A Trusted Evaluation Method Based on Challenge-Response Model in Distributed Network Environment
-
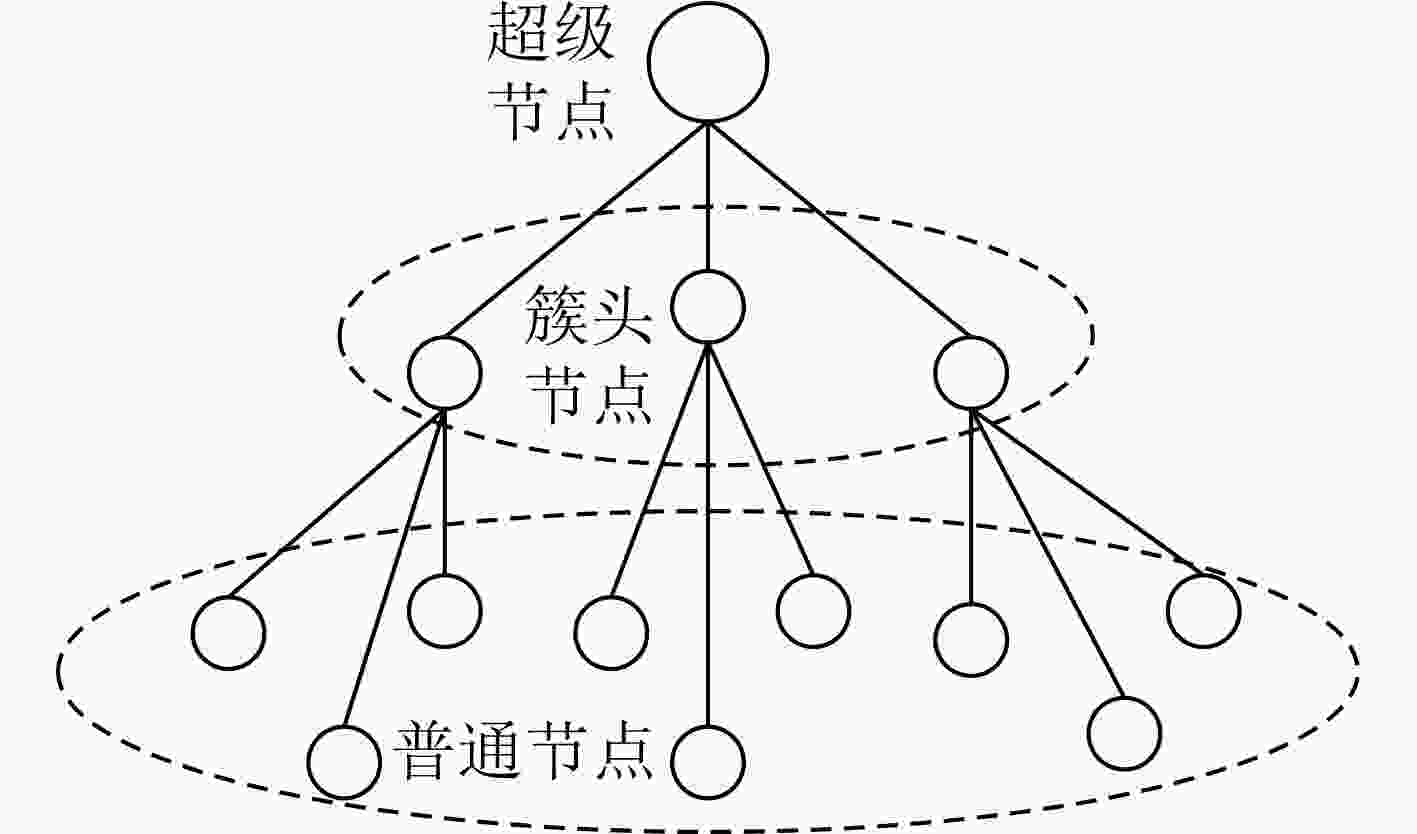
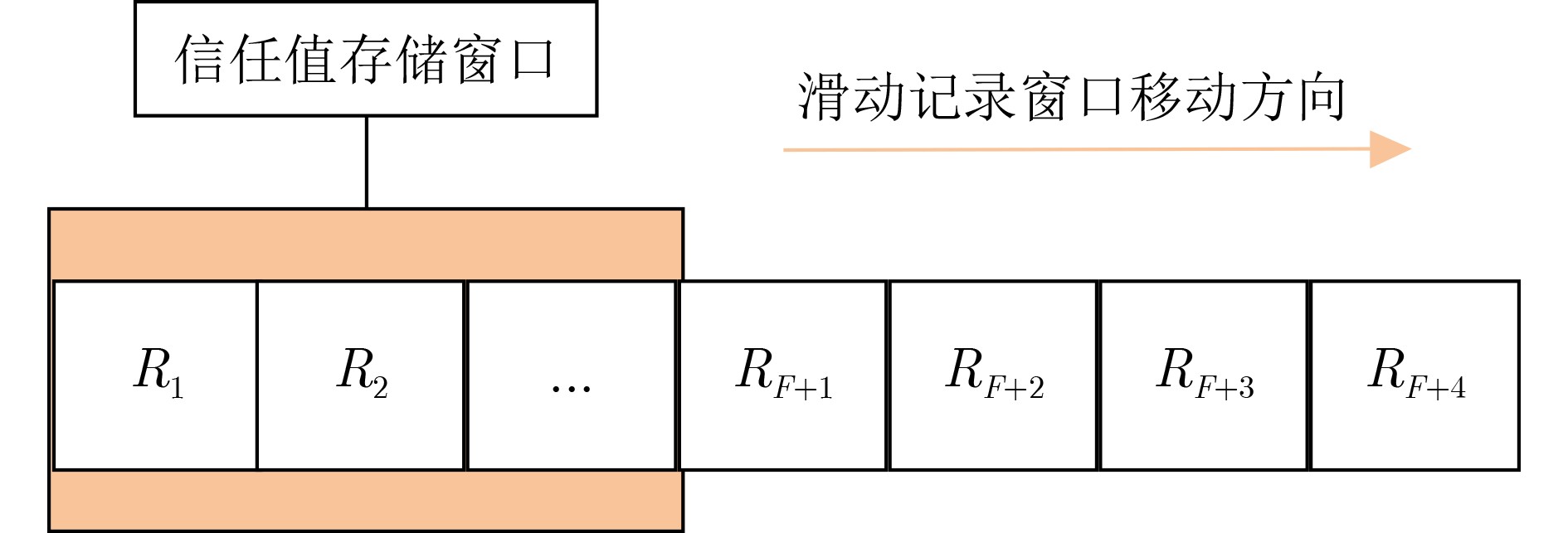
摘要: 运用信任模型进行可信评估是解决分布式网络安全问题的重要手段。然而,目前大部分研究工作把研究重点放在如何收集更完整的信任证据,以及如何利用一些新手段如机器学习、区块链等评估节点信任值,很少对如何获取节点可靠的初始信任值进行研究。实际上,针对分布式网络提出的很多信任模型都依赖于历史信任证据,而初次对网络进行可信评估时并不具备相关历史信息。基于此,该文面向分布式网络环境的安全问题,提出了基于挑战-响应模型的可信评估方法。首先利用挑战-响应模型获取节点可靠的初始信任值,并利用此初始信任值对网络中的节点进行分簇,在簇内进行信任值计算和信任值更新,完成分布式网络环境下完整的可信评估流程。仿真结果表明,相较于统一设置初始信任值的方式,该文所提方法能对恶意节点、自私节点的信任值有较准确的预测,同时对恶意节点的检测率也更高。Abstract: Using trust models to conduct trust evaluation is an efficient way to solve the security problem in distributed networks. However, most of the researches focus on collecting trust evidence completely or using new methods such as machine learning, blockchain to conduct trust evaluation. Few of the researches focus on how to obtain reliable initial trust of network nodes. In fact, many trust models for the distributed network rely on historical trust evidence, but the historical information is unavailable for the first trust evaluation. To address this problem, a trust evaluation method based on challenge-response model is proposed. First, the challenge-response model is leveraged to obtain a reliable initial trust. Then, the trust is used for trust evaluation process, including clustering, trust calculation and trust update. Simulation results show that the proposed method has better performance than the unified initialization trust based method, in terms of the prediction accuracy for malicious nodes and selfish nodes, as well as the detection rate for malicious nodes.
-
Key words:
- Trust evaluation /
- Distributed network /
- Challenge-response model /
- Initial trust
-
表 1 内部攻击过程及后果
攻击阶段 攻击过程 攻击带来的后果 1 捕获某些物理节点 破解并获得被捕获节点存储的关键机密数据 2 将被捕获的节点或者克隆节点重新部署到原网络 扰乱网络正常通信 3 控制被捕获节点发起各种内部攻击 发起数据包篡改、重放攻击、黑洞攻击等内部攻击,威胁整个网络运行 -
[1] KURDI H A. HonestPeer: An enhanced EigenTrust algorithm for reputation management in P2P systems[J]. Journal of King Saud University - Computer and Information Sciences, 2015, 27(3): 315–322. doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2014.10.002 [2] SUN Y L, YU Wei, HAN Zhu, et al. Information theoretic framework of trust modeling and evaluation for ad hoc networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2006, 24(2): 305–317. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2005.861389 [3] ZHANG Degao, GAO Jinxin, LIU Xiaohuan, et al. Novel approach of distributed & adaptive trust metrics for MANET[J]. Wireless Networks, 2019, 25(6): 3587–3603. doi: 10.1007/s11276-019-01955-2 [4] JIANG Jinfang, HAN Guangjie, WANG Feng, et al. An efficient distributed trust model for wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2015, 26(5): 1228–1237. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2014.2320505 [5] JIANG Jinfang, ZHU Xinyu, HAN Guangjie, et al. A dynamic trust evaluation and update mechanism based on C4.5 decision tree in underwater wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(8): 9031–9040. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2999566 [6] HAN Guangjie, HE Yu, JIANG Jinfang, et al. Fault-tolerant trust model for hybrid attack mode in underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Network, 2020, 34(5): 330–336. doi: 10.1109/MNET.001.2000006 [7] NGUYEN T, HOANG D, NGUYEN D, et al. Initial trust establishment for personal space IoT systems[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Atlanta, USA, 2017: 784–789. [8] 张志华, 罗守山, 朱洪亮, 等. WSN异步休眠模式下节点捕获早期检测方法[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2018, 41(3): 32–38. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2017-228ZHANG Zhihua, LUO Shoushan, ZHU Hongliang, et al. A node capture early detection scheme for WSN in asynchronous sleep mode[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2018, 41(3): 32–38. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2017-228 [9] LIN Xiaodong. CAT: Building couples to early detect node compromise attack in wireless sensor networks[C]. 2009 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, Honolulu, USA, 2009: 1–6. [10] VERGNAUD D. Comment on “efficient and secure outsourcing scheme for RSA decryption in internet of things”[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(11): 11327–11329. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3004346 [11] DESAI S S and NENE M J. Node-level trust evaluation in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(8): 2139–2152. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2894027 [12] DESAI S S and NENE M J. Multihop trust evaluation using memory integrity in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 4092–4100. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3101051 [13] FANG Weidong, ZHANG Chuanlei, SHI Zhidong, et al. BTRES: Beta-based trust and reputation evaluation system for wireless sensor networks[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2016, 59: 88–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2015.06.013 [14] UZUNOĞLU B. An adaptive Bayesian approach with subjective logic reliability networks for preventive maintenance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2020, 69(3): 916–924. doi: 10.1109/TR.2019.2916722 [15] DING Zhuai, YUE Zijie, YANG Shanlin, et al. A novel trust model based overlapping community detection algorithm for social networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2020, 32(11): 2101–2114. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2019.2914201 [16] BOUDAGDIGUE C, BENSLIMANE A, KOBBANE A, et al. Trust management in industrial internet of things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 3667–3682. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.2997179 [17] ZHANG Juanjuan, SUN Qibo, ZHOU Ao, et al. A novel trust update mechanism based on sliding window for trust management system[C]. The 16th International Conference on Computational Science and its Applications, Beijing, China, 2016: 521–528. [18] XIONG Li and LIU Ling. PeerTrust: Supporting reputation-based trust for peer-to-peer electronic communities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2004, 16(7): 843–857. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2004.1318566 [19] WANG Tian, LI Yang, FANG Weiwei, et al. A comprehensive trustworthy data collection approach in sensor-cloud systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Big Data, 2022, 8(1): 140–151. doi: 10.1109/TBDATA.2018.2811501 -






 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载:
