Multipath Measurements Clustering of Over-The-Horizon Radar Based on Affinity Propagation
-
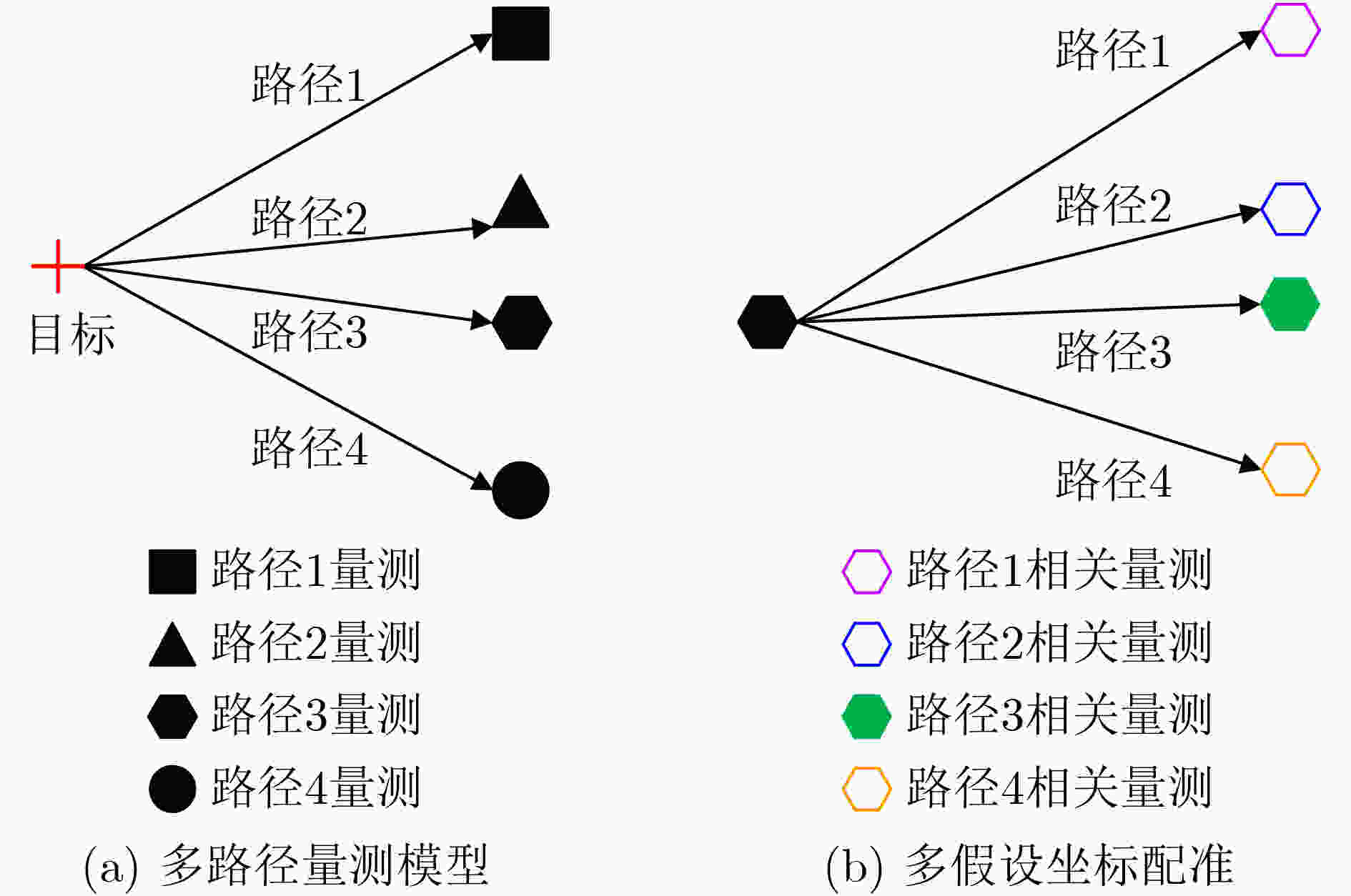
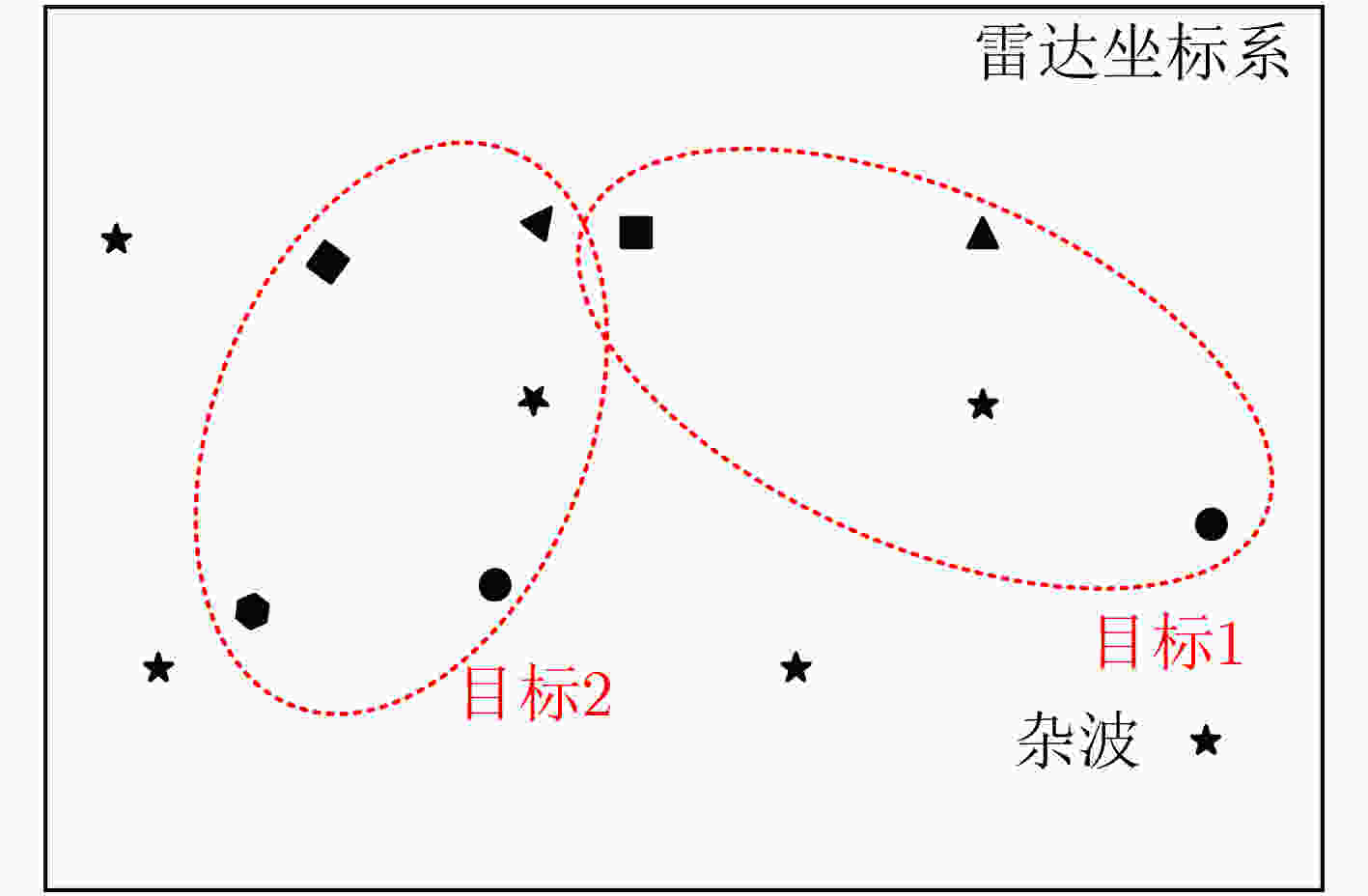
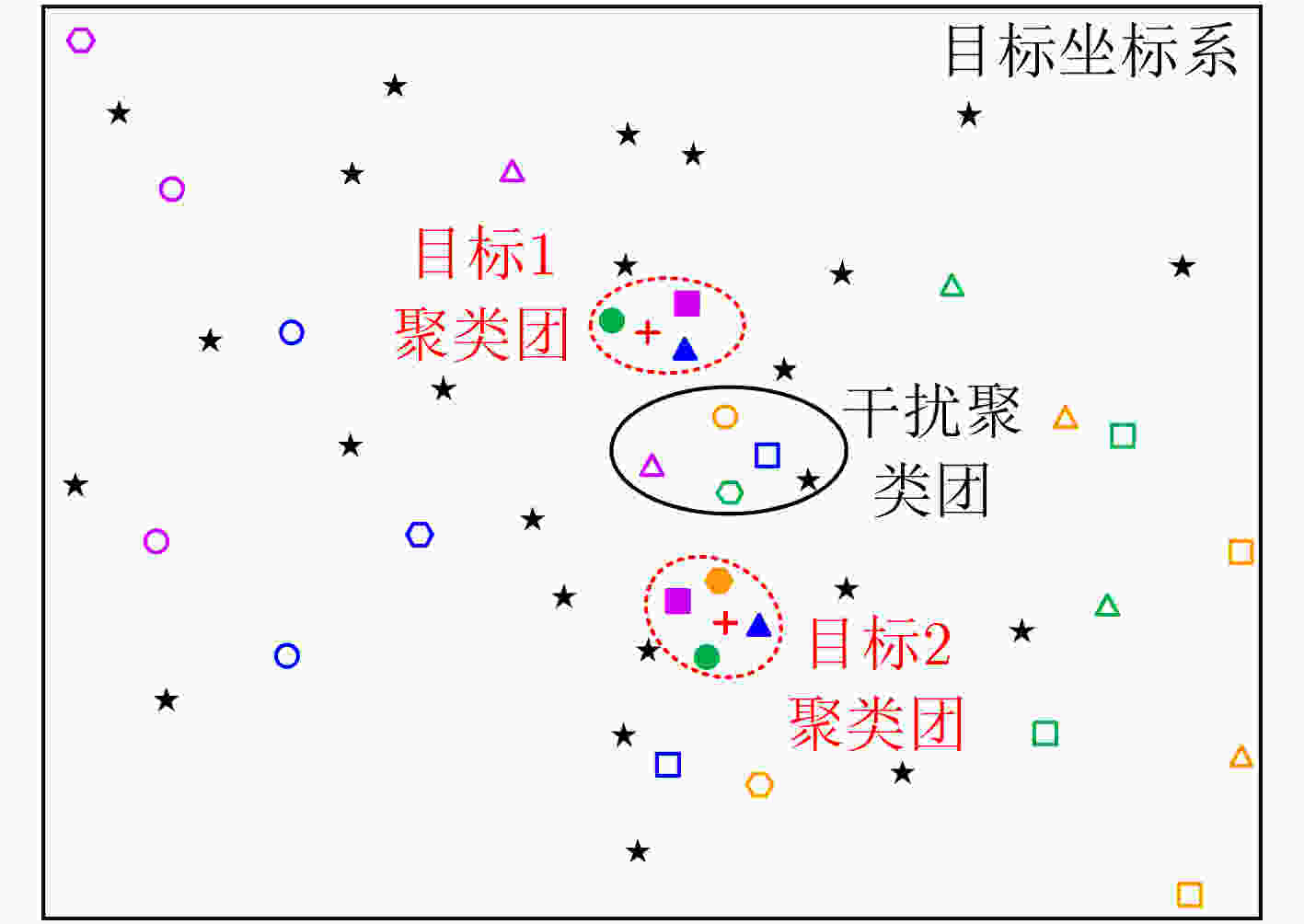
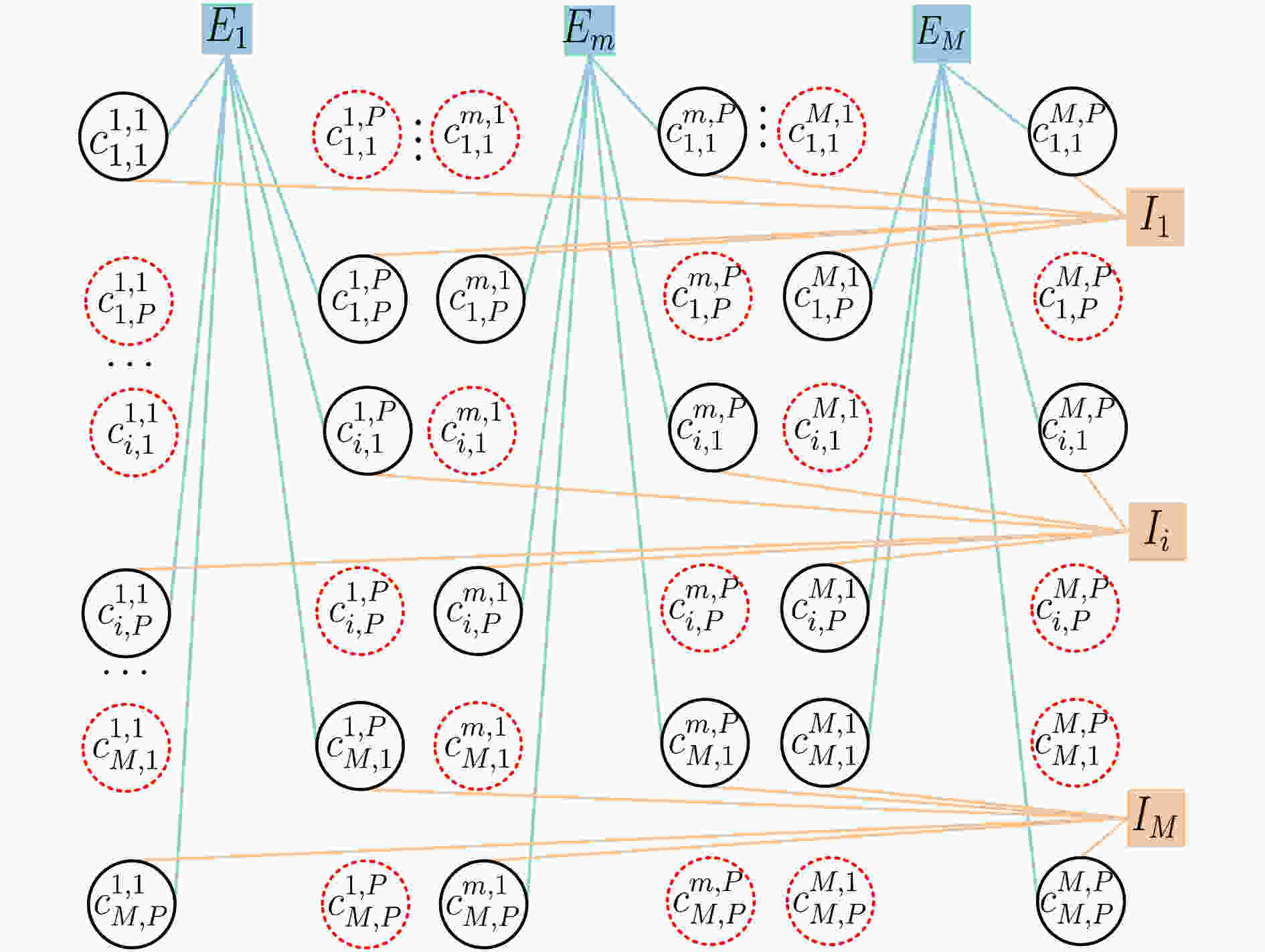
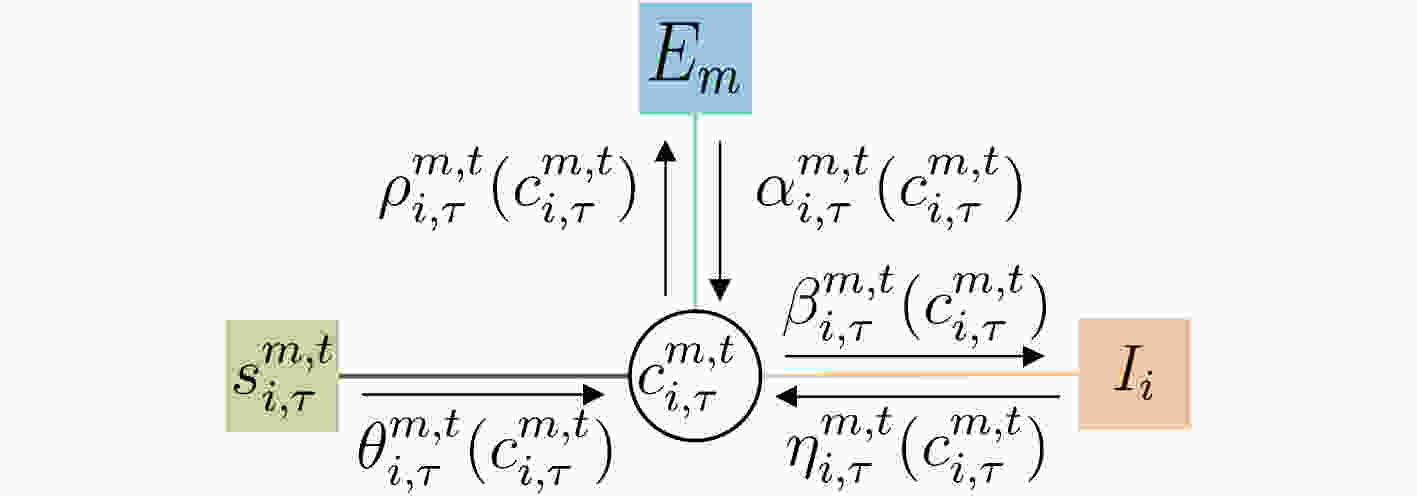
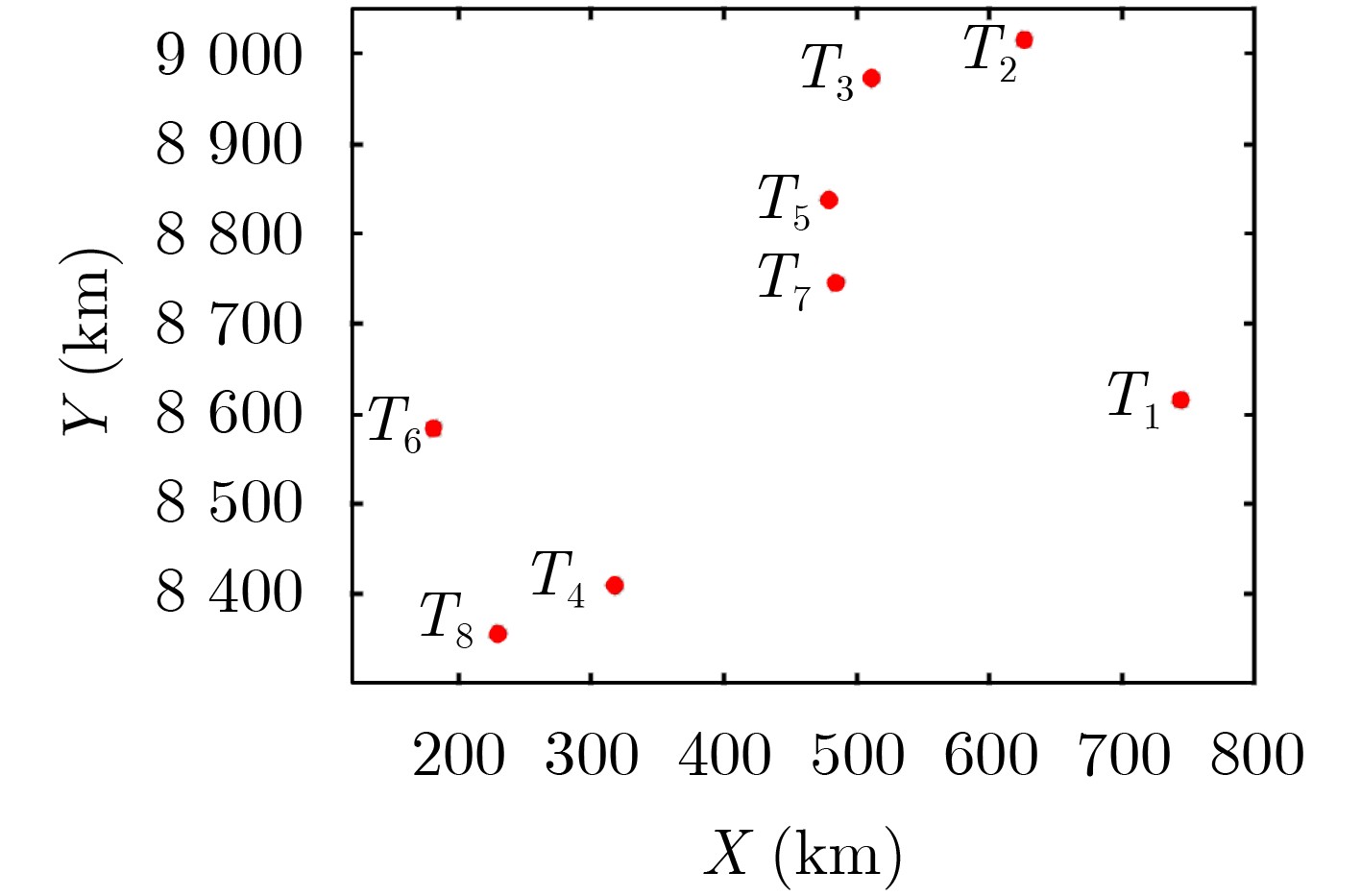
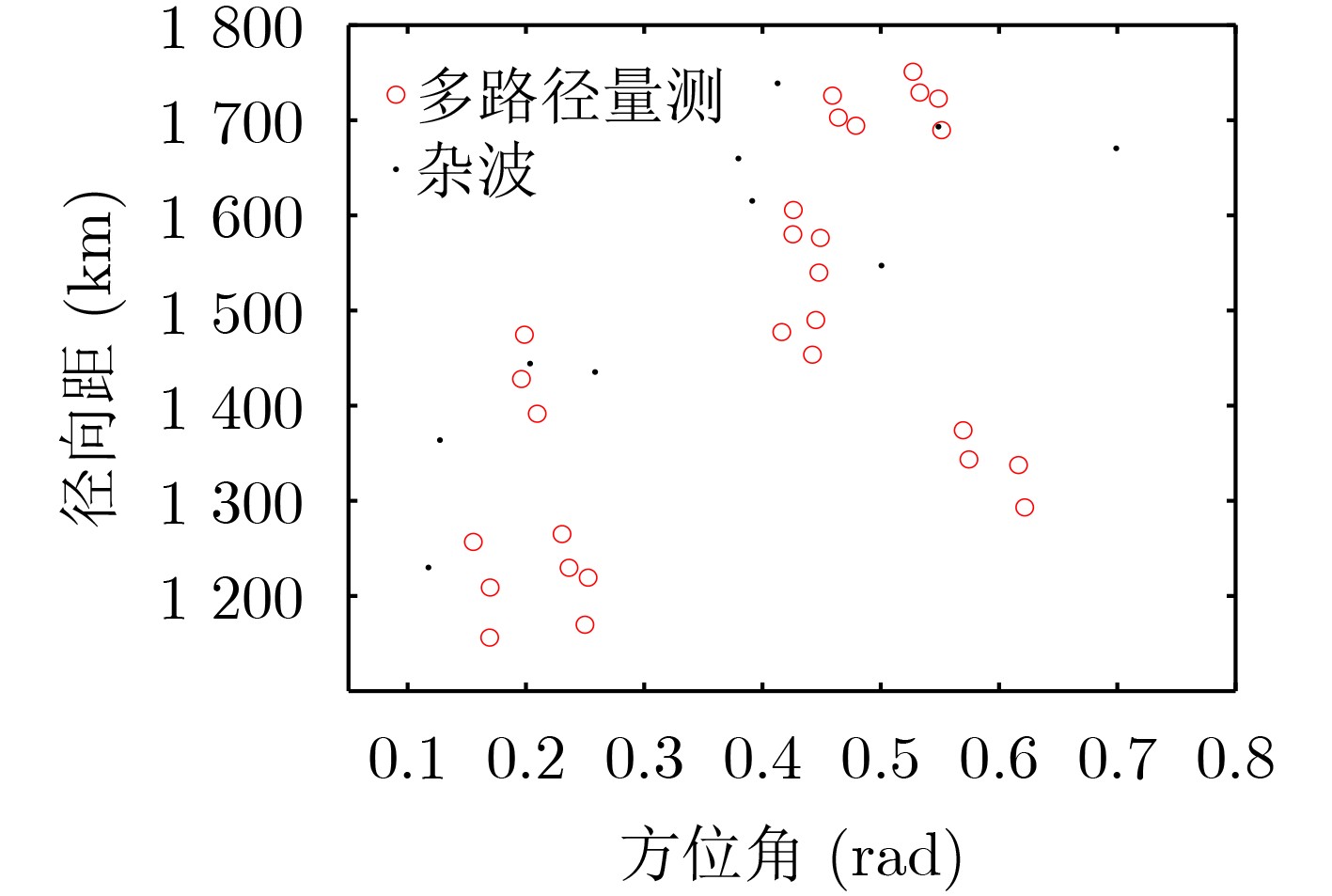
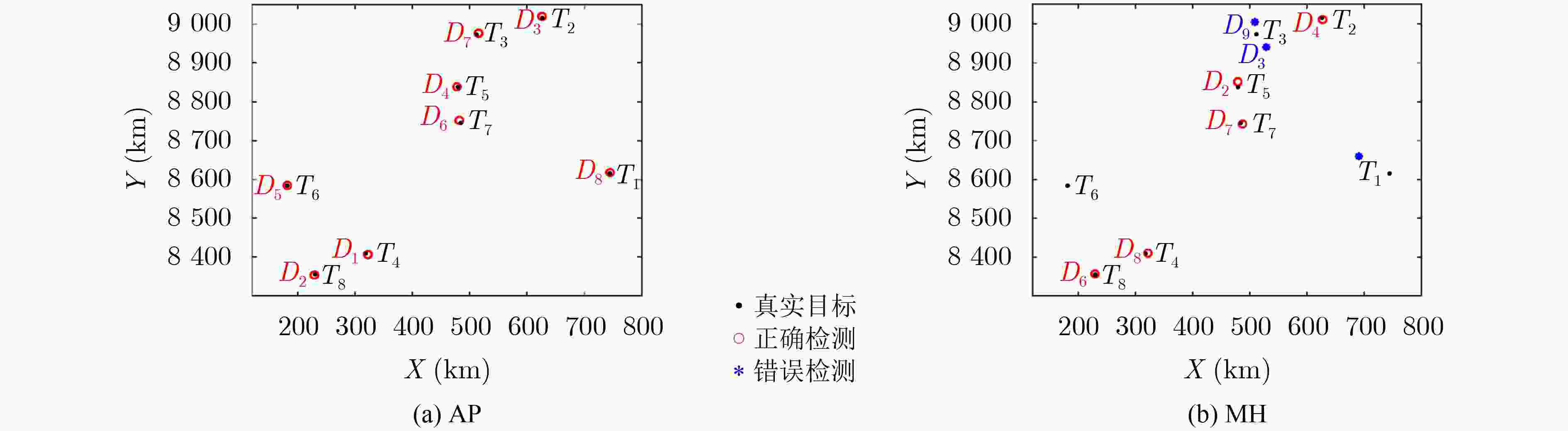
摘要: 电离层多层结构特性使得天波雷达(OTHR)与目标之间存在多条信号传播路径,进而可能对单目标产生多路径量测。该文考虑了天波雷达多路径量测聚类问题,其需要同时对多路径量测进行电离层传播路径辨识和聚类。由于天波雷达量测模型假设1个目标通过1种电离层传播路径至多产生1个量测,因此需要考虑多路径聚类约束。该文将相似性传播聚类扩展到多路径约束模型,并提出一种新的多路径相似性传播聚类算法。该算法通过构建多路径量测聚类的概率图模型,将聚类问题转化为概率图模型隐变量的推断问题,采用最大和置信传播算法近似求解聚类变量的最大后验概率。算法优点包括可以自动识别聚类团数目,单次消息传播的时间复杂度为量测个数和传播路径个数乘积的平方。仿真实验分析表明,所提算法较多路径多假设聚类算法具有更好的聚类性能。Abstract: The multi-layer structure of the ionosphere can support several signal propagation paths between the sky-wave Over-The-Horizon Radar (OTHR) and targets, often giving rise to multipath measurements for a single target. The problem of multipath measurements clustering for OTHR is considered, which needs to solve the problems of multipath measurements recognition and measurements clustering at the same time. OTHR measurements model assumes that a target can generate at most one measurement through an ionospheric propagation path, and multipath clustering constraints need to be considered. In this paper, affinity propagation clustering is extended to multipath constraint model, and a new multipath constraint affinity propagation clustering algorithm is proposed. The algorithm transforms the clustering problem into an inference problem by constructing the probabilistic graphical model of multipath measurements clustering, and uses the max-sum belief propagation to approximate the maximum a posteriori probability of the clustering matrix. The advantages of the algorithm include that it identifies automatically the number of clusters, and the computational complexity scales quadratically in the number of measurements and the number of propagation paths. Simulation results show that, the proposed method can outperform multiple hypothesis multipath clustering algorithm.
-
表 1 假设个数随着目标个数变化表
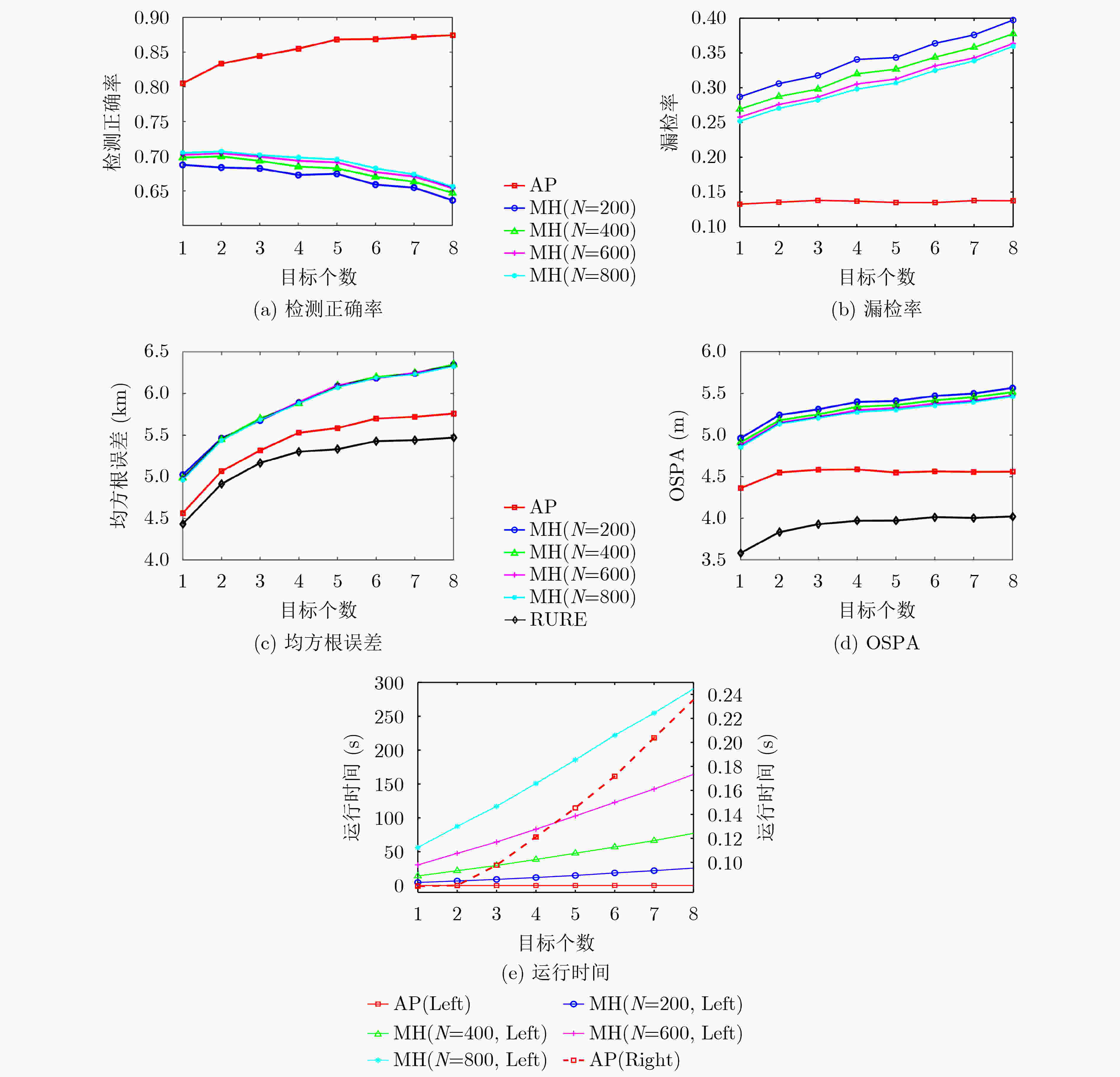
目标数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 假设数 3e6 2e7 9e7 3e8 7e8 2e9 3e9 6e9 表 2 内存消耗(kB)随目标个数变化表
算法 目标数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 AP 70.8 71.50 70.5 77.2 92.2 96.8 98.8 99.7 MH(N=200) 77.1 72.2 78.1 103.5 102.2 97.6 100.0 102.7 MH(N=400) 83.3 80.9 78.4 106.9 116.0 110.5 104.3 105.3 MH(N=600) 81.1 102.1 125.3 94.7 145.7 95.5 133.3 128.5 MH(N=800) 92.3 107.5 119.3 117.0 130.4 139.1 131.1 136.3 -
[1] 周万幸. 天波超视距雷达发展综述[J]. 电子学报, 2011, 39(6): 1373–1378.ZHOU Wanxing. An overview on development of skywave over-the-horizon radar[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011, 39(6): 1373–1378. [2] 郭振, 王增福, 兰华, 等. 基于空间相关电离层模型的天波雷达目标跟踪[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 354–362. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201030GUO Zhen, WANG Zengfu, LAN Hua, et al. Over-the-horizon radar target tracking based on spatial correlation ionosphere model[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 354–362. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201030 [3] 李擎宇, 陈建文, 鲍拯. 认知天波雷达环境感知波形设计算法研究[J]. 雷达科学与技术, 2020, 18(3): 267–273,278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.03.006LI Qingyu, CHEN Jianwen, and BAO Zheng. Waveform design of environment sensing for cognitive skywave radar[J]. Radar Science and Technology, 2020, 18(3): 267–273,278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2337.2020.03.006 [4] RUTTEN M G and PERCIVAL D J. Joint ionospheric and target state estimation for multipath OTHR track fusion[J]. SPIE, 2001, 4473: 118–129. [5] SARUNIC P W, WHITE K B, and RUTTEN M G. OTHR Multipath and multi-sensor track fusion algorithm development: DSTO-RR-0223[R]. Australia: Defense Science and Technology Organization, 2001. [6] LAN Hua, SUN Shuai, WANG Zengfu, et al. Joint Target detection and tracking in multipath environment: A variational Bayesian approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(3): 2136–2156. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2942706 [7] LAN Hua, WANG Zengfu, BAI Xianglong, et al. Measurement-level target tracking fusion for Over-the-Horizon Radar network using message passing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(3): 1600–1623. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.3044109 [8] BHATTACHARJEE P and MITRA P. A survey of density based clustering algorithms[J]. Frontiers of Computer Science, 2021, 15(1): 151308. doi: 10.1007/s11704-019-9059-3 [9] AHMED M, SERAJ R, and ISLAM S M S. The k-means algorithm: A comprehensive survey and performance evaluation[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9(8): 1295. doi: 10.3390/electronics9081295 [10] FREY B J and DUECK D. Clustering by passing messages between data points[J]. Science, 2007, 315(5814): 972–976. doi: 10.1126/science.1136800 [11] GIVONI I E and FREY B J. A binary variable model for affinity propagation[J]. Neural Computation, 2009, 21(6): 1589–1600. doi: 10.1162/neco.2009.05-08-785 [12] TAHERI S and BOUYER A. Community detection in social networks using affinity propagation with adaptive similarity matrix[J]. Big Data, 2020, 8(3): 189–202. doi: 10.1089/big.2019.0143 [13] ARZENO N M and VIKALO H. Evolutionary clustering via message passing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2021, 33(6): 2452–2466. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2019.2954869 [14] DE LAET T, BRUYNINCKX H, and DE SCHUTTER J. Shape-based online multitarget tracking and detection for targets causing multiple measurements: Variational Bayesian clustering and lossless data association[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2477–2491. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.83 [15] UR-REHMAN A, NAQVI S M, MIHAYLOVA L, et al. Multi-target tracking and occlusion handling with learned variational Bayesian clusters and a social force model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(5): 1320–1335. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2504340 [16] GUERRIERO M, WILLETT P, and GLAZ J. Distributed target detection in sensor networks using scan statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(7): 2629–2639. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2017567 [17] VINET L and ZHEDANOV A. A 'missing' family of classical orthogonal polynomials[J]. Journal of Physics A:Mathematical and Theoretical, 2011, 44(8): 085201. doi: 10.1088/1751-8113/44/8/085201 [18] CORALUPPI S, GUERRIERO M, WILLETT P, et al. Fuse-before-track in large sensor networks[J]. Journal of Advances in Information Fusion, 2010, 5(1): 18–31. [19] LI Tiancheng, CORCHADO J M, SUN Shudong, et al. Clustering for filtering: Multi-object detection and estimation using multiple/massive sensors[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, (388/389): 172–190. [20] LI Tiancheng, PINTADO F D L P, CORCHADO J M, et al. Multi-source homogeneous data clustering for multi-target detection from cluttered background with misdetection[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2017, 60: 436–446. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2017.07.012 [21] BERMEJO-SOLERA M and OTERO J. Simple and highly accurate formulas for the computation of Transverse Mercator coordinates from longitude and isometric latitude[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2009, 83(1): 1–12. doi: 10.1007/s00190-008-0224-y [22] JULIER S J and UHLMANN J K. Unscented filtering and nonlinear estimation[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2004, 92(3): 401–422. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2003.823141 [23] RUTTEN M G, MASKELL S, BRIERS M, et al. Multipath track association for over-the-horizon radar using Lagrangian relaxation[J]. SPIE, 5428, 2004: 452–463 . [24] 郭振, 王增福, 白向龙, 等. 消息传递方法及其在信息融合中的应用[J]. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(10): 2443–2455. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2021.0367,2021GUO Zhen, WANG Zengfu, BAI Xianglong, et al. Message passing methods and their applications in information fusion[J]. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(10): 2443–2455. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2021.0367,2021 [25] AEBERHARD M, SCHLICHTHARLE S, KAEMPCHEN N, et al. Track-to-track fusion with asynchronous sensors using information matrix fusion for surround environment perception[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2012, 13(4): 1717–1726. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2012.2202229 [26] SCHUHMACHER D, VO B T, and VO B N. A consistent metric for performance evaluation of multi-object filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(8): 3447–3457. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.920469 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
