Multilevel Semantic Maps Based on Visual Simultaneous Localization and Mapping in Dynamic Scenarios
-
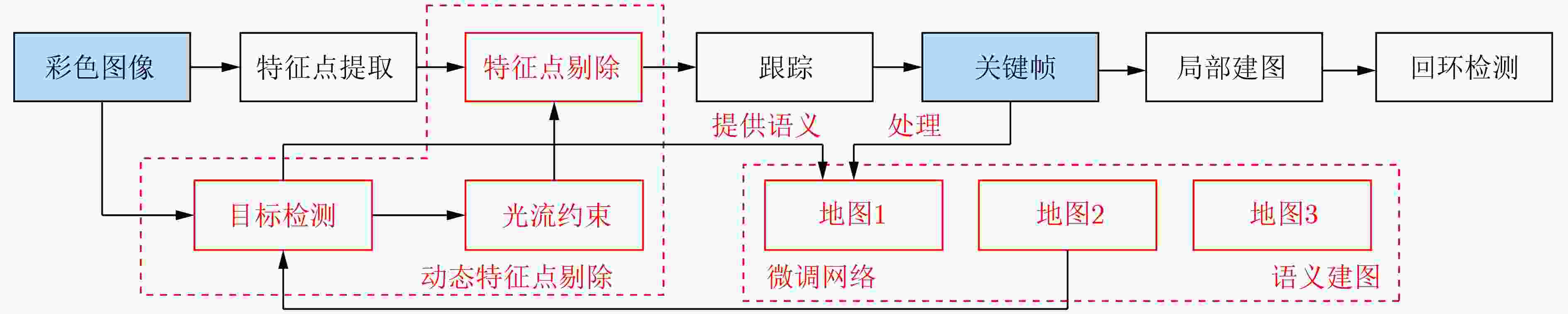
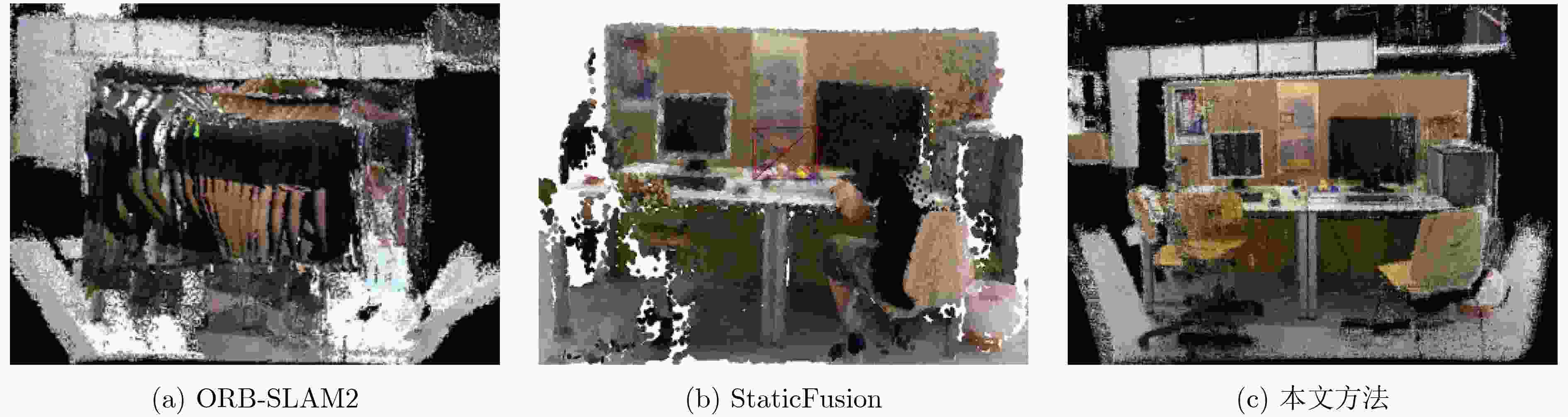
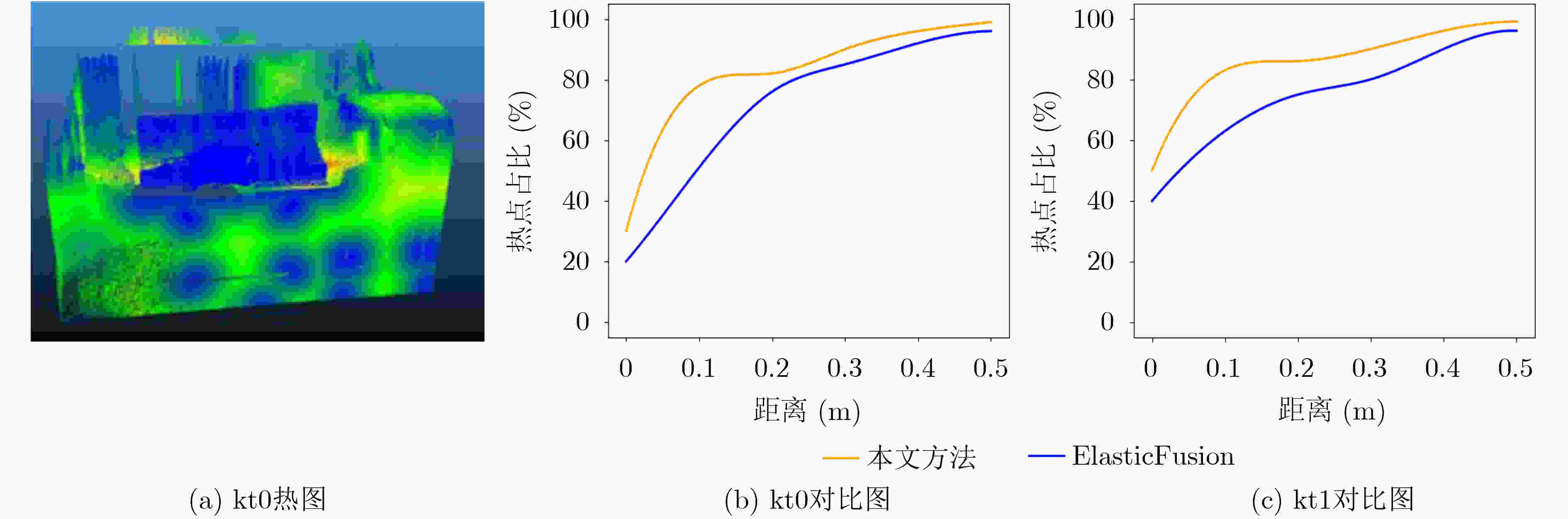
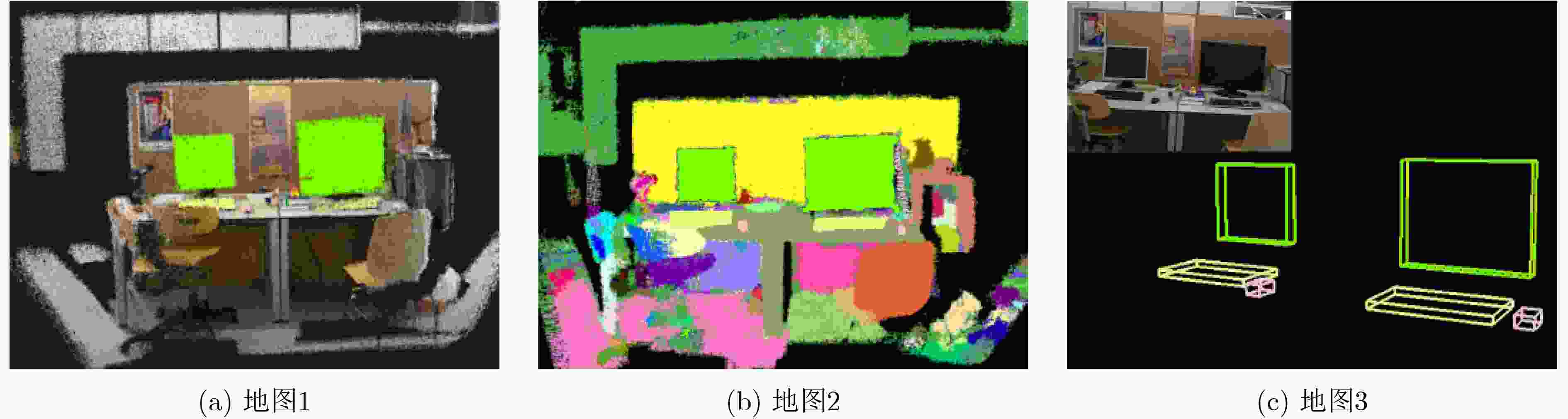
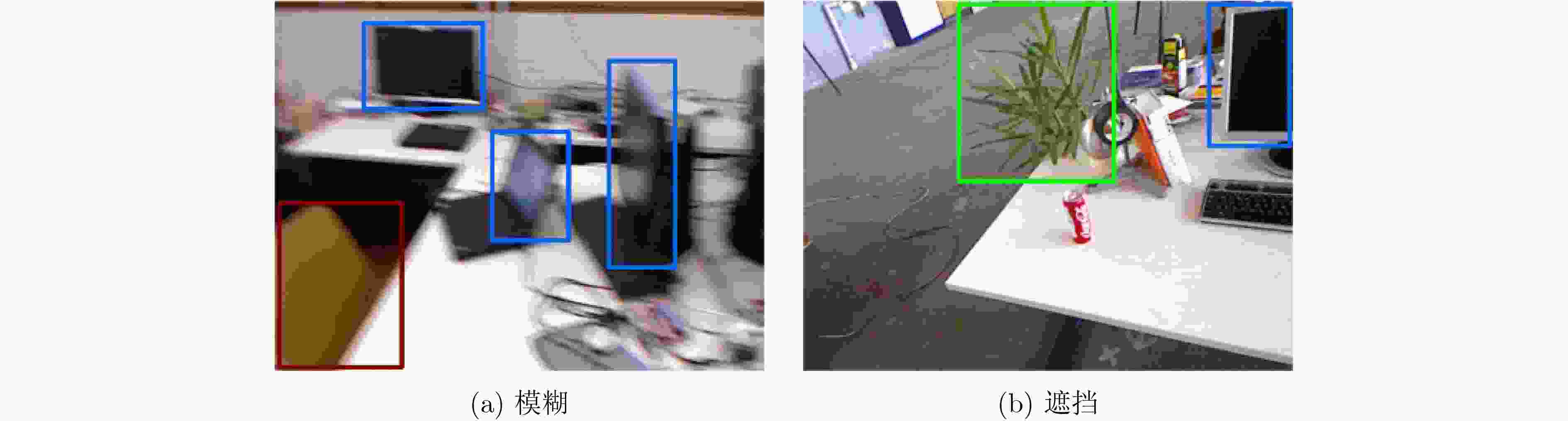
摘要: 为提高视觉同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)技术的环境适应性和语义信息理解能力,该文提出一种可以在动态场景下实现多层次语义地图构建的视觉SLAM方案。首先利用被迫移动物体与动态目标间的空间位置关系,并结合目标检测网络和光流约束判断真正的动态目标,从而剔除动态特征点;其次提出一种基于超体素的快速点云分割方案,将基于静态区域构建的3维地图进行优化,构建了物体级的点云语义地图;同时构建的语义地图可以提供更高精度的训练数据样本,进一步用来提升目标检测网络性能。在TUM和ICL-NUIM数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在定位精度上远优于目前主流的动态场景下的视觉SLAM方案,证明了该方法在高动态场景中具有较好的稳定性和鲁棒性;在建图精度和质量上,经过将重建的不同种类地图与各个现有方法进行比较,验证了提出的多层次语义地图构建的方法在静态和高动态场景中的有效性与适用性。
-
关键词:
- 视觉同时定位与地图构建技术 /
- 语义建图 /
- 动态场景 /
- 点云分割 /
- 目标检测
Abstract: To cope with the moving objects in dynamic environments and make the robots truly understand the surroundings, a visual Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) system is proposed to estimate simultaneously trajectory and object-level dense 3D semantic maps in dynamic environments. Object detection and optical flow results are leveraged to identify those actually moving objects. To improve semantic mapping accuracy, an unsupervised algorithm is employed to segment 3D point cloud into meaningful clusters with semantic cues. The semantic maps are further used to improve object detection model, by fine-tuning with hard examples coming from semantic maps in challenging conditions. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments which compare the proposed method to comparable state-of-the-art approaches show that the proposed method achieves improved accuracy and robustness in dynamic scenes. -
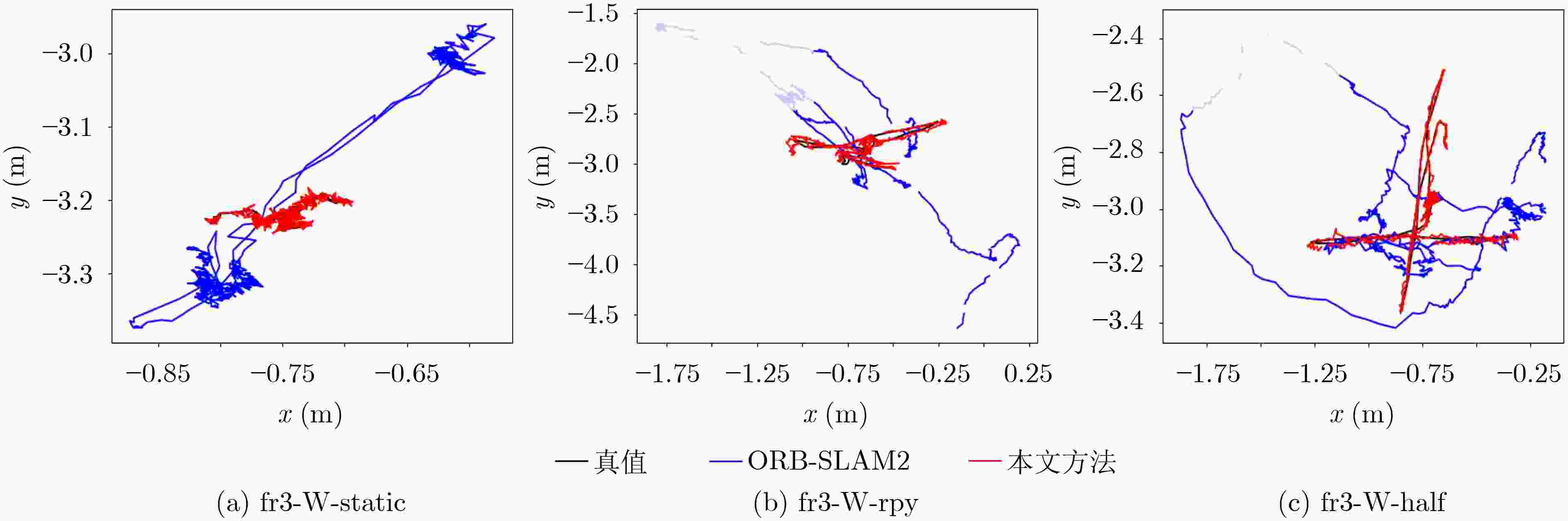
表 1 绝对轨迹误差(Absolute Trajectory Error, ATE)和相对位姿误差(Relative Pose Error, RPE)在不同方法下的数据对比
数据集 ATE(m) 现有方法 本文方法 ORB-SLAM2 BaMVO SPW LC-CRF DynaSLAM DS-SLAM 目标检测 光流约束 最终结果 fr3-W-static 0.3516 0.0082 0.0235 0.0111 0.0072 0.0081 0.0094 0.0112 0.0069 fr3-W-xyz 0.4563 0.2233 0.0551 0.0158 0.0164 0.0247 0.0152 0.0231 0.0132 fr3-W-half 0.4673 0.1940 0.0563 0.0318 0.0240 0.0303 0.0276 0.0259 0.0228 fr3-W-rpy 0.7946 0.1477 0.1593 0.0516 0.0367 0.0442 0.1325 0.0789 0.0488 RPE(m/s) fr3-W-static 0.0153 0.0068 0.0084 0.0062 0.0091 0.0066 0.0112 0.0094 0.0059 fr3-W-xyz 0.0261 0.0248 0.0086 0.0094 0.0217 0.0233 0.0238 0.0189 0.0116 fr3-W-half 0.0411 0.0244 0.0375 0.0158 0.0148 0.0297 0.0223 0.0386 0.0145 ffr3-W-rpy 0.0647 0.0155 0.0198 0.0423 0.0314 0.0503 0.0352 0.0279 0.0248 表 2 不同数据训练YOLOv3后准确率和召回率的对比
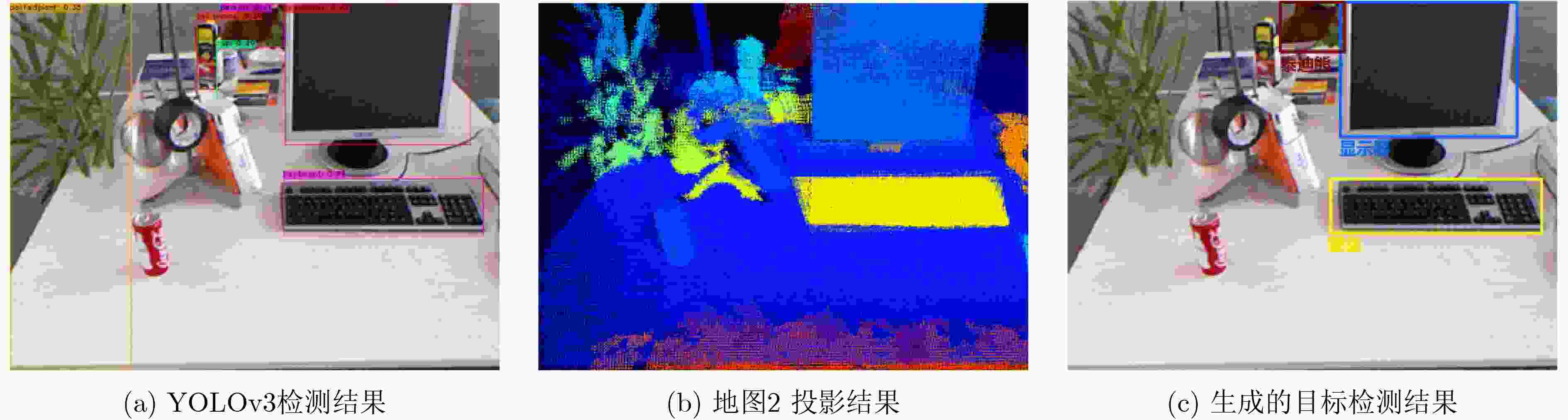
类别 准确率/召回率 显示屏 椅子 盆栽 水瓶 鼠标 VOC 61.7/63.8 56.5/60.7 35.6/51.7 – – VOC+本文样本 71.2/76.1 68.6/73.2 54.1/62.9 – – COCO 65.3/66.4 49.9/52.3 27.7/36.8 23.6/34.5 69.9/71.1 COCO+本文样本 72.4/75.8 61.2/63.9 53.1/66.2 51.5/60.8 77.4/78.9 -
[1] ROSINOL A, ABATE M, CHANG Yun, et al. Kimera: An open-source library for real-time metric-semantic localization and mapping[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 2020: 1689–1696. [2] QIN Tong, LI Peiliang, and SHEN Shaojie. VINS-mono: A robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2018, 34(4): 1004–1020. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2853729 [3] CAMPOS C, ELVIRA R, RODRÍGUEZ J J G, et al. ORB-SLAM3: An accurate open-source library for visual, visual–inertial, and multimap SLAM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021, 37(6): 1874–1890. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2021.3075644 [4] MUR-ARTAL R and TARDÓS J D. ORB-SLAM2: An open-source SLAM system for monocular, stereo, and RGB-D cameras[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2017, 33(5): 1255–1262. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103 [5] LONG Ran, RAUCH C, ZHANG Tianwei, et al. RigidFusion: Robot localisation and mapping in environments with large dynamic rigid objects[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(2): 3703–3710. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3066375 [6] JI Tete, WANG Chen, and XIE Lihua. Towards real-time semantic RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi'an, China, 2021: 11175–11181. [7] ZHANG Tianwei, ZHANG Huayan, LI Yang, et al. FlowFusion: Dynamic dense RGB-D SLAM based on optical flow[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 2020: 7322–7328. [8] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. [9] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. [10] HE Kaiming, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980–2988. [11] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, and CIPOLLA R. SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481–2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [12] RUNZ M, BUFFIER M, and AGAPITO L. MaskFusion: Real-time recognition, tracking and reconstruction of multiple moving objects[C]. 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), Munich, Germany, 2018: 10–20. [13] BESCOS B, FÁCIL J M, CIVERA J, et al. DynaSLAM: Tracking, mapping, and inpainting in dynamic scenes[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(4): 4076–4083. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2860039 [14] YU Chao, LIU Zuxin, LIU Xinjun, et al. DS-SLAM: A semantic visual SLAM towards dynamic environments[C]. 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 2018: 1168–1174. [15] LIU Yubao and MIURA J. RDS-SLAM: Real-time dynamic SLAM using semantic segmentation methods[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 23772–23785. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3050617 [16] MCCORMAC J, HANDA A, DAVISON A, et al. SemanticFusion: Dense 3D semantic mapping with convolutional neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 2017: 4628–4635. [17] FAN Yingchun, ZHANG Qichi, LIU Shaofeng, et al. Semantic SLAM with more accurate point cloud map in dynamic environments[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 112237–112252. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3003160 [18] CHENG Jiyu, WANG Chaoqun, MAI Xiaochun, et al. Improving dense mapping for mobile robots in dynamic environments based on semantic information[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(10): 11740–11747. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3023696 [19] REDMON J and FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[C]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2018: 1804–2767. [20] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]. 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 740–755. [21] PHAM T T, EICH M, REID I, et al. Geometrically consistent plane extraction for dense indoor 3D maps segmentation[C]. 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea (South), 2016: 4199–4204. [22] ZHONG Fangwei, WANG Sheng, ZHANG Ziqi, et al. Detect-SLAM: Making object detection and SLAM mutually beneficial[C]. 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Tahoe, USA, 2018: 1001–1010. [23] STURM J, ENGELHARD N, ENDRES F, et al. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems[C]. 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 2012: 573–580. [24] HANDA A, WHELAN T, MCDONALD J, et al. A benchmark for RGB-D visual odometry, 3D reconstruction and SLAM[C]. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 2014: 1524–1531. [25] KIM D H and KIM J H. Effective background model-based RGB-D dense visual odometry in a dynamic environment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2016, 32(6): 1565–1573. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2016.2609395 [26] LI Shile and LEE D. RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments using static point weighting[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 2(4): 2263–2270. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2724759 [27] DU Zhengjun, HUANG Shisheng, MU Taijiang, et al. Accurate dynamic SLAM using CRF-based long-term consistency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2022, 28(4): 1745–1757. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2020.3028218 [28] WHELAN T, SALAS-MORENO R F, GLOCKER B, et al. ElasticFusion: Real-time dense SLAM and light source estimation[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2016, 35(14): 1697–1716. doi: 10.1177/0278364916669237 [29] SCONA R, JAIMEZ M, PETILLOT Y R, et al. StaticFusion: Background reconstruction for dense RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 3849–3856. -





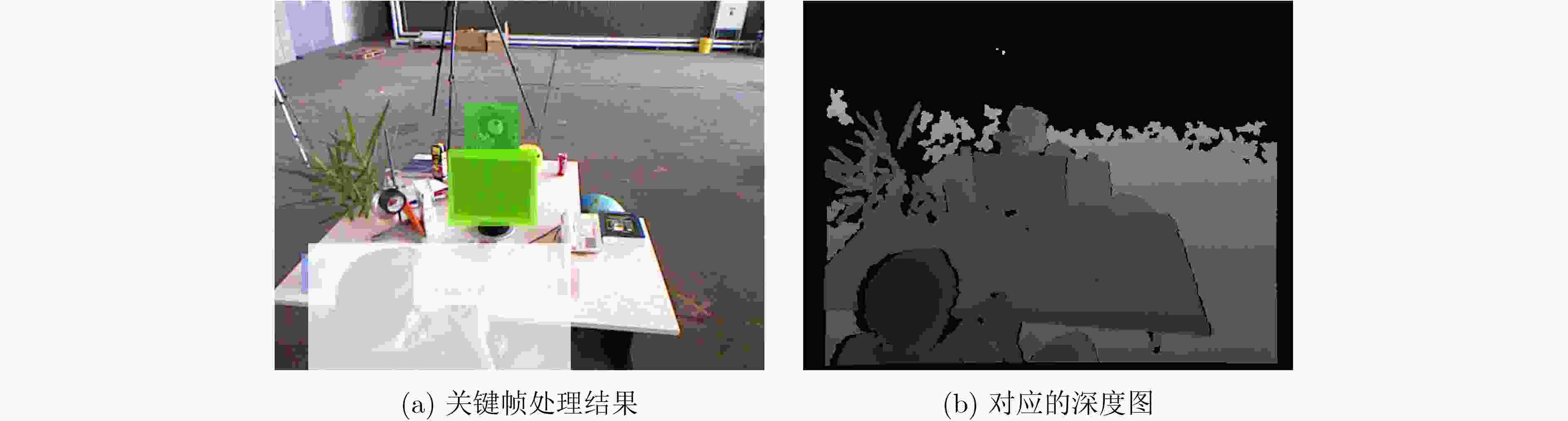
 下载:
下载:
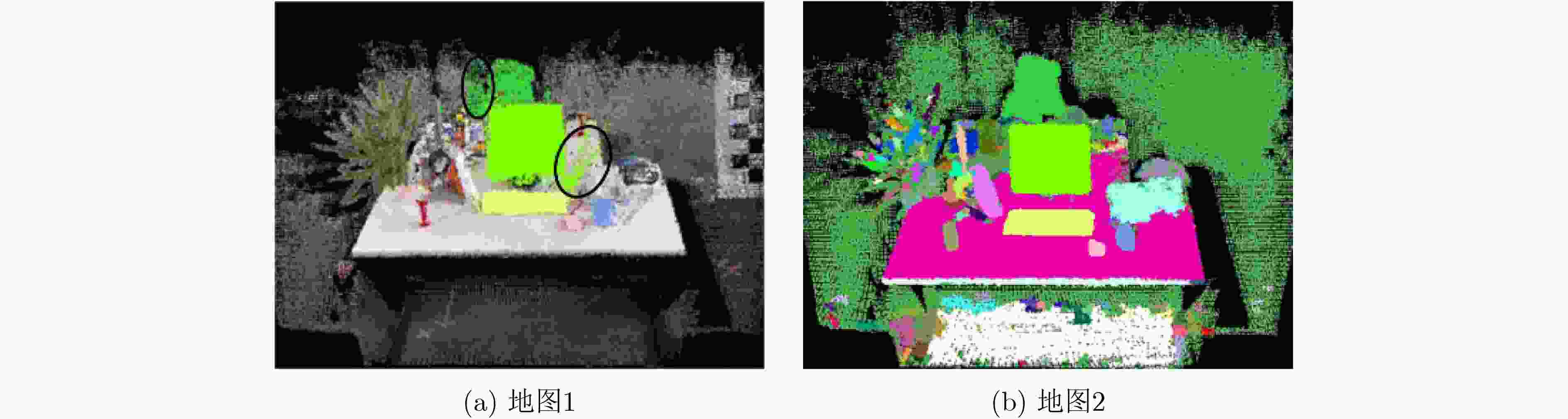
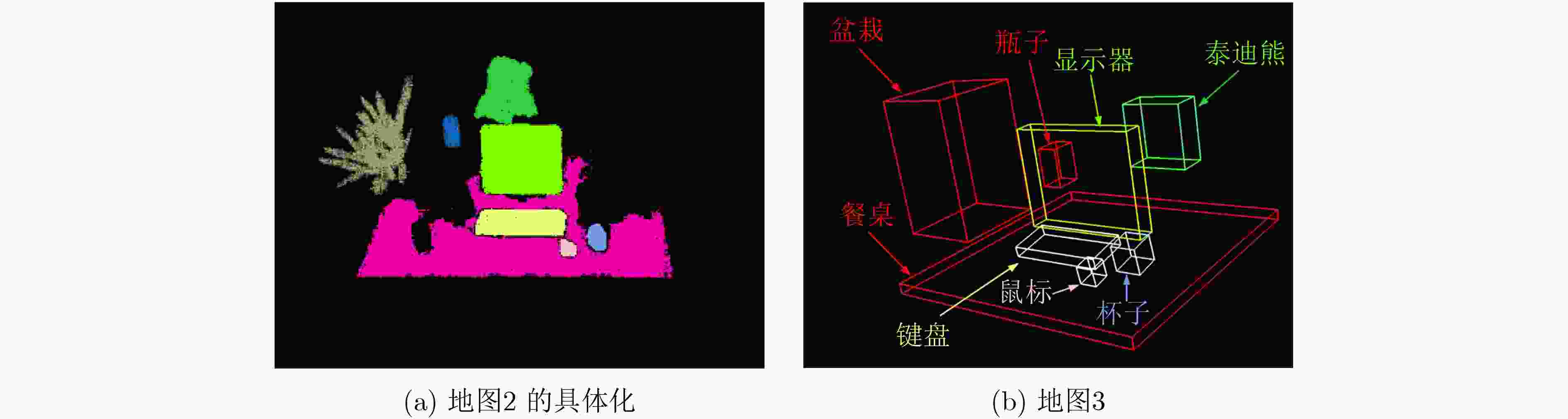



 下载:
下载:
