| [1] |
WU Jie and WANG Yunsheng. Hypercube-based multipath social feature routing in human contact networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2014, 63(2): 383–396. doi: 10.1109/TC.2012.209
|
| [2] |
LIN Limei, XU Li, HUANG Yanze, et al. On exploiting priority relation graph for reliable multi-path communication in mobile social networks[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 477: 490–507. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.10.035
|
| [3] |
GAO Chuangen, DU Hai, WU Weili, et al. Viral marketing of online game by DS decomposition in social networks[J]. Theoretical Computer Science, 2020, 803: 10–21. doi: 10.1016/j.tcs.2019.03.006
|
| [4] |
ETESAMI S R, BOLOUK S, NEDIĆ A, et al. Influence of conformist and manipulative behaviors on public opinion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2019, 6(1): 202–214. doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2018.2806179
|
| [5] |
张宪立, 唐建新, 曹来成. 基于反向PageRank的影响力最大化算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 40(1): 96–102. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019061066ZHANG Xianli, TANG Jianxin, and CAO Laicheng. Influence maximization algorithm based on reverse PageRank[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2020, 40(1): 96–102. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019061066
|
| [6] |
顾益军, 解易, 张培晶. 面向有组织犯罪分析的人际关系网络节点重要性评价研究[J]. 中国人民公安大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 19(4): 66–68.GU Yijun, XIE Yi, and ZHANG Peijing. Research on the importance evaluation of interpersonal network nodes for organized crime analysis[J]. Journal of People’s Public Security University of China:Science and Technology, 2013, 19(4): 66–68.
|
| [7] |
BÓTA A and KRÉSZ M. A high resolution clique-based overlapping community detection algorithm for small-world networks[J]. Informatica, 2015, 39(2): 177–187.
|
| [8] |
黄宏程, 赖礼城, 胡敏, 等. 基于严格可控理论的社交网络信息传播控制方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(7): 1707–1714. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170966HUANG Hongcheng, LAI Licheng, HU Min, et al. Information propagation control method in social networks based on exact controllability theory[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(7): 1707–1714. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170966
|
| [9] |
陈慧敏, 金思辰, 林微, 等. 新冠疫情相关社交媒体谣言传播量化分析[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2021, 58(7): 1366–1384. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2021.20200818CHEN Huimin, JIN Sichen, LIN Wei, et al. Quantitative analysis on the communication of COVID-19 related social media rumors[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2021, 58(7): 1366–1384. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2021.20200818
|
| [10] |
KEMPE D, KLEINBERG J, and TARDOS É. Maximizing the spread of influence through a social network[C]. The Ninth ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Washington, USA, 2003: 137–146.
|
| [11] |
PENG Sancheng, WANG Guojun, ZHOU Yongmei, et al. An immunization framework for social networks through big data based influence modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2019, 16(6): 984–995. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2017.2731844
|
| [12] |
DOOSTMOHAMMADIAN M, RABIEE H R, and KHAN U A. Centrality-based epidemic control in complex social networks[J]. Social Network Analysis and Mining, 2020, 10(1): 32. doi: 10.1007/s13278-020-00638-7
|
| [13] |
CHANG S, PIERSON E, KOH P W, et al. Mobility network models of COVID-19 explain inequities and inform reopening[J]. Nature, 2021, 589(7840): 82–87. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2923-3
|
| [14] |
WANG Zhishuang, XIA Chengyi, CHEN Zengqiang, et al. Epidemic propagation with positive and negative preventive information in multiplex networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(3): 1454–1462. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2960605
|
| [15] |
HU Xiping, CHU T H S, LEUNG V C M, et al. A survey on mobile social networks: Applications, platforms, system architectures, and future research directions[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(3): 1557–1581. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2014.2371813
|
| [16] |
顾洁, 王筱纶, 胡安安. 社交网络信息竞争扩散的关键节点策略研究[J]. 情报科学, 2020, 38(3): 78–86. doi: 10.13833/j.issn.1007-7634.2020.03.013GU Jie, WANG Xiaolun, and HU An’an. Seeding strategy of competitive diffusion in social network[J]. Information Science, 2020, 38(3): 78–86. doi: 10.13833/j.issn.1007-7634.2020.03.013
|
| [17] |
COLIZZA V, FLAMMINI A, SERRANO M A, et al. Detecting rich-club ordering in complex networks[J]. Nature Physics, 2006, 2(2): 110–115. doi: 10.1038/nphys209
|
| [18] |
GHOSHAL A K, DAS N, and DAS S. Influence of community structure on misinformation containment in online social networks[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 213: 106693. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106693
|
| [19] |
SAXENA A, MALIK V, and IYENGAR S R S. Estimating the degree centrality ranking of a node[J]. Social Analysis and Mining, 2018, 8(1): 1–20.
|





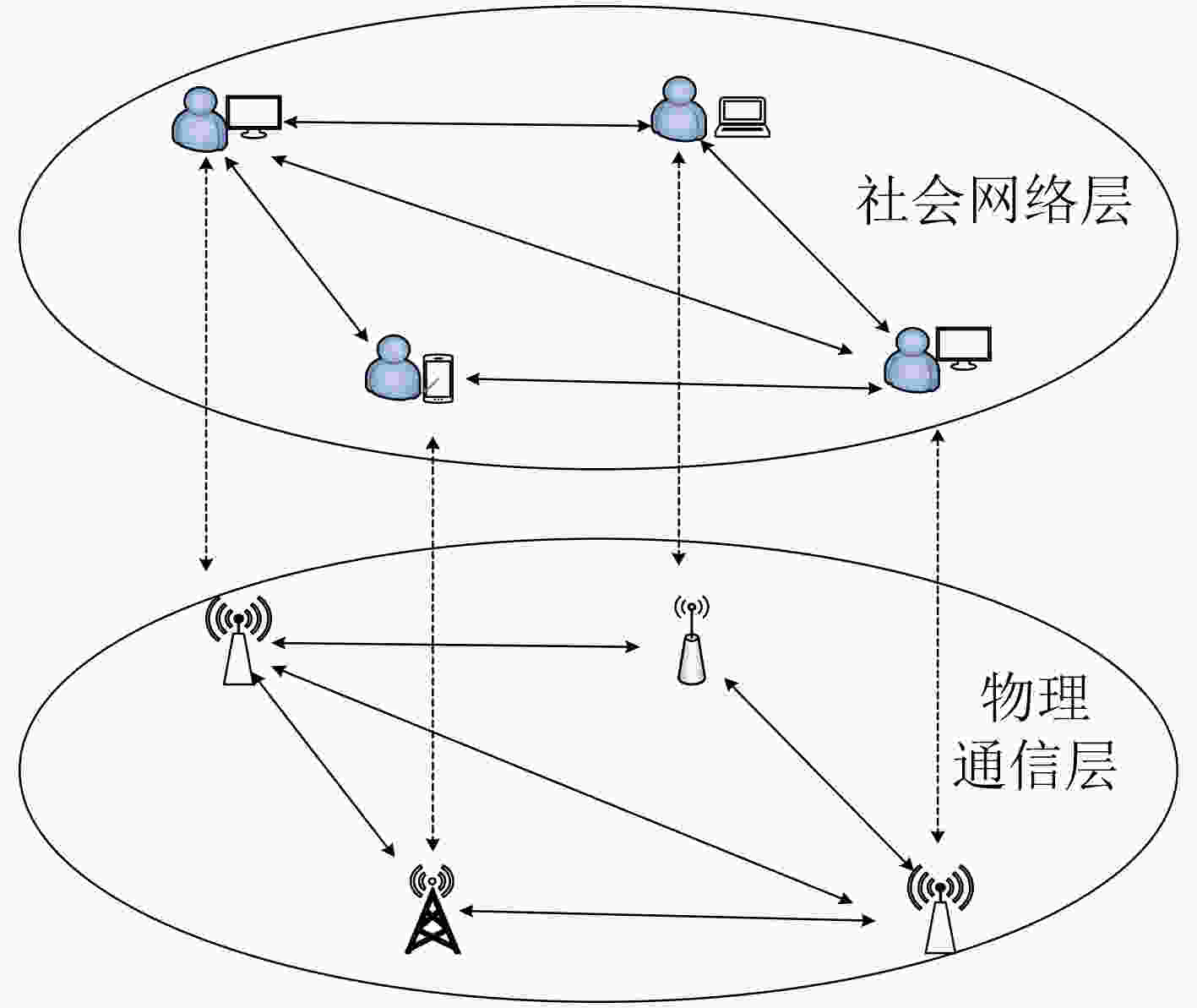
 下载:
下载:
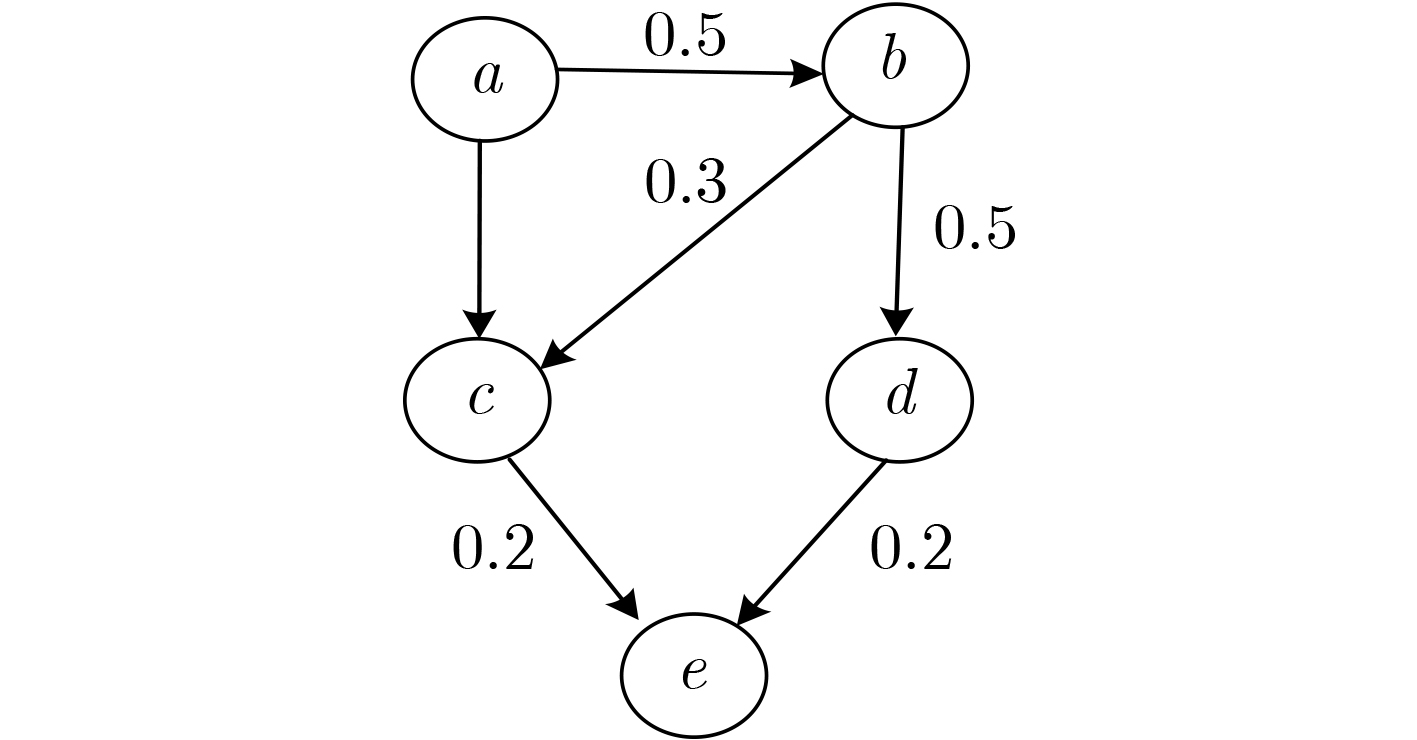
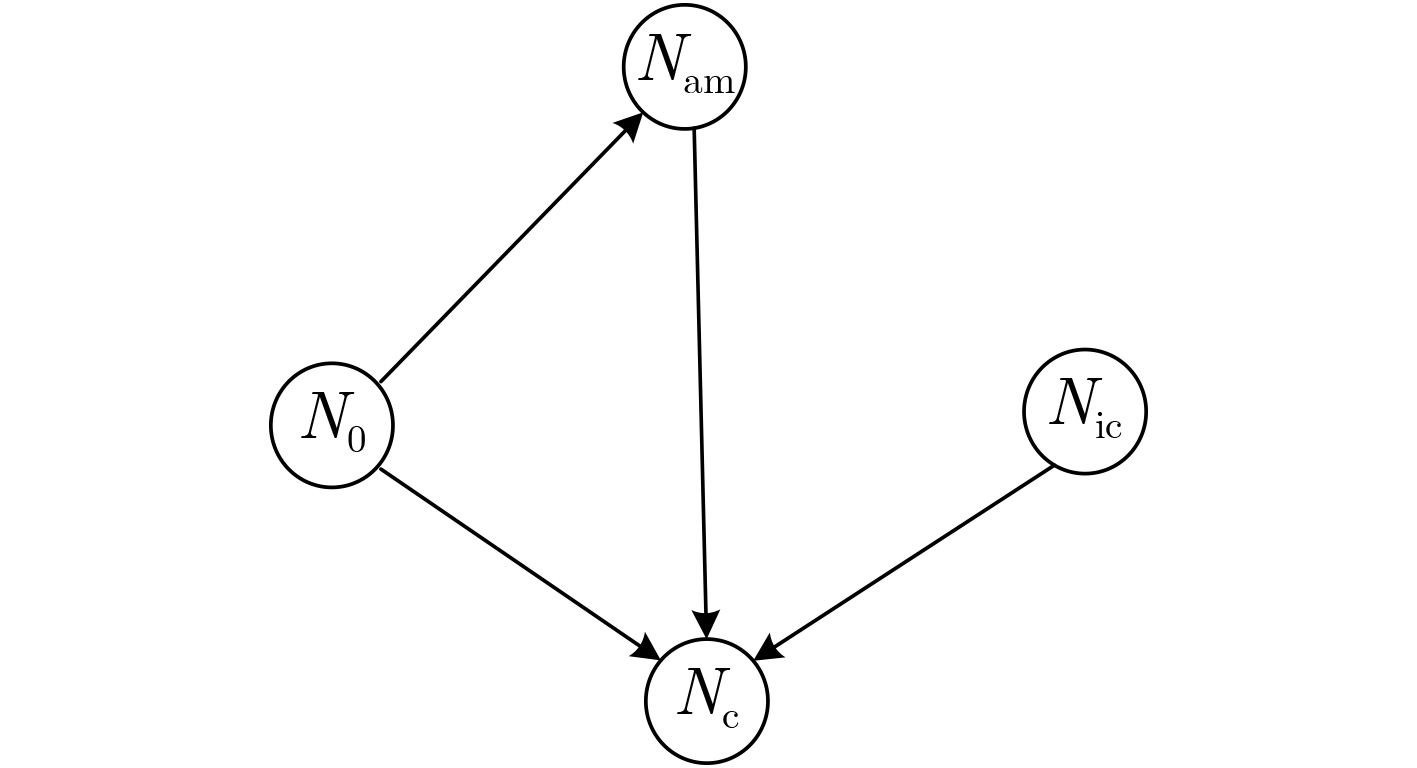
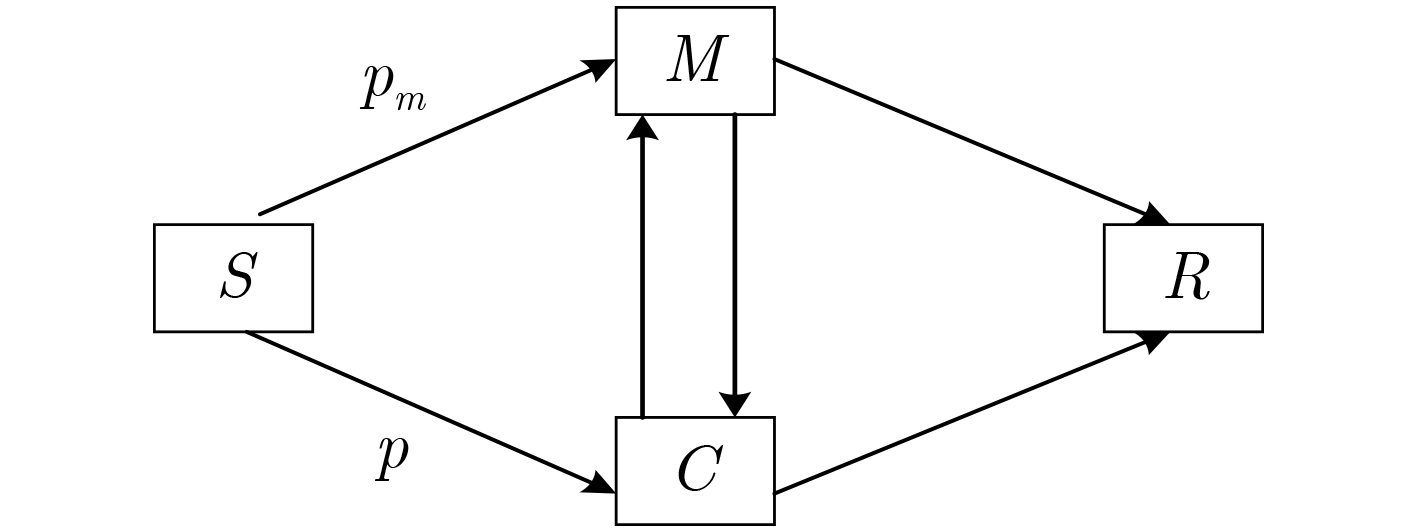
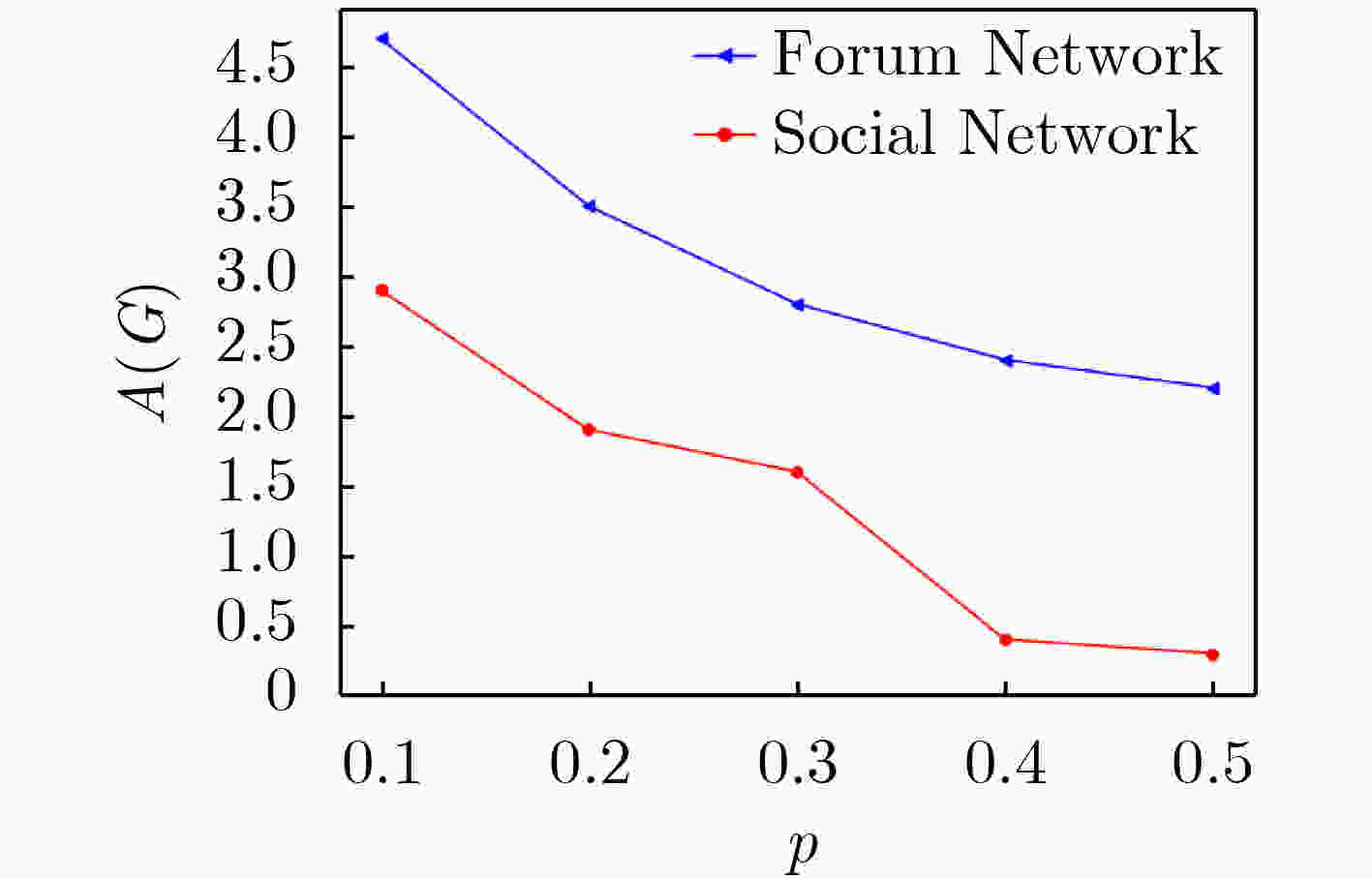
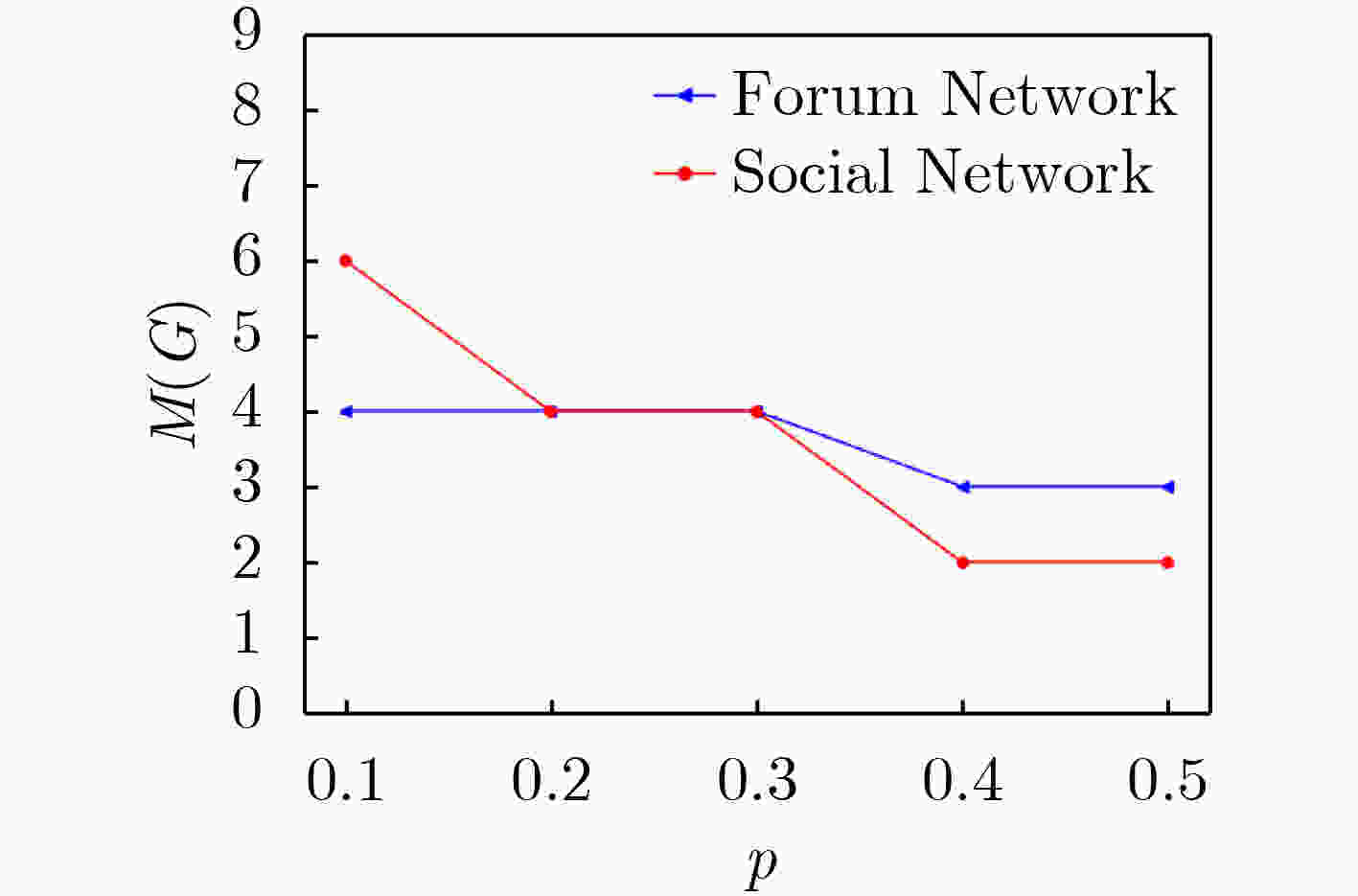
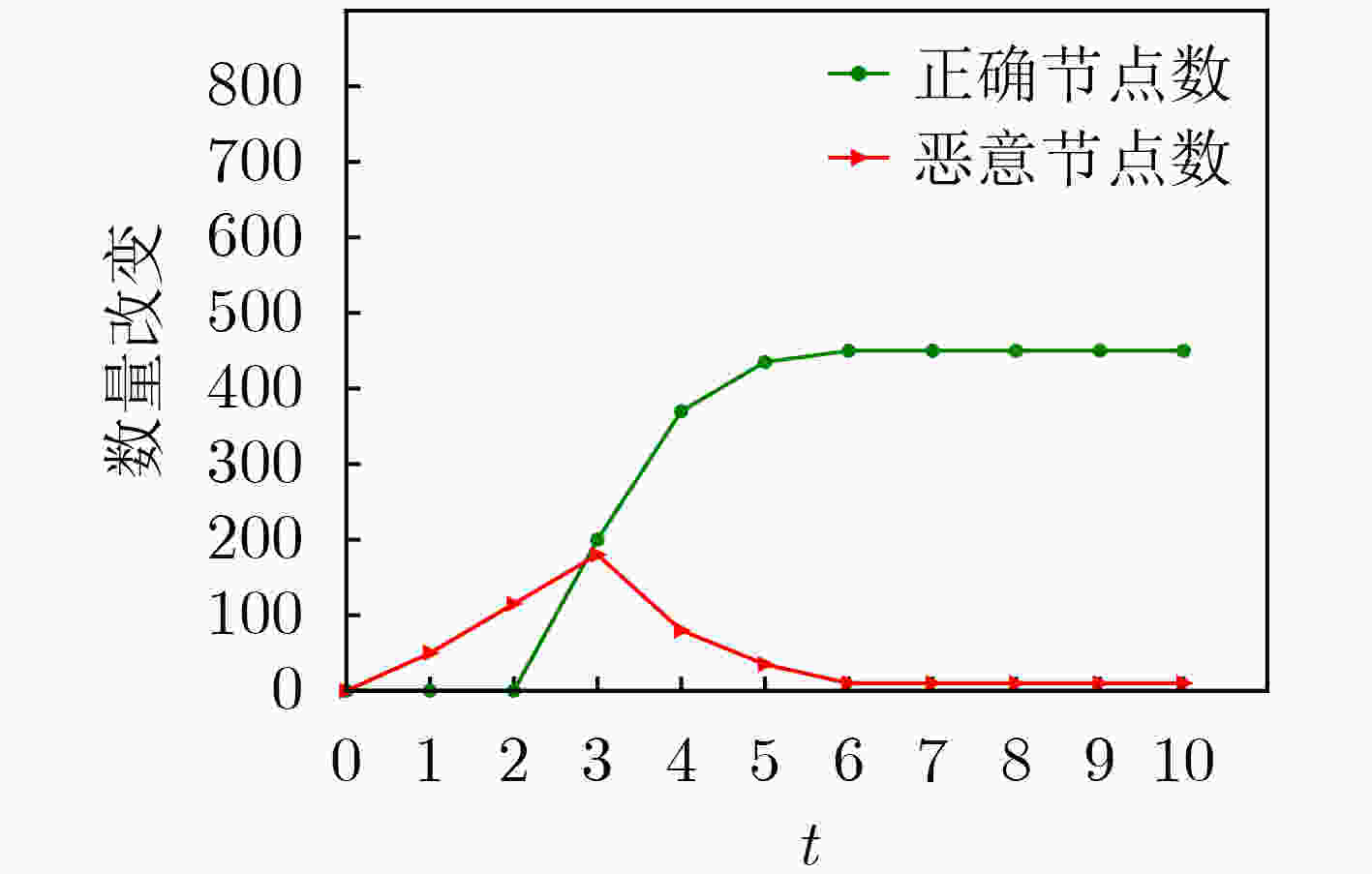
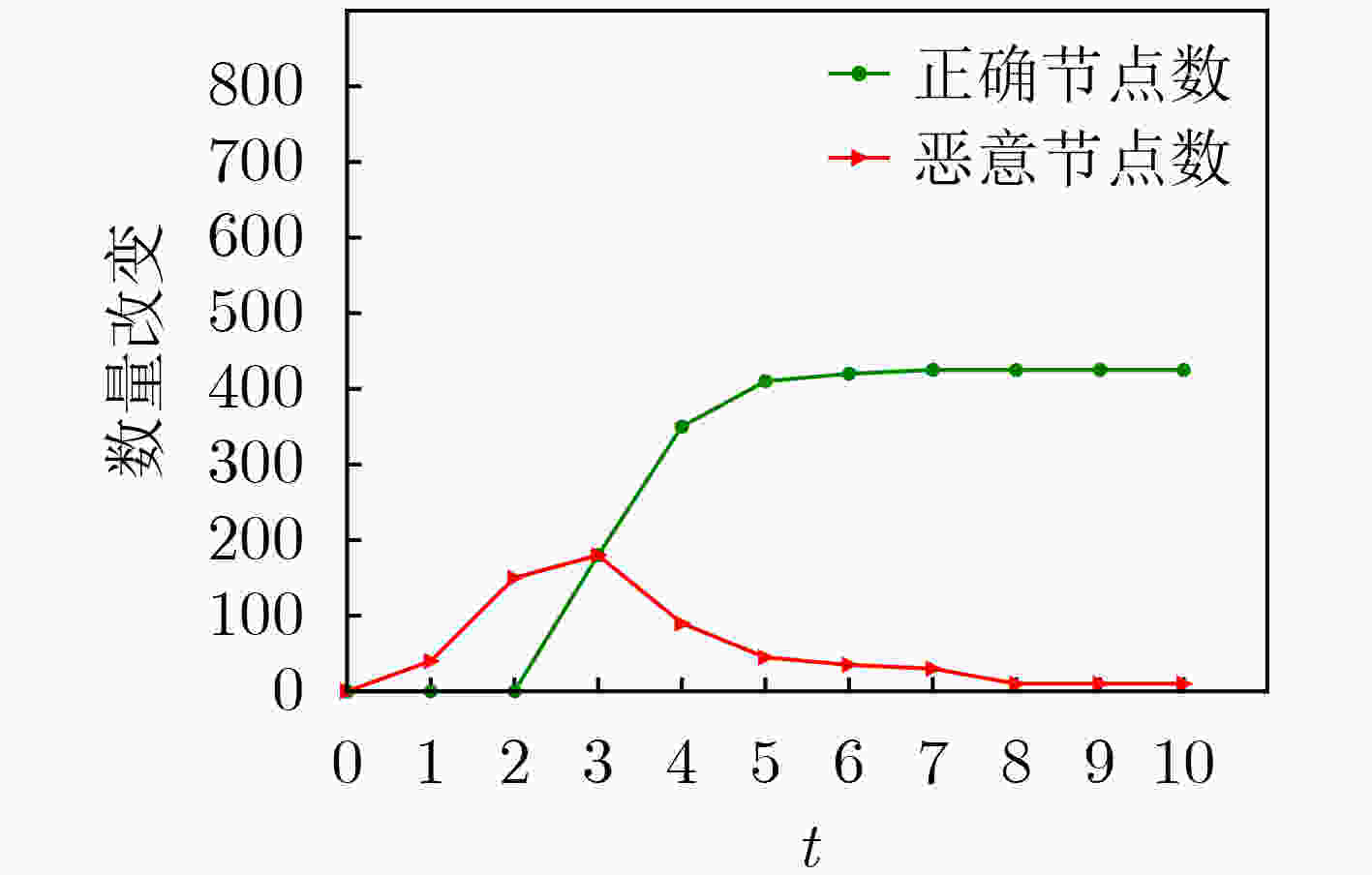
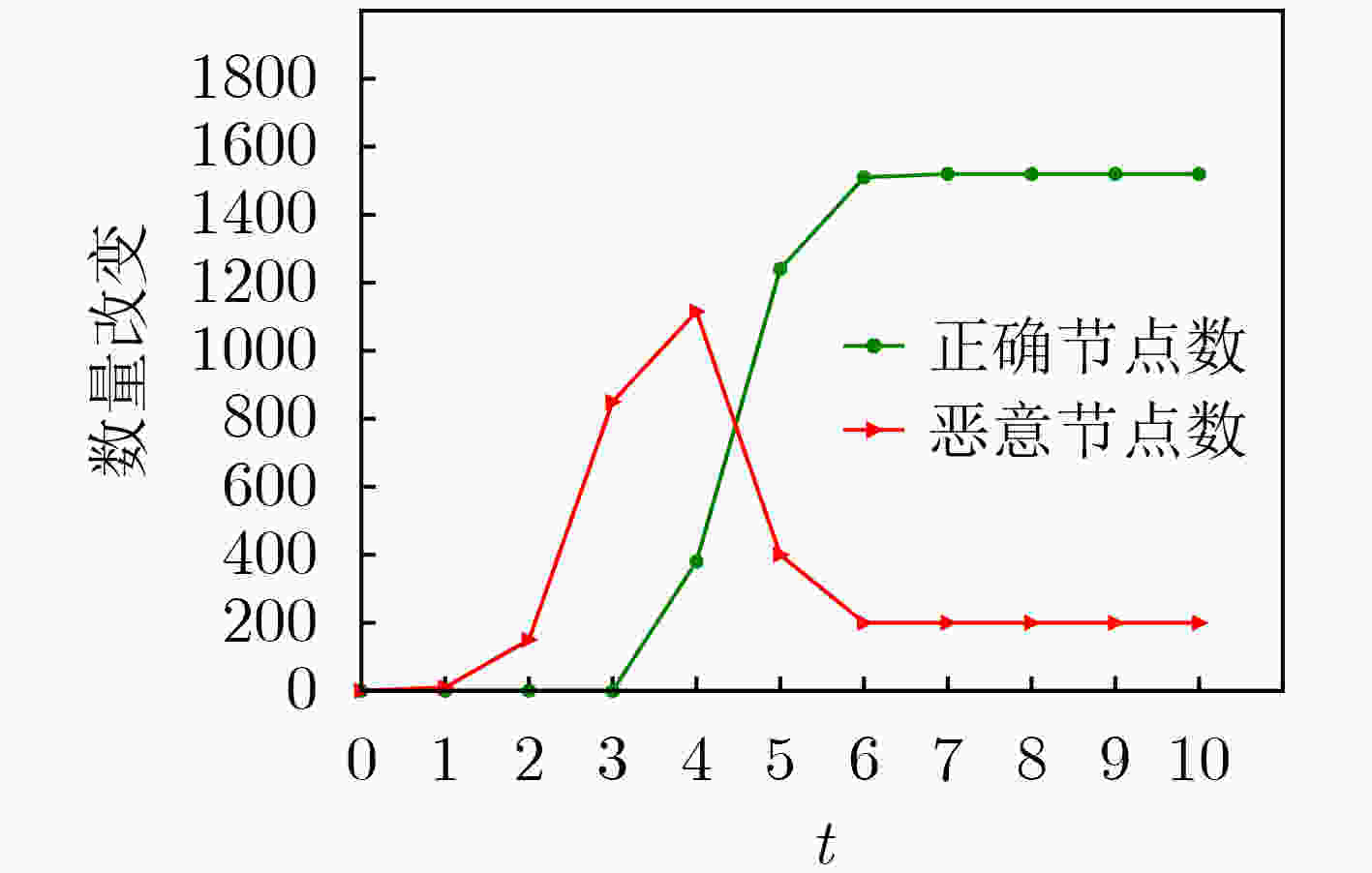
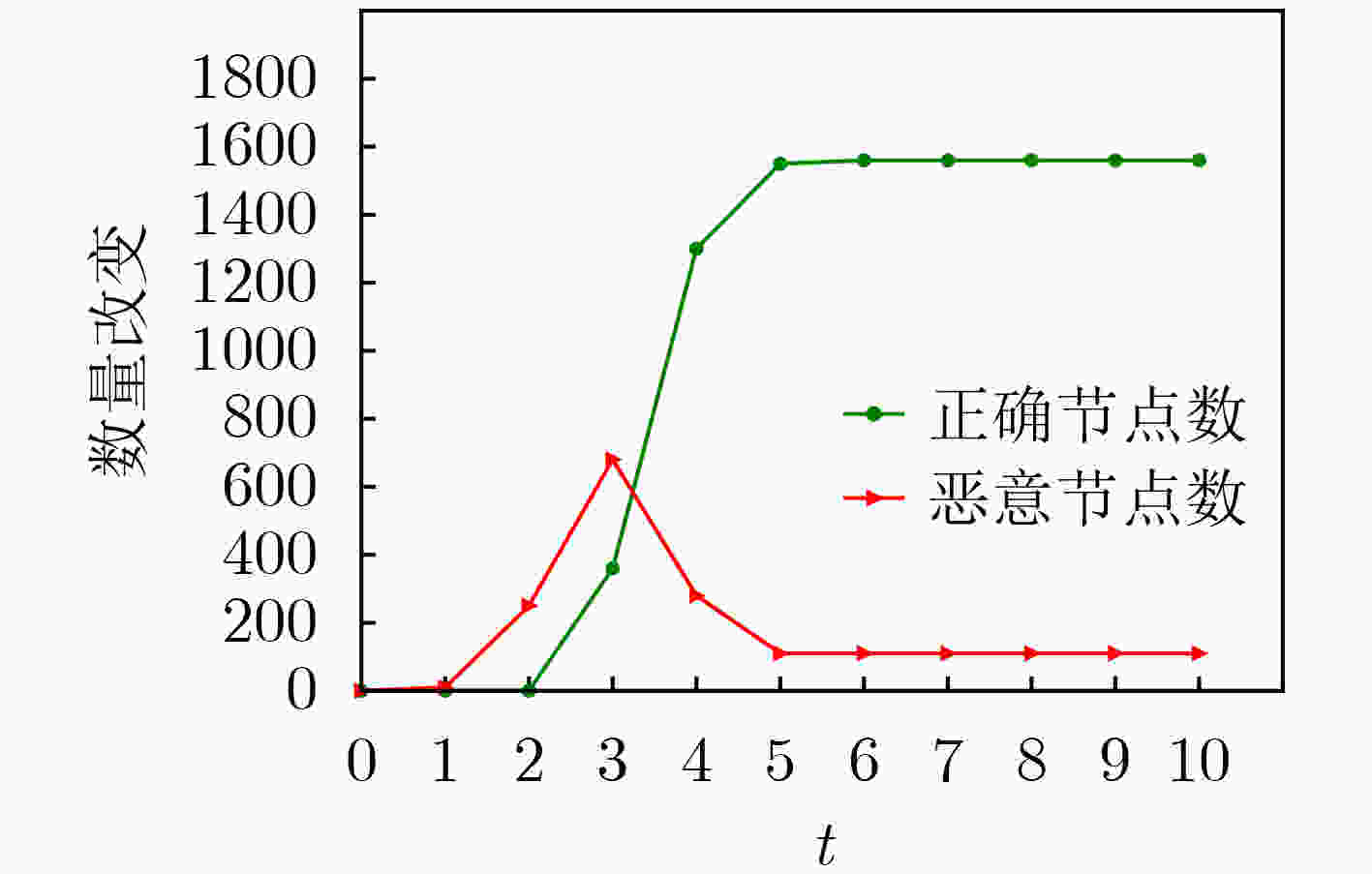
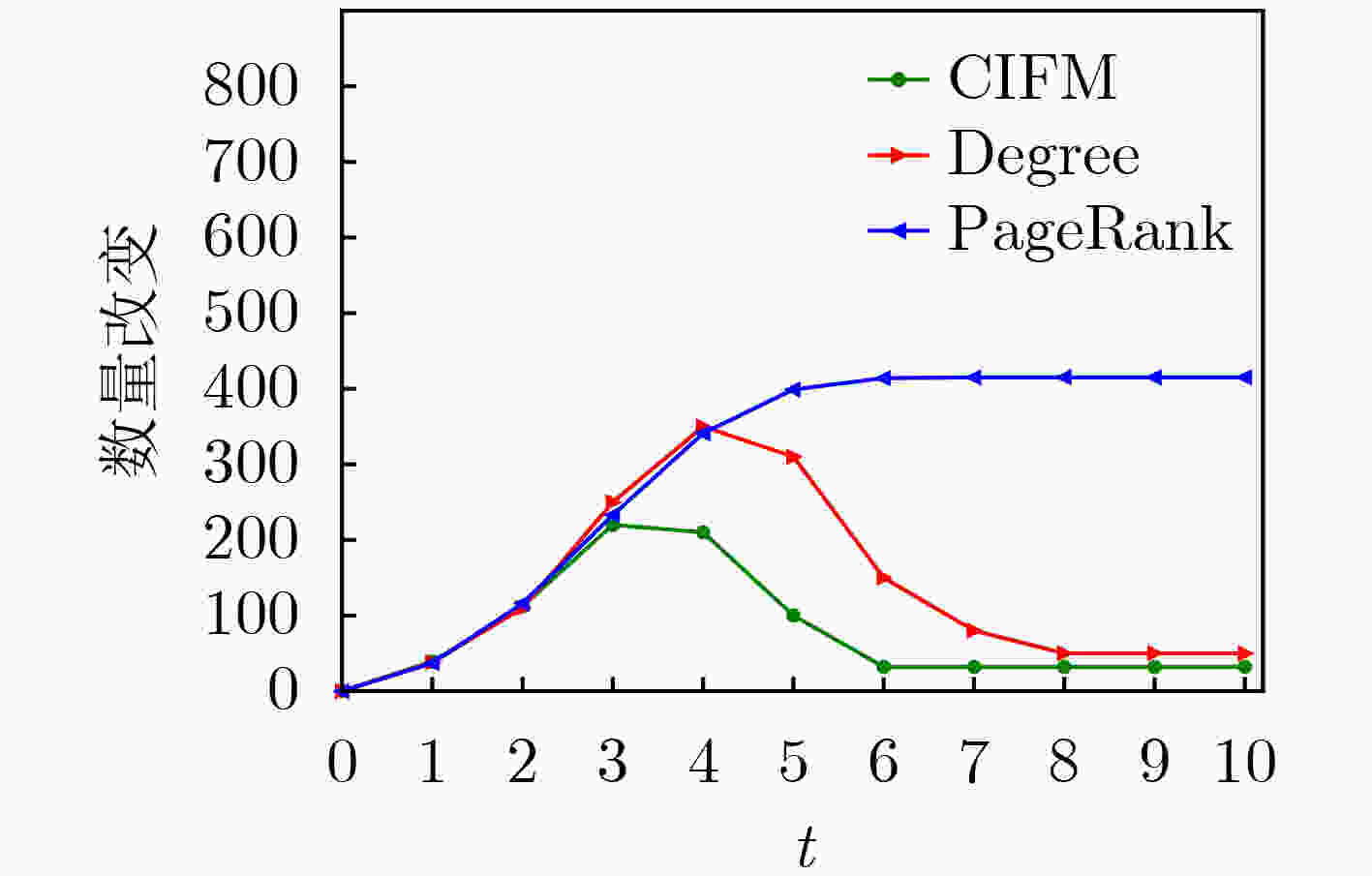
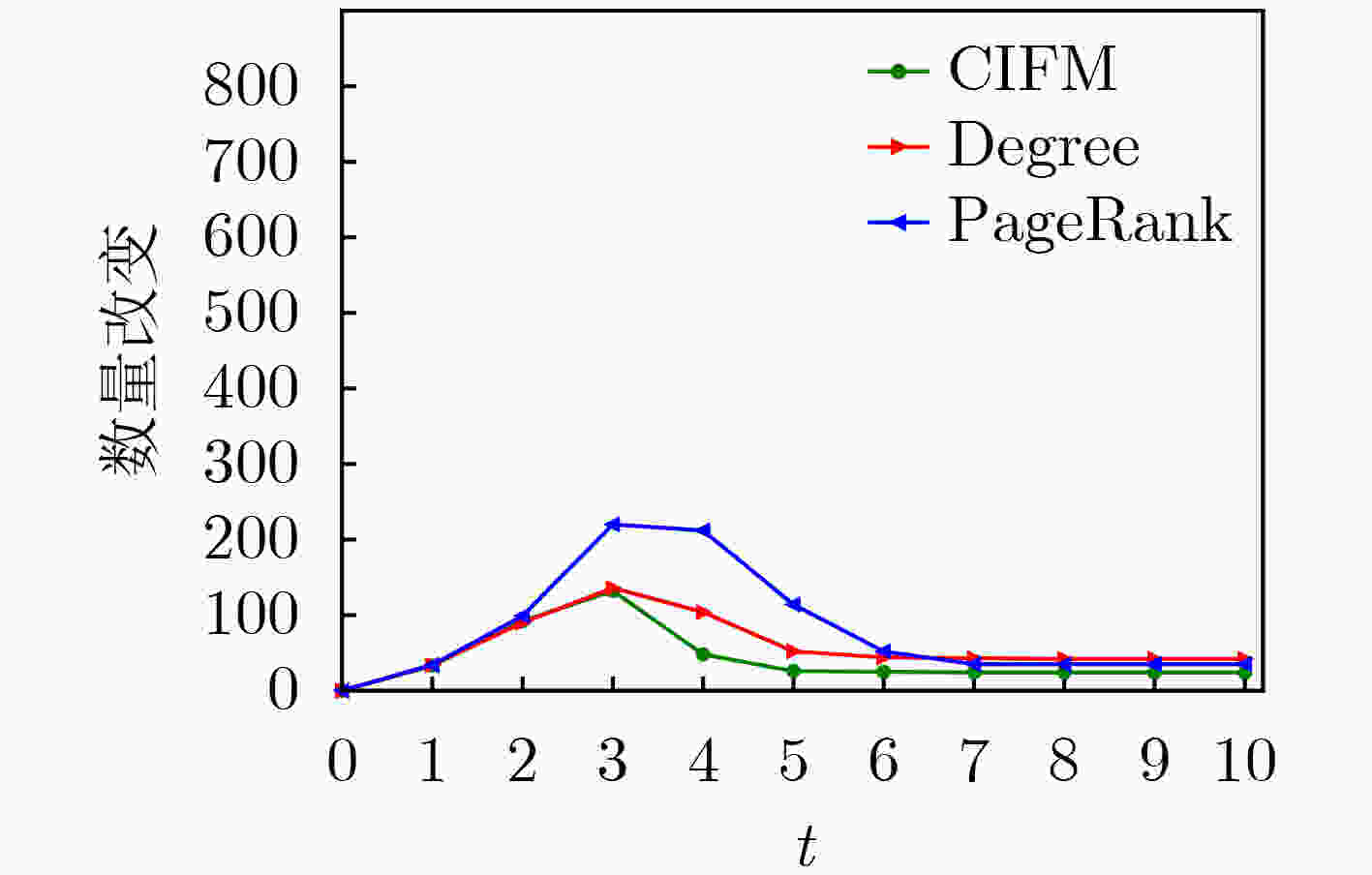


 下载:
下载:
