Zero-shot Learning for Low-light Image Enhancement Based on Dual Iteration
-
摘要: 针对低光照条件下拍摄图像质量低下的问题,该文提出一种基于双重迭代的零样本低照度图像增强方法。其外层迭代通过卷积神经网络估计增强参数,再由内层迭代进行图像增强,增强结果进一步用于计算损失函数并反馈更新外层的参数估计网络,最终通过多轮迭代生成高质量的图像。在该框架下,还设计了多尺度增强系数估计模块、基于注意力的像素级大气光估计模块,并提出了基于亮度对比度、大气光、颜色均衡以及图像平滑性先验的无监督损失函数。大量实验结果表明,该方法可有效将低光照图像增强为高质量的清晰图像,其性能优于现有的同类方法。同时该方法基于零样本学习,不需任何训练数据集,具有良好的普适性。Abstract: In this paper, a novel zero-shot low-light image enhancement framework is proposed based on dual iterations. The outer iteration uses a network to estimate the enhancement parameters, with which the inner iteration improves actually the image, and the results are applied to calculating the loss functions and updating the outer network. After multiple rounds of iterations, high-quality images can be obtained. Within this framework, an adaptive parameter estimation module and an attention-based pixel-wise atmosphere estimation module are designed. In addition, unsupervised loss functions based on light, contrast, color balance and image smoothness priors are proposed. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed method obtains high quality clear images from low-light ones, and outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, the proposed method belongs to zero-shot learning, which does not need training dataset and thus can be widely applied.
-
Key words:
- Image enhancement /
- Low-light /
- Unsupervised learning /
- Zero-shot learning /
- Iterative enhancement
-
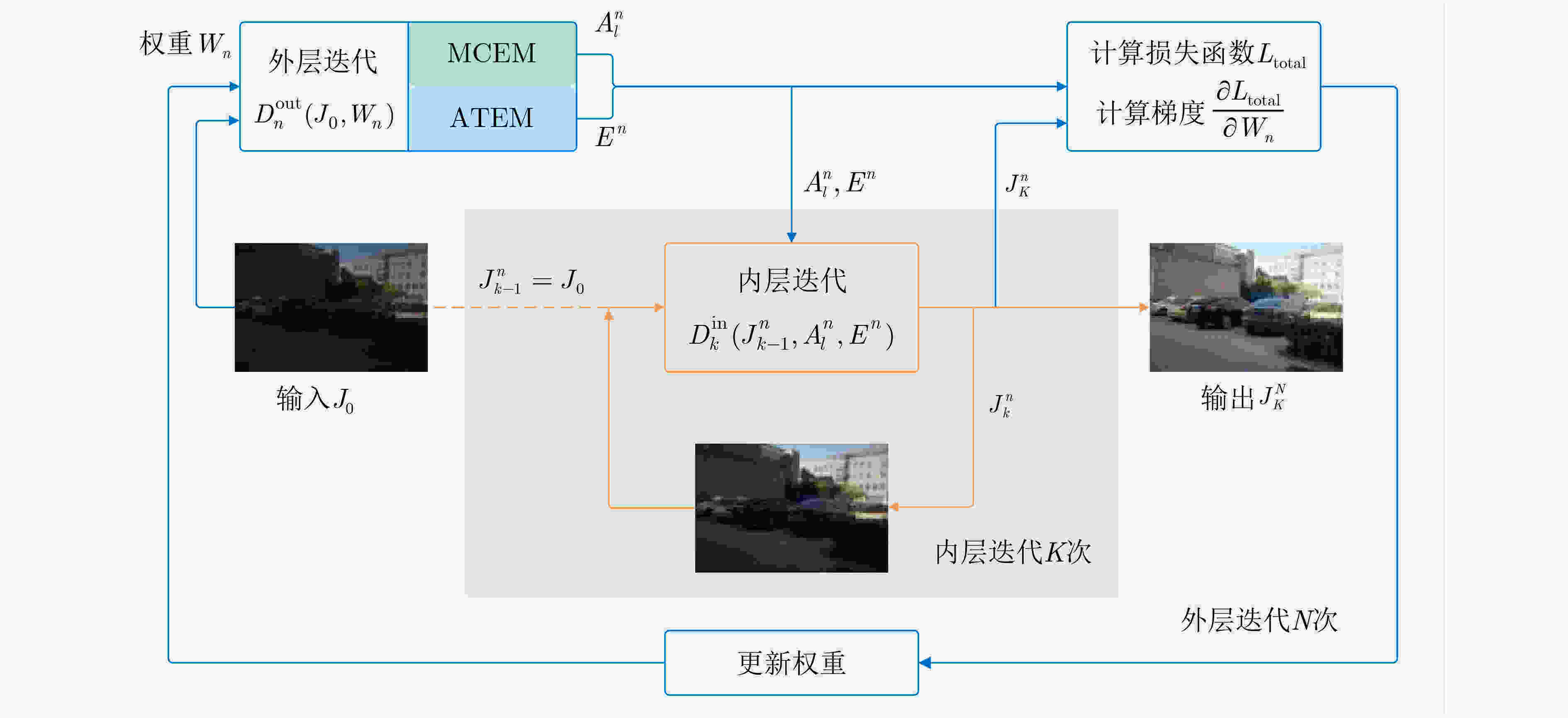
表 1 双重迭代流程
输入:低照度图像${J_0}$;初始权重${W_1}$;迭代次数$K$,$N$;学习率
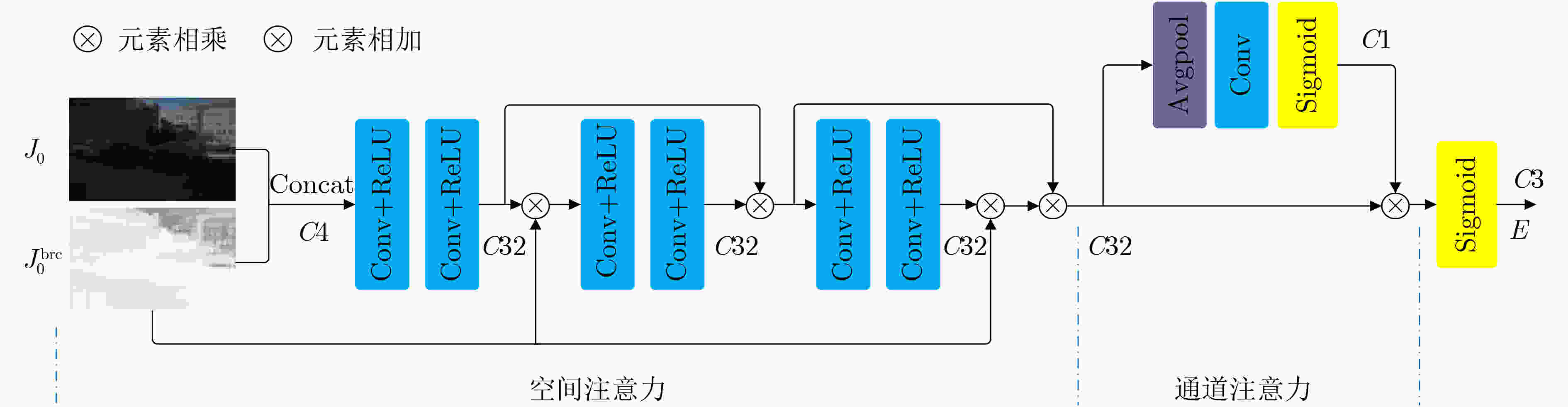
$\alpha $;迭代计数$n$=1,$k$;While($n < N$)do: 载入权重${W_n}$; 计算:$ D_n^{{\text{out}}}({J_0},{W_n}) $,$ A_l^n = {\text{MCEM}}{}_l({J_0}) $,${E^n} = {\text{ATEM}}({J_0})$;
初始化$k$=1;While($k < K$)do: 计算:$ J_k^n = D_k^{{\text{in}}}(J_{k - 1}^n,A_l^n,{E^n}) $; End While 经过$K$次内层迭代,第$n$次外层迭代的中间结果为:$J_K^n$
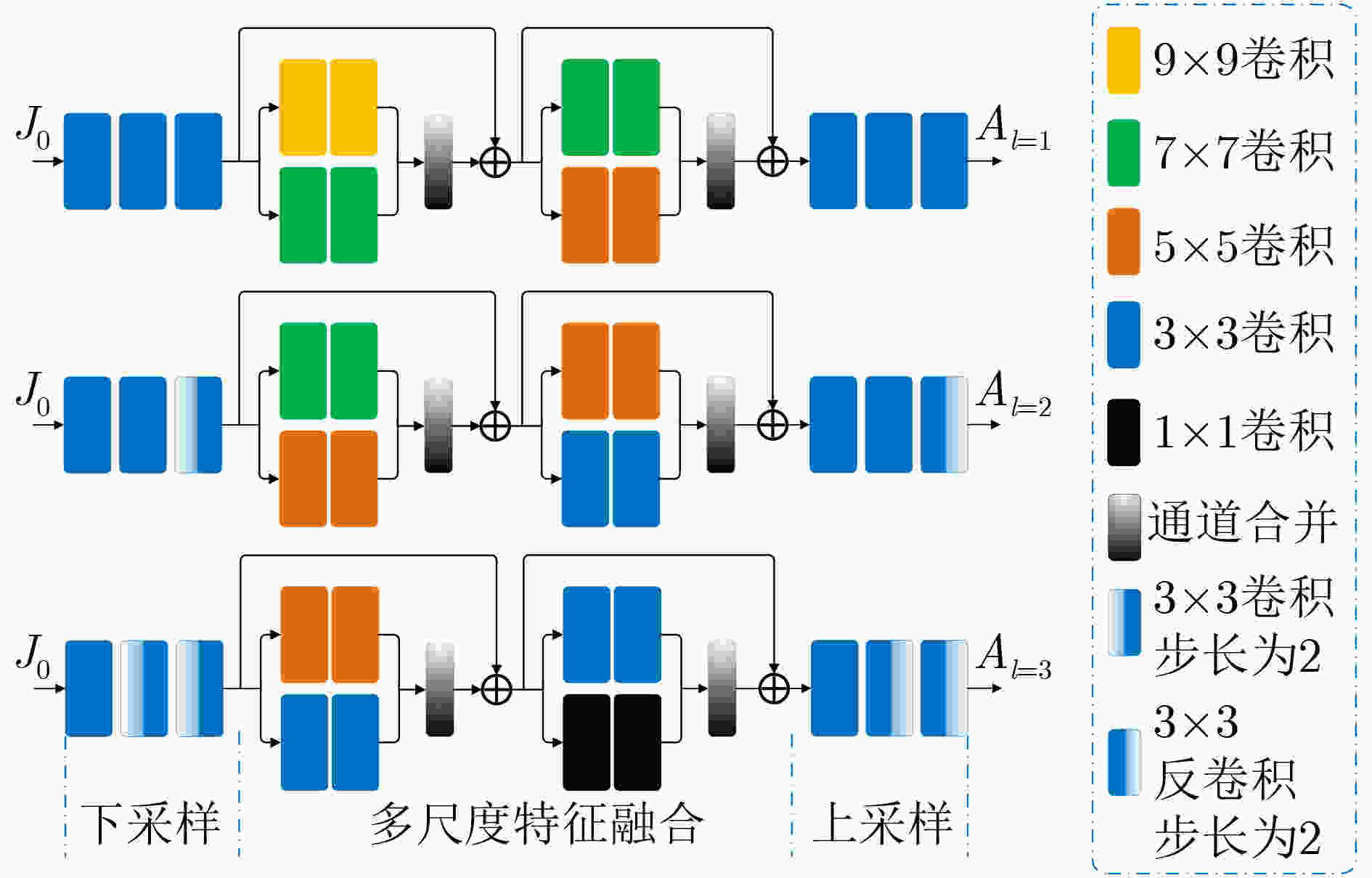
根据$J_K^n$计算损失函数${L_{{\text{total}}}}$和梯度$\dfrac{{\partial {L_{{\text{total}}}}}}{{\partial {W_n}}}$;更新权重:${W_{n + 1}} = {W_n} - \alpha \cdot \dfrac{{\partial {L_{{\text{total}}}}}}{{\partial {W_n}}}$; End While 输出:最终结果为$J_K^N$ 表 2 多尺度增强系数估计模块(MCEM)网络参数表
模块 参数 下采样 多尺度特征融合 上采样 MCEM(l=1) 输出通道数 32, 32, 64 32, 32, 32, 32 32, 32, 3 激活函数 ReLU ReLU, ReLU ReLU, ReLU, Tanh MCEM(l=2) 输出通道数 32,32,64 32, 32, 32, 32 32, 32, 3 激活函数 ReLU ReLU, ReLU ReLU, ReLU, Tanh MCEM( l=3) 输出通道数 32,32,64 32, 32, 32, 32 32, 32, 3 激活函数 ReLU ReLU, ReLU ReLU, ReLU, Tanh 表 3 LOL-v2测试集上不同方法的客观评价指标
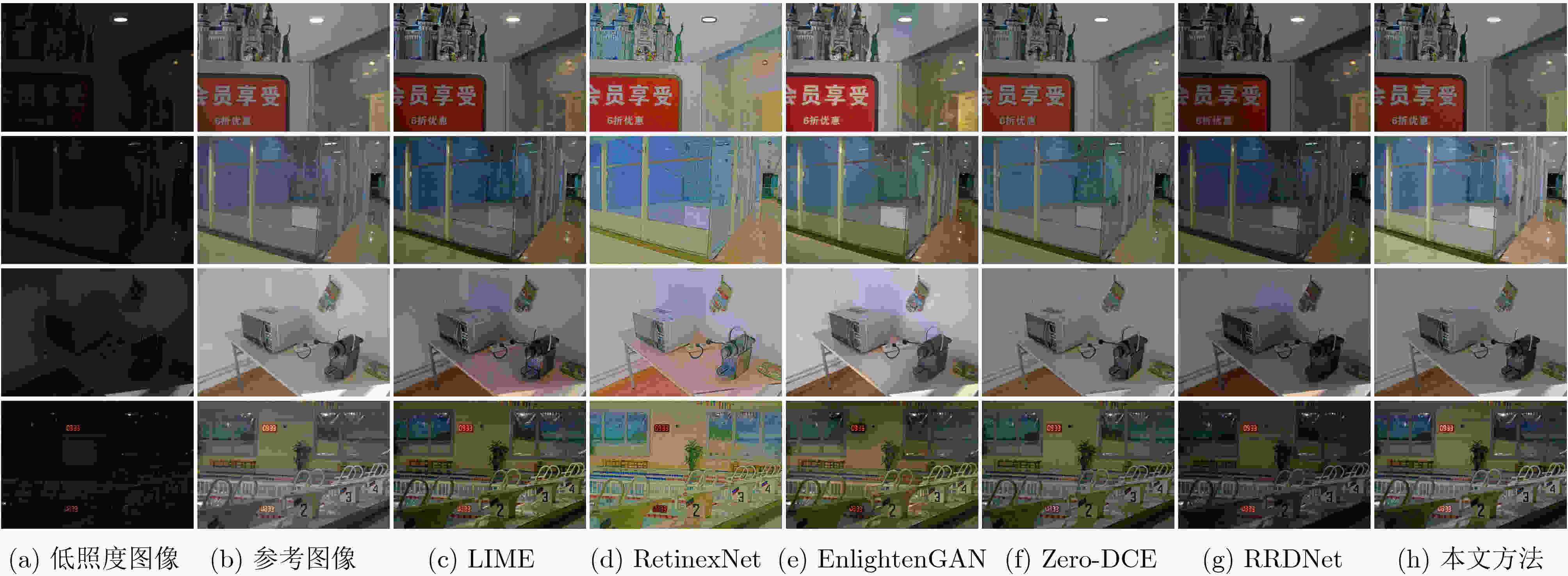
指标 LIME RetinexNet EnlightenGAN Zero-DCE RRDNet 本文方法 PSNR(dB)↑ 18.06 16.26 18.52 18.94 16.23 20.68 SSIM↑ 0.57 0.49 0.59 0.59 0.53 0.62 MAE↓ 9.45 10.38 7.78 8.35 12.71 7.21 VGG16-PFS↓ 1.07 1.66 1.04 0.98 1.53 0.91 CEIQ↑ 2.99 3.07 3.16 2.91 2.64 3.15 NIQE↓ 6.56 6.38 6.35 6.39 6.66 6.23 SSEQ↓ 29.24 37.15 23.22 26.04 21.71 26.58 表 4 夜间实拍图像测试集上不同方法的客观评价指标
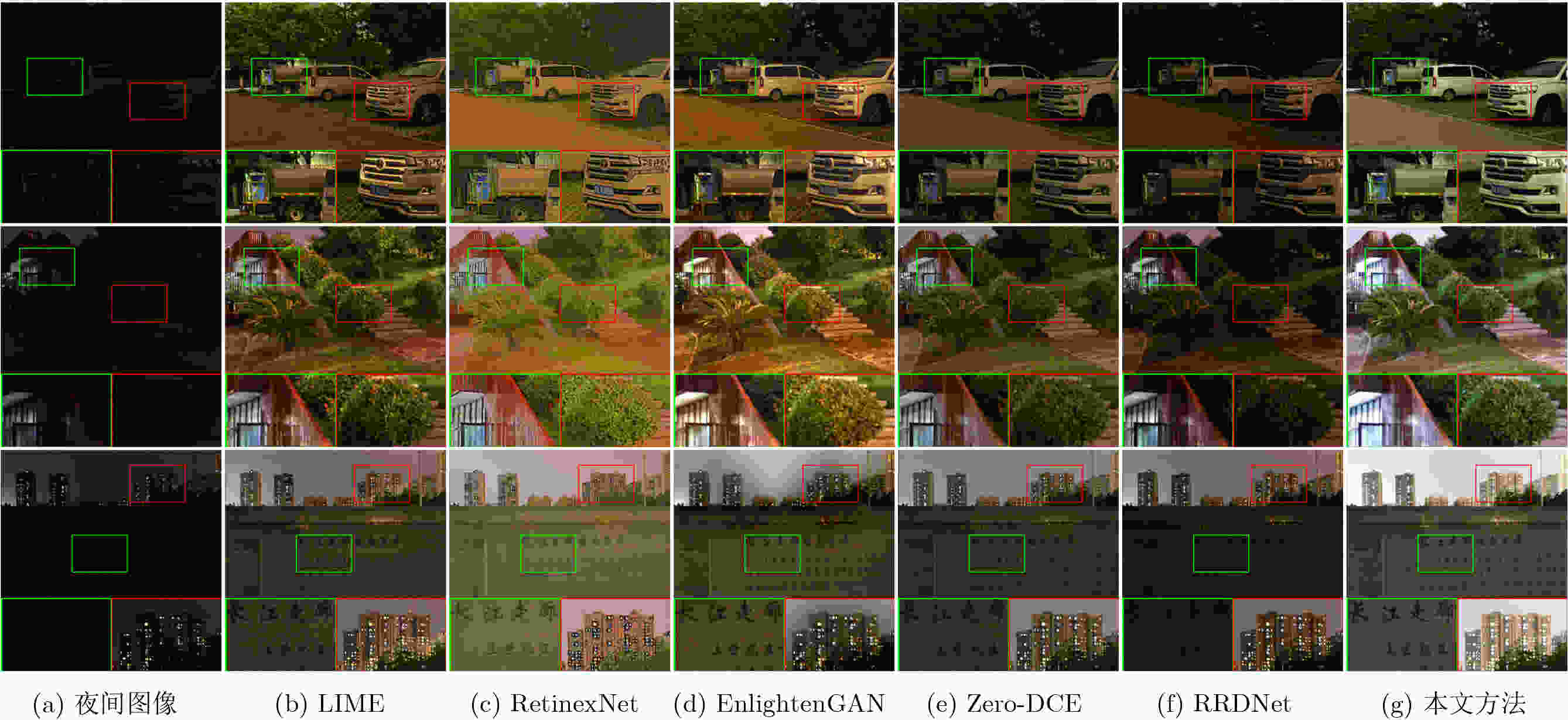
指标 LIME RetinexNet EnlightenGAN Zero-DCE RRDNet 本文方法 CEIQ↑ 2.89 2.94 3.02 2.77 2.46 3.01 NIQE↓ 6.28 6.11 7.43 6.35 6.86 6.06 SSEQ↓ 14.58 27.13 18.90 14.31 16.54 12.73 表 5 消融实验结果
指标 $ \beta {L_{{\text{bc}}}} $ $\beta {L_{{\text{bc}}}} + \gamma {L_{{\text{cwb}}}}$ $\beta {L_{{\text{bc}}}} + \gamma {L_{{\text{cwb}}}} + \mu {L_{{\text{sm}}}}$ ${L_{{\text{total}}}}$ PSNR(dB) 13.66 14.76 18.12 20.68 SSIM 0.40 0.48 0.57 0.62 -
[1] 杨燕, 王志伟. 基于均值不等关系优化的自适应图像去雾算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 755–763. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190368YANG Yan and WANG Zhiwei. Adaptive image dehazing algorithm based on mean unequal relation optimization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 755–763. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190368 [2] PAN Jinshan, REN Wenqi, HU Zhe, et al. Learning to Deblur images with exemplars[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(6): 1412–1425. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2832125 [3] LI Chongyi, ANWAR S, and PORIKLI F. Underwater scene prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 98: 107038. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107038 [4] 陈勇, 詹帝, 刘焕淋. 基于物理模型与边界约束的低照度图像增强算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(12): 2962–2969. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170267CHEN Yong, ZHAN Di, and LIU Huanlin. Enhancement algorithm for low-lighting images based on physical model and boundary constraint[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(12): 2962–2969. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170267 [5] 柳长源, 王琪, 毕晓君. 基于多通道多尺度卷积神经网络的单幅图像去雨方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(9): 2285–2292. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190755LIU Changyuan, WANG Qi, and BI Xiaojun. Research on rain removal method for single image based on multi-channel and multi-scale CNN[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(9): 2285–2292. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190755 [6] PIZER S M, AMBURN E P, AUSTIN J D, et al. Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations[J]. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 1987, 39(3): 355–368. doi: 10.1016/S0734-189X(87)80186-X [7] IBRAHIM H and KONG N S P. Brightness preserving dynamic histogram equalization for image contrast enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2007, 53(4): 1752–1758. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2007.4429280 [8] RAHMAN Z, JOBSON D J, and WOODELL G A. Multi-scale retinex for color image enhancement[C]. Proceedings of 3rd IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Lausanne, Switzerland, 1996: 1003–1006. [9] GUO Xiaojie, LI Yu, and LING Haibin. LIME: Low-light image enhancement via illumination map estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(2): 982–993. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2639450 [10] LI Mading, LIU Jiaying, YANG Wenhan, et al. Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(6): 2828–2841. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2810539 [11] DONG Xuan, WANG Guan, PANG Yi, et al. Fast efficient algorithm for enhancement of low lighting video[C]. 2011 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Barcelona, Spain, 2011: 1–6. [12] LORE K G, AKINTAYO A, SARKAR S, et al. LLNet: A deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 650–662. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.06.008 [13] WEI Chen, WANG Wenjing, YANG Wenhan, et al. Deep Retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1808.04560, 2018. [14] REN Wenqi, LIU Sifei, MA Lin, et al. Low-light image enhancement via a deep hybrid network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(9): 4364–4375. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2910412 [15] JIANG Yifan, GONG Xinyu, LIU Ding, et al. EnlightenGAN: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2340–2349. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3051462 [16] GUO Chunle, LI Chongyi, GUO Jichang, et al. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 1777–1786. [17] ZHU Anqi, ZHANG Lin, SHEN Ying, et al. Zero-shot restoration of underexposed images via robust Retinex decomposition[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), London, UK, 2020: 1–6. [18] 方明, 刘小晗, 付飞蚺. 基于注意力的多尺度水下图像增强网络[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3513–3521. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200836FANG Ming, LIU Xiaohan, and FU Feiran. Multi-scale underwater image enhancement network based on attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3513–3521. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200836 [19] LI Tao, ZHU Chuang, SONG Jiawen, et al. Low-light image enhancement using CNN and bright channel prior[C]. IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 2017: 3215–3219, [20] HE Kaiming, SUN Jian, TANG Xiaoou, et al. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341–2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [21] LIU Ziwei, LI Xiaoxiao, LUO Ping, et al. Deep learning markov random field for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(8): 1814–1828. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2737535 [22] MERTENS T, KAUTZ J, and VAN REETH F. Exposure fusion: A simple and practical alternative to high dynamic range photography[J]. Computer Graphics Forum, 2009, 28(1): 161–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2008.01171.x [23] YANG Wenhan, WANG Wenjing, HUANG Haofeng, et al. Sparse gradient regularized deep retinex network for robust low-light image enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2072–2086. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3050850 [24] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556, 2014. [25] MITTAL A, SOUNDARARAJAN R, and BOVIK A C. Making a 'Completely Blind' image quality analyzer[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(3): 209–212. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2227726 [26] LIU Lixiong, LIU Bao, HUANG Hua, et al. No-reference image quality assessment based on spatial and spectral entropies[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2014, 29(8): 856–863. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2014.06.006 [27] WU Jun, XIA Zhaoqiang, REN Yifeng, et al. No-reference quality assessment for contrast-distorted image[C]. 2016 Sixth International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA), Oulu, Finland, 2016: 1–5. -





 下载:
下载:



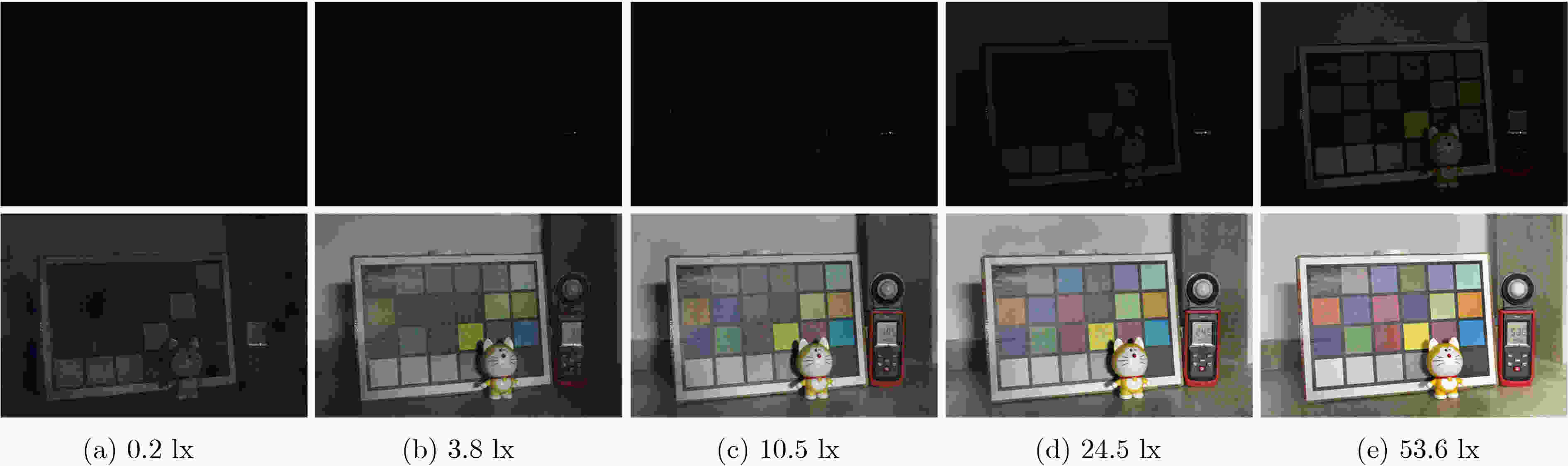
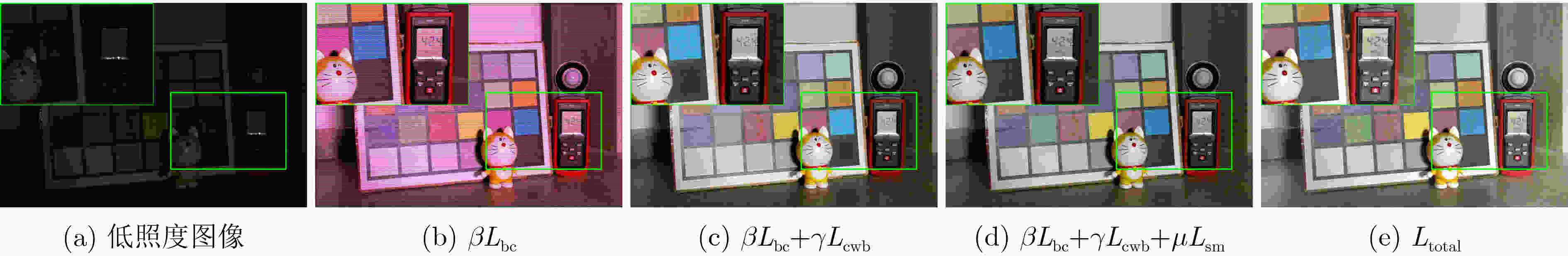
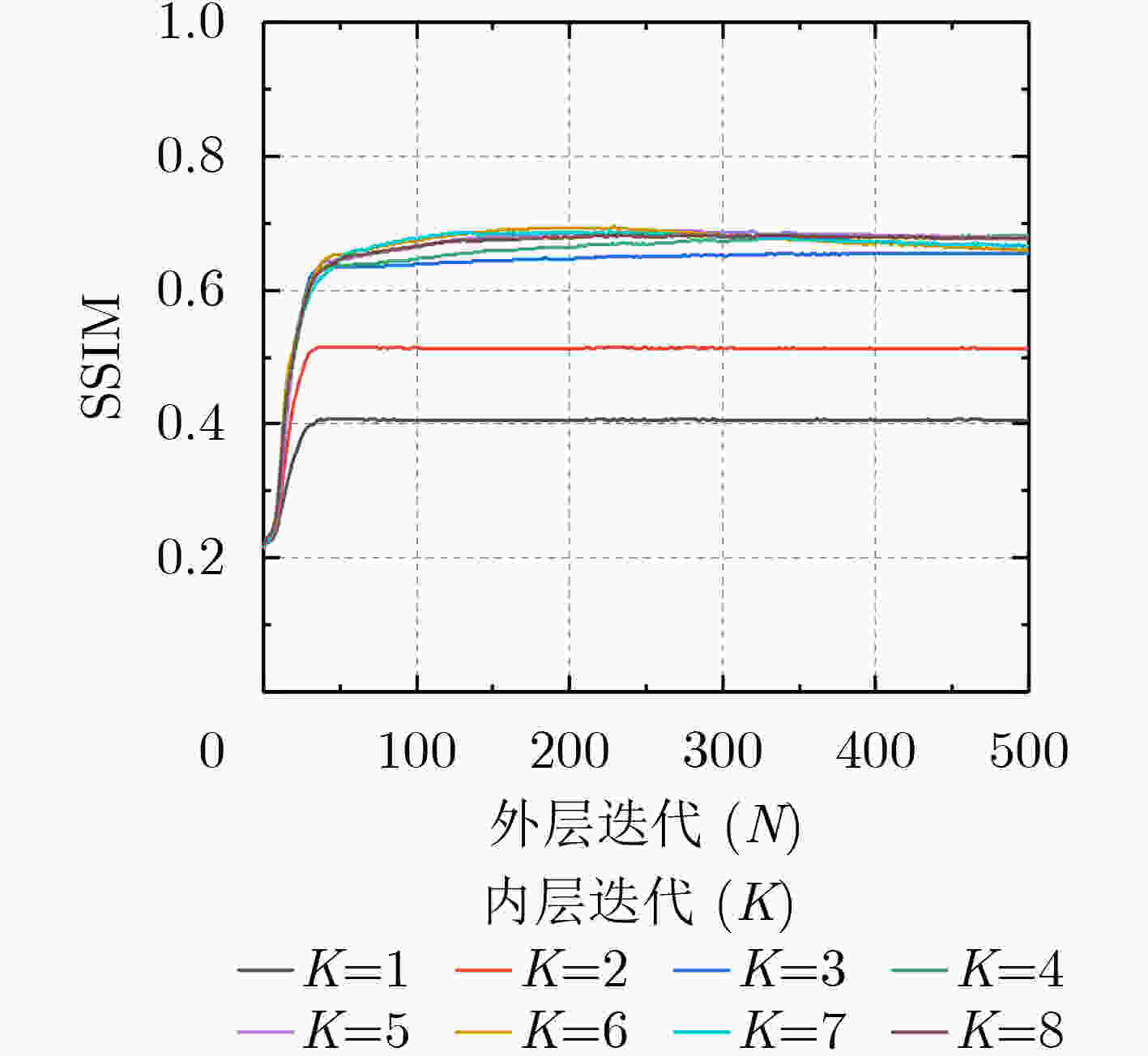


 下载:
下载:
