Multi-scale Cross-Modality Person Re-identification Method Based on Shared Subspace Features
-
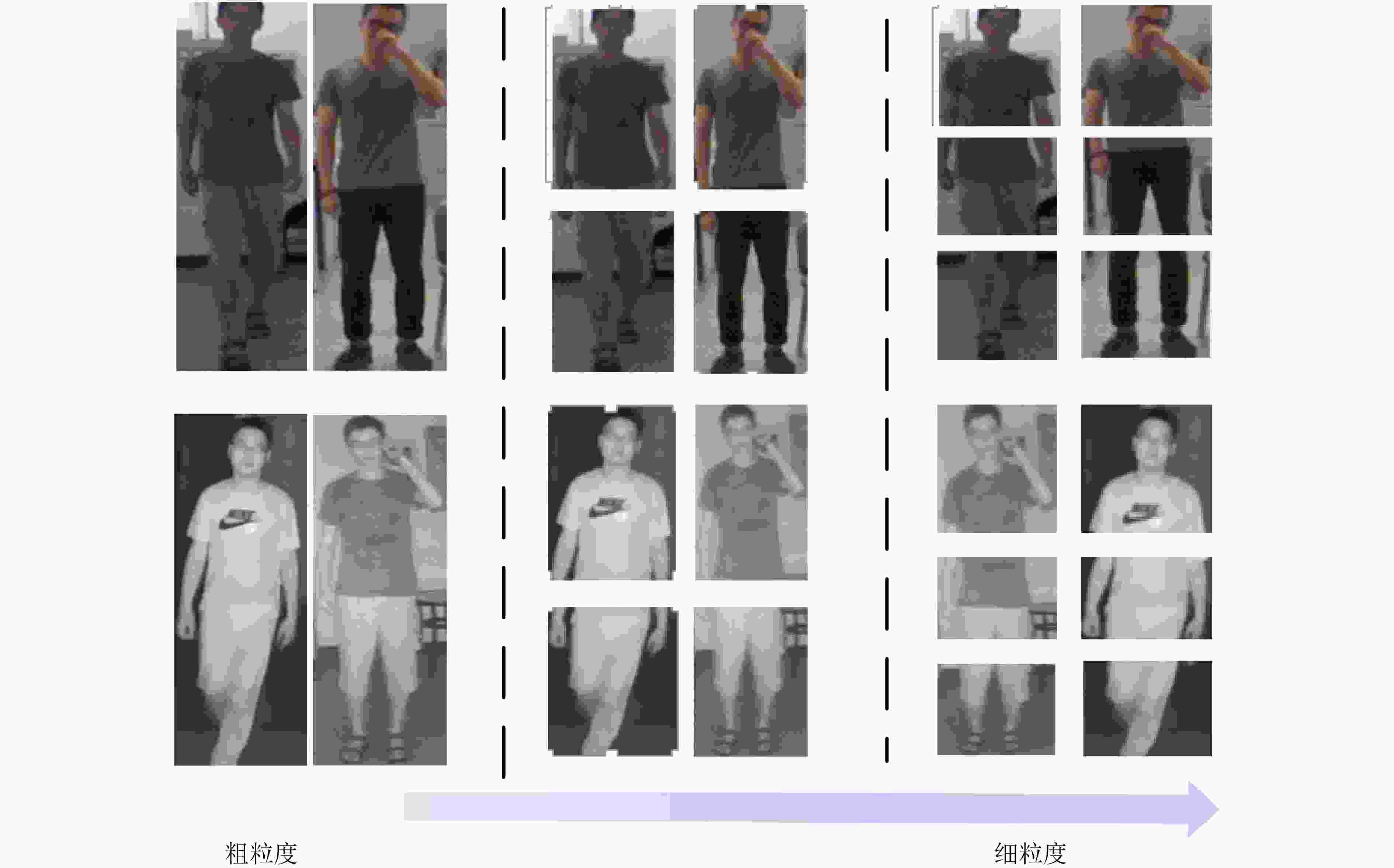
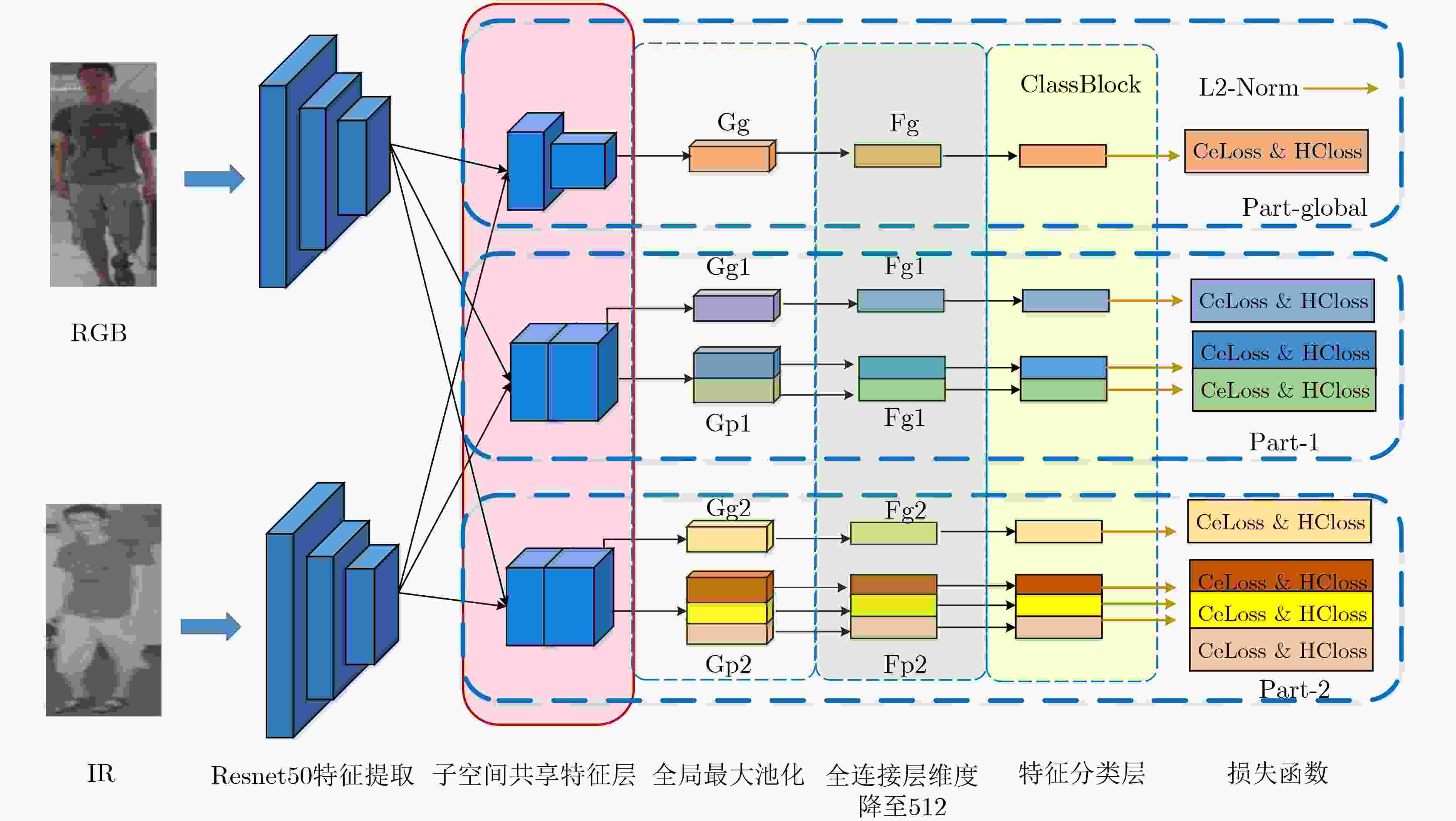
摘要: 跨模态行人重识别(Re-ID)是智能监控系统所面临的一项具有很大挑战的问题,现有的跨模态研究方法中主要基于全局或局部学习表示有区别的模态共享特征。然而,很少有研究尝试融合全局与局部的特征表示。该文提出一种新的多粒度共享特征融合(MSFF)网络,该网络结合了全局和局部特征来学习两种模态的不同粒度表示,从骨干网络中提取多尺度、多层次的特征,全局特征表示的粗粒度信息与局部特征表示的细粒度信息相互协同,形成更具有区别度的特征描述符。此外,为使网络能够提取更有效的共享特征,该文还针对网络中的两种模态的嵌入模式提出了子空间共享特征模块的改进方法,改变传统模态特征权重的特征嵌入方式。将该模块提前放入骨干网络中,使两种模态的各自特征映射到同一子空间中,经过骨干网络产生更丰富的共享权值。在两个公共数据集实验结果证明了所提方法的有效性,SYSU-MM01数据集最困难全搜索单镜头模式下平均精度mAP达到了60.62%。Abstract: Cross-modal person Re-IDentification (Re-ID) is a challenging problem for intelligent surveillance systems, and existing cross-modal research approaches are mainly based on global or local learning representation of differentiated modal shared features. However, few studies have attempted fuse global and local feature representations. A new Multi-granularity Shared Feature Fusion (MSFF) network is proposed in this paper, which combines global and local features to learn different granularities representations of the two modalities, extracting multi-scale and multi-level features from the backbone network, where the coarse granularity information of the global feature representation and the fine granularity information of the local feature representation collaborate with each other to form more differentiated feature descriptors. In addition, in order to extract more effective shared features for the network, the paper also proposes an improved method of subspace shared feature module for embedding modes of the two modalities in the network, changing the feature embedding mode of traditional modal feature weights. The module is put into the backbone network in advance so that the respective features of the two modalities are mapped into the same subspace to generate richer shared weights through the backbone network. The experimental results in two public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method, and the average accuracy mAP in the most difficult full-search single-shot mode of SYSU-MM01 dataset reaches 60.62%.
-
表 1 网络3个分支的结构设置
Branch Part Map size Dims Feature Part-global 1 12×4 512 Fg Part-1 1+2 24×8 512×2+512 Fg1/Fp1 Part-2 1+3 24×8 512×3+512 Fg2/Fp2 表 2 在SYSU-MM01的All-search模式下和其他方法对比实验结果(%)
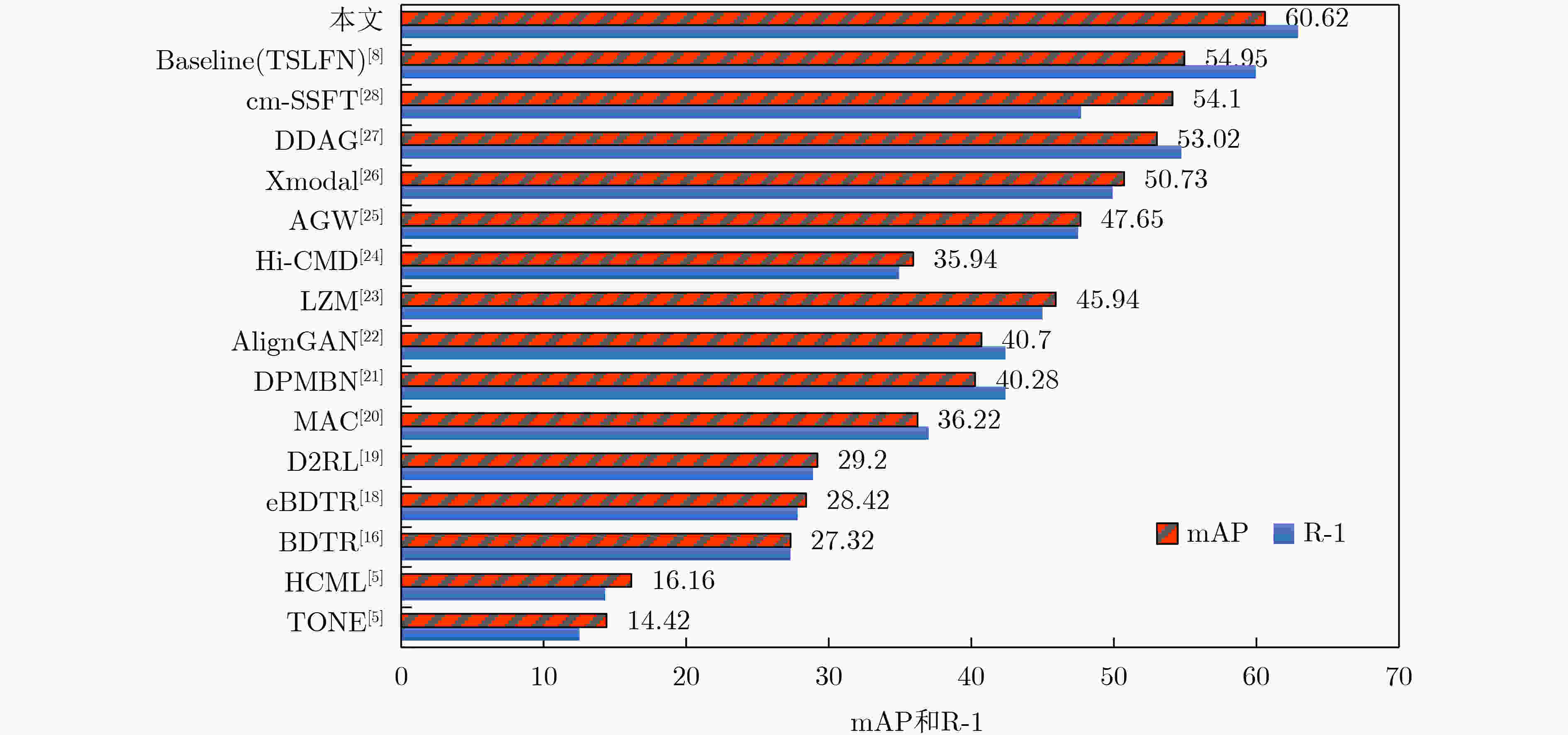
方法 单镜头 多镜头 R-1 R-10 R-20 mAP R-1 R-10 R-20 mAP One-Stream[17] 12.04 49.68 66.74 13.67 19.13 58.14 75.05 8.59 Two-stream[17] 11.65 47.99 65.50 12.85 16.33 58.35 74.46 8.03 Zero-padding[17] 14.80 54.12 71.33 15.95 – 61.40 78.41 10.89 TONE[5] 12.52 50,72 68.60 14.42 – – – – HCML[5] 14.32 53.16 69.17 16.16 – – – – BDTR[16] 27.32 66.96 81.7 27.32 – – – – eBDTR[18] 27.82 67.34 81.34 28.42 – – – – D2RL[19] 28.90 70.60 82.40 29.20 – – – – MAC[20] 33.26 79.04 90.09 36.22 – – – – DPMBN[21] 37.02 79.46 89.87 40.28 – – – – AlignGAN[22] 42.40 85.00 93.70 40.70 51.50 89.40 95.70 33.90 LZM[23] 45.00 89.06 – 45.94 – – – – Hi-CMD[24] 34.94 77.58 – 35.94 – – – – AGW[25] 47.50 84.39 92.14 47.65 – – – – Xmodal[26] 49.92 89.79 95.96 50.73 47.56 88.13 95.98 36.08 DDAG[27] 54.75 90.39 95.81 53.02 – – – – cm-SSFT[28] 67.60 89.20 93.90 63.20 64.4 91.2 95.7 62.0 Baseline(TSLFN)[8] 59.96 91.50 96.82 54.95 62.09 93.74 97.85 48.02 本文 62.93 93.68 97.67 60.62 68.42 95.71 98.22 54.51 表 3 在RegDB数据集和其它方法对比实验结果(%)
方法 Visible to Infrared Infrared to Visible R-1 R-10 R-20 mAP R-1 R-10 R-20 mAP Zero-padding[17] 17.75 34.21 44.35 18.90 16.63 34.68 44.25 17.82 HCML[5] 24.44 47.53 56.78 20.08 21.70 45.02 55.58 22.24 BDTR[16] 33.56 58.61 67.43 32.76 32.92 58.46 68.43 31.96 eBDTR[18] 34.62 58.96 68.72 33.46 34.21 58.74 68.64 32.49 AlignGAN[22] 57.90 – – 53.60 56.30 – – 53.40 MAC[20] 36.43 62.36 71.63 37.03 36.20 61.68 70.99 36.63 Xmodal[26] 62.21 83.13 91.72 60.18 – – – – DDAG[27] 69.34 86.19 91.49 63.46 68.06 85.15 90.31 61.80 cm-SSFT*[28] 72.30 – – 72.90 71.00 – – 71.70 Baseline(TSLFN)[8] – – – – – – – – 本文 78.06 91.36 96.12 72.43 – – – – 表 4 网络各个模块在SYSU-MM01数据集All-search single模式下实验结果(%)
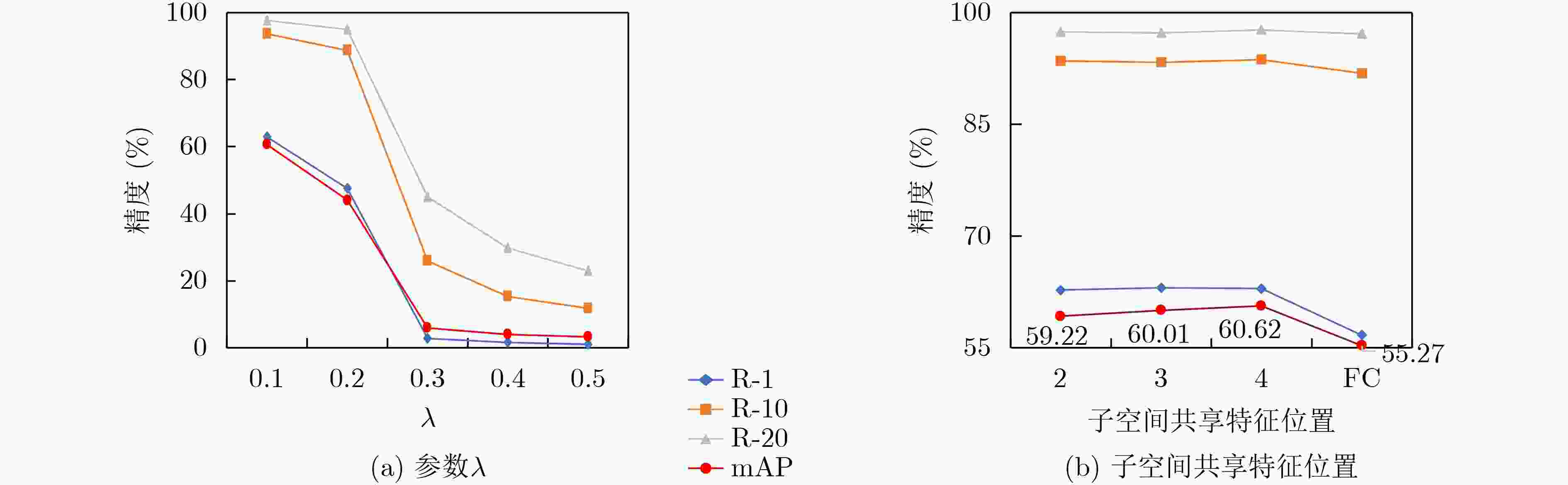
子空间共享特征模块 Part-global Part-1 Part-2 R-1 R-10 R-20 mAP P × √ √ √ 56.67 91.85 97.14 55.27 Pg-1 √ × √ √ 61.63 93.02 97.51 58.41 Pg-2 √ √ × √ 61.63 92.63 96.92 57.83 Pg-3 √ √ √ × 57.44 91.53 97.01 55.28 MSFF √ √ √ √ 62.93 93.68 97.67 60.62 -
[1] 王粉花, 赵波, 黄超, 等. 基于多尺度和注意力融合学习的行人重识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(12): 3045–3052. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190998WANG Fenhua, ZHAO Bo, HUANG Chao, et al. Person Re-identification based on multi-scale network attention fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(12): 3045–3052. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190998 [2] 周智恒, 刘楷怡, 黄俊楚, 等. 一种基于等距度量学习策略的行人重识别改进算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(2): 477–483. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180336ZHOU Zhiheng, LIU Kaiyi, HUANG Junchu, et al. Improved metric learning algorithm for person Re-identification based on equidistance[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(2): 477–483. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180336 [3] 陈鸿昶, 吴彦丞, 李邵梅, 等. 基于行人属性分级识别的行人再识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2239–2246. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180740CHEN Hongchang, WU Yancheng, LI Shaomei, et al. Person Re-identification based on attribute hierarchy recognition[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2239–2246. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180740 [4] CHEN Yingcong, ZHU Xiatian, ZHENG Weishi, et al. Person reidentification by camera correlation aware feature augmentation[J]. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, , 2017, 40(2): 392–408. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2666805 [5] YE Mang, LAN Xiangyuan, LI Jiawei, et al. Hierarchical discriminative learning for visible thermal person Re-identification[C]. The 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, USA, 2018: 7501–7508. [6] DAI Pingyang, JI Rongrong, WANG Haibin, et al. Cross-modality person Re-identification with generative adversarial training[C]. The Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 677–683. [7] YE Mang, SHEN Jianbing and SHAO Ling. Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification via Homogeneous Augmented Tri-Modal Learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 16: 728–739. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.3001665 [8] ZHU Yuanxin, YANG Zhao, WANG Li, et al. Hetero-center loss for cross-modality person Re-identification[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 386: 97–109. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.12.100 [9] WANG Guanshuo, YUAN Yufeng, CHEN Xiong, et al. Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person Re-identification[C]. The 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Korea (South), 2018: 274–282. [10] BAI Xian, YANG Mingkun, HUANG Tengteng, et al. Deep-person: Learning discriminative deep features for person Re-identification[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 98: 107036. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107036 [11] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [12] AlMAZAN J, GAJIC B, MURRAY N, et al. Re-ID done right: Towards good practices for person Re-identification[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.05339, 2018. [13] IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 448–456. [14] WANG Guan’an, ZHANG Tianzhu, YANG Yang, et al. Cross-modality paired-images generation for RGB-infrared person Re-identification[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 12144–12151. [15] NGUYEN D T, HONG H G, KIM K W, et al. Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(3): 605. doi: 10.3390/s17030605 [16] YE Mang, WANG Zheng, LAN Xiangyuan, et al. Visible thermal person Re-identification via dual-constrained top-ranking[C]. The Twenty-Seventh International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 1092–1099. [17] WU Ancong, ZHENG Weishi, YU Hongxing, et al. RGB-infrared cross-modality person Re-identification[C]. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5390–5399. [18] YE Mang, LAN Xiangyuan, WANG Zheng, et al. Bi-directional center-constrained top-ranking for visible thermal person Re-identification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 407–419. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2921454 [19] WANG Zhixiang, WANG Zheng, ZHENG Yinqiang, et al. Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person Re-identification[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 618–626. [20] WU Ancong, ZHENG Weishi, GONG Shaogang, et al. RGB-IR person Re-identification by cross-modality similarity preservation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(6): 1765–1785. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01290-1 [21] XIANG Xuezhi, LV Ning, YU Zeting, et al. Cross-modality person Re-identification based on dual-path multi-branch network[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(23): 11706–11713. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2936916 [22] WANG Guan’an, ZHANG Tianzhu, CHENG Jian, et al. RGB-infrared cross-modality person Re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment[C]. The IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 3622–3631. [23] BASARAN E, GÖKMEN M, and KAMASAK M E. An efficient framework for visible–infrared cross modality person Re-identification[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2020, 87: 115933. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2020.115933 [24] CHOI S, LEE S, KIM Y, et al. Hi-CMD: Hierarchical cross-modality disentanglement for visible-infrared person Re-identification[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10254–10263. [25] YE Mang, SHEN Jianbing, LIN Gaojie, et al. Deep learning for person Re-identification: A survey and outlook[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 44(6): 2872–2893. [26] LI Diangang, WEI Xing, HONG Xiaopeng, et al. Infrared-visible cross-modal person Re-identification with an X modality[C]. The 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, USA, 2020: 4610–4617. [27] YE Mang, SHEN Jianbing, CRANDALL D J, et al. Dynamic dual-attentive aggregation learning for visible-infrared person Re-identification[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 229–247. [28] LU Yan, WU Yue, LIU Bin, et al. Cross-modality person Re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 13376–13386. -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
