Deep Compressive Sensing Image Reconstruction Network Based on Non-Local Prior
-
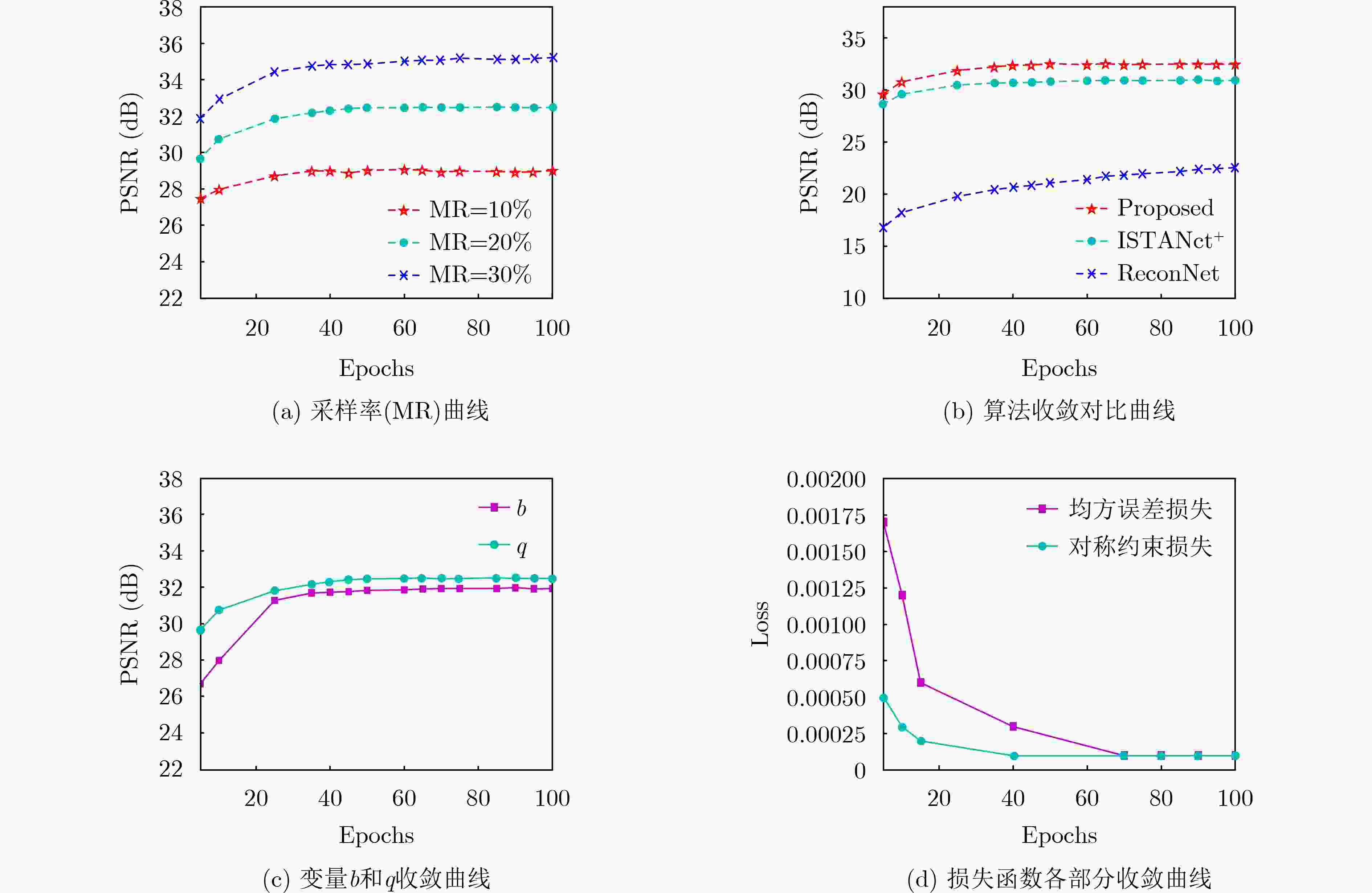
摘要: 传统的基于迭代的压缩感知(CS)图像重构算法易于集成图像先验信息,但存在性能不足、计算复杂度高等缺点。基于深度学习的图像重构算法重构性能通常优于传统的重构算法,并且具有更低的重构计算成本。因此,为了设计出一种更有效利用先验信息的深度学习图像重构算法,该文提出基于非局部先验的深度压缩感知图像重构网络。首先,将稀疏性和非局部先验相结合建立压缩感知图像重构模型,然后通过半二次方分裂法将模型分解为3个子问题,每一个子问题的求解都在深度学习的框架下展开,最后联合建立端到端的可训练的图像重构模型。仿真实验表明,在测试的采样率与数据集下该文所提算法的峰值信噪比与当前主流的重构算法SCSNet相比平均提升了0.18 dB,与CSNet算法相比平均提升了约1.59 dB,与ISTA-Net+算法相比平均提升了约2.09 dB。Abstract: The traditional iterative-based Compressive Sensing (CS) image reconstruction algorithm is easy to integrate image prior information, but it has shortcomings such as insufficient performance and high computational complexity. The performance of the image reconstruction algorithm based on deep learning is better than the traditional reconstruction algorithm significantly, and it has lower time cost. Therefore, in order to design a deep learning image reconstruction algorithm that uses prior information more effectively, a deep compressive sensing image reconstruction network based on non-local priors is proposed. Firstly, the sparseness and non-local prior are combined to establish a compressed sensing image reconstruction model. Secondly, the model is decomposed into three sub-problems by the half quadratic splitting method. The solution of each sub-problem is carried out under the framework of deep learning. Finally, an end-to-end trainable image reconstruction model is jointly established. Simulation experiments show that the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the proposed algorithm under the tested sampling rate and dataset is improved by 0.18 dB, 1.59 dB, 2.09 dB on average compared with the current mainstream reconstruction algorithm SCSNet, CSNet, ISTA-Net+ respectively.
-
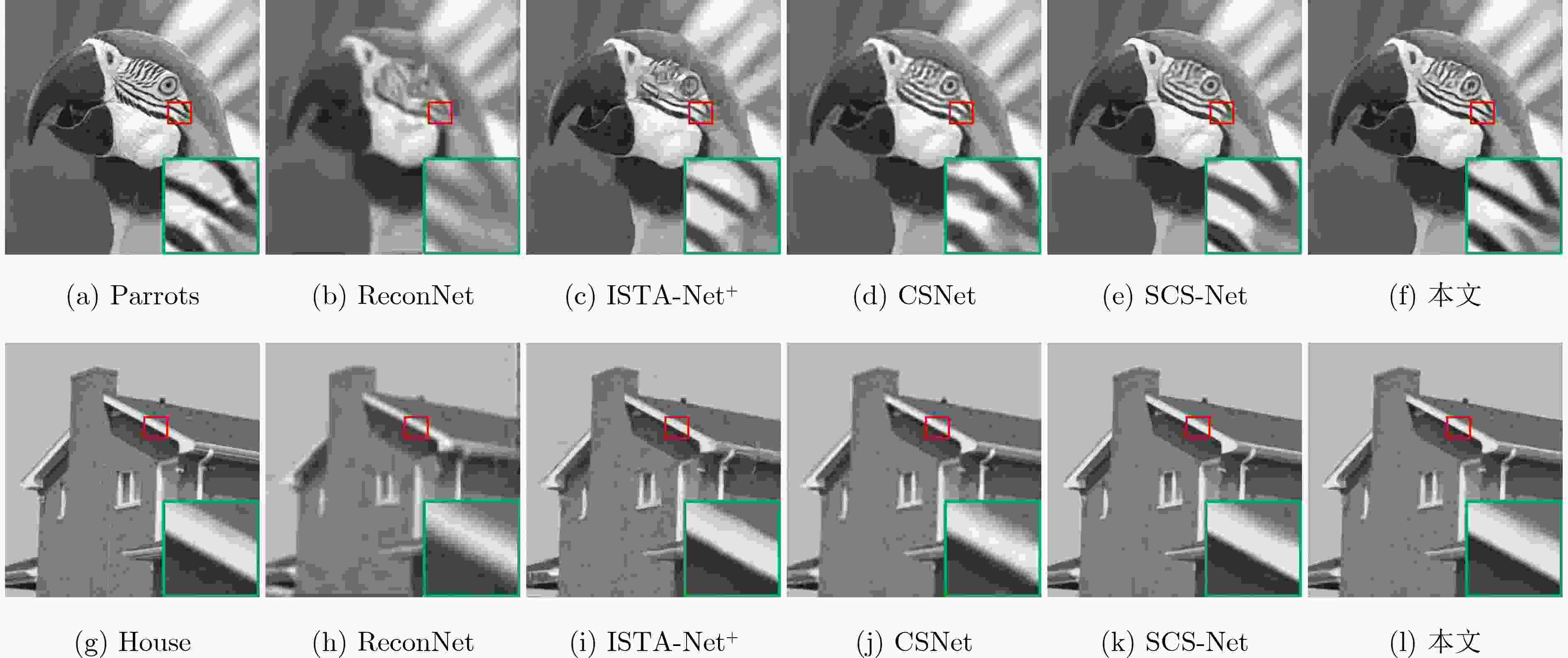
表 1 不同图像下各种重构算法的PSNR(dB)对比
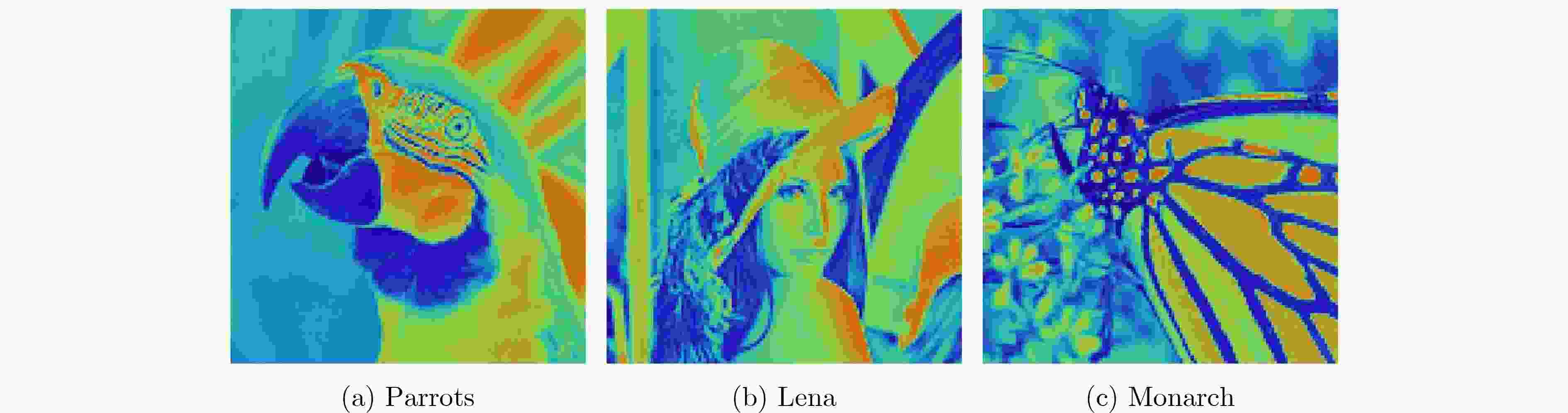
采样率(%) 算法 Monarch House Barbara Lena Parrots Peppers Boats Cameraman 10 ReconNet 21.51 26.69 22.50 24.47 23.23 22.67 24.15 21.66 CSNet 26.73 31.68 24.24 28.57 27.40 26.66 28.80 24.92 ISTA-Net+ 25.72 30.49 23.52 27.50 26.37 27.13 27.41 23.76 SCSNet 28.88 32.69 24.43 29.29 28.10 28.22 30.11 25.71 本文 28.97 33.02 24.51 29.47 28.95 29.12 30.04 26.18 20 ReconNet 22.89 27.95 22.87 25.39 24.56 24.04 25.98 22.64 CSNet 29.57 33.42 24.98 30.75 29.77 28.42 30.97 26.79 ISTA-Net+ 31.01 34.99 26.78 31.14 29.96 32.45 31.91 27.65 SCSNet 32.86 35.55 26.84 32.36 31.29 31.87 33.57 28.53 本文 32.88 36.40 27.14 32.76 32.16 33.64 33.76 29.10 30 ReconNet 29.21 33.61 25.65 33.74 26.88 29.77 30.20 26.90 CSNet 32.58 36.47 28.38 33.35 32.87 30.75 33.21 28.64 ISTA-Net+ 34.80 37.07 30.13 33.45 32.91 35.54 35.22 30.35 SCSNet 35.58 37.92 31.43 35.22 34.13 34.50 36.30 30.65 本文 35.65 38.04 31.32 35.25 35.07 36.00 36.76 31.43 表 2 不同数据集下各种重构算法的PSNR(dB)对比
采样率(%) 数据集 ReconNet CSNet ISTA-Net+ SCS-Net 本文 10 Set5 24.31 31.54 28.61 32.77 31.70 Set11 22.45 27.37 26.49 28.48 29.01 BSD68 23.62 27.59 25.85 27.28 28.13 平均 23.46 28.83 26.98 29.51 29.61 20 Set5 26.51 34.54 32.72 36.15 35.04 Set11 24.44 29.33 30.80 31.82 32.49 BSD68 25.12 29.51 29.03 29.79 30.96 平均 25.36 31.13 30.85 32.59 32.83 30 Set5 27.78 36.69 35.45 38.45 37.24 Set11 25.74 30.98 33.70 34.62 35.12 BSD68 26.27 31.01 31.47 31.87 33.20 平均 26.60 32.89 33.54 34.98 35.19 平均 25.14 30.95 30.46 32.36 32.54 -
[1] CANDÈS E J, WAKIN M B, and BOYD S P. Enhancing sparsity by reweighted ℓ1 minimization[J]. Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 2008, 14(5/6): 877–905. doi: 10.1007/s00041-008-9045-x [2] DONOHO D L. Compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289–1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [3] BARANIUK R G, CANDÈS E, NOWAK R, et al. compressive sampling[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(2): 1433–1452. doi: 10.4171/022 [4] SHI Wuzhen, LIU Shaohui, JIANG Feng, et al. Video compressed sensing using a convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(2): 425–438. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2020.2978703 [5] ROGERS C A and POPESCU D C. Compressed sensing MIMO radar system for extended target detection[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(1): 1381–1389. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.3000500 [6] KUMAR P A, GUNASUNDARI R, and AARTHI R. Systematic analysis and review of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) reconstruction techniques[J]. Current Medical Imaging, 2021, 17(8): 943–955. doi: 10.2174/1573405616666210105125542 [7] DENG Jun, REN Guanghui, JIN Yansheng, et al. Iterative weighted gradient projection for sparse reconstruction[J]. Information Technology Journal, 2011, 10(7): 1409–1414. doi: 10.3923/itj.2011.1409.1414 [8] JI Shihao, XUE Ya, and CARIN L. Bayesian compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(6): 2346–2356. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2007.914345 [9] MALLAT S G and ZHANG Zhifeng. Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1993, 41(12): 3397–3415. doi: 10.1109/78.258082 [10] QIN Jing, LI Shuang, NEEDELL D, et al. Stochastic greedy algorithms for multiple measurement vectors[J]. Inverse Problems and Imaging, 2021, 15(1): 79–107. doi: 10.3934/ipi.2020066 [11] LIU Jiahao, WU Qisong, and AMIN M G. Multi-Task Bayesian compressive sensing exploiting signal structures[J]. Signal Processing, 2021, 178: 107804. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2020.107804 [12] ABDELHAY M A, KORANY N O, and EL-KHAMY S E. Synthesis of uniformly weighted sparse concentric ring arrays based on off-grid compressive sensing framework[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2021, 20(4): 448–452. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2021.3052174 [13] GONG Yu, XIAO Shaoqiu, ZHENG Yu, et al. Synthesis of multiple-pattern planar arrays by the multitask Bayesian compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2021, 20(8): 1587–1591. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2021.3091613 [14] DONG Weisheng, SHI Guangming, LI Xin, et al. Compressive sensing via nonlocal low-rank regularization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(8): 3618–3632. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2329449 [15] FRIEDLAND S, LI Qun, and SCHONFELD D. Compressive sensing of sparse tensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(10): 4438–4447. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2348796 [16] ZHANG Jian, ZHAO Debin, and GAO Wen. Group-based sparse representation for image restoration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(8): 3336–3351. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2323127 [17] MOUSAVI A, PATEL A B, and BARANIUK R G. A deep learning approach to structured signal recovery[C]. 2015 53rd Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing (Allerton), Monticello, USA, 2015: 1336–1343. [18] KULKARNI K, LOHIT S, TURAGA P, et al. ReconNet: Non-iterative reconstruction of images from compressively sensed measurements[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 449–458. [19] YAO Hantao, DAI Feng, ZHANG Shiliang, et al. DR2-Net: Deep residual reconstruction network for image compressive sensing[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 359: 483–493. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.05.006 [20] SHI Wuzhen, JIANG Feng, LIU Shaohui, et al. Image compressed sensing using convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 375–388. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2928136 [21] SHI Wuzhen, JIANG Feng, LIU Shaohui, et al. Scalable convolutional neural network for image compressed sensing[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, USA, 2019: 12282–12291. [22] ZHANG Jian and GHANEM B. ISTA-Net: Interpretable optimization-inspired deep network for image compressive sensing[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 1828–1837. [23] ZHANG Jian, ZHAO Chen, and GAO Wen. Optimization-inspired compact deep compressive sensing[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2020, 14(4): 765–774. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2020.2977507 [24] CHEN Chen, TRAMEL E W, and FOWLER J E. Compressed-sensing recovery of images and video using multihypothesis predictions[C]. 2011 Conference Record of the Forty Fifth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ASILOMAR), Pacific Grove, USA, 2011: 1193–1198. [25] MUN S and FOWLER J E. Residual reconstruction for block-based compressed sensing of video[C]. 2011 Data Compression Conference, Snowbird, USA, 2011: 183–192. [26] 唐述, 谢显中. 多正则化混合约束的模糊图像盲复原方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(4): 770–776. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140949TANG Shu and XIE Xianzhong. Multi-regularization hybrid constraints method for blind image restoration[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(4): 770–776. doi: 10.11999/JEIT140949 [27] SHI Wenzhe, CABALLERO J, HUSZÁR F, et al. Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1874–1883. [28] WANG Xiaolong, GIRSHICK R, GUPTA A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]. The 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, USA, 2018: 7794–7803. [29] BEVILACQUA M, ROUMY A, GUILLEMOT C, et al. Low-complexity single-image super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbor embedding[C]. British Machine Vision Conference, Surrey, UK, 2012: 135. [30] MARTIN D, FOWLKES C, TAL D, et al. A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics[C]. Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. ICCV 2001, Vancouver, Canada, 2001: 416–423 -





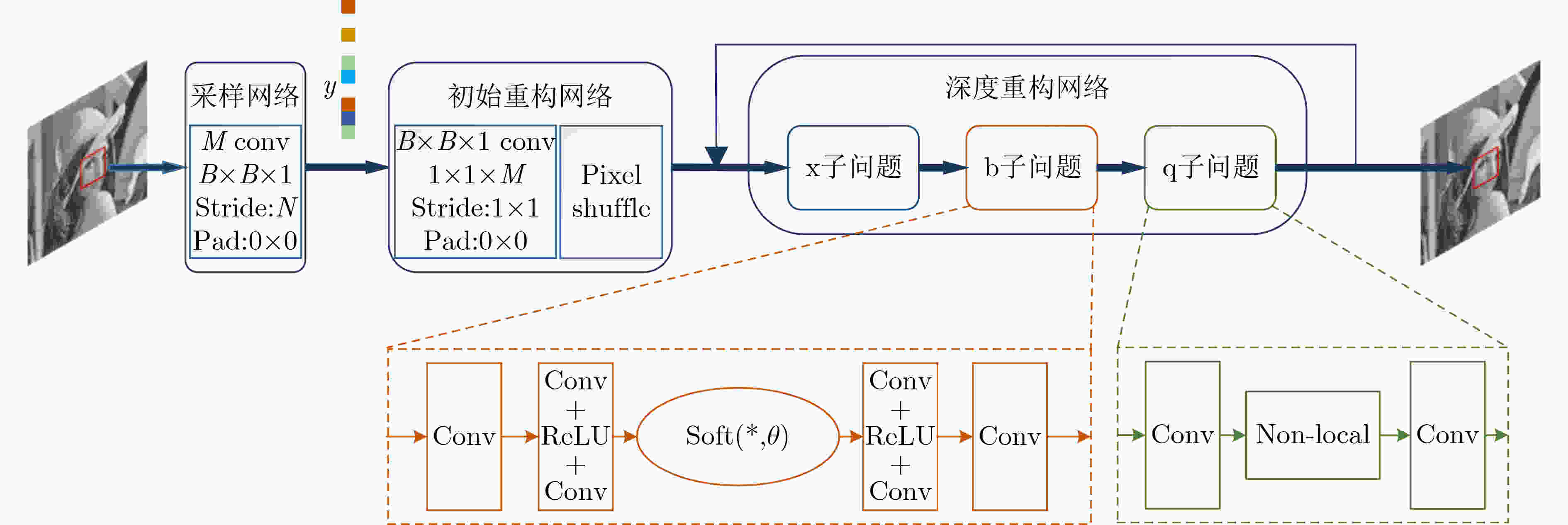
 下载:
下载:

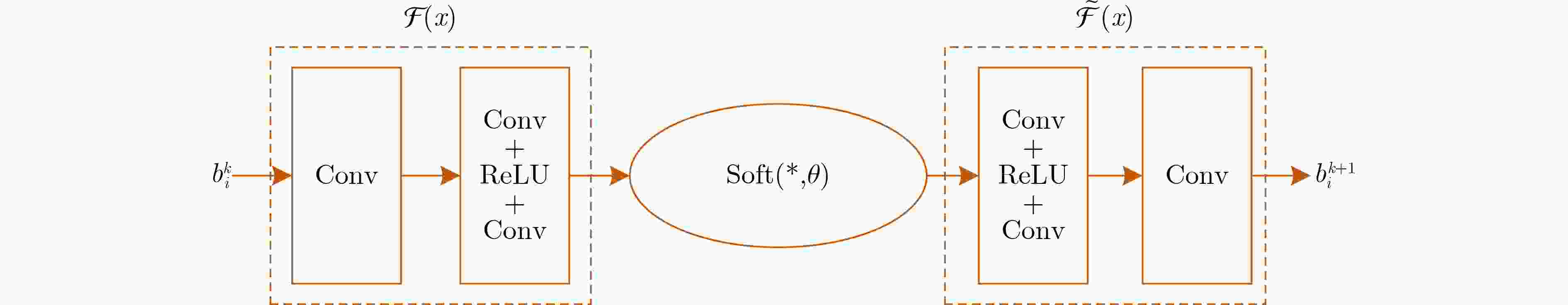
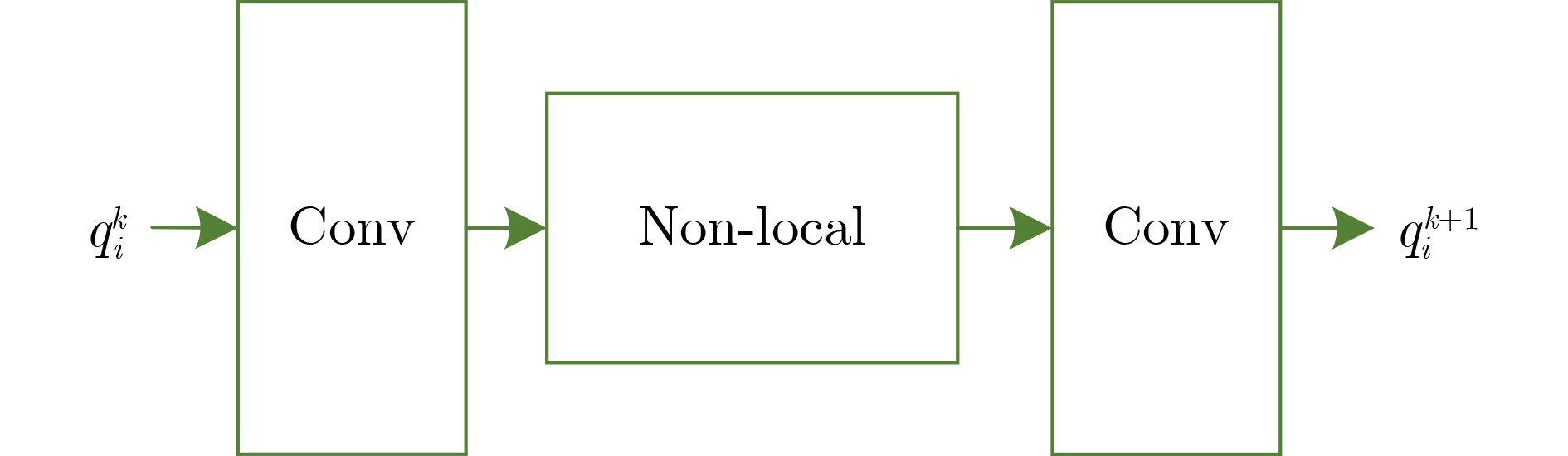
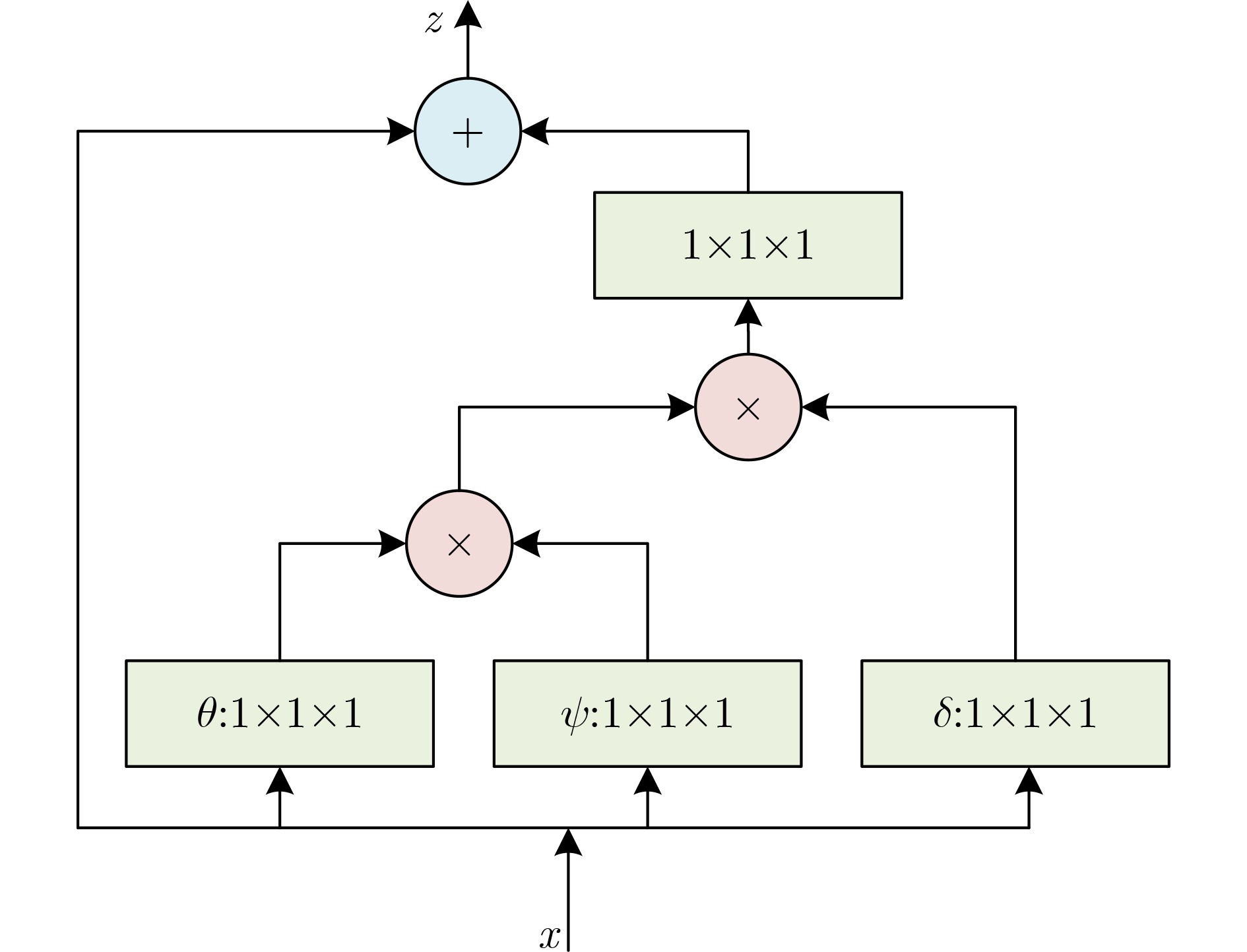





 下载:
下载:
