User Assignment for Wireless Communication Assisted by Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
-
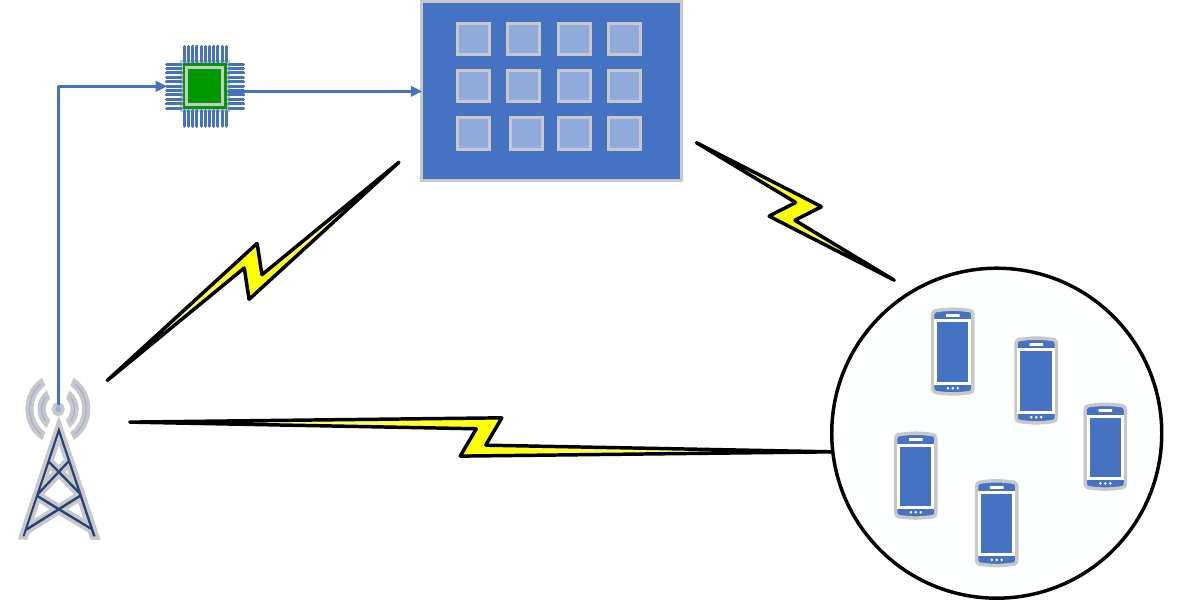
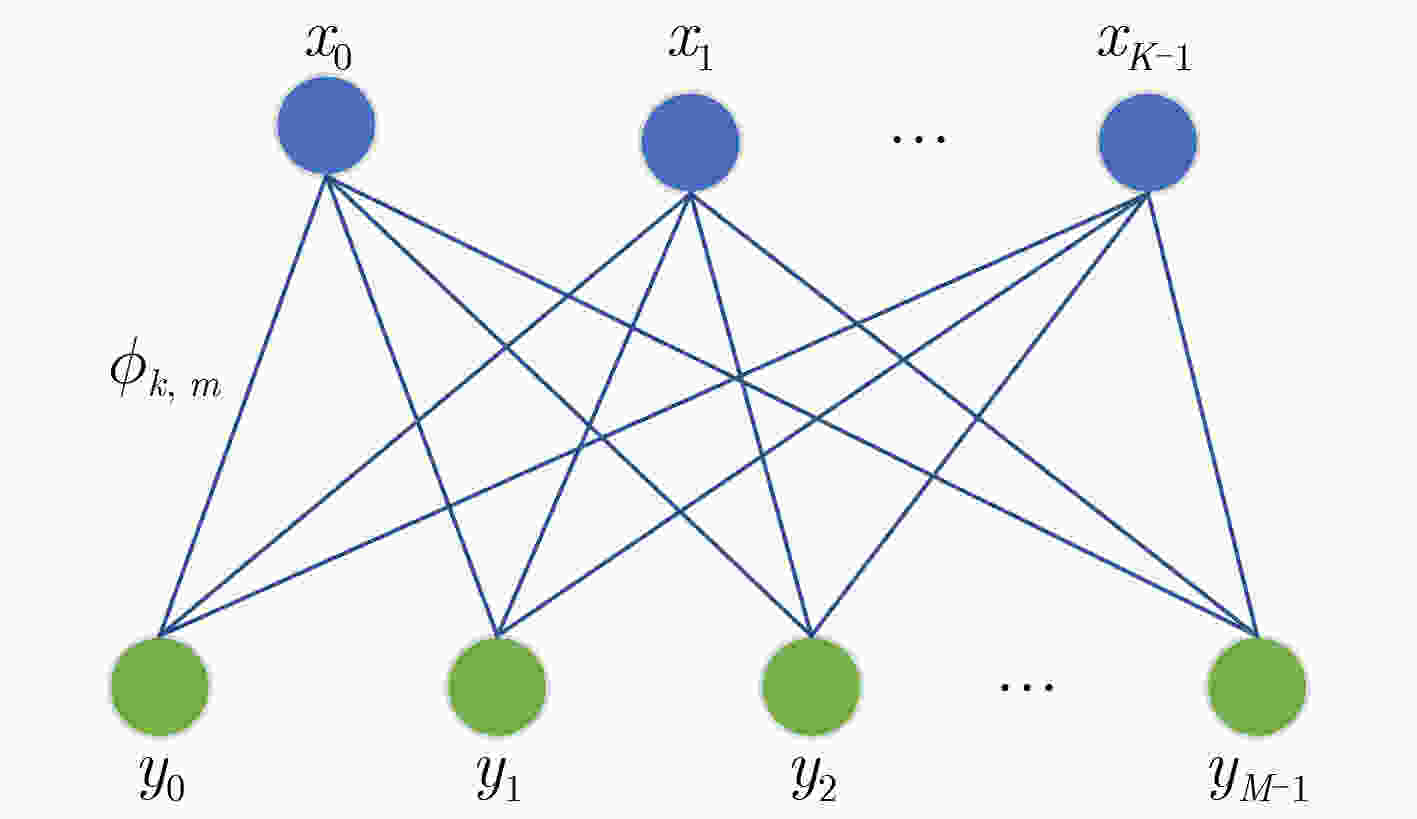
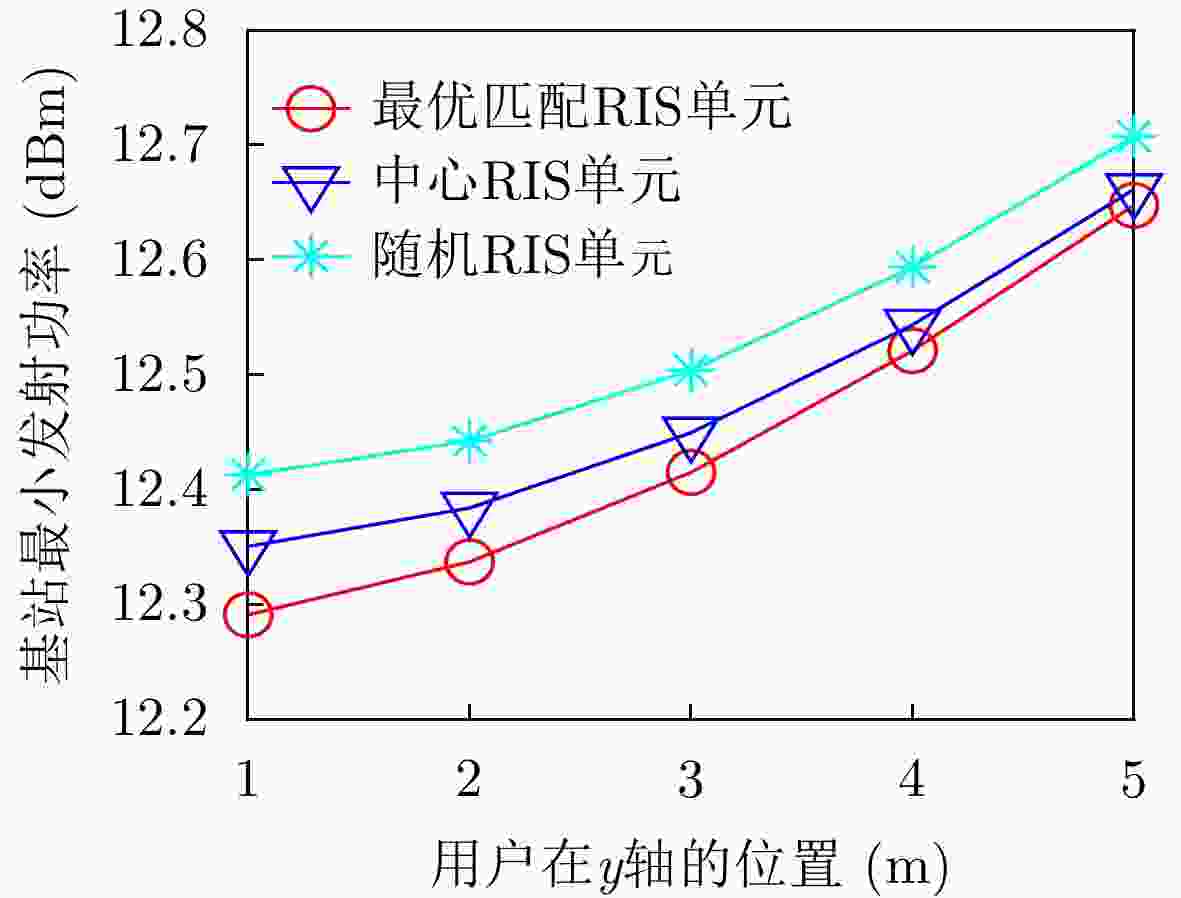
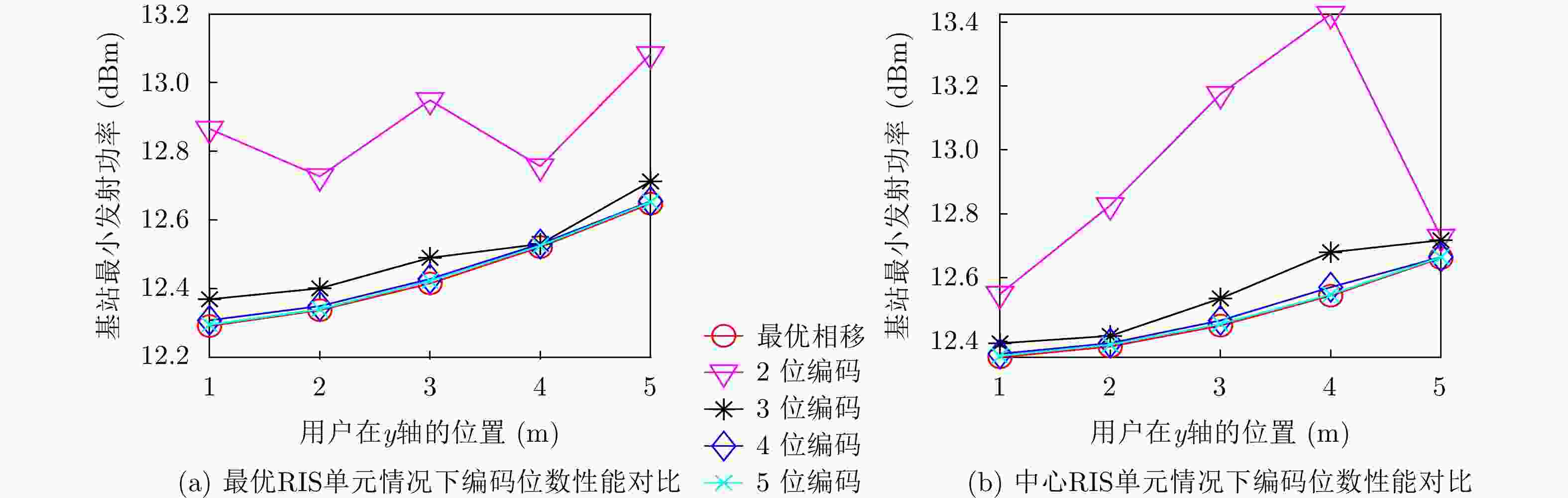
摘要: 可重构智能表面(RIS)是一种成本效益高的解决方案,可通过大量低成本的无源反射元件,提高无线通信系统的能源效益。在远场情况时,许多工作都是假设以RIS的中心作为反射点为前提展开研究。对于多用户的远场情况而言,用户位置不同会增加基站(BS)的功耗。该文以BS发射功率为代价矩阵,利用Kuhn-Munkres (KM)算法将用户与RIS单元进行匹配。该用户匹配方法在接收信噪比约束下,可以减少BS的发射功率。仿真结果表明,该文所采用的用户与RIS单元匹配方法与随机RIS单元相比,最多可以减少1%的BS功耗。Abstract: The Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) is a new and cost-effective solution for achieving high energy efficiency through massive low-cost passive elements. In the far field case, a lot of work are carried out on the assumption that the center of RIS is the reflection point. In the case of multi-user far field, the difference of user positions will increase the power consumption of Base Station(BS). Users and RIS cells are matched by resorting to Kuhn-Munkres(KM) algorithm in this paper, taking the transmitting power of BS as cost matrix. Under the constraints of SNR, the transmitting power of BS can be reduced by the user assignment method. Simulation results show that the matching method between users and RIS units adopted in this paper can reduce BS power consumption by up to 1% compared with random units of RIS.
-
表 1 仿真参数
参数 数值 RIS大小${s_M}$ 0.84 m2 天线增益$G$ 1 波长$\lambda $ 0.1 m 路径损失指数$\alpha $ 2 噪声功率${\sigma ^2}$ –96 dBm 信噪比阈值${r_{0}}$ 48 dB -
[1] ZHANG Zhengquan, XIAO Yue, MA Zheng, et al. 6G wireless networks: Vision, requirements, architecture, and key technologies[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2019, 14(3): 28–41. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2019.2921208 [2] STRINATI E C, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, SCIANCALEPORE V, et al. Wireless environment as a service enabled by reconfigurable intelligent surfaces: The RISE-6G perspective[C]. 2021 Joint European Conference on Networks and Communications & 6G Summit, Porto, Portugal, 2021: 562–567. [3] HAN Huimei, ZHAO Jun, ZHAI Wenchao, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface aided power control for physical-layer broadcasting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(11): 7821–7836. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3104871 [4] BASAR E, DI RENZO M, DE ROSNY J, et al. Wireless communications through reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 116753–116773. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935192 [5] DI RENZO M, DEBBAH M, PHAN-HUY D T, et al. Smart radio environments empowered by reconfigurable AI meta-surfaces: An idea whose time has come[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2019, 2019(1): 129. doi: 10.1186/s13638-019-1438-9 [6] ABEYWICKRAMA S, ZHANG Rui, WU Qingqing, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface: Practical phase shift model and beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(9): 5849–5863. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3001125 [7] LIANG Yingchang, CHEN Jie, LONG Ruizhe, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for smart wireless environments: Channel estimation, system design and applications in 6G networks[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2021, 64(10): 200301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-3261-5 [8] YANG Yifei, ZHANG Shuowen, and ZHANG Rui. IRS-enhanced OFDMA: Joint resource allocation and passive beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(6): 760–764. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2968303 [9] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Beamforming optimization for intelligent reflecting surface with discrete phase shifts[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 2019: 7830–7833. [10] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Beamforming optimization for wireless network aided by intelligent reflecting surface with discrete phase shifts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(3): 1838–1851. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2958916 [11] LI Yiqing, JIANG Miao, ZHANG Qi, et al. Joint beamforming design in multi-cluster MISO NOMA reconfigurable intelligent surface-aided downlink communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(1): 664–674. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3032695 [12] QIAN X, DI RENZO M, LIU J, et al. Beamforming through reconfigurable intelligent surfaces in single-user MIMO systems: SNR distribution and scaling laws in the presence of channel fading and phase noise[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(1): 77–81. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3021058 [13] ZHANG Hongliang, DI Boya, SONG Lingyang, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces assisted communications with limited phase shifts: How many phase shifts are enough?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(4): 4498–4502. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2973073 [14] ZENG Shuhao, ZHANG Hongliang, DI Boya, et al. Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) assisted wireless coverage extension: RIS orientation and location optimization[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(1): 269–273. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3025345 [15] ÖZDOGAN Ö, BJÖRNSON E, and LARSSON E G. Intelligent reflecting surfaces: Physics, propagation, and pathloss modeling[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(5): 581–585. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2960779 [16] TANG Wankai, CHEN Mingzheng, CHEN Xiangyu, et al. Wireless communications with reconfigurable intelligent surface: Path loss modeling and experimental measurement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 421–439. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3024887 [17] HU Sha, CHITTI K, RUSEK F, et al. User assignment with distributed Large Intelligent Surface (LIS) systems[C]. The IEEE 29th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Bologna, Italy, 2018: 1–6. [18] MUNKRES J. Algorithms for the assignment and transportation problems[J]. Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1957, 5(1): 32–38. doi: 10.1137/0105003 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
