Underwater Acoustic Spread Spectrum Communications Based on Space-Time Cluster Processing
-
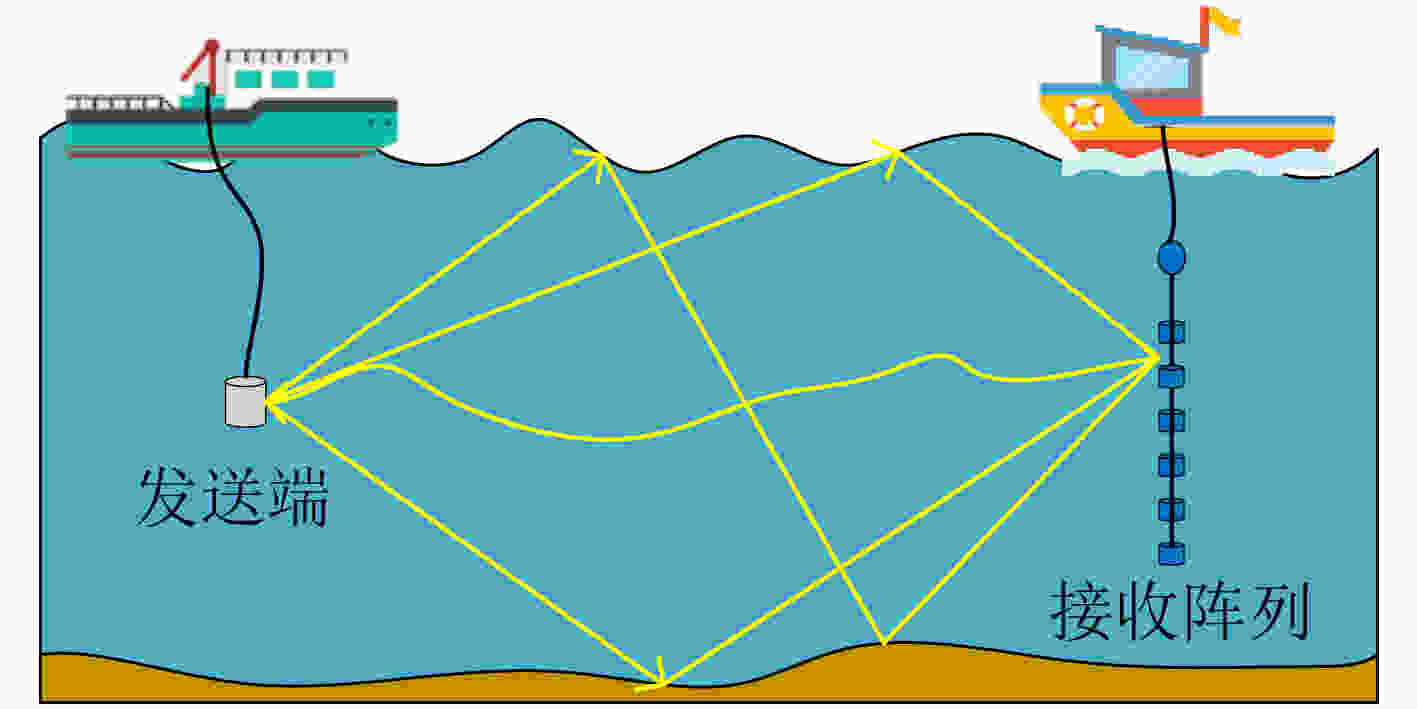
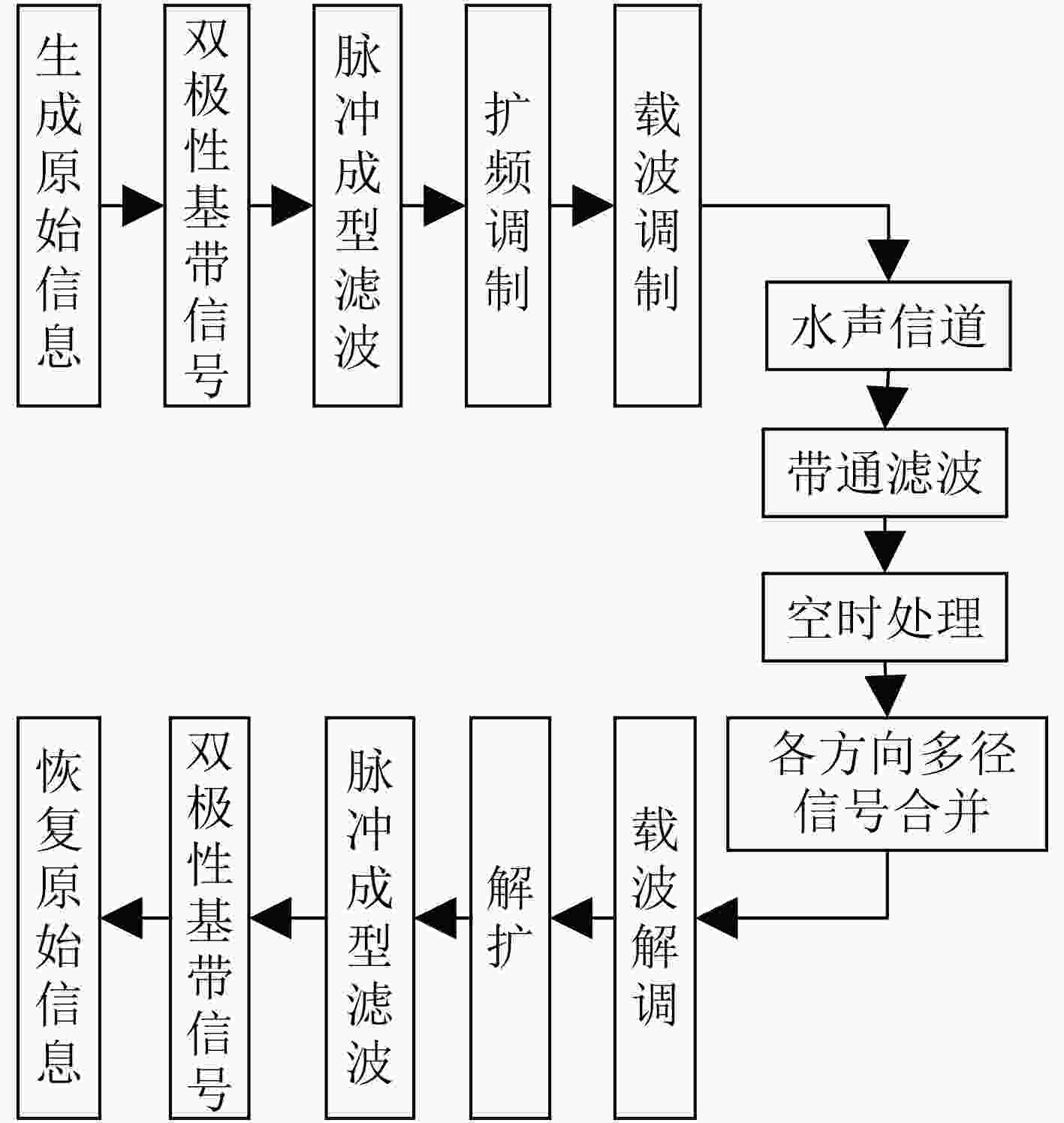
摘要: 由于海洋干扰严重,水声通信十分困难。扩频通信技术具有良好的抗干扰性能,能够保证在复杂的海洋环境中进行可靠的通信,常被用于水声通信中。水声信道是典型的相干多径信道。沿不同路径到达的信号具有不同的传播时延和到达角,因此接收信号具有时空特性。即接收信号具有时延扩展和角度扩展。多径信号的相干叠加导致接收信号中存在严重的符号间干扰。为了充分利用水声信号的时空聚类特性,该文设计了一个空时处理器,分别对沿每条路径到达的信号进行滤波。结合时空簇的多样性,可以有效提高通信系统的可靠性。提出了一种基于空时聚类处理的水声扩频通信方案。并在仿真和实验中对该通信方案进行了比较和分析,以验证其性能优势。Abstract: Due to the serious interference in the ocean, underwater acoustic communications are very difficult. Spread spectrum communication technology has good anti-interference performance, and it can ensure reliable communications in complex marine environment, it is often used in underwater acoustic communications. Underwater acoustic channels are typical coherent multipath channels. The signals arriving along different paths have different propagation delays and angles of arrival, so received signals have space-time clustering characteristic. That is, received signals have time delay spread and angle spread. The coherent superposition of multipath signals leads to serious inter symbol interference in received signals. In order to take advantage of the space-time clustering characteristic of the underwater acoustic signals, a space-time processor is designed to filter the signals arriving along each path respectively. The reliability of the communication system can be effectively improved by combining the diversity of space-time clusters. An underwater acoustic spread spectrum communication scheme is proposed based on space-time cluster processing. This communication scheme is compared and analyzed in the simulation and the experiment, to verify its performance advantages.
-
表 1 仿真参数
采样频率 载频 通信带宽 扩频序列长度 48 kHz 3 kHz 2 kHz 15 表 2 仿真模拟的多径信道参数
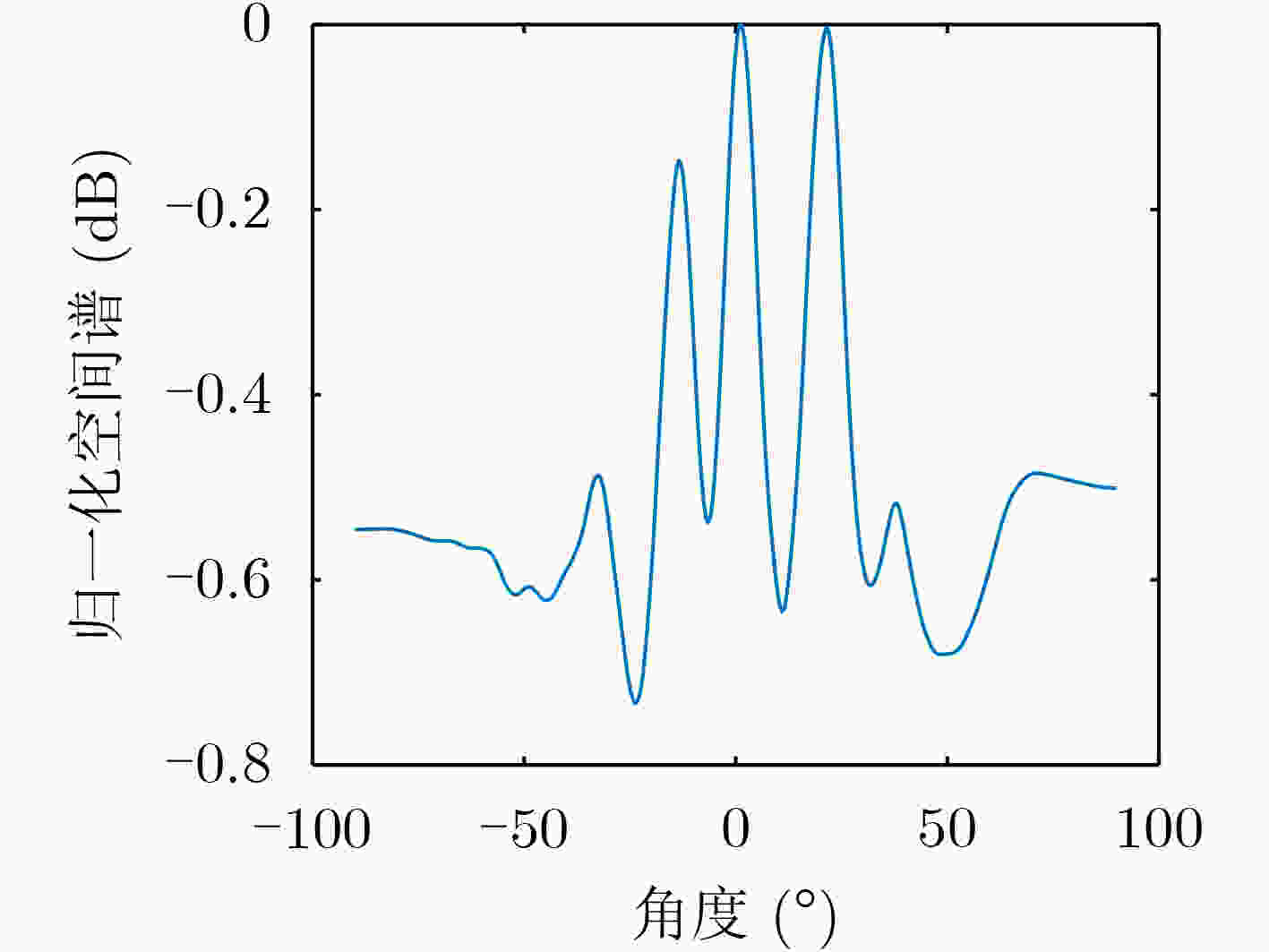
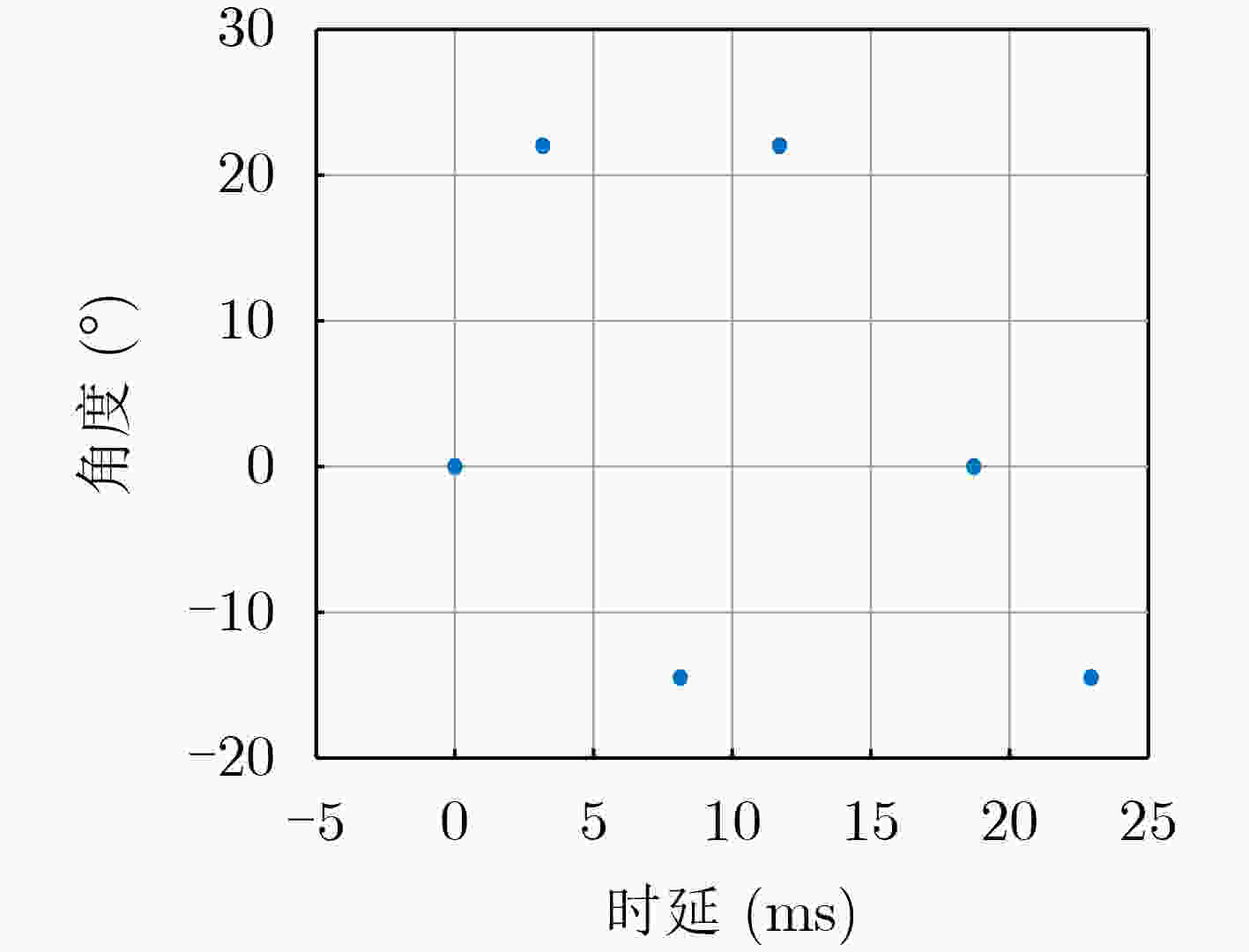
路径 归一化振幅 相对延迟(ms) 角度(°) 1 1 0 0 2 0.900 3.167 22.020 3 0.850 8.563 –14.480 4 0.800 11.710 22.020 5 0.750 18.710 0 6 0.600 23.380 –14.480 表 3 多径信道参数
路径 幅度(10–4) 时延(s) 角度(°) 1 2.85714312 2.33333325 0.00000000 2 2.74721126 2.42670321 15.9453955 表 4 不同接收模式下MCSK调制的平均判决矩阵峰均比与误码率
调制方式MCSK 单阵元接收 阵列接收后同相叠加 阵列接收后空时处理 判决矩阵峰均比均值 3.0751 4.8466 5.0433 平均误码率 0.4300 0.2100 0.0900 -
[1] CHITRE M, SHAHABUDEEN S, FREITAG L, et al. Recent advances in underwater acoustic communications & networking[C]. OCEANS 2008, Quebec City, Canada, 2008. [2] ETTER P C, HAAS C H, and RAMANI D V. Advanced concepts for underwater acoustic channel modeling[C]. American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2014, 2014. [3] YU Yang, ZHOU Feng, and QIAO Gang. M-ary code shift keying spread spectrum underwater acoustic communication[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(23): 234301. doi: 10.7498/aps.61.234301 [4] YU Yang, ZHOU Feng, QIAO Qang, et al. Orthogonal M-ary code shift keying spread spectrum underwater acoustic communication[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 62(3): 279–288. [5] YIN Yanling, ZHOU Feng, QIAO Gang, et al. Burst mode hybrid spread spectrum technology for covert acoustic communication[C]. 2013 OCEANS - San Diego, San Diego, USA, 2013: 1–8. doi: 0.23919/OCEANS.2013.6741030. [6] XU Xiaomei. Development and applications of underwater acoustic communication and networks[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2009, 28(6): 811–816. doi: 10.3969/j.issn1000-3630.2009.06.026 [7] LI Jianghui, LIAO Li, and ZAKHAROV Y V. Space-time cluster combining for UWA communications[C]. OCEANS 2016-Shanghai, Shanghai, China, 2016. [8] LIU Zhiqiang, YOO K, YANG T C, et al. Long-range double-differentially coded spread-spectrum acoustic communications with a towed array[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2014, 39(3): 482–490. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2013.2264994 [9] ZHOU Feng, ZHANG Wenbo, QIAO Gang, et al. Novel spread spectrum based underwater acoustic communication technology for low signal-to-noise ratio environments[C]. International Conference on Intelligent Robotics and Applications, Shenyang, China, 2019. [10] BERNARD C, BOUVET P J, POTTIER A, et al. Multiuser chirp spread spectrum transmission in an underwater acoustic channel applied to an AUV fleet[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(5): 1527. doi: 10.3390/s20051527 [11] QU Fengzhong, YANG Liuqing, and YANG T C. High reliability direct-sequence spread spectrum for underwater acoustic communications[C]. OCEANS 2009, Biloxi, USA, 2009. [12] ZHAI Lijie and DUAN Haisheng. A modified ISM estimation algorithm for direction of arrival (DOA) of wideband coherent signal[C]. 2018 4th International Conference on Education, Management and Information Technology (ICEMIT 2018), Boca Raton, USA, 2018. [13] TAGA F and SHIMOTAHIRA H. A novel spatial smoothing technique for the MUSIC algorithm[J]. IEICE Transactions on Communications, 1995, E78-B(11): 1513–1517. [14] FRIEDLANDER B. A sensitivity analysis of the MUSIC algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1990, 38(10): 1740–1751. doi: 10.1109/29.60105 [15] SHI Yaowu, CHEN Miao, SHAN Zetao, et al. Spatial smoothing technique for coherent signal DOA estimation based on eigen space MUSIC algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition) , 2017, 47(1): 268–273. doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb201701039 [16] GUL S, ZAIDI S S H, KHAN R, et al. Underwater acoustic channel modeling using BELLHOP ray tracing method[C]. 2017 14th International Bhurban Conference on Applied Sciences and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan, 2017: 665–670. [17] RIES S. Digital time-delay beamforming with interpolated signals[J]. Signal Processing, 2004, 84(12): 2403–2423. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2004.08.003 [18] LI Xiaoya, LIU Yuanyuan, ZHANG Rong, et al. Fractional delay compensation and it's FPGA implementation in multi antenna system[J]. Digital Communication, 2014, 41(2): 45–49,80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3824.2014.02.011 -





 下载:
下载:

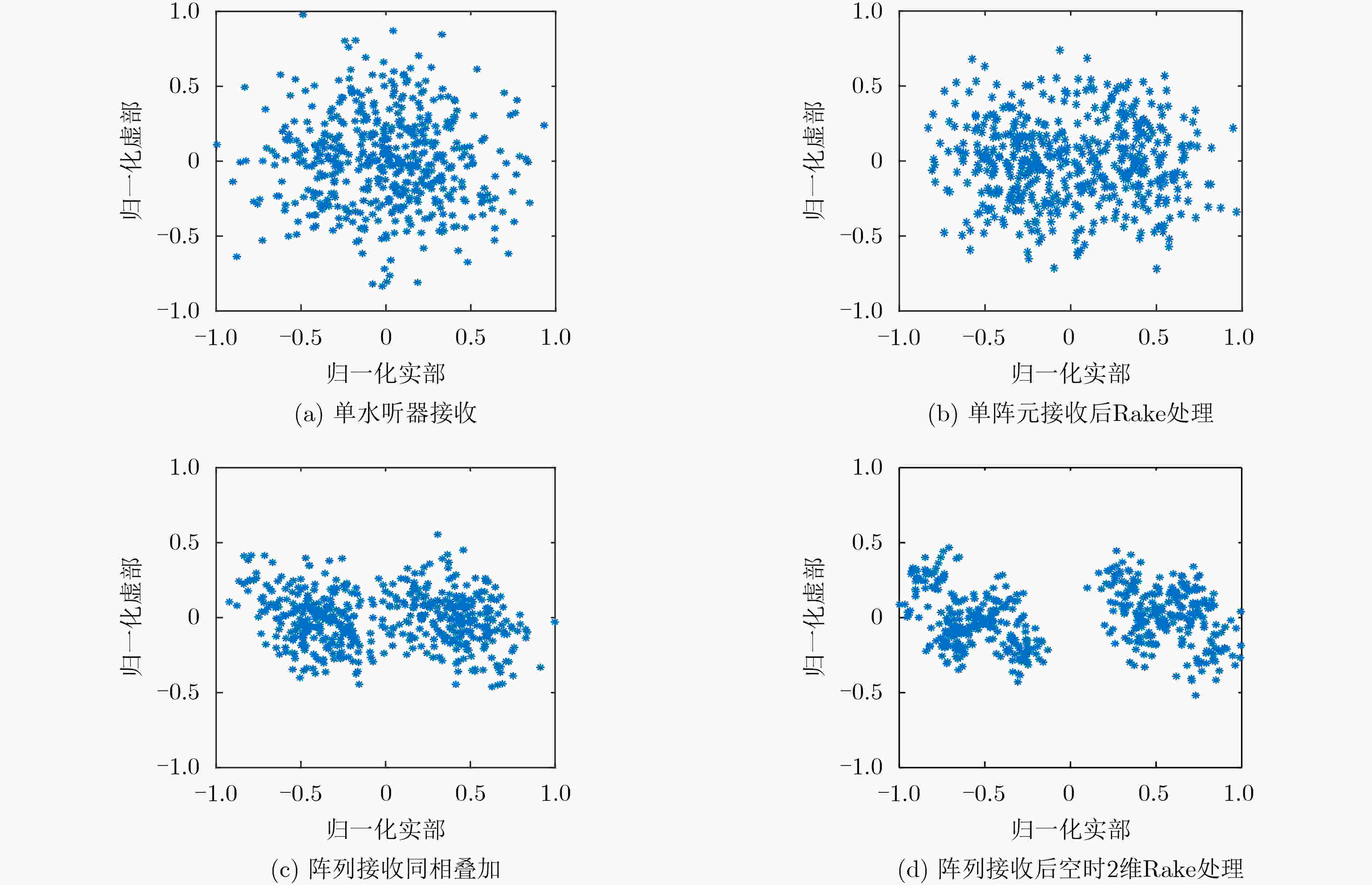
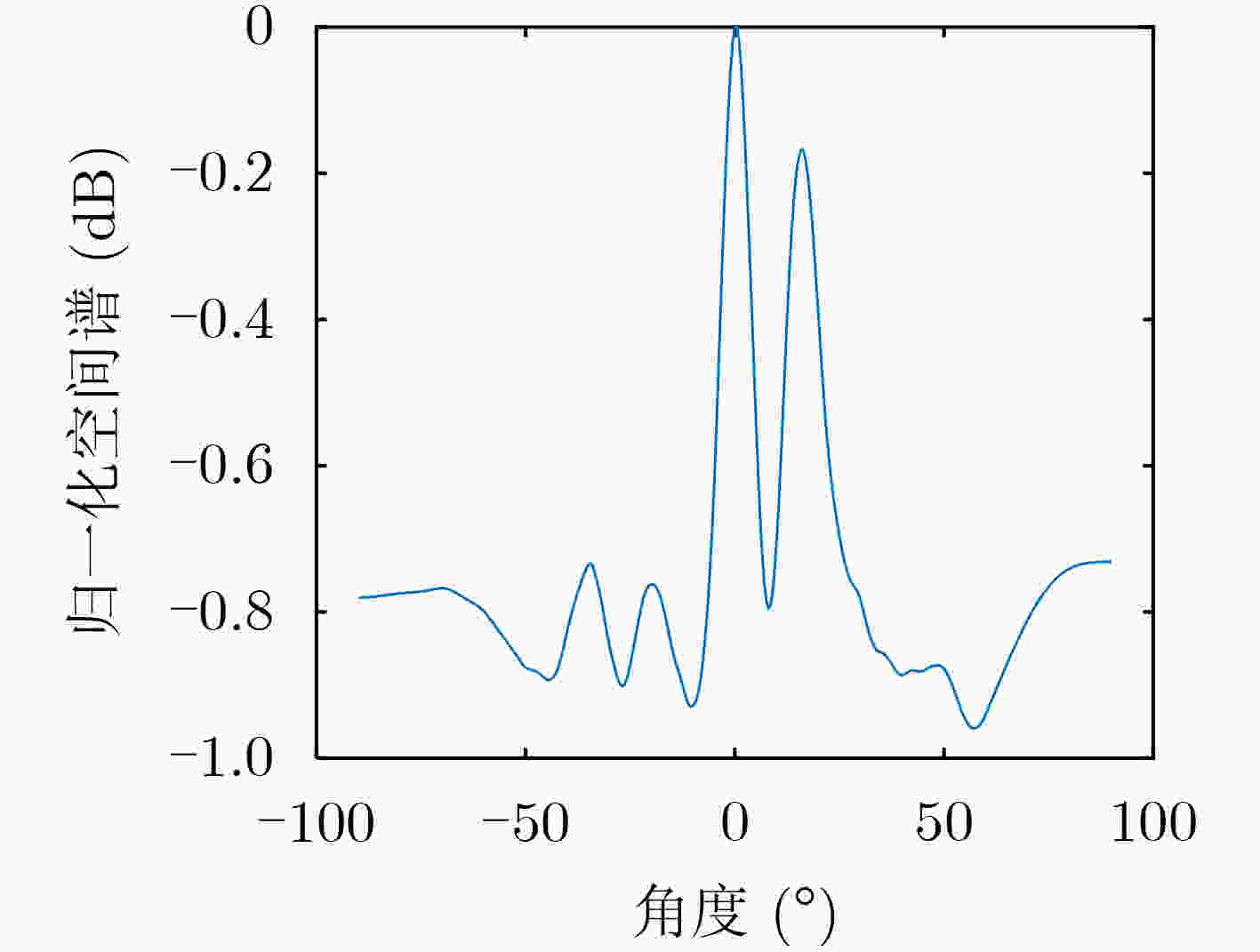
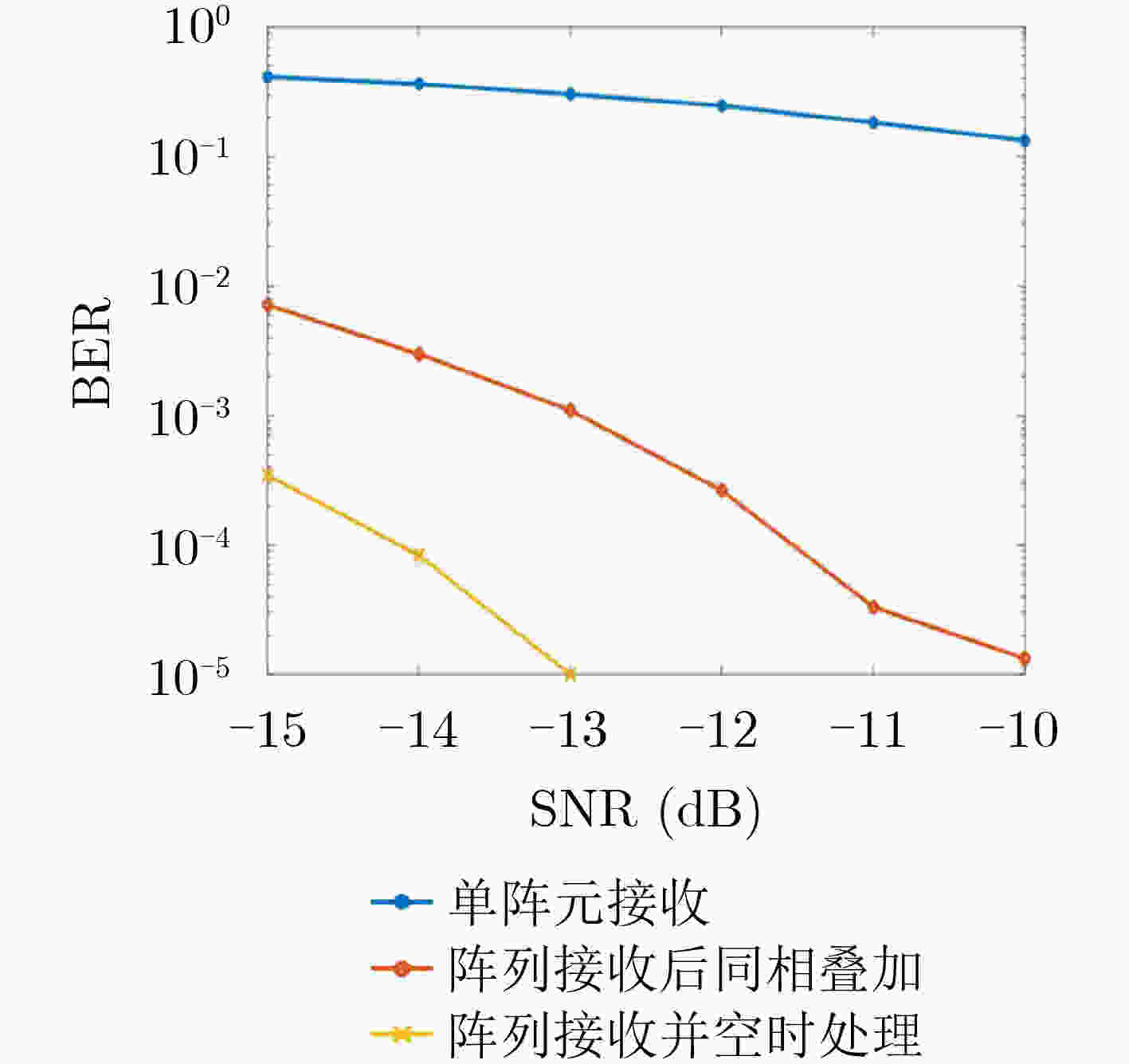
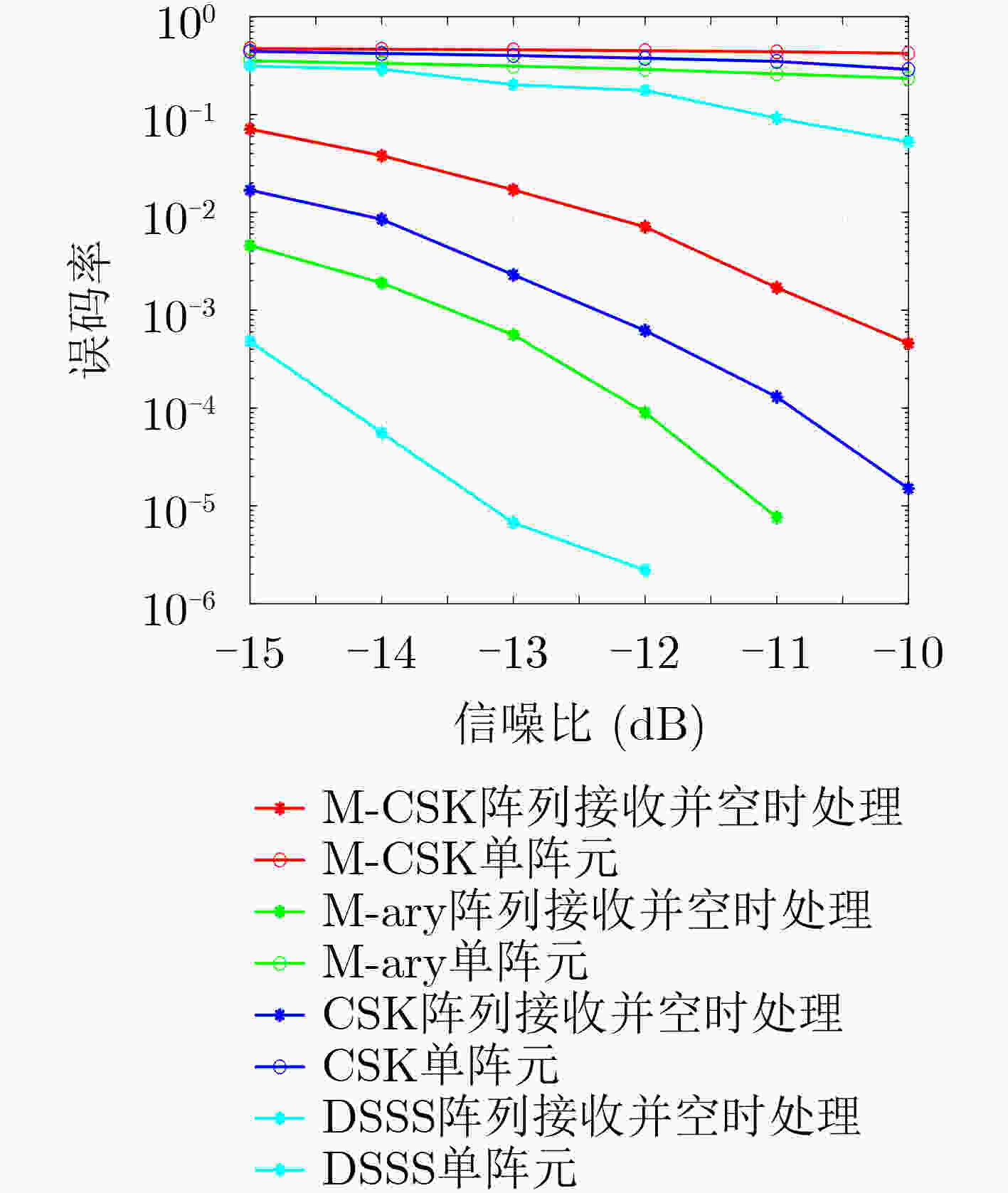

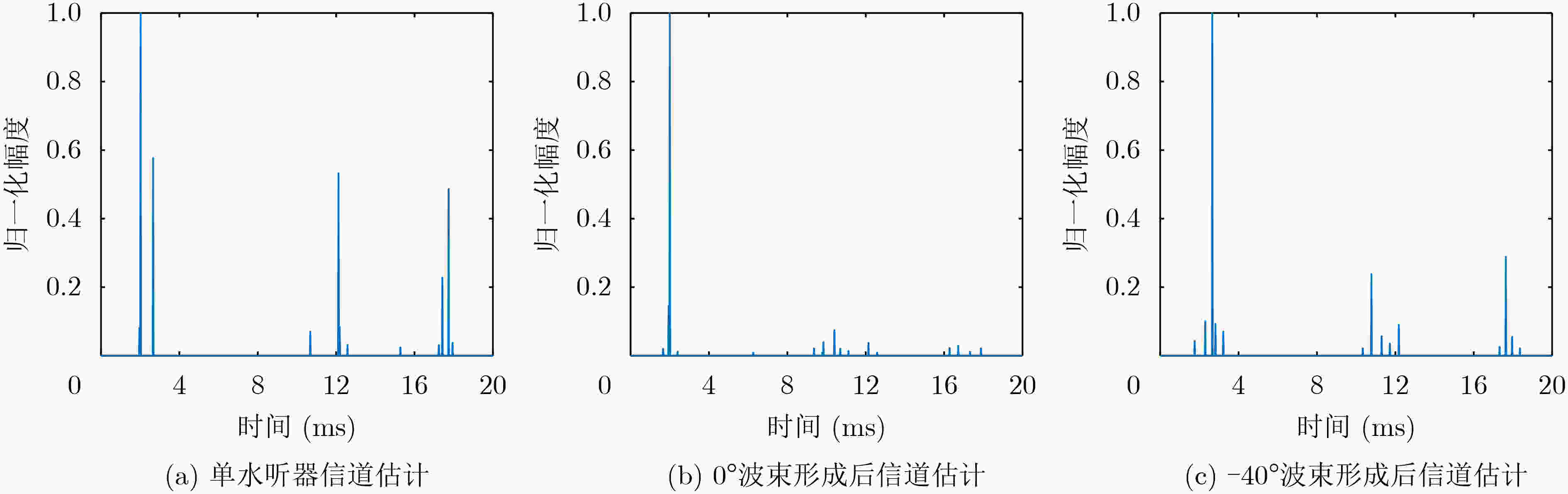
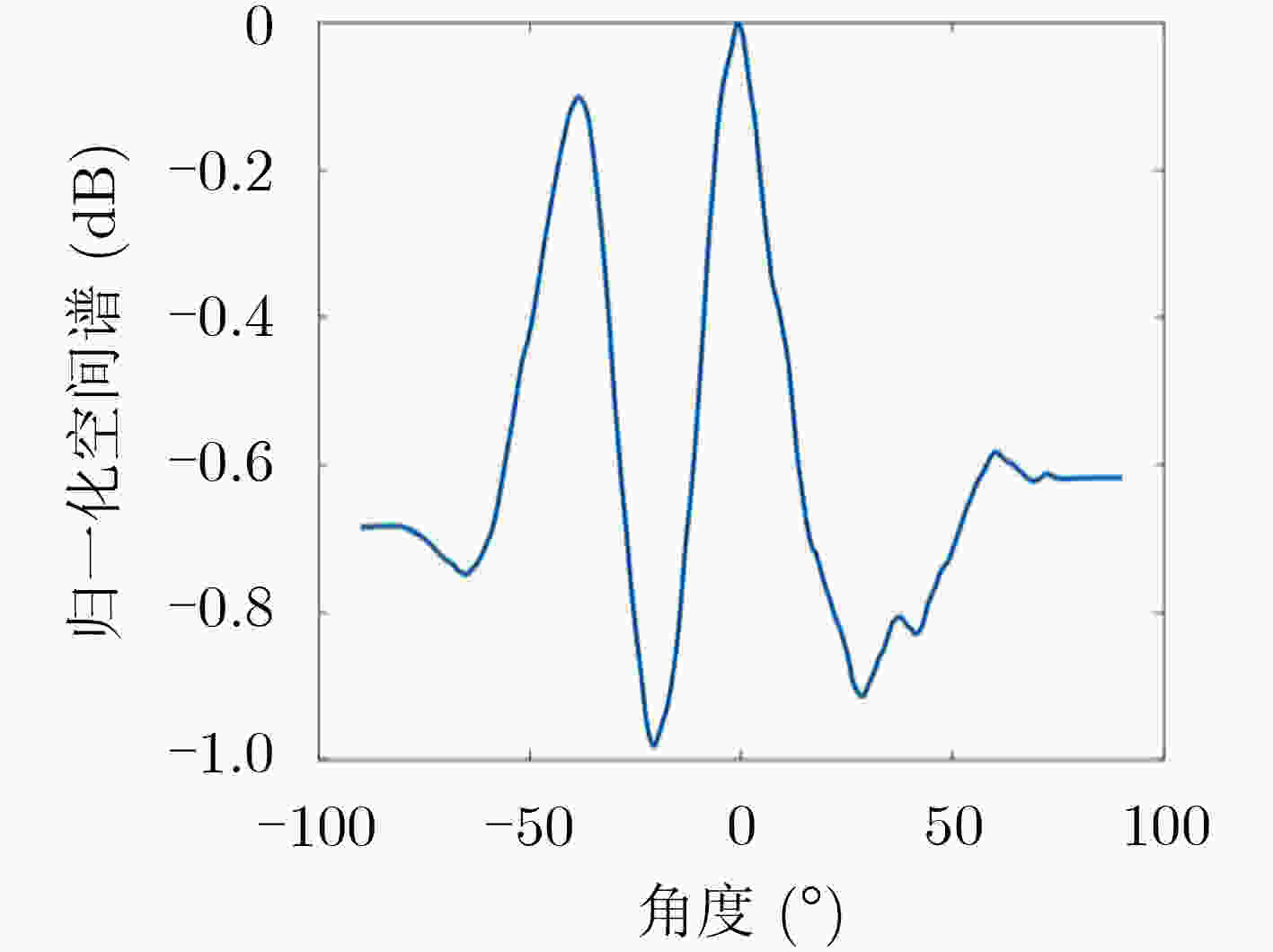
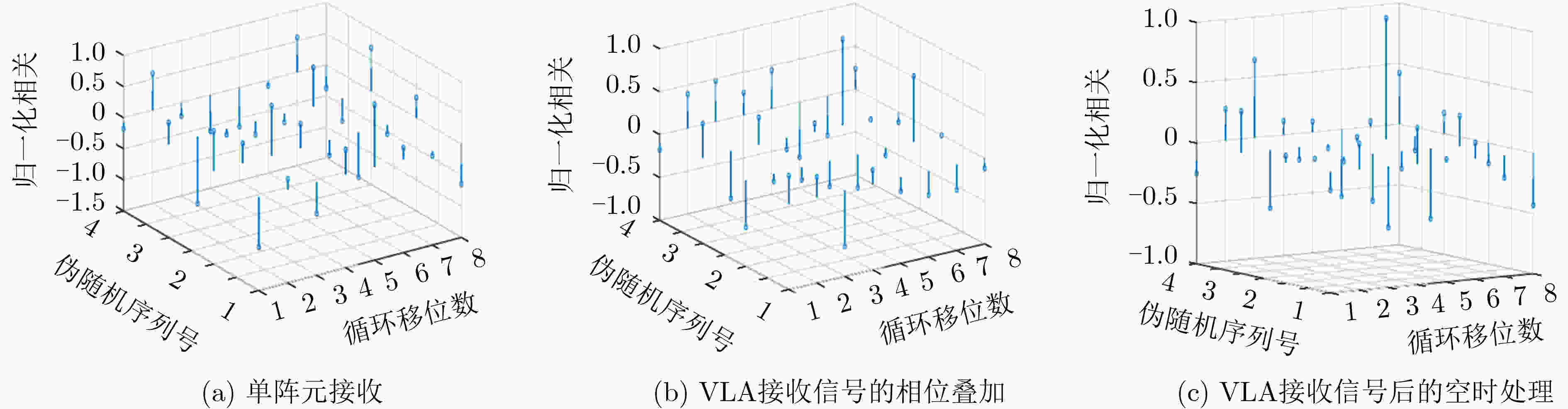


 下载:
下载:
