Physical Layer Security Algorithm of Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface-assisted Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Communication System Based on Reinforcement Learning
-
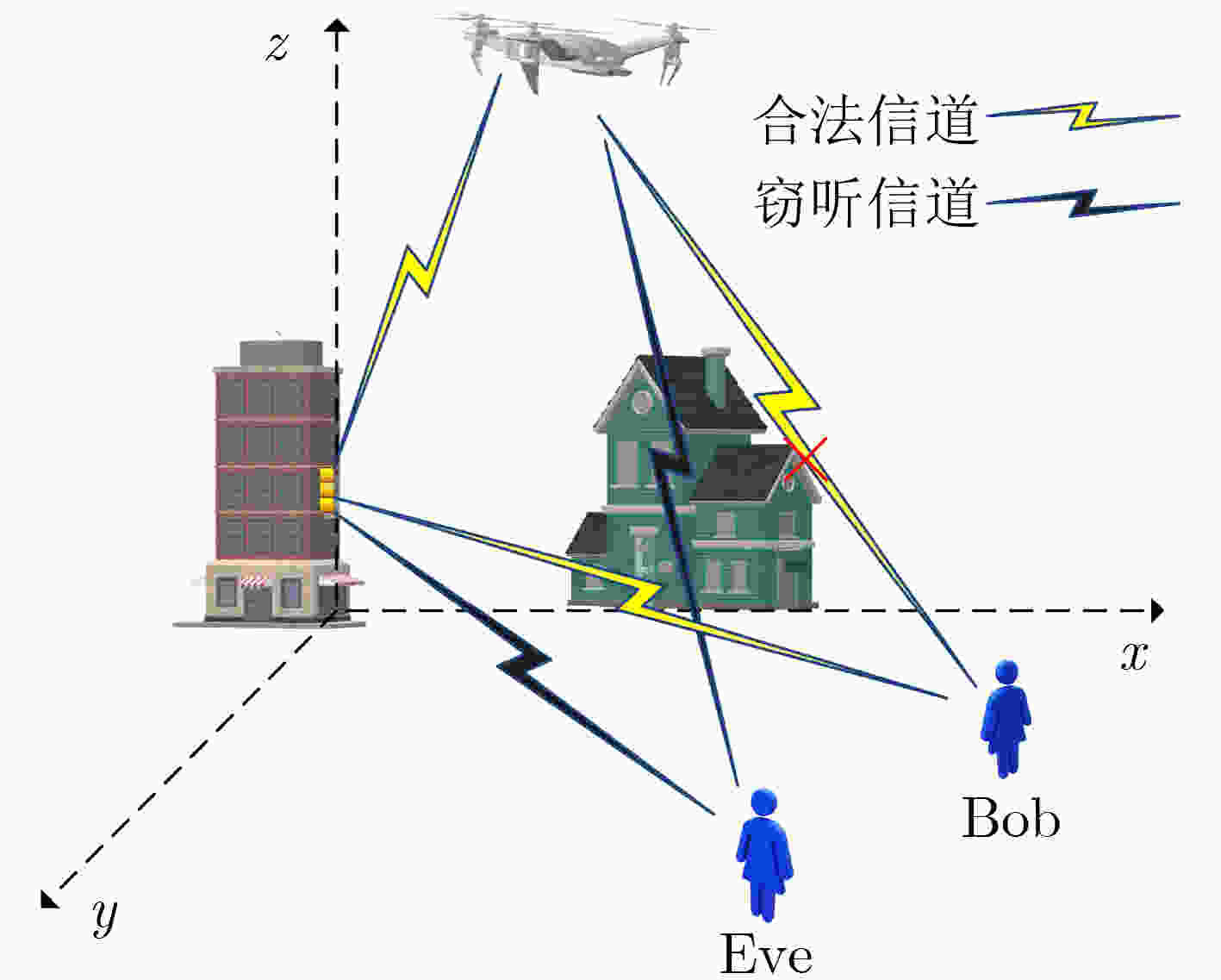
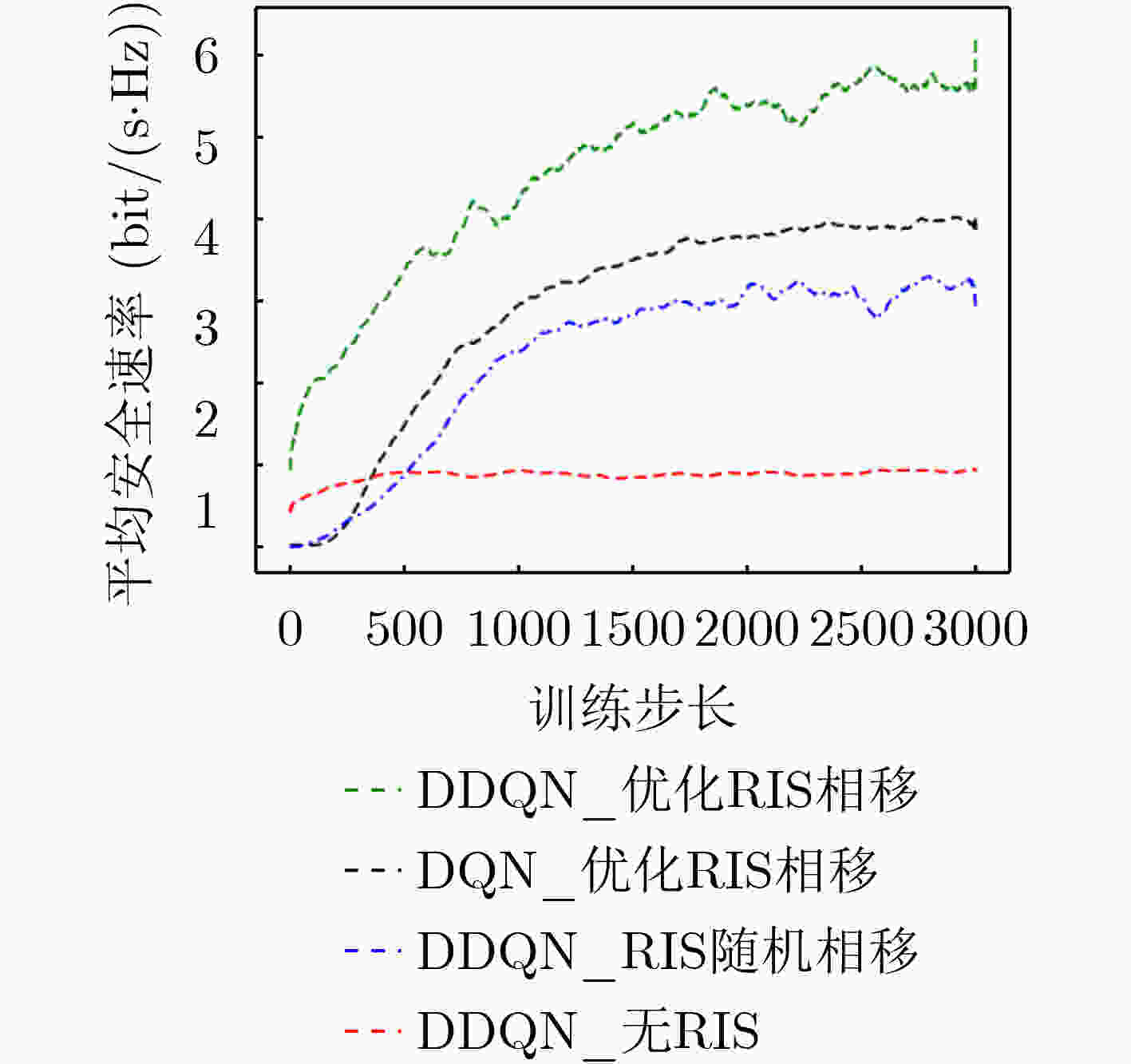
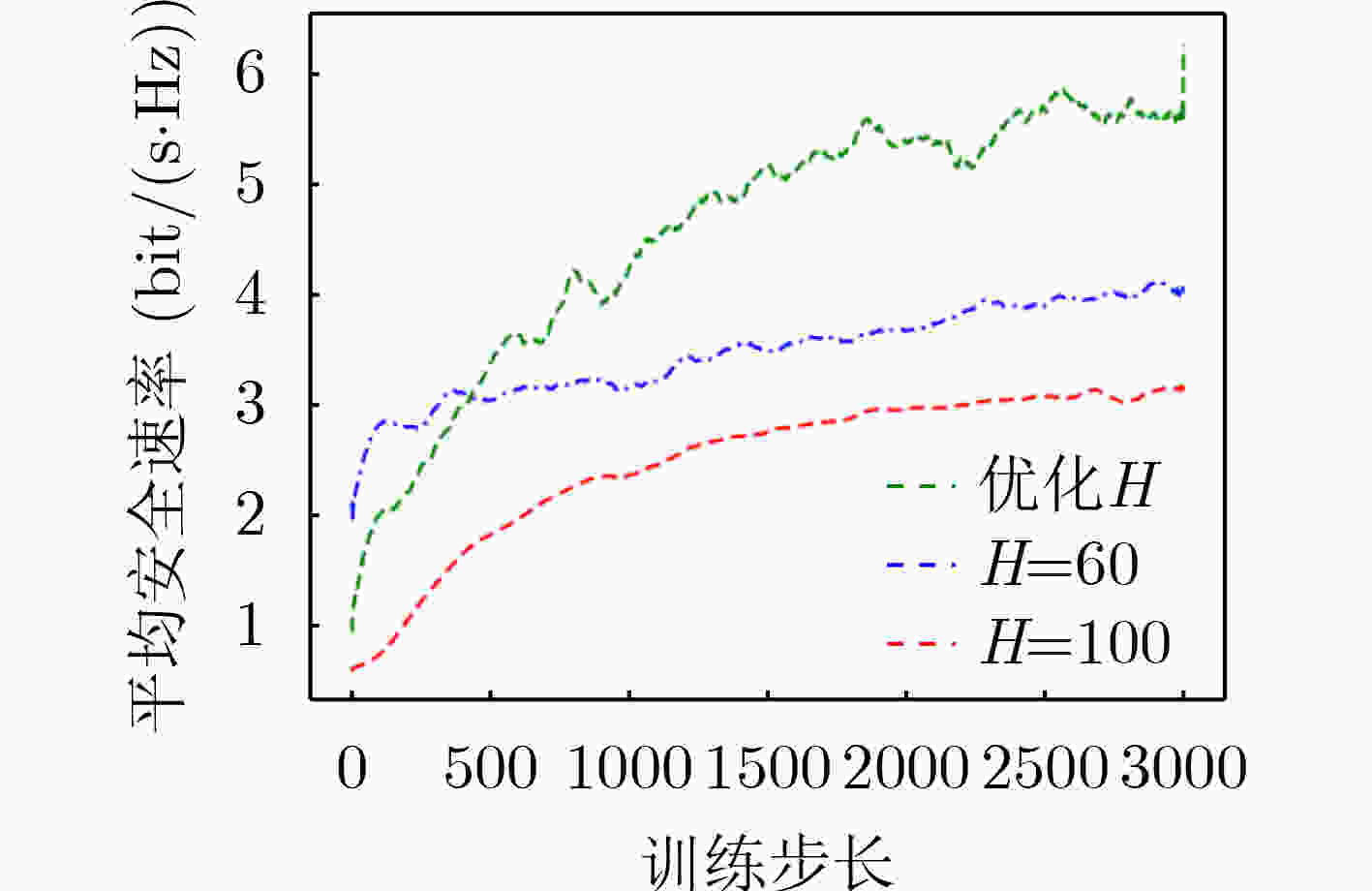
摘要: 该文从物理层安全的角度出发研究了智能超表面(RIS)辅助的无人机(UAV) 3D轨迹优化。具体地说,当RIS辅助的UAV向地面用户进行无线传输时,通过联合优化RIS相移和UAV的3D轨迹来最大化物理层安全速率。然而,由于目标函数是非凸的,传统的优化技术很难直接求解。深度强化学习能够处理无线通信中动态复杂的优化问题,该文基于强化学习双深度Q网络(DDQN)设计一种联合优化RIS相移和无人机3D轨迹算法,最大化可实现的平均安全速率。仿真结果表明,所设计的RIS辅助UAV通信优化算法可以获得比固定飞行高度的连续凸逼近算法(SCA)、随机相移下的RIS算法和没有RIS的算法有更高的安全速率。Abstract: In this paper, the optimization problem of the 3D trajectory for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) assisted by Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) in physical layer security is studied. Specifically, when the RIS assisted UAV transmits wirelessly information to the ground user, the physical layer security rate is maximized by jointly optimizing the RIS phase shift and the UAV's 3D trajectory. However, because the objective function is non convex, the traditional optimization technology is difficult to solve it directly. The dynamic and complex optimization problems in wireless communication can be solved by deep reinforcement learning. Based on reinforcement learning Double Deep Q Network (DDQN), a joint optimization algorithm of RIS phase shift and UAV 3D trajectory is designed in this paper to maximize the achievable average safety rate. The simulation results show that the designed RIS assisted UAV communication optimization algorithm can obtain higher safety rate than the Successive Convex Approximation (SCA) algorithm with fixed flight altitude, RIS algorithm with random phase shift and algorithm without RIS.
-
表 1 联合优化UAV轨迹和RIS相移算法(算法1)
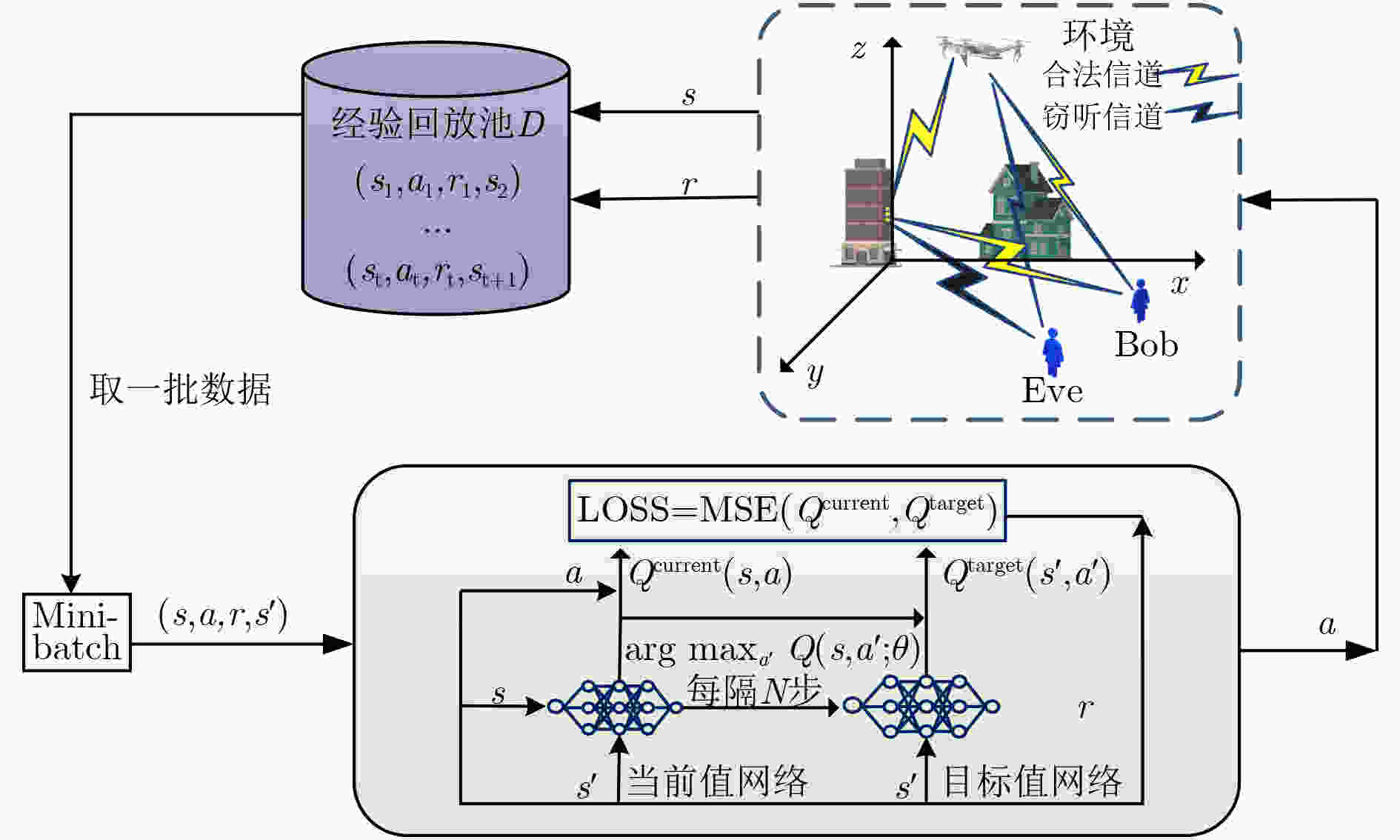
初始化RIS辅助UAV安全通信环境, 时隙数T, 经验回放池D, 当前网络参数$ \theta $, 目标网络参数$ {\theta ^ - } $; for episode = 1:E 获得$ {s^1} $; for $ t $= 1:T 通过$ \varepsilon $-贪婪算法,在状态${s^{{t} } }$下选取动作${a^{{t} } }$; if UAV 超出服务区域或者速度超出最大值; 动作不再执行,并且UAV将会得到惩罚; end 执行动作${a^{{t} } }$,调整UAV的轨迹,得到奖励${r^{{t} } }$和${s^{ {{t + 1} } } }$; 将${\text{(} }{s^{{t} } },{a^{{t} } },{r^{{t} } },{s^{ {{t + 1} } } })$ 收集到经验回放池; ${s^{{t} } } = {s^{ {{t + 1} } } }$; end 计算RIS最优相移${\theta _{ {{nt} } } }{\text{ = (} }2{\pi }/\lambda )(n - 1)d(\phi _{{t} }^{ {\text{ur} } } - \phi _{{m} }^{ {\text{rm} } })$; 从经验池中选择一批数据${\text{(} }{s^{{t} } },{a^{{t} } },{r^{{t} } },{s^{ {{t + 1} } } })$; 通过式(18)计算目标Q值; 通过式(19)最小化损失函数; 通过式(20)对每个K步更新目标网络; end 表 2 仿真参数设置
参数 值 服务区域, 小区个数C 1000 m × 1000 m, 10000 用户M, 时隙T, 回合E 6, 3000, 300 带宽B, UAV功率 P, 噪声值$ \sigma $ 2 MHz, 5 mW, –169 dBm/Hz $ {\tau _{\min }} $, $ {\tau _{\max }} $, N, $ {\theta _i}[1] $ 1 s, 3 s, 100, 0° $ V_{\max }^h $, $V_{ {\text{max} } }^{{v} }$,任务Dk 10 m/s,10 m/s, 512~1024 kb 飞行高度$ h_0^u $, $ {h_{\min }} $, $ {h_{\max }} $ 100 m, 30 m, 100 m 折扣因子 $ \gamma $ 0.9 阻塞参数a, b 9.61, 0.16 -
[1] ZHOU Xiaobo, WU Qingqing, YAN Shihao, et al. UAV-enabled secure communications: Joint trajectory and transmit power optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 4069–4073. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2900157 [2] WU Qingqing, ZENG Yong, and ZHANG Rui. Joint trajectory and communication design for multi-UAV enabled wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(3): 2109–2121. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2789293 [3] ZENG Yong, ZHANG Rui, and LIM T J. Throughput maximization for UAV-enabled mobile relaying systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2016, 64(12): 4983–4996. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2016.2611512 [4] ZHAO Nan, CHENG Fen, YU F R, et al. Caching UAV assisted secure transmission in hyper-dense networks based on interference alignment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(5): 2281–2294. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2792014 [5] ZHAN Cheng, ZENG Yong, and ZHANG Rui. Energy-efficient data collection in UAV enabled wireless sensor network[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(3): 328–331. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2017.2776922 [6] FU Yujing, MEI Haibo, WANG Kezhi, et al. Joint optimization of 3D trajectory and scheduling for solar-powered UAV systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(4): 3972–3977. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3063310 [7] YAN Shihao, ZHOU Xiangyun, YANG Nan, et al. Artificial-noise-aided secure transmission in wiretap channels with transmitter-side correlation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(12): 8286–8297. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2613860 [8] YAN Shihao, YANG Nan, LAND I, et al. Three artificial-noise-aided secure transmission schemes in wiretap channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(4): 3669–3673. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2779508 [9] ZHANG Guangchi, WU Qingqing, CUI Miao, et al. Securing UAV communications via joint trajectory and power control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(2): 1376–1389. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2892461 [10] LI An, WU Qingqing, and ZHANG Rui. UAV-enabled cooperative jamming for improving secrecy of ground wiretap channel[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(1): 181–184. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2018.2865774 [11] WU Qingqing, LIU Liang, and ZHANG Rui. Fundamental trade-offs in communication and trajectory design for UAV-enabled wireless network[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2019, 26(1): 36–44. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2018.1800221 [12] LI Sixian, DUO Bin, YUAN Xiaojun, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted UAV communication: Joint trajectory design and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(5): 716–720. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2966705 [13] FANG Sisai, CHEN Gaojie, and LI Yonghui. Joint optimization for secure intelligent reflecting surface assisted UAV networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(2): 276–280. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3027969 [14] FANG Junhao, YANG Zhaohui, ANJUM N, et al. Secure intelligent reflecting surface assisted UAV communication networks[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Montreal, Canada, 2021. [15] 陈新颖, 盛敏, 李博, 等. 面向6G的无人机通信综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 781–789. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210789CHEN Xinying, SHENG Min, LI Bo, et al. Survey on unmanned aerial vehicle communications for 6G[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(3): 781–789. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210789 [16] XU Yongjun, XIE Hao, WU Qingqing, et al. Robust max-min energy efficiency for RIS-aided HetNets with distortion noises[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(2): 1457–1471. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3141798 [17] XU Yongjun, GAO Zhengnian, WANG Zhengqiang, et al. RIS-enhanced WPCNs: Joint radio resource allocation and passive beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(8): 7980–7991. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3096603 [18] ZHANG Jiayi, DU Hongyang, SUN Qiang, et al. Physical layer security enhancement with reconfigurable intelligent surface-aided networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 3480–3495. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3083409 [19] HUANG Chongwen, ZAPPONE A, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(8): 4157–4170. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922609 [20] HUANG Chongwen, MO Ronghong, and YUEN C. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multiuser MISO systems exploiting deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(8): 1839–1850. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3000835 [21] ZHANG Yu, ZHUANG Zirui, GAO Feifei, et al. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for secure UAV communications[C]. 2020 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Seoul, Korea, 2020: 1–5. [22] FU Fang, JIAO Qi, YU F R, et al. Securing UAV-to-vehicle communications: A curiosity-driven deep Q-learning network (C-DQN) approach[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Montreal, Canada, 2021. [23] ZHANG Yu, MOU Zhiyu, GAO Feifei, et al. UAV-enabled secure communications by multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 11599–11611. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3014788 [24] MEI Haibo, YANG Kun, LIU Qiang, et al. 3D-trajectory and phase-shift design for RIS-assisted UAV systems using deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(3): 3020–3029. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2022.3143839 [25] WATKINS C J C H and DAYAN P. Q-learning[J]. Machine Learning, 1992, 8(3/4): 279–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00992698 [26] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Playing atari with deep reinforcement learning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.5602, 2013. [27] NASIR Y S and GUO Dongning. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for dynamic power allocation in wireless networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(10): 2239–2250. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2019.2933973 -





 下载:
下载:

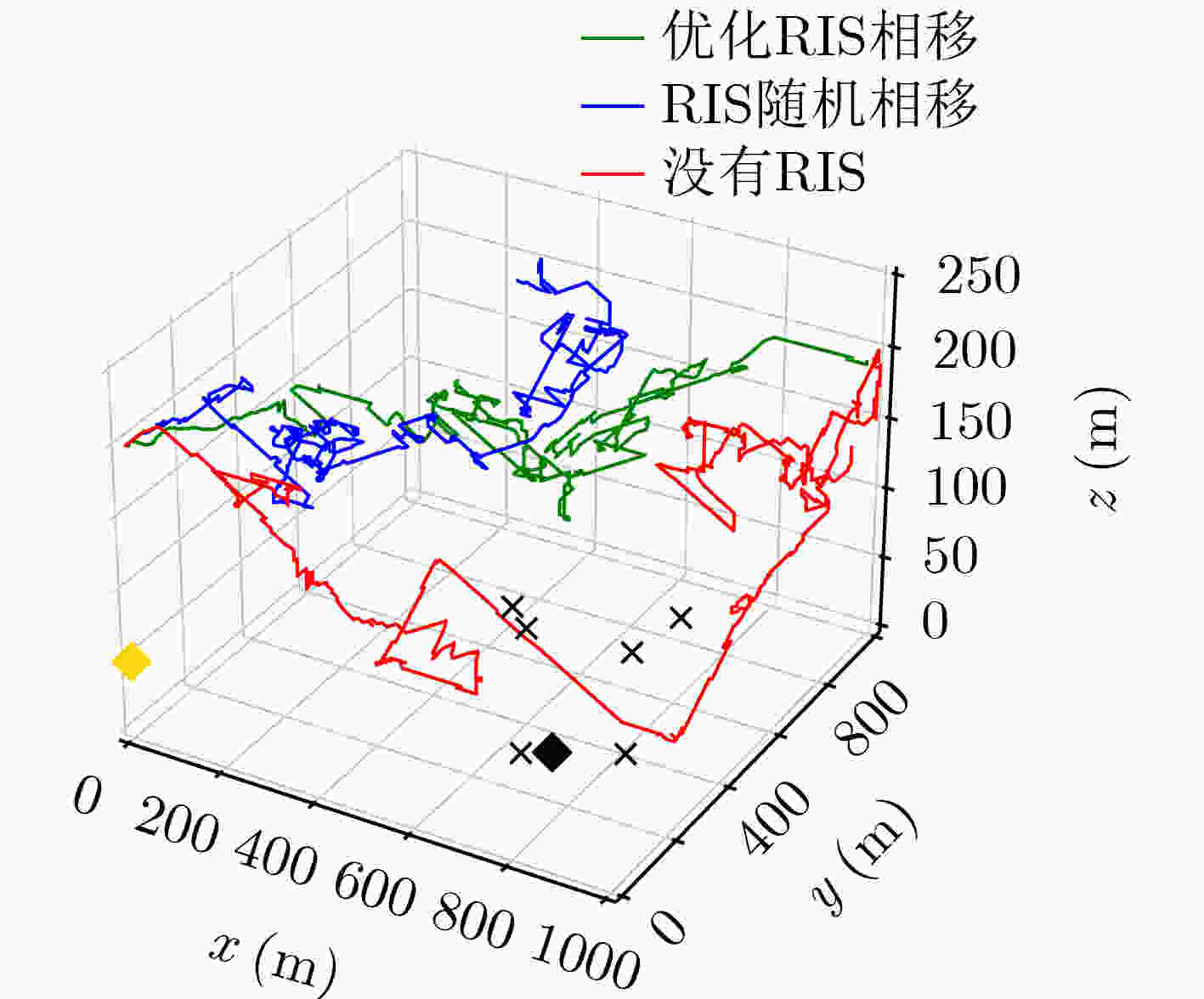
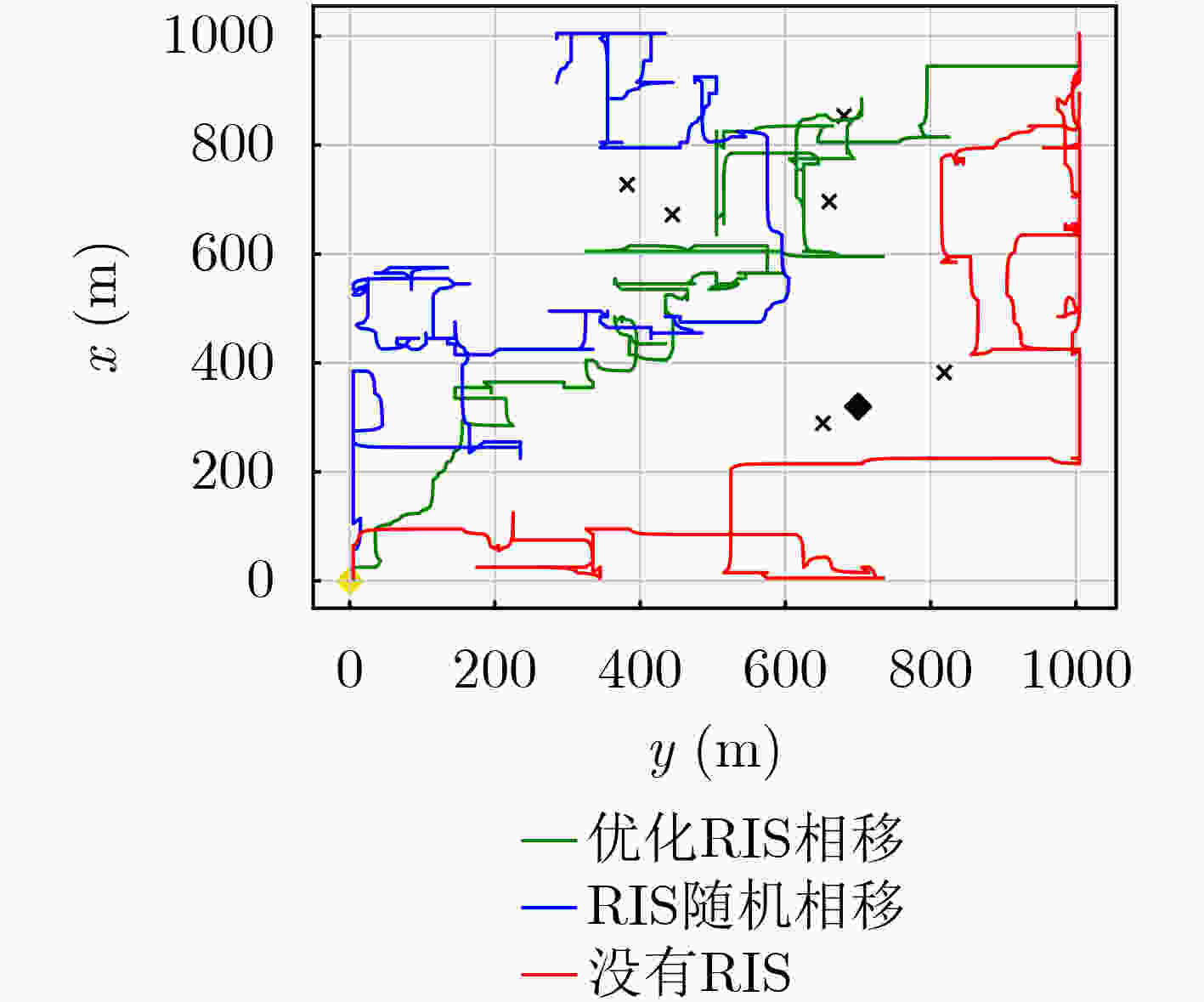


 下载:
下载:
