Small-scale Pedestrian Detection Based on Feature Enhancement Strategy
-
摘要: 行人检测中,小尺度行人时常被漏检、误检。为了提升小尺度行人的检测准确率并且降低其漏检率,该文提出一个特征增强模块。首先,考虑到小尺度行人随着网络加深特征逐渐减少的问题,特征融合策略突破特征金字塔层级结构的约束,融合深层、浅层特征图,保留了大量小尺度行人特征。然后,考虑到小尺度行人特征容易与背景信息发生混淆的问题,通过自注意力模块联合通道注意力模块建模特征图空间、通道关联性,利用小尺度行人上下文信息和通道信息,增强了小尺度行人特征并且抑制了背景信息。最后,基于特征增强模块构建了一个小尺度行人检测器。所提方法在CrowdHuman数据集中小尺度行人的检测准确率为19.8%,检测速度为22帧/s,在CityPersons数据集中小尺度行人的误检率为13.1%。结果表明该方法对于小尺度行人的检测效果优于其他对比算法且实现了较快的检测速度。Abstract: In pedestrian detection, small-scale pedestrians are often missed and mistakenly detected. In order to improve detection precision and reduce miss detection rate of small-scale pedestrians, a feature enhancement module is proposed. First, considering the problem that small-scale pedestrians feature gradually decreases as network goes deeper, feature fusion strategy breaks through the constraints of feature pyramid structure and fuses deep and shallow feature maps to retain lots of small-scale pedestrian features. Then, considering the problem that small-scale pedestrian features are easily confused with background information, self-attention module combined with channel attention module models the spatial and channel correlation of feature maps, using small-scale pedestrian contextual information and channel information to enhance small-scale pedestrian features and suppress background information. Finally, a small-scale pedestrian detector is constructed based on the feature enhancement module. For small-scale pedestrians, the proposed algorithm has 19.8% detection accuracy, 22 frames per second speed on CrowdHuman dataset and 13.1% miss rate on CityPersons dataset. The results show that the proposed algorithm performs better than other compared algorithms for small-scale pedestrian detection and achieves faster detection speed.
-
Key words:
- Pedestrian detection /
- Small-scale pedestrian /
- Feature enhancement module
-
表 1 COCO数据集中目标尺度划分标准
区域 目标尺度 ${\rm{area}} < {32^2}$个像素点 small ${32^2} < {\rm{area}} < {96^2}$个像素点 middle ${96^2} < {\rm{area}}$个像素点 large 表 2 CityPersons[13]数据集中部分子集划分标准
子集 行人高度 遮挡程度 Bare >50 PXs 0.1≤occlusion Reasonable >50 PXs occlusion<0.35 Partial >50 PXs 0.1<occlusion≤0.35 Heavy >50 PXs 0.35<occlusion≤0.8 表 3 模块验证实验结果(%)
方法 AP ↑ AP50 ↑ AP75 ↑ Small AP ↑ Middle AP ↑ Large AP ↑ Baseline 45.2 71.7 47.5 18.0 44.7 62.5 Baseline+特征融合策略 45.2 71.7 47.8 20.1 45.6 60.5 Baseline+特征融合策略+自注意力模块 45.7 72.3 48.4 19.5 44.9 61.8 Baseline+通道注意力模块 44.5 71.3 46.9 19.1 45.0 59.9 本文模型 46.9 72.7 49.8 19.8 46.5 63.8 表 4 对比实验结果(%)
表 6 泛化性实验结果(%)
方法 Bare MR↓ Reasonable MR↓ Partial MR↓ Heavy MR↓ Small MR↓ Medium MR↓ Large MR↓ RepLoss[20] 7.6 13.2 16.8 56.9 – – – TLL[21] 10.0 15.5 17.2 53.6 – – – ALFNet[22] 8.4 12.0 11.4 51.9 19.0 5.7 6.6 CAFL[23] 7.6 11.4 12.1 50.4 – – – LBST[24] – 12.8 – – – – – OR-CNN[25] 6.7 12.8 15.3 55.7 – – – CSP[26] 7.3 11.0 10.4 49.3 16.0 3.7 6.5 MFGP[27] 8.0 10.9 10.9 49.9 – – – 文献[28] 7.9 10.6 10.2 50.2 14.3 3.5 7.0 本文模型 7.2 10.6 11.3 50.7 13.1 3.7 7.5 -
[1] 张功国, 吴建, 易亿, 等. 基于集成卷积神经网络的交通标志识别[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 31(4): 571–577. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.04.019ZHANG Gongguo, WU Jian, YI Yi, et al. Traffic sign recognition based on ensemble convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 31(4): 571–577. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2019.04.019 [2] 高新波, 路文, 查林, 等. 超高清视频画质提升技术及其芯片化方案[J]. 重庆邮电大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 32(5): 681–697. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2020.05.001GAO Xinbo, LU Wen, ZHA Lin, et al. Quality elevation technique for UHD video and its VLSI solution[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications:Natural Science Edition, 2020, 32(5): 681–697. doi: 10.3979/j.issn.1673-825X.2020.05.001 [3] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. [4] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. [5] LU Chengye, WU Sheng, JIANG Chunxiao, et al. Weak harmonic signal detection method in chaotic interference based on extended Kalman filter[J]. Digital Communications and Networks, 2019, 5(1): 51–55. doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2018.10.004 [6] LUO Xiong, LI Jianyuan, WANG Weiping, et al. Towards improving detection performance for malware with a correntropy-based deep learning method[J]. Digital Communications and Networks, 2021, 7(4): 570–579. doi: 10.1016/j.dcan.2021.02.003 [7] LI Jianan, LIANG Xiaodan, WEI Yunchao, et al. Perceptual generative adversarial networks for small object detection[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 1951–1959. [8] CAI Zhaowei and VASCONCELOS N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality object detection[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6154–6162. [9] HU Han, GU Jiayuan, ZHANG Zheng, et al. Relation networks for object detection[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3588–3597. [10] KRISHNA H and JAWAHAR C V. Improving small object detection[C]. Proceedings of the 4th IAPR Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, Nanjing, China, 2017: 340–345. [11] WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M, WU Y H, et al. CSPNeT: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, United States, 2020: 1571–1580. [12] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/tpami.2015.2389824 [13] GE Zheng, LIU Songtao, WANG Feng, et al. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO series in 2021[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.08430, 2021. [14] SHAO Shuai, ZHAO Zijian, LI Boxun, et al. CrowdHuman: A benchmark for detecting human in a crowd[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.00123, 2018. [15] ZHANG Shanshan, BENENSON R, and SCHIELE B. CityPersons: A diverse dataset for pedestrian detection[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 4457–4465. [16] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, and LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934, 2020. [17] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(2): 318–327. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2858826 [18] ZHOU Xingyi, WANG Dequan, and KRÄHENBÜHL P. Objects as points[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.07850, 2019. [19] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]. Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 91–99. [20] WANG Xinlong, XIAO Tete, JIANG Yuning, et al. Repulsion loss: Detecting pedestrians in a crowd[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7774–7783. [21] SONG Tao, SUN Leiyu, XIE Di, et al. Small-scale pedestrian detection based on topological line localization and temporal feature aggregation[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 554–569. [22] LIU Wei, LIAO Shengcai, HU Weidong, et al. Learning efficient single-stage pedestrian detectors by asymptotic localization fitting[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 643–659. [23] FEI Chi, LIU Bin, CHEN Zhu, et al. Learning pixel-level and instance-level context-aware features for pedestrian detection in crowds[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 94944–94953. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2928879 [24] CAO Jiale, PANG Yanwei, HAN Jungong, et al. Taking a look at small-scale pedestrians and occluded pedestrians[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 3143–3152. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2957927 [25] ZHANG Shifeng, WEN Longyin, BIAN Xiao, et al. Occlusion-aware R-CNN: Detecting pedestrians in a crowd[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 657–674. [26] LIU Wei, LIAO Shengcai, REN Weiqiang, et al. High-level semantic feature detection: A new perspective for pedestrian detection[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 5182–5191. [27] ZHANG Yihan. Multi-scale object detection model with anchor free approach and center of gravity prediction[C]. Proceedings of 2020 IEEE 5th Information Technology and Mechatronics Engineering Conference (ITOEC), Chongqing, China, 2020: 38–45. [28] 陈勇, 谢文阳, 刘焕淋, 等. 结合头部和整体信息的多特征融合行人检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1453–1460. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210268CHEN Yong, XIE Wenyang, LIU Huanlin, et al. Multi-feature fusion pedestrian detection combining head and overall information[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1453–1460. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210268 -





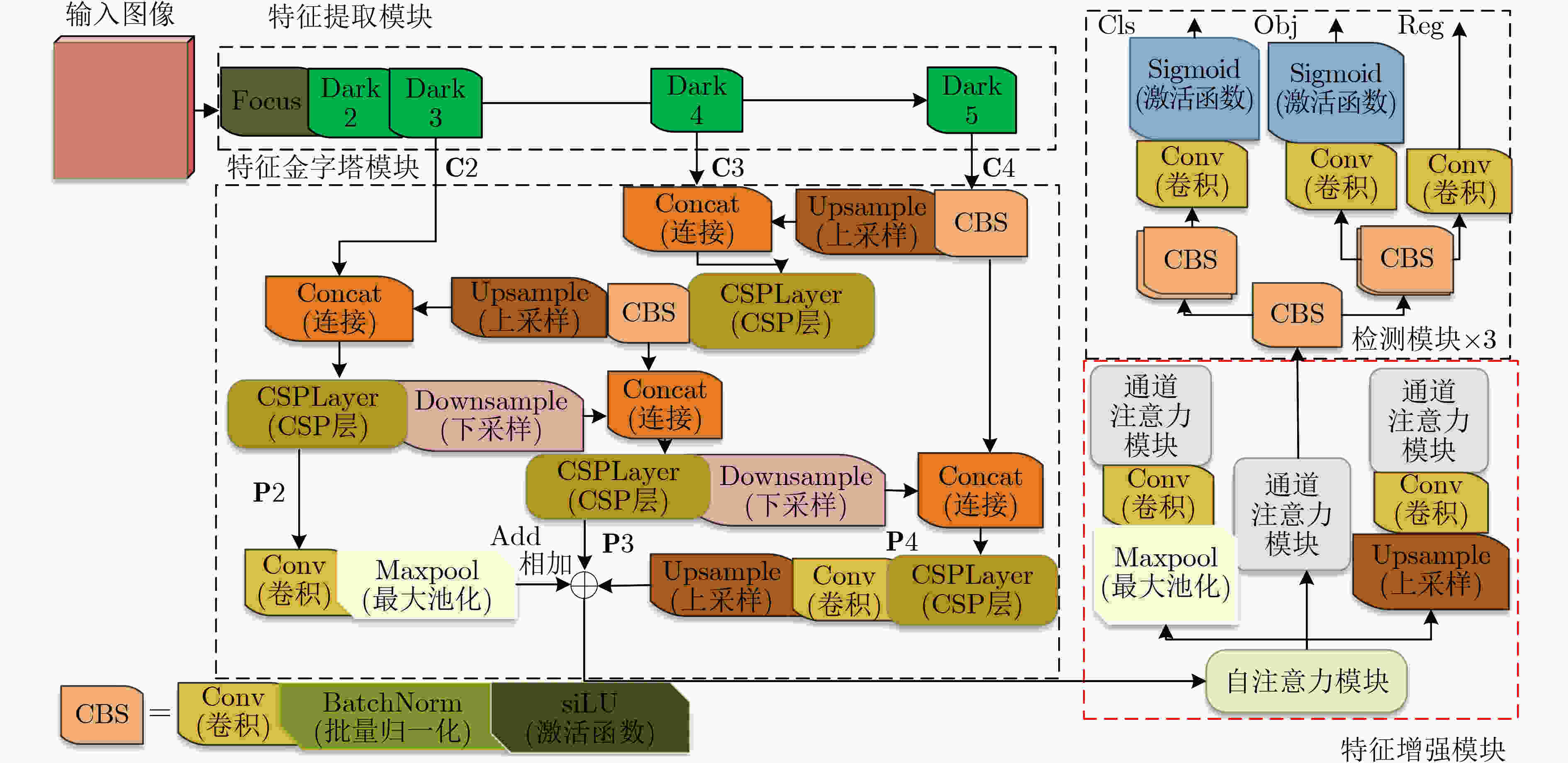
 下载:
下载:
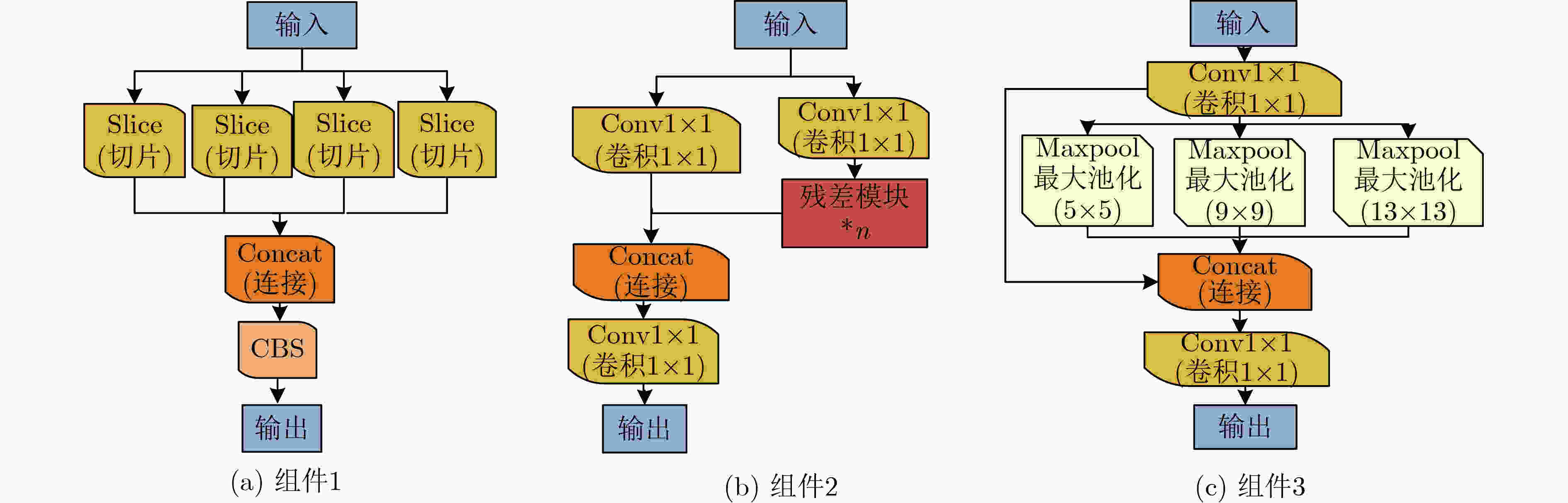
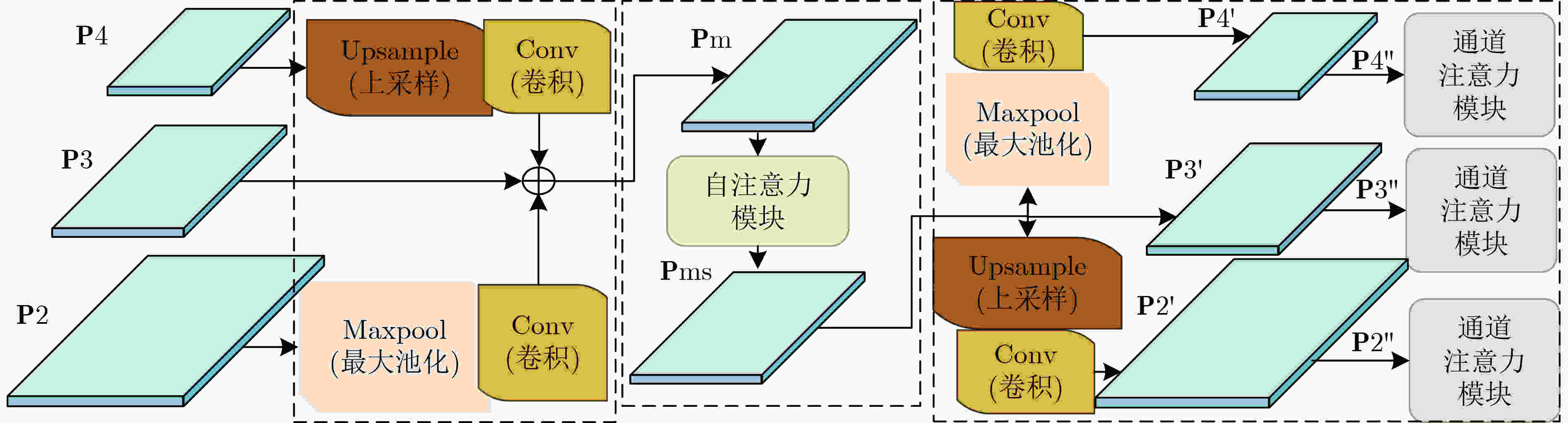
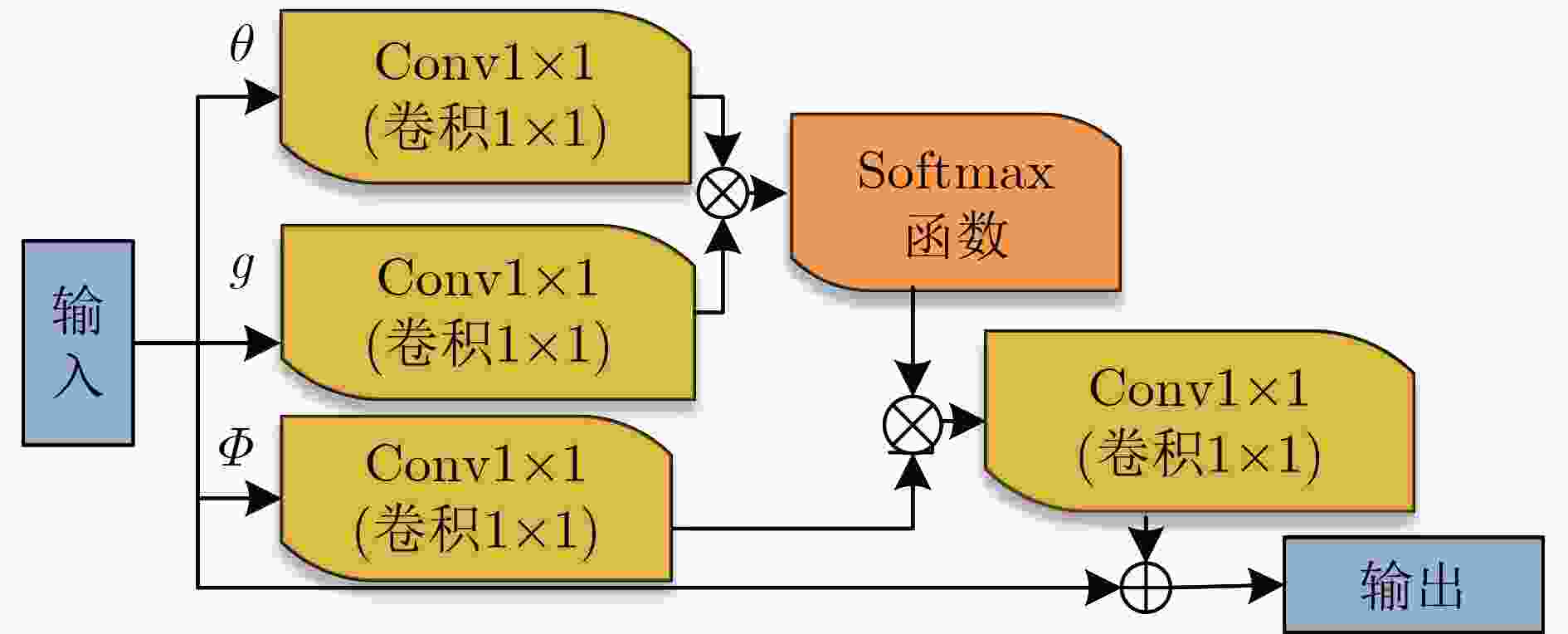
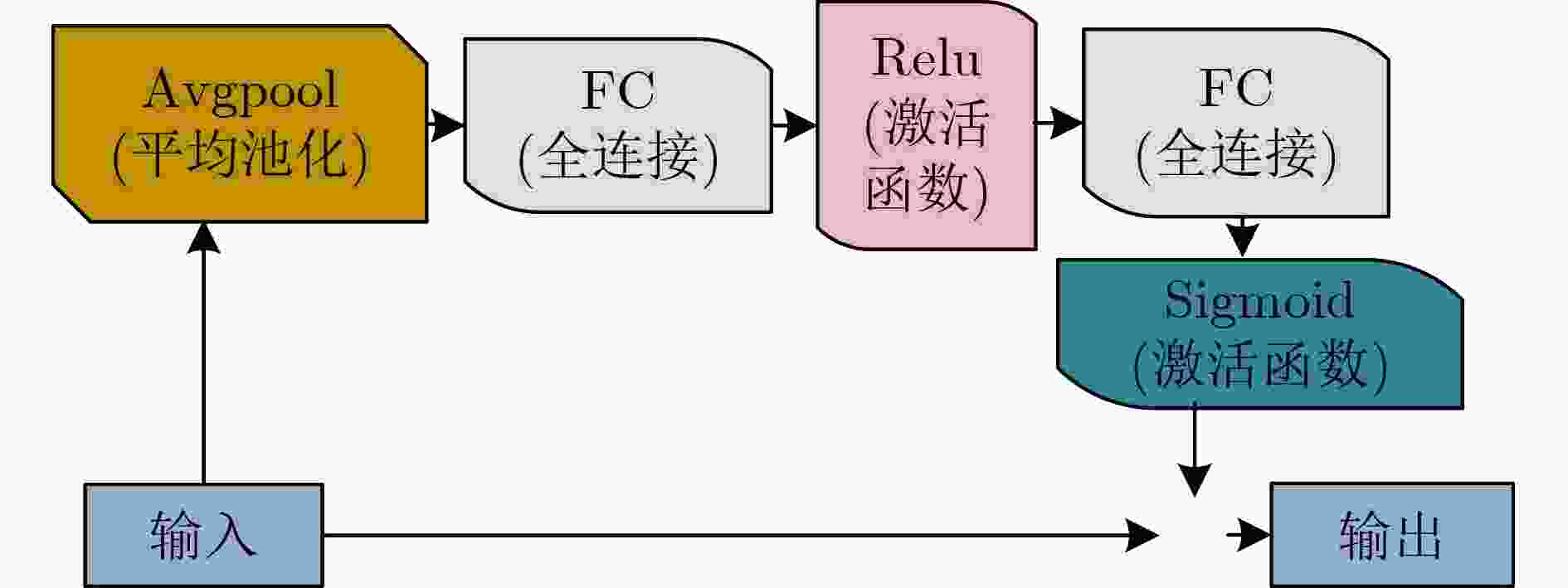



 下载:
下载:
