Three Subnets Image Dehazing Method Based on Transfer Learning
-
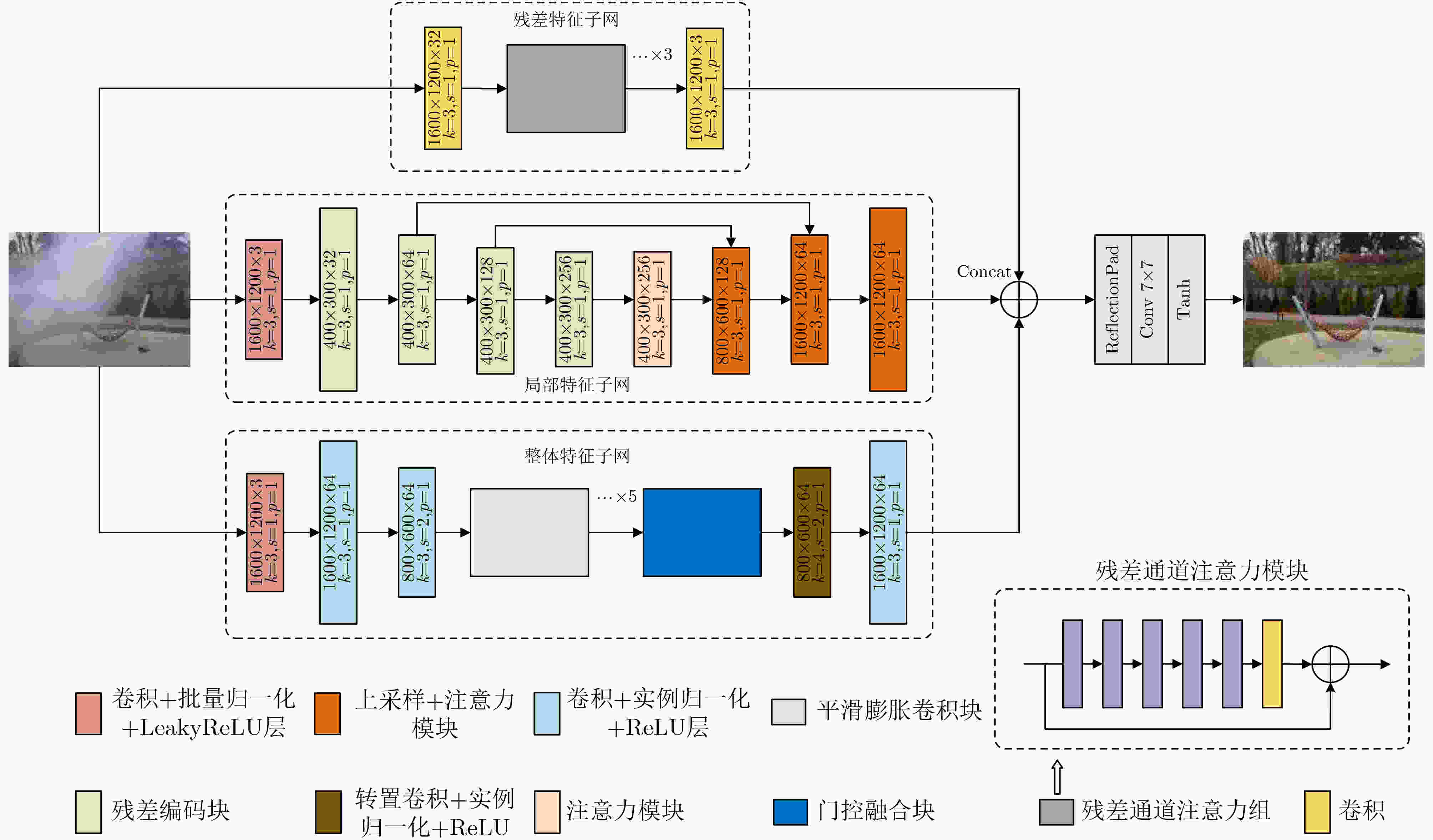
摘要: 目前大部分图像去雾算法只在一种或几种均匀雾图数据集中有较好的表现,对于不同风格或非均匀雾图数据集去雾效果较差,同时算法在实际应用中会因模型泛化能力差导致模型场景受限。针对上述情况,该文提出一种基于迁移学习的卷积神经网络(CNN)用于解决去雾算法中非均匀雾图处理效果不佳和模型泛化能力差等问题。首先,该文使用ImageNet预训练的模型参数作为迁移学习模型的初始参数,以加速模型训练收敛速度。其次,主干网络模型由3个子网组成:残差特征子网络、局部特征提取子网络和整体特征提取子网络。3子网结合以保证模型可从整体和局部两个方面进行特征提取,在现实雾场景(浓雾、非均匀雾)中获得较好的去雾效果。该文在模型训练效率、去雾质量和雾图场景选择灵活性3个方面进行了研究和改进,为衡量模型性能,模型选择在去雾难度较大的非均匀雾图数据集NTIRE2020和NTIRE2021上进行定量与定性实验。实验结果证明3子网模型在图像主观和客观评价指标两个方面都取得了较好的效果。该文模型改善了算法泛化性能差和小数据集难以进行模型训练的问题,可将该文成果广泛应用于小规模数据集和多变场景图像的去雾工作中。Abstract: Most image dehazing algorithms perform well in one or several homogeneous hazy map datasets, but process poor performance in datasets with different styles or nonhomogeneous hazy map datasets. Meanwhile, in practical application, the algorithm will be limited in model scenes due to poor model generalization ability. In view of the above situation, a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based on transfer learning is proposed to alleviate problems such as nonhomogeneous hazy map dehazing and defective generalization ability. ImageNet pre-trained model parameters are utilized as the initial parameters of the transfer learning model. In order to accelerate the convergence rate of model training, the algorithm is able to adapt quickly to different datasets. The model is composed of three subnets: residual feature sub network, local network and the overall feature extraction of feature extraction sub network. The model is ensured by the combination of three subnets to extract features from both the whole image feature and the local image feature, and achieves excellent dehazing effect in real hazy scenes (homogeneous and nonhomogeneous haze). In summary, the proposed method improves the model efficiency, haze removal quality and convenience of hazy map scene selection. To quantitatively and qualitatively measure the performance of the model, experiments are performed on NTIRE2020 and NTIRE2021, which are nonhomogeneous hazy map datasets with high haze removal difficulty. Experimental results show that the three-subnets model achieves outstanding results in both subjective and objective evaluation metrics. Unsatisfactory generalization performance of the algorithm and training difficulty are improved in small datasets. The architecture of three subnets can be widely utilized in small-scale datasets and changeable scene image dehazing projects.
-
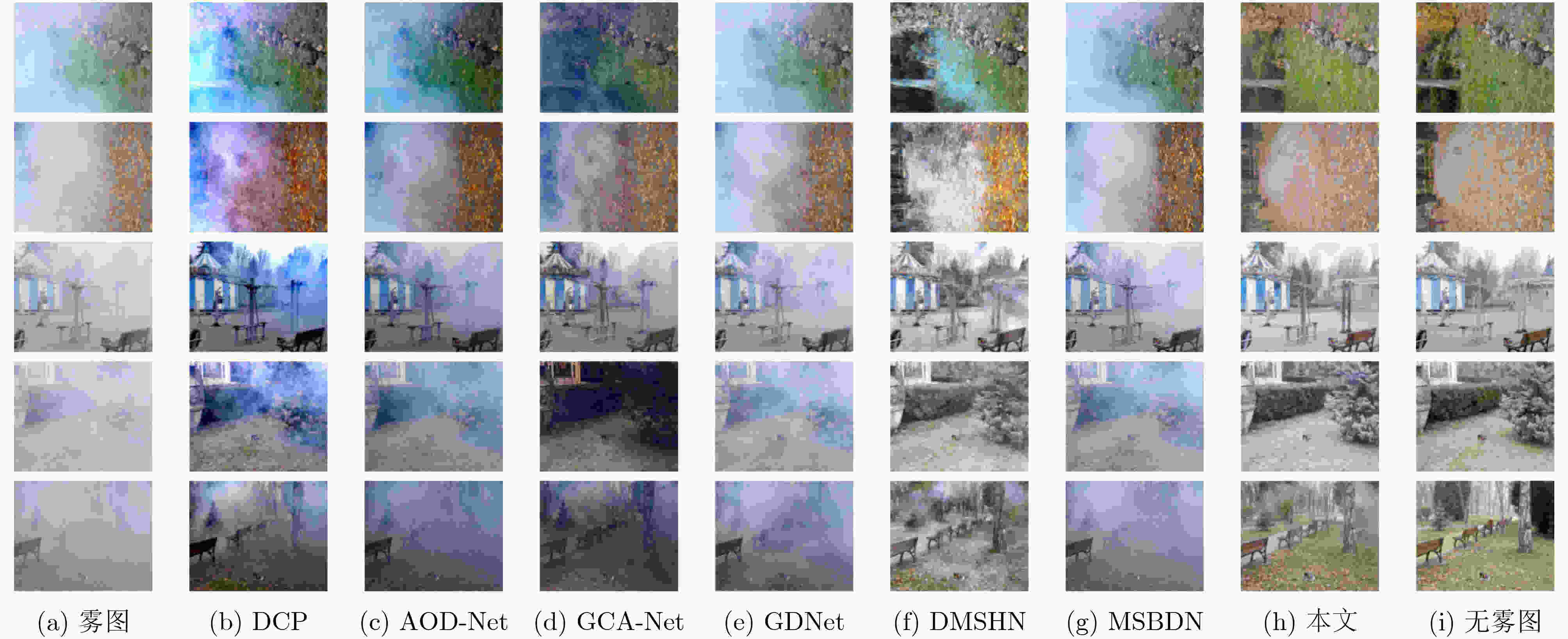
表 1 3子网模型结果与主流去雾算法去雾图像数值比较表
算法 指标 PSNR↑ SSIM↑ LPIPS↓ 运行时间 (s)↓ DCP 10.79 0.34 0.432 13.45 AOD-Net 11.67 0.38 0.471 3.39 GCA-Net 11.09 0.34 0.402 4.48 GDNet 13.56 0.58 0.473 3.02 DMSHN 12.05 0.31 0.376 2.96 MSBDN 12.05 0.32 0.478 5.14 本文 15.73 0.69 0.326 3.47 GT +∞ 1 0 × 表 2 3子网模型结果与2子网去雾图像质量数值对比
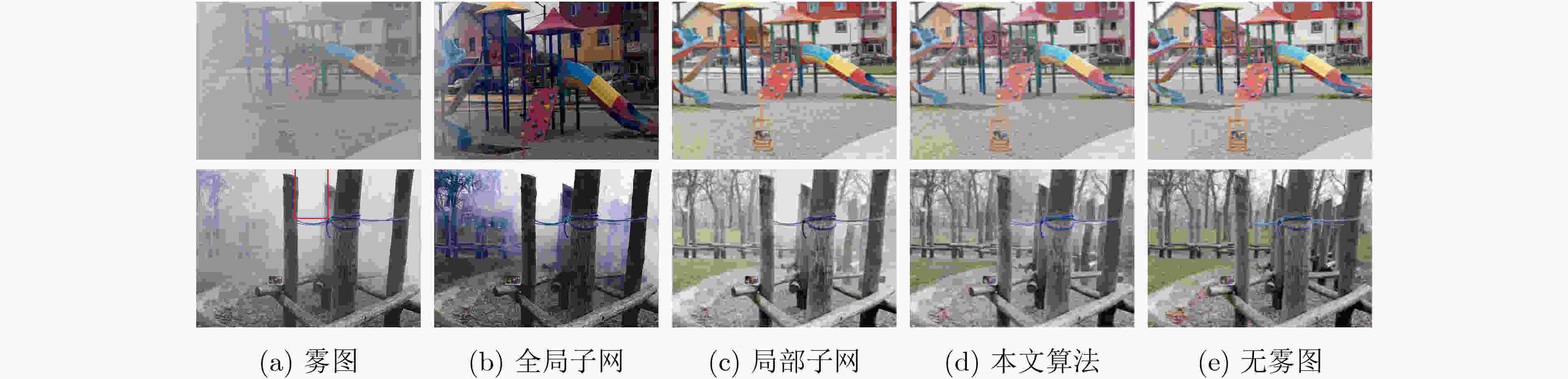
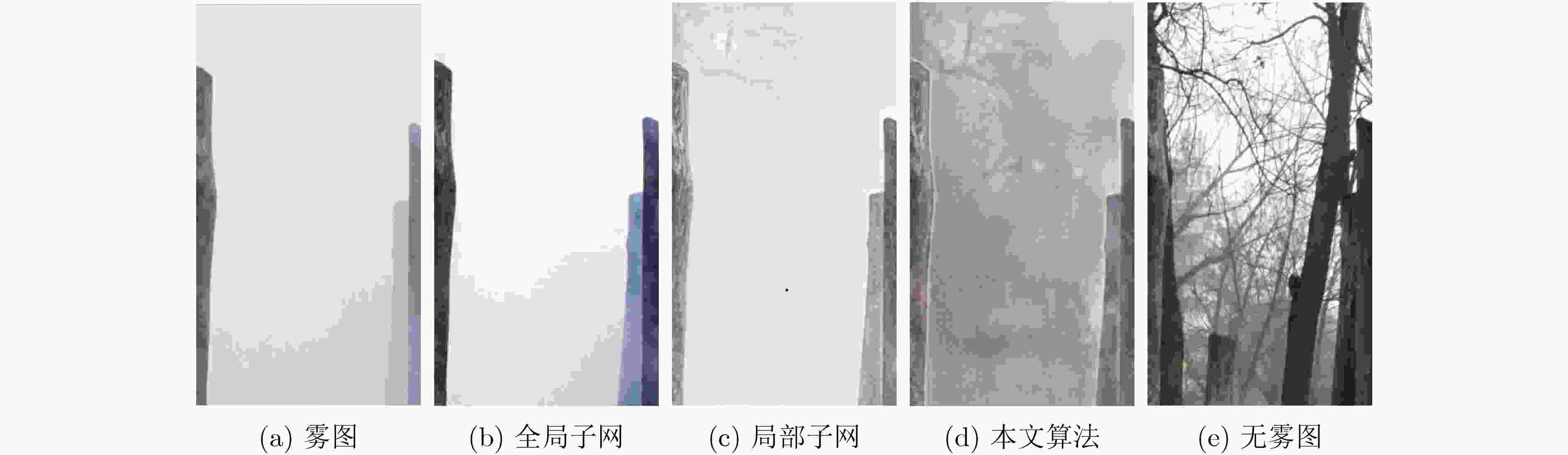
PSNR SSIM LPIPS 模型参数 全局特征提取子网 13.9719 0.6750 0.309 0.67M 局部特征提取子网 21.2036 0.7822 0.256 47.37M 本文算法 21.7329 0.7923 0.262 47.86M -
[1] HOWARD J N. Scattering phenomena. (Book reviews: Optics of the atmosphere. Scattering by molecules and particles)[J]. Science, 1977, 196(4294): 1084–1085. doi: 10.1126/science.196.4294.1084.b [2] PIZER S M, AMBURN E P, AUSTIN J D, et al. Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations[J]. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 1987, 39(3): 355–368. doi: 10.1016/S0734-189X(87)80186-X [3] OPPENHEIM A V. Speech analysis-synthesis system based on homomorphic filtering[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1969, 45(2): 458–465. doi: 10.1121/1.1911395 [4] ZHANG Dengsheng. Wavelet transform[M]. ZHANG Dengsheng. Fundamentals of Image Data Mining: Analysis, Features, Classification and Retrieval. Cham: Springer, 2021. [5] LAND E H. The retinex[J]. American Scientist, 1964, 52(2): 247–264. [6] HE Kaiming, SUN Jian, and TANG Xiaoou. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341–2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [7] TAN R T. Visibility in bad weather from a single image[C]. 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, USA, 2008: 1–8. [8] 杨燕, 王志伟. 基于均值不等关系优化的自适应图像去雾算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 755–763. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190368YANG Yan and WANG Zhiwei. Adaptive image Dehazing algorithm based on mean unequal relation optimization[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 755–763. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190368 [9] RAIKWAR S C and TAPASWI S. Lower bound on transmission using non-linear bounding function in single image Dehazingin[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 4832–4847. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2975909 [10] 潘金山. 基于深度学习的图像去模糊方法研究进展[J]. 计算机科学, 2021, 48(3): 9–13. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.201200043PAN Jinshan. Research progress on deep learning-based image deblurring[J]. Computer Science, 2021, 48(3): 9–13. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.201200043 [11] CAI Bolun, XU Xiangmin, JIA Kui, et al. DehazeNet: An end-to-end system for single image haze removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(11): 5187–5198. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2598681 [12] LI Boyi, PENG Xiulian, WANG Zhangyang, et al. AOD-Net: All-in-one dehazing network[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017. [13] ZHANG He and PATEL V M. Densely connected pyramid dehazing network[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3194–3203. [14] LIU Xiaohong, MA Yongrui, SHI Zhihao, et al. GridDehazeNet: Attention-based multi-scale network for image dehazing[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 7313–7322. [15] DONG Hang, PAN Jinshan, XIANG Lei, et al. Multi-scale boosted dehazing network with dense feature fusion[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 2154–2164. [16] ZHAO Shiyu, ZHANG Lin, SHEN Ying, et al. RefineDNet: A weakly supervised refinement framework for single image dehazing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 3391–3404. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3060873 [17] YU Yankun, LIU Huan, FU Minghan, et al. A two-branch neural network for non-homogeneous dehazing via ensemble learning[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Nashville, USA, 2021: 193–202. [18] SHAO Yuanjie, LI Lerenhan, REN Wenqi, et al. Domain adaptation for image dehazing[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, USA, 2020: 2808–2817. [19] DONG Yu, LIU Yihao, ZHANG He, et al. FD-GAN: Generative adversarial networks with fusion-discriminator for single image dehazing[C]. 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 10729–10736. [20] FU Minghan, LIU Huan, YU Yankun, et al. DW-GAN: A discrete wavelet transform GAN for NonHomogeneous dehazing[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Nashville, USA, 2021: 203–212. [21] LI Yuenan, LIU Yuhang, YAN Qixin, et al. Deep dehazing network with latent ensembling architecture and adversarial learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 1354–1368. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3044208 [22] 汤勇明, 戴荣时, 俞峰, 等. 视频图像去雾算法的自适应机制设计及FPGA加速实现[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(9): 2542–2551. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200554TANG Yongming, DAI Rongshi, YU Feng, et al. Design of adaptive video image dehazing algorithm and FPGA accelerated implementation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(9): 2542–2551. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200554 [23] DENG Jia, DONG Wei, SOCHER R, et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database[C]. 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 2009: 248–255. [24] GAO Shanghua, CHENG Mingming, ZHAO Kai, et al. Res2Net: A new multi-scale backbone architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(2): 652–662. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2938758 [25] YU F and KOLTUN V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions[J]. arXiv: 1511.07122, 2015. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
