UAV Assisted Communication and Resource Scheduling in Cell-free Massive MIMO Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach
-
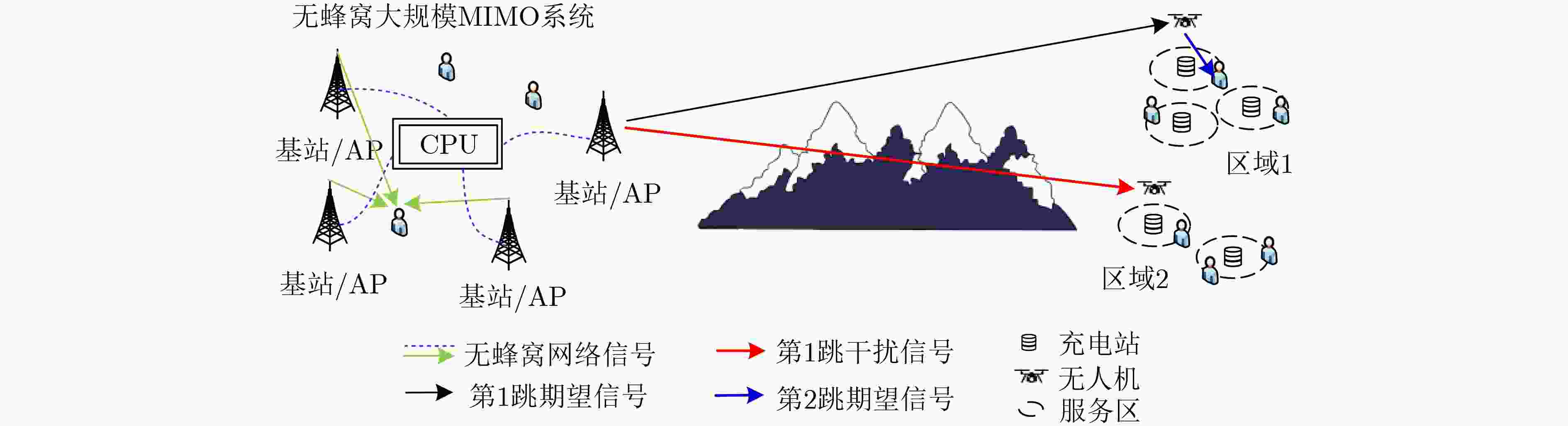
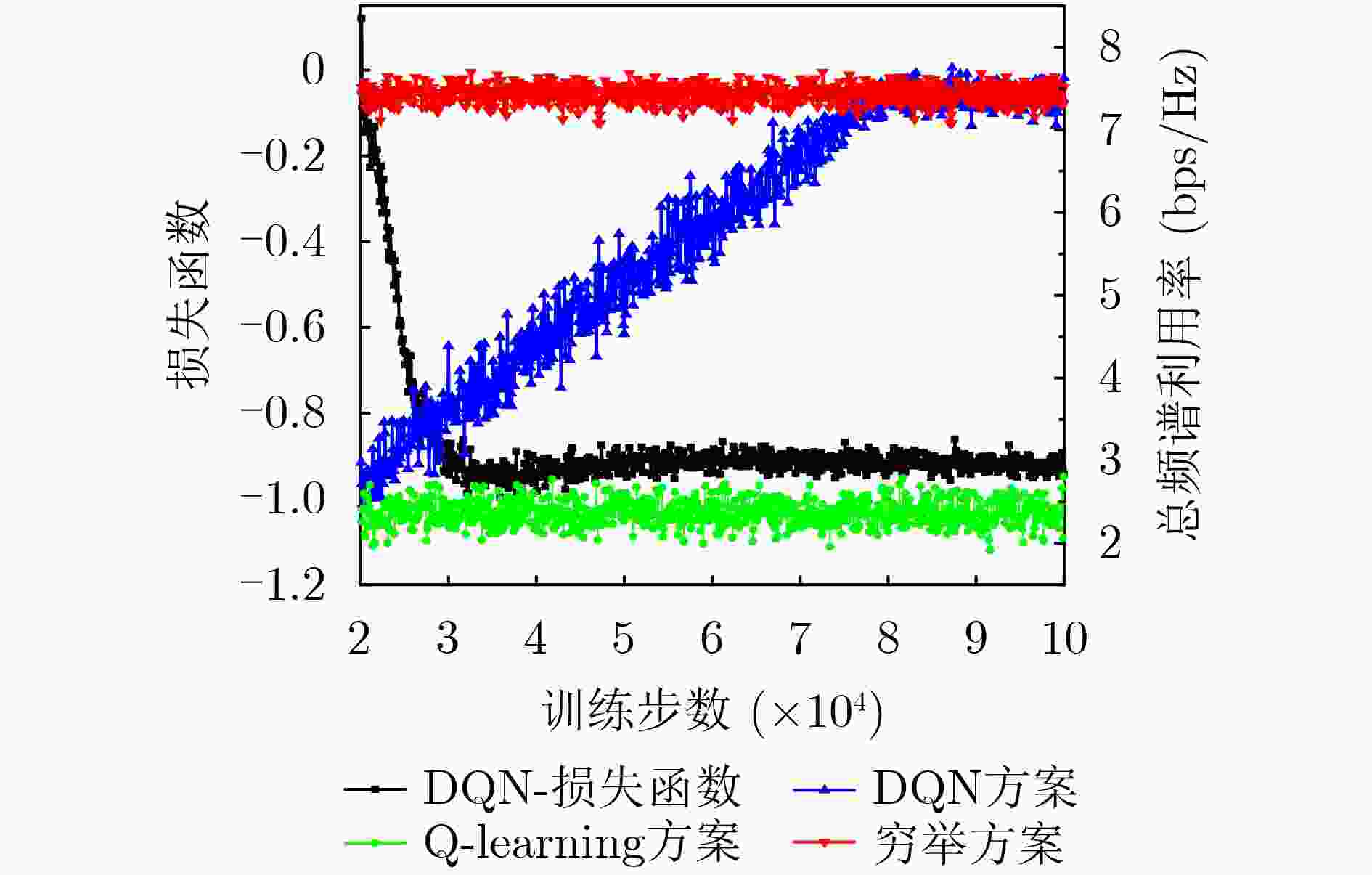
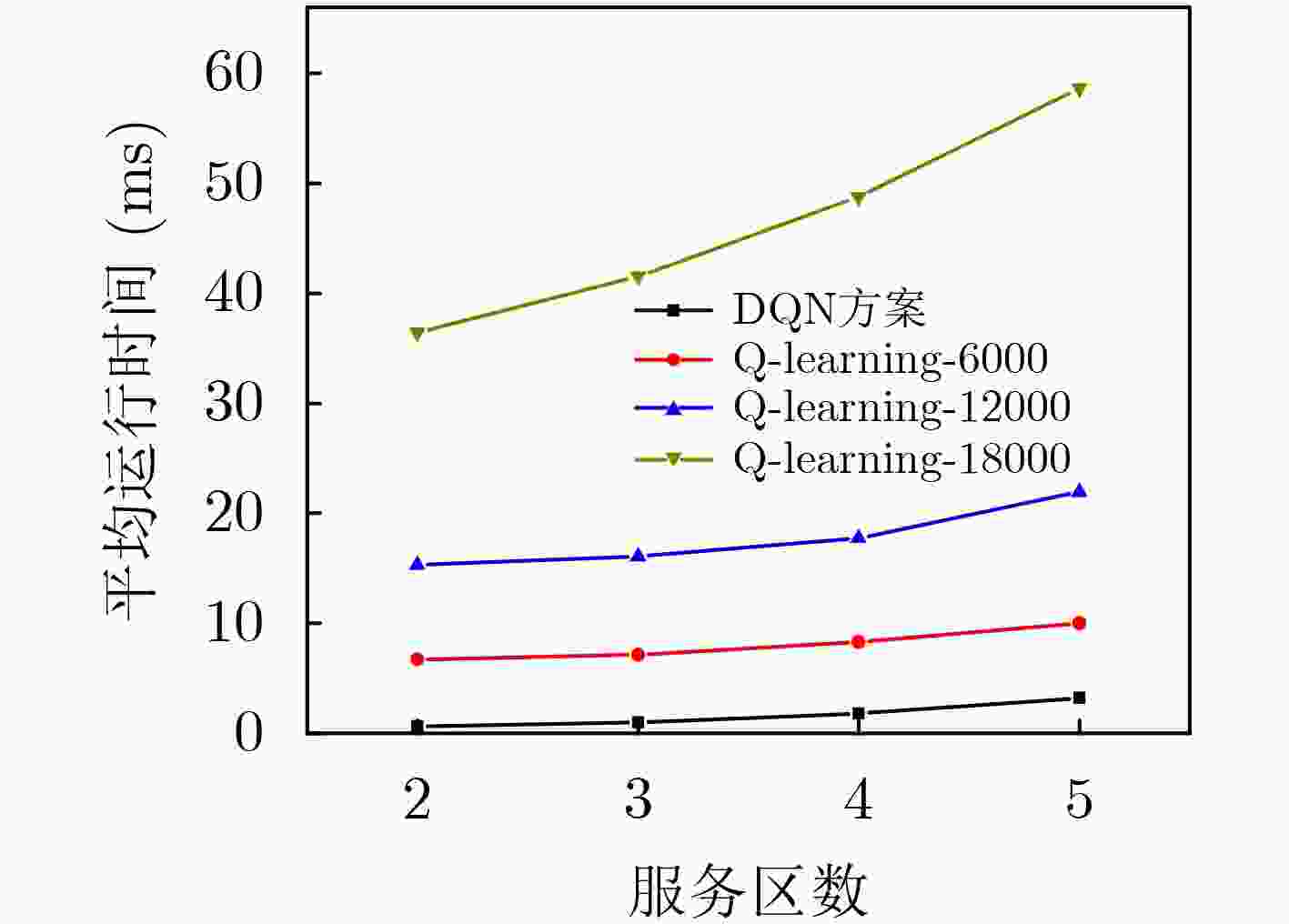
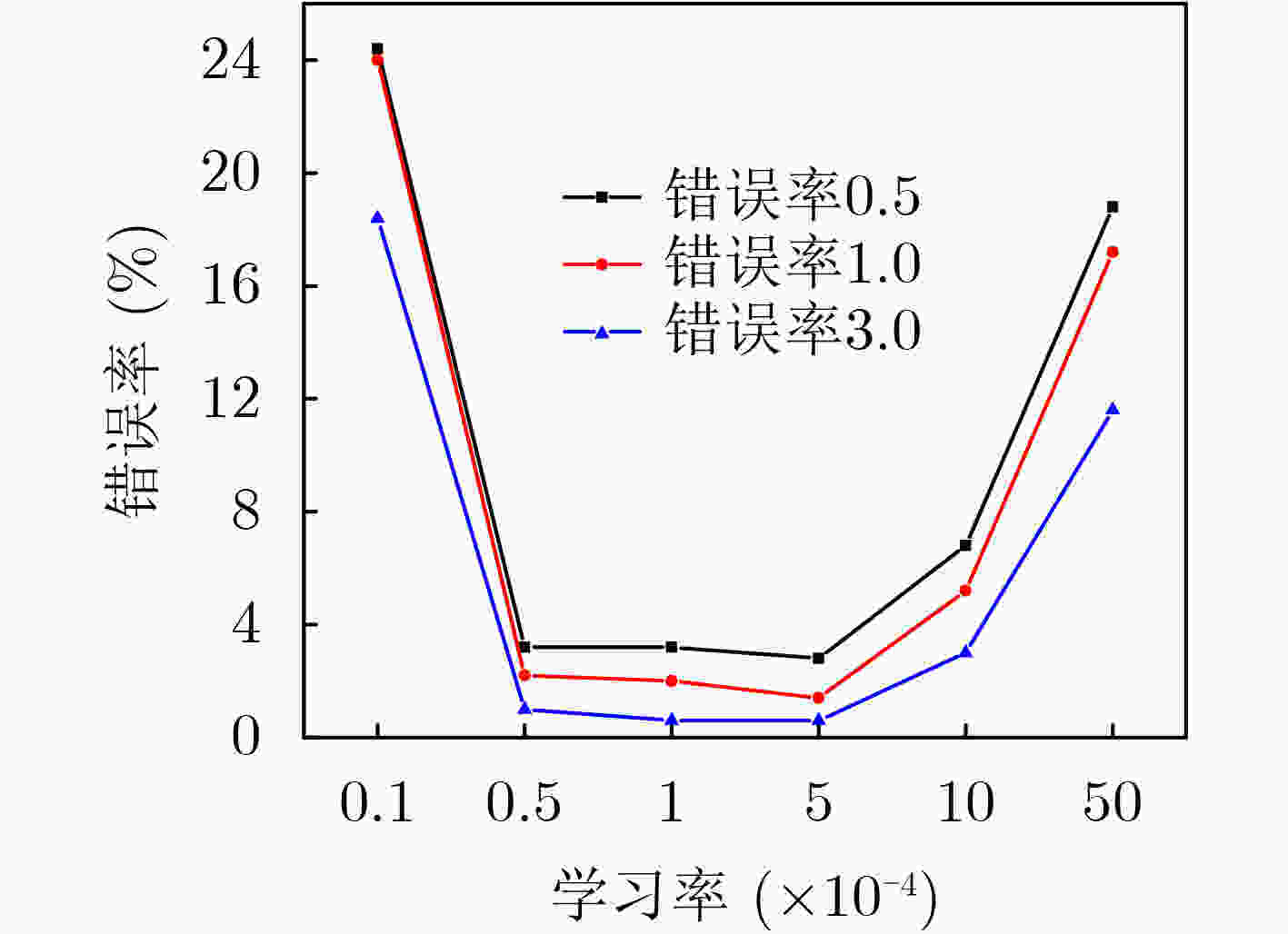
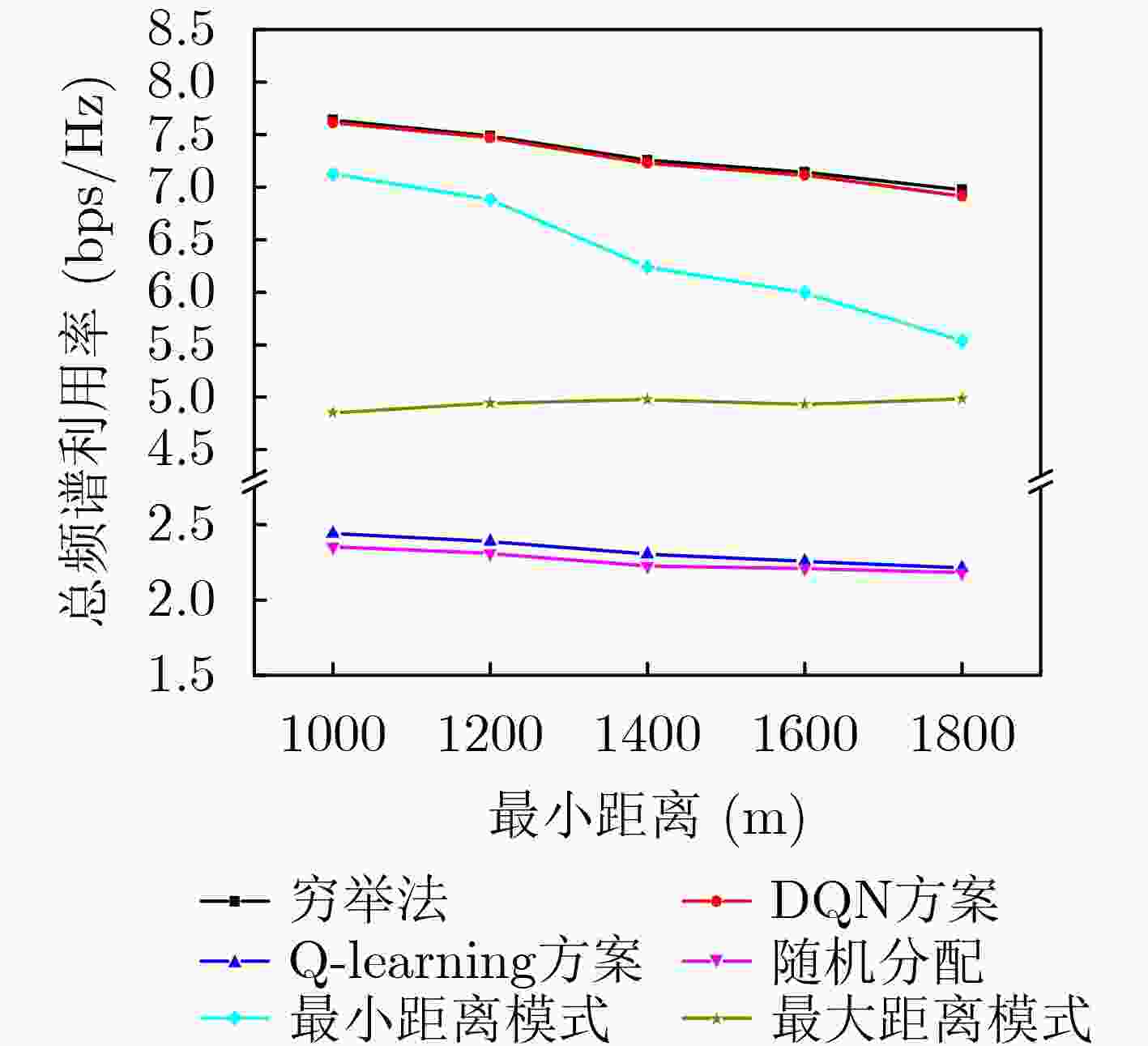
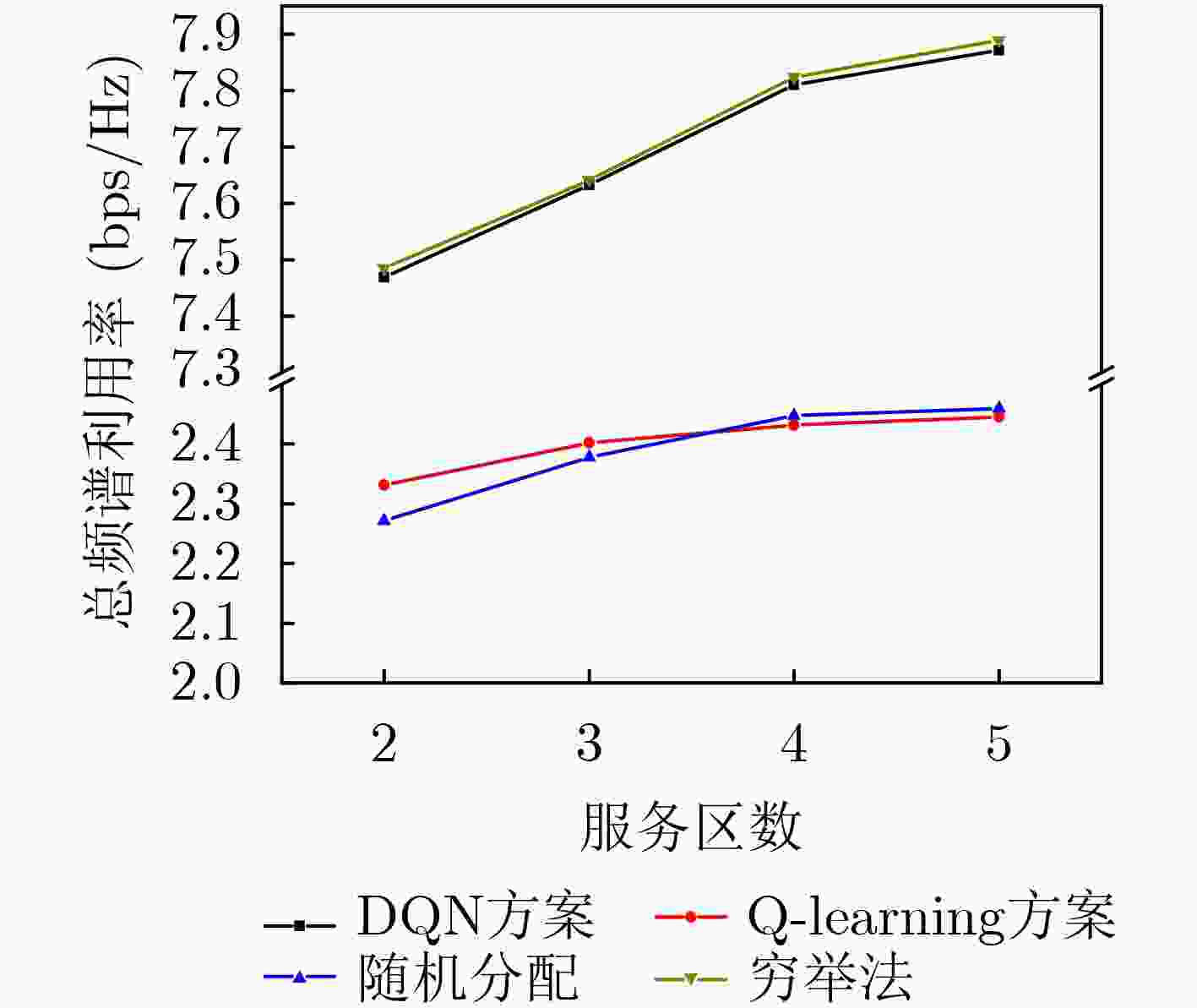
摘要: 无蜂窝大规模多入多出(MIMO)网络中分布式接入点(AP)同时服务多个用户,可以实现较大区域内虚拟MIMO的大容量传输;而无人机辅助通信能够为该目标区域热点或边缘用户提供覆盖增强。为了降低反馈链路负载,并有效提升无人机辅助通信的频谱利用率,该文研究了基于AP功率分配、无人机服务区选择和接入用户选择的联合调度;首先将AP功率分配和无人机服务区选择问题联合建模为双动作马尔可夫决策过程 (DAMDP),提出了基于Q-learning和卷积神经网络(CNN)的深度强化学习(DRL)算法;然后将用户调度构造为一个0-1优化问题,并分解成子问题来求解。仿真结果表明,该文提出的基于DRL的资源调度方案与现有方案相比,可以有效提升无蜂窝大规模MIMO网络中频谱利用率。
-
关键词:
- 无蜂窝大规模MIMO /
- 无人机辅助通信 /
- 资源调度 /
- 深度增强学习
Abstract: Distributed Access Points (AP) in the cell-free massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) networks serve multiple users at the same time, which can achieve large-capacity transmission of virtual MIMO in a larger area. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) assisted communication can provide coverage enhancement for hotspots or edge users in this area. In order to improve the spectrum efficiency and reduce the feedback overhead, a joint resource scheduling scheme that includes AP power allocation, UAV service zone selection and user scheduling is proposed in this paper. Firstly, the AP power allocation and the UAV service zone selection problems are jointly modeled as a Double-Action Markov Decision Process (DAMDP). Then, a Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) algorithm based on Q-learning and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) is proposed. Furthermore, the user scheduling problem is formulated as a 0-1 optimization problem and solved by dividing into sub-problems. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed DRL-based resource scheduling scheme exhibits a higher spectrum efficiency than existing schemes. -
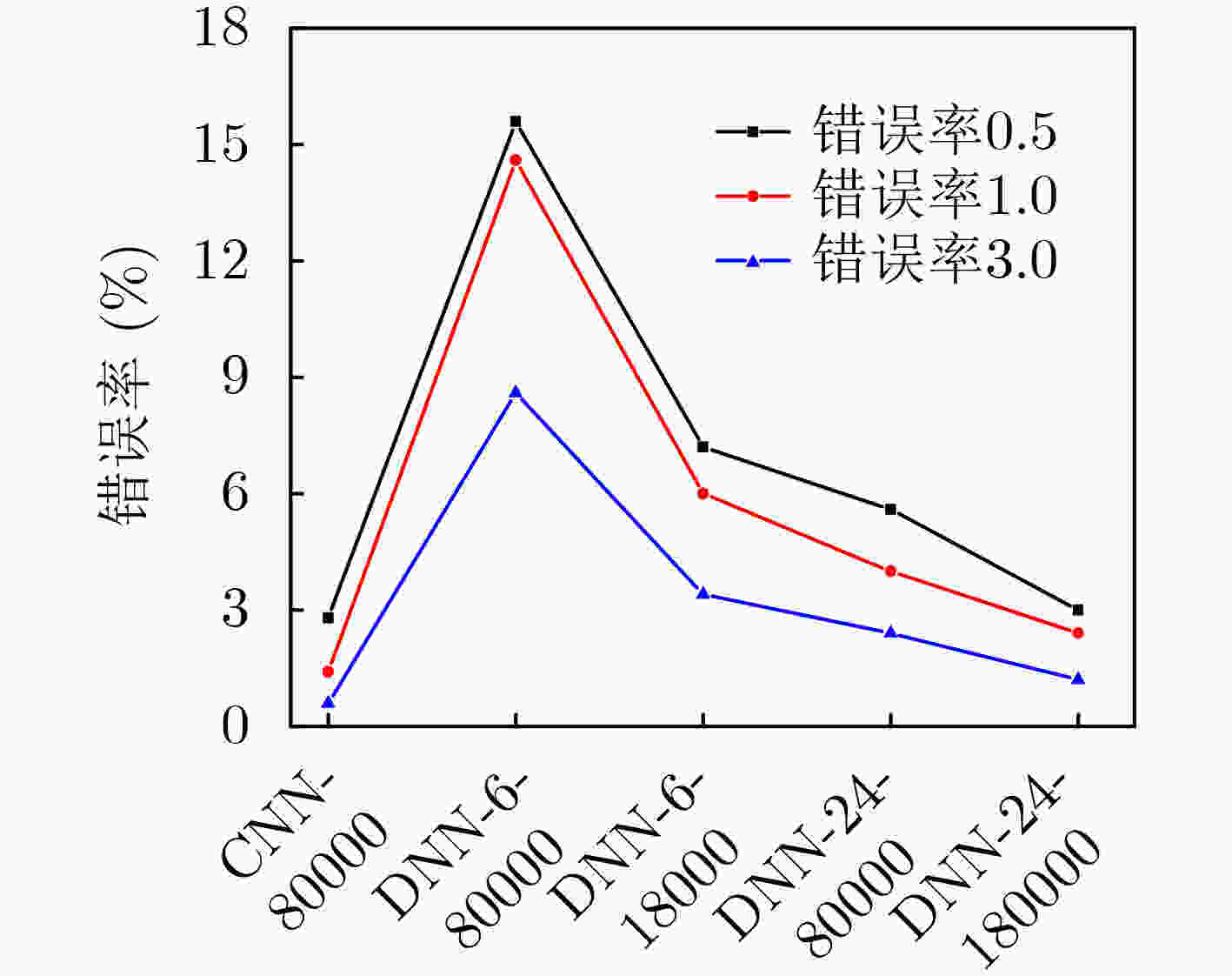
表 1 DQN算法框架
层级 输入 内核 激活函数 输出 卷积层1 $ \left( {\sum {{M_l}} } \right) \times N \times 1 $ 3×3, 8 ReLU $ \left( {\sum {{M_l}} } \right) \times N \times {\text{8}} $ 卷积层2 $ \left( {\sum {{M_l}} } \right) \times N \times {\text{8}} $ 3×3, 16 ReLU $ \left( {\sum {{M_l}} } \right) \times N \times {\text{16}} $ 全连接层1 $ \left( {\sum {{M_l}} } \right) \times N \times {\text{16}} $ NA ReLU 1024 全连接层2 1024 NA Linear $ \prod {\left( {{M_l} \times N} \right)} $ -
[1] NGO H Q, ASHIKHMIN A, YANG Hong, et al. Cell-free massive MIMO versus small cells[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(3): 1834–1850. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2655515 [2] 尤肖虎, 尹浩, 邬贺铨. 6G与广域物联网[J]. 物联网学报, 2020, 4(1): 3–11. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2020.00158YOU Xiaohu, YIN Hao, and WU Hequan. On 6G and wide-area IoT[J]. Chinese Journal on Internet of Things, 2020, 4(1): 3–11. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2020.00158 [3] GU Shushi, ZHANG Qinyu, and XIANG Wei. Coded storage-and-computation: A new paradigm to enhancing intelligent services in space-air-ground integrated networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(6): 44–51. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2000108 [4] ZHAO Jianwei, GAO Feifei, WU Qihui, et al. Beam tracking for UAV mounted SatCom on-the-Move with massive antenna array[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(2): 363–375. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2804239 [5] JIANG Xu, YANG Zhutian, ZHAO Nan, et al. Resource allocation and trajectory optimization for UAV-enabled multi-user covert communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(2): 1989–1994. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3053936 [6] ZHAO Jianwei, GAO Feifei, KUANG Linling, et al. Channel tracking with flight control system for UAV mmWave MIMO communications[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(6): 1224–1227. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2018.2824800 [7] AMMAR H A, ADVE R, SHAHBAZPANAHI S, et al. Downlink resource allocation in multiuser cell-free MIMO networks with user-centric clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(3): 1482–1497. [8] AMMAR H A, ADVE R, SHAHBAZPANAHI S, et al. Distributed resource allocation optimization for user-centric cell-free MIMO networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, To be published. [9] XIA Xinjiang, ZHU Pengcheng, LI Jiamin, et al. Joint user selection and transceiver design for cell-free with network-assisted full duplexing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(12): 7856–7870. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3088485 [10] WANG Dongming, ZHANG Chuan, DU Yongqiang, et al. Implementation of a cloud-based cell-free distributed massive MIMO system[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(8): 61–67. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2000106 [11] WANG Dongming, WANG Menghan, ZHU Pengcheng, et al. Performance of network-assisted full-duplex for cell-free massive MIMO[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(3): 1464–1478. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2962158 [12] ZHENG Jiakang, ZHANG Jiayi, and AI Bo. UAV communications with WPT-aided cell-free massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(10): 3114–3128. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3088632 [13] D’ANDREA C, GARCIA-RODRIGUEZ A, GERACI G, et al. Analysis of UAV communications in cell-free massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2020, 1: 133–147. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2020.2964983 [14] SAMIR M, EBRAHIMI D, ASSI C, et al. Leveraging UAVs for coverage in cell-free vehicular networks: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2021, 20(9): 2835–2847. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2020.2991326 [15] XI Xing, CAO Xianbin, YANG Peng, et al. Joint user association and UAV location optimization for UAV-aided communications[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(6): 1688–1691. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2937077 [16] GUO Yijun, YIN Sixing, and HAO Jianjun. Resource allocation and 3-D trajectory design in wireless networks assisted by rechargeable UAV[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(3): 781–784. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2892721 [17] ZHANG Guangchi, YAN Haiqiang, ZENG Yong, et al. Trajectory optimization and power allocation for multi-hop UAV relaying communications[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 48566–48576. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2868117 [18] ZHAO Chenxi, LIU Junyu, SHENG Min, et al. Multi-UAV trajectory planning for energy-efficient content coverage: A decentralized learning-based approach[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(10): 3193–3207. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3088669 [19] MNIH V, KAVUKCUOGLU K, SILVER D, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529–533. doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [20] KOUSHIK A M, HU Fei, and KUMAR S. Deep Q-learning-based node positioning for throughput-optimal communications in dynamic UAV swarm network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2019, 5(3): 554–566. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2019.2907520 [21] CUI Jingjing, LIU Yuanwei, and NALLANATHAN A. Multi-agent reinforcement learning-based resource allocation for UAV networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(2): 729–743. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2935201 [22] DING Ruijin, GAO Feifei, and SHEN X S. 3D UAV trajectory design and frequency band allocation for energy-efficient and fair communication: A deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(12): 7796–7809. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3016024 [23] DING Ruijin, XU Yadong, GAO Feifei, et al. Trajectory design and access control for air-ground coordinated communications system with multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. To be published. [24] HE Ying, ZHANG Zheng, YU F R, et al. Deep-reinforcement-learning-based optimization for cache-enabled opportunistic interference alignment wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(11): 10433–10445. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2751641 [25] HE Dawei, SUN Wei, and SHI Lei. The novel mobility models based on spiral line for aerial backbone networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 11297–11314. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2965616 [26] SUTTON R S and BARTO A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction[M]. 2nd ed. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018: 1–130. [27] ZHANG Ran, WANG Miao, CAI L X, et al. Learning to be proactive: Self-regulation of UAV based networks with UAV and user dynamics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(7): 4406–4419. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3058533 [28] WANG Xue, JIN Tao, HU Liangshuai, et al. Energy-efficient power allocation and Q-learning-based relay selection for relay-aided D2D communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(6): 6452–6462. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.2985873 [29] WANG Xiuhong, QIAO Qingli, and WANG Zheng’ou. Chaotic neural network technique for “0–1” programming problems[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2003, 14(4): 99–105. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
