Specific Emitter Identification Based on Continuous Learning and Joint Feature Extraction
-
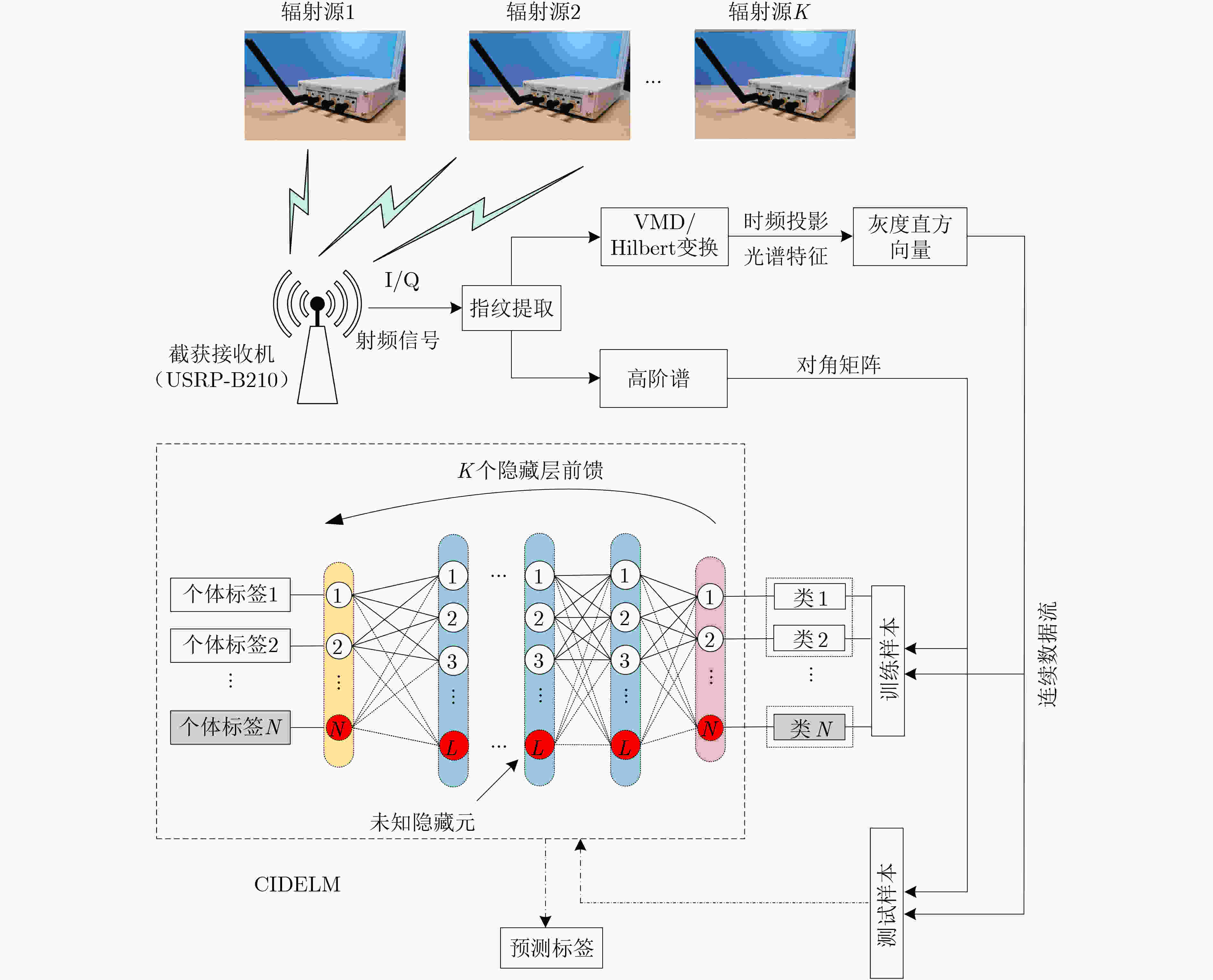
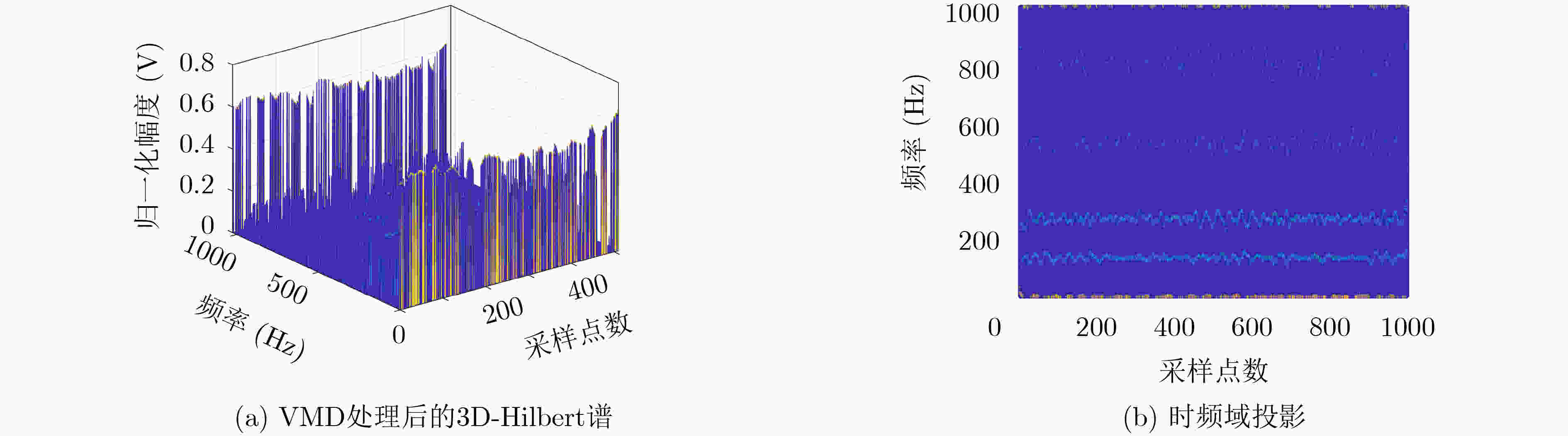
摘要: 针对特定辐射源识别(SEI)识别准确率较低和单次样本学习花销较大的问题,该文提出一种基于增量式学习的SEI方法,设计多个连续增量深度极限学习机(CIDELM)。从截获信号中分别提取变分模态分解(VMD)后的Hilbert谱投影和高阶谱,降维后作为射频指纹(RFF)用于分类;在极限学习机(ELM)中采用稀疏自编码结构对多个隐含层进行无监督训练,并利用参数搜索策略确定最佳隐含层数和隐节点个数,实现对多批次标记样本的连续在线匹配。实验结果表明,该方法对不同调制方式、载波频率和收发距离均能表现出良好兼容性,能够实现对于多个辐射源个体的有效识别。Abstract: Considering the problem of low recognition accuracy of Specific Emitter Identification (SEI) and high cost of single training, an SEI scheme based on incremental learning is proposed in this paper, multiple Continuous Incremental Deep Extreme Learning Machine(CIDELM) are designed. The Hilbert spectrum projection and higher-order spectrum processed by Variational Mode Decomposition (VMD) are extracted from the original signal, and they are used as the Radio Fingerprint Feature (RFF) for classification after dimensionality reduction. In the Extreme Learning Machine (ELM), the sparse self-encoding structure is introduced to perform unsupervised training on multiple hidden layers, and the parameter search strategy is used to determine the best number of hidden layers and hidden nodes, realizing online multi-batch labeled samples continuous matching. The results show that the algorithm can show good compatibility with different modulation modes, carrier frequencies and transmission distances, and can effectively identify multiple transmitters.
-
表 1 算法时间复杂度分析
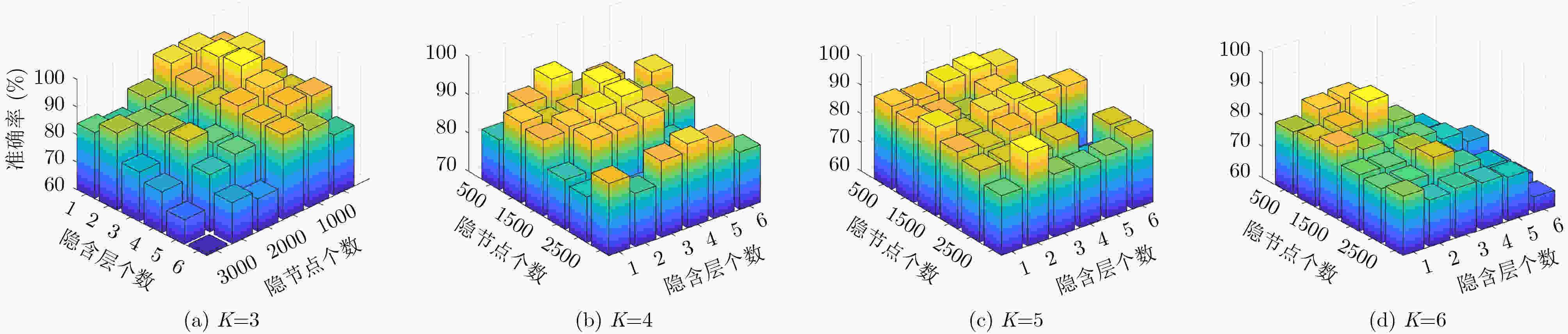
辐射源数量 平均迭代时间(s) 平均识别时间(s) K = 3 51.17 5.06 K = 4 56.48 5.57 K = 5 65.34 5.56 K = 6 70.55 6.41 -
[1] POLAK A C, DOLATSHAHI S, and GOECKEL D L. Identifying wireless users via transmitter imperfections[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2011, 29(7): 1469–1479. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2011.110812 [2] ELDEMERDASH Y A, DOBRE O A, ÜRETEN O, et al. Identification of cellular networks for intelligent radio measurements[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(8): 2204–2211. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2017.2687539 [3] DOBRE O A. Signal identification for emerging intelligent radios: Classical problems and new challenges[J]. IEEE Instrumentation & Measurement Magazine, 2015, 18(2): 11–18. doi: 10.1109/MIM.2015.7066677 [4] ZHANG Zhongshan, LONG Keping, and WANG Jianping. Self-organization paradigms and optimization approaches for cognitive radio technologies: A survey[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2013, 20(2): 36–42. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2013.6507392 [5] YUAN Yingjun, WANG Xiang, HUANG Zhitao, et al. Detection of radio transient signal based on permutation entropy and GLRT[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2015, 82(2): 1047–1057. doi: 10.1007/s11277-014-2265-2 [6] DANEV B and CAPKUN S. Transient-based identification of wireless sensor nodes[C]. 2009 IEEE International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, San Francisco, USA, 2009: 25–36. [7] URETEN O and SERINKEN N. Bayesian detection of Wi-Fi transmitter RF fingerprints[J]. Electronics Letters, 2005, 41(6): 373–374. doi: 10.1049/el:20057769 [8] GUO Shanzeng, WHITE R E, and LOW M. A comparison study of radar emitter identification based on signal transients[C]. 2018 IEEE Radar Conference, Oklahoma City, USA, 2018: 286–291. [9] GENÇOL K, KARA A, and AT N. Improvements on deinterleaving of radar pulses in dynamically varying signal environments[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2017, 69: 86–93. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2017.06.010 [10] WANG Wenhao, SUN Zhi, PIAO Sixu, et al. Wireless physical-layer identification: Modeling and validation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(9): 2091–2106. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2552146 [11] YUAN Yingjun, HUANG Zhitao, WU Hao, et al. Specific emitter identification based on Hilbert-Huang transform-based time-frequency-energy distribution features[J]. IET Communications, 2014, 8(13): 2404–2412. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2013.0865 [12] ZHANG Jingwen, WANG Fanggang, DOBRE O A, et al. Specific emitter identification via Hilbert–Huang transform in single-hop and relaying scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(6): 1192–1205. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2520908 [13] SATIJA U, TRIVEDI G, BISWAL G, et al. Specific emitter identification based on variational mode decomposition and spectral features in single hop and relaying scenarios[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14(3): 581–591. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2855665 [14] PAN Yiwei, YANG Sihan, PENG Hua, et al. Specific emitter identification based on deep residual networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 54425–54434. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2913759 [15] AGHNAIYA A, DALVEREN Y, and KARA A. On the performance of variational mode decomposition-based radio frequency fingerprinting of Bluetooth devices[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(6): 1704. doi: 10.3390/s20061704 [16] SA Kejin, LANG Dapeng, WANG Chenggang, et al. Specific emitter identification techniques for the internet of things[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 1644–1652. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2962626 [17] SUN Liting, WANG Xiang, YANG Afeng, et al. Radio frequency fingerprint extraction based on multi-dimension approximate entropy[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 471–475. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2978333 [18] 秦鑫, 黄洁, 王建涛, 等. 基于无意调相特性的雷达辐射源个体识别[J]. 通信学报, 2020, 41(5): 104–111. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020084QIN Xin, HUANG Jie, WANG Jiantao, et al. Radar emitter identification based on unintentional phase modulation on pulse characteristic[J]. Journal on Communications, 2020, 41(5): 104–111. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2020084 [19] WANG Xinyue, SU Chang, and SUN Songlin. An improved method of radar emitter fingerprint recognition based on GS-SVM[C]. 2019 19th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2019: 244–248. [20] 韩洁, 张涛, 王欢欢, 等. 基于3D-Hibert能量谱和多尺度分形特征的通信辐射源个体识别[J]. 通信学报, 2017, 38(4): 99–109. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017080HAN Jie, ZHANG Tao, WANG Huanhuan, et al. Communication emitter individual identification based on 3D-Hibert energy spectrum and multi-scale fractal features[J]. Journal on Communications, 2017, 38(4): 99–109. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2017080 [21] QIAN Yunhan, QI Jie, KUAI Xiaoyan, et al. Specific emitter identification based on multi-level sparse representation in automatic identification system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 2872–2884. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3068010.5 [22] REN Kan, YE Hongliang, GU Guohua, et al. Pulses classification based on sparse auto-encoders neural networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 92651–92660. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2927724 [23] WANG Yu, GUI Guan, GACANIN H, et al. An efficient specific emitter identification method based on complex-valued neural networks and network compression[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(8): 2305–2317. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3087243 [24] YU Jiabao, HU Aiqun, LI Guyue, et al. A robust RF fingerprinting approach using multisampling convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(4): 6786–6799. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2911347 [25] WU Qingyang, FERES C, KUZMENKO D, et al. Deep learning based RF fingerprinting for device identification and wireless security[J]. Electronics Letters, 2018, 54(24): 1405–1407. doi: 10.1049/el.2018.6404 [26] HE Boxiang and WANG Fanggang. Cooperative specific emitter identification via multiple distorted receivers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 3791–3806. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.3001721 [27] DRAGOMIRETSKIY K and ZOSSO D. Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(3): 531–544. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675 [28] HUANG Guangbin, ZHU Qinyu, and SIEW C K. Extreme learning machine: A new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks[C]. 2014 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Budapest, Hungary, 2004: 985–990. [29] TANG Jiexiong, DENG Chenwei, and HUANG Guangbin. Extreme learning machine for multilayer perceptron[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks & Learning Systems, 2016, 27(4): 809–821. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2424995 [30] LE Batuan, XIAO Dong, MAO Yachun, et al. Coal quality exploration technology based on an incremental multilayer extreme learning machine and remote sensing images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(7): 4192–4201. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2018.2890040 [31] LE Batuan, XIAO Dong, MAO Yachun, et al. Coal exploration based on a multilayer extreme learning machine and satellite images[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 44328–44339. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2860278 -





 下载:
下载:
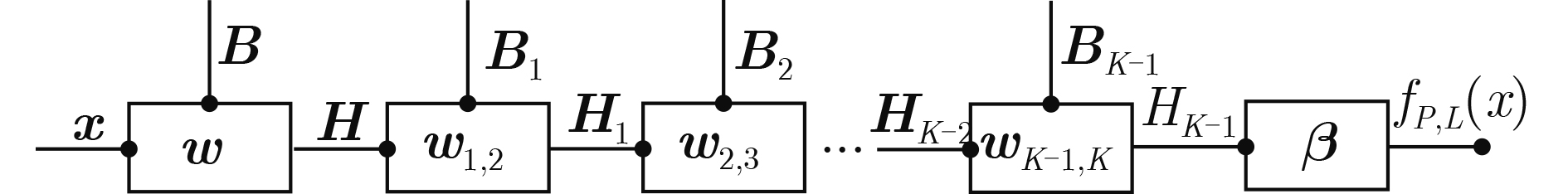

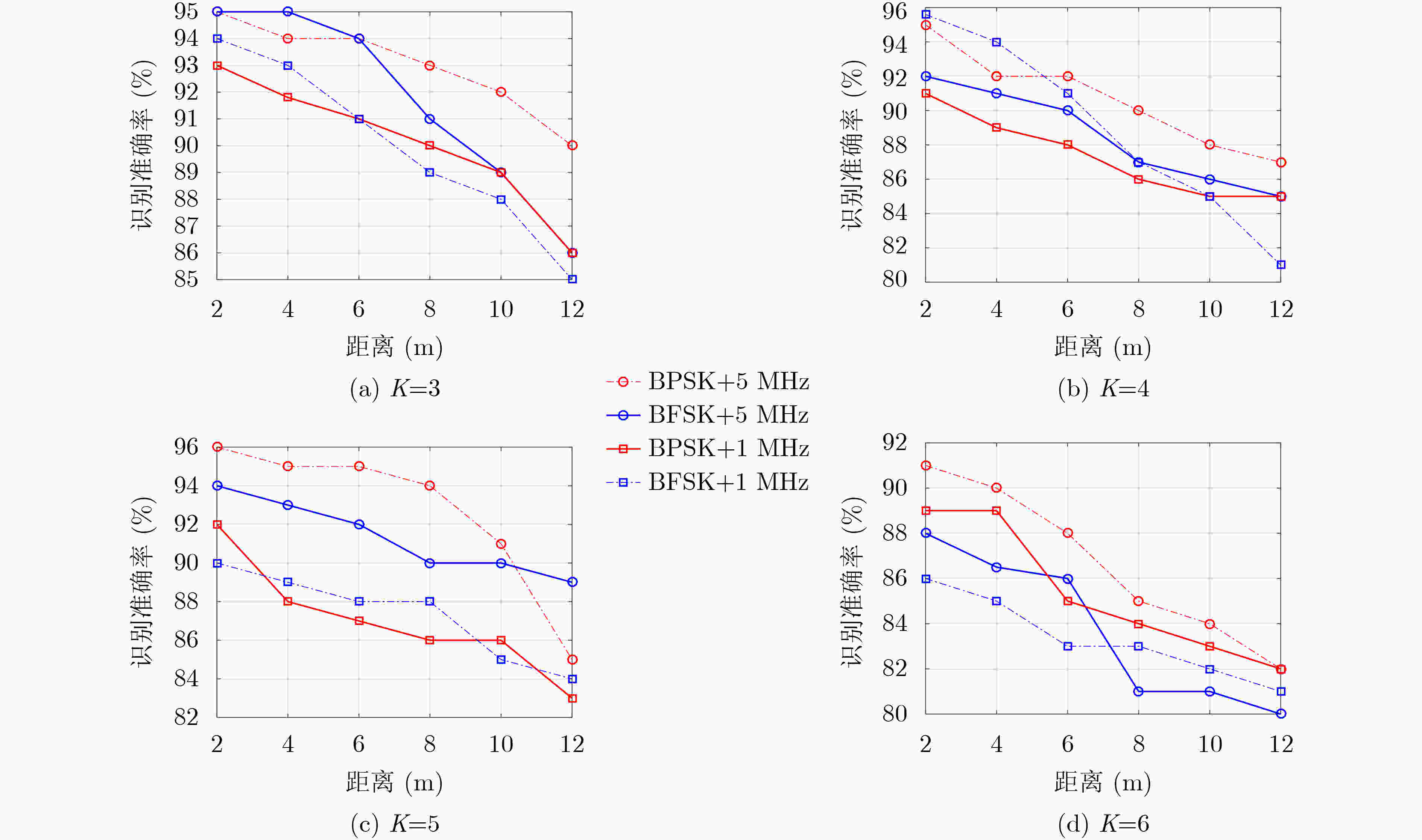
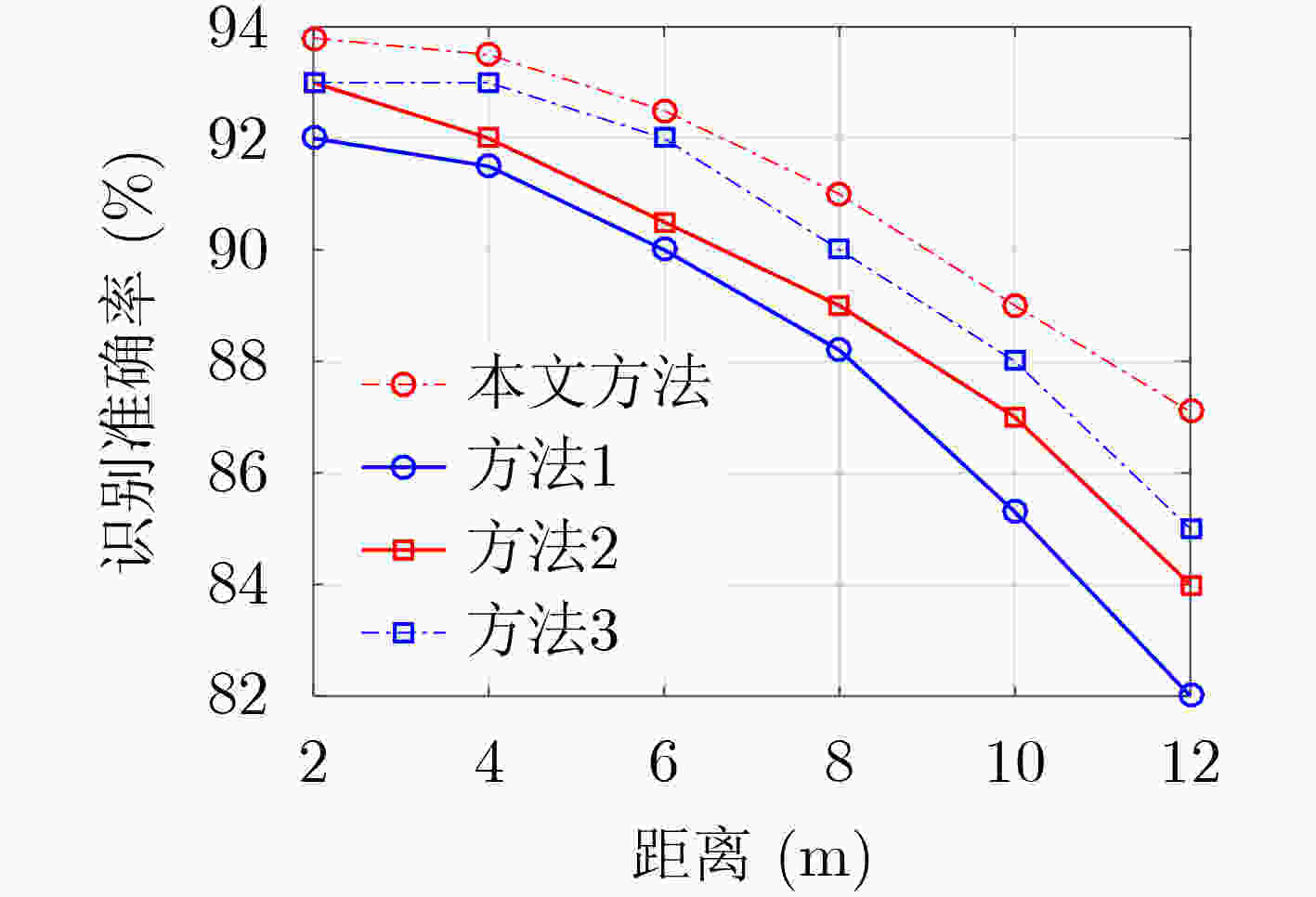


 下载:
下载:
