Collaborative Convolutional Transformer Network Based on Skeleton Action Recognition
-
摘要: 近年来,基于骨架的人体动作识别任务因骨架数据的鲁棒性和泛化能力而受到了广泛关注。其中,将人体骨骼建模为时空图的图卷积网络取得了显著的性能。然而图卷积主要通过一系列3D卷积来学习长期交互联系,这种联系偏向于局部并且受到卷积核大小的限制,无法有效地捕获远程依赖关系。该文提出一种协作卷积Transformer网络(Co-ConvT),通过引入Transformer中的自注意力机制建立远程依赖关系,并将其与图卷积神经网络(GCNs)相结合进行动作识别,使模型既能通过图卷积神经网络提取局部信息,也能通过Transformer捕获丰富的远程依赖项。另外,Transformer的自注意力机制在像素级进行计算,因此产生了极大的计算代价,该模型通过将整个网络分为两个阶段,第1阶段使用纯卷积来提取浅层空间特征,第2阶段使用所提出的ConvT块捕获高层语义信息,降低了计算复杂度。此外,原始Transformer中的线性嵌入被替换为卷积嵌入,获得局部空间信息增强,并由此去除了原始模型中的位置编码,使模型更轻量。在两个大规模权威数据集NTU-RGB+D和Kinetics-Skeleton上进行实验验证,该模型分别达到了88.1%和36.6%的Top-1精度。实验结果表明,该模型的性能有了很大的提高。
-
关键词:
- 动作识别 /
- 图卷积网络 /
- 自注意力机制 /
- Transformer
Abstract: In recent years, skeleton-based human action recognition has attracted widespread attention because of the robustness and generalization ability of skeleton data. Among them, the graph convolutional network that models the human skeleton into a spatiotemporal graph has achieved remarkable performance. However, graph convolutions learn mainly long-term interactive connections through a series of 3D convolutions, which are localized and limited by the size of convolution kernels, which can not effectively capture long-range dependencies. In this paper, a Collaborative Convolutional Transformer (Co-ConvT) network is proposed to establish remote dependencies by introducing Transformer's self-attention mechanism and combining it with Graph Convolutional Neural Networks (GCNs) for action recognition, enabling the model to extract local information through graph convolution while capturing the rich remote dependencies through Transformer. In addition, Transformer's self-attention mechanism is calculated at the pixel level, a huge computational cost is generated. The model divides the entire network into two stages. The first stage uses pure convolution to extract shallow spatial features, and the second stage uses the proposed ConvT block to capture high-level semantic information, reducing the computational complexity. Moreover, the linear embeddings in the original Transformer are replaced with convolutional embeddings to obtain local spatial information enhancement, and thus removing the positional encoding in the original model, making the model lighter. Experimentally validated on two large-scale authoritative datasets NTU-RGB+D and Kinetics-Skeleton, the model achieves respectively Top-1 accuracy of 88.1% and 36.6%. The experimental results demonstrate that the performance of the model is greatly improved. -
表 1 在Kinetics-skeleton数据集上与其他模型的性能对比(%)
表 2 在NTU-60数据集上与其他模型的性能对比(%)
表 3 在参数和精度方面与基线模型的对比
表 4 不同嵌入方法和移除位置编码在Kinetics-skeleton数据集上对性能的影响(%)
嵌入方法 位置编码 Top-1精度 Top-5精度 线性嵌入 × 35.2 58.1 卷积嵌入 √ 35.1 57.8 卷积嵌入 × 35.4 58.3 表 5 不同ConvT层数在Kinetics-skeleton数据集的识别精度(%)
层数 Top-1 Top-5 2 35.2 57.7 3 35.5 58.1 4 35.6 58.3 5 35.4 58.0 6 35.1 57.7 -
[1] 石跃祥, 周玥. 基于阶梯型特征空间分割与局部注意力机制的行人重识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 195–202. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201006SHI Yuexiang and ZHOU Yue. Person re-identification based on stepped feature space segmentation and local attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 195–202. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201006 [2] NIEPERT M, AHMED M, and KUTZKOV K. Learning convolutional neural networks for graphs[C]. The 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, USA, 2016: 2014–2023. [3] YAN Sijie, XIONG Yuanjun, and LIN Dahua. Spatial temporal graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. The Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Thirtieth Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference and Eighth AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 912. [4] CHENG Ke, ZHANG Yifan, HE Xiangyu, et al. Skeleton-based action recognition with shift graph convolutional network[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 180–189. [5] LIU Ziyu, ZHANG Hongwen, CHEN Zhenghao, et al. Disentangling and unifying graph convolutions for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 140–149. [6] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [7] MEINHARDT T, KIRILLOV A, LEAL-TAIXE L, et al. TrackFormer: Multi-object tracking with transformers[J]. arXiv: 2101.02702, 2021. [8] SUN Peize, CAO Jinkun, JIANG Yi, et al. TransTrack: Multiple object tracking with transformer[J]. arXiv: 2012.15460, 2020. [9] ZHENG CE, ZHU Sijie, MENDIETA M, et al. 3D human pose estimation with spatial and temporal transformers[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 11636–11645. [10] CHU Peng, WANG Jiang, YOU Quanzeng, et al. TransMOT: Spatial-temporal graph transformer for multiple object tracking[J]. arXiv: 2104.00194, 2021. [11] FERNANDO B, GAVVES E, ORAMAS J M, et al. Modeling video evolution for action recognition[C]. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 5378–5387. [12] LI Shuai, LI Wanqing, COOK C, et al. Independently Recurrent Neural Network (IndRNN): Building a longer and deeper RNN[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 5457–5466. [13] LI Chao, ZHONG Qiaoyong, XIE Di, et al. Skeleton-based action recognition with convolutional neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Hong Kong, China, 2017: 597–600. [14] ZHANG Pengfei, LAN Cuiling, ZENG Wenjun, et al. Semantics-guided neural networks for efficient skeleton-based human action recognition[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1109–1118. [15] ZHANG Xikun, XU Chang, and TAO Dacheng. Context aware graph convolution for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 14321–14330. [16] 曾胜强, 李琳. 基于姿态校正与姿态融合的2D/3D骨架动作识别方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2022, 39(3): 900–905. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.07.0286ZENG Shengqiang and LI Lin. 2D/3D skeleton action recognition based on posture transformation and posture fusion[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2022, 39(3): 900–905. doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2021.07.0286 [17] 李扬志, 袁家政, 刘宏哲. 基于时空注意力图卷积网络模型的人体骨架动作识别算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(7): 1915–1921. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2020091515LI Yangzhi, YUAN Jiazheng, and LIU Hongzhe. Human skeleton-based action recognition algorithm based on spatiotemporal attention graph convolutional network model[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2021, 41(7): 1915–1921. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2020091515 [18] LI Maosen, CHEN Siheng, CHEN Xu, et al. Actional-structural graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3590–3598. [19] SHI Lei, ZHANG Yifan, CHENG Jian, et al. Two-stream adaptive graph convolutional networks for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 12018–12027. [20] DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[C/OL]. The 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021. [21] TOUVRON H, CORD M, DOUZE M, et al. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention[L/OL]. The 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2021: 10347–10357. [22] RAMACHANDRAN P, PARMAR N, VASWANI A, et al. Stand-alone self-attention in vision models[C]. Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 7. [23] SHARIR G, NOY A, and ZELNIK-MANOR L. An image is worth 16x16 words, what is a video worth?[J]. arXiv: 2103.13915, 2021. [24] PLIZZARI C, CANNICI M, and MATTEUCCI M. Spatial temporal transformer network for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Milano, Italy, 2021: 694–701. [25] BA J L, KIROS J R, and HINTON G E. Layer normalization[J]. arXiv: 1607.06450, 2016. [26] SHAHROUDY A, LIU Jun, NG T T, et al. NTU RGB+D: A large scale dataset for 3D human activity analysis[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1010–1019. [27] KAY W, CARREIRA J, SIMONYAN K, et al. The kinetics human action video dataset[J]. arXiv: 1705.06950, 2017. [28] CHO S, MAQBOOL M H, LIU Fei, et al. Self-attention network for skeleton-based human action recognition[C]. 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass, USA, 2020: 624–633. [29] TANG Yansong, TIAN Yi, LU Jiwen, et al. Deep progressive reinforcement learning for skeleton-based action recognition[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 5323–5332. [30] LI Chao, ZHONG Qiaoyong, XIE Di, et al. Co-occurrence feature learning from skeleton data for action recognition and detection with hierarchical aggregation[C]. The Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 786–792. -





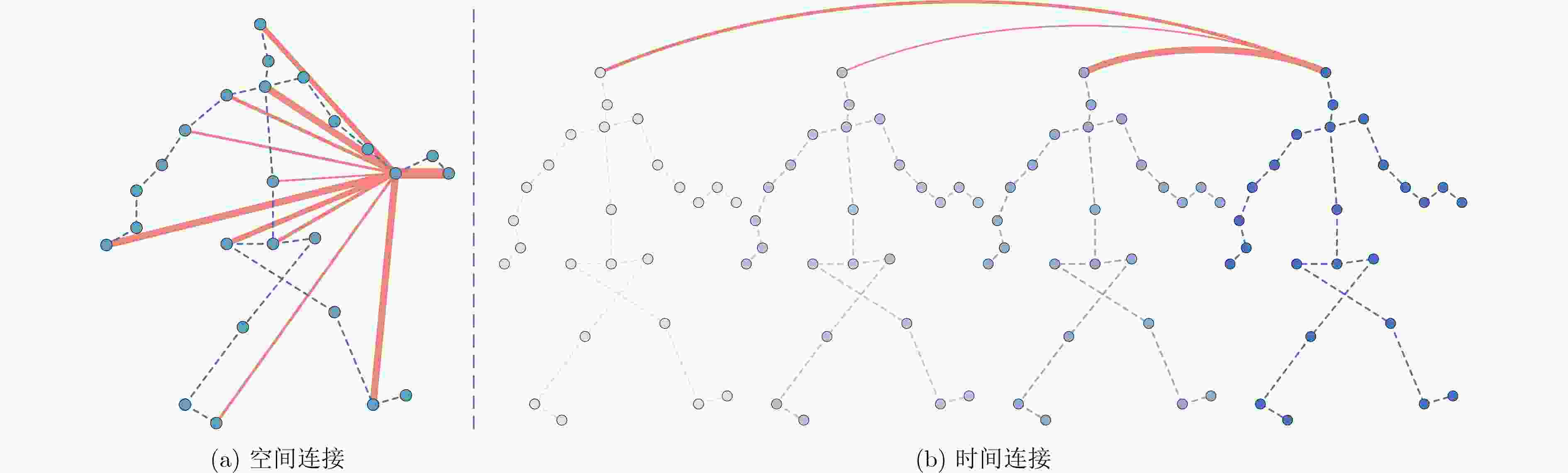
 下载:
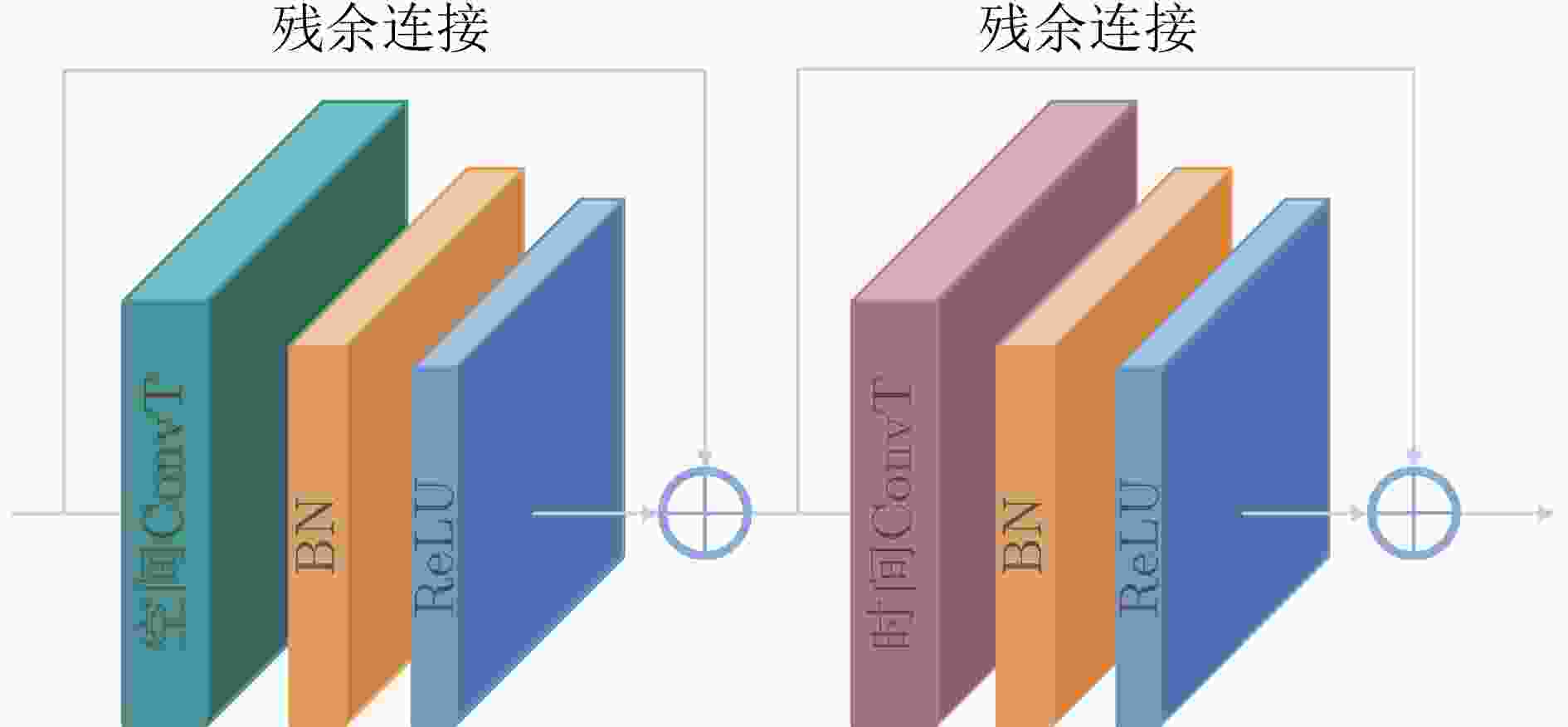
下载:

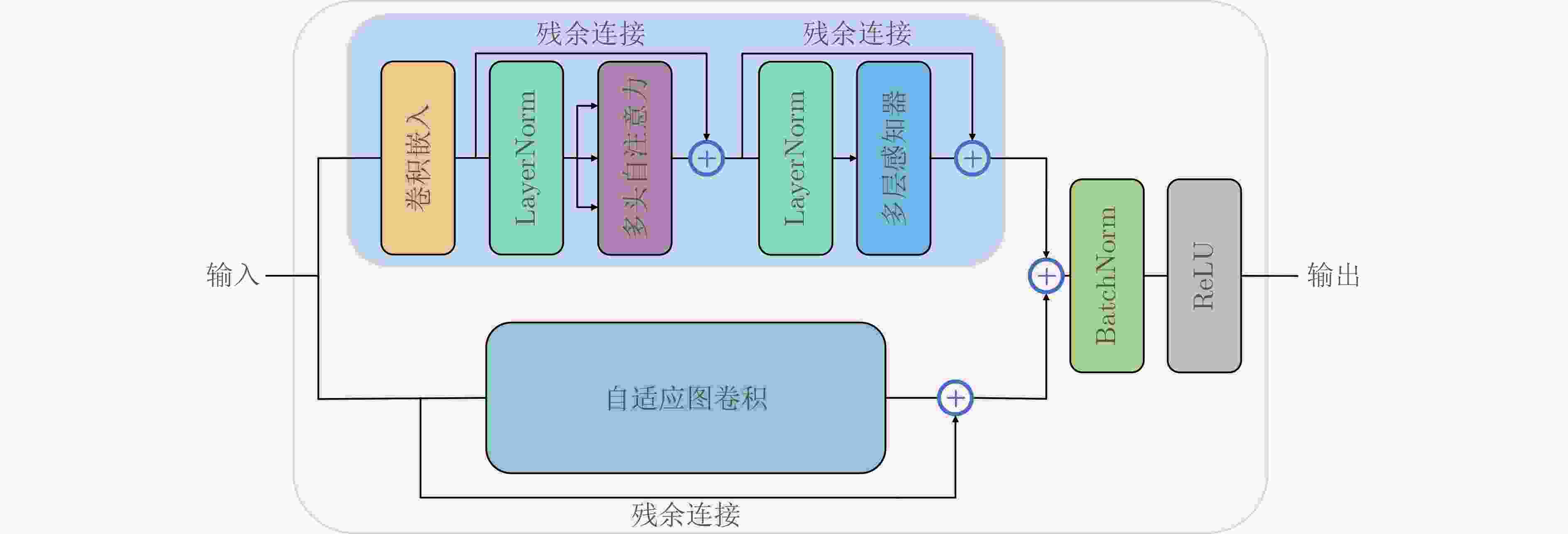
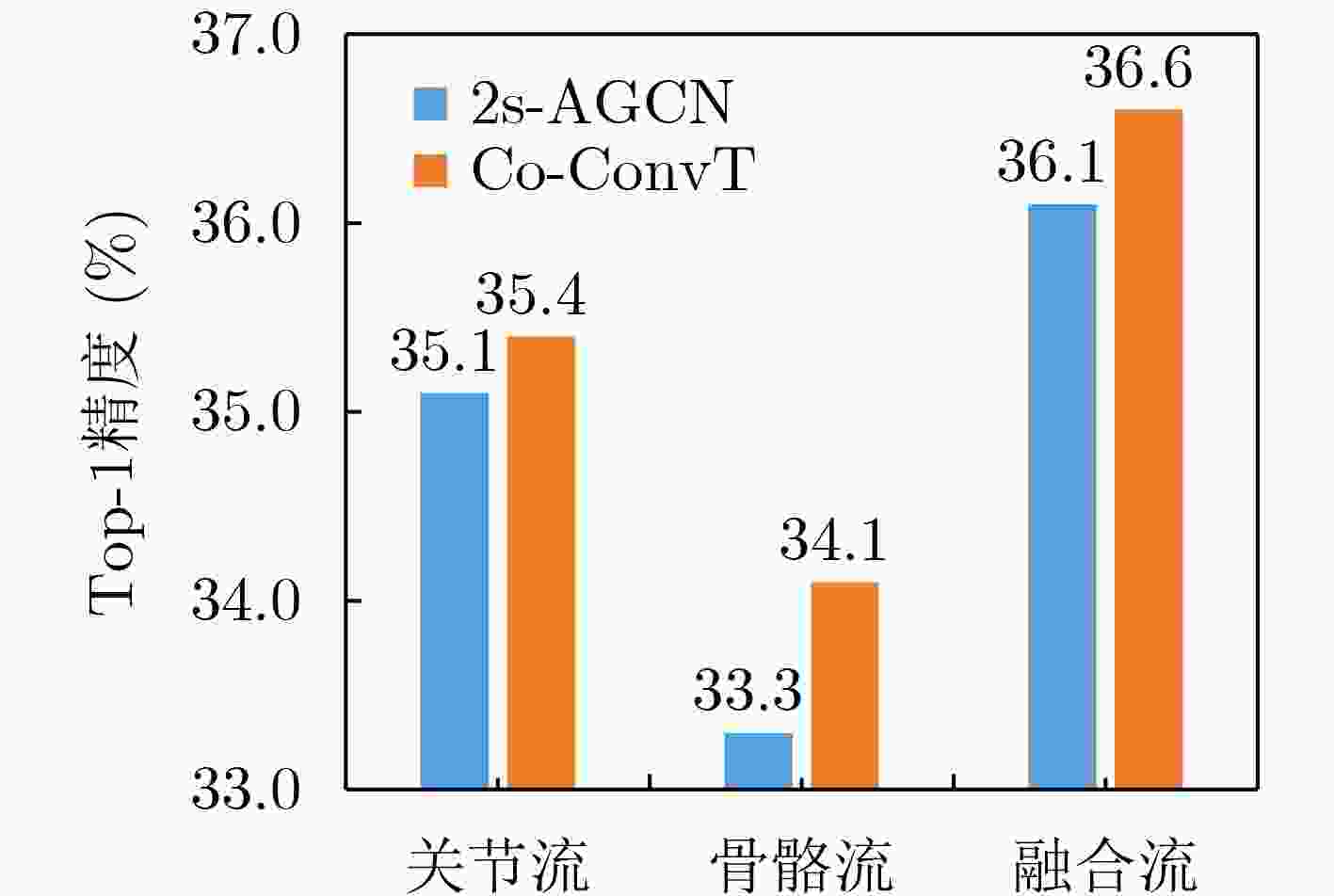


 下载:
下载:
