Container Based Microservice Selection for Multi-workflow in Edge Computing Paradigm
-
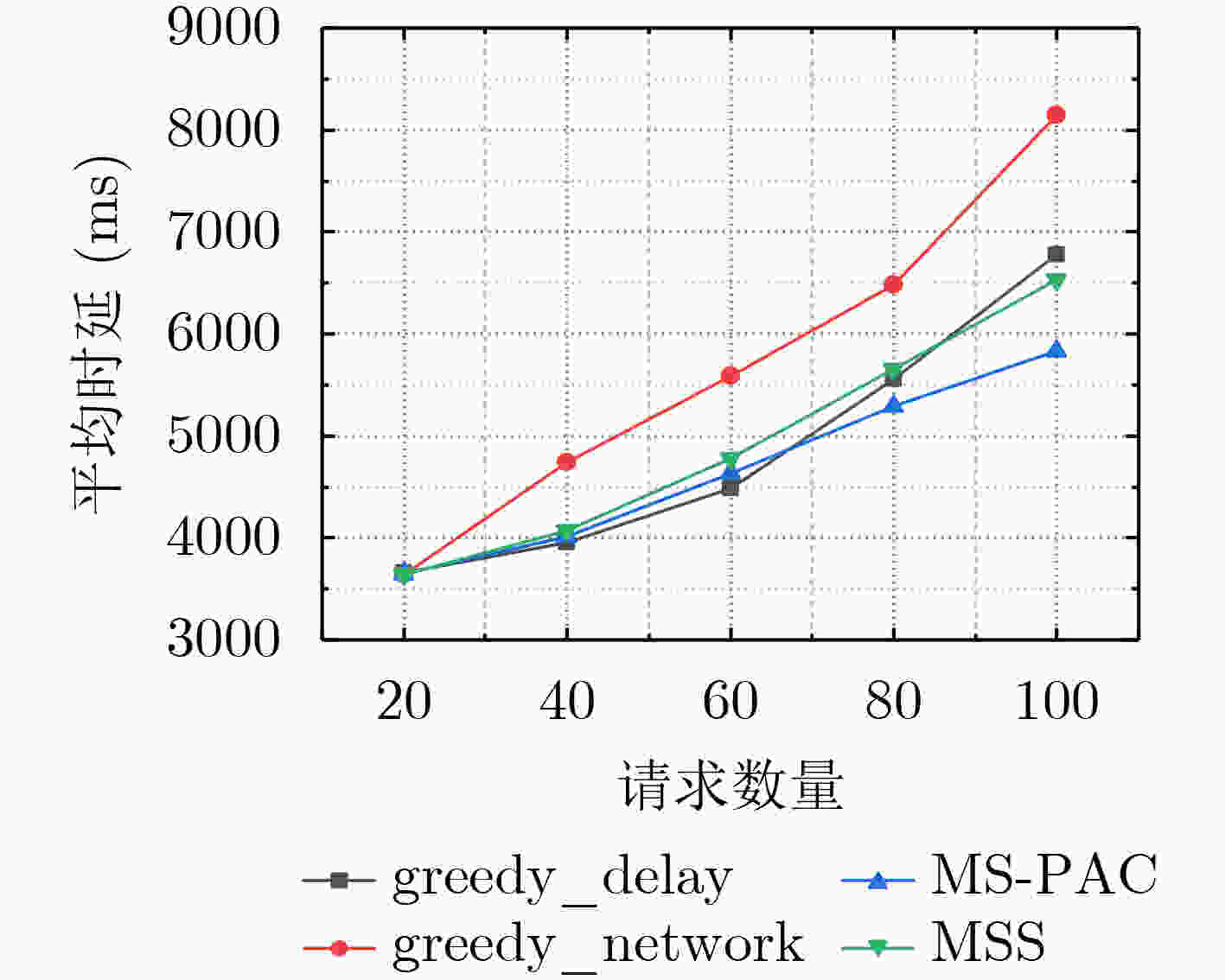
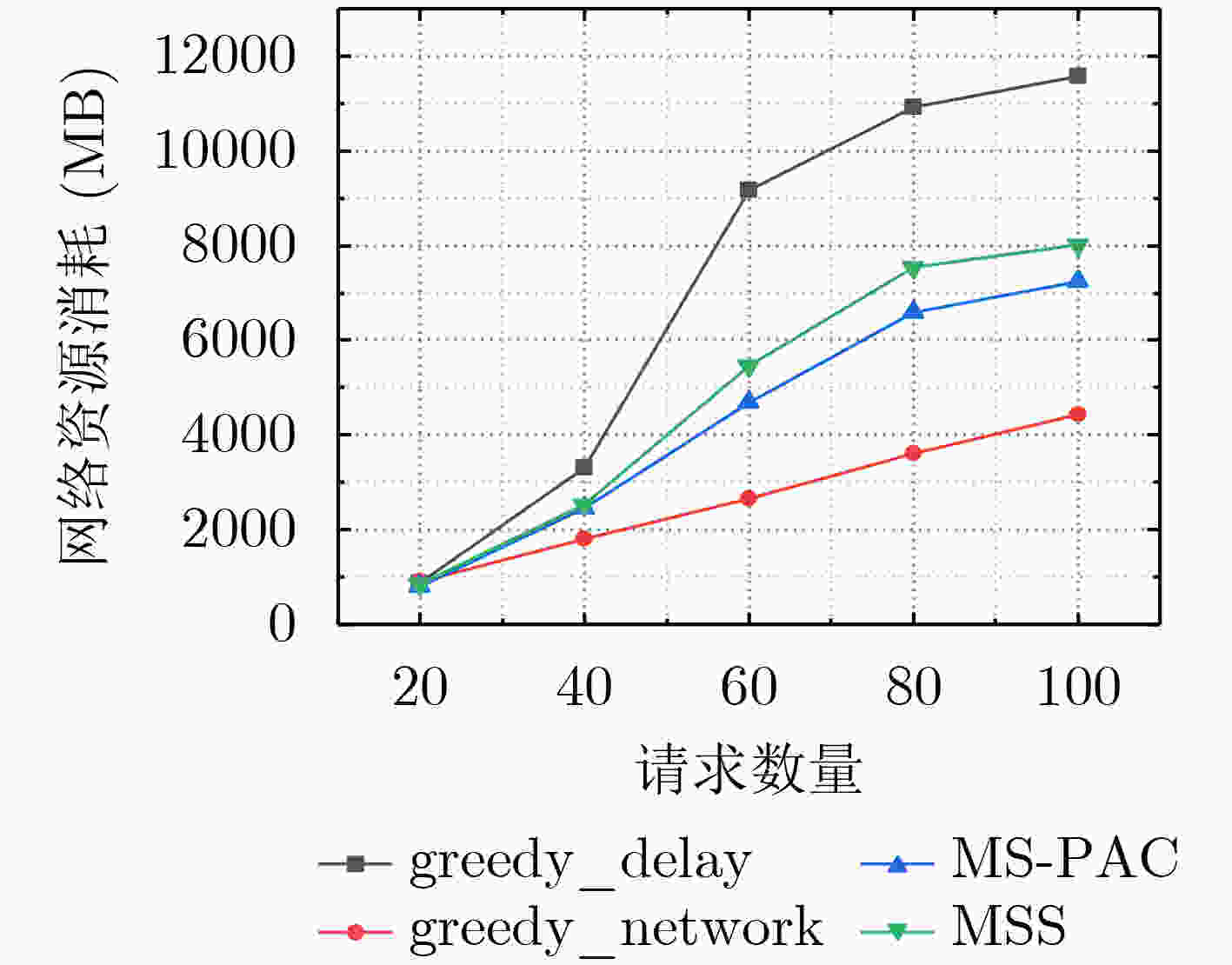
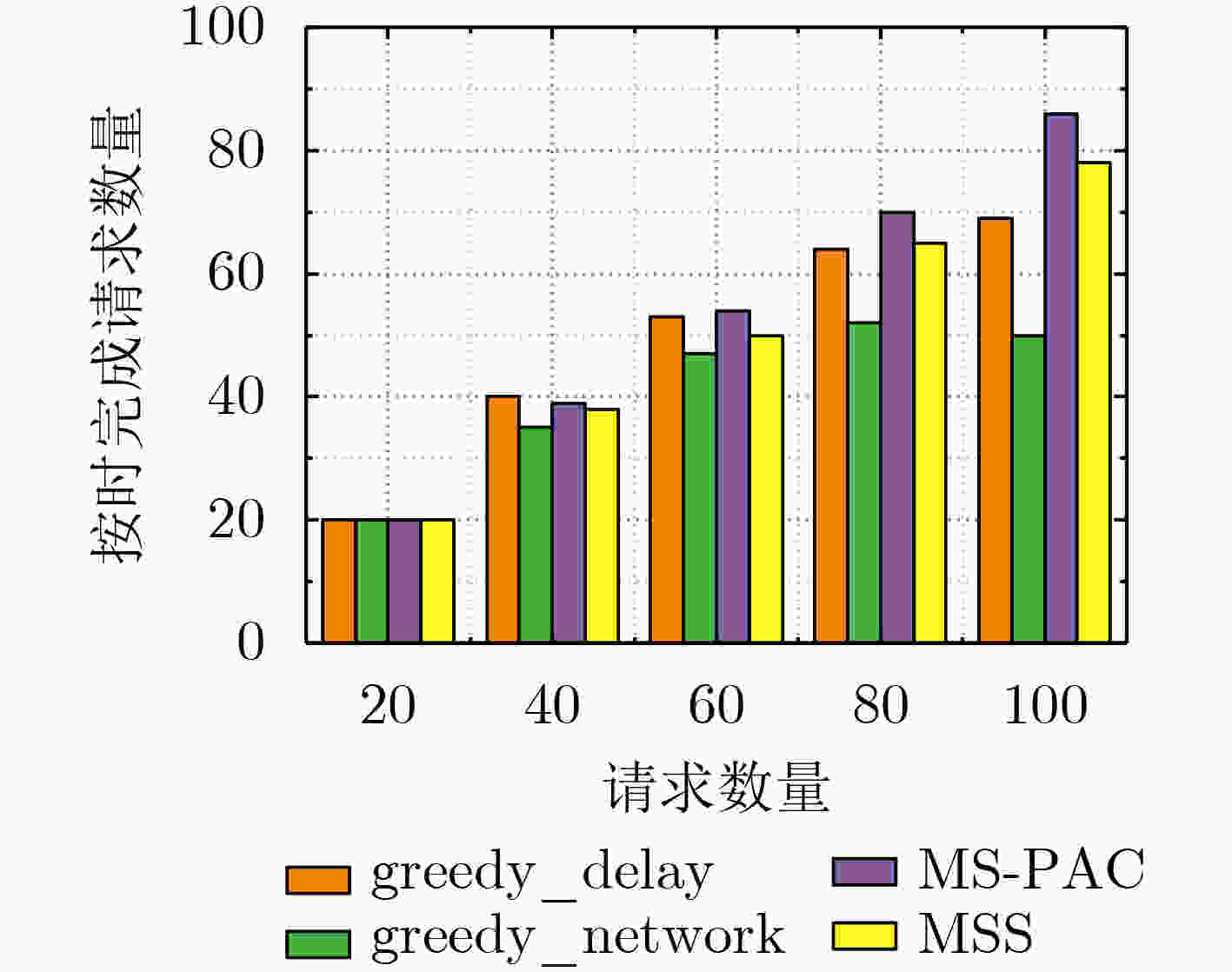
摘要: 边缘计算已经成为物联网(IOT)的有效解决方案,微服务模型将物联网应用程序划分为一组松散耦合、相互依赖的细粒度微服务。由于边缘节点资源有限,并发请求争夺容器实例,如何在移动边缘计算环境下为复杂工作流应用的并发请求生成合适的微服务执行方案是一个需要解决的重要问题。为此,该文首先建立了基于容器的微服务选择架构,并构建了服务时延模型和网络资源消耗模型,以减少平均延迟和网络消耗。其次,提出一种基于优先级机制和改进蚁群的微服务选择算法(MS-PAC),利用任务截止时间优先分配紧急任务以保证延迟,并利用蚁群算法的信息素机制寻找全局最优解。实验表明,该算法能有效地降低平均时延和网络消耗。Abstract: Edge computing has become an effective solution for the Internet Of Things (IOT) and the microservice model divides the IOT application into a group of loosely coupled and interdependent fine-grained microservices. Due to the limit resource of edge nodes and concurrent requests compete for container instances, how to generate an appropriate microservice selection scheme for concurrent requests of complex workflow application in mobile edge computing environment is an important problem to be solved. Therefore, a container based microservice selection architecture is established in this paper firstly, and the service delay model and network resource consumption model are constructed to reduce the average delay and network consumption. Secondly, Microservice Selection algorithm based on Priority mechanism and improved Ant Colony (MS-PAC) based on priority mechanism and improved ant colony algorithm is proposed, which uses the task deadline to assign urgent tasks first to ensure the delay, and uses the pheromone mechanism of ant colony algorithm to find the global optimal solution. Experimentation demonstrates that the proposed algorithm can reduce the average delay and network consumption effectively.
-
Key words:
- Microservice selection /
- Edge computing /
- Container scheduling /
- Workflow /
- Network consumption
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
仿真参数 值 竞争因子$ \lambda $ 4 容器新建因子$ \gamma $ 5 信息素权重$ \alpha $ 1.0 启发式信息权重$ \beta $ 1.0 全局局部蒸发参数$ {\rho _g} $ 0.1 局部信息素蒸发参数$ {\rho _l} $ 0.8 -
[1] 黄杰, 肖志清, 毛冬. 面向电力物联网的云边数据协同方法[J]. 电力信息与通信技术, 2022, 20(1): 35–42. doi: 10.16543/j.2095-641x.electric.power.ict.2022.01.005HUANG Jie, XIAO Zhiqing, and MAO Dong. Cloud-edge data collaboration method for power IoTs[J]. Electric Power Information and Communication Technology, 2022, 20(1): 35–42. doi: 10.16543/j.2095-641x.electric.power.ict.2022.01.005 [2] MA Hua, HU Zhigang, LI Keqin, et al. Variation-aware cloud service selection via collaborative QoS prediction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2021, 14(6): 1954–1969. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2019.2895784 [3] LI Chunlin, BAI Jingpan, and TANG Jianhang. Joint optimization of data placement and scheduling for improving user experience in edge computing[J]. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 2019, 125: 93–105. doi: 10.1016/j.jpdc.2018.11.006 [4] DENG Shuiguang, ZHAO Hailiang, YIN Jianwei, et al. Edge intelligence: The confluence of edge computing and artificial intelligence[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(8): 7457–7469. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2984887 [5] LI He, OTA K, and DONG Mianxiong. Learning IoT in edge: Deep learning for the internet of things with edge computing[J]. IEEE Network, 2018, 32(1): 96–101. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.1700202 [6] CHEN Lulu, XU Yangchuan, LU Zhihui, et al. IoT microservice deployment in edge-cloud hybrid environment using reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(16): 12610–12622. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3014970 [7] MAZLAMI G, CITO J, and LEITNER P. Extraction of microservices from monolithic software architectures[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Web Services, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 524–531. [8] KANG Hui, LE M, and TAO Shu. Container and microservice driven design for cloud infrastructure DevOps[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Engineering, Berlin, Germany, 2016: 202–211. [9] ZHOU Ao, WANG Shangguang, WAN Shaohua, et al. LMM: Latency-aware micro-service mashup in mobile edge computing environment[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2020, 32(19): 15411–15425. doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04693-w [10] DING Zhijun, WANG Sheng, and PAN Meiqin. QoS-constrained service selection for networked microservices[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 39285–39299. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2974188 [11] ZHANG Haitao, YANG Ning, XU Zhengjun, et al. Microservice based video cloud platform with performance-aware service path selection[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Web Services, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 306–309. [12] LI Songyuan, HUANG Jiwei, CHENG Bo, et al. FASS: A fairness-aware approach for concurrent service selection with constraints[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Web Services, Milan, Italy, 2019: 255–259. [13] 陈昊崴, 邓水光, 赵海亮, 等. 面向移动边缘的组合服务选择及优化[J]. 计算机学报, 2022, 45(1): 82–97. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.00082CHEN Haowei, DENG Shuiguang, ZHAO Hailiang, et al. Composite service selection and optimization for mobile edge systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2022, 45(1): 82–97. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2022.00082 [14] RODRIGUEZ M A and BUYYA R. Scheduling dynamic workloads in multi-tenant scientific workflow as a service platforms[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018, 79: 739–750. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.05.009 [15] MSEDDI A, JAAFAR W, ELBIAZE H, et al. Joint container placement and task provisioning in dynamic fog computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 10028–10040. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2935056 [16] TANG Zhiqing, ZHOU Xiaojie, ZHANG Fuming, et al. Migration modeling and learning algorithms for containers in fog computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Services Computing, 2019, 12(5): 712–725. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2018.2827070 [17] GOUDARZI M, WU Huaming, PALANISWAMI M, et al. An application placement technique for concurrent IoT applications in edge and fog computing environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2021, 20(4): 1298–1311. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2020.2967041 [18] HUANG Xumin, YU Rong, XIE Shengli, et al. Task-container matching game for computation offloading in vehicular edge computing and networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2021, 22(10): 6242–6255. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2020.2990462 [19] LIAO Zhuofan, PENG Jingsheng, XIONG Bing, et al. Adaptive offloading in mobile-edge computing for ultra-dense cellular networks based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Cloud Computing, 2021, 10(1): 15. doi: 10.1186/s13677-021-00232-y [20] YOU Qian and TANG Bing. Efficient task offloading using particle swarm optimization algorithm in edge computing for industrial internet of things[J]. Journal of Cloud Computing, 2021, 10(1): 41. doi: 10.1186/s13677-021-00256-4 [21] BHARATHI S, CHERVENAK A, DEELMAN E, et al. Characterization of scientific workflows[C]. The 2008 Third Workshop on Workflows in Support of Large-Scale Science, Austin, USA, 2008: 1–10. [22] WU Hongyue, DENG Shuiguang, LI Wei, et al. Service selection for composition in mobile edge computing systems[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Web Services, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 355–358. -





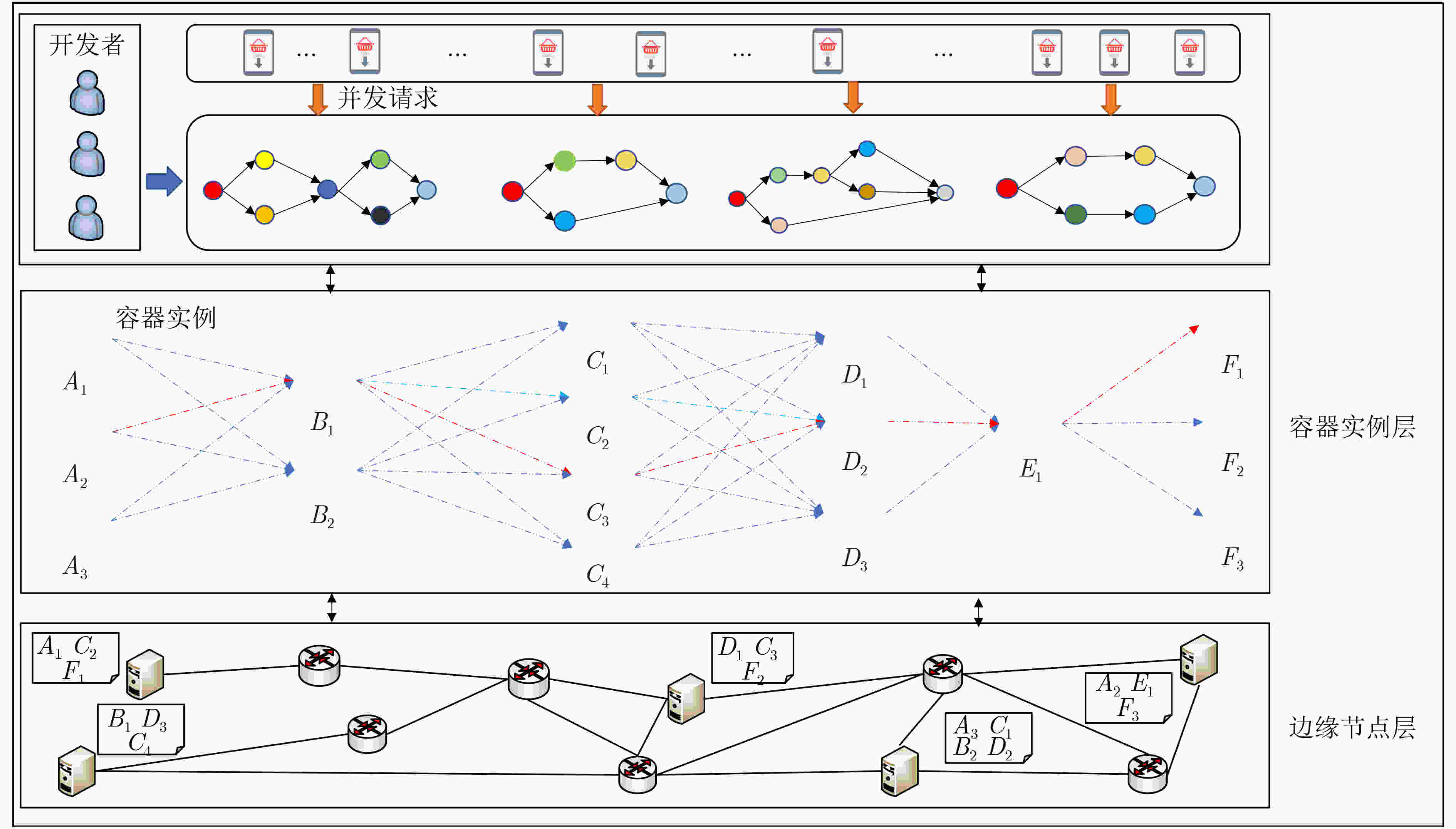
 下载:
下载:
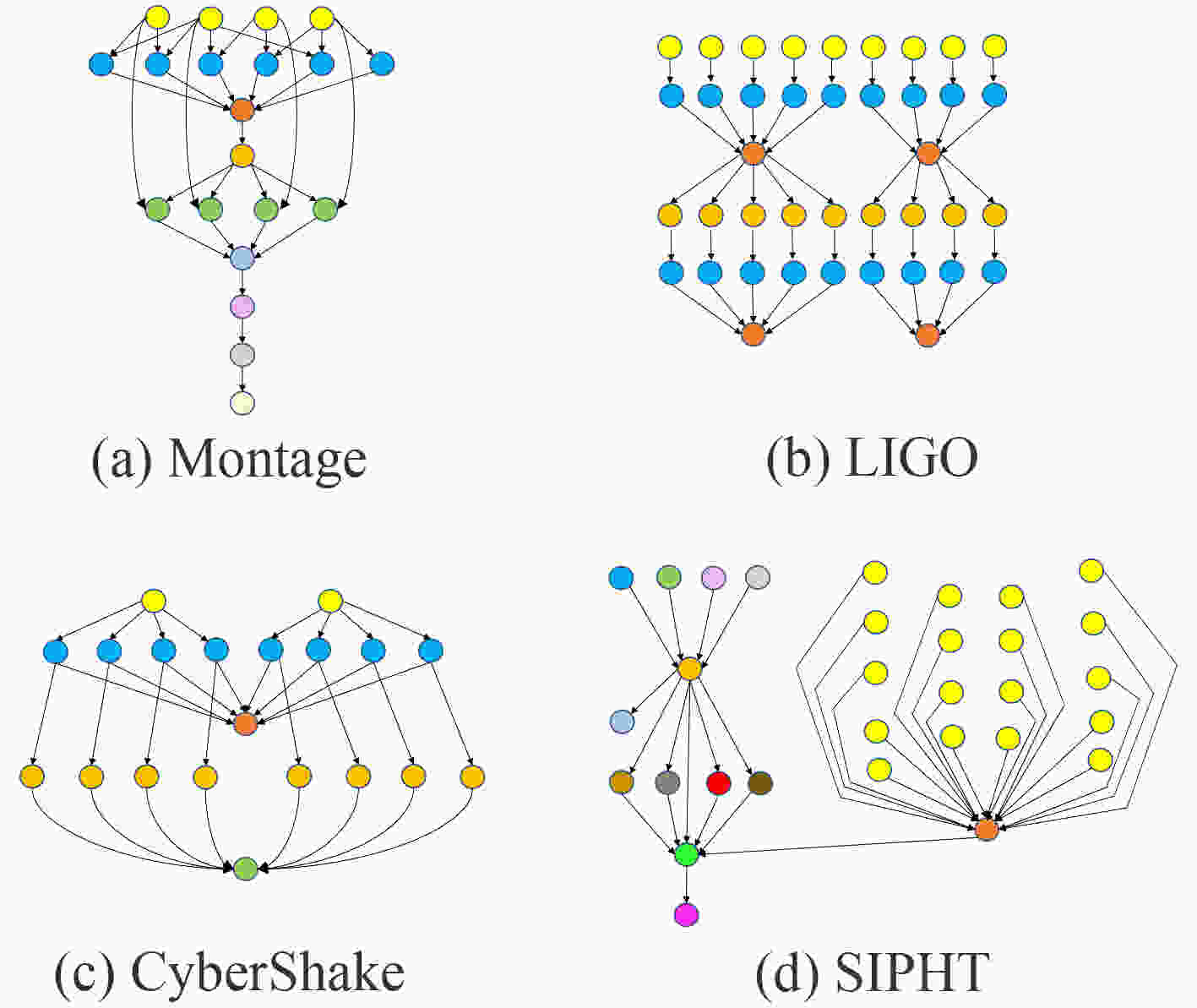
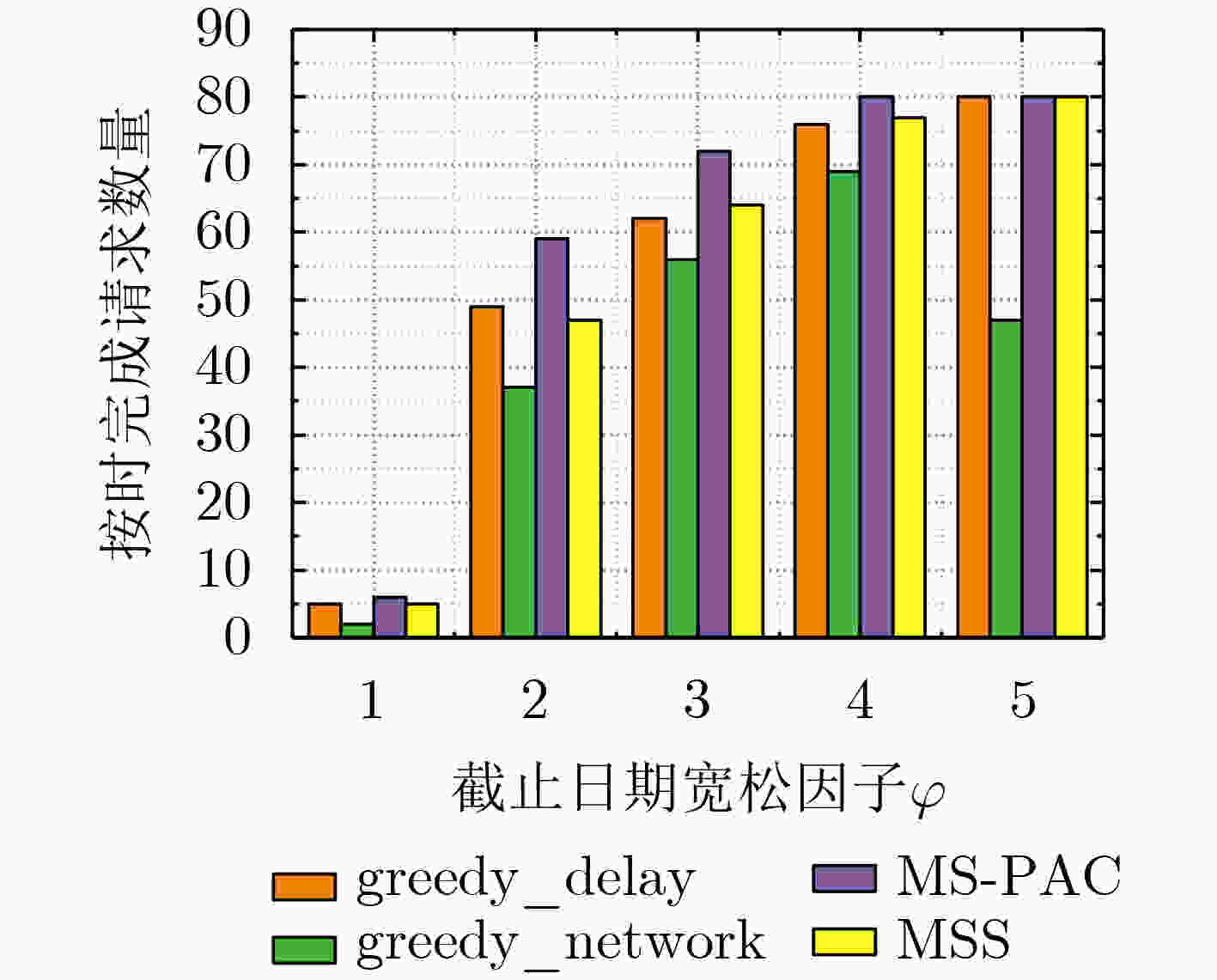
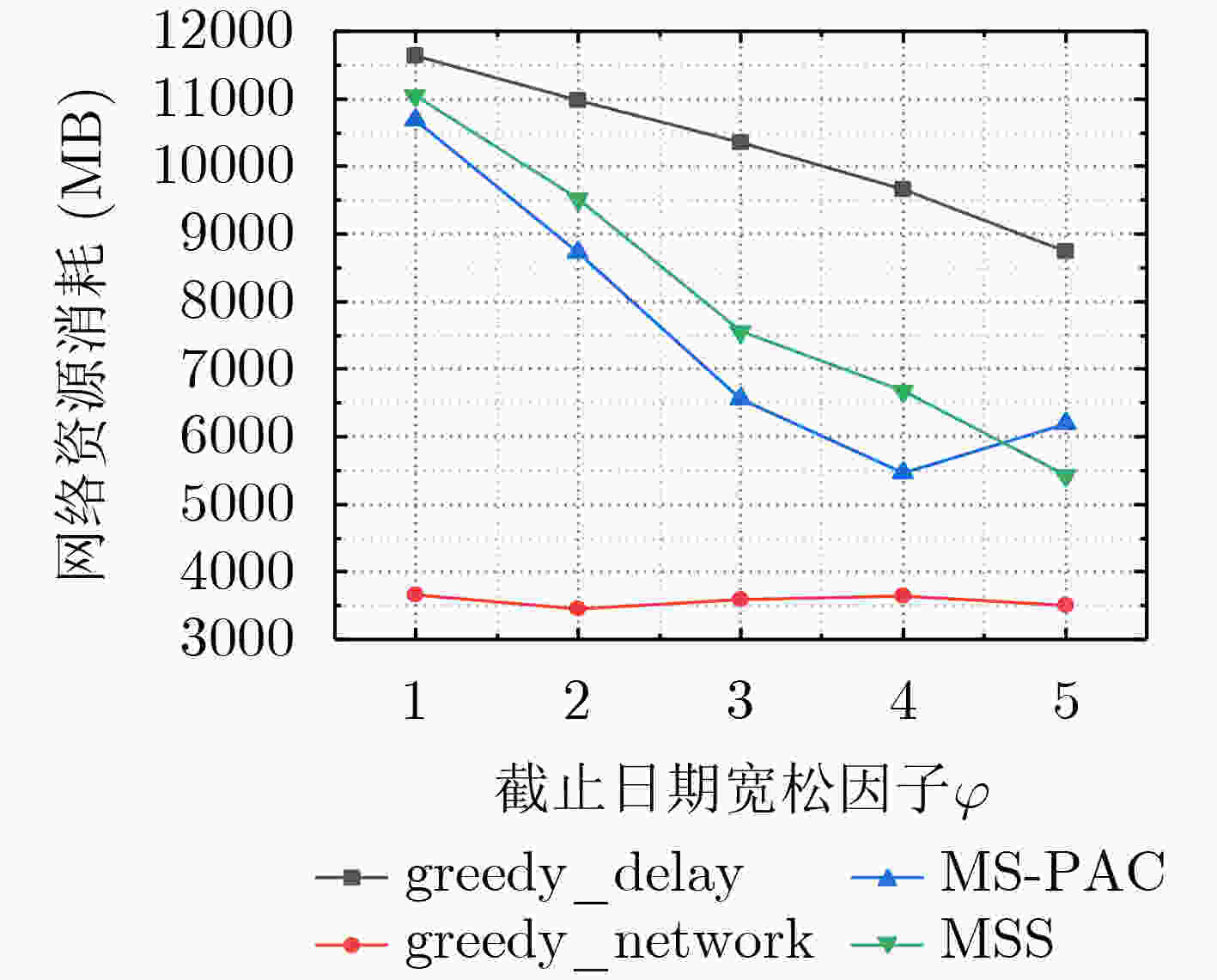


 下载:
下载:
