| [1] |
MCMAHAN B and RAMAGE D. Federated learning: Collaborative machine learning without centralized training data[EB/OL]. https://starrymind.tistory.com/180, 2017.
|
| [2] |
NIKNAM S, DHILLON H S, and REED J H. Federated learning for wireless communications: Motivation, opportunities, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(6): 46–51. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900461
|
| [3] |
LIU Yi, PENG Jialiang, KANG Jiawen, et al. A secure federated learning framework for 5G networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(4): 24–31. doi: 10.1109/MWC.01.1900525
|
| [4] |
McMAHAN B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data[C]. The 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2017: 1273–1282.
|
| [5] |
LI Tian, SAHU A K, ZAHEER M, et al. Federated optimization in heterogeneous networks[C]. Machine Learning and Systems 2020, Austin, USA, 2020, 2: 429–450.
|
| [6] |
MILLS J, HU Jia, and MIN Geyong. Communication-efficient federated learning for wireless edge intelligence in IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(7): 5986–5994. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2956615
|
| [7] |
LI Tian, SANJABI M, BEIRAMI A, et al. Fair resource allocation in federated learning[C]. The 8th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2019: 1–27.
|
| [8] |
LIU Lumin, ZHANG Jun, SONG S H, et al. Client-edge-cloud hierarchical federated learning[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6.
|
| [9] |
ABAD M S H, OZFATURA E, GUNDUZ D, et al. Hierarchical federated learning ACROSS heterogeneous cellular networks[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 8866–8870.
|
| [10] |
SUN Haifeng, LI Shiqi, YU F R, et al. Toward communication-efficient federated learning in the internet of things with edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(11): 11053–11067. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2994596
|
| [11] |
SHI Yuanming, YANG Kai, JIANG Tao, et al. Communication-efficient edge AI: Algorithms and systems[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(4): 2167–2191. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2020.3007787
|
| [12] |
LUO Siqi, CHEN Xu, WU Qiong, et al. HFEL: Joint edge association and resource allocation for cost-efficient hierarchical federated edge learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(10): 6535–6548. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3003744
|
| [13] |
KHAN L U, RAJ PANDEY S, TRAN N H, et al. Federated learning for edge networks: Resource optimization and incentive mechanism[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(10): 88–93. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900649
|
| [14] |
TRAN N H, BAO Wei, ZOMAYA A, et al. Federated learning over wireless networks: Optimization model design and analysis[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2019-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 2019: 1387–1395.
|
| [15] |
LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791
|





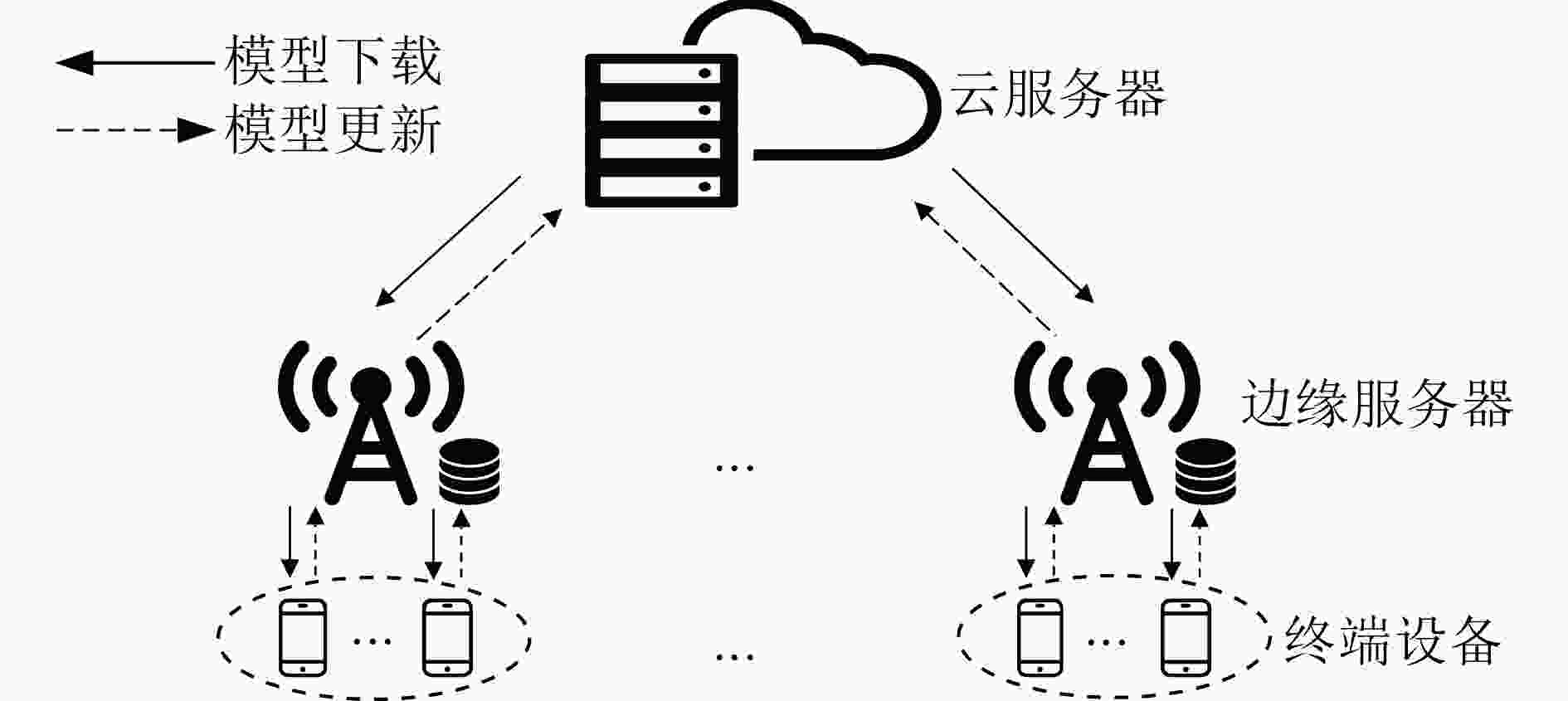
 下载:
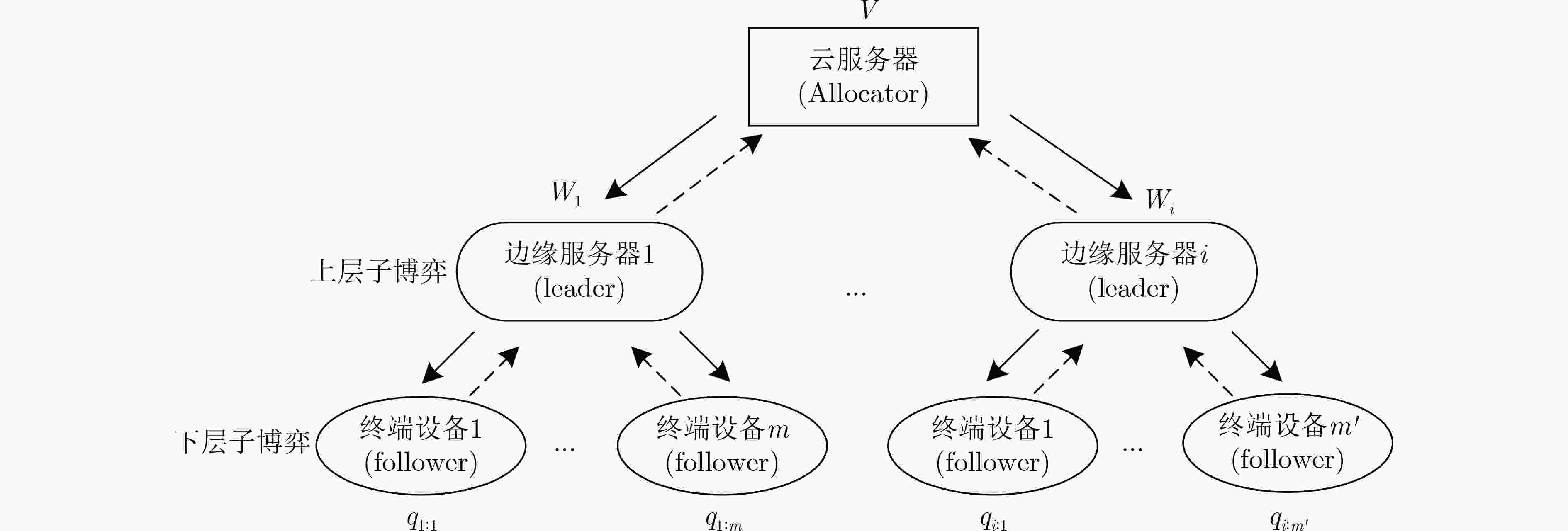
下载:
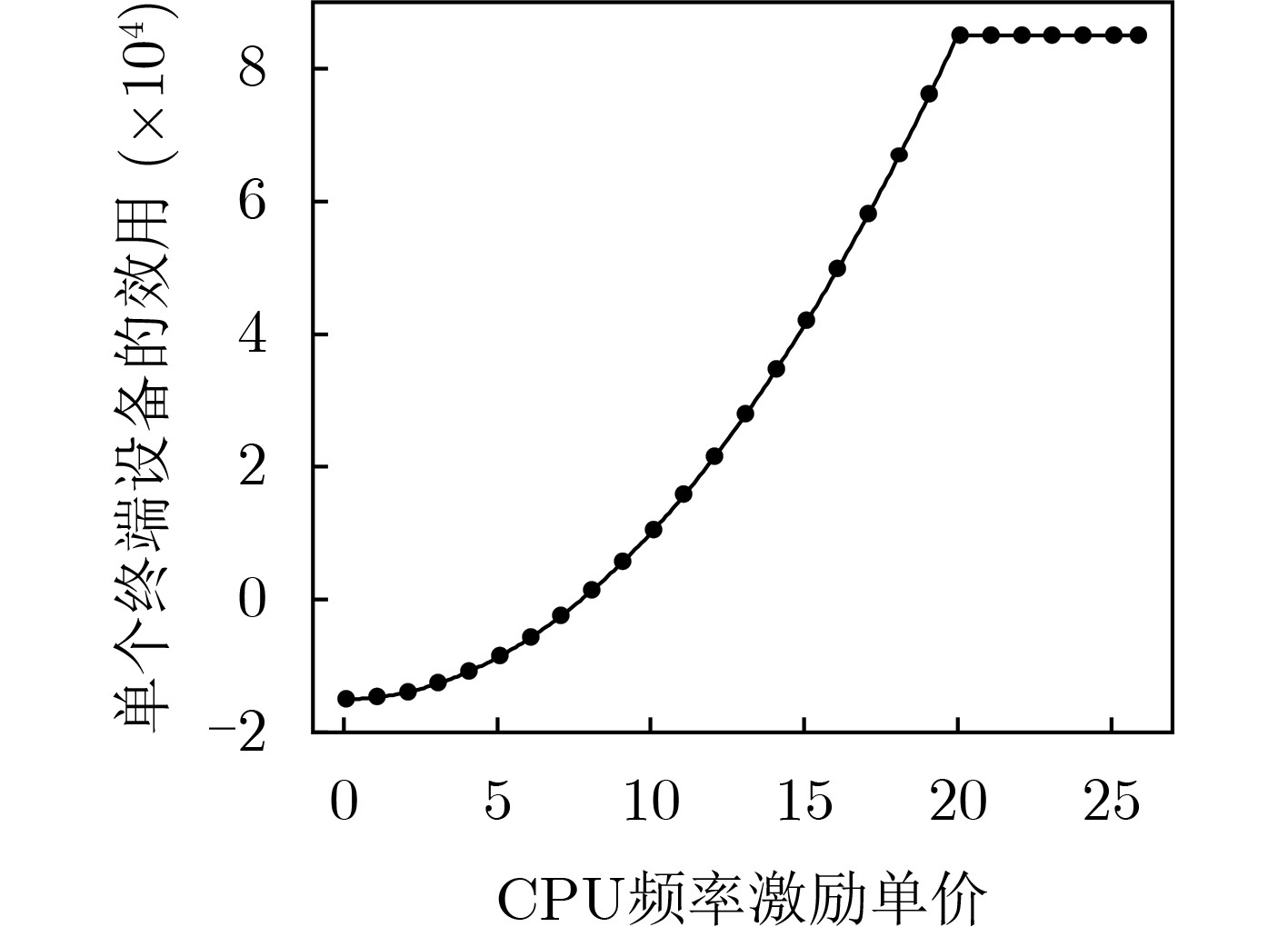


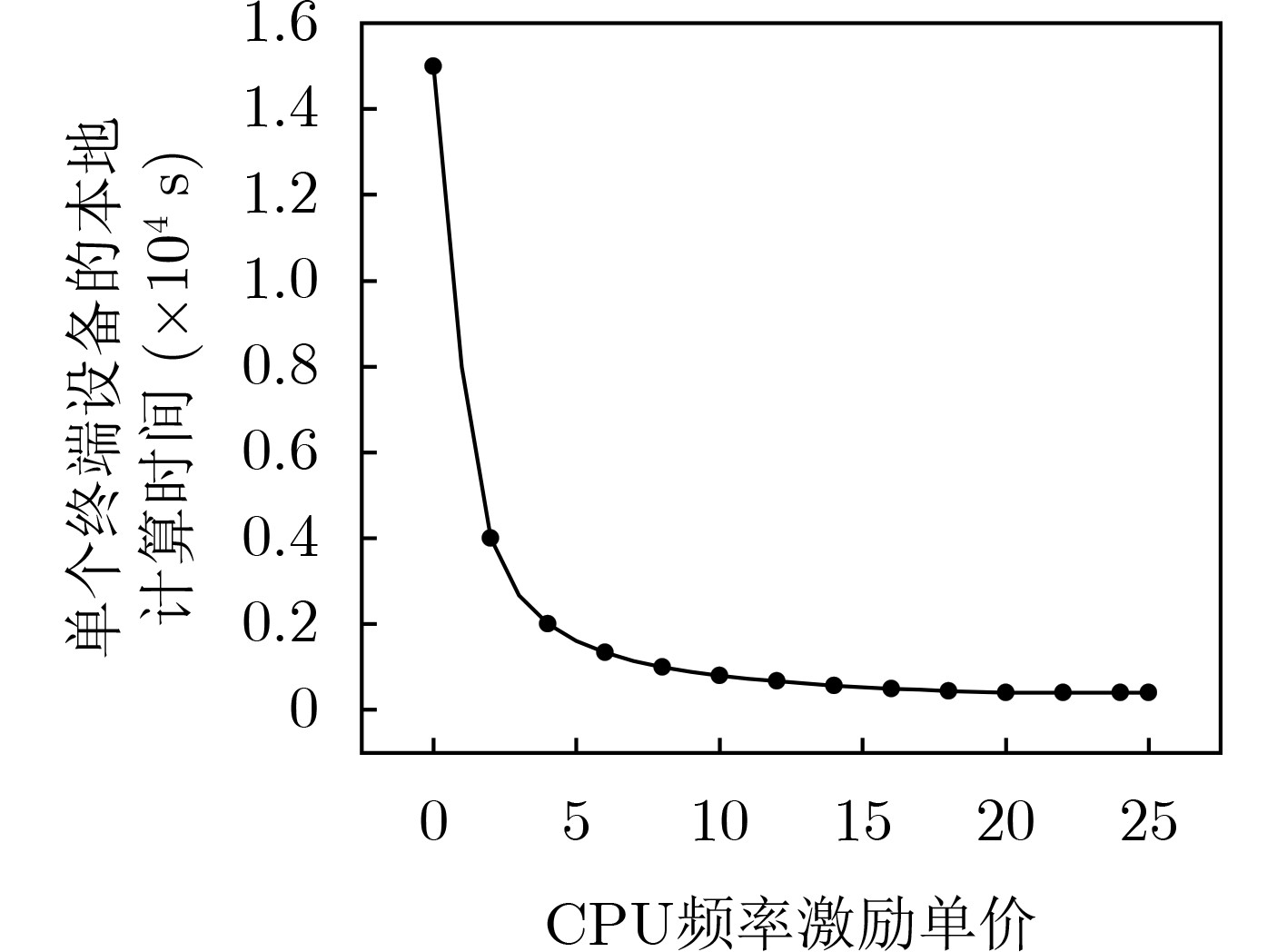

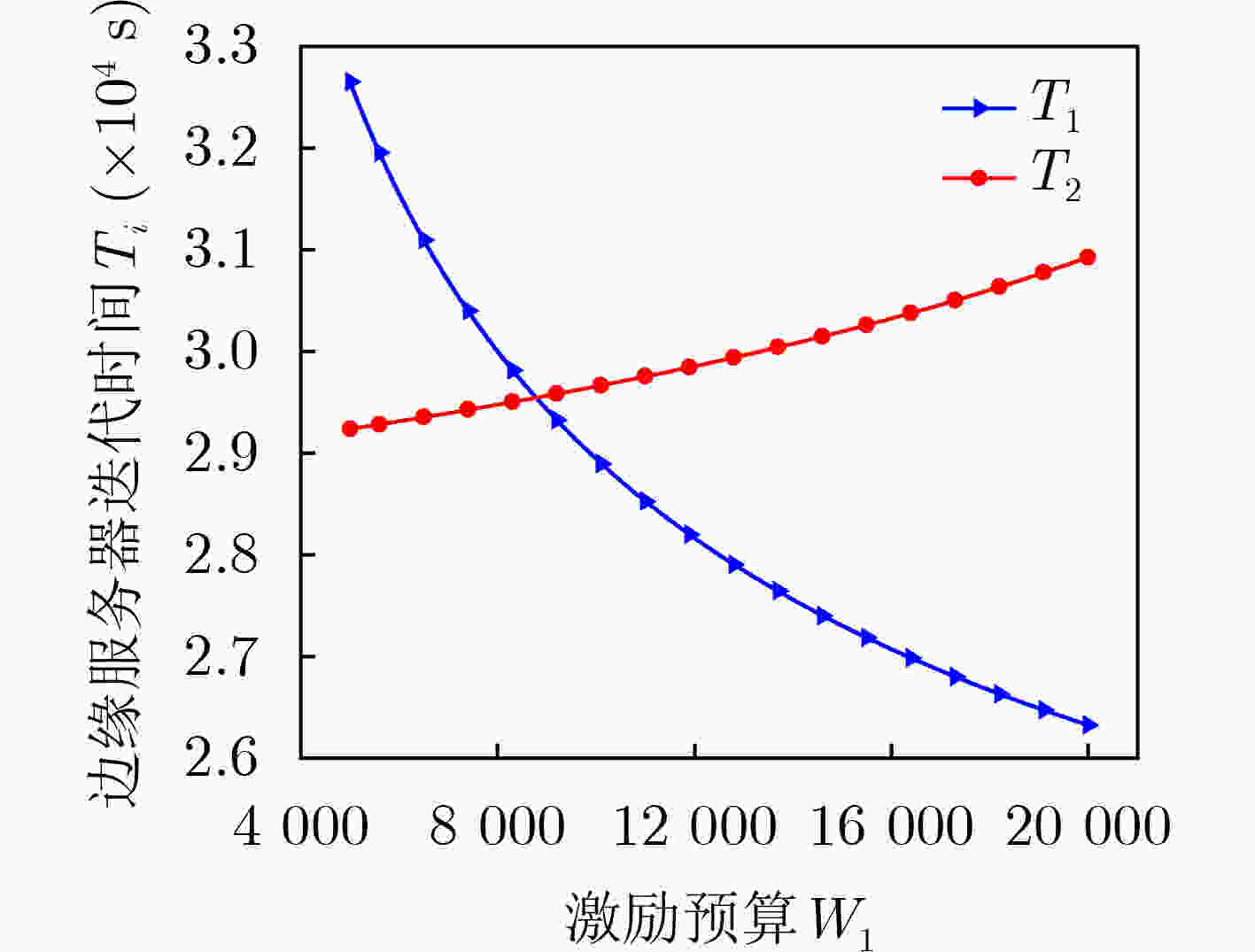



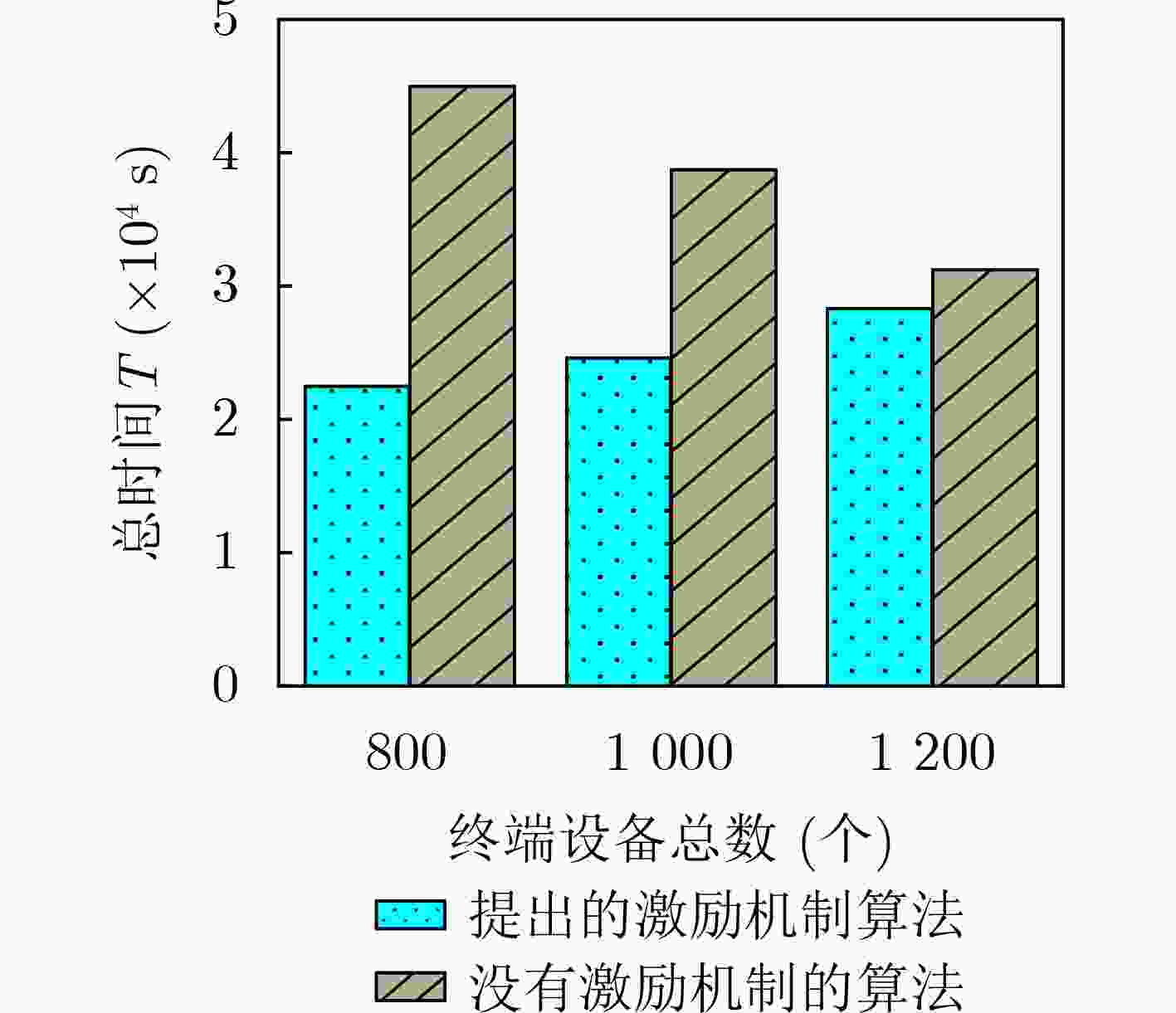


 下载:
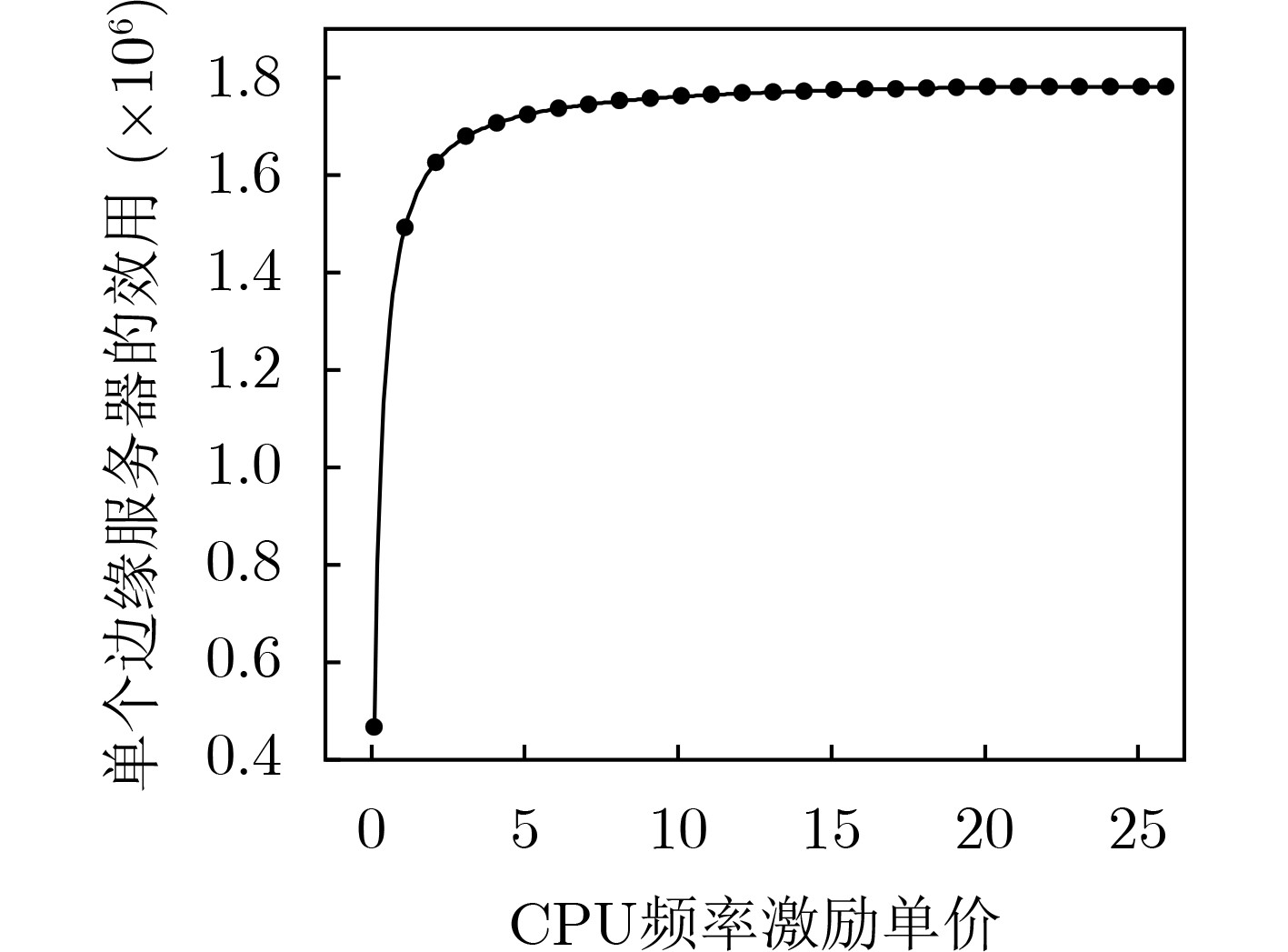
下载:
