Fast Light Field Camera Calibration for Industrial Inspection
-
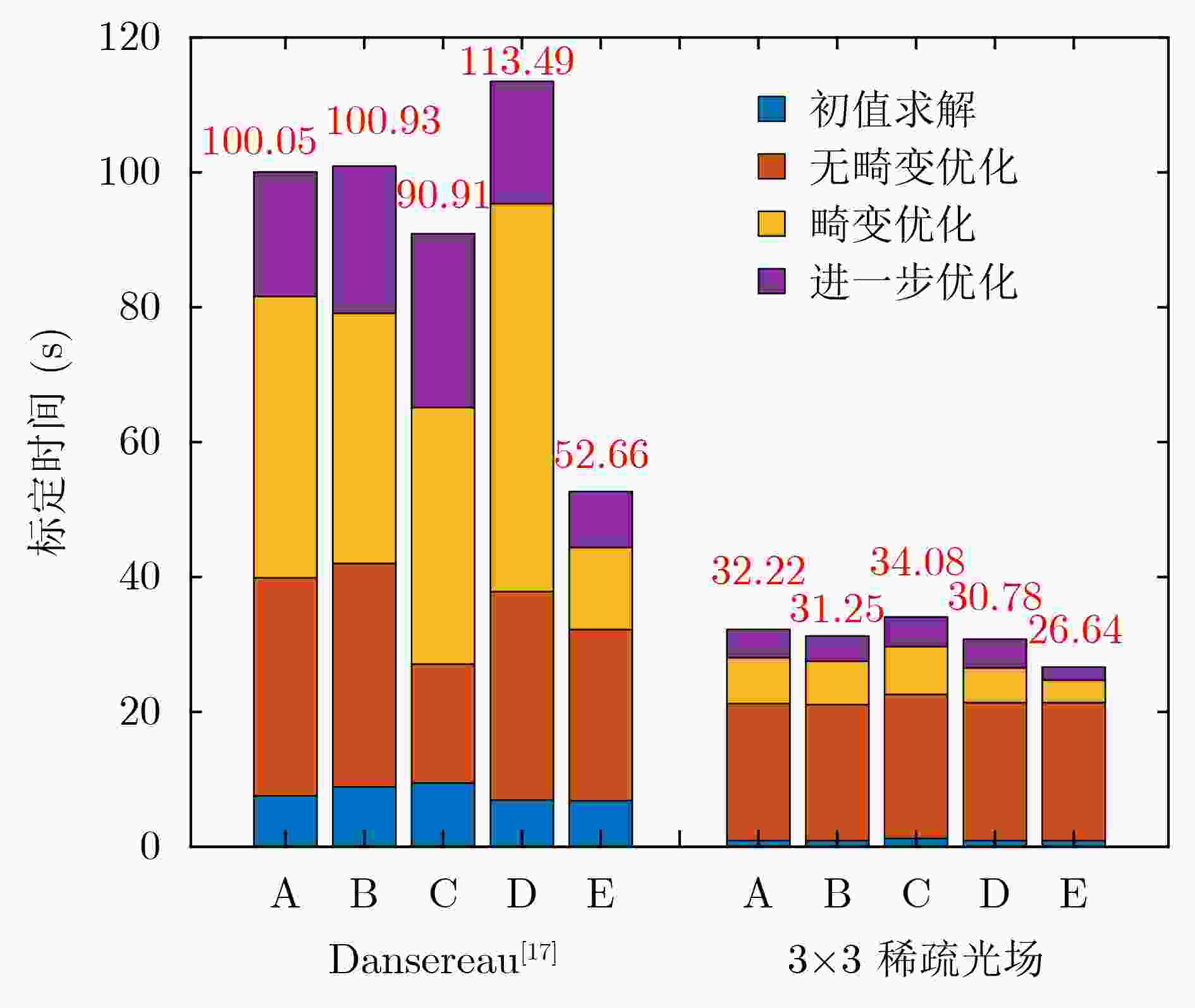
摘要: 由于光场数据量大,现有光场相机标定算法存在速度慢、无法快速校准工业检测中光场相机的参数变化、降低工业检测效率的问题。该文基于稀疏光场成像模型优化光场数据,提出光场相机快速标定算法。该算法以清晰度作为图像质量评价指标,从光场数据中选取高质量、具有代表性的稀疏视图,构建稀疏光场;接着利用稀疏光场求解相机参数初值并优化,得到最佳参数。实验结果表明,与现有最优标定算法相比,该方法不仅提高平均标定速度70%以上,在现有5个数据集的平均标定时间从101.27 s减少到30.99 s,而且保持标定精度在最优水平,在公开数据集PlenCalCVPR2013DatasetA的标定误差仅为0.0714 mm。Abstract: To solve the problem of the slow speed of the existing light field camera calibration algorithm, which makes it unable to quickly calibrate camera parameter changes in industrial inspection and reduce the efficiency of industrial inspection. A fast calibration algorithm for light field cameras is proposed. It selects high-quality, representative sparse views from the light field data based on image clarity, and establishes the sparse light field, which is used for calibration. Compared with the existing optimal approach, the proposed method not only increases the average calibration speed by more than 70%, reducing the average calibration time from 101.27 s to 30.99 s in the existing five datasets, but also maintains the calibration accuracy at the optimal level. The calibration error in the public dataset PlenCalCVPR2013DatasetA is only 0.0714 mm.
-
Key words:
- Industrial inspection /
- Light field cameras /
- Fast calibration /
- Sparse light field
-
表 1 标定数据集
数据集 数量(张) 尺寸
(mm)角点数量
(个)图像大小
(像素)视角数量
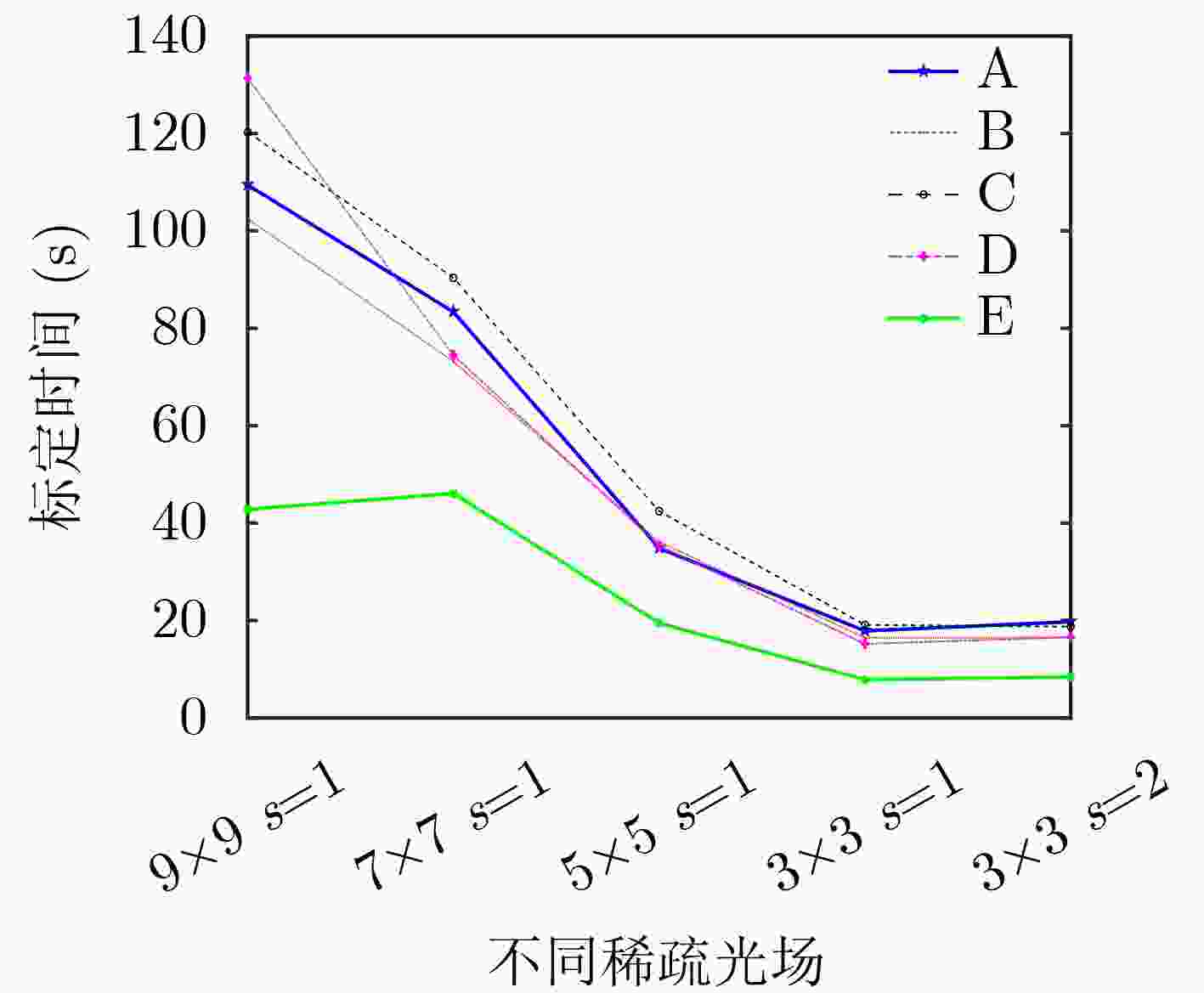
(个)A 10 3.61×3.61 19×19 3280×3280 9×9 B 10 3.61×3.61 19×19 3280×3280 9×9 C 12 7.22×7.22 19×19 3280×3280 9×9 D 10 7.22×7.22 19×19 3280×3280 9×9 E 17 35.0×35.1 6×8 3280×3280 9×9 表 2 不同稀疏光场方案的射线重投影误差(mm)和标定时间(s)
数据集 9×9 7×7 5×5 3×3 s=1 3×3 s=2 A(10) 0.0749(109.43) 0.0733(83.3) 0.0739(34.85) 0.0714(19.73) 0.0728(17.87) B(10) 0.0455(102.47) 0.0439(73.18) 0.0419(36.14) 0.0403(16.52) 0.0432(16.46) C(12) 0.0917(120.28) 0.0901(90.34) 0.0872(42.44) 0.0910(18.72) 0.0825(19.09) D(10) 0.0845(131.38) 0.0805(74.49) 0.0805(35.36) 0.0760(16.56) 0.0811(15.20) E(17) 0.1941(42.81) 0.1883(46.09) 0.1765(19.47) 0.1581(8.39) 0.1838(7.87) 表 3 9×9稠密光场标定方法在不同子视图的标定误差
位置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0.1271 0.0936 0.0783 0.0826 0.0842 0.0827 0.0828 0.1047 0.1586 2 0.0854 0.0814 0.0837 0.0821 0.0811 0.0824 0.0835 0.0810 0.0941 3 0.0795 0.0823 0.0800 0.0762 0.0748 0.0768 0.0811 0.0821 0.0809 4 0.0789 0.0825 0.0799 0.0732 0.0719 0.0743 0.0791 0.0812 0.0777 5 0.0785 0.0818 0.0781 0.0728 0.0718 0.0747 0.0797 0.0815 0.0769 6 0.0798 0.0816 0.0808 0.0758 0.0755 0.0785 0.0857 0.0859 0.0788 7 0.0824 0.0845 0.0841 0.0815 0.0820 0.0851 0.0903 0.0847 0.0833 8 0.1009 0.0830 0.0869 0.0909 0.0893 0.0896 0.0868 0.0824 0.0979 9 0.2154 0.1390 0.0876 0.0871 0.0877 0.0855 0.0839 0.1219 0.1937 表 4 3×3稀疏光场标定方法在不同子视图的标定误差
位置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 0.1831 0.1290 0.0869 0.0796 0.0783 0.0803 0.0949 0.1447 0.2174 2 0.1178 0.0829 0.0765 0.0746 0.0740 0.0741 0.0760 0.0879 0.1363 3 0.0933 0.0761 0.0732 0.0718 0.0714 0.0714 0.0723 0.0770 0.1051 4 0.0887 0.0764 0.0738 0.0707 0.0705 0.0709 0.0716 0.0739 0.0954 5 0.0884 0.0755 0.0732 0.0707 0.0706 0.0714 0.0724 0.0740 0.0934 6 0.0910 0.0746 0.0742 0.0723 0.0726 0.0734 0.0758 0.0774 0.0972 7 0.1010 0.0783 0.0751 0.0746 0.0753 0.0760 0.0777 0.0797 0.1098 8 0.1442 0.0923 0.0803 0.0803 0.0782 0.0772 0.0777 0.0932 0.1470 9 0.2773 0.1872 0.1106 0.0902 0.0828 0.0848 0.1039 0.1723 0.2604 表 5 不同方法的射线重投影误差对比(mm)
-
[1] 周志良. 光场成像技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2012.ZHOU Zhiliang. Research on light field imaging technology[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2012. [2] 张春萍, 王庆. 光场相机成像模型及参数标定方法综述[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(6): 264–275. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0609004ZHANG Chunping and WANG Qing. Survey on imaging model and calibration of light field camera[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2016, 43(6): 264–275. doi: 10.3788/CJL201643.0609004 [3] 方璐, 戴琼海. 计算光场成像[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(1): 0111001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0111001FANG Lu and DAI Qionghai. Computational light field imaging[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(1): 0111001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0111001 [4] HEINZE C, SPYROPOULOS S, HUSSMANN S, et al. Automated robust metric calibration algorithm for multifocus plenoptic cameras[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2016, 65(5): 1197–1205. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2015.2507412 [5] ILLGNER K, RESTREPO J, JAISWAL S P, et al. Lightfield imaging for industrial applications[J]. SPIE, 2020, 11525, 1152526. [6] 刘艳, 李腾飞. 对张正友相机标定法的改进研究[J]. 光学技术, 2014, 40(6): 565–570. doi: 10.13741/j.cnki.11-1879/o4.2014.06.017LIU Yan and LI Tengfei. Research of the improvement of Zhang's camera calibration method[J]. Optical Technique, 2014, 40(6): 565–570. doi: 10.13741/j.cnki.11-1879/o4.2014.06.017 [7] CHUCHVARA A, BARSI A, and GOTCHEV A. Fast and accurate depth estimation from sparse light fields[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 2492–2506. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2959233 [8] HE Bingwei and LI Y F. A novel method for camera calibration using vanishing points[C]. 14th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice, Xiamen, China, 2007: 44–47. [9] 孟宪哲, 牛少彰, 吴小媚, 等. 基于相机标定的非对称裁剪检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(10): 2409–2414. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00357MENG Xianzhe, NIU Shaozhang, WU Xiaomei, et al. Detecting asymmetric cropping based on camera calibration[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(10): 2409–2414. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00357 [10] 刘碧霞, 李绍滋, 郭锋, 等. 一种简单快速的相机标定新方法[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2011, 33(1): 88–93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2011.01.017LIU Bixia, LI Shaozi, GUO Feng, et al. A new easy fast camera self-calibration technique[J]. Computer Engineering and Science, 2011, 33(1): 88–93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2011.01.017 [11] 陈钊正, 陈启美. 基于摄像机自标定的视频对比度能见度检测算法与实现[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2010, 32(12): 2907–2912. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01630CHEN Zhaozheng and CHEN Qimei. Video contrast visibility detection algorithm and its implementation based on camera self-calibration[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2010, 32(12): 2907–2912. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2009.01630 [12] SU Pochang, SHEN Ju, XU Wanxin, et al. A fast and robust extrinsic calibration for RGB-D camera networks[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(1): 235. doi: 10.3390/s18010235 [13] MIKHELSON I V, LEE P G, SAHAKIAN A V, et al. Automatic, fast, online calibration between depth and color cameras[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2014, 25(1): 218–226. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2013.03.010 [14] GARAU N, DE NATALE F G B, and CONCI N. Fast automatic camera network calibration through human mesh recovery[J]. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 2020, 17(6): 1757–1768. doi: 10.1007/s11554-020-01002-w [15] BOK Y, JEON H G, and KWEON I S. Geometric calibration of micro-lens-based light field cameras using line features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(2): 287–300. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2541145 [16] LIU Yuxuan, MO Fan, ALEKSANDROV M, et al. Accurate calibration of standard plenoptic cameras using corner features from raw images[J]. Optics Express, 2021, 29(1): 158–169. doi: 10.1364/OE.405168 [17] DANSEREAU D G, PIZARRO O, and WILLIAMS S B. Decoding, calibration and rectification for Lenselet-based Plenoptic cameras[C]. 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 2013: 1027–1034. [18] DIGUMARTI S T, DANIEL J, RAVENDRAN A, et al. Unsupervised learning of depth estimation and visual odometry for sparse light field cameras[C]. 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Prague, Czech Republic, 2021: 278–285. [19] MONTEIRO N B, BARRETO J P, and GASPAR J A. Standard plenoptic cameras mapping to camera arrays and calibration based on DLT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(11): 4090–4099. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2954305 -





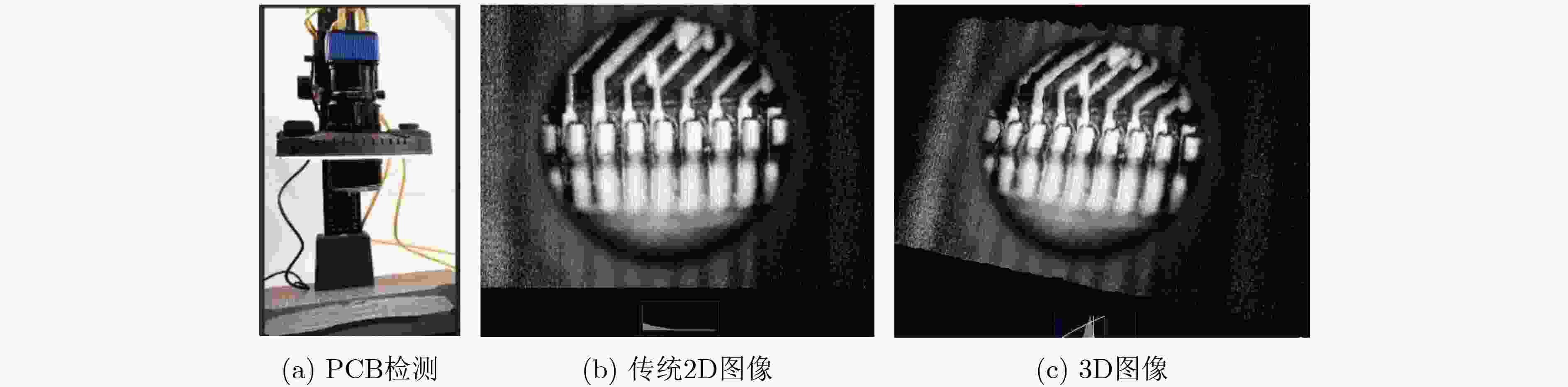
 下载:
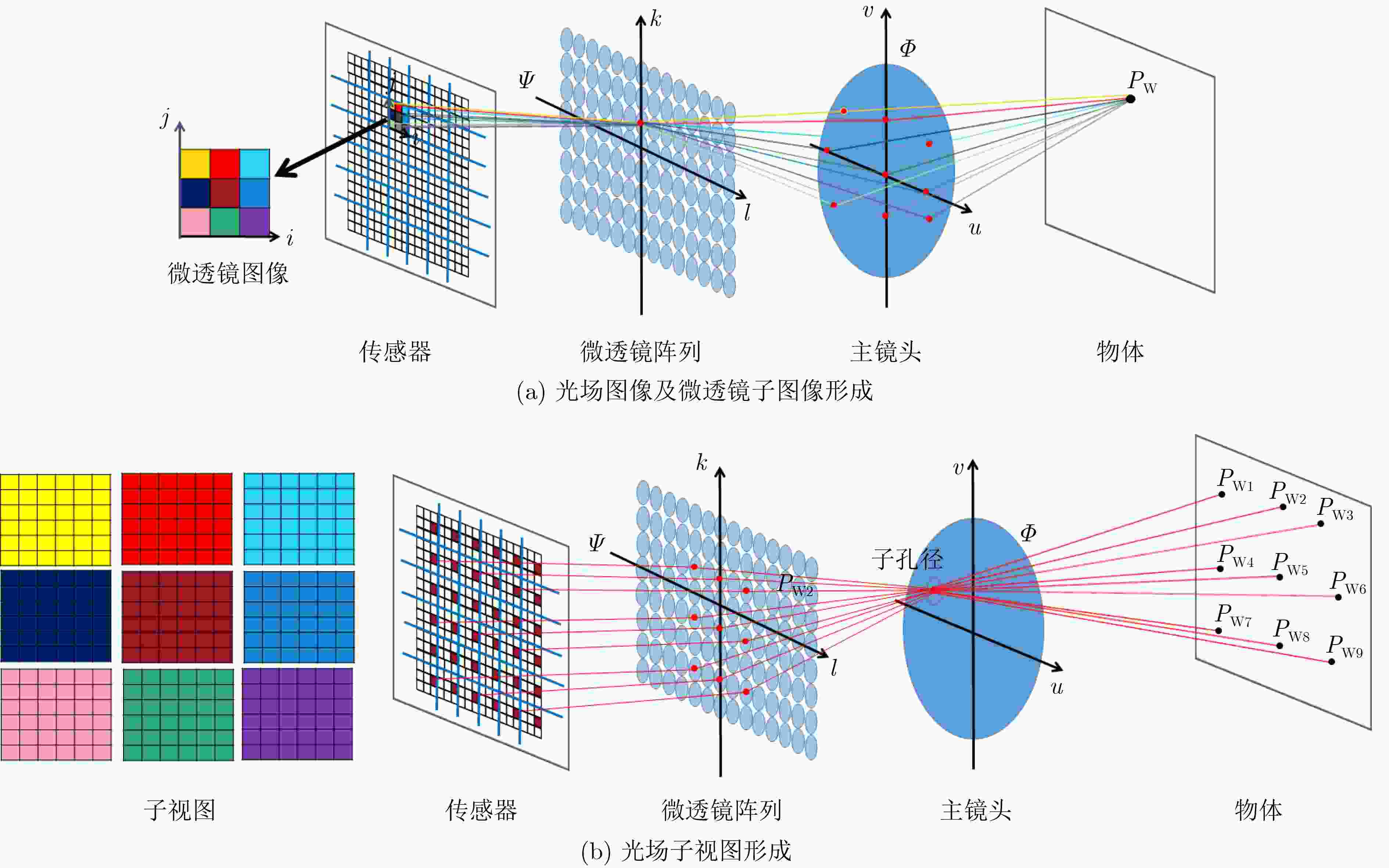
下载:

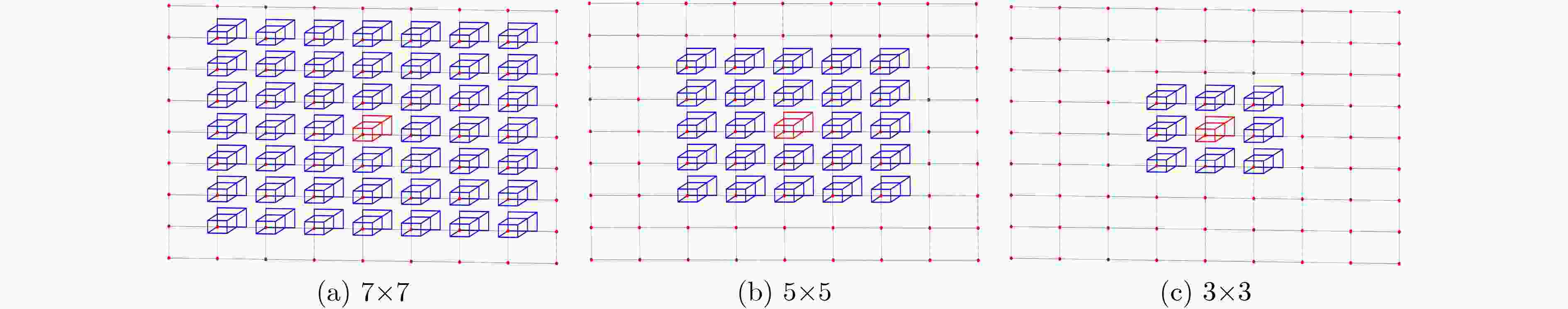
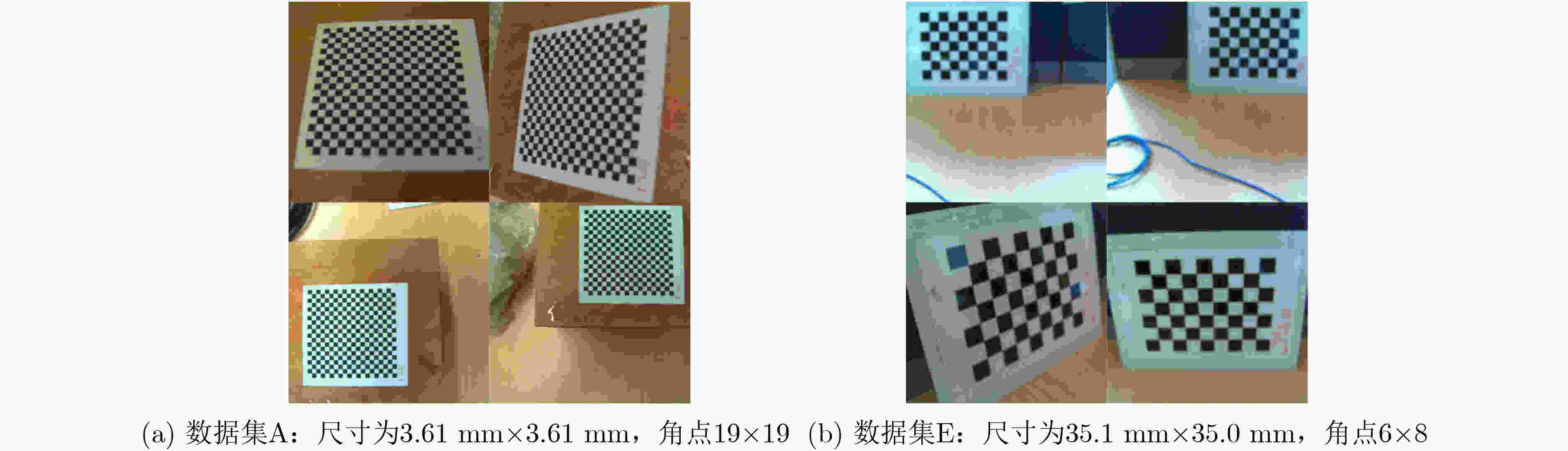


 下载:
下载:
