Research on MEMS Electric Field Sensor with Low Driving Voltage Based on Lead Zirconate Titanate
-
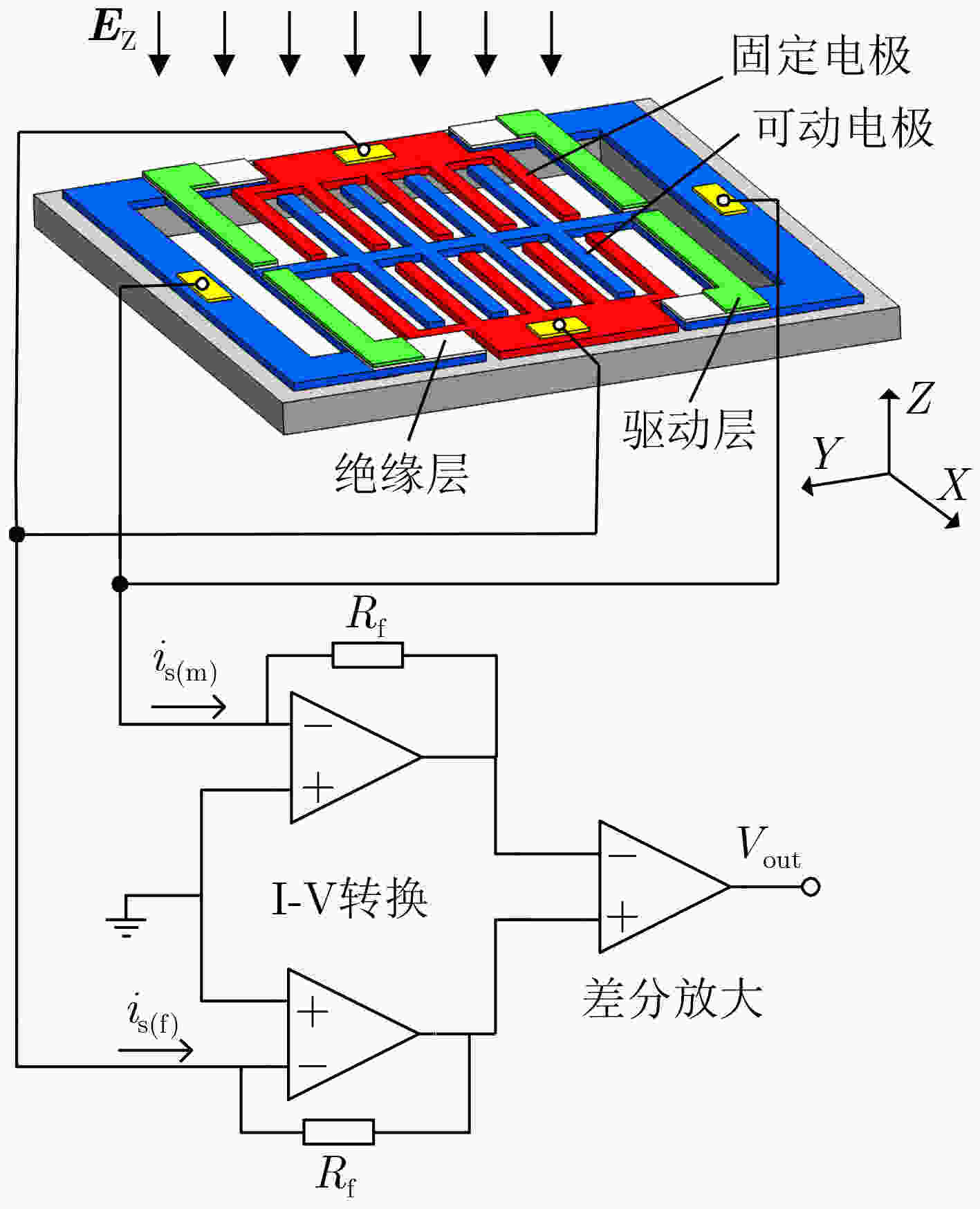
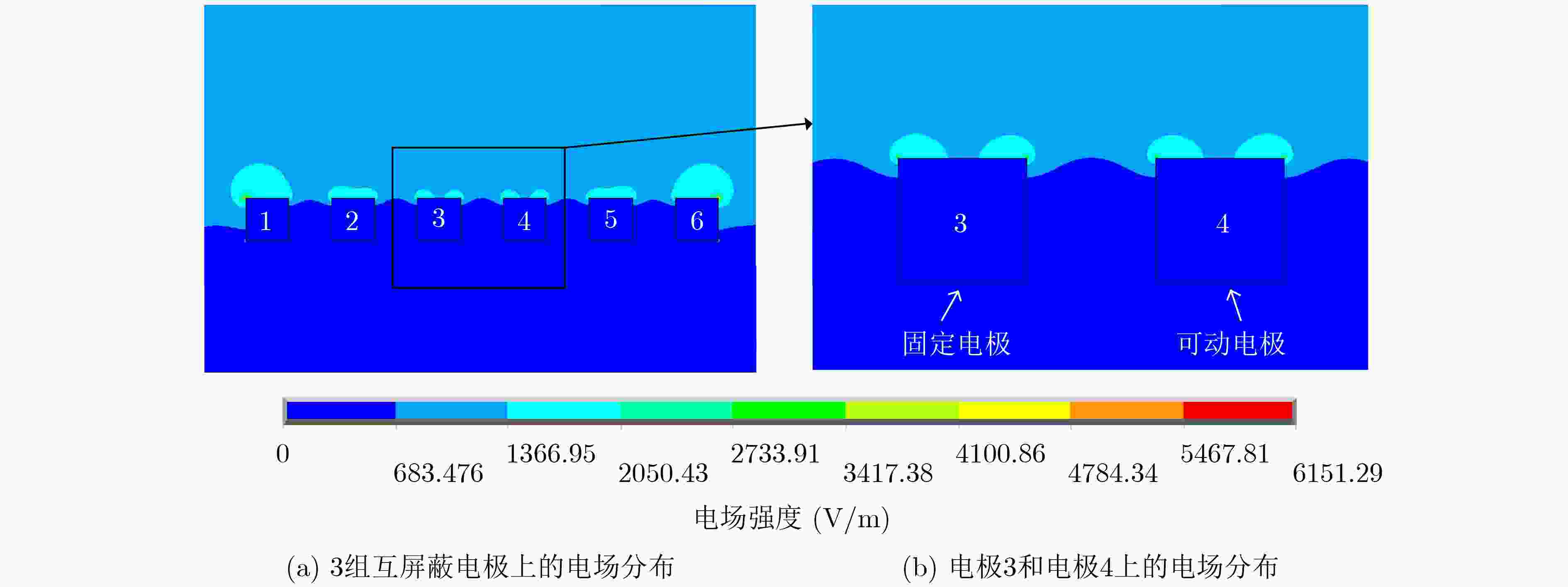
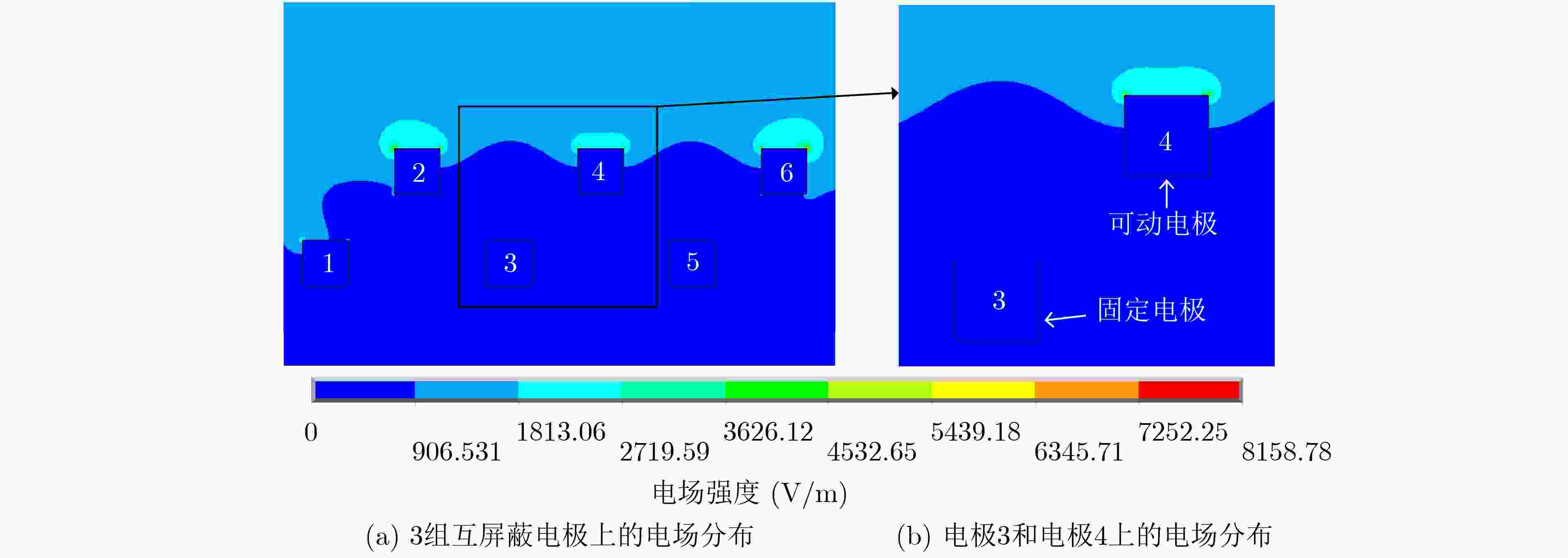
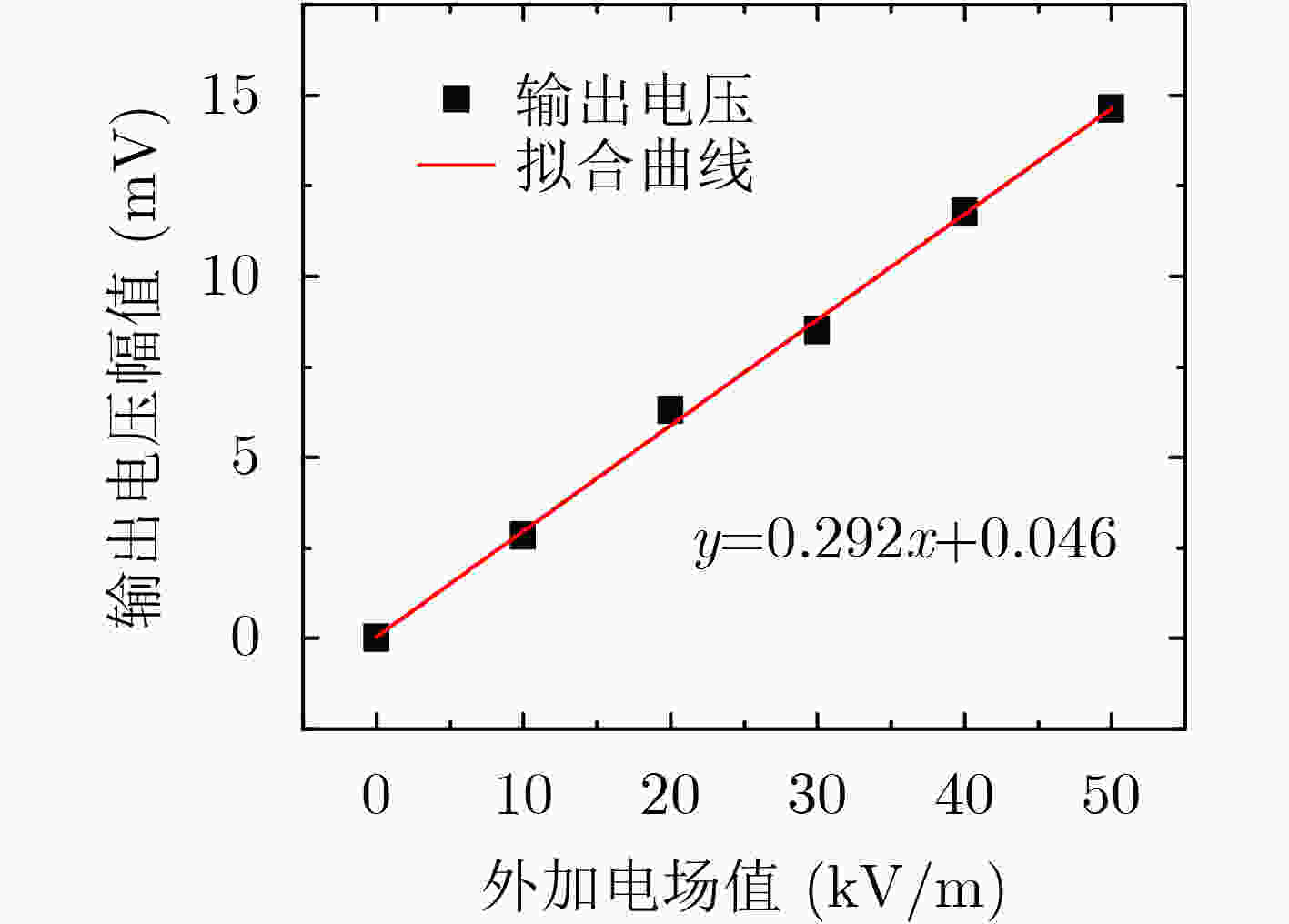
摘要: 该文提出一种基于锆钛酸铅(PZT)的低电压驱动微机电系统(MEMS)电场传感器。该传感器基于电荷感应原理,其敏感单元由固定电极和可动电极构成。固定电极与可动电极均为感应电极,同时两者又是屏蔽电极。在PZT压电材料的驱动下,可动电极产生垂直于敏感芯片基底的振动并且与固定电极形成交互屏蔽,当存在待测电场时,分别在可动电极和固定电极上产生相位差为180°的感应电流信号。该文进行了传感器的设计和有限元仿真,提出敏感微结构的加工工艺流程,突破了基于PZT压电材料的可动电极MEMS工艺兼容制备技术,完成了敏感芯片制备,对传感器进行了性能测试。该传感器具有工作电压低的突出优点。实验测试表明,在0~50 kV/m电场强度范围内,采用1 V交流驱动电压,电场传感器的灵敏度为0.292 mV/(kV/m),线性度为2.89%。Abstract: A Micro-Electro-Mechanical System (MEMS) electric field sensor with low driving voltage based on Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT) is proposed. Based on the charge-induction principle, the sensitive units are composed of fixed electrodes and movable electrodes. All the fixed and movable electrodes work as sensing electrodes, in the meantime, they are also mutually shielding electrodes. Driven by the piezoelectric material PZT, the movable electrodes vibrate perpendicularly to the substrate of the sensitive chip, and they are mutually shielded with the fixed electrodes. When there is an electric field to be measured, induced current signals with a phase difference of 180° are generated respectively on the movable electrodes and the fixed electrodes. The design and finite element simulation of the sensor are carried out, the fabrication process of the sensitive microstructure is proposed, the MEMS process compatible preparation technology of movable electrode based on PZT piezoelectric material is broken through, the microsensor chip is successfully produced, and the performance of the sensor is tested. The sensor has the advantage of low working voltage. Experimental results show that, with 1 V AC driving voltage, the sensitivity of the electric field sensor system is 0.292 mV/(kV/m) and the linearity is 2.89% in the range of 0~50 kV/m electric field intensity.
-
表 1 仿真结构参数
结构参数 参数值 结构参数 参数值(μm) 梁1的长度 1900 μm 可动电极的长度 600 梁1的宽度 100 μm 可动电极的宽度 5 梁1的厚度 4 μm 可动电极之间的间隙 15 梁2的长度 650 μm 可动电极的厚度 4 梁2的宽度 60 μm PZT薄膜的长度 650 梁2的厚度 4 μm PZT薄膜的宽度 53 可动电极的数量 84×2 PZT薄膜的厚度 0.6 -
[1] 任仁, 陈贤祥, 夏善红, 等. 空间电磁环境监测用双探针式星载电场探测仪[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2012, 34(10): 2489–2493. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00299REN Ren, CHEN Xianxiang, XIA Shanhong, et al. Spaceborne double-probe electric field sensor for space electromagnetic environment monitoring[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2012, 34(10): 2489–2493. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2012.00299 [2] ZENG Qingfeng, WANG Zhenhui, GUO Fengxia, et al. The application of lightning forecasting based on surface electrostatic field observations and radar data[J]. Journal of Electrostatics, 2013, 71(1): 6–13. doi: 10.1016/j.elstat.2012.10.007 [3] CUI Yong, SONG Xiao, WANG Chen, et al. Ground-level DC electric field sensor for overhead HVDC/HVAC transmission lines in hybrid corridors[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2020, 14(19): 4173–4178. doi: 10.1049/iet-gtd.2019.1413 [4] 张成铭, 徐晓英, 舒晓榕, 等. 静电放电对PCB轨线耦合的实验及仿真研究[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2020, 34(5): 103–111. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B1902854ZHANG Chengming, XU Xiaoying, SHU Xiaorong, et al. Experimental and simulation study on the coupling with the PCB trace by electrostatic discharge[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2020, 34(5): 103–111. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B1902854 [5] 王颖. 电场传感器研究综述[J]. 传感器技术与应用, 2021, 9(1): 24–33. doi: 10.12677/JSTA.2021.91004WANG Ying. Review of electric field sensors[J]. Journal of Sensor Technology and Application, 2021, 9(1): 24–33. doi: 10.12677/JSTA.2021.91004 [6] RONCIN A, SHAFAI C, and SWATEK D R. Electric field sensor using electrostatic force deflection of a micro-spring supported membrane[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2005, 123/124: 179–184. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2005.02.018 [7] 杨鹏飞, 彭春荣, 张海岩, 等. SOI微型电场传感器的设计与测试[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(11): 2771–2774. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01285YANG Pengfei, PENG Chunrong, ZHANG Haiyan, et al. Design and testing of a SOI electric-field microsensor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(11): 2771–2774. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.01285 [8] BAHREYNI B, WIJEWEERA G, SHAFAI C, et al. Analysis and design of a micromachined electric-field sensor[J]. Journal of Microelectromechanical Systems, 2008, 17(1): 31–36. doi: 10.1109/JMEMS.2007.911870 [9] KOBAYASHI T, OYAMA S, OKADA H, et al. An electrostatic field sensor driven by self-excited vibration of sensor/actuator integrated piezoelectric micro cantilever[C]. 2012 IEEE 25th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Paris, France, 2012: 527–530. [10] YANG Pengfei, PENG Chunrong, FANG Dongming, et al. Design, fabrication and application of an SOI-based resonant electric field microsensor with coplanar comb-shaped electrodes[J]. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 2013, 23(5): 055002. doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/23/5/055002 [11] CHEN Tao, SHAFAI C, RAJAPAKSE A, et al. Micromachined ac/dc electric field sensor with modulated sensitivity[J]. Sensors and Actuators A:Physical, 2016, 245: 76–84. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2016.04.054 [12] 杨鹏飞, 陈博, 闻小龙, 等. 一种基于MEMS芯片的新型地面大气电场传感器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(6): 1536–1540. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150994YANG Pengfei, CHEN Bo, WEN Xiaolong, et al. A novel MEMS chip-based ground atmospheric electric field sensor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(6): 1536–1540. doi: 10.11999/JEIT150994 [13] CHU Zhaozhi, PENG Chunrong, REN Ren, et al. A high sensitivity electric field microsensor based on torsional resonance[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(1): 286. doi: 10.3390/s18010286 [14] 储昭志, 彭春荣, 任仁, 等. 一种扭转谐振式MEMS电场传感器[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2019, 38(6): 83–85,88. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2019)06-0083-03CHU Zhaozhi, PENG Chunrong, REN Ren, et al. A MEMS-based electric field sensor with torsional resonance[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2019, 38(6): 83–85,88. doi: 10.13873/J.1000-9787(2019)06-0083-03 [15] 雷虎成, 夏善红, 彭春荣, 等. 一种压电驱动互屏蔽电极MEMS电场传感器[J]. 微纳电子与智能制造, 2020, 2(4): 52–58. doi: 10.19816/j.cnki.10-1594/tn.2020.04.052LEI Hucheng, XIA Shanhong, PENG Chunrong, et al. Piezoelectric driven MEMS electric field sensor with mutual shielding electrodes[J]. Micro/nano Electronics and Intelligent Manufacturing, 2020, 2(4): 52–58. doi: 10.19816/j.cnki.10-1594/tn.2020.04.052 [16] 闻小龙, 杨鹏飞, 储昭志, 等. 基于MEMS的距离自适应型非接触静电仪[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(10): 3068–3074. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200571WEN Xiaolong, YANG Pengfei, CHU Zhaozhi, et al. A daptive-distance noncontact electrostatic meter based on MEMS technology[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(10): 3068–3074. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200571 [17] 朱莎, 曾晗, 王师奇, 等. 一种新型微加工交直流电场传感器设计[J]. 仪表技术与传感器, 2021(6): 41–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2021.06.008ZHU Sha, ZENG Han, WANG Shiqi, et al. Design of novel micromachined AC/DC electric field sensor[J]. Instrument Technique and Sensor, 2021(6): 41–45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2021.06.008 [18] WEN Xiaolong, YANG Pengfei, ZHANG Zhouwei, et al. Resolution-enhancing structure for the electric field microsensor chip[J]. Micromachines, 2021, 12(8): 936. doi: 10.3390/mi12080936 [19] WEN Xiaolong, YANG Pengfei, CHU Zhaozhi, et al. Toward atmospheric electricity research: A low-cost, highly sensitive and robust balloon-borne electric field sounding sensor[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(12): 13405–13416. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3070130 -





 下载:
下载:


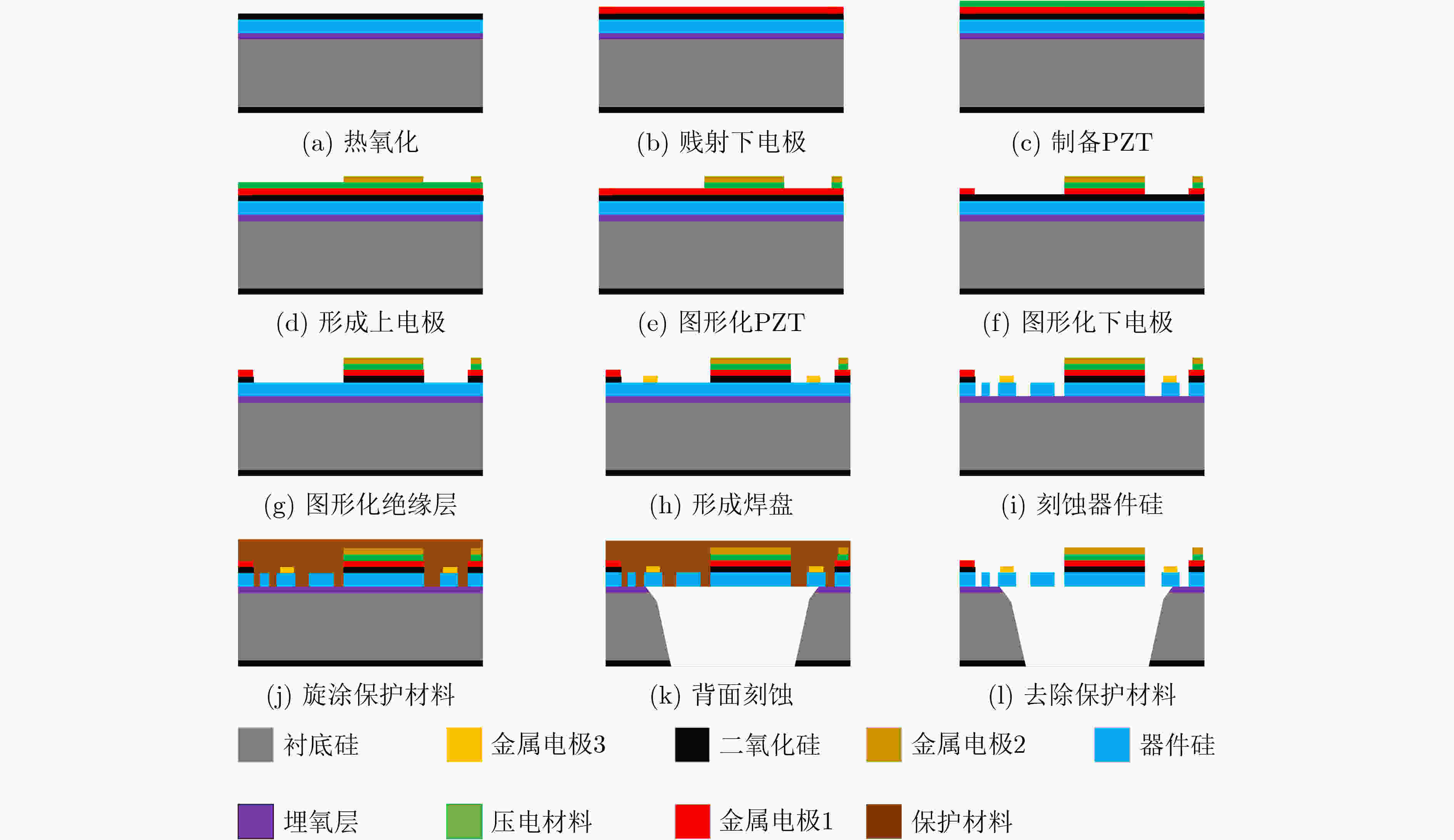
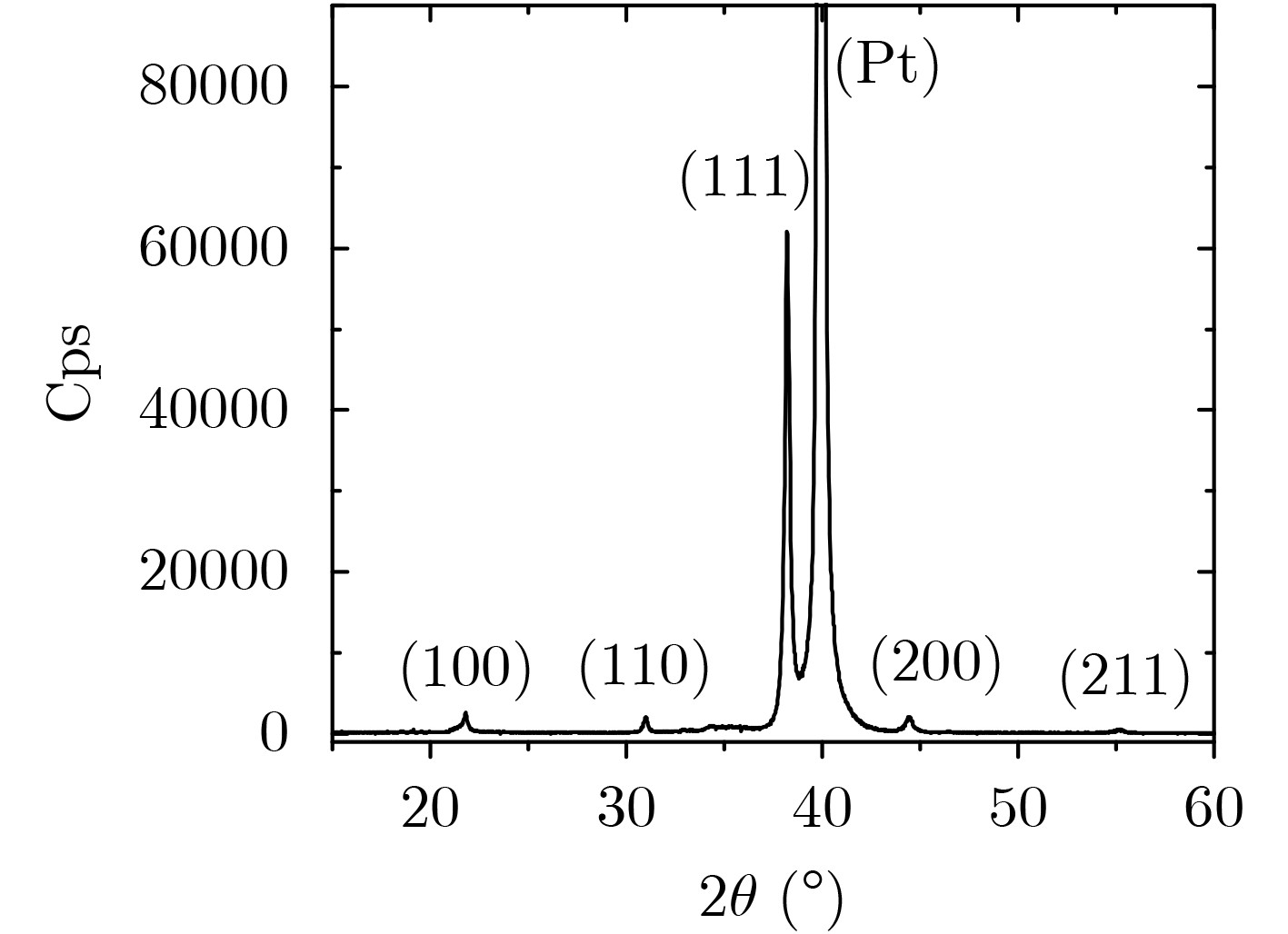
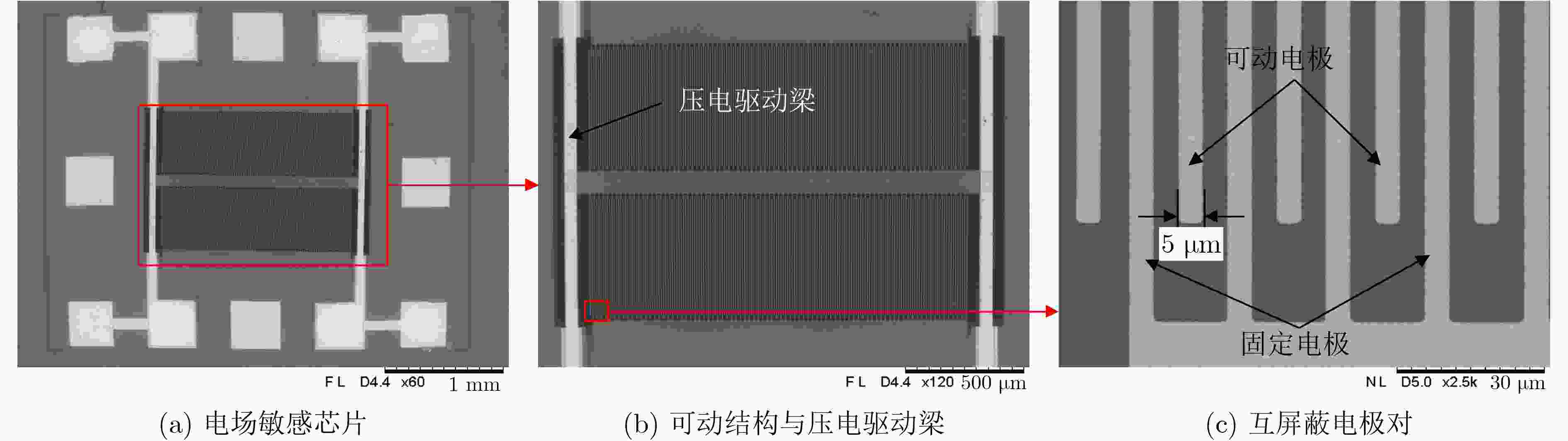
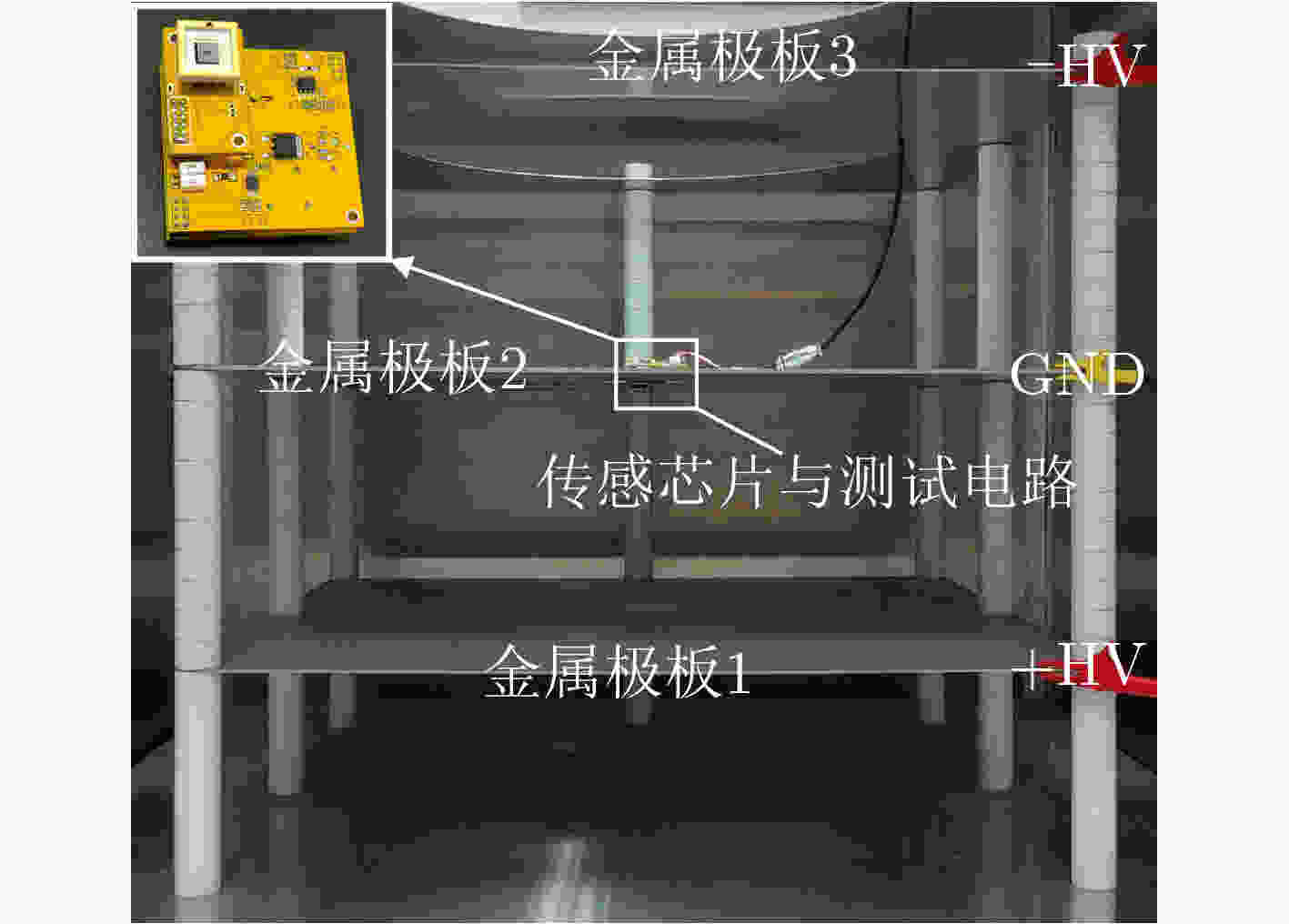


 下载:
下载:
