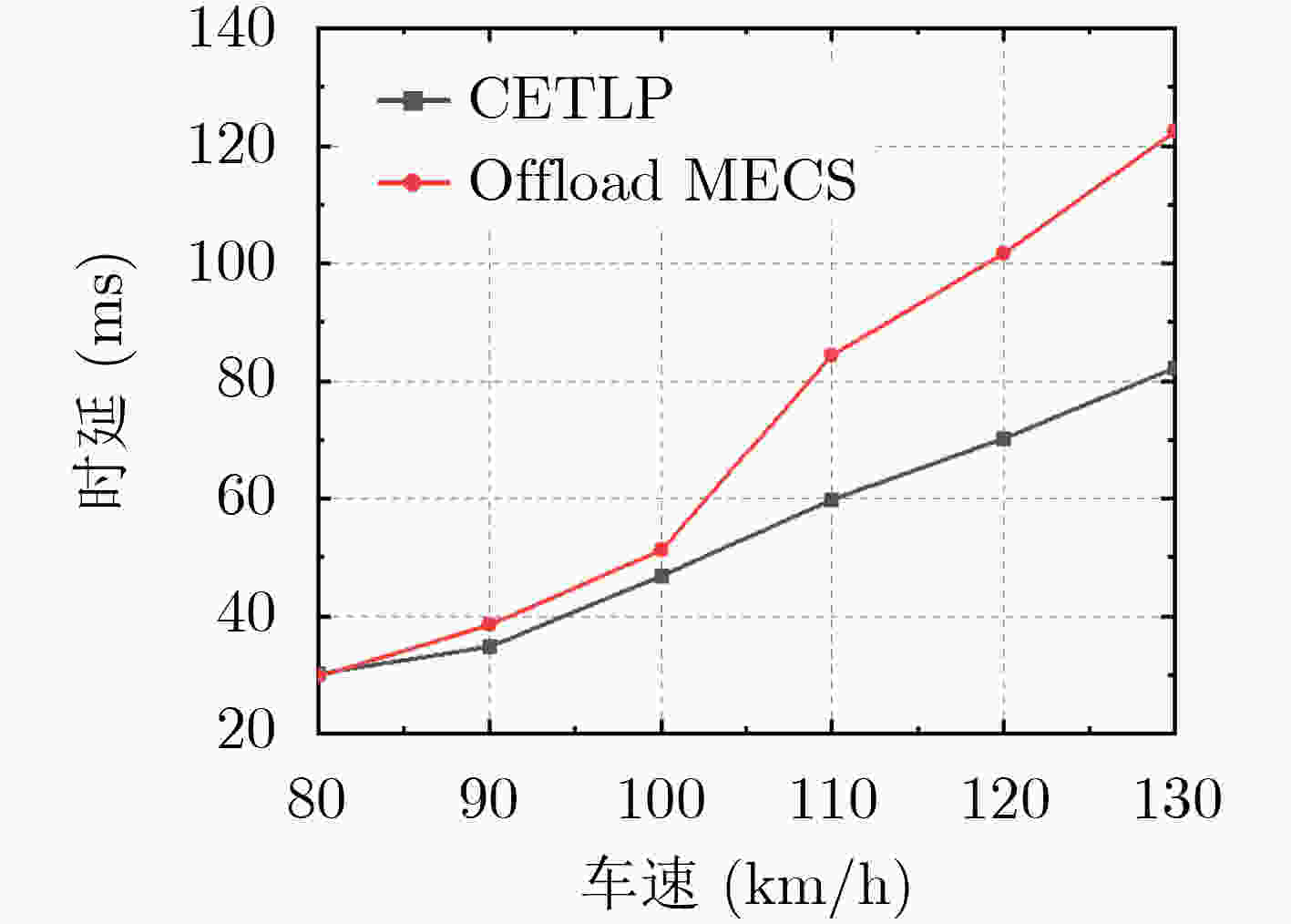
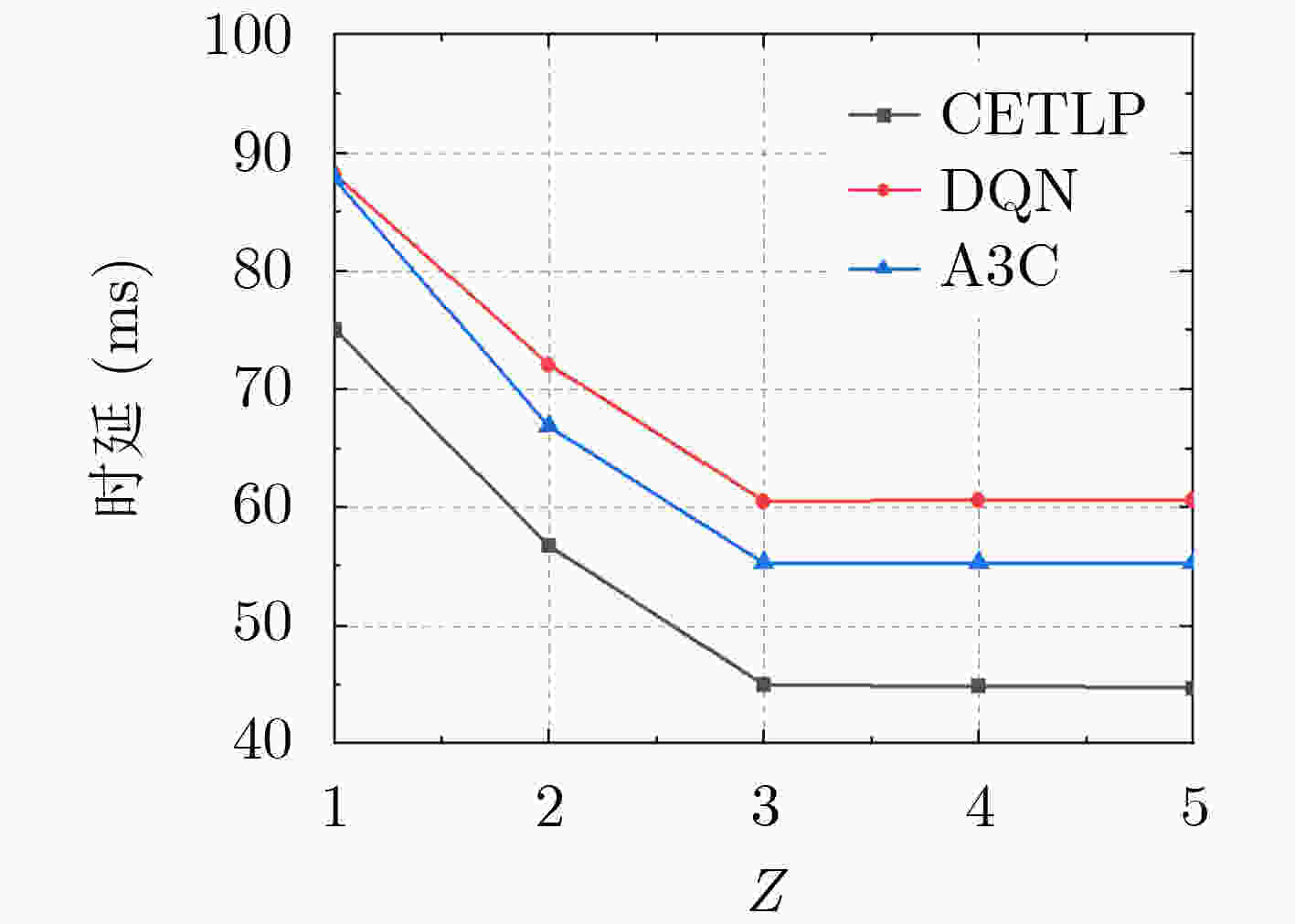
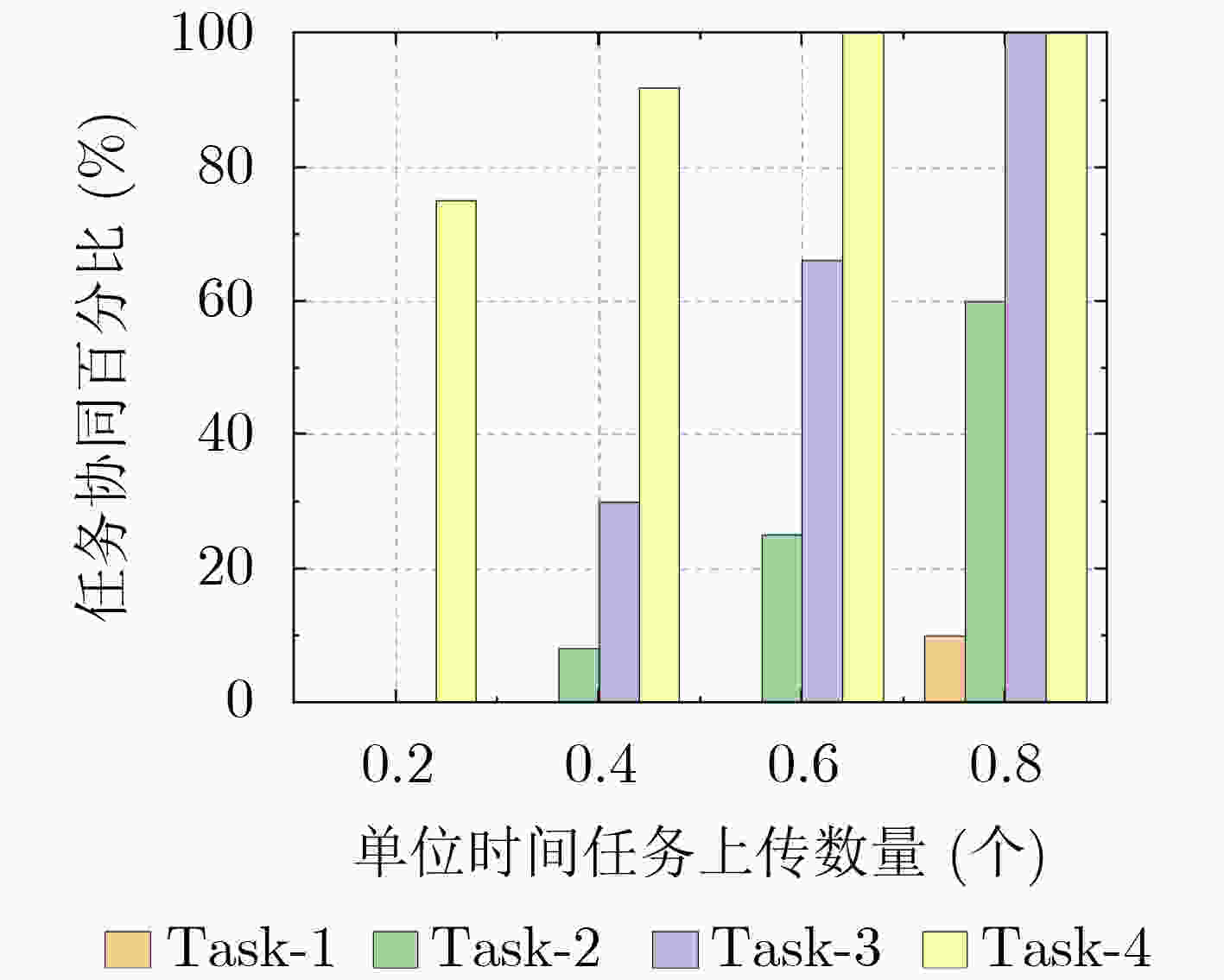


 下载:
下载:
