Low-altitude Wind Shear Wind Speed Estimation Method Based on GAMP-STAP in Complex Terrain Environment
-
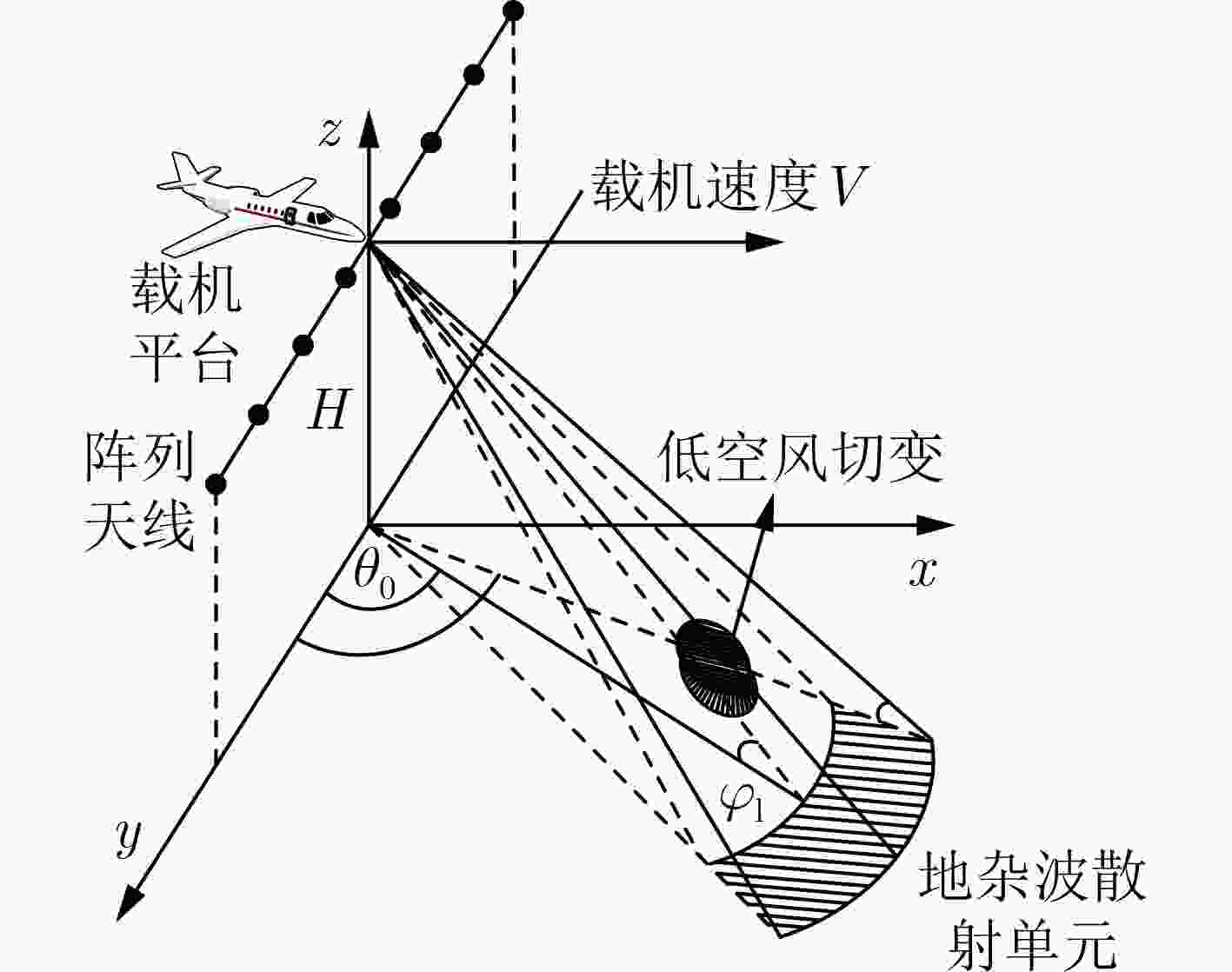
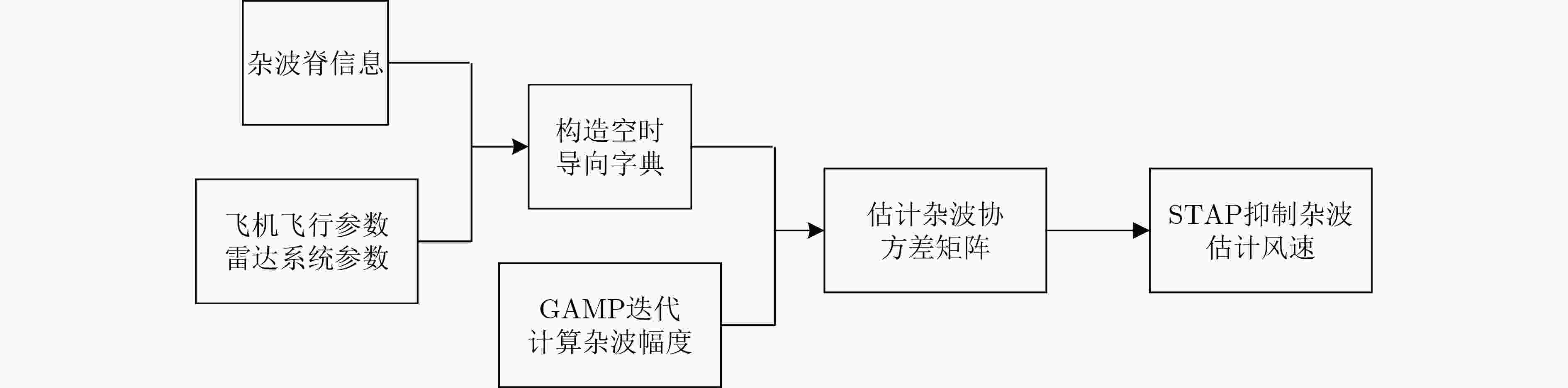
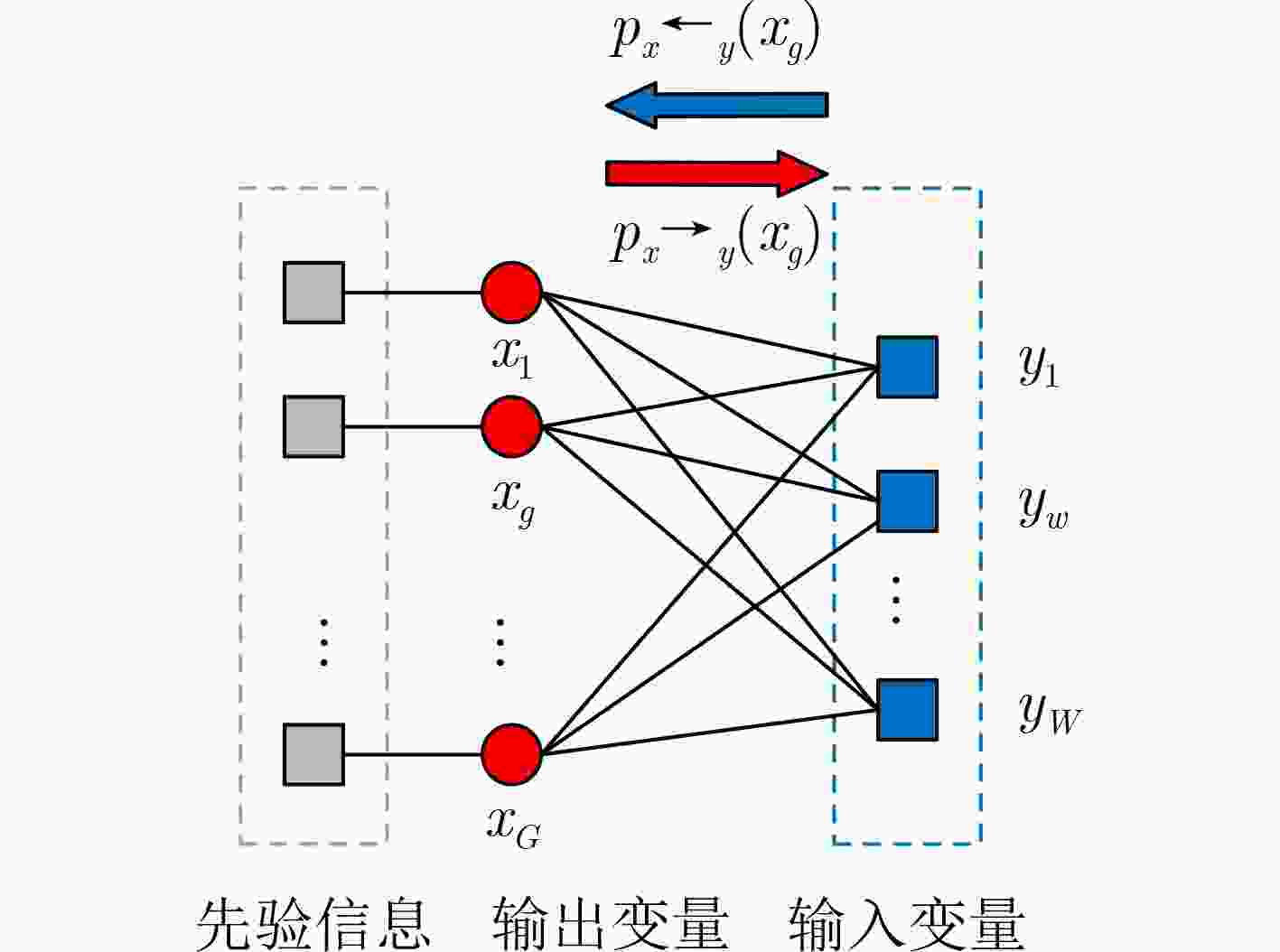
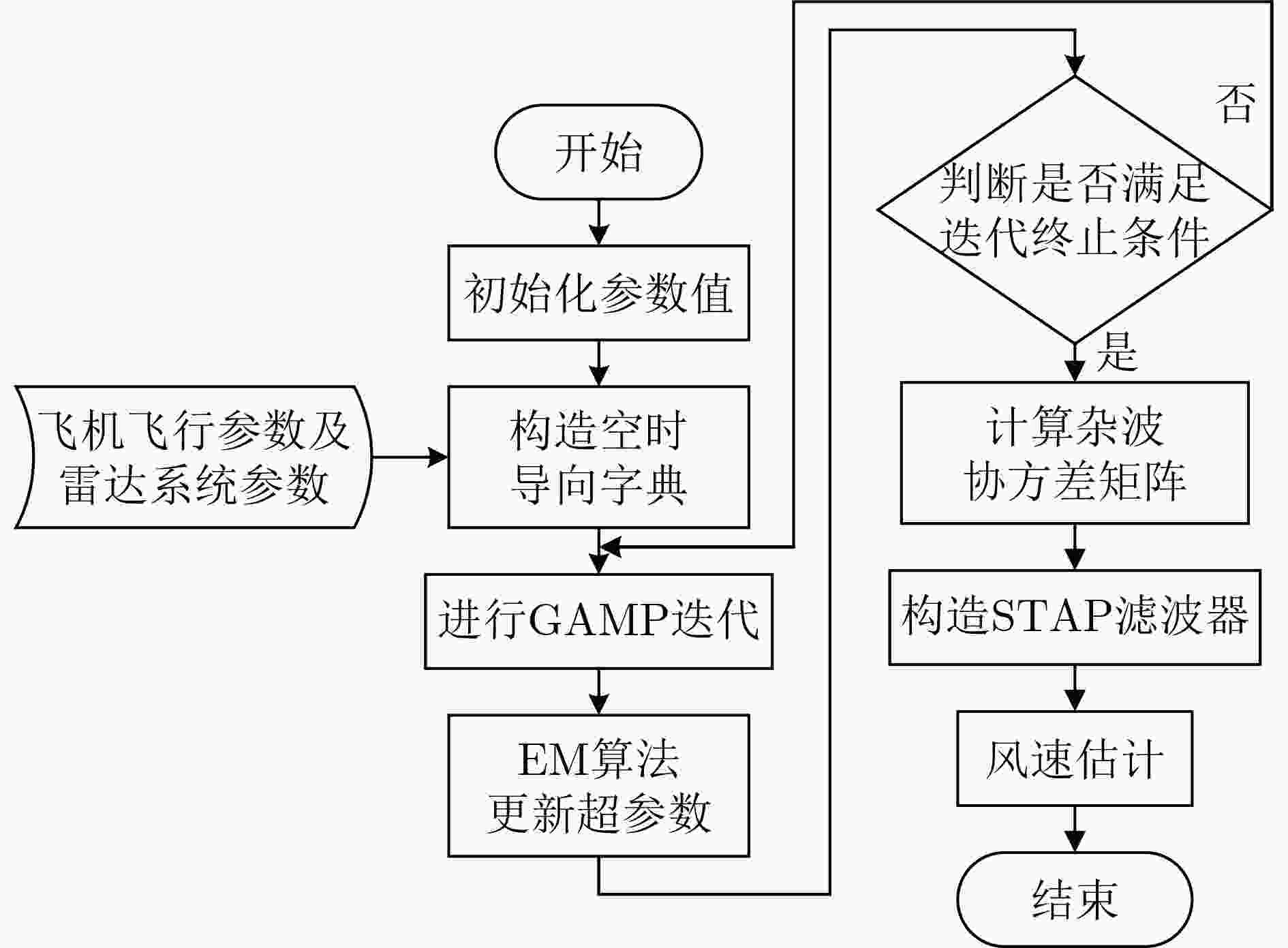
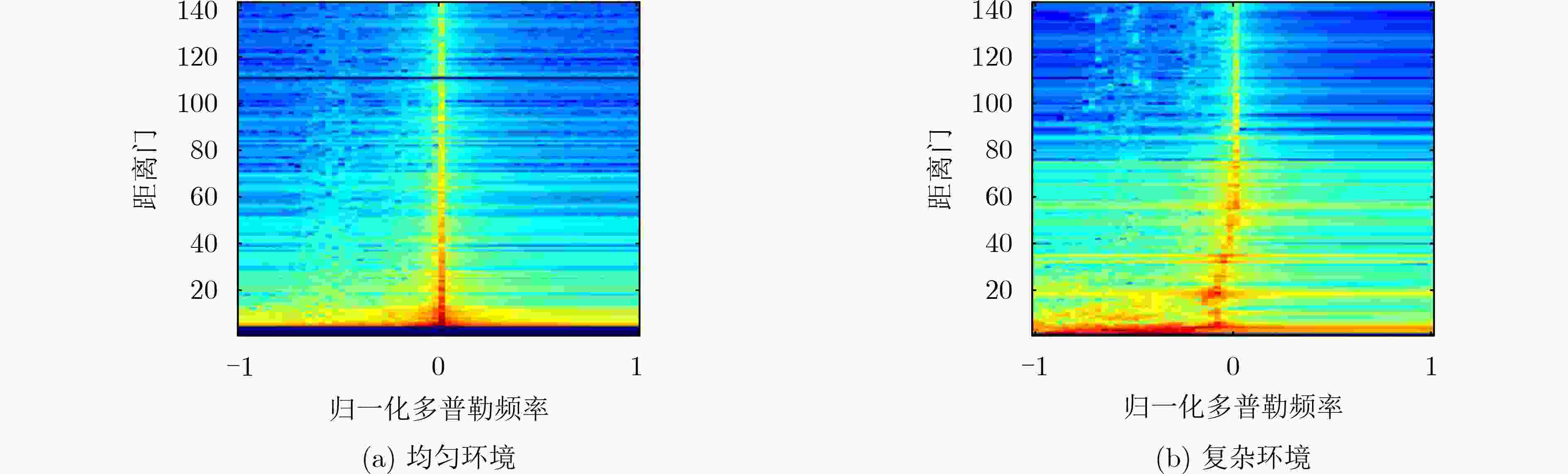
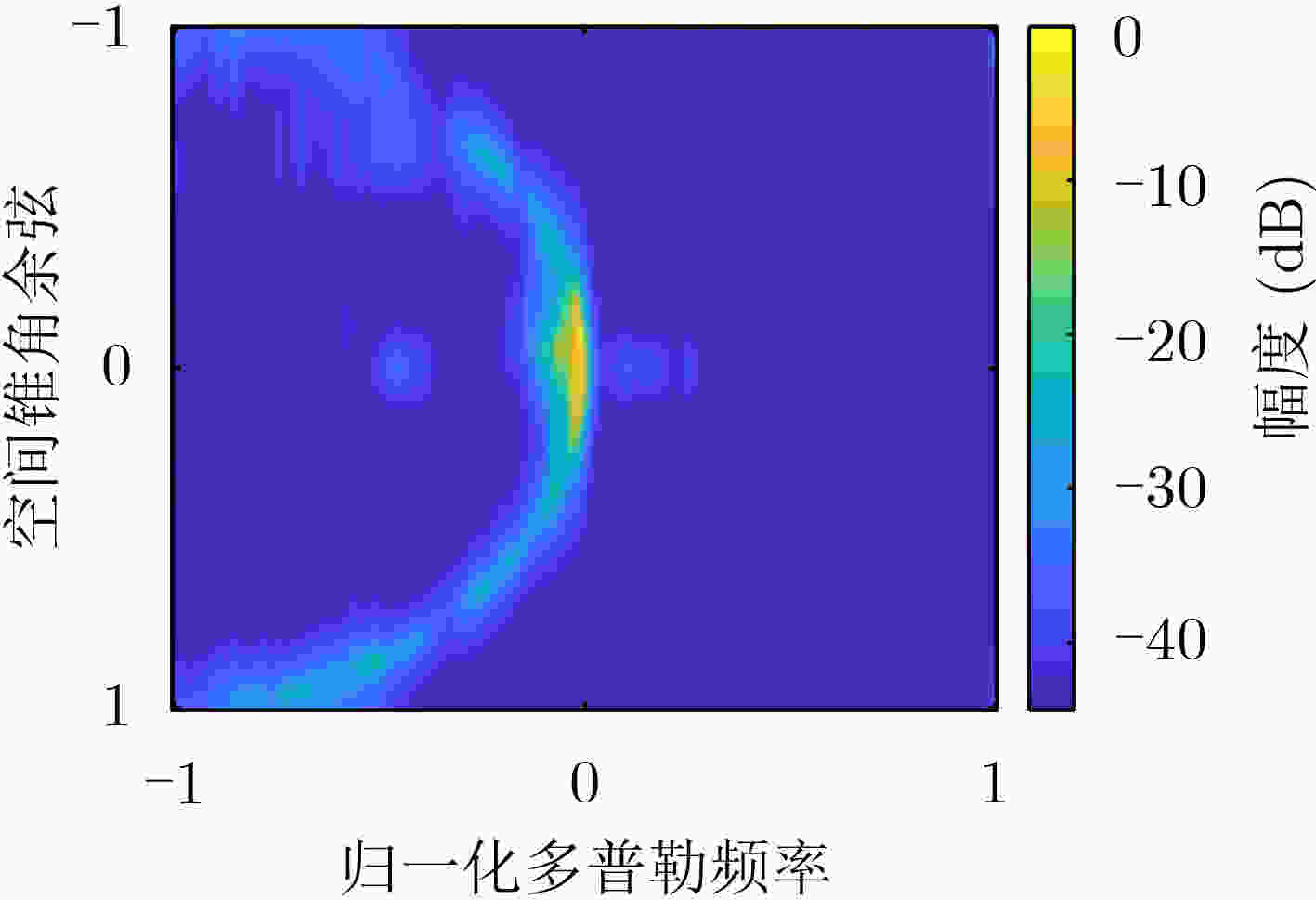
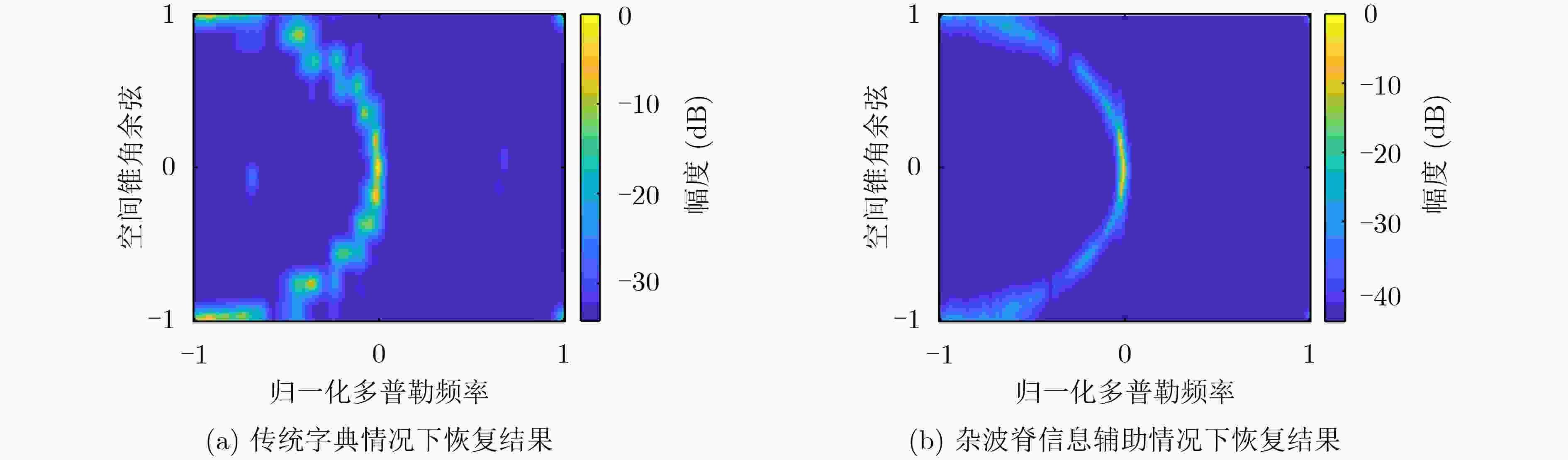
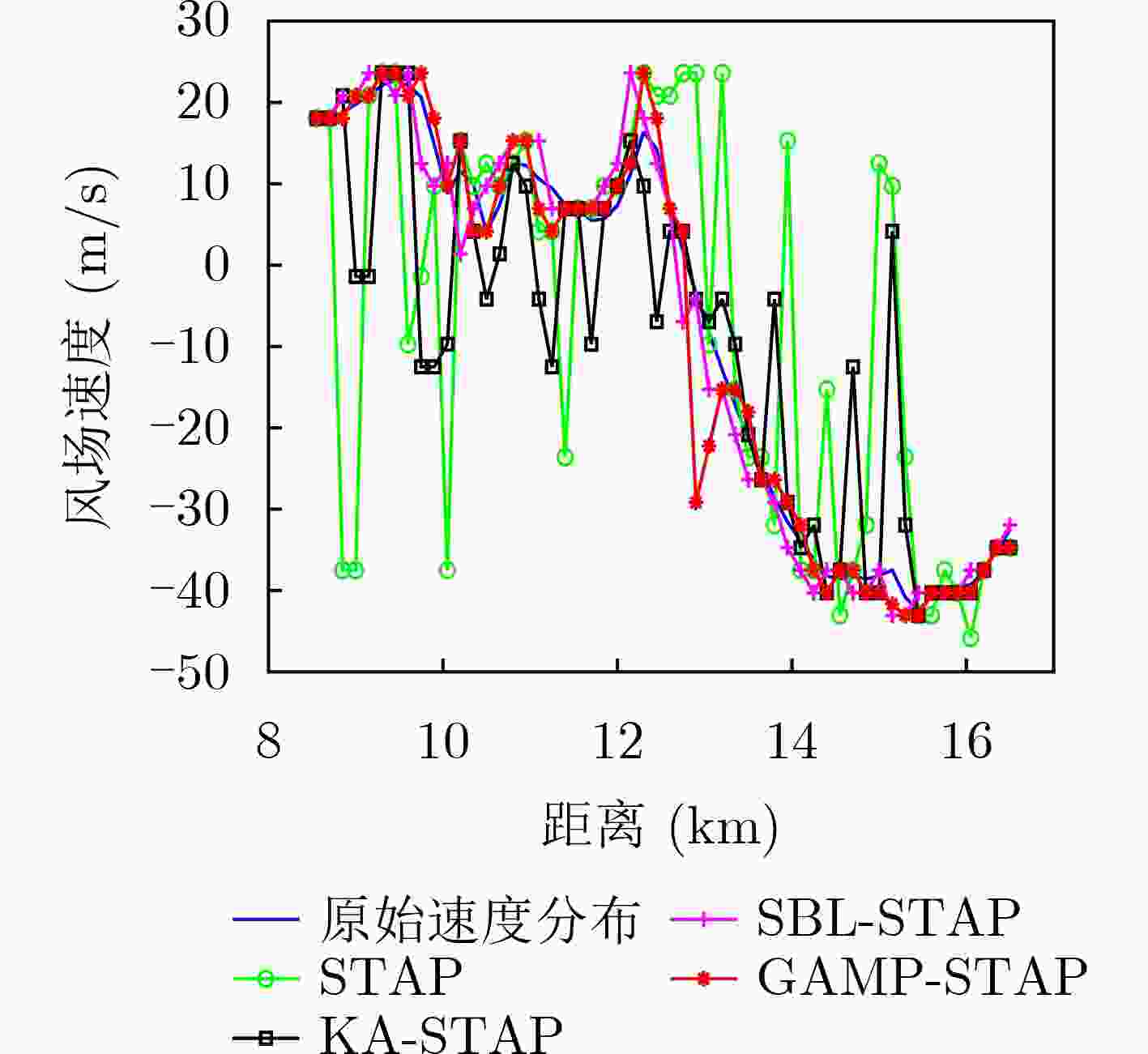
摘要: 针对机载气象雷达在复杂的地形环境下探测低空风切变时,地杂波呈现非均匀特征和难以获取足够的独立同分布(IID)样本,导致空时自适应处理(STAP)杂波抑制性能变差,使得风切变风速估计不准的问题。该文基于杂波信号稀疏特性,提出一种广义近似消息传递(GAMP)STAP方法,GAMP-STAP仅利用少量的样本在复杂地形环境下实现了风速较准确的估计。该方法首先利用杂波脊的先验信息构造稀疏字典,然后在贝叶斯框架下利用GAMP算法估计杂波幅度,恢复杂波功率谱,进而计算杂波协方差矩阵,最后构造STAP滤波器实现杂波抑制以及风切变风速估计。后续实验仿真结果证明了该方法的有效性。Abstract: When airborne weather radar is used to detect low-altitude wind shear under complex terrain environment, ground clutter presents non-uniform characteristics and it is difficult to obtain enough Independent Identically Distributed (IID) samples, which affects the clutter suppression effect of Space-Time Adaptive Processing and makes the estimation of wind shear wind speed inaccurate. Based on the sparse characteristics of clutter signals, a Generalized Approximate Message Passing (GAMP) Space-Time Adaptive Processing (STAP) method is proposed in this paper. GAMP-STAP achieves accurate estimation of wind speed in complex terrain environment with only a small number of samples. Firstly, a sparse dictionary is constructed based on the prior information of the clutter ridge, then GAMP algorithm is used to estimate the clutter amplitude and recover the clutter power spectrum under the Bayesian framework, and then the clutter covariance matrix is calculated. Finally, STAP filter is constructed to achieve clutter suppression and wind shear wind speed estimation. Simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 雷达系统仿真参数
参数 值 参数 值 载机高度(m) 600 阵元数 8 载机速度(m/s) 87.5 采样脉冲数 64 雷达波长(m) 0.032 主瓣方向(°) (90, 0) 脉冲重复频率(Hz) 7000 杂噪比(dB) 40 距离分辨率(m) 150 信噪比(dB) 5 表 2 算法运行时间对比
方法 运行环境 计算机CPU 计算复杂度 运行时间(s) 传统SBL-STAP MATLAB R2018b 3.4 GHz Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-6700,内存12 GB $ O\left( {{W^3}} \right) $ 511 GAMP-STAP $ O\left( {WG} \right) $ 73 -
[1] DESHPANDE M D and STATON L. Determination of windspeed within a weather storm using airborne Doppler radar[C]. IEEE Proceedings of the SOUTHEASTCON’91, Williamsburg, USA, 1991: 508–519. [2] 中国民用航空局. 《新时代民航强国建设行动纲要》出台[EB/OL]. http://www.caac.gov.cn/XWZX/MHYW/201812/t20181211_193411.html, 2018.Civil Aviation Administration of China. Action plan for building a civil aviation power in the new era[EB/OL]. http://www.caac.gov.cn/XWZX/MHYW/201812/t20181211_193411.html, 2018. [3] WARD J. Space-time adaptive processing for airborne radar[C]. Proceedings of 1995 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Detroit, USA, 1995. [4] KLEMM R. Space-time adaptive processing: principles and applications [Book Review][J]. Electronics & Communication Engineering Journal, 1999, 11(4): 172. [5] REED I S, MALLETT J D, and BRENNAN L E. Rapid convergence rate in adaptive arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1974, AES-10(6): 853–863. doi: 10.1109/TAES.1974.307893 [6] 李海, 刘志鑫, 王杰, 等. 基于DDD-GMB的低空风切变风速估计方法[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(1): 67–76. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.01.009LI Hai, LIU Zhixin, WANG Jie, et al. Low-altitude windshear wind speed estimation method based on DDD-GMB[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(1): 67–76. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.01.009 [7] PECKHAM C D, HAIMOVICH A M, AYOUB T F, et al. Reduced-rank STAP performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2000, 36(2): 664–676. doi: 10.1109/7.845257 [8] 李海, 周盟, 陈筱浅, 等. 基于多通道联合自适应处理的微下击暴流中心风速估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(7): 1619–1625. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161094LI Hai, ZHOU Meng, CHEN Xiaoqian, et al. Multiple Doppler channels joint adaptive processing based central wind speed estimation for microburst[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(7): 1619–1625. doi: 10.11999/JEIT161094 [9] KANG Naixin, SHANG Zheran, and DU Qinglei. Knowledge-aided structured covariance matrix estimator applied for radar sensor signal detection[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(3): 664. doi: 10.3390/s19030664 [10] 苏昱煜. 机载雷达自适应干扰抑制和基于先验知识的空时信号处理[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2020.SU Yuyu. Adaptive interference suppression and knowledge aided space time signal processing for airborne radar[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2020. [11] 段克清, 袁华东, 许红, 等. 稀疏恢复空时自适应处理技术研究综述[J]. 电子学报, 2019, 47(3): 748–756. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.03.033DUAN Keqing, YUAN Huadong, XU Hong, et al. An overview on sparse recovery space-time adaptive processing technique[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2019, 47(3): 748–756. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2019.03.033 [12] 阳召成. 基于稀疏性的空时自适应处理理论和方法[D]. [博士论文], 国防科学技术大学, 2013.YANG Zhaocheng. Theory and methods of sparsity-based space-time adaptive processing[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], National University of Defense Technology, 2013. [13] 王千里. 基于自适应网格的稀疏信号处理方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 电子科技大学, 2020.WANG Qianli. Research on sparse signal processing based on adaptive grid[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2020. [14] BAI Gatai, TAO Ran, ZHAO Juan, et al. Parameter-searched OMP method for eliminating basis mismatch in space-time spectrum estimation[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 138: 11–15. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.03.003 [15] DUAN Keqing, XU Hong, YUAN Huadong, et al. Three-dimensional sparse recovery space-time adaptive processing for airborne radar[J]. The Journal of Engineering, 2019, 2019(19): 5478–5482. doi: 10.1049/joe.2019.0343 [16] ZHU Jiang, ZHANG Qi, MENG Xiangming, et al. Vector approximate message passing algorithm for compressed sensing with structured matrix perturbation[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 166: 107248. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2019.107248 [17] 项璟. 广义近似消息传递算法的研究与应用[D]. [硕士论文], 燕山大学, 2018.XIANG Jing. Research and application of generalized approximate message passing algorithm[D]. [Master dissertation], Yanshan University, 2018. [18] VILA J P and SCHNITER P. Expectation-maximization Gaussian-mixture approximate message passing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(19): 4658–4672. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2272287 [19] LI Hai, WANG Jie, FAN Yi, et al. High-fidelity inhomogeneous ground clutter simulation of airborne phased array PD radar aided by digital elevation model and digital land classification data[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(9): 2925. doi: 10.3390/s18092925 [20] BRINGI V N and CHANDRASEKAR V. Polarimetric Doppler Weather Radar: Principles and Applications[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005: 1–100. [21] 李海, 宋迪, 程伟杰, 等. 回波功率筛选与数字地表分类数据辅助的低空风切变风速估计方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2286–2291. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190894LI Hai, SONG Di, CHENG Weijie, et al. Echo power screening and digital land classification data-assisted wind speed estimation of low-altitude wind-shear[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2286–2291. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190894 [22] DUAN Keqing, LIU Weijian, DUAN Guangqing, et al. Off-grid effects mitigation exploiting knowledge of the clutter ridge for sparse recovery STAP[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2018, 12(5): 557–564. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2017.0425 [23] RIEDL M and POTTER L C. Knowledge-aided Bayesian space-time adaptive processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(4): 1850–1861. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2805141 [24] RANGAN S. Generalized approximate message passing for estimation with random linear mixing[C]. 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory Proceedings, St. Petersburg, Russia, 2011. [25] 高乐, 毕东杰, 彭礼彪, 等. 基于GAMP的近场毫米波成像快速算法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2019, 48(2): 168–173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.02.002GAO Le, BI Dongjie, PENG Libiao, et al. Fast near-field millimeter-wave imaging algorithm via generalized approximate message passing[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2019, 48(2): 168–173. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2019.02.002 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
