Review of Security for Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks
-
摘要: 水下无线传感器网络(UWSNs)广泛应用于如灾害预警、资源勘探等各种领域,然而易受到恶意攻击,迫切需要发展能够适应其通信带宽窄、传播时延长、时空不确定性严重等特性的安全机制。首先,该文从水下无线传感器网络的特性及安全需求入手,对其面临的安全威胁进行了分析。然后,对水下无线传感器网络中的加密、认证、信任管理、入侵检测、安全定位、安全同步和安全路由各类安全机制进行了综述。最后,对水下无线传感器网络安全研究中面临的缺少实际测试及相关数据集等挑战以及利用网络特性发展安全机制的未来研究方向进行了探讨。Abstract: Underwater Wireless Sensor Networks (UWSNs) are widely used in disaster warning, resource exploration and other fields. However, UWSNs are vulnerable to malicious attacks. Therefore, it is urgent to develop a security mechanism that can adapt to its characteristics, e.g. communication band width, propagation time extension, and severe spatio-temporal uncertainty. First, based on the analysis of the characteristics and security requirements of UWSNs, the security threats UWSNs face are discussed in this paper. Then, the security mechanisms of UWSNs are summarized, including encryption, authentication, trust management, intrusion detection, secure location, secure synchronization and secure routing. Finally, the challenges of lack of practical tests and relevant data sets in the security research of UWSNs are discussed, as well as the future research direction of developing security mechanism based on network characteristics.
-
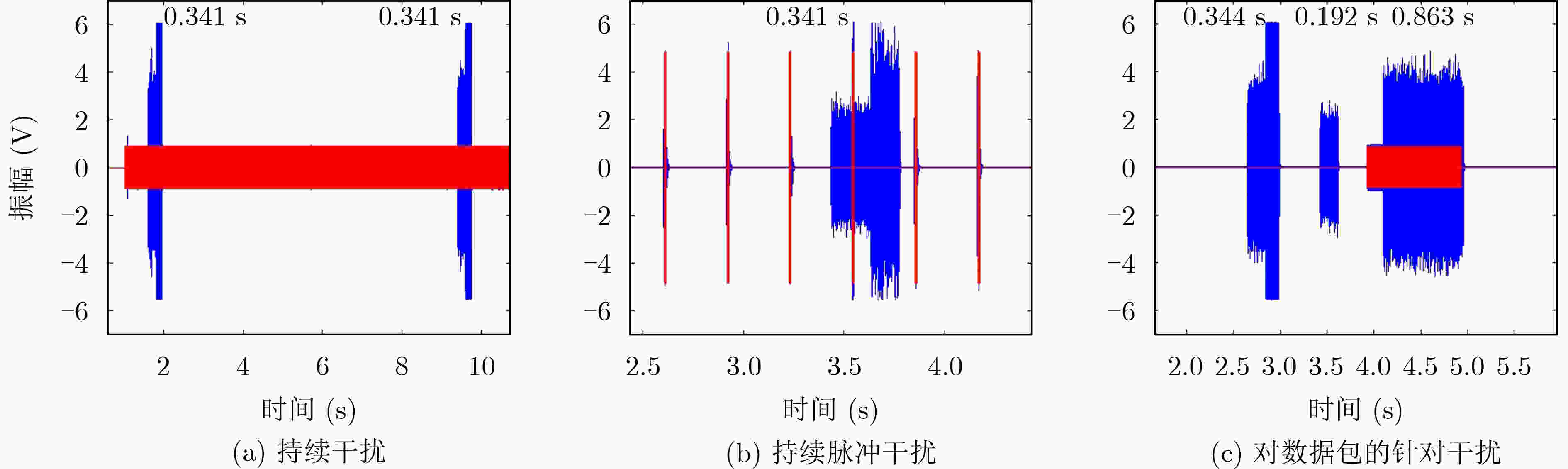
图 3 对LinkQuest调制解调器的几种干扰方案[14]
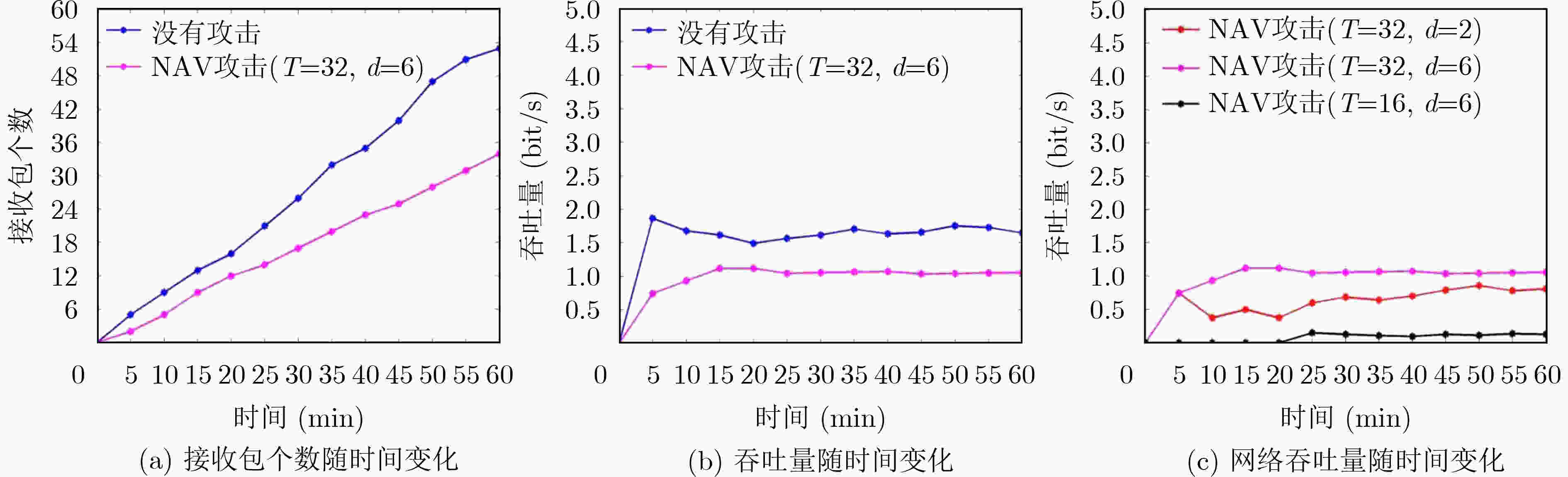
图 4 NAV干扰攻击对网络性能的影响[17]
表 1 网络性能[13]
攻击 PDR(%) PSR(%) TP(bit/s) 无攻击 100 100 140.0660 持续干扰 0 100 0 随机干扰 54 100 30.0900 反应式 0 100 0 白噪声 100 100 139.8205 表 2 UWSNs中的安全需求
安全需求 目标 数据保密性 防止敏感信息在开放水声信道中被恶意节点窃取 数据完整性 确保接收端能够获取完整正确有效的数据、控制及调度等信息 数据新鲜性 确保数据为最新的,而不被恶意节点故意延迟重放 网络可用性 UWSNs的重要服务需要在网络中存在攻击或某些节点故障后仍然可用 入侵检测和隔离 对于成功破解身份认证信息伪装为合法节点的恶意节点,UWSNs应当能够准确识别其恶意行为并对其进行有效隔离,
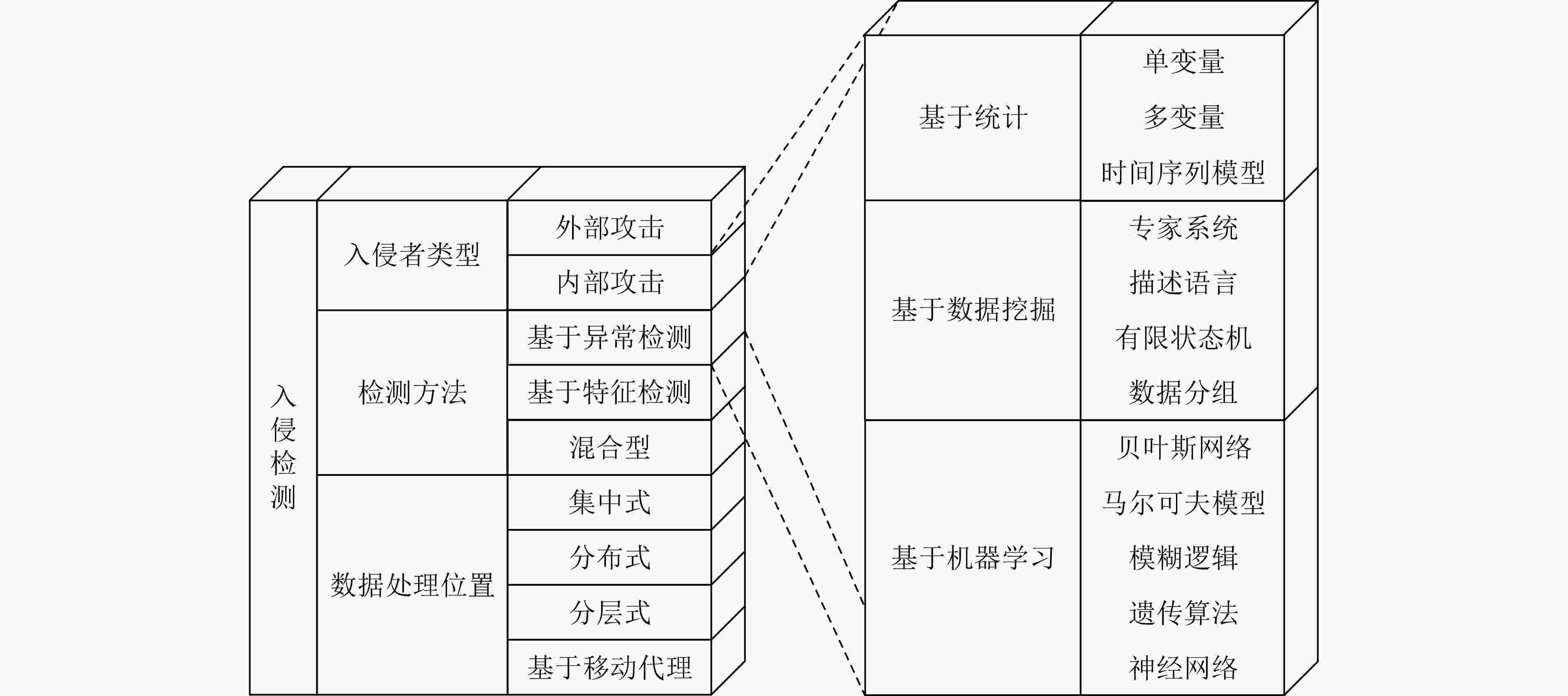
防止其对网络产生长期的负面影响表 3 陆地和水下无线传感器网络中的入侵检测机制
检测方法 针对的攻击 网络类型 评价 不完全信息随机博弈论[29] 未指定攻击类型 WSNs 该法用于优化IDS的资源分配,需要传感器节点数量具有一定冗余,
不适用于节点稀疏分布的UWSNs二元逻辑回归[30] 网络层攻击 WSNs 该法需要训练建立回归模型。训练阶段需要模拟无攻击存在的真实环境,
对于UWSNs具有一定的挑战扩展卡尔曼滤波[31] 虚假数据注入 WSNs 该法依赖于WSNs节点间观测数据的高度时空相关性,不适用于具有时空
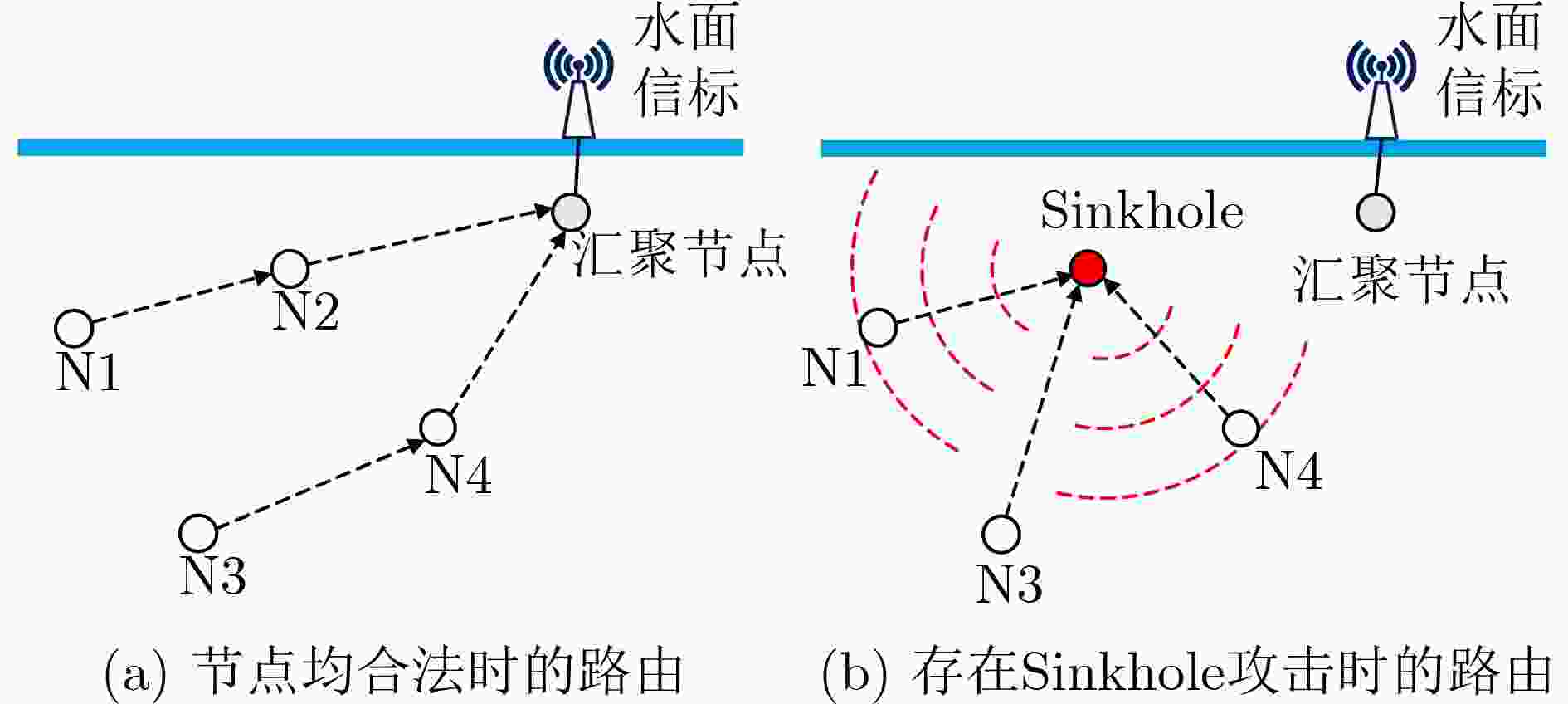
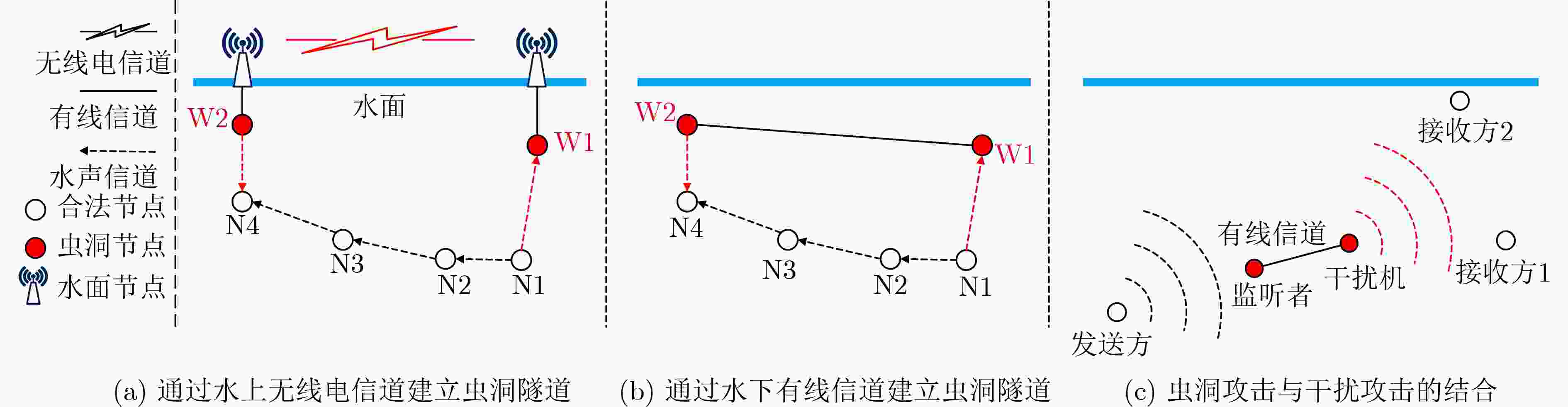
不确定性且节点稀疏分布的UWSNs加权信任管理[32] 内部攻击 WSNs 适用于UWSNs;基于加权算法的方法,经验权重和信任阈值的确定具有一定主观性 对特定包的行为分析[33] 恶意丢包、篡改 UWSNs 未考虑环境因素导致的丢包行为 利用往返时间异常特点[34] 虫洞攻击 UWSNs 对网络结构具有一定要求,且未考虑信道时空不确定性 表 4 UWSNs中安全定位、同步协议
文献 协议类型 协议机制 一种基于信任模型的水下无线传感器网络协同
安全定位算法[35]安全定位 基于信任模型识别并隔离恶意丢弃、修改定位信息节点 一种新的协同定位测量信息异常检测方法[37] 安全定位 基于自适应神经模糊推理系统检测异常的声距信息,保证测距信息准确 水下传感器网络异步定位的隐私保护解决方案[38] 安全定位 避免位置信息的泄露 基于证据理论的水下传感器网络安全距离定位[39] 安全定位 基于信任模型,选择最可信的节点进行定位 一种基于集群的水下无线传感器网络安全同步协议[40] 安全同步 基于中心超椭球支持向量机检测异常端到端时延 水声网络中带异常点检测的垂直和水平同步服务[41] 安全同步 基于关联检测和统计信誉检测离群时间戳,识别内部攻击节点 -
[1] CUI Junhong, KONG Jiejun, GERLA M, et al. The challenges of building mobile underwater wireless networks for aquatic applications[J]. IEEE Network, 2006, 20(3): 12–18. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2006.1637927 [2] DEMIRORS E, SKLIVANITIS G, SANTAGATI G E, et al. Design of a software-defined underwater acoustic modem with real-time physical layer adaptation capabilities[C]. The International Conference on Underwater Networks & Systems, Rome, Italy, 2014: 25. [3] YAN Hai, WAN Lei, ZHOU Shengli, et al. DSP based receiver implementation for OFDM acoustic modems[J]. Physical Communication, 2012, 5(1): 22–32. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2011.09.001 [4] AKYILDIZ I F and WANG Xudong. A survey on wireless mesh networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2005, 43(9): S23–S30. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2005.1509968 [5] FREITAG L, GRUND M, SINGH S, et al. The WHOI micro-modem: An acoustic communications and navigation system for multiple platforms[C]. OCEANS 2005 MTS/IEEE, Washington, USA, 2005: 1086–1092. [6] ZHANG Wenbo, HAN Guangjie, WANG Xin, et al. A node location algorithm based on node movement prediction in underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(3): 3166–3178. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2963406 [7] QARABAQI P and STOJANOVIC M. Statistical characterization and computationally efficient modeling of a class of underwater acoustic communication channels[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2013, 38(4): 701–717. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2013.2278787 [8] STOJANOVIC M. On the relationship between capacity and distance in an underwater acoustic communication channel[J]. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 2007, 11(4): 34–43. doi: 10.1145/1347364.1347373 [9] STOJANOVIC M and PREISIG J. Underwater acoustic communication channels: Propagation models and statistical characterization[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2009, 47(1): 84–89. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2009.4752682 [10] LI Baosheng, ZHOU Shengli, STOJANOVIC M, et al. Multicarrier communication over underwater acoustic channels with nonuniform doppler shifts[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2008, 33(2): 198–209. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2008.920471 [11] JIANG Shengming. On securing underwater acoustic networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2019, 21(1): 729–752. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2864127 [12] WANG Qiu, DAI Hongning, LI Xuran, et al. Eavesdropping attacks in underwater acoustic networks[C]. The 10th International Conference on Information, Communications and Signal Processing (ICICS), Singapore, 2015: 1–5. [13] ZUBA M, SHI Zhijie, PENG Zheng, et al. Vulnerabilities of underwater acoustic networks to denial-of-service jamming attacks[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2015, 8(16): 2635–2645. doi: 10.1002/sec.507 [14] SAMIR M, KOWALSKI M, ZHOU Shengli, et al. An experimental study of effective jamming in underwater acoustic links[C]. The 11th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems, Philadelphia, USA, 2014: 737–742. [15] GOETZ M, AZAD S, CASARI P, et al. Jamming-resistant multi-path routing for reliable intruder detection in underwater networks[C]. The Sixth ACM International Workshop on Underwater Networks, Seattle, USA, 2011: 10. [16] CAMPAGNARO F, TRONCHIN D, SIGNORI A, et al. Replay-attack countermeasures for underwater acoustic networks[C]. The Global Oceans 2020: Singapore – U. S. Gulf Coast, Biloxi, USA, 2020: 1–9. [17] 张俊清. 水声网络协议干扰技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国舰船研究院, 2017.ZHANG Junqing. Research on protocol interferences against underwater acoustic network[D]. [Master dissertation], China Ship Research and Development Academy, 2017. [18] ZHANG Junqing, ZHANG Gangqiang, and LIU Junkai. Wormhole attack detecting in underwater acoustic communication networks[C]. 2021 OES China Ocean Acoustics (COA), Harbin, China, 2021: 647–650. [19] LI Hong, HE Yunhua, CHENG Xiuzhen, et al. Security and privacy in localization for underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2015, 53(11): 56–62. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2015.7321972 [20] SU Zhong, LIN Chuang, REN Fengyuan, et al. Security mechanisms analysis of wireless sensor networks specific routing attacks[C]. 2006 First International Symposium on Pervasive Computing and Applications, Urumqi, China, 2006: 579–584. [21] LI Xun, HAN Guangjie, QIAN Aihua, et al. Detecting sybil attack based on state information in underwater wireless sensor networks[C]. The 21st International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks, Split, Croatia, 2013: 1–5. [22] PENG Chunyan, DU Xiujuan, LI Keqin, et al. An ultra-lightweight encryption scheme in underwater acoustic networks[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2016, 2016: 8763528. doi: 10.1155/2016/8763528 [23] 刘俊凯, 董阳泽, 张刚强. 隐蔽通信中基于水声信道的密钥生成技术[J]. 应用声学, 2019, 38(4): 681–687. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2019.04.027LIU Junkai, DONG Yangze, and ZHANG Gangqiang. Key generation technology based on underwater acoustic channel estimation in covert communication[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics, 2019, 38(4): 681–687. doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2019.04.027 [24] DIAMANT R, CASARI P, and TOMASIN S. Cooperative authentication in underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(2): 954–968. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2886896 [25] DU Jiaxin, HAN Guangjie, LIN Chuan, et al. ITrust: An anomaly-resilient trust model based on isolation forest for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2022, 21(5): 1684–1696. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2020.3028369 [26] JIANG Jinfang, ZHU Xinyu, HAN Guangjie, et al. A dynamic trust evaluation and update mechanism based on C4.5 decision tree in underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(8): 9031–9040. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2999566 [27] HE Yu, HAN Guangjie, JIANG Jinfang, et al. A trust update mechanism based on reinforcement learning in underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2022, 21(3): 811–821. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2020.3020313 [28] DAS A P, THAMPI S M, and LLORET J. Anomaly detection in UASN localization based on time series analysis and fuzzy logic[J]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2020, 25(1): 55–67. doi: 10.1007/s11036-018-1192-y [29] MOOSAVI H and BUI F M. A game-theoretic framework for robust optimal intrusion detection in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2014, 9(9): 1367–1379. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2014.2332816 [30] IOANNOU C, VASSILIOU V, and SERGIOU C. An intrusion detection system for wireless sensor networks[C]. The 24th International Conference on Telecommunications (ICT), Limassol, Cyprus, 2017: 1–5. [31] SUN Bo, SHAN Xuemei, WU Kui, et al. Anomaly detection based secure in-network aggregation for wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2013, 7(1): 13–25. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2012.2223531 [32] BAO Fenye, CHEN I R, CHANG M, et al. Hierarchical trust management for wireless sensor networks and its applications to trust-based routing and intrusion detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2012, 9(2): 169–183. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2012.031912.110179 [33] DARGAHI T, JAVADI H H S, and SHAFIEI H. Securing underwater sensor networks against routing attacks[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2017, 96(2): 2585–2602. doi: 10.1007/s11277-017-4313-1 [34] MURGOD T R and SUNDARAM S M. Cluster based detection and reduction techniques to identify wormhole attacks in underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications (IJACSA), 2020, 11(7): 58–63. doi: 10.14569/IJACSA.2020.0110708 [35] HAN Guangjie, LIU Li, JIANG Jinfang, et al. A collaborative secure localization algorithm based on trust model in underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(2): 229. doi: 10.3390/s16020229 [36] DELCOURT M and LE BOUDEC J Y. TDOA source-localization technique robust to time-synchronization attacks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 16: 4249–4264. doi: 10.1109/tifs.2020.3001741 [37] XU Bo, LI Shengxin, RAZZAQI A A, et al. A novel measurement information anomaly detection method for cooperative localization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 3516918. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3077981 [38] ZHAO Haiyan, YAN Jing, LUO Xiaoyuan, et al. Privacy preserving solution for the asynchronous localization of underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2020, 7(6): 1511–1527. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2020.1003312 [39] MISRA S, OJHA T, and MADHUSOODHANAN P. SecRET: Secure range-based localization with evidence theory for underwater sensor networks[J]. ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive Systems, 2020, 15(1): 2. doi: 10.1145/3431390 [40] XU Ming, LIU Guangzhong, ZHU Daqi, et al. A cluster-based secure synchronization protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2014, 10(4): 398610. doi: 10.1155/2014/398610 [41] HU Fei, MALKAWI Y, KUMAR S, et al. Vertical and horizontal synchronization services with outlier detection in underwater acoustic networks[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2008, 8(9): 1165–1181. doi: 10.1002/wcm.559 [42] 李挺, 冯勇. 无线传感器网络安全路由研究综述[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2012, 29(12): 4412–4419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2012.12.003LI Ting and FENG Yong. Survey on secure routing research in wireless sensor networks[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2012, 29(12): 4412–4419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2012.12.003 [43] MENON V, MIDHUNCHAKKARAVARTHY D, JOHN S, et al. A secure and energy-efficient opportunistic routing protocol with void avoidance for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. Turkish Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences, 2020, 28(4): 2303–2315. doi: 10.3906/elk-2001-51 [44] BHARAMAGOUDRA M R and MANVI S S. Agent-based secure routing for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. International Journal of Communication Systems, 2017, 30(13): e3281. doi: 10.1002/dac.3281 [45] SAEED K, KHALIL W, AHMED S, et al. SEECR: Secure energy efficient and cooperative routing protocol for underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 107419–107433. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3000863 [46] NGUYEN N T, LE T T T, NGUYEN H H, et al. Energy-efficient clustering multi-hop routing protocol in a UWSN[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(2): 627. doi: 10.3390/s21020627 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
