Service Function Chain Anomaly Detection Based on Distributed Generative Adversarial Network in Network Slicing Scenario
-
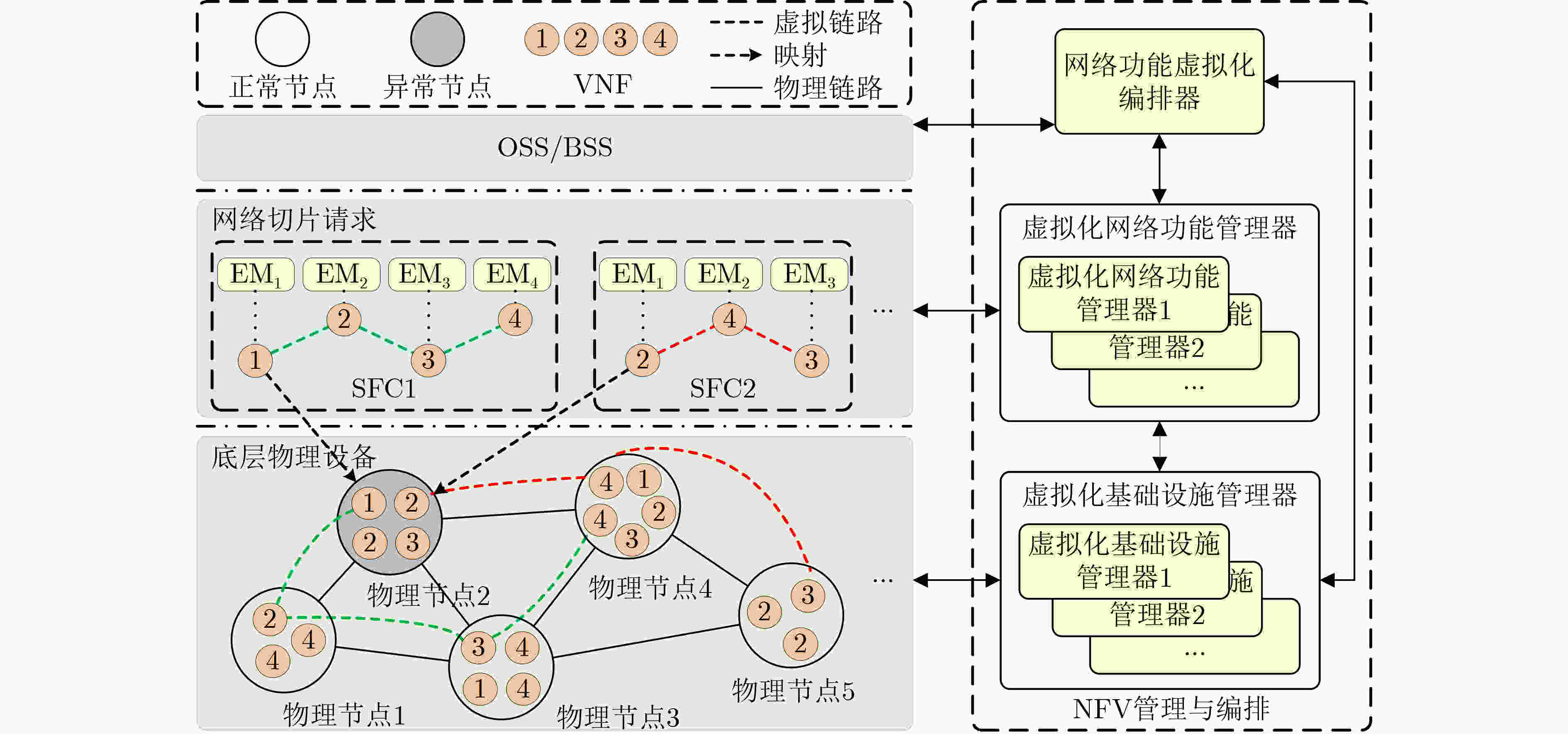
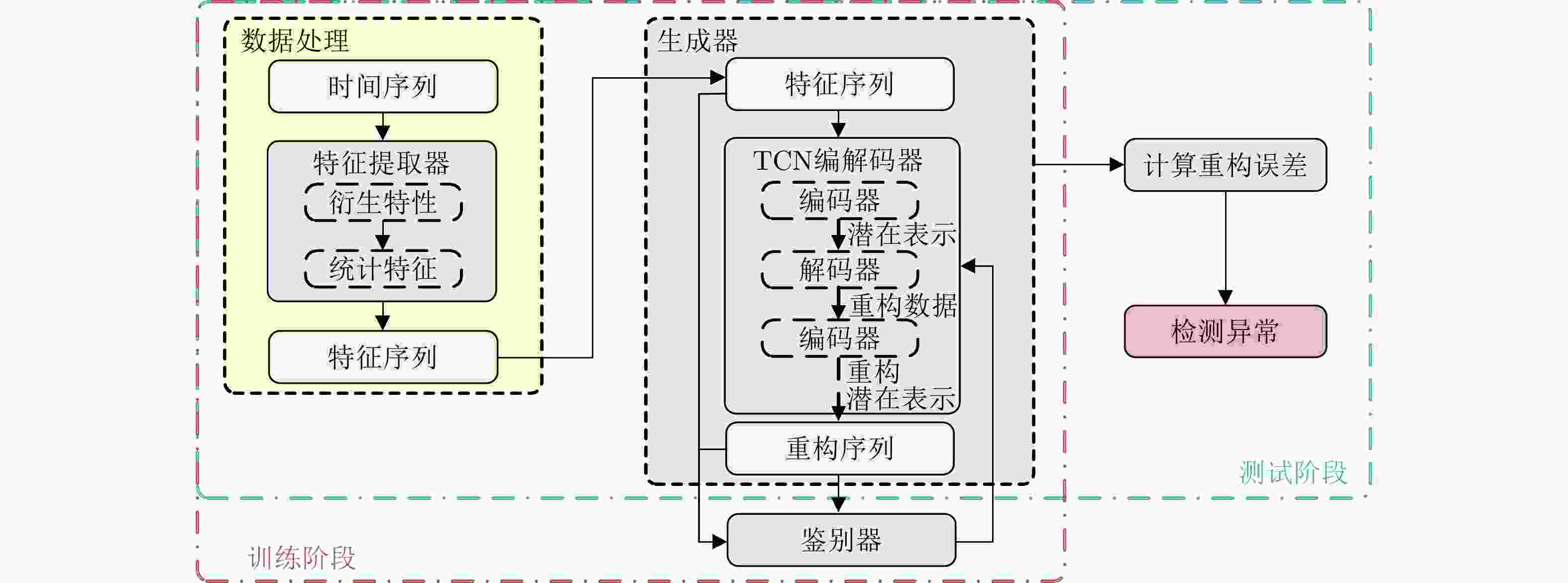
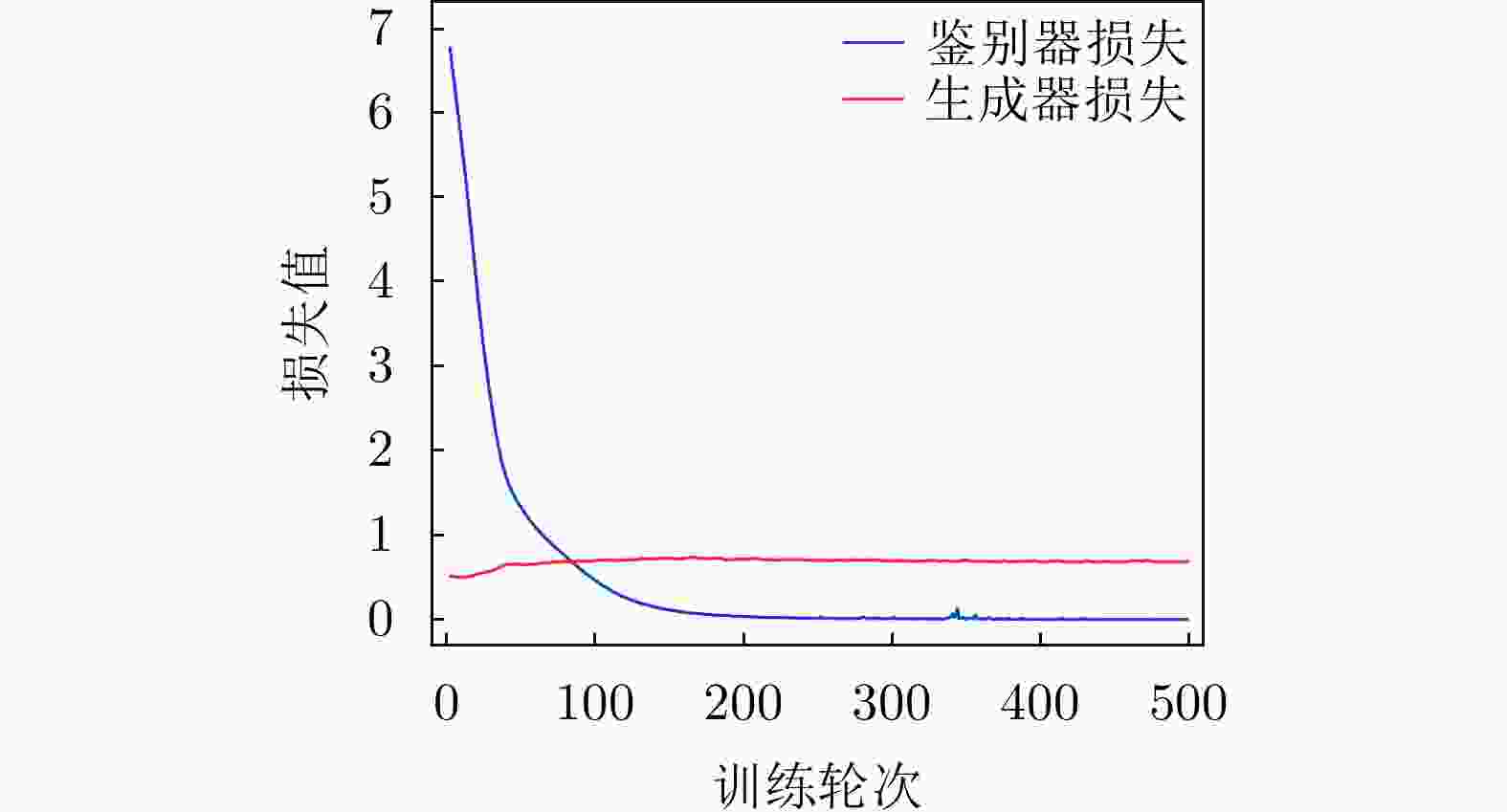
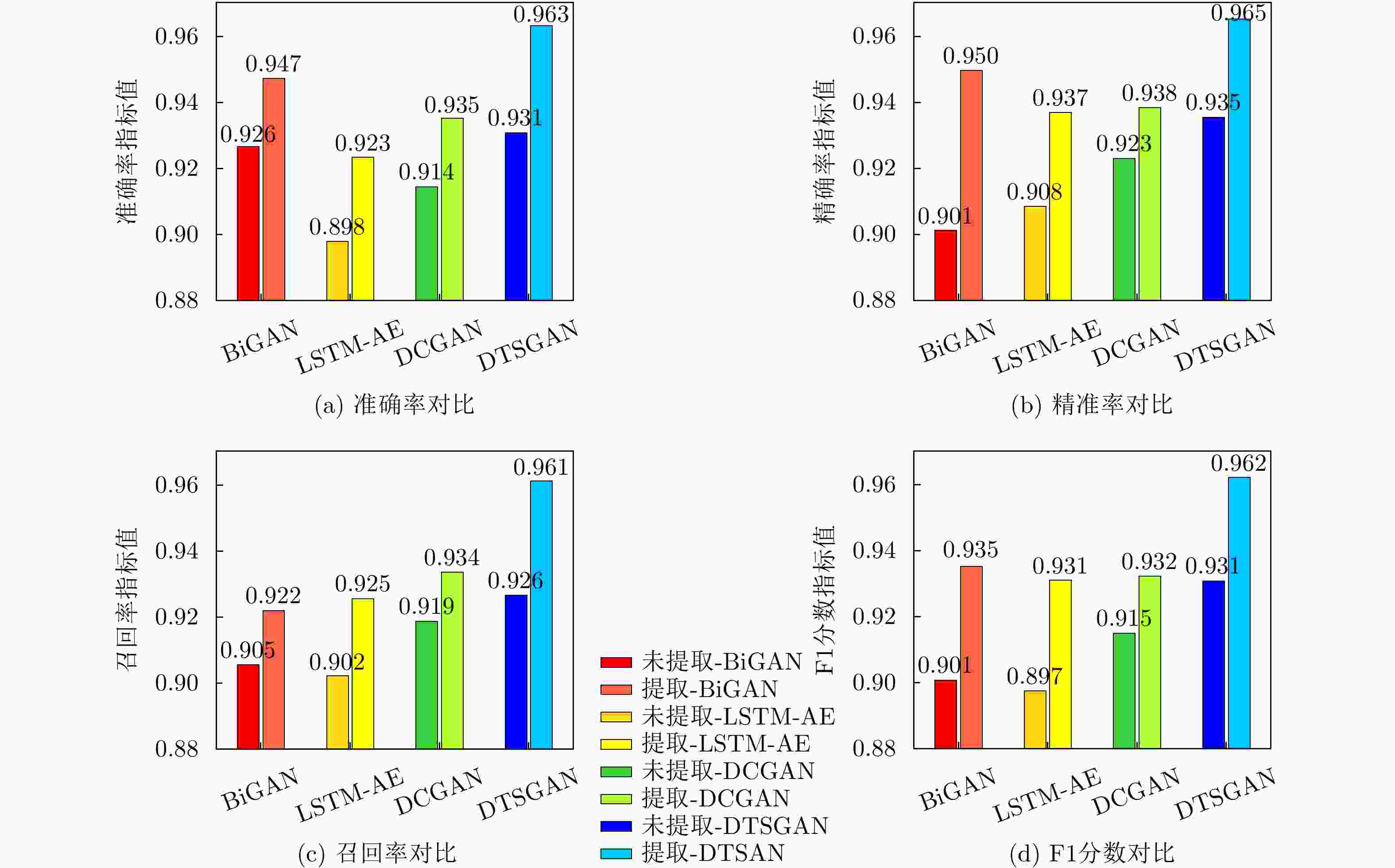
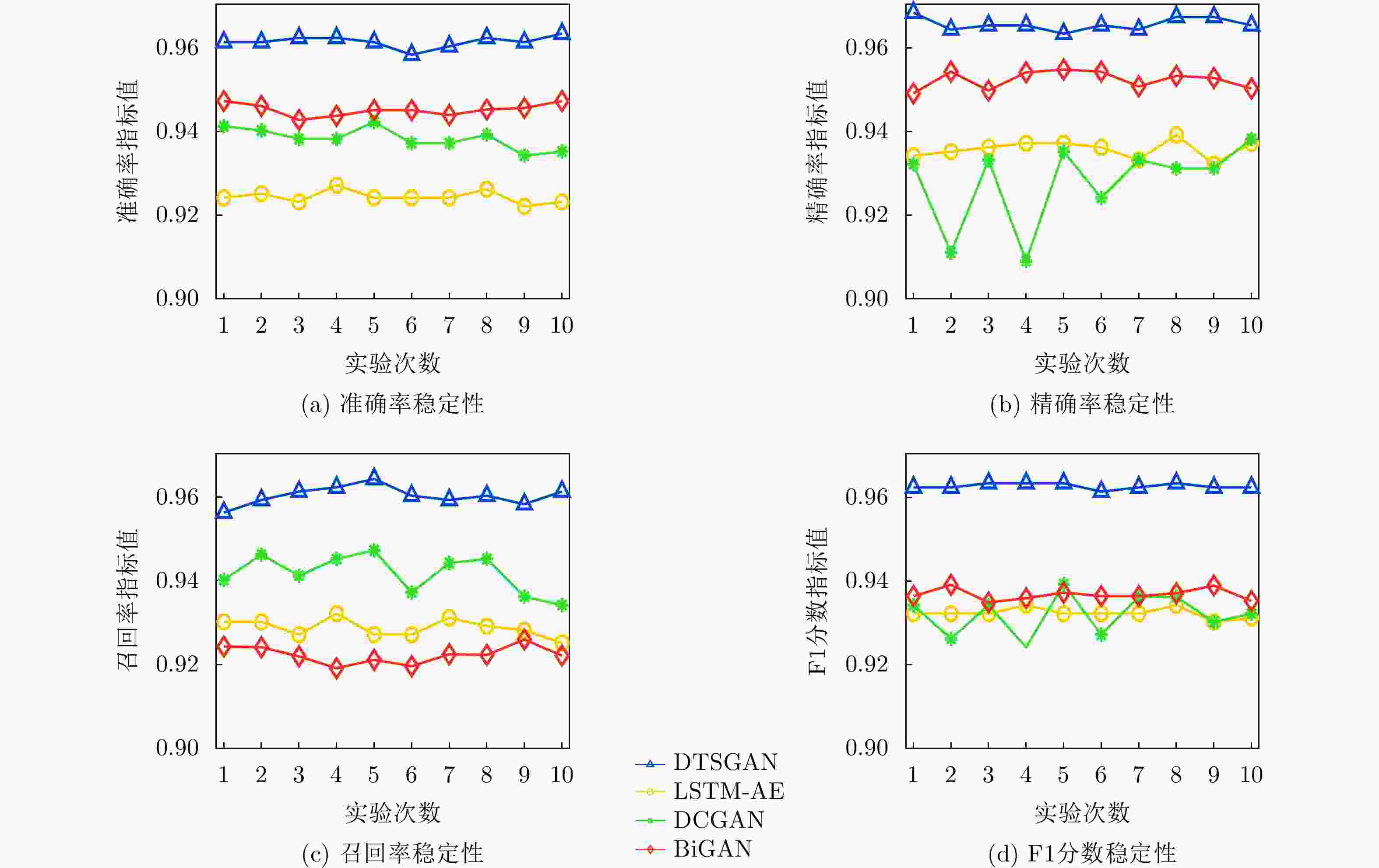
摘要: 针对网络切片场景中,由于软硬件异常而导致服务功能链(SFC)异常的问题,该文提出一种基于分布式生成对抗网络(GAN)的时间序列异常检测模型(DTSGAN)。首先,为学习SFC中正常数据的特征,提出分布式GAN架构,对SFC中包含的多个虚拟网络功能(VNF)进行异常检测;其次,针对时间序列数据构建一种基于滑动窗口数据特征提取器,通过提取数据的两种衍生特性和8种统计特征以挖掘深层次特征,得到特征序列;最后,为学习并重构数据特征,提出时间卷积网络(TCN)与自动编码器(AE)构建的3层编解码器作为分布式生成器,生成器通过异常得分函数衡量重构数据与输入数据的差异以检测VNF的状态,进而完成SFC的异常检测。在数据集Clearwater上采用准确率、精确率、召回率和F1分数这4个性能指标验证了该文所提模型的有效性和稳定性。Abstract: For the problem of Service Function Chain (SFC) anomalies due to hardware and software anomalies in network slicing scenarios, a Distributed Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based Time Series anomaly detection model (DTSGAN) is proposed. First, to learn the characteristics of normal data in SFC, a distributed GAN architecture is proposed for anomaly detection of multiple Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) contained in SFC. Then, a feature extractor based on sliding window data is constructed for time series data, and the feature sequence is obtained by extracting two derived characteristics and eight statistical features of the data to mine the deep-level features. Finally, in order to learn and reconstruct data characteristics, a three-layer codec constructed by Time Convolutional Network (TCN) and Auto-Encoder (AE) is proposed as a distributed generator, which measures the difference between reconstructed data and input data by anomaly score function to detect the state of VNF, and then completes the anomaly detection of SFC. The effectiveness and stability of the proposed model are verified on the dataset Clearwater using four evaluation metrics: accuracy, precision, recall and F1 score.
-
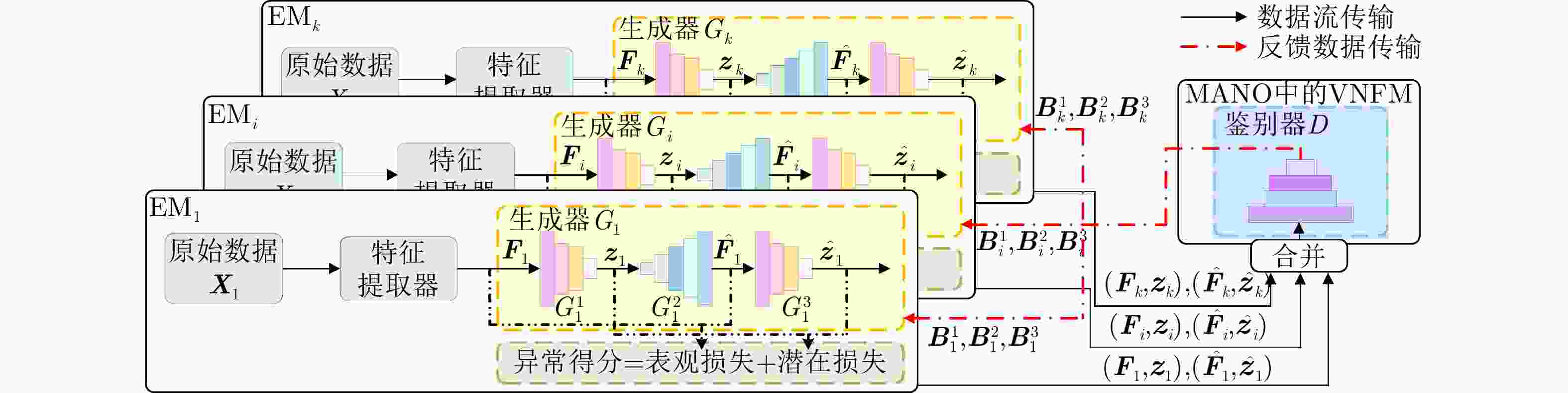
算法1 DTSGAN在MANO中的训练 输入:数据流$ ({{\boldsymbol{F}}_i},{{\boldsymbol{z}}_i}),({{{ {\boldsymbol {\boldsymbol{F}}}}}_i},{{{\hat {\boldsymbol z}}}_i}) $ 输出:误差项$ {\boldsymbol{B}}_i^1,{\boldsymbol{B}}_i^2,{\boldsymbol{B}}_i^3 $,鉴别器输出$ D({{{\hat {\boldsymbol F}}}_i},{{{\hat {\boldsymbol z}}}_i}) $ (1) function ${{\rm{MANODIS}}} (({ {\boldsymbol{F} }_i},{ {\boldsymbol{z} }_i}),({ { {\hat {\boldsymbol F} } }_i},{ { {\hat {\boldsymbol z} } }_i}),d,k)$ // 鉴别器$ D $训
练函数(2) for $ j \in [1,b] $ do // 鉴别器$ D $训练轮数为$ b $ (3) for $ i \in [1,k] $ do // $ {\text{E}}{{\text{M}}_i} $的个数为$ k $ (4) 从$ {\text{E}}{{\text{M}}_i} $中获得数据流$ ({{\boldsymbol{F}}_i},{{\boldsymbol{z}}_i}),({{{\hat {\boldsymbol F}}}_i},{{{\hat {\boldsymbol z}}}_i}) $ (5) 计算第$ i $个梯度$ \Delta {{\boldsymbol{w}}_{{\text{d}}i}} $ (6) if $ j = d $ do (7) 分别根据式(8)—式(10)计算$ G_i^1 $,$ G_i^2 $, $ G_i^3 $的误差项$ {\boldsymbol{B}}_i^1 $,
$ {\boldsymbol{B}}_i^2 $, $ {\boldsymbol{B}}_i^3 $(8) 将鉴别器结果$ {\boldsymbol{B}}_i^1,{\boldsymbol{B}}_i^2,{\boldsymbol{B}}_i^3,D({{{\hat {\boldsymbol F}}}_i},{{{\hat {\boldsymbol z}}}_i}) $发送至相应的
$ {\text{E}}{{\text{M}}_i} $(9) end if (10) end for (11) 对$ k $个梯度求平均值得到$ \Delta {{\boldsymbol{w}}_{\text{d}}} $ (12) 使用$ \Delta {{\boldsymbol{w}}_{\text{d}}} $更新鉴别器$ D $参数$ {{\boldsymbol{w}}_{\text{d}}} $ (13) end for (14) end function 算法2 DTSGAN在$ {\text{E}}{{\text{M}}_i} $中的训练 输入:特征序列$ {{\mathbf{F}}_i} $,鉴别器反馈$ {\mathbf{B}}_i^1,{\mathbf{B}}_i^2,{\mathbf{B}}_i^3 $ 输出:数据流$ ({{\mathbf{F}}_i},{{\mathbf{z}}_i}),({{{\hat {\boldsymbol F}}}_i},{{{\hat {\boldsymbol z}}}_i}) $ (1) function $ {\text{EMGEN}}({{\mathbf{F}}_i},{\mathbf{B}}_i^1,{\mathbf{B}}_i^2,{\mathbf{B}}_i^3,L) $ // 生成器$ {G_i} $训练函数 (2) 编码器$ G_i^1 $提取潜在表示$ {{\mathbf{z}}_i} $ (3) 解码器$ G_i^2 $重构特征序列$ {{{\hat {\boldsymbol F}}}_i} $ (4) 编码器$ G_i^3 $重构潜在表示$ {{{\hat {\boldsymbol z}}}_i} $ (5) 将数据流$ ({{\mathbf{F}}_i},{{\mathbf{z}}_i}),({{{\hat {\boldsymbol F}}}_i},{{{\hat {\boldsymbol z}}}_i}) $发送至鉴别器$ D $ (6) if $ L \ne 1 $ do // 训练轮数为$ L $ (7) 从鉴别器$ D $获取误差项$ {\mathbf{B}}_i^1,{\mathbf{B}}_i^2,{\mathbf{B}}_i^3 $ (8) 分别根据式(15)—式(17)计算计算$ G_i^1 $,$ G_i^2 $, $ G_i^3 $的梯度
$ \Delta {\mathbf{w}}_i^{1,l} $, $ \Delta {\mathbf{w}}_i^{2,l} $, $ \Delta {\mathbf{w}}_i^{3,l} $(9) 使用$ \Delta {\mathbf{w}}_i^{1,l} $,$ \Delta {\mathbf{w}}_i^{2,l} $, $ \Delta {\mathbf{w}}_i^{3,l} $更新生成器$ {G_i} $参数
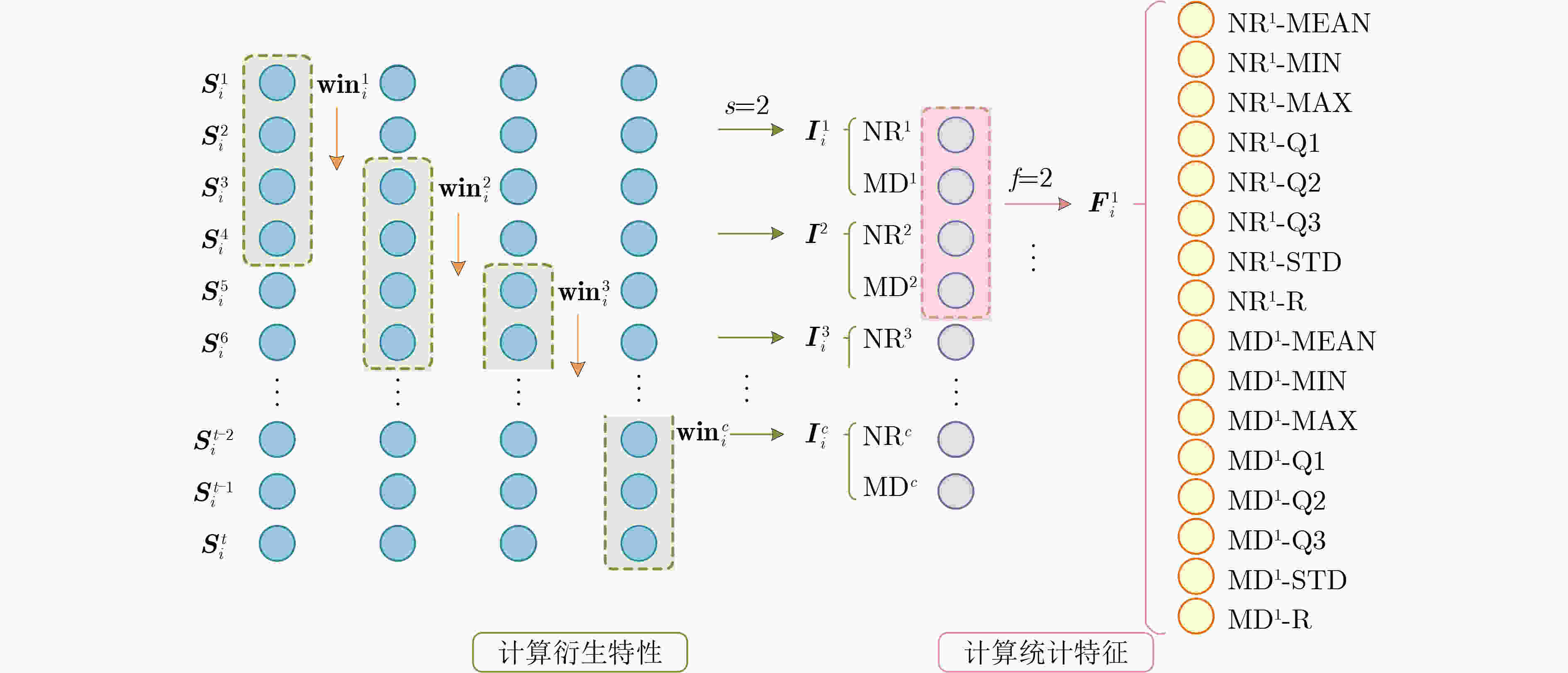
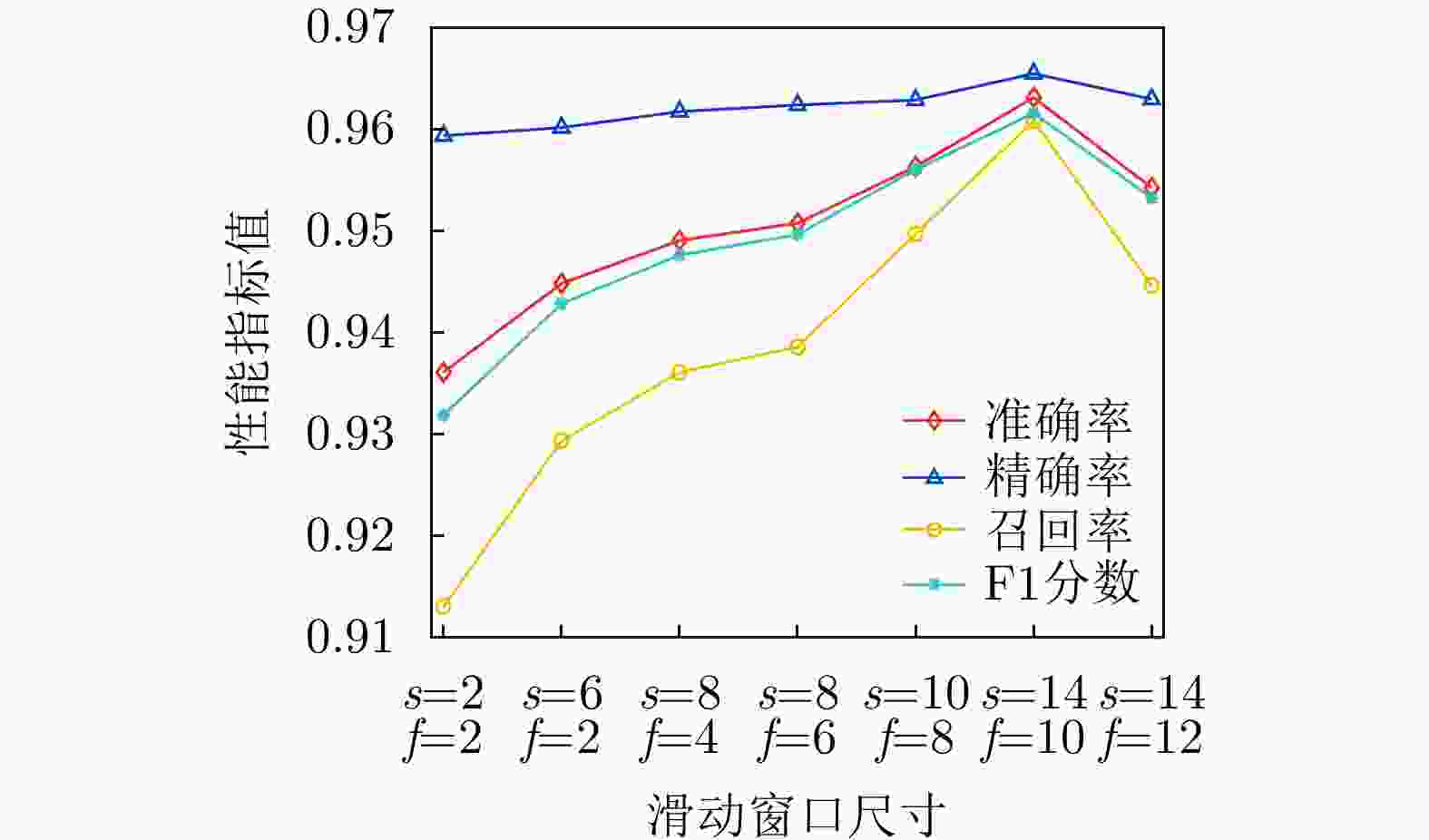
$ {\mathbf{w}}_i^1,{\mathbf{w}}_i^2,{\mathbf{w}}_i^3 $(10) end if (11) end function 表 1 滑动窗口尺寸设置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 衍生特性滑动窗口尺寸$ s $ 2 6 8 8 10 14 14 统计特征滑动窗口尺寸$ f $ 2 2 4 6 8 10 12 -
[1] ESCOLAR A M, CALERO J, and WANG Q. SliceNetVSwitch: Definition, design and implementation of 5G multi-tenant network slicing in software data paths[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2020, 17(4): 2212–2225. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2020.3029653 [2] CHERRARED S, IMADALI S, FABRE E, et al. A survey of fault management in network virtualization environments: Challenges and solutions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2019, 16(4): 1537–1551. doi: 10.1109/TNSM.2019.2948420 [3] SAUVANAUD C, LAZRI K, KAANICHE M, et al. Anomaly detection and root cause localization in virtual network functions[C]. 2016 IEEE 27th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE), Ottawa, Canada, 2016: 196–206. [4] COTRONEO D, NATELLA R, and ROSIELLO S. A fault correlation approach to detect performance anomalies in virtual network function chains[C]. 2017 IEEE 28th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE), Toulouse, France, 2017: 90–100. [5] BLAISE A, WONG S, and AGHVAMI A H. Virtual network function service chaining anomaly detection[C]. 2018 25th International Conference on Telecommunications (ICT), Saint-Malo, France, 2018: 411–415. [6] BASHAR M A and NAYAK R. TAnoGAN: Time series anomaly detection with generative adversarial networks[C]. 2020 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Canberra, Australia, 2020: 1778–1785. [7] DONG Weishan, YUAN Ting, YANG Kai, et al. Autoencoder regularized network for driving style representation learning[C]. Twenty-Sixth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Melbourne, Australia, 2017: 1603–1609. [8] KINGMA D P and BA L J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. International Conference on Learning Representations 2015, San Diego, USA, 2015. [9] JIANG Wenqian, HONG Yang, ZHOU Beitong, et al. A GAN-based anomaly detection approach for imbalanced industrial time series[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 143608–143619. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2944689 [10] BENDRISS J. Cognitive management of SLA in software-based networks[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Institut National des Télécommunications, 2018. [11] DONAHUE J, KRÄHENBÜHL P, and DARRELL T. Adversarial feature learning[J]. arXiv: 1605.09782, 2016. [12] RADFORD A, METZ L, and CHINTALA S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[J]. arXiv: 1511.06434, 2015. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
