Driven Non-linear Digital Self Interference Cancellation for In-Band Full Duplex Systems Based on Convolution Long Short-term Memory Deep Neural Network
-
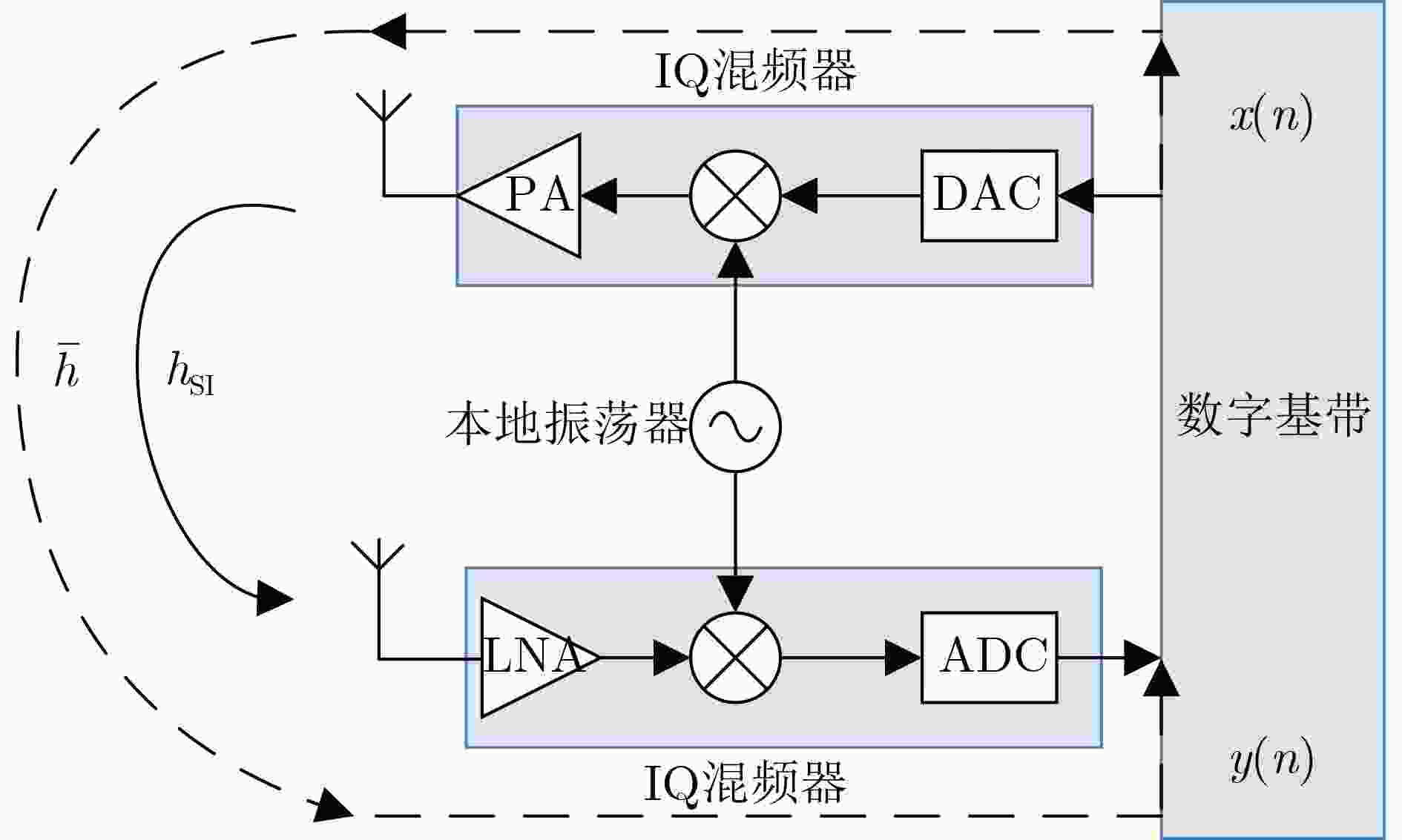
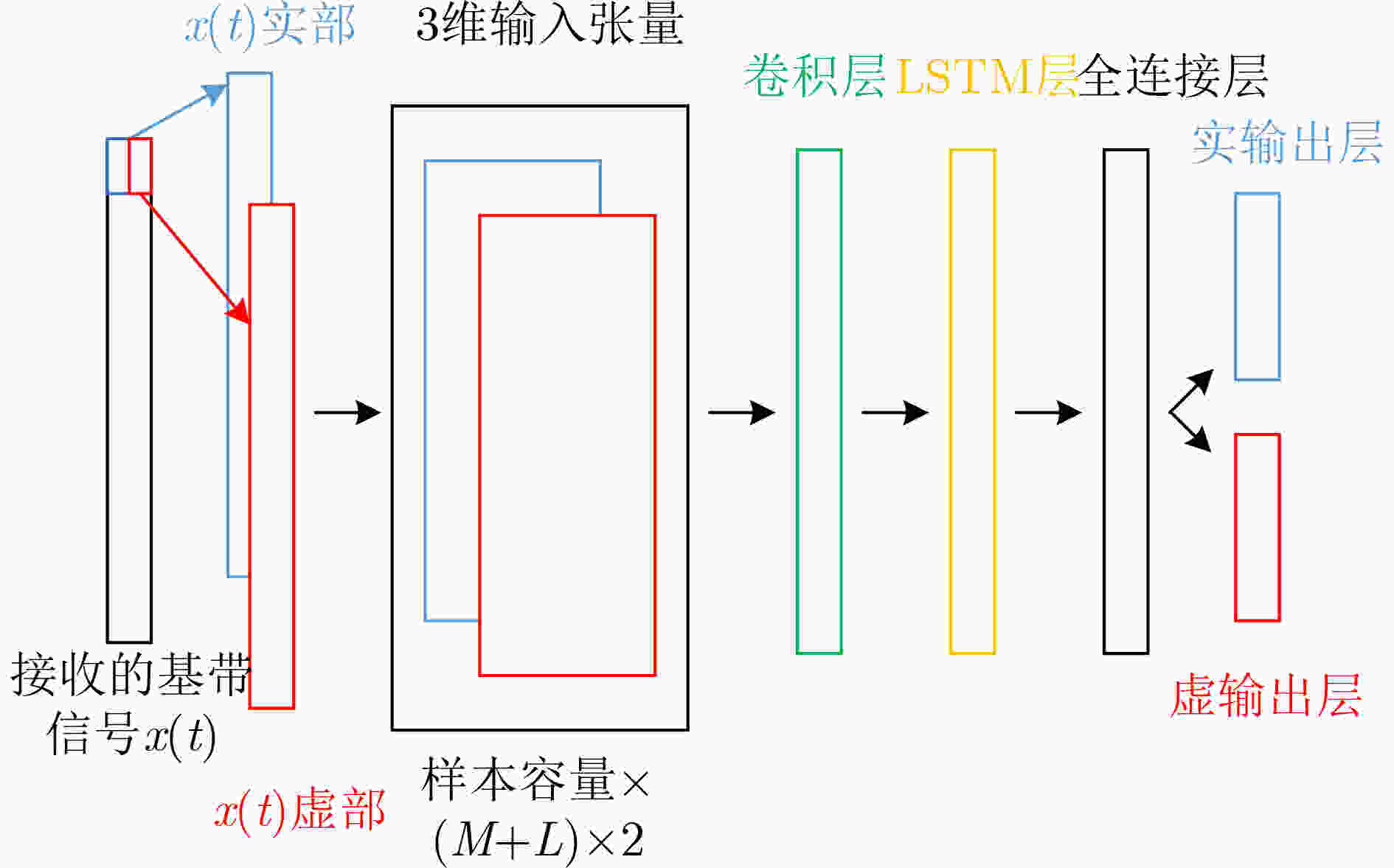
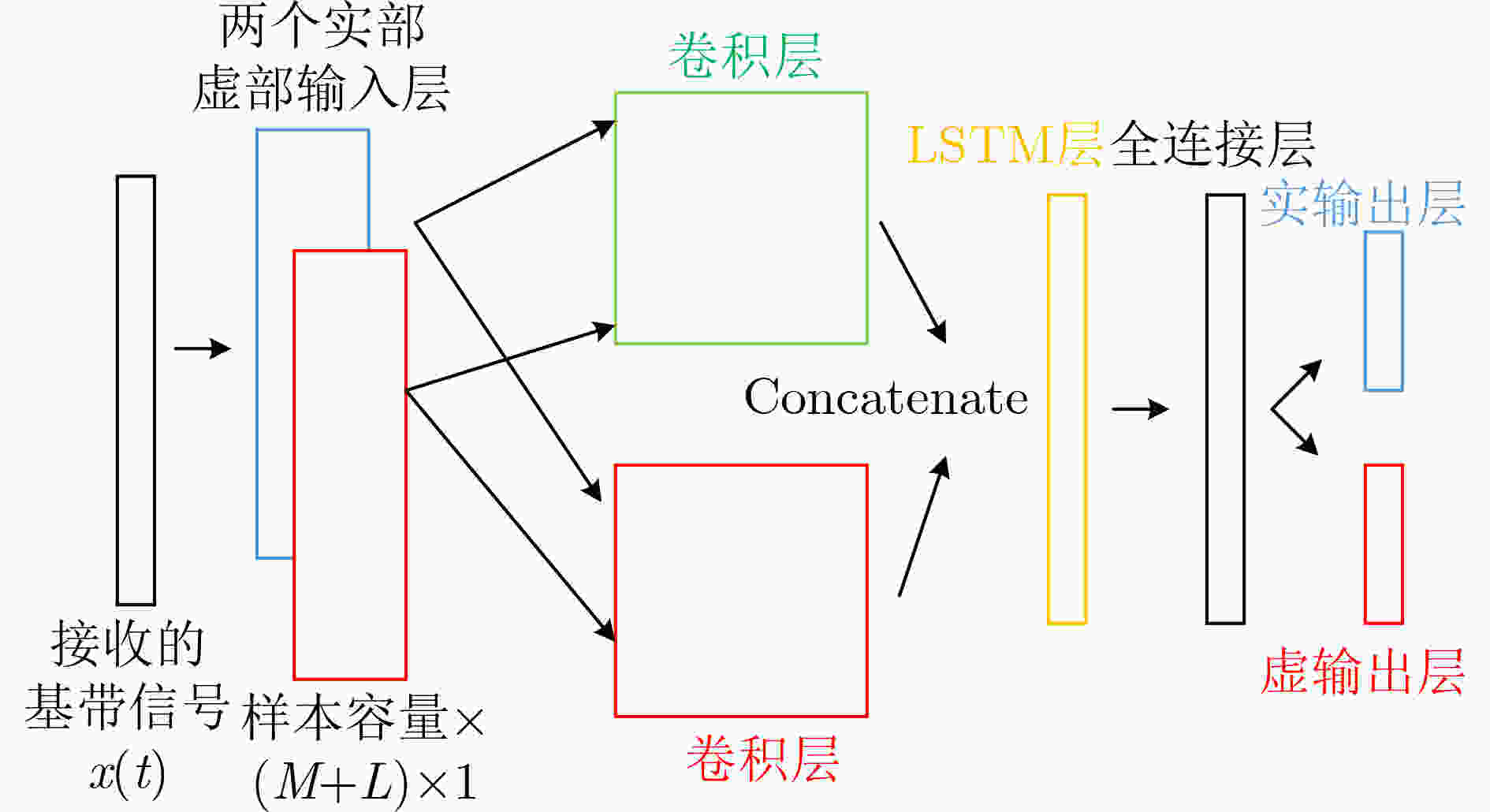
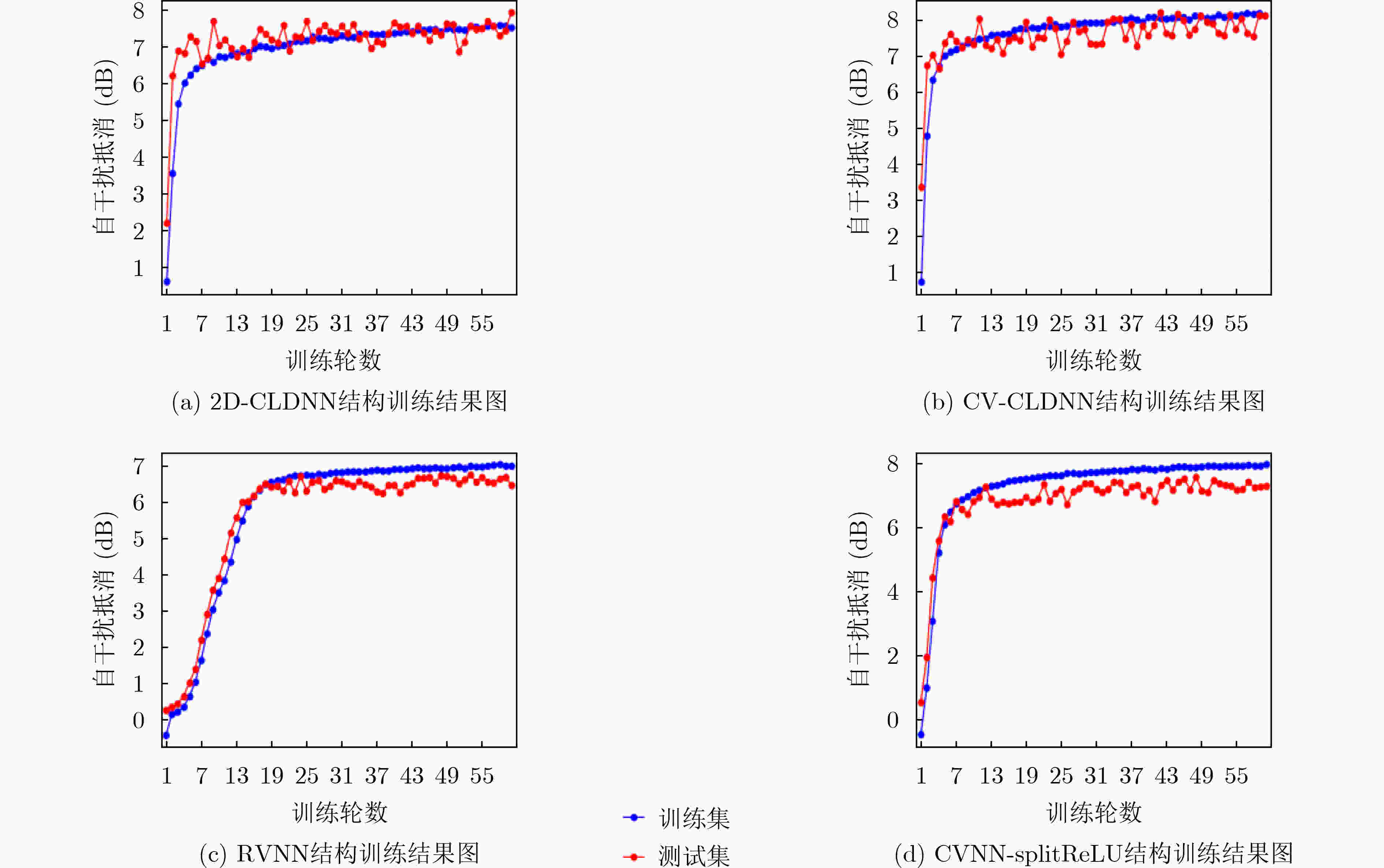
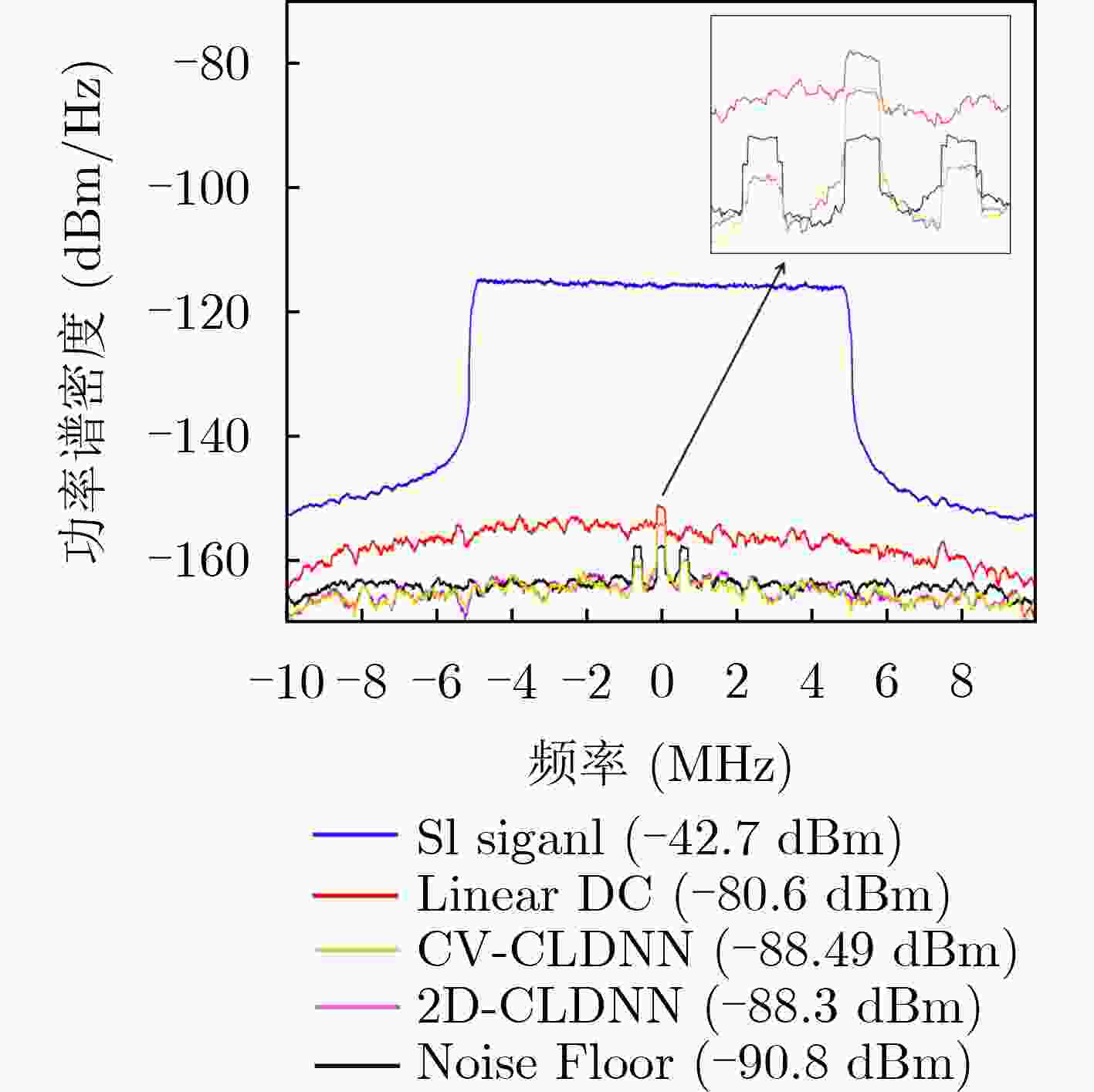
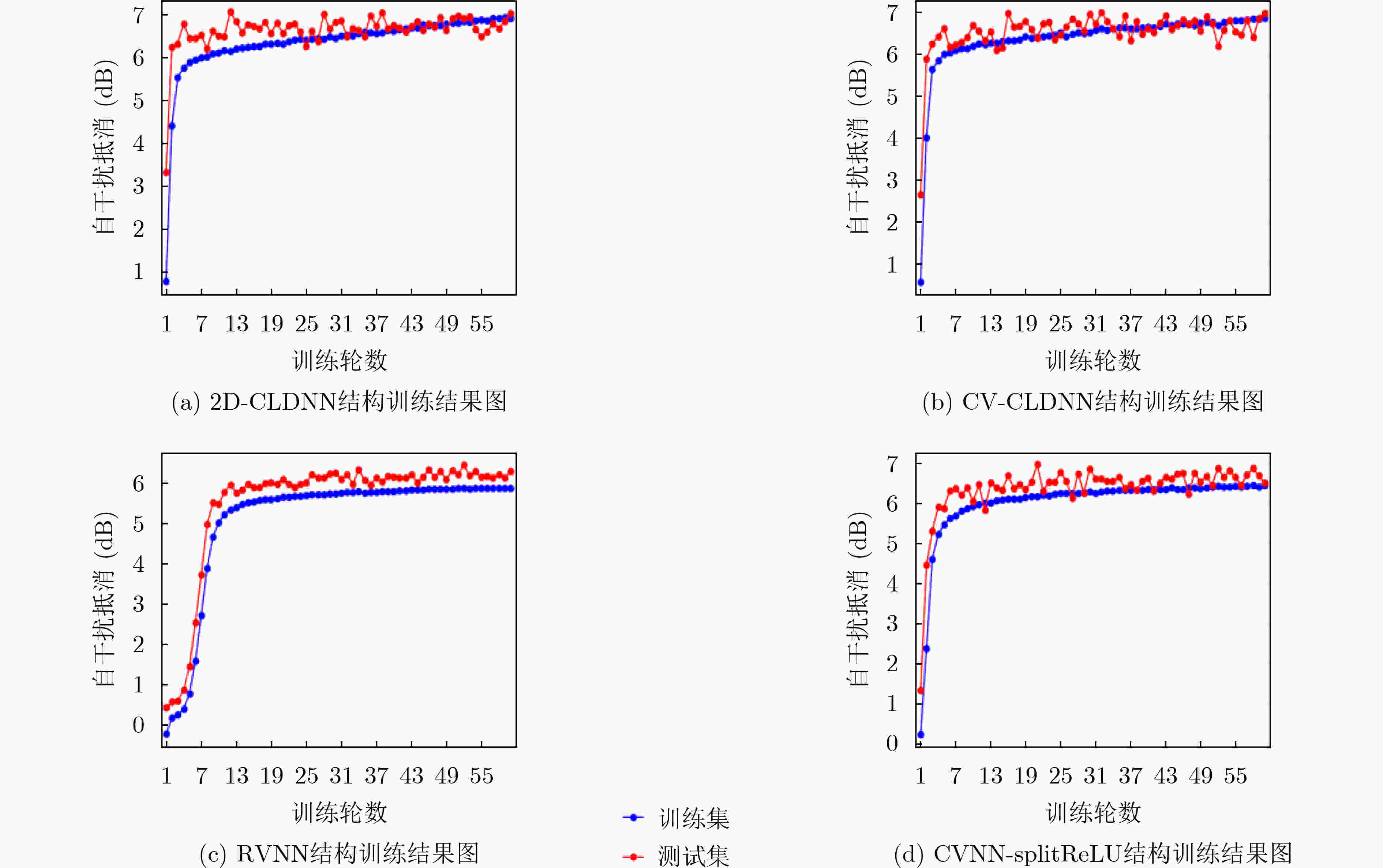
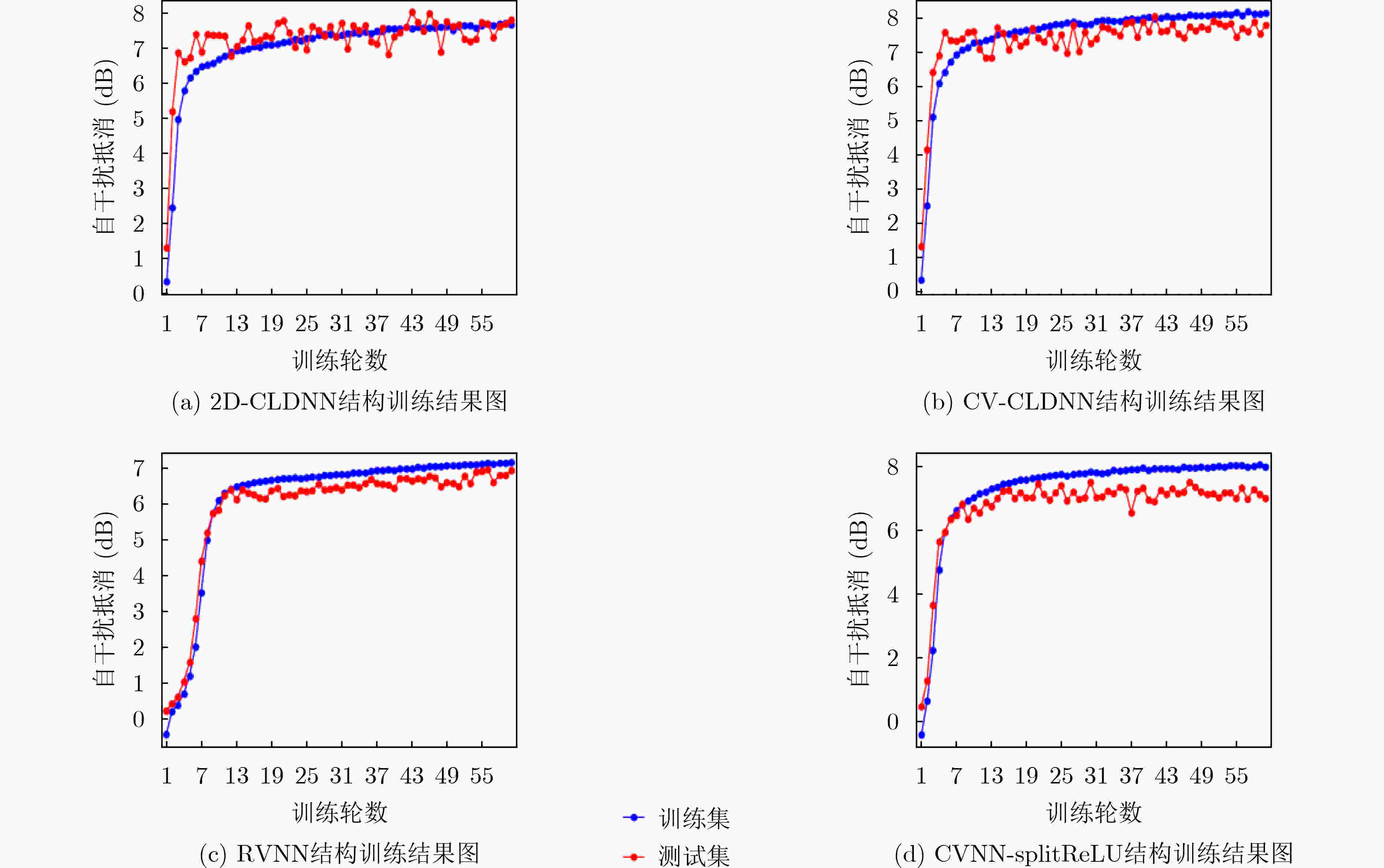
摘要: 带内全双工(IBFD)技术能够有效提高无线通信系统的频谱效率,近年来引起了广泛关注。然而,同时发送和接收引起的线性和非线性自干扰给IBFD带来了巨大挑战。传统的非线性自干扰消除主要是基于多项式模型和深度神经网络(DNN)来实现。多项式模型方法存在模型失配导致自干扰效果恶化的风险,而DNN方法无法针对高维数据特有的空频相关性、时间相关性等特点进行处理。该文基于卷积长短时记忆深度神经网络(CLDNN),通过在输入层中引入3维张量以及在卷积层设置复数卷积层结构,分别设计了两种重建自干扰信号的网络结构——2维CLDNN(2D-CLDNN)和复值CLDNN(CV-CLDNN),充分利用卷积神经网络局部感知和权值共享的优势,在高维特征中学习到更抽象的低维特征,从而提高自干扰消除的效果。实际场景中获得数据的评估结果显示,当功率放大器记忆长度M和自干扰信道多径长度L满足M+L=13时,通过总共60次训练轮数,该文提出的结构比传统DNN方法在非线性自干扰消除方面可以实现至少26%的改进,训练轮数也有明显减少。
-
关键词:
- 卷积长短时记忆深度神经网络 /
- 非线性自干扰消除 /
- 带内全双工 /
- 同时发送和接收 /
- 神经网络
Abstract: In-Band Full Duplex (IBFD) technology can effectively improve the spectral efficiency of wireless communication system, which has attracted extensive attention in recent years. However, the linear and nonlinear self interference caused by simultaneous transmission and reception brings great challenges to IBFD. The traditional nonlinear self interference cancellation is mainly based on polynomial model and Deep Neural Network(DNN). Polynomial-model-based method has the risk of deterioration of self-interference effect caused by model mismatch, while DNN-based method can not deal with the unique characteristics of space-frequency correlation and time correlation of high-dimensional data. Based on Convolution Long short-term memory Deep Neural Network(CLDNN), two network structures for reconstructing self-interference signals, Two-Dimensional CLDNN(2D-CLDNN) and Complex-Value-CLDNN(CV-CLDNN), are designed by introducing three-dimensional tensor in the input layer and setting complex convolution layer structure in the convolution layer, which makes full use of the advantages of local perception and weight sharing of convolutional neural network, so as to learn more abstract low-dimensional features from high-dimensional features, so as to improve the effect of self-interference cancellation. The evaluation results of the data obtained in the actual scene show that, when the memory length M of power amplifier and the multipath length L of self interference channel meet M+L=13, through a total of 60 training epochs, the structure proposed in this paper can achieve at least 26% improvement in nonlinear self-interference cancellation compared to the traditional DNN method, the training period is also significantly reduced. -
表 1 各方法在M+L不同条件下的非线性自干扰消除性能(dB)
方法 M+L =8 M+L =13 M+L =20 2D-CLDNN 6.63 7.71 7.65 CV-CLDNN 6.67 7.89 7.59 Polynomial 6.14 6.94 6.89 RVNN 5.94 6.25 6.61 CVNN-splitReLU 6.15 7.08 6.77 -
[1] 李彤, 沈莹, 潘文生, 等. 时间异步全双工数字域分段卷积自干扰抑制技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1395–1401. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210024LI Tong, SHEN Ying, PAN Wensheng, et al. A timing asynchronous full duplex digital self-interference suppression method by segment convolution[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1395–1401. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210024 [2] 唐友喜. 同时同频全双工原理与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016.TANG Youxi. No Division Duplex: Full Duplex Principles and Applications[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. [3] SABHARWAL A, SCHNITER P, GUO Dongning, et al. In-band full-duplex wireless: Challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2014, 32(9): 1637–1652. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2014.2330193 [4] BALATSOUKAS-STIMMING A, AUSTIN A C M, BELANOVIC P, et al. Baseband and RF hardware impairments in full-duplex wireless systems: Experimental characterisation and suppression[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2015, 2015: 142. doi: 10.1186/s13638-015-0350-1 [5] ISAKSSON M, WISELL D, and RONNOW D. A comparative analysis of behavioral models for RF power amplifiers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2006, 54(1): 348–359. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.860500 [6] BALATSOUKAS-STIMMING A. Non-linear digital self-interference cancellation for in-band full-duplex radios using neural networks[C]. 2018 IEEE 19th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Kalamata, Greece, 2018: 1–5. [7] KORPI D, ANTTILA L, and VALKAMA M. Nonlinear self-interference cancellation in MIMO full-duplex transceivers under crosstalk[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2017, 2017(1): 24. doi: 10.1186/s13638-017-0808-4 [8] KRISTENSEN A T, BURG A, and BALATSOUKAS-STIMMING A. Advanced machine learning techniques for self-interference cancellation in full-duplex radios[C]. 53rd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2019: 1149–1153. [9] WANG Qing, HE Fangmin, and MENG Jin. Performance comparison of real and complex valued neural networks for digital self-interference cancellation[C]. 2019 IEEE 19th International Conference on Communication Technology, Xi'an, China, 2019: 1193–1199. [10] LIU Xiaoyu, YANG Diyu, and EL GAMAL A. Deep neural network architectures for modulation classification[C]. 2017 51st Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2017: 915–919. [11] HUANG Jicun, RUAN S, HSU W C, et al. 3D-CLDNN: An effective architecture on deep neural network for sEMG-based lower limb abnormal recognition[C]. 2019 IEEE 8th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Osaka, Japan, 2019: 906–907. [12] SAINATH T N, VINYALS O, SENIOR A, et al. Convolutional, long short-term memory, fully connected deep neural networks[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), South Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 4580–4584. [13] EMAM A, SHALABY M, ABOELAZM M A, et al. A comparative study between CNN, LSTM, and CLDNN models in the context of radio modulation classification[C]. 2020 12th International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEENG), Cairo, Egypt, 2020: 190–195. [14] WANG Tianqi, WEN Chaokai, JIN Shi, et al. Deep learning-based CSI feedback approach for time-varying massive MIMO channels[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(2): 416–419. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2874264 [15] GUO Jiajia, WEN Chaokai, JIN Shi, et al. Convolutional neural network-based multiple-Rate compressive sensing for massive MIMO CSI feedback: Design, simulation, and analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(4): 2827–2840. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2968430 [16] HIROSE A and YOSHIDA S. Generalization characteristics of complex-valued feedforward neural networks in relation to signal coherence[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(4): 541–551. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2183613 [17] TRABELSI C, BILANIUK O, ZHANG Ying, et al. Deep complex networks[C]. 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
