A Multi-sensor Adaptive Observation Iteratively Updating GM-PHD Tracking Algorithm
-
摘要: 针对多传感器观测数据质量不同且未知时,多传感器量测迭代更新高斯混合概率假设密度(GM-PHD)滤波器跟踪算法的结果对更新顺序敏感的问题,该文提出一种多传感器自适应量测迭代更新GM-PHD跟踪算法AIU-GM-PHD。首先基于多传感器融合一致性度量,提出一种用于在线评估各传感器跟踪结果质量的方法;然后对多传感器迭代融合顺序进行优化,最后构建相应的多传感器GM-PHD融合跟踪算法。为了解决多传感器自适应顺序迭代融合无法体现传感器质量差距的问题,提出了一种自适应带权伪量测迭代更新GM-PHD跟踪算法PAIU-GM-PHD。仿真结果表明,与常规多传感器迭代更新GM-PHD跟踪算法相比,所提算法能够获得鲁棒性更好、精度更高的跟踪结果。
-
关键词:
- 多传感器多目标跟踪 /
- 随机有限集 /
- 自适应融合 /
- 高斯混合概率假设密度滤波器 /
- 量测迭代更新
Abstract: For the problem that the results of multi-sensor measurement iteratively updating Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density (GM-PHD) tracking algorithm is sensitive to the updating order if the qualities of multi-sensor observation data are different and unknown, a multi-sensor Adaptive observation Iteratively Updating GM-PHD tracking algorithm (AIU-GM-PHD) is proposed. Firstly, based on the multi-sensor fusion consistency measure, a method is proposed to evaluate the online quality of each sensor's tracking results. Then, the sequence of multi-sensor iterative fusion is optimized. Finally, the corresponding multi-sensor GM-PHD fusion tracking algorithm is constructed. To solve the problem that the multi-sensor adaptive order iterative fusion can not reflect the sensor quality gap, an Adaptive Iteratively Updating GM-PHD tracking algorithm PAIU-GM-PHD with weighted pseudo measurements is proposed. The simulation results show that, compared with the conventional multi-sensor iterative update GM-PHD tracking algorithm, the proposed algorithms can obtain more robust and accurate tracking results. -
表 1 实验1场景设置
检测概率 杂波数量 场景1 $p_d^1 = 0.95,{\text{ } }p_d^2 = 0.85,{\text{ } }p_d^3 = 0.75,{\text{ } }p_d^4 = 0.65$ ${\lambda _1} = 2,0{\text{ } }{\lambda _2} = 20,{\text{ } }{\lambda _3} = 20,{\text{ } }{\lambda _4} = 20$ 场景2 $p_d^1 = 0.90,{\text{ } }p_d^2 = 0.90,{\text{ } }p_d^3 = 0.90,{\text{ } }p_d^4 = 0.90$ ${\lambda _1} = 20,{\text{ } }{\lambda _2} = 30,{\text{ } }{\lambda _3} = 40,{\text{ } }{\lambda _4} = 50$ 表 2 实验2场景设置
检测概率 杂波数量 场景1 $p_{{d} }^1 = 0.95,{\text{ } }p_{{d} }^2 = 0.85,{\text{ } }p_{{d} }^3 = 0.75,{\text{ } }p_{{d} }^4 = 0.65$ $ {\lambda _1} = 20,{\text{ }}{\lambda _2} = 20,{\text{ }}{\lambda _3} = 20,{\text{ }}{\lambda _4} = 20 $ 场景2 ${p}_{ {d} }^{1}=0.90,\text{}\text{}\text{}\text{}\text{}\text{}\text{}\text{}\text{ }{p}_{ {d} }^{2}=0.90,\text{ }{p}_{ {d} }^{3}=0.90,\text{ }{p}_{ {d} }^{4}=0.90\text{}\text{}$ ${\lambda _1} = 20,{\text{ }}{\lambda _2} = 30,{\text{ }}{\lambda _3} = 40,{\text{ }}{\lambda _4} = 50$ 场景3 $p_{{d} }^1 = 0.95,{\text{ } }p_{{d} }^2 = 0.85,{\text{ } }p_{{d} }^3 = 0.75,{\text{ } }p_{{d} }^4 = 0.65$ ${\lambda _1} = 20,{\text{ }}{\lambda _2} = 30,{\text{ }}{\lambda _3} = 40,{\text{ }}{\lambda _4} = 50$ 表 3 场景1仿真结果
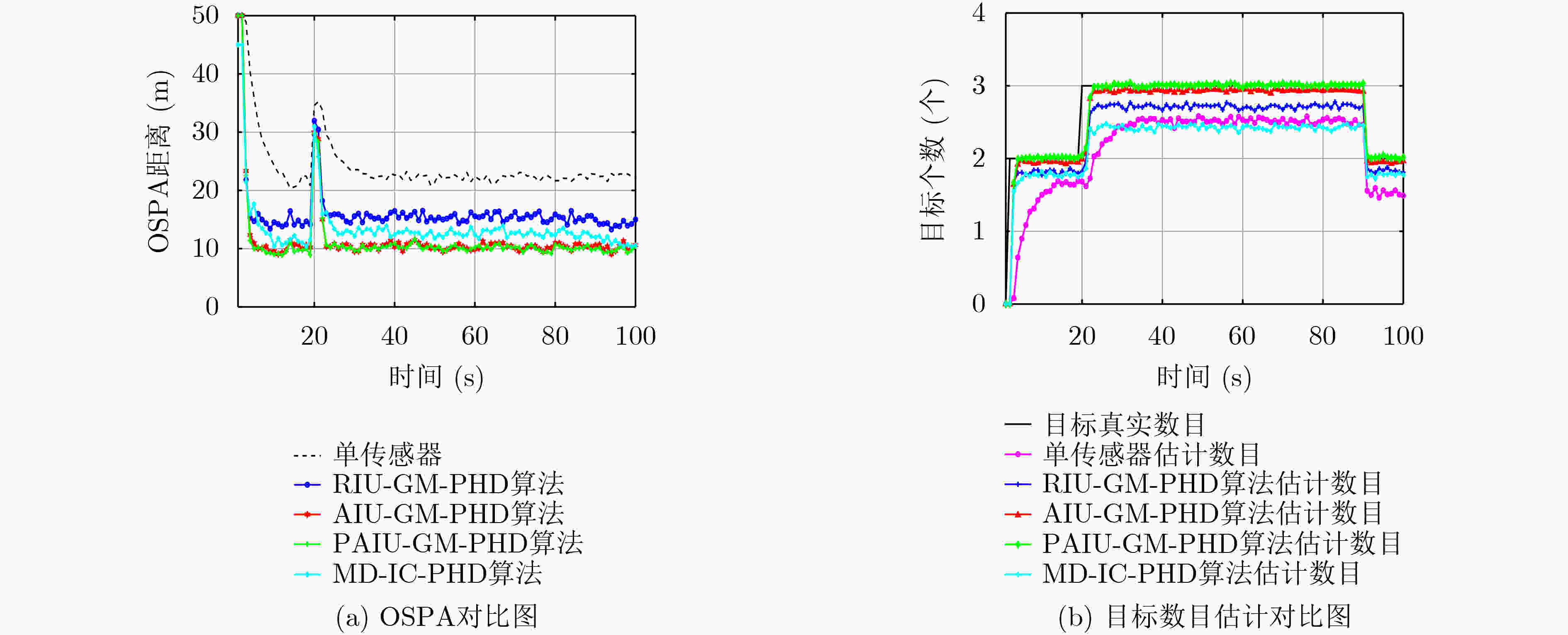
算法 OSPA精度 目标数目估计(真实3) 单传感器GM-PHD 22.8412 2.5361 RIU-GM-PHD 15.6506 2.7581 AIU-GM-PHD 10.5369 2.9808 PAIU-GM-PHD 10.3282 3.0557 MD-IC-PHD 12.9869 2.4657 表 4 场景2仿真结果
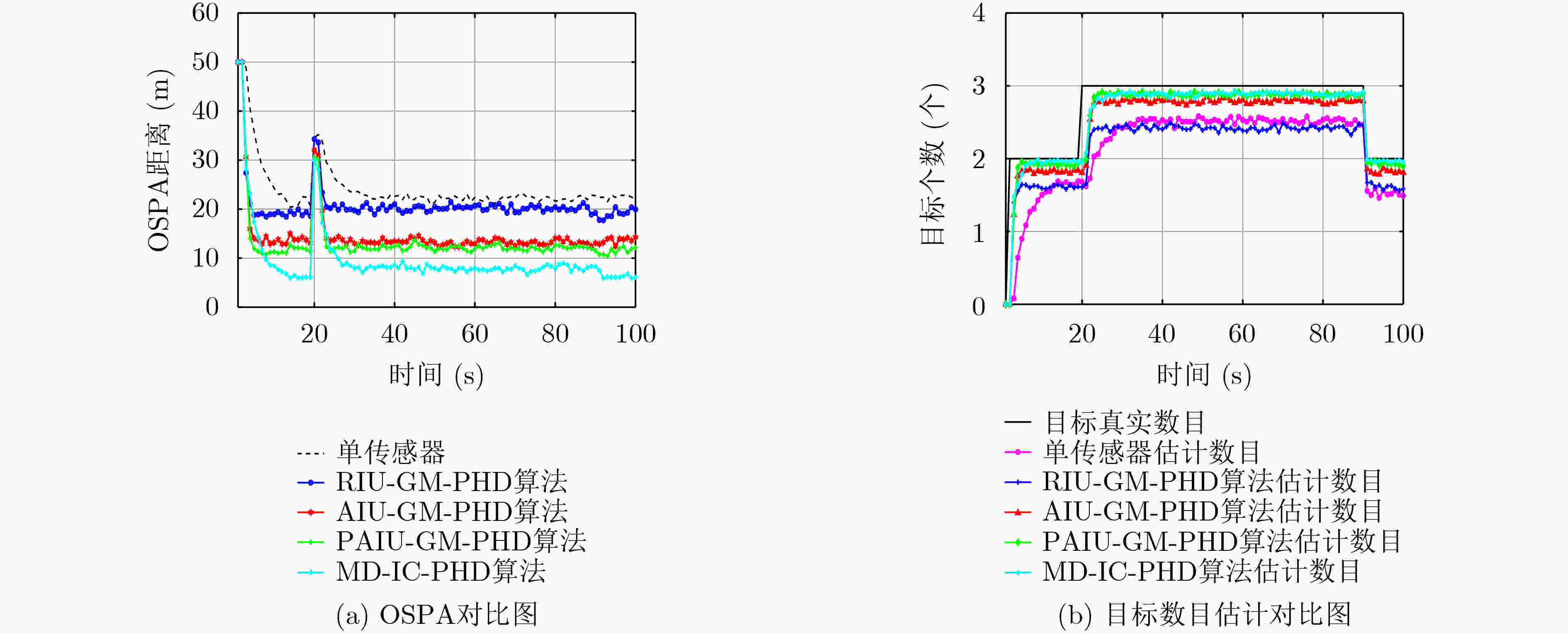
算法 OSPA精度 目标数目估计(真实3) 单传感器GM-PHD 22.8412 2.5361 RIU-GM-PHD 20.4843 2.4578 AIU-GM-PHD 13.4627 2.8301 PAIU-GM-PHD 12.2804 2.9288 MD-IC-PHD 8.1814 2.9336 表 5 场景3仿真数据
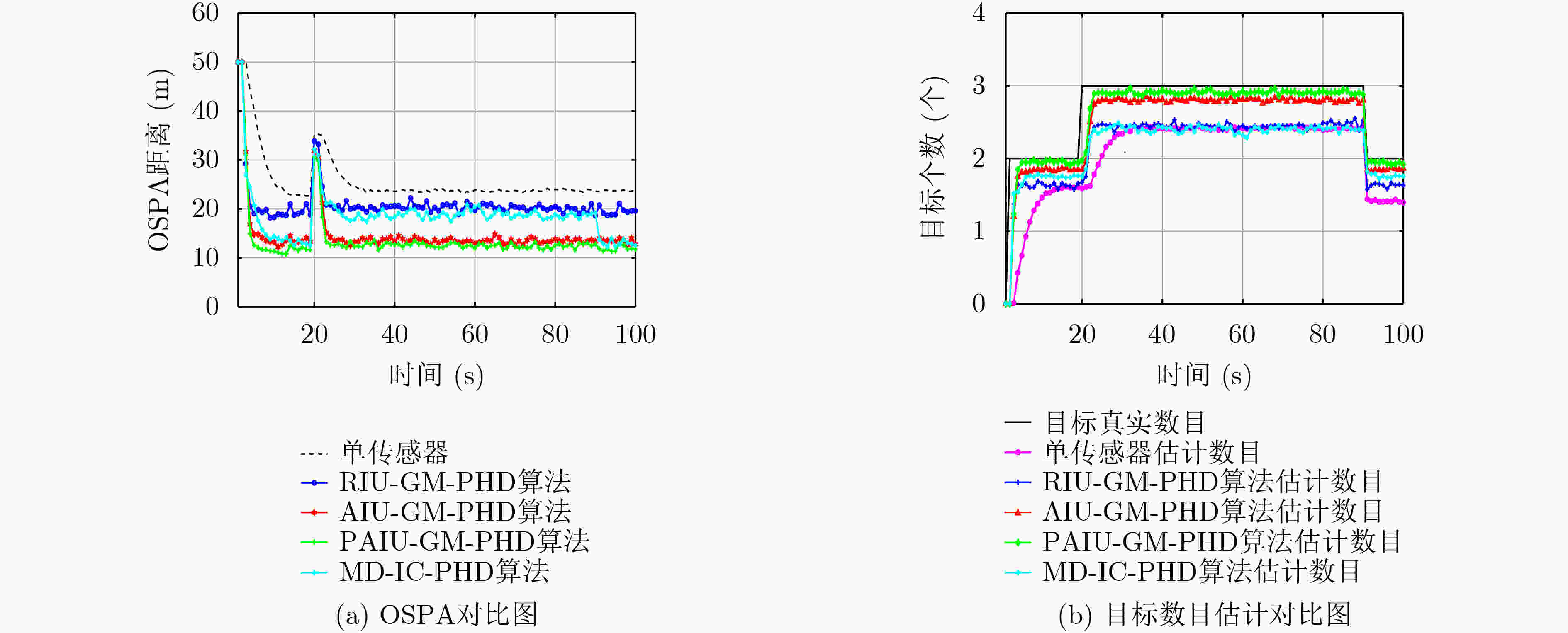
算法 OSPA精度 目标数估计(真实3) 单传感器GM-PHD 24.3033 2.4351 RIU-GM-PHD 20.5465 2.4874 AIU-GM-PHD 13.6899 2.8429 PAIU-GM-PHD 12.7136 2.9526 MD-IC-PHD 19.0824 2.4410 表 6 3 种算法时间复杂度对比
算法 时间复杂度 空间复杂度 单帧时间消耗(s) RIU-GM-PHD $(2L - 1) \cdot O(n)$ $O(d)$ 15.37 AIU-GM-PHD $(2L - 1) \cdot O(n) + L \cdot O(s)$ $O(d) + O(L)$ 19.02 PAIU-GM-PHD $(2L - 1) \cdot O(n) + L \cdot (O(s) + O(j))$ $O(d) + 2 \cdot O(L)$ 20.01 -
[1] 杨威, 付耀文, 龙建乾, 等. 基于有限集统计学理论的目标跟踪技术研究综述[J]. 电子学报, 2012, 40(7): 1440–1448. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.07.025YANG Wei, FU Yaowen, LONG Jianqian, et al. Research review of target tracking technology based on the theory of finite set statistics[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2012, 40(7): 1440–1448. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2012.07.025 [2] 黄静琪, 胡琛, 孙山鹏, 等. 一种基于异步传感器网络的空间目标分布式跟踪方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(5): 1132–1139. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190460HUANG Jingqi, HU Chen, SUN Shanpeng, et al. A distributed space target tracking algorithm based on asynchronous multi-sensor networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(5): 1132–1139. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190460 [3] MA Ke, ZHANG Hanguang, WANG Rentao, et al. Target tracking system for multi-sensor data fusion[C]. The 2nd Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Chengdu, China, 2017: 1768–1772. [4] LIANG Shuang, ZHU Yun, LI Hao, et al. Nearest-neighbour joint probabilistic data association filter based on random finite set[C]. 2019 International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences, Chengdu, China, 2019: 1–6. [5] BAR-SHALOM Y and TSE E. Tracking in a cluttered environment with probabilistic data association[J]. Automatica, 1975, 11(5): 451–460. doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(75)90021-7 [6] VENUS A, LEITINGER E, TERTINEK S, et al. A message passing based adaptive PDA algorithm for robust radio-based localization and tracking[C]. 2021 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf21), Atlanta, USA, 2021: 1–6. [7] ANGLE R B, STREIT R L, and EFE M. A low computational complexity JPDA filter with superposition[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28(1): 1031–1035. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3082040 [8] BAR-SHALOM Y, FORTMANN T E, and CABLE P G. Tracking and data association[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1990, 87(2): 918–919. doi: 10.1121/1.398863 [9] CARTHEL C, LENOACH J, CORALUPPI S, et al. Analysis of MHT and GBT approaches to disparate-sensor fusion[C]. The IEEE 23rd International Conference on Information Fusion, Rustenburg, South Africa, 2020: 1–7. [10] MORI S, CHONG C Y, WISHNER R P, et al. Multitarget multi sensor tracking problems: A general Bayesian approach[C]. 1983 American Control Conference, San Francisco, USA, 1983: 452–457. [11] LEUNG K Y K, INOSTROZA F, and ADAMS M. Relating random vector and random finite set estimation in navigation, mapping, and tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(17): 4609–4623. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2701330 [12] SONG Yan, HU Jianwang, and JI Bing. A survey of PHD filtering method based on random finite set[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Mechatronics Engineering and Information Technology, Dalian, China, 2017: 199–204. [13] GARCÍA-FERNÁNDEZ Á F and MASKELL S. Continuous-discrete trajectory PHD and CPHD filters[C]. The IEEE 23rd International Conference on Information Fusion, Rustenburg, South Africa, 2020: 1–8. [14] CHOI M E and SEO S W. Robust multitarget tracking scheme based on Gaussian mixture probability hypothesis density filter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(6): 4217–4229. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2479363 [15] GU Zihao, WANG Ping, and LIU Fuqiang. Cooperative vehicle tracking using SMC-PHD integrated with interacting multiple models[C]. 2020 IEEE MTT-S International Wireless Symposium, Shanghai, China, 2020: 1–3. [16] MA W K, VO B N, SINGH S S, et al. Tracking an unknown time-varying number of speakers using TDOA measurements: A random finite set approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2006, 54(9): 3291–3304. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.877658 [17] DA Kai, LI Tiancheng, ZHU Yongfeng, et al. Recent advances in multisensor multitarget tracking using random finite set[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2021, 22(1): 5–24. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.2000266 [18] XU Jian, HUANG Fangming, and HUANG Zhilinag. The multi-sensor PHD filter: Analytic implementation via Gaussian mixture and effective binary partition[C]. The 16th International Conference on Information Fusion, Istanbul, Turkey, 2013: 945–952. [19] 熊伟, 顾祥岐, 徐从安, 等. 多编队目标先后出现时的无先验信息跟踪方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1619–1626. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190508XIONG Wei, GU Xiangqi, XU Congan, et al. Tracking method without prior information when multi-group targets appear successively[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1619–1626. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190508 [20] MEYER F, KROPFREITER T, WILLIAMS J L, et al. Message passing algorithms for scalable multitarget tracking[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2018, 106(2): 221–259. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2018.2789427 [21] HAN Shentu, QIAN Hanming, PENG Dongliang, et al. An unbalanced weighted sequential fusing multi-sensor GM-PHD algorithm[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(2): 366. doi: 10.3390/s19020366 [22] NAGAPPA S and CLARK D E. On the ordering of the sensors in the iterated-corrector probability hypothesis density (PHD) filter[C]. SPIE 8050, Signal Processing, Sensor Fusion, and Target Recognition XX, Orlando, USA, 2011: 80500M. [23] LIU Long, JI Hongbing, and FAN Zhenhua. Improved iterated-corrector PHD with Gaussian mixture implementation[J]. Signal Processing, 2015, 114: 89–99. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.01.007 [24] LIU Long, JI Hongbing, ZHANG Wenbo, et al. Multi-sensor fusion for multi-target tracking using measurement division[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(9): 1451–1461. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5567 [25] 王宝树, 李芳社. 基于数据融合技术的多目标跟踪算法研究[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 1998, 25(3): 269–272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.1998.03.001WANG Baoshu and LI Fangshe. The research on multiple targets tracking based on the data fusion technique[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 1998, 25(3): 269–272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2400.1998.03.001 [26] MAHLER R. Approximate multi sensor CPHD and PHD filters[C]. The 13th International Conference on Information Fusion, Edinburgh, UK, 2010: 1–8. [27] BEARD M, VO B T, and VO B N. OSPA(2): Using the OSPA metric to evaluate multi-target tracking performance[C]. 2017 International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 2017: 86–91. [28] STREIT R L. Poisson Point Process: Imaging, Tracking, and Sensing[M]. New York: Springer, 2010: 273–280. -





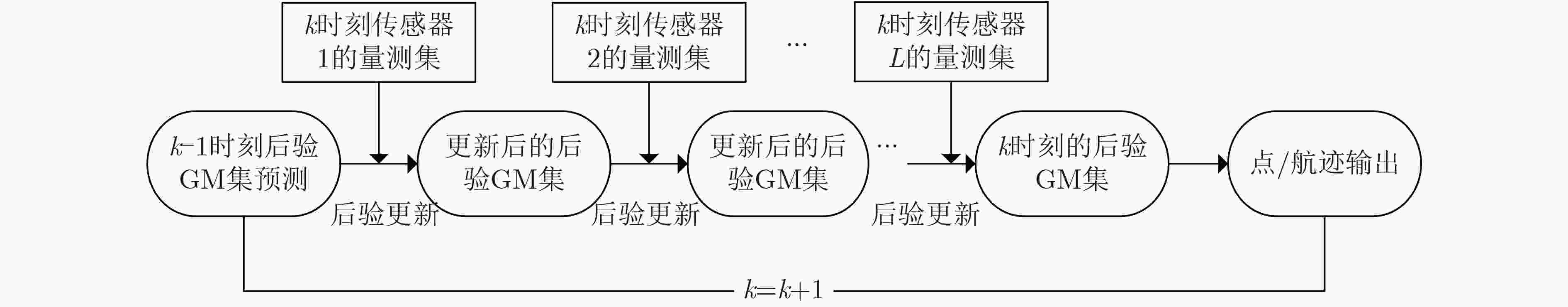
 下载:
下载:
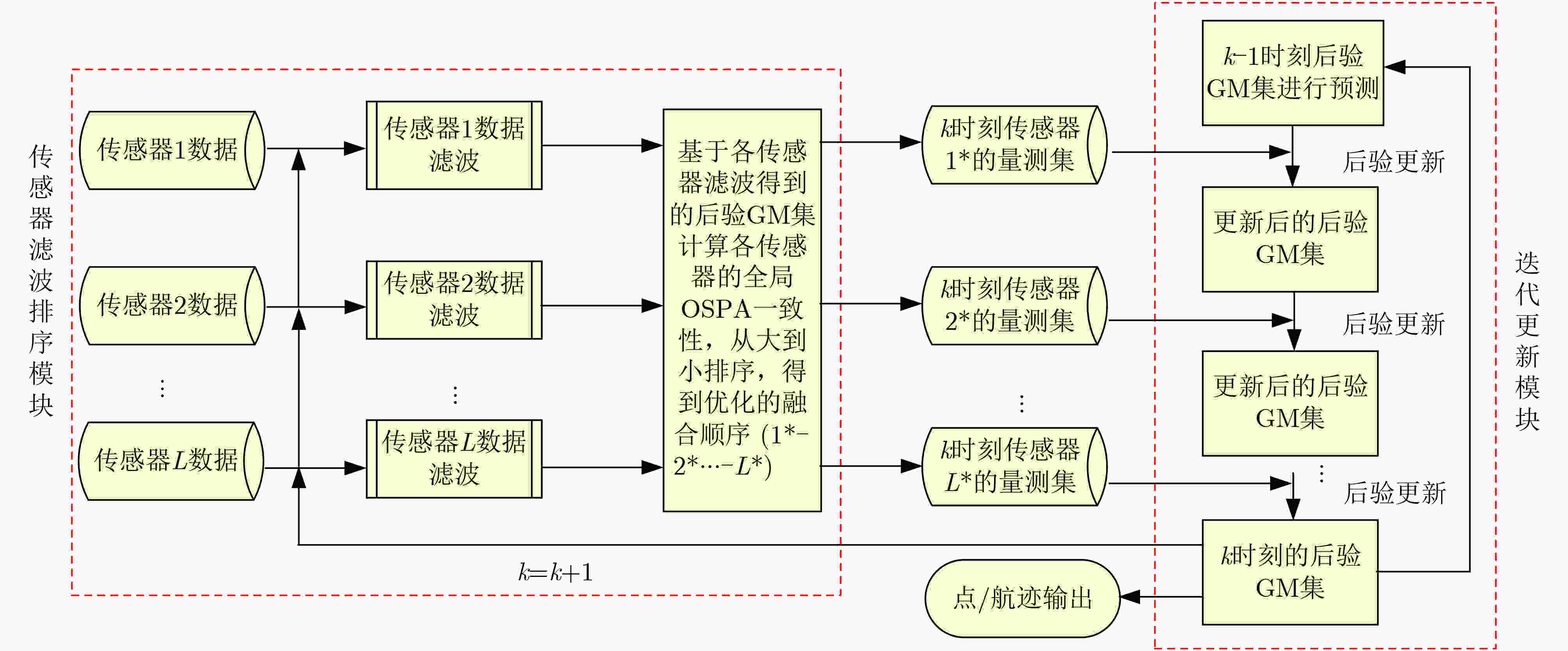
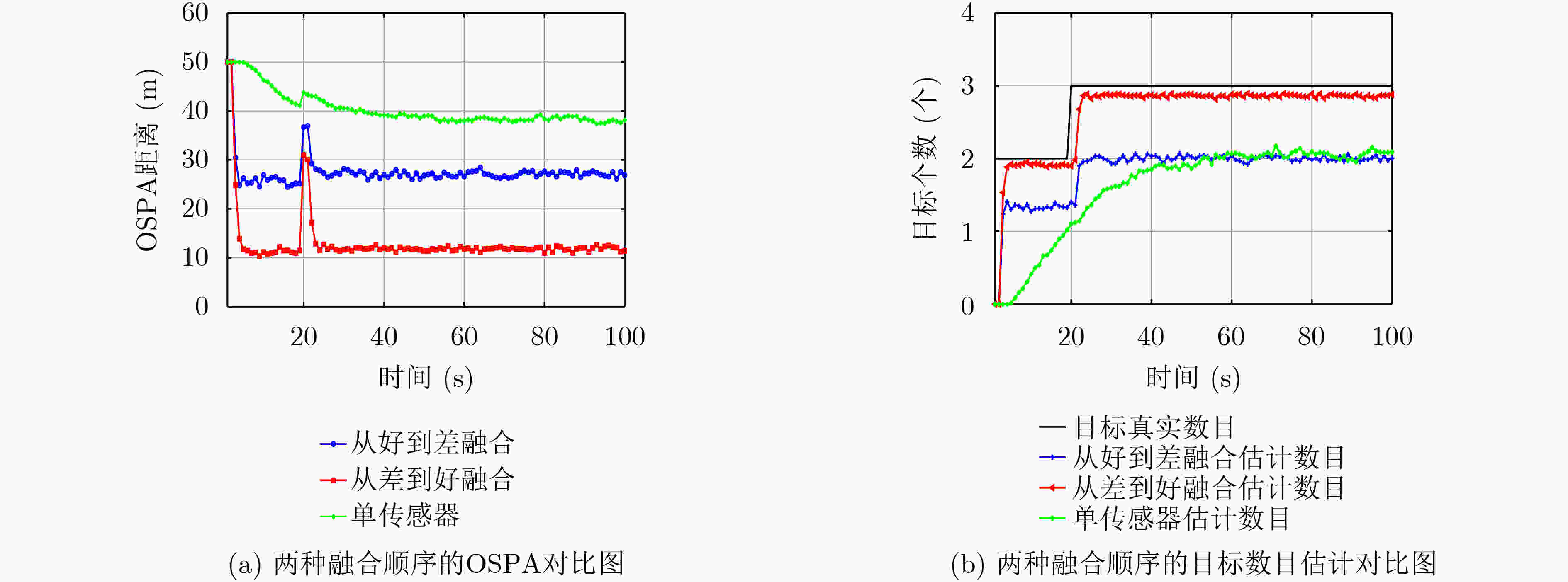
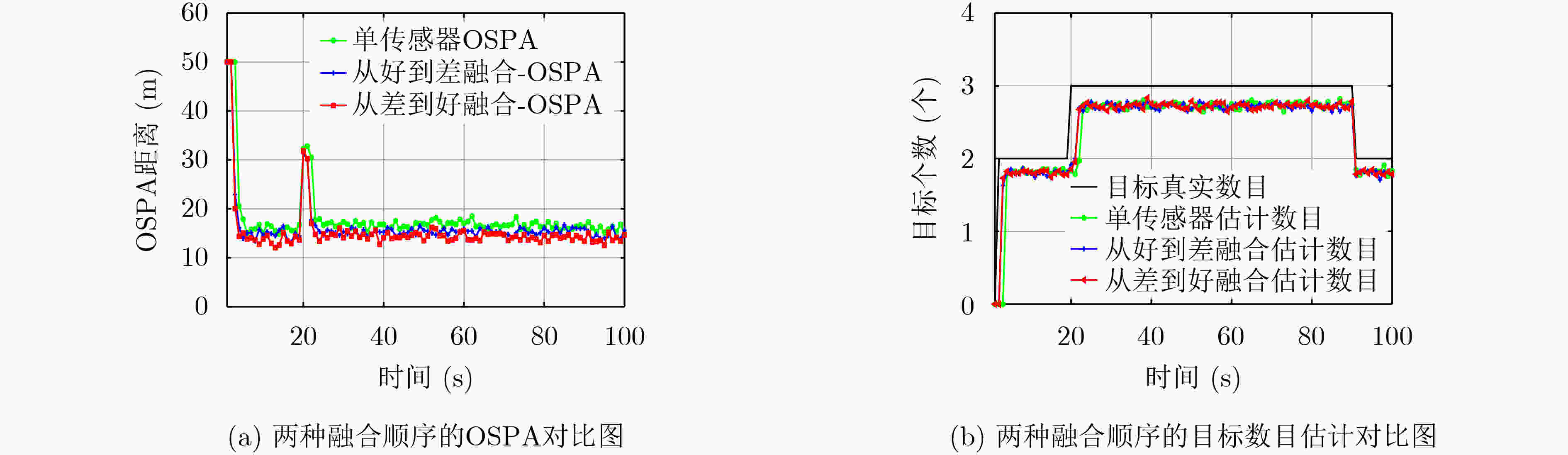


 下载:
下载:
