Clustering and Relay Selection Method for Cellular Network-oriented D2D Multicast Communication
-
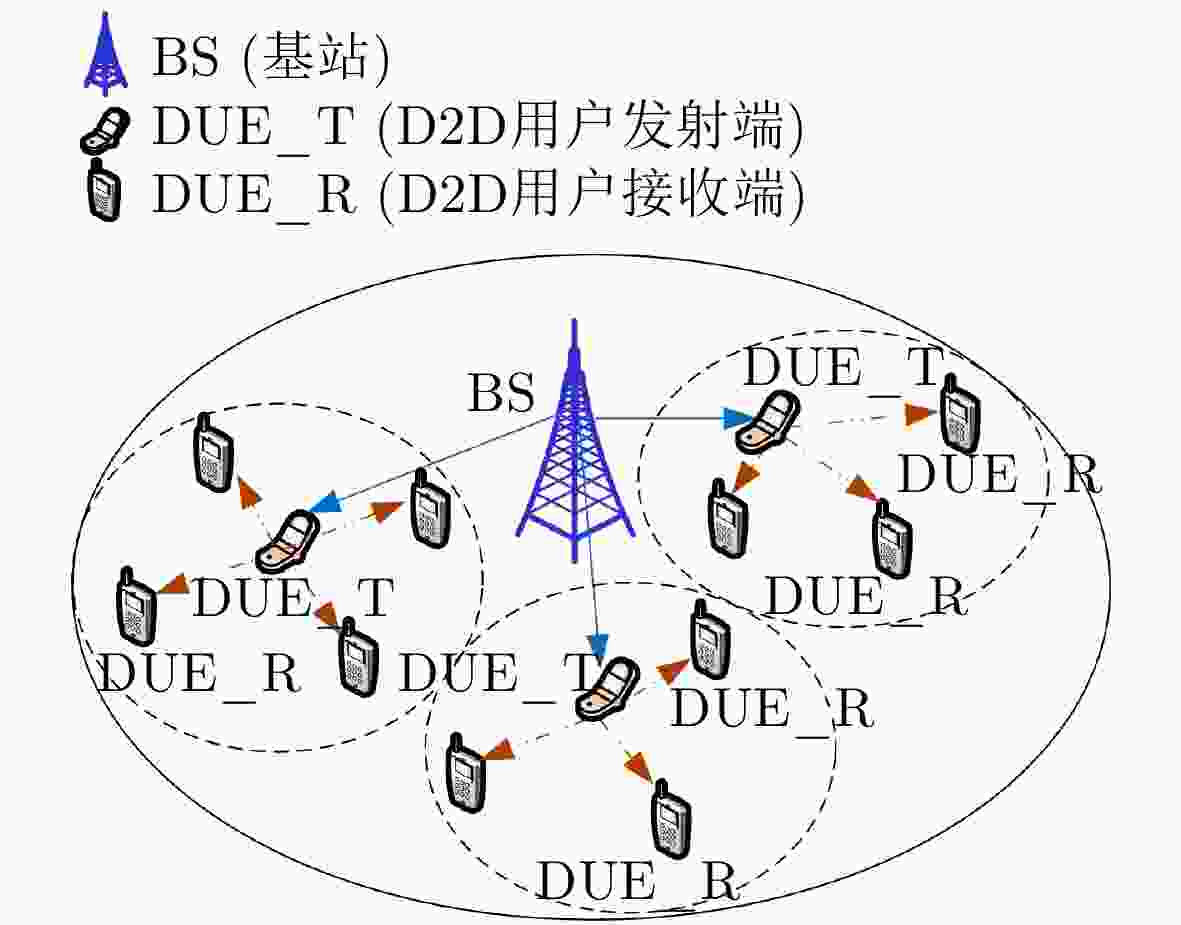
摘要: 传统蜂窝网络中,信道衰减的随机性和不确定性导致小区边缘用户的接收性能很差,尤其是面向视频传输等速率要求较高时其弊端更加凸显。D2D通信因其配置灵活性可作为传统蜂窝网络架构的有利补充,能有效改善边缘用户的性能。该文针对D2D通信的多播传输,分析了系统最小时延成本下的中继数量和分簇算法,提出一种基于分簇和中继选择的低时延D2D多播方案。该方案可以自适应选择多播重传中的中继的数量和中继节点到基站的距离,同时给出最优的带宽资源分配机制。仿真结果表明,与其他方案相比,所提方法能有效减少系统时延,提高边缘用户体验和系统性能。Abstract: In traditional cellular networks, the randomness and uncertainty of channel attenuation lead to poor reception performance for cell-edge users, especially for video transmission and other high-speed requirements, its drawbacks are more prominent. D2D (Device-to-Device) communication can be used as a beneficial supplement to the traditional cellular network architecture because of its configuration flexibility, and the performance of edge users can be improved effectively. Aiming at the multicast transmission of D2D communication, the number of relays and the clustering algorithm are analyzed under the minimum delay cost of the system, and a low-latency D2D multicast scheme is proposed based on clustering and relay selection. This scheme can adaptively select the number of relays in the multicast retransmission and the distance from the cluster center to the base station, and at the same time, it provides an optimal bandwidth resource allocation mechanism. The simulation results show that compared with other schemes, the proposed strategy can effectively reduce the system delay and improve the edge user experience and system performance.
-
Key words:
- Device-to-Device (D2D) /
- Multicast communication /
- Clustering
-
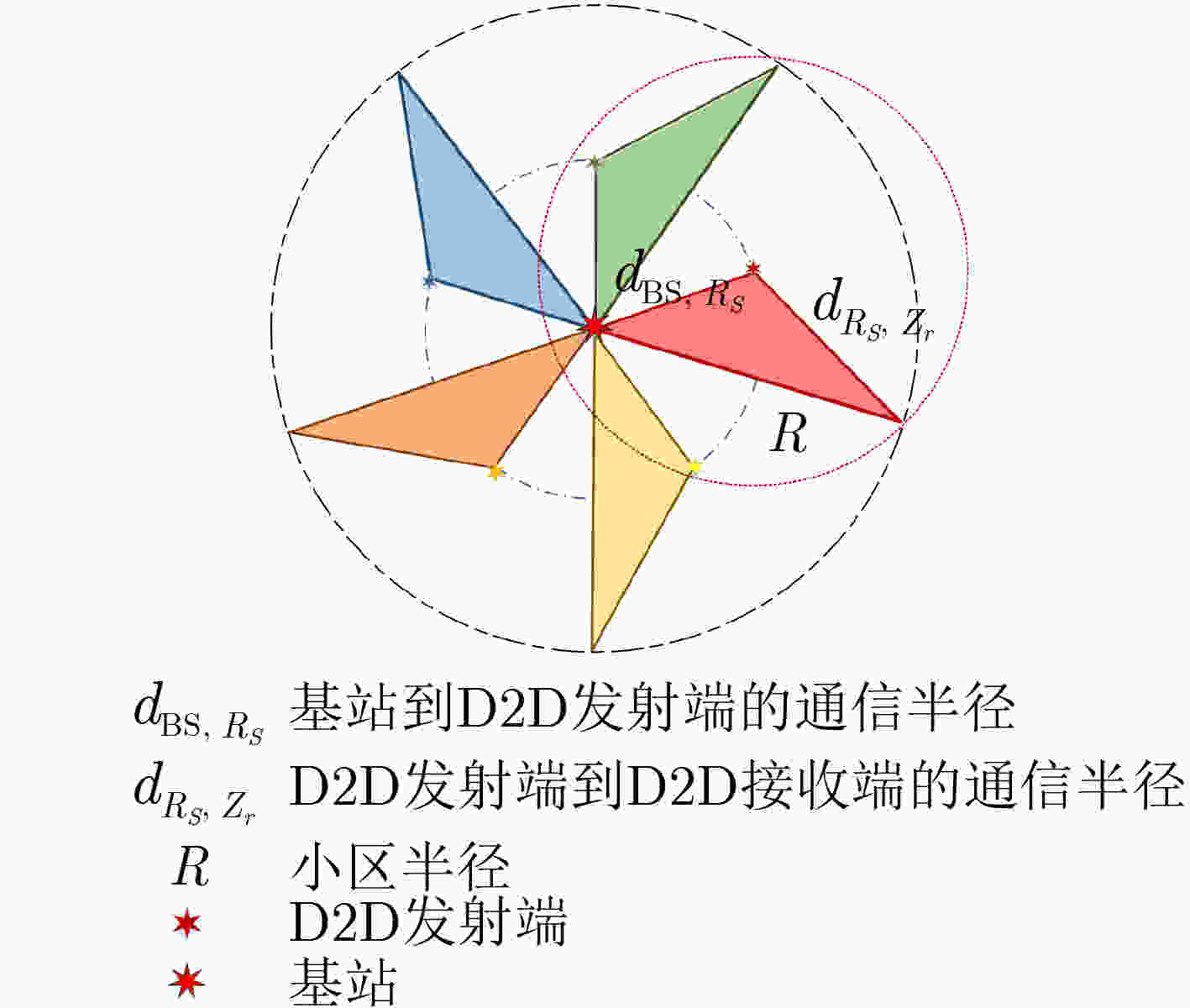
算法1 暴力搜索算法 输入:$ B $,$ {P_T} $,${P_{ {{\rm{BS}}} } }$,$ D $,$ \alpha $,$ N $,$ {n_0} $,$ R $ 输出:${d_{ {{\rm{BS}}} ,{R_s} } }$,$ S $ (1)初始化中继节点$ S $的取值范围$ S \in [{S_{\min }},{S_{\max }}] $; (2)for ${d_{ {{\rm{BS}}} ,{R_s} } } = 1$ to $ R $ (3) for $ S = {S_{\min }} $ to $ {S_{\max }} $ (4) 计算通信系统的总时延; (5) end for (6)end for (7)得到使系统总时延最小的$ S $和${d_{ {{\rm{BS}}} ,{R_s} } }$; 算法2 等角度分簇算法 输入:$ N $,$ S $,$ {d_{{\rm{BS}} ,{R_s}}} $,$ \varphi $ 输出:$ {b_{{R_s},{Z_r}}} $,$ {\text{cluster\_x(}}{R_s}{\text{)}} $,$ {\text{cluster\_y(}}{R_s}{\text{)}} $ (1)令$ s $和$ r $初始值为1,获取所有用户的位置信息,其横纵坐标分别表示为$ {\text{x\_user}}\left( i \right),{\text{y\_user}}\left( i \right),\forall i \in [1,N] $; (2)计算用户$ i $的夹角$\theta \_{{\rm{user}}} (i) = \arctan \dfrac{ {x\_{ {\rm{user} } } (i)} }{ { {\text{y} }\_{ {\rm{user} } } (i)} },\forall i \in [1,N]$; (3)for $ i = 1 $ to $ N $
(4) $ {\delta _i} \leftarrow \left| {\sqrt {{\text{x\_user}}{{(i)}^2} + {\text{y\_user}}{{(i)}^2}} - {d_{{\rm{BS}} ,{R_s}}}} \right| $;(5)end for (6)中继节点横坐标$ {\text{cluster\_x(}}{R_s}{\text{)}} \leftarrow {\text{x\_user}}(\arg \mathop {\min }\limits_i {\text{\{ }}{\delta _i}{\text{\} }},i{\text{ = (1,2,}}\cdots{\text{,}}N{\text{)}}) $; (7)中继节点纵坐标$ {\text{cluster\_y(}}{R_s}{\text{)}} \leftarrow {\text{y\_user}}(\arg \mathop {\min }\limits_i {\text{\{ }}{\delta _i}{\text{\} }},i{\text{ = (1,2,}}\cdots{\text{,}}N{\text{)}}) $; (8)中继节点的夹角$\omega = \dfrac{ { {\text{cluster\_x(} }{R_s}{\text{)} } } }{ { {\text{cluster\_y(} }{R_s}{\text{)} } } }$; (9)for $ i = 1 $ to $ N $ (10) if $\theta {\text{\_user(} }i{\text{)} } \in \left[\omega {\text{ - } }\dfrac{\varphi }{2},\omega {\text{ + } }\dfrac{\varphi }{2}\right]$ (11) then $ {Z_r} \leftarrow i $并将该用户依附于该中继节点,$ {b_{{R_s},{Z_r}}} = 1 $; (12) else $ {Z_r} \leftarrow i $,$ {b_{{R_s},{Z_r}}} = 0 $; (13) $ r \leftarrow r + 1 $; (14) end if (15)end for (16)for $ s = 2 $ to $ S $ (17) 第$ s $个理论中继节点的横纵坐标分别为
$ \begin{gathered} {\text{cluster\_x}}(s) = {d_{{\rm{BS}} ,{R_s}}} \cdot \sin [\omega + (s - 1) \cdot \varphi ], \\ {\text{cluster\_y}}(s) = {d_{{\rm{BS}} ,{R_s}}} \cdot \cos [\omega + (s - 1) \cdot \varphi ] \\ \end{gathered} $;(18) for $ i = 1 $ to $ N $
(19) $ {\delta _i} \leftarrow \left| {\sqrt {{\text{x\_user}}{{(i)}^2} + {\text{y\_user}}{{(i)}^2}} - \sqrt {{\text{cluster\_x}}{{(s)}^2} + {\text{cluster\_y}}{{(s)}^2}} } \right| $;(20) end for (21) 优化中继节点横坐标$ {\text{cluster\_x(}}{R_s}{\text{)}} \leftarrow {\text{x\_user}}(\arg \mathop {\min }\limits_i {\text{\{ }}{\delta _i}{\text{\} ,}}i{\text{ = (1,2,}}\cdots{\text{,}}N{\text{)}}) $; (22) 优化中继节点纵坐标$ {\text{cluster\_y(}}{R_s}{\text{)}} \leftarrow {\text{y\_user}}(\arg \mathop {\min }\limits_i {\text{\{ }}{\delta _i}{\text{\} ,}}i{\text{ = (1,2,}}\cdots{\text{,}}N{\text{)}}) $; (23) for $ i = 1 $ to $ N $
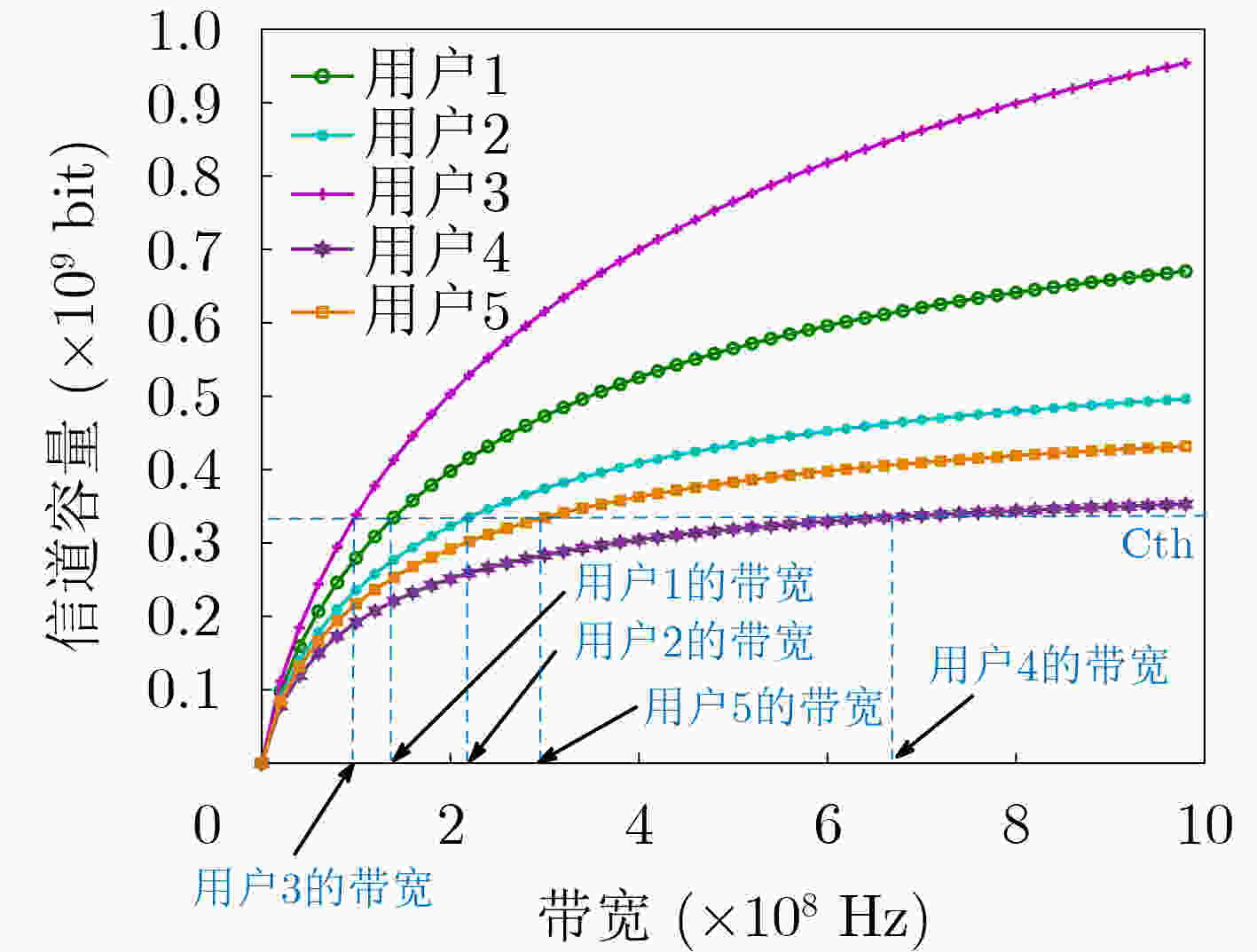
(24) if $\theta {\text{\_user(} }i{\text{)} } \in \left[\omega + s \cdot \varphi {\text{ - } }\dfrac{3}{2}\varphi ,\omega + s \cdot \varphi - \dfrac{\varphi }{2}\right]$(25) then$ {Z_r} \leftarrow i $并将该用户依附于该中继节点,$ {b_{{R_s},{Z_r}}} = 1 $; (26) else $ {Z_r} \leftarrow i $,$ {b_{{R_s},{Z_r}}} = 0 $; (27) $ r \leftarrow r + 1 $; (28) end if (29) end for (30)end for 算法3 自适应比例带宽分配算法 输入:$ {C_m} $, $ {b_{{R_s},{Z_r}}} $, $ S $, $ B $, $ \delta $ 输出:$ {M^*} $ (1)初始化步长$ j $和${C_{ {{\rm{th}}} } }$ (2)repeat (3) 根据香农公式和$ {C_{{th} }} $,利用二分法求解每个簇的带宽与系统
总带宽的比值$ {\lambda _{{R_s}}} $;(4) $ M \leftarrow \left\{ {{\lambda _{{R_1}}},{\lambda _{{R_2}}}, \cdots ,{\lambda _{{R_S}}}} \right\} $; (5) $ \mu \leftarrow {\lambda _{{R_1}}} + {\lambda _{{R_2}}} + \ldots + {\lambda _{{R_S}}} $; (6) if $ \mu > 1 $ then ${C_{{\rm{th}}} } \leftarrow {C_{{\rm{th}}} } - j \cdot \left| {\mu - 1} \right| \cdot B$; (7) else ${C_{{\rm{th}}} } \leftarrow {C_{{\rm{th}}} } + j \cdot \left| {\mu - 1} \right| \cdot B$; (8) end if (9)until $ \left| {1 - \mu } \right| < \delta $,其中$ \delta = {10^{ - 4}} $。 (10)if $ \mu > 1 $ (11) then $ \lambda _{{R_s}}^* \leftarrow {\lambda _l} - \left( {1 - \mu } \right) $ where $ l \leftarrow \mathop {\arg \max }\limits_{{R_s} \in A} {\lambda _{{R_s}}} $; (12)else $ \lambda _{{R_s}}^* \leftarrow {\lambda _l}{\text{ + }}\left( {1 - \mu } \right) $ where $ l \leftarrow \mathop {\arg \min }\limits_{{R_s} \in A} {\lambda _{{R_s}}} $; (13)end if (14)$ {M^*} \leftarrow \left\{ {\lambda _{{R_1}}^*,\lambda _{{R_2}}^*, \cdots ,\lambda _{{R_S}}^*} \right\} $。 算法4 本文算法 输入:$ B $, $ {P_T} $, ${P_{ {{\rm{\rm{BS}}}} } }$, $ D $, $ \alpha $, $ N $, $ {n_0} $, $ R $, $ A $, $ Z $ 输出:$ T $ (1)初始化阈值$\varDelta > 0$,并对$ {b_{{R_s},{Z_r}}} $进行0或1随机赋值; (2)repeat (3) 根据D2D用户依附关系$ {b_{{R_s},{Z_r}}} $,利用暴力搜索算法(算法1),解出使得系统总时延最小的$ {d_{{\rm{BS}} ,{R_s}}} $,簇数$ S $以及中继节点的横纵坐标
$ {\text{cluster\_x(}}{R_s}{\text{)}} $和$ {\text{cluster\_y(}}{R_s}{\text{)}} $;(4) 根据步骤(3)得到的$ {d_{{\rm{BS}} ,{R_s}}} $和$ S $利用等角度分簇算法(算法2)进行分簇并更新D2D用户依附关系$ b_{{R_s},{Z_r}}^\prime $, $ d_{{\rm{BS}} ,{R_s}}^\prime $以及中继节点的横纵坐
标$ {\text{cluster\_x(}}{R_s}{\text{)'}} $和$ {\text{cluster\_y(}}{R_s}{\text{)'}} $;(5) $ \delta \leftarrow \left| {d_{{\rm{BS}} ,{R_s}}^\prime - {d_{{\rm{BS}} ,{R_s}}}} \right| $; (6) until $\delta < \varDelta$; (7)输出最佳的D2D用户依附关系$ b_{{R_s},{Z_r}}^* $,中继节点的横纵坐标$ {\text{cluster\_x(}}{R_s}{{\text{)}}^*} $和$ {\text{cluster\_y(}}{R_s}{{\text{)}}^*} $以及$ d_{{\rm{\rm{BS}}} ,{R_s}}^* $; (8)根据步骤(7)得到的D2D用户依附关系$ b_{{R_s},{Z_r}}^* $,中继节点的横纵坐标$ {\text{cluster\_x(}}{R_s}{{\text{)}}^*} $和$ {\text{cluster\_y(}}{R_s}{{\text{)}}^*} $,利用等自适应带宽分配算法(算
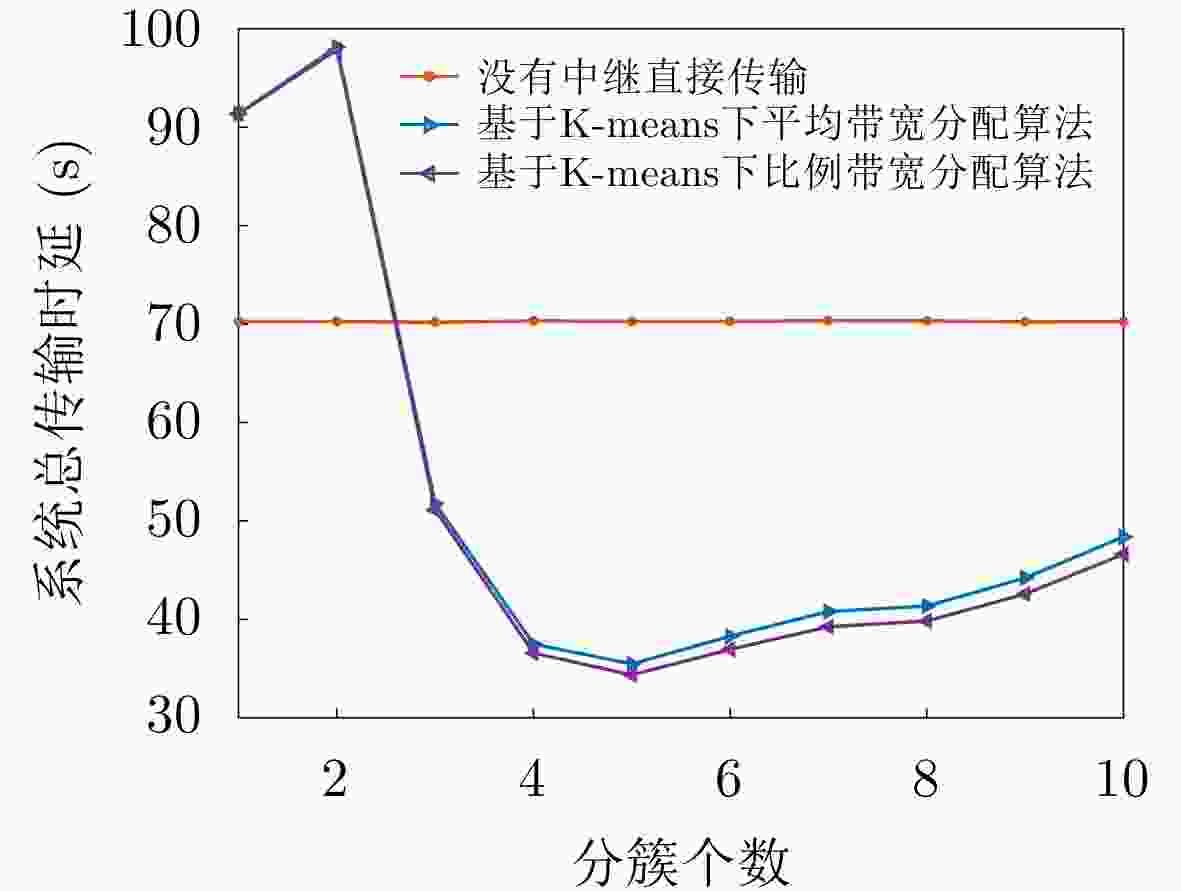
法3)求得每个簇的最佳带宽分配比例;(9)根据式(2)和式(6)计算求得通信系统的总时延$ T = {T_{{\text{\rm{BS}}},S}} + {T_D} $。 表 1 系统仿真参数
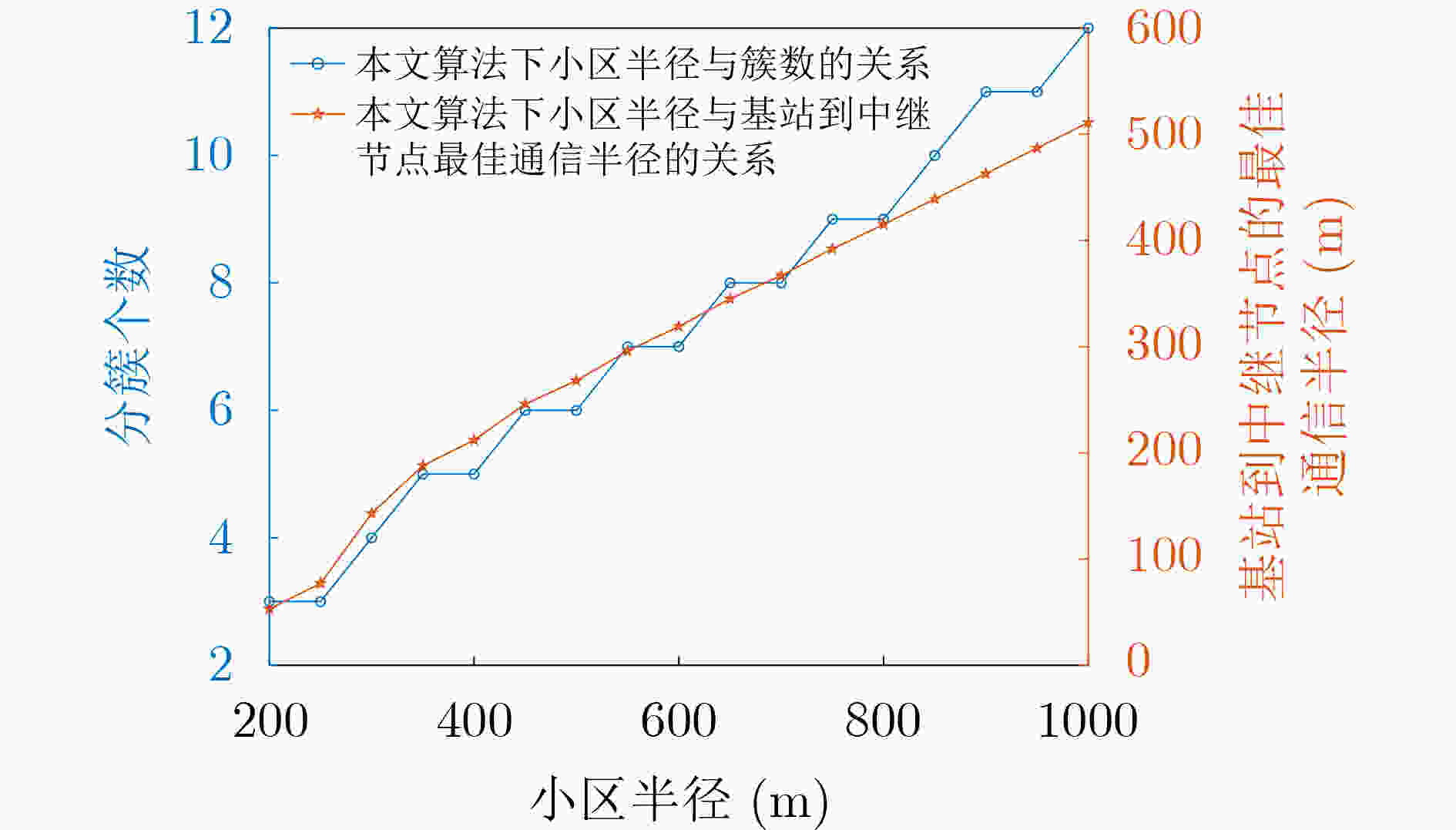
参数 数值 小区半径($ R $) 200~1000 m 数据包($ D $) 10 Mbit 热噪声功率($ {n_0} $) –144 dBm 信道带宽($ B $) 106 Hz 路损系数($ \alpha $) 4 用户数($ N $) 100~1000 基站发射功率(${P_{{\rm{BS}}} }$) 20~30 dBm D2D用户发射功率($ {P_T} $) 20~30 dBm -
[1] XU Yanli, LI Xujie, and ZHANG Jun. Device-to-device content delivery in cellular networks: Multicast or unicast[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(5): 4401–4414. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2787723 [2] LI Xujie, SUN Ying, ZHOU Siyuan, et al. User pairing scheme in mobility-aware D2D communication system[J]. IET Communications, 2020, 14(4): 655–664. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2019.0472 [3] WANG Xue, JIN Tao, HU Liangshuai, et al. Energy-efficient power allocation and Q-learning-based relay selection for relay-aided D2D communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(6): 6452–6462. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2985873 [4] 徐勇军, 谷博文, 杨洋, 等. 基于不完美CSI的D2D通信网络鲁棒能效资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2189–2198. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200587XU Yongjun, GU Bowen, YANG Yang, et al. Robust energy-efficient resource allocation algorithm in D2D communication networks with imperfect CSI[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2189–2198. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200587 [5] 曾孝平, 李诗琪, 杨凡, 等. D2D通信中一种基于非数据辅助误差适量幅度的同信道干扰控制方法及其性能分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(9): 2663–2671. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200473ZENG Xiaoping, LI Shiqi, YANG Fan, et al. NDA-EVM based co-channel interference control method and performance analysis in D2D communication[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(9): 2663–2671. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200473 [6] YANG Lianxin, WU Dan, CAI Yueming, et al. Learning-based user clustering and link allocation for content recommendation based on D2D multicast communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2020, 22(8): 2111–2125. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2019.2949434 [7] FENG Lei, YANG Zhixiang, YANG Yang, et al. Smart mode selection using online reinforcement learning for VR broadband broadcasting in D2D assisted 5G HetNets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2020, 66(2): 600–611. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2020.2977577 [8] SONG Wei. Analysis of a distance-based pairing scheme for collaborative content distribution via device-to-device communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(9): 9245–9256. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2930885 [9] 赵太飞, 林亚茹, 马倩文, 等. 无人机编队中无线紫外光隐秘通信的能耗均衡算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(12): 2969–2975. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190965ZHAO Taifei, LIN Yaru, MA Qianwen, et al. Energy balance algorithm for wireless ultraviolet secret communication in UAV formation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(12): 2969–2975. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190965 [10] JABI M, PEDERSOLI M, MITICHE A, et al. Deep clustering: On the link between discriminative models and K-means[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(6): 1887–1896. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2962683 [11] WANG Lichun and CHENG S H. Data-driven resource management for ultra-dense small cells: An affinity propagation clustering approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2019, 6(3): 267–279. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2018.2842113 [12] 梁彦霞, 姜静, 孙长印, 等. 超密集组网下一种基于干扰增量降低的分簇算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 495–502. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181144LIANG Yanxia, JIANG Jing, SUN Changyin, et al. A cluster algorithm based on interference increment reduction in ultra-dense network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 495–502. doi: 10.11999/JEIT181144 [13] SOOR S, CHALLA A, DANDA S, et al. Iterated watersheds, a connected variation of K-means for clustering GIS data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2021, 9(2): 626–636. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2019.2910147 [14] KHAN I, LUO Zongwei, HUANG J Z, et al. Variable weighting in fuzzy k-means clustering to determine the number of clusters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2020, 32(9): 1838–1853. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2019.2911582 -





 下载:
下载:
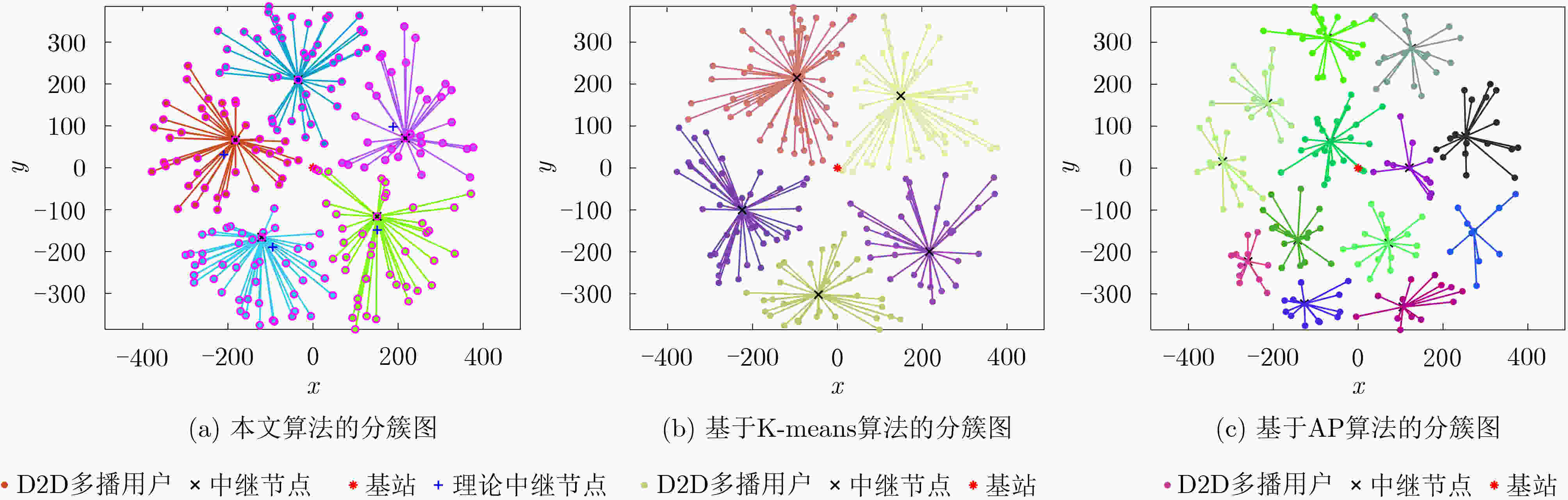
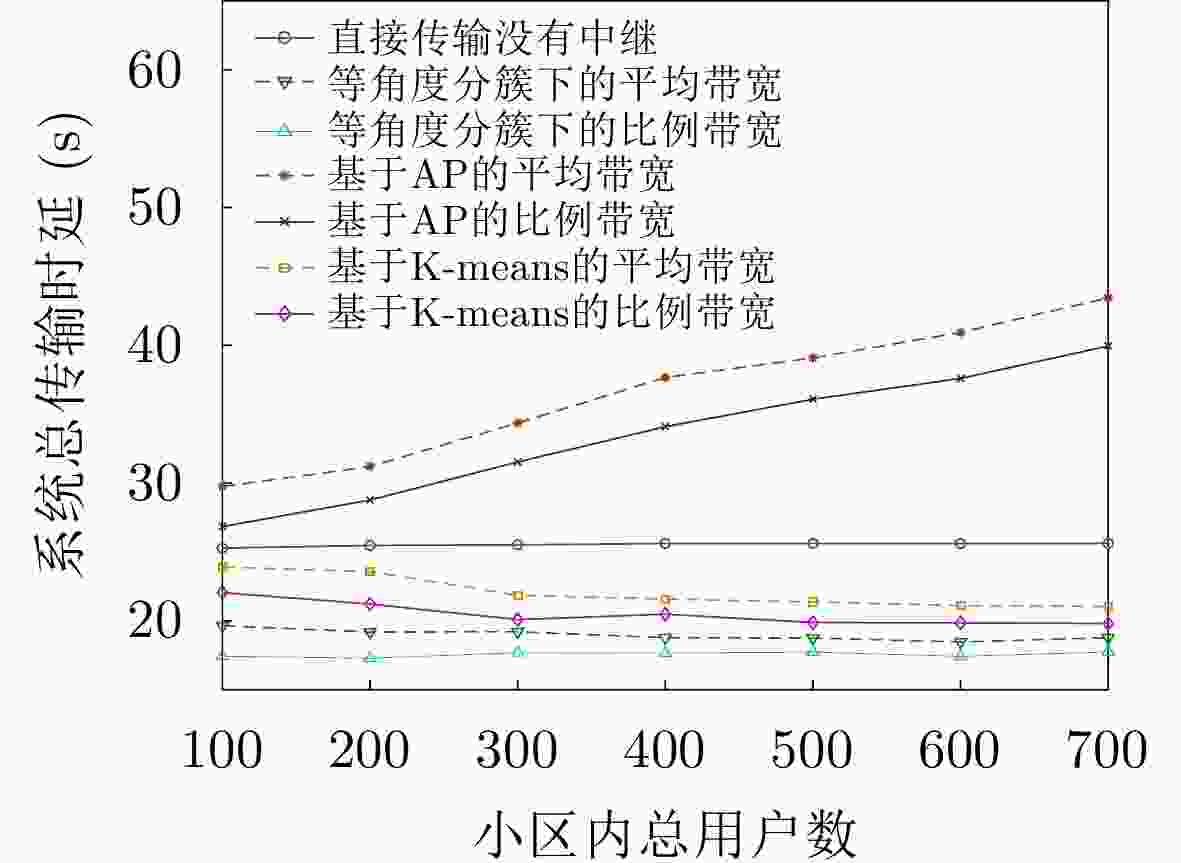
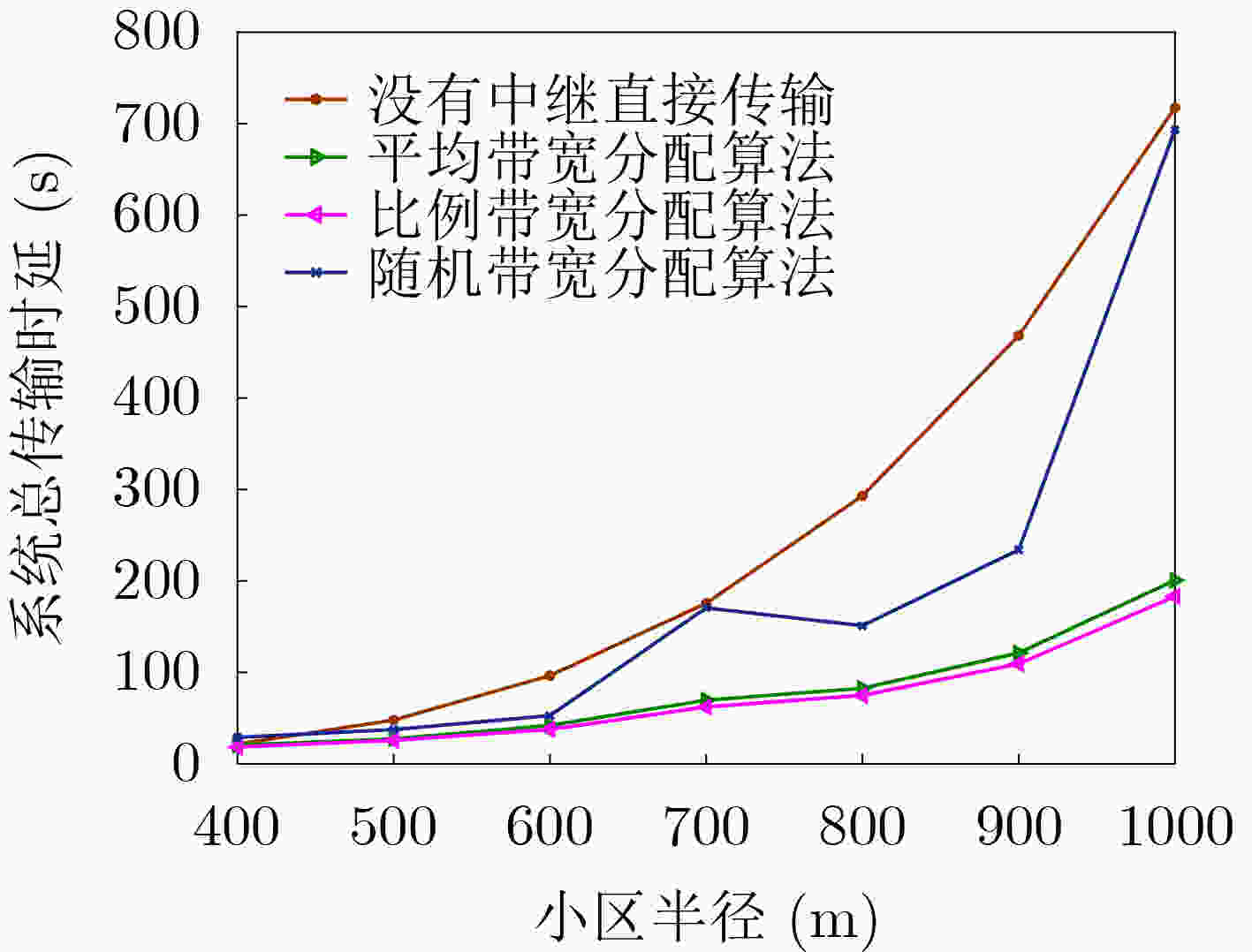
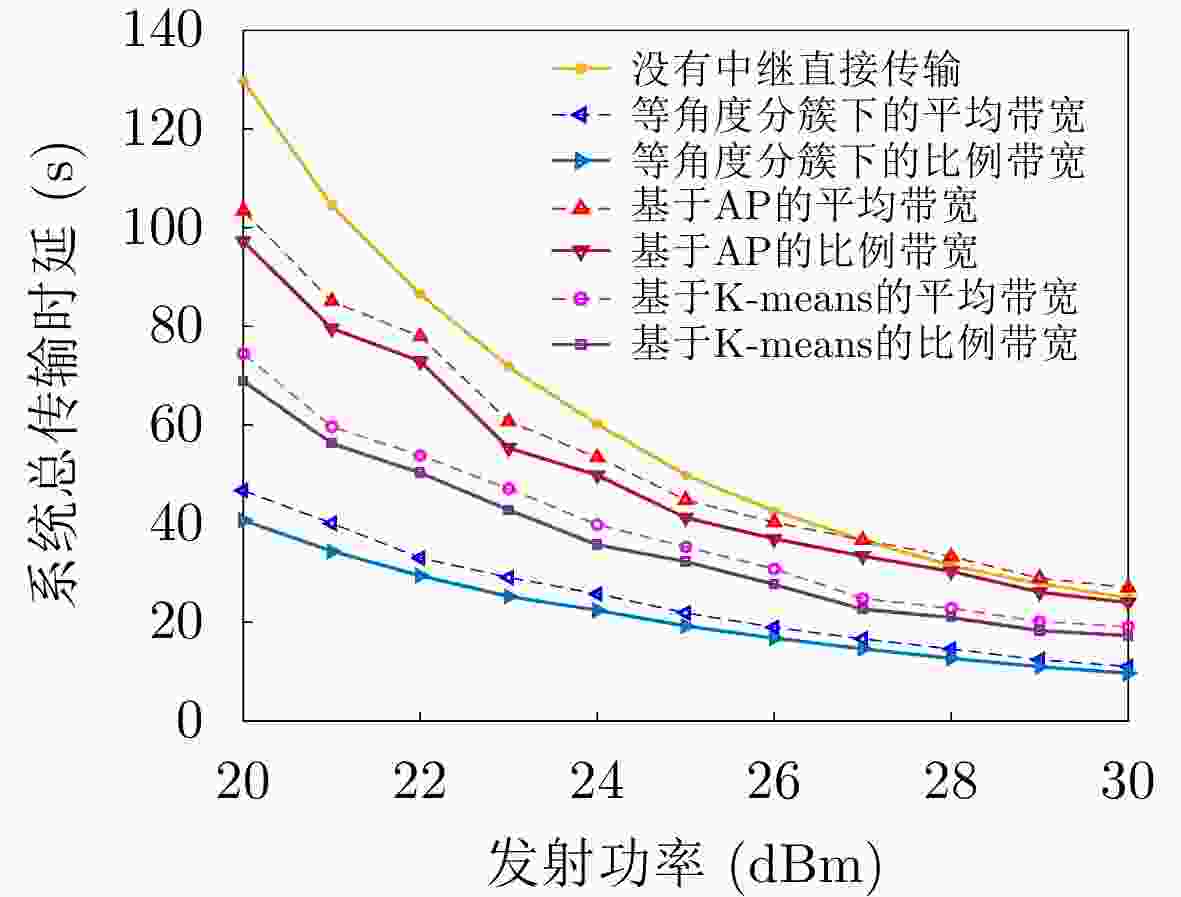


 下载:
下载:
