Robust Beamforming Design for Aggregated Visible Light Communication and Radio Frequency Systems
-
摘要: 该文首次研究了可见光通信(VLC)与射频(RF) 聚合系统稳健波束成形设计。具体来说,在VLC和RF信道状态信息(CSIs)都不完美的情况下,该文提出了稳健波束成形设计方案,研究了同时满足最小速率要求和调光控制约束的总传输功率最小化问题。然而,稳健波束成形设计问题存在无限多的约束,这是难以处理的。通过半正定松弛(SDR),首先对非凸原问题进行松弛,然后利用
$\mathcal{S}$ 引理将其重新表述为凸半正定规划(SDP),用内点方法可以有效地求解。最后,数值仿真结果验证了所提稳健VLC-RF聚合系统的鲁棒性和有效性。-
关键词:
- 可见光通信 /
- 可见光与射频聚合系统 /
- 稳健波束成形
Abstract: The robust beamforming design for the aggregated Visible Light Communication (VLC) and Radio Frequency (RF) system are studied for the first time. Specifically, with imperfect Channel State Informations (CSIs) of both VLC and RF channels, robust beam formers design schemes are proposed to minimize the transmit power of the aggregated VLC-RF system, while satisfying both the minimum rate requirements and dimming control constraints. However, there are infinite constraints of the robust beamforming design problem, which is intractable in general. Through Semi-Definite Relaxation (SDR), the non-convex original problem is relaxed firstly, and then conservative reformulated it into a convex Semi-Definite Program (SDP) by exploiting$\mathcal{S}$ lemma, which can be efficiently solved by interior point methods. Finally, the robust and effectiveness of the proposed robust aggregated VLC-RF scheme are verified by numerical simulation results. -
表 1 仿真参数表
VLC链路 RF链路 仿真参数及符号 参数值 仿真参数及符号 参数值 噪声功率谱密度$\sigma _{\text{v}}^2$ ${10^{ - 21}}{\text{ }}{{\text{A}}^{\text{2}}}{\text{/Hz}}$ 噪声功率谱密度$\sigma _{\text{r}}^{\text{2}}$ $ - 57{\text{ dBm/Hz}}$ PD的有效探测面积${A_{\text{v}}}$ $1{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$ 功率放大器效率${\mu _{\text{r}}}$ 0.45 PD的视场角$\varPsi$ 90° RF链路距离${d_{{\text{v}},k}}$ $3{\text{ m}}$ LED的半功率角${\theta _{1/2}}$ 60° 接收角${\psi _k}$ 45° LED允许的最大电流${I_{\text{H}}}$ $10{\text{ A}}$ 中心载波频率$f$ $2.4{\text{ GHz}}$ 带宽$ {B_{\text{v}}} $ $20{\text{ MHz}}$ 带宽$ {B_{\text{r}}} $ $10{\text{ MHz}}$ -
[1] TRAN G N and KIM S. Performance analysis of short packets in NOMA VLC systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 6505–6517. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3141865 [2] Qualcomm. An internet of everything that works for everyone[EB/OL]. https://www.qualcomm.com/news/onq/2015/05/13/internet-everything-works-everyone, 2015. [3] Cisco: A platform for business innovation and revenue generation[EB/OL]. http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/serviceprovider-wi-fi/solutionoverviewc22-642482.2020.9. [4] ZHAO Yiheng and CHI Nan. Partial pruning strategy for a dual-branch multilayer perceptron-based post-equalizer in underwater visible light communication systems[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(10): 15562–15572. doi: 10.1364/OE.393443 [5] WANG Li, WANG Xuanzheng, KANG Jian, et al. A 75-Mb/s RGB PAM-4 visible light communication transceiver system with pre- and post-equalization[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2021, 39(5): 1381–1390. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2020.3034227 [6] JOVICIC A, LI Junyi, and RICHARDSON T. Visible light communication: Opportunities, challenges and the path to market[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2013, 51(12): 26–32. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2013.6685754 [7] YANG Helin, ZHONG Wende, CHEN Chen, et al. Integration of visible light communication and positioning within 5G networks for internet of things[J]. IEEE Network, 2020, 34(5): 134–140. doi: 10.1109/MNET.011.1900567 [8] MA Shuai, ZHANG Fan, LI Hang, et al. Aggregated VLC-RF systems: Achievable rates, optimal power allocation, and energy efficiency[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(11): 7265–7278. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3010294 [9] TANG Aimin, XU Chao, ZHAI Bangzhao, et al. Design and implementation of an integrated visible light communication and WiFi system[C]. The IEEE 15th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (MASS), Chengdu, China, 2018: 157–165. [10] ISMAIL T, GAD M E, and MOKHTAR B. Integrated VLC/RF wireless technologies for reliable content caching system in vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 51855–51864. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3070397 [11] YANG Liwei, ZHANG Wenjie, ZHANG Yan, et al. Hybrid optical wireless network based on visible light communications (VLC)-WiFi heterogeneous interconnection[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Communication Engineering and Technology (ICCET), Nagoya, Japan, 2019: 35–38. [12] KAHN J M and BARRY J R. Wireless infrared communications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1997, 85(2): 265–298. doi: 10.1109/5.554222 [13] PALOMAR D P and JIANG Y. MIMO transceiver design via majorization theory[J]. Foundations and Trends in Communications and Information Theory, 2006, 3(4/5): 331–551. [14] 马帅. 存在信道误差的无线通信系统的稳健信号处理方法[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2016.MA Shuai. Robust signal processing for wireless communication systems with erroneous channel state information[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2016. [15] MARSHOUD H, DAWOUD D, KAPINAS V M, et al. MU-MIMO precoding for VLC with imperfect CSI[C]. The 4th International Workshop on Optical Wireless Communications (IWOW), Istanbul, Turkey, 2015: 93–97. [16] 贺阳. 可见光通信网络的信道容量和非正交多址接入研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国矿业大学, 2020.HE Yang. Research on channel capacity and non-orthogonal multiple access in visible communication networks[D]. [Master dissertation], China University of Mining and Technology, 2020. [17] MA Shuai, YANG Ruixin, LI Hang, et al. Achievable rate with closed-form for SISO channel and broadcast channel in visible light communication networks[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2017, 35(14): 2778–2787. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2017.2704619 [18] YAO Sike and ZHANG Xiaoyu. Joint beamforming and DC bias optimization in VLC with dimming control[C]. The IEEE 85th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Sydney, Australia, 2017: 1–5. [19] GRUSSLER C, RANTZER A, and GISELSSON P. Low-rank optimization with convex constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(11): 4000–4007. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2813009 [20] LUO Zhiquan, MA W K, SO A M C, et al. Semidefinite relaxation of quadratic optimization problems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(3): 20–34. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.936019 -







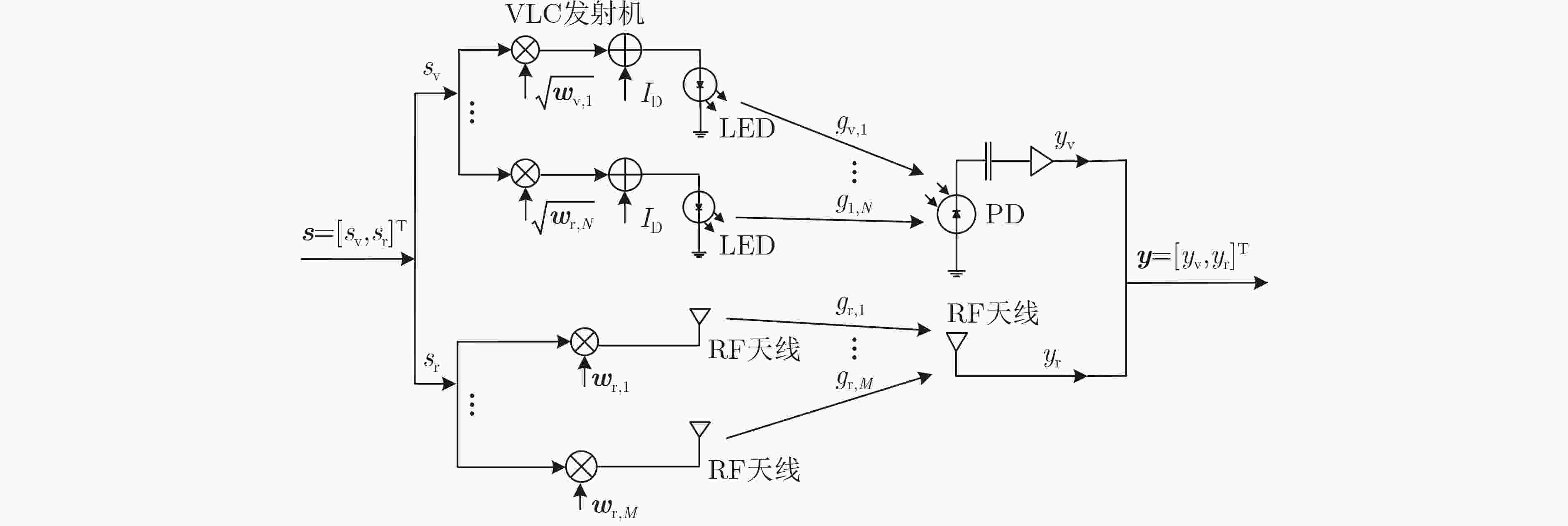
 下载:
下载:
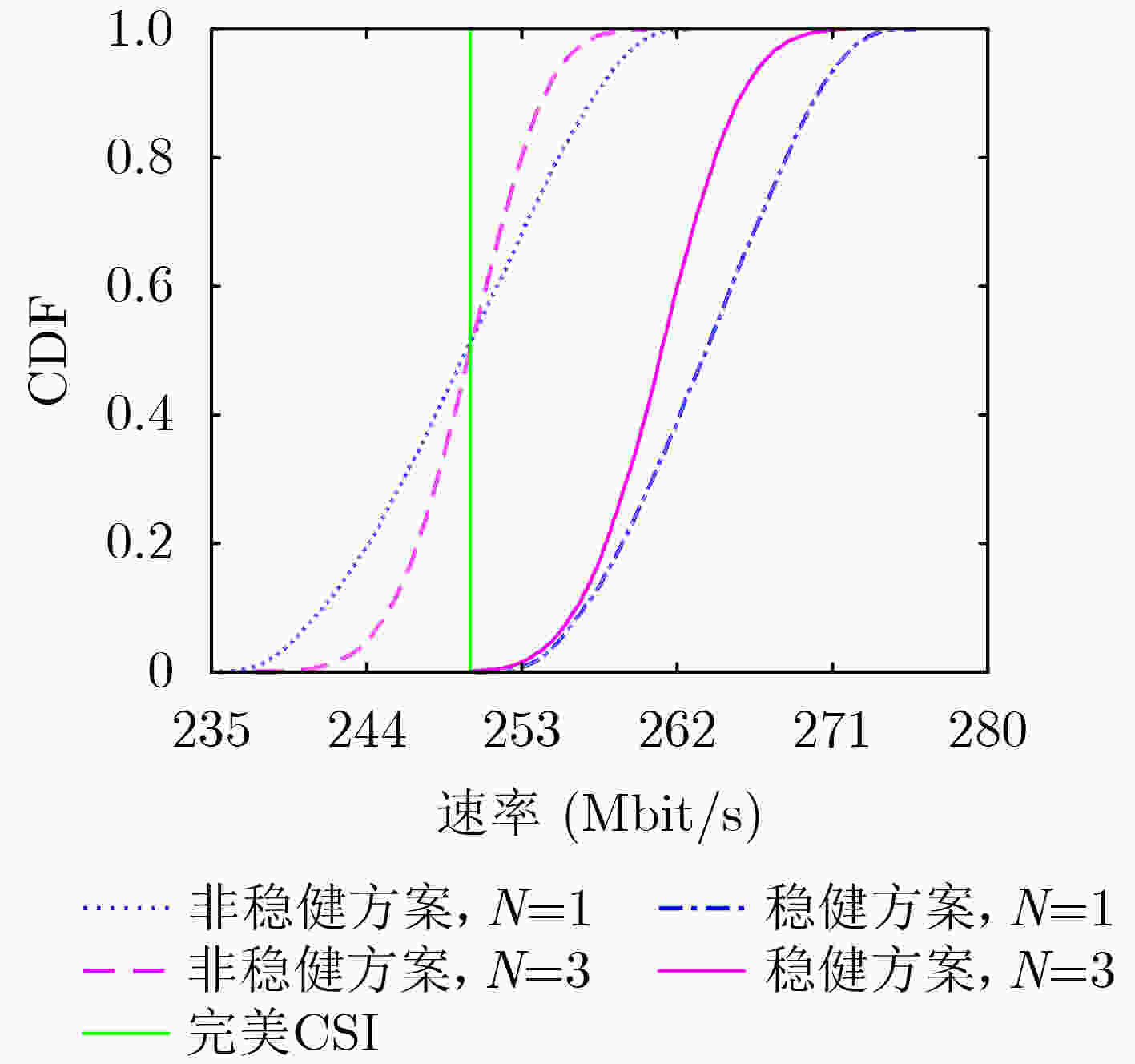
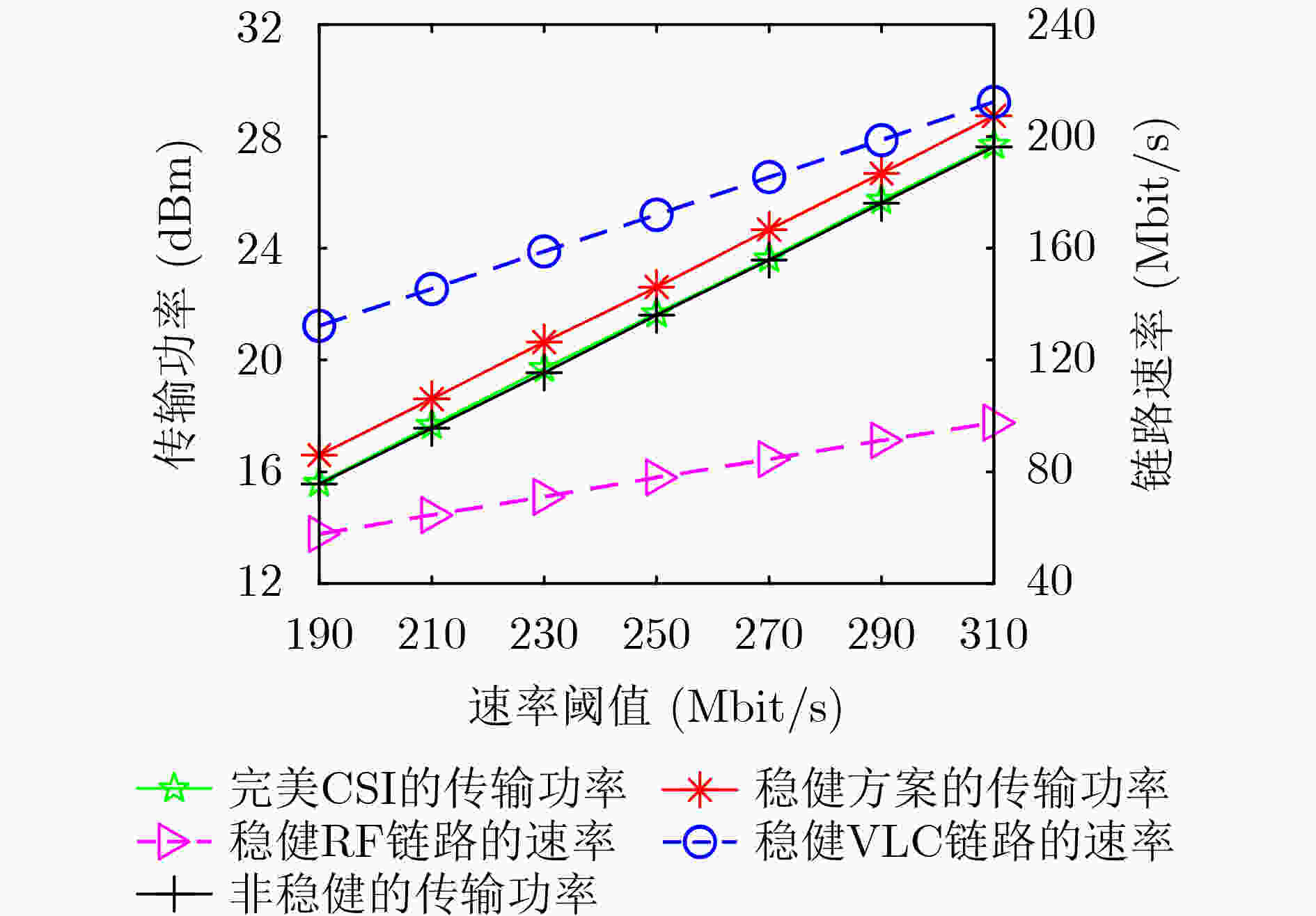



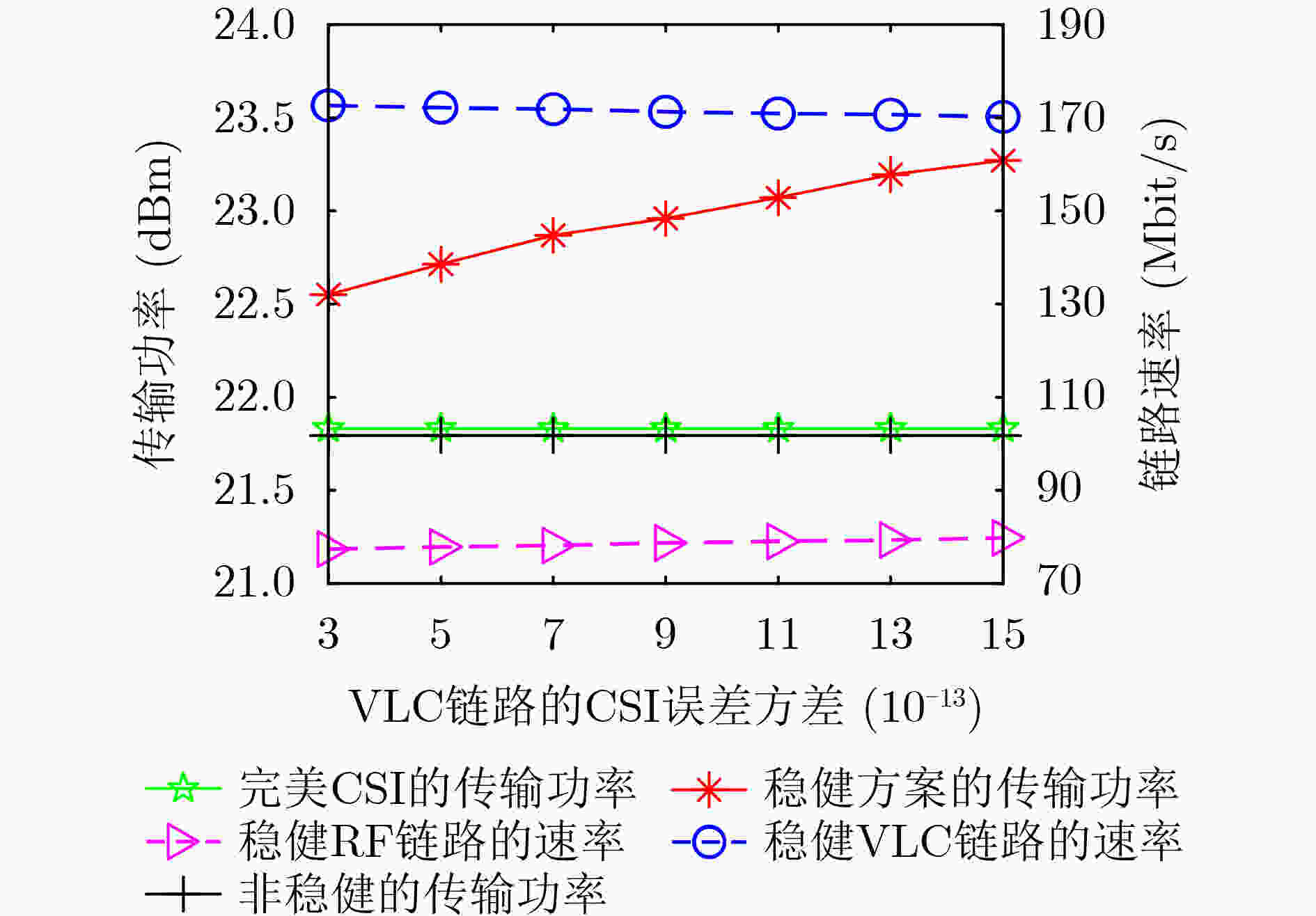


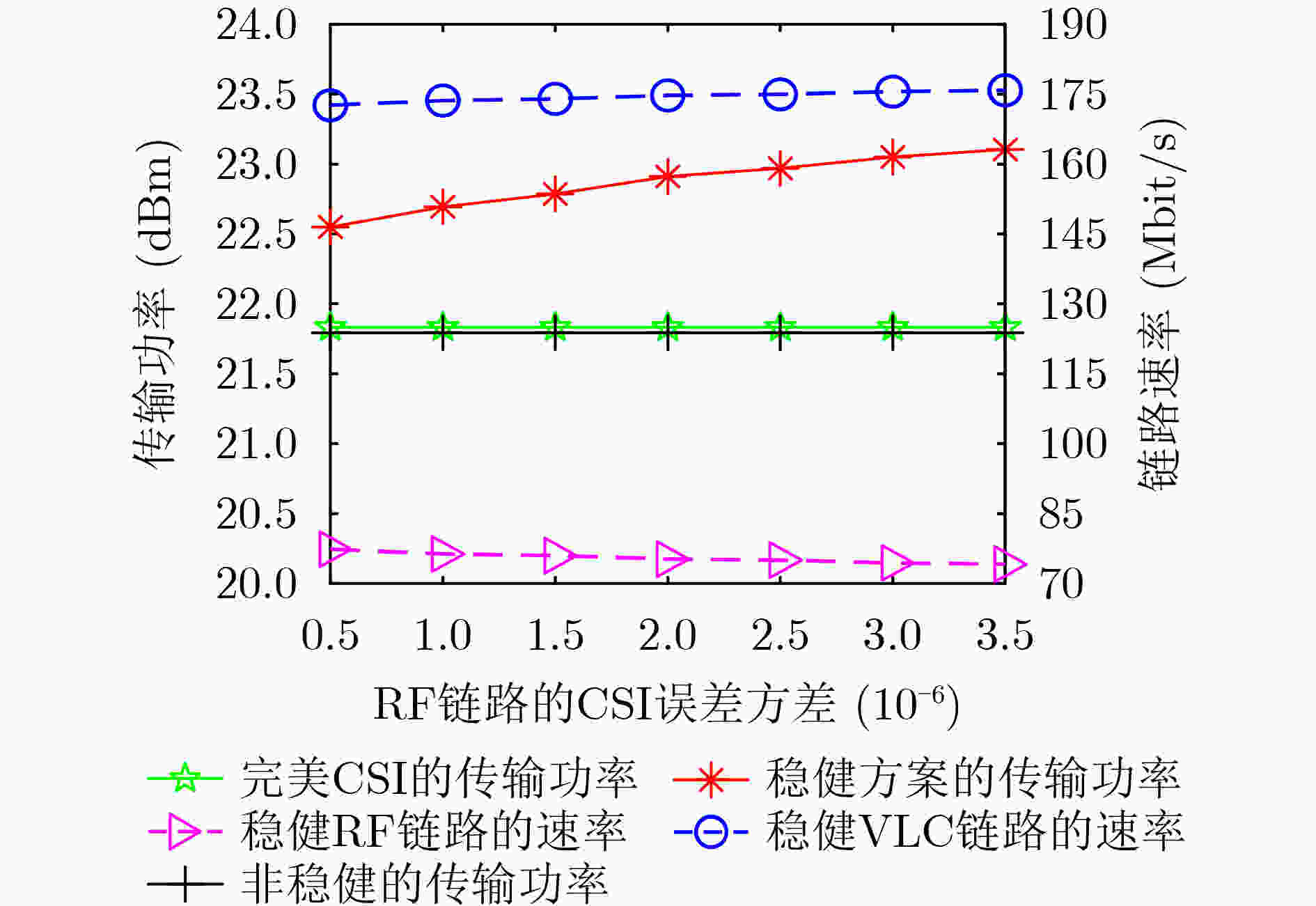


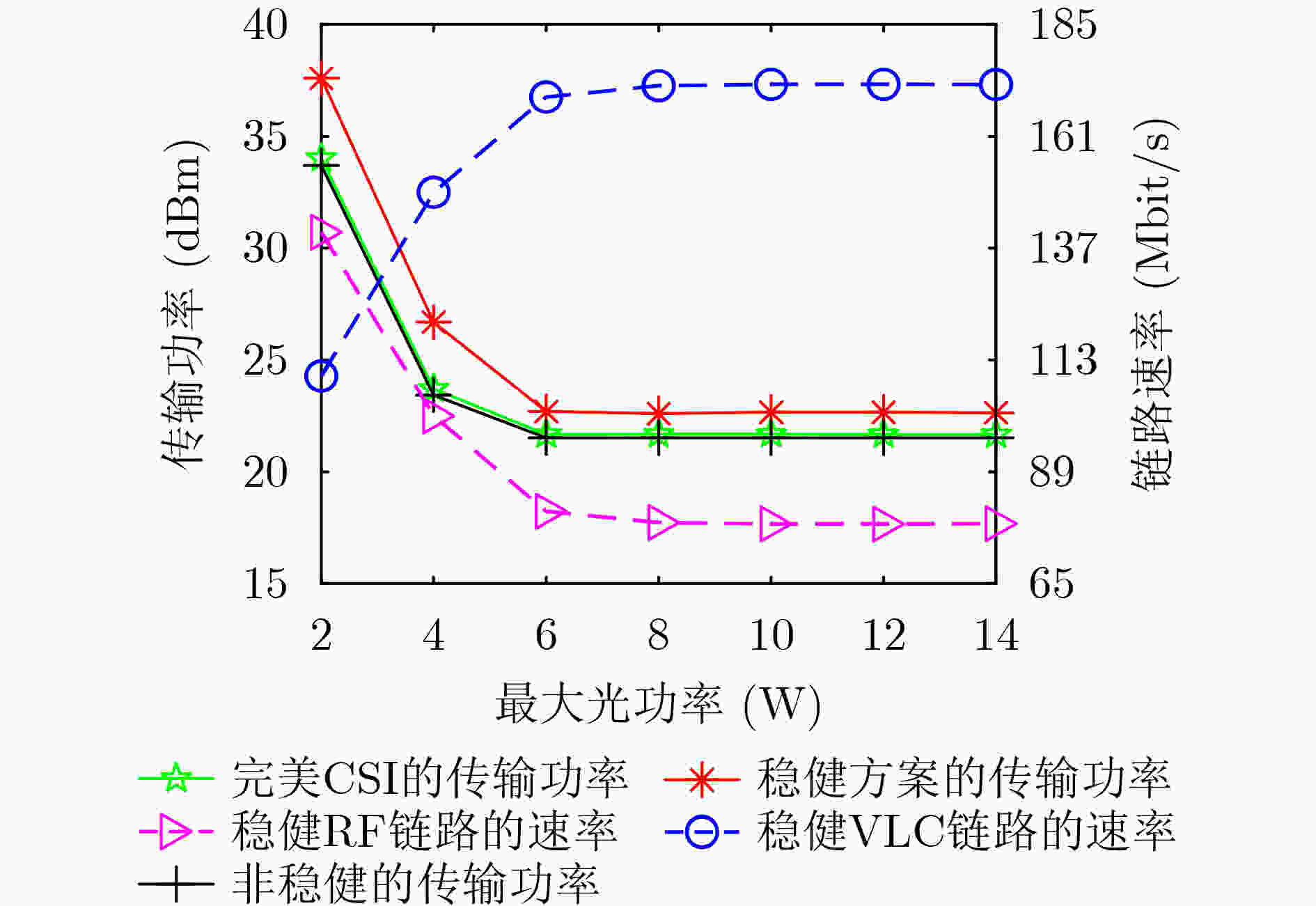



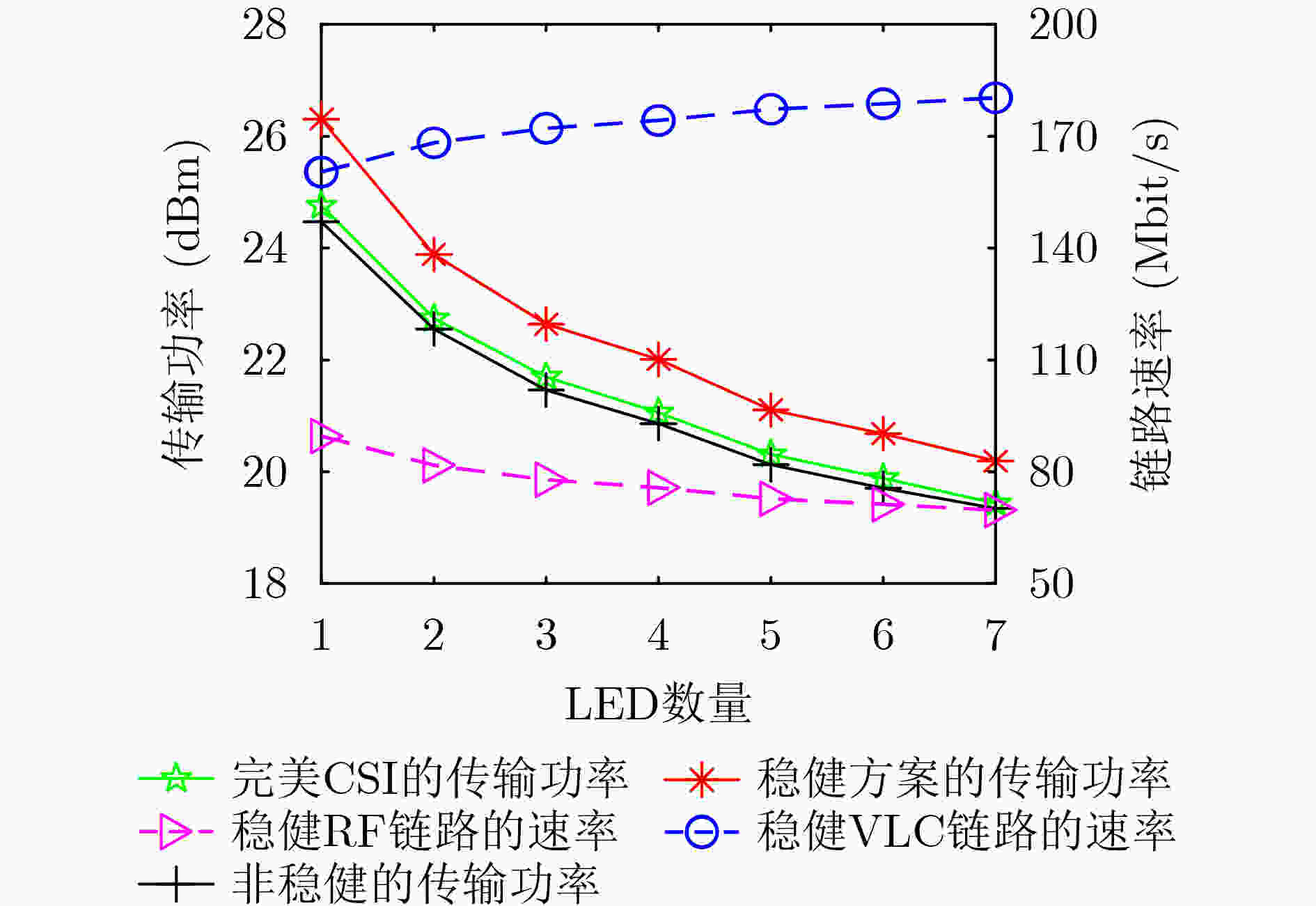



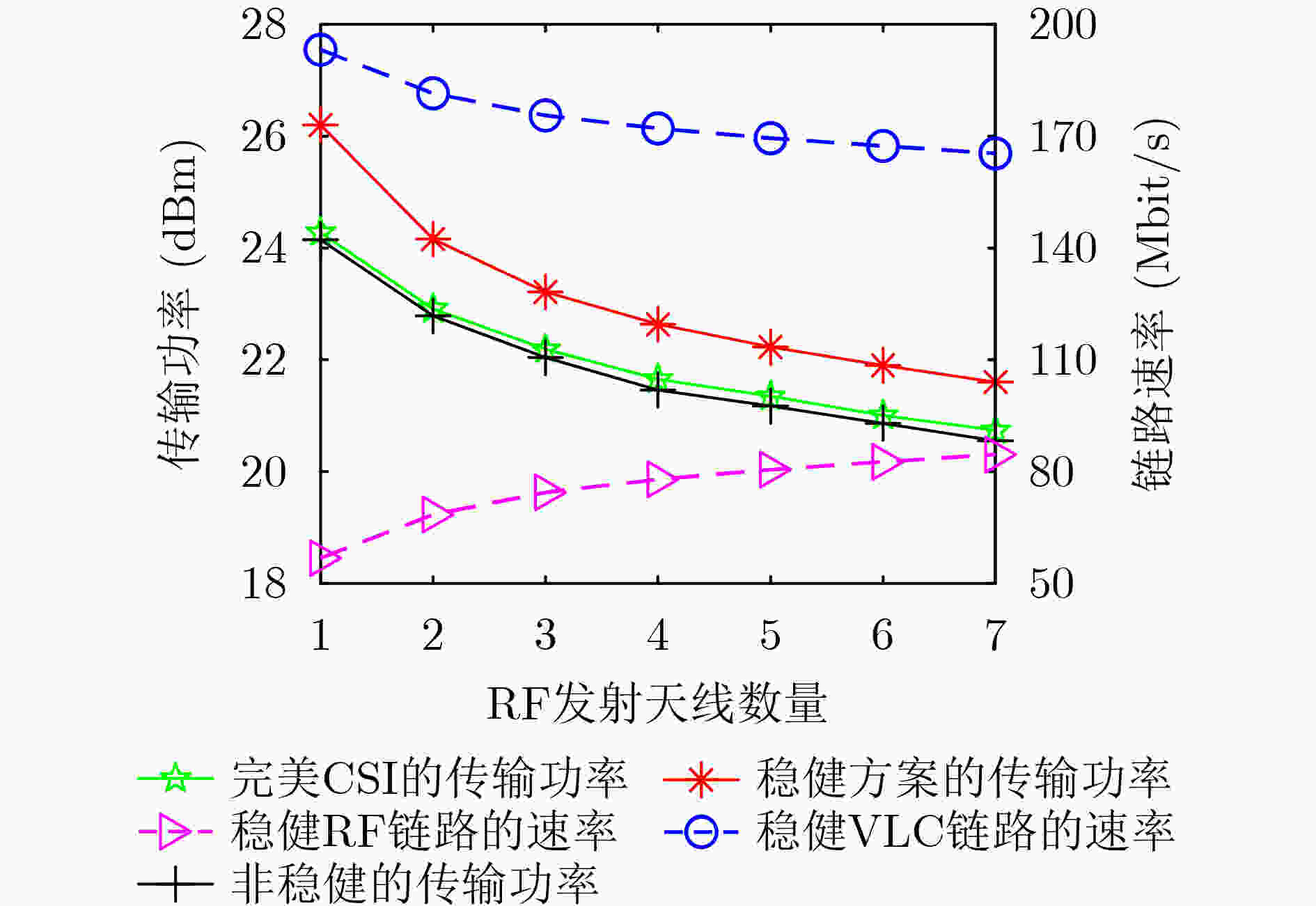





 下载:
下载:
