Low-light Image Enhancement Method Based on Shifted Window Multi-head Self-attention U-shaped Network
-
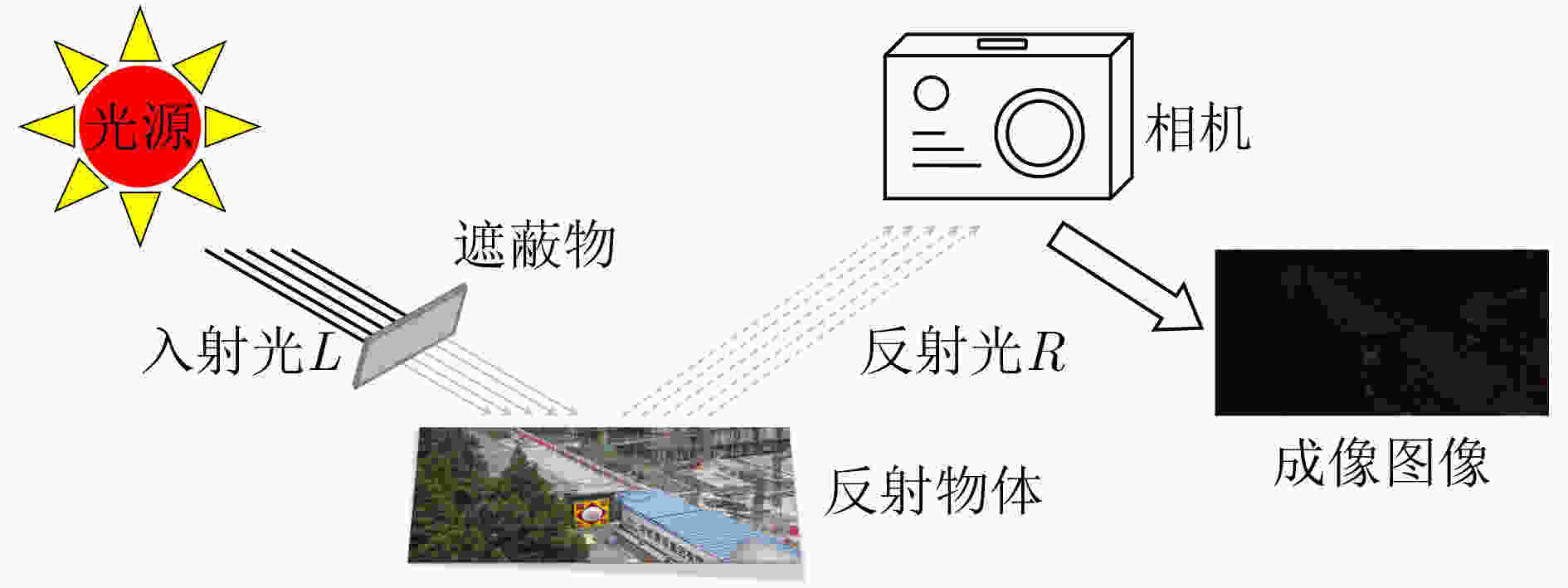
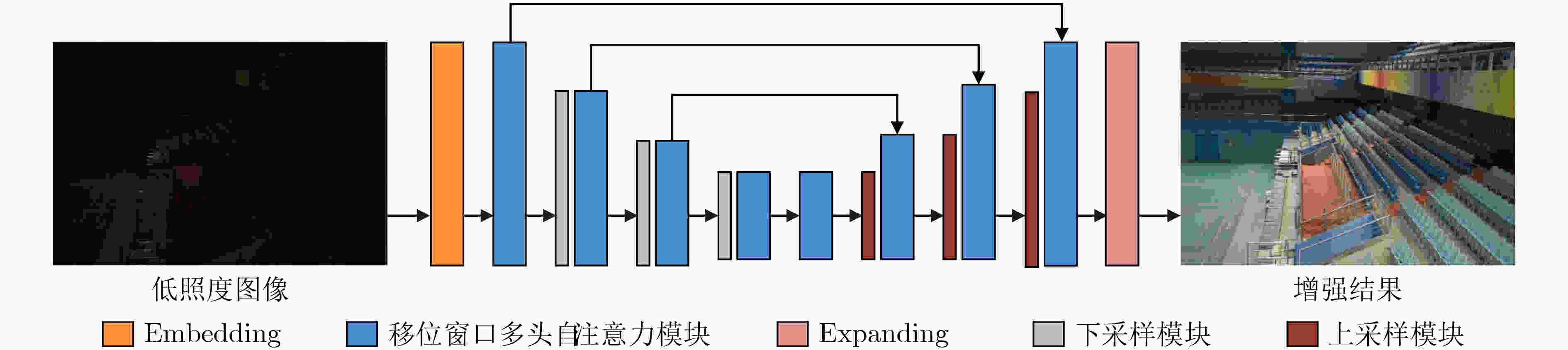
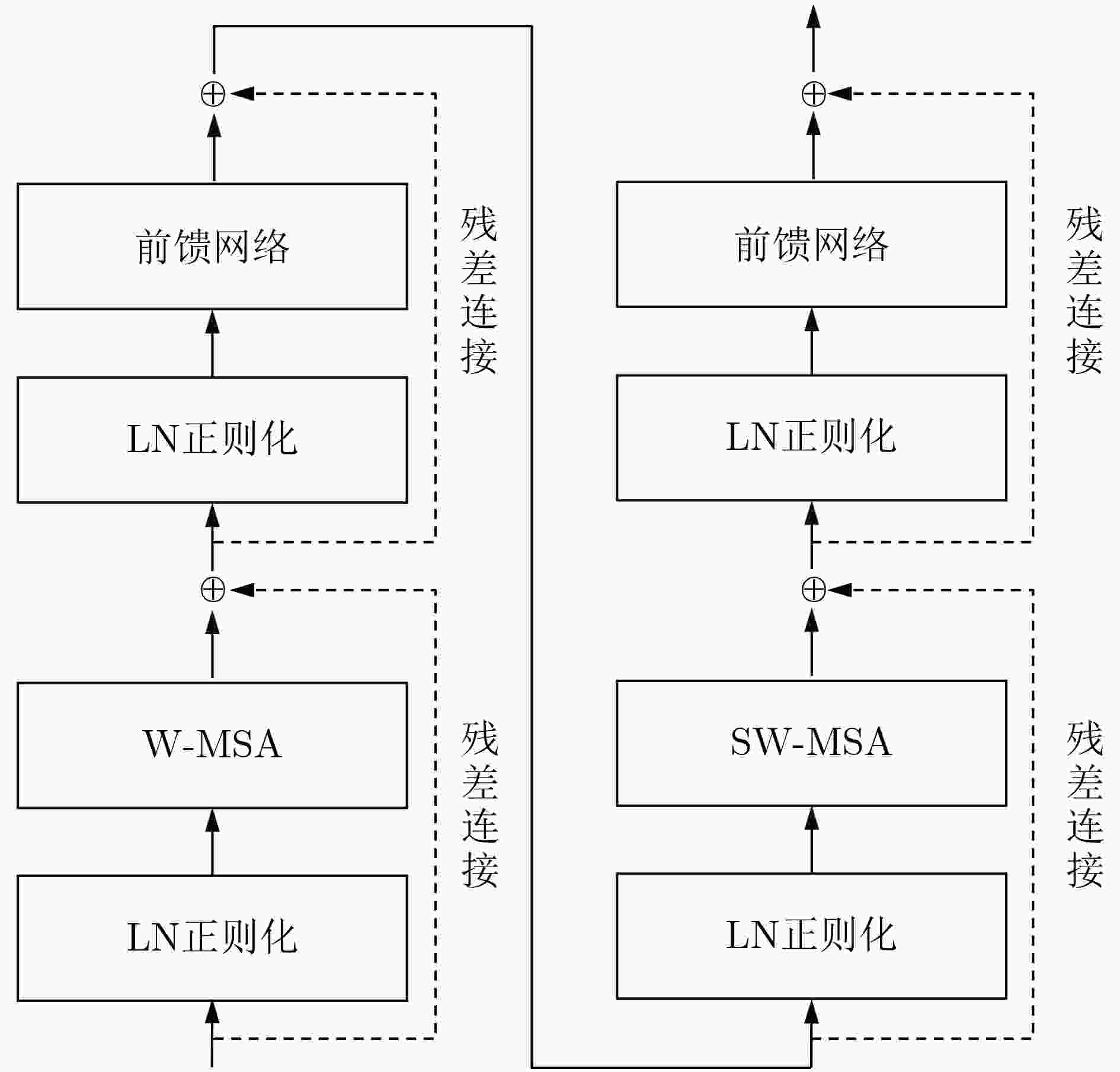
摘要: 针对低照度图像增强模型中的亮度提升、噪声抑制以及保持纹理颜色一致性等难点问题,该文提出一种基于移位窗口自注意力机制的低照度图像增强方法。该文以U型结构为基本框架,以移位窗口多头自注意力模型为基础,构建了由编码器、解码器以及跳跃连接组成的图像增强网络。该网络将自注意力机制的特征提取优势应用到低照度图像增强领域,建立图像特征信息之间的长期依赖关系,能够有效获取全局特征。将所提方法与当前流行的算法进行定量和定性对比试验,主观感受上,该文方法显著提升了图像亮度,抑制图像噪声效果明显并较好地保持了纹理细节和颜色信息;在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性(SSIM)和图像感知相似度(LPIPS)等客观指标方面,该方法较其他方法的最优值分别提高了0.35 dB, 0.041和0.031。实验结果表明,该文所提方法能够有效提升低照度图像的主观感受质量和客观评价指标,具有一定的应用价值。Abstract: Considering the difficult problems of brightness enhancement, noise suppression and maintaining texture color consistency in the low-light image enhancement model, a low-light image enhancement method based on the shifted window self-attention mechanism is proposed. Based on the U-shaped structure and the multi-head self-attention model of shifted windows, an image enhancement network composed of encoders, decoders and jump connections is constructed. The feature extraction advantages of the self-attention mechanism are applied to the field of low-light image enhancement and long-term dependence between image feature information is established, which can obtain global features effectively. The proposed method is compared width current popular algorithms in quantitative and qualitative comparison experiments, subjectively, the brightness of the image and noise suppression are significantly improved, and simultaneously better maintains the color information that highlights the texture details by the proposed method. In terms of objective indicators such as Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio(PSNR), Structural SIMilarity index(SSIM), and Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (LPIPS), which are improved 0.35 dB, 0.041 and 0.031 respectively compared with the optimal values of other methods. The experimental results show that the subjective perception quality and objective evaluation indicators of low-light images can be effectively improved by the proposed method, indicating a certain application value
-
Key words:
- Image processing /
- Deep learning /
- Low-light image enhancement
-
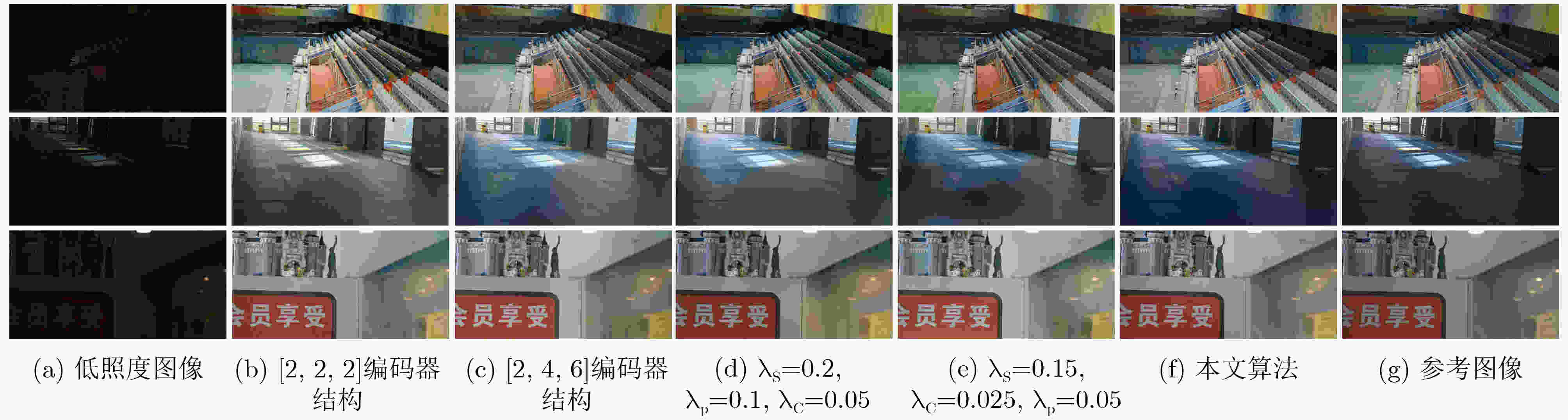
表 1 不同算法处理后客观评价指标结果图
序号 MBLLEN RetinexNet KinD GLADNet SIE Zero-DCE 本文算法 PSNR(dB) 17.73 16.46 19.95 19.50 17.13 18.53 20.30 SSIM 0.706 0.494 0.813 0.756 0.731 0.659 0.854 LPIPS 0.250 0.441 0.138 0.240 0.259 0.234 0.107 表 2 不同编码器结构在测试集上客观评价指标
编码器不同层中移位窗口
自注意力模块数量PSNR(dB) SSIM LPIPS [2, 2, 2] 19.49 0.843 0.121 [2, 2, 6] 20.30 0.854 0.107 [2, 4, 6] 20.10 0.849 0.122 表 3 不同损失函数系数在测试集上客观评价指标
损失函数系数 PSNR
(dB)SSIM LPIPS $ {\lambda _{\text{s}}} $=0.2, $ {\lambda _{\text{p}}} $=0.1, $ {\lambda _{\text{c}}} $=0.05 20.18 0.843 0.144 $ {\lambda _{\text{s}}} $=0.15, $ {\lambda _{\text{p}}} $=0.05, $ {\lambda _{\text{c}}} $=0.025 19.82 0.830 0.158 $ {\lambda _{\text{s}}} $=0.25, $ {\lambda _{\text{p}}} $=0.2, $ {\lambda _{\text{c}}} $=0.05 20.30 0.854 0.107 -
[1] KIM W, JEONG J, and YOU J. Contrast enhancement using histogram equalization based on logarithmic mapping[J]. Optical Engineering, 2012, 51(6): 067002. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.51.6.067002 [2] CELIK T. Spatial entropy-based global and local image contrast enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(12): 5298–5308. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2014.2364537 [3] JOBSON D J, RAHMAN Z, and WOODELL G A. Properties and performance of a center/surround retinex[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(3): 451–462. doi: 10.1109/83.557356 [4] JOBSON D J, RAHMAN Z, and WOODELL G A. A multiscale retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(7): 965–976. doi: 10.1109/83.597272 [5] WANG Shuhang, ZHENG Jin, HU Haimiao, et al. Naturalness preserved enhancement algorithm for non-uniform illumination images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(9): 3538–3548. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2261309 [6] LI Mading, LIU Jiaying, YANG Wenhan, et al. Structure-revealing low-light image enhancement via robust retinex model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(6): 2828–2841. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2810539 [7] LORE K G, AKINTAYO A, and SARKAR S. LLNet: A deep autoencoder approach to natural low-light image enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 650–662. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.06.008 [8] WEI Chen, WANG Wenjing, YANG Wenhan, et al. Deep retinex decomposition for low-light enhancement[C]. 2018 British Machine Vision Conference, Newcastle, UK, 2018: 1–12. [9] ZHANG Yonghua, ZHANG Jiawan, and GUO Xiaojie. Kindling the darkness: A practical low-light image enhancer[C]. The 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 2019: 1632–1640. [10] CHEN Chen, CHEN Qifeng, XU Jia, et al. Learning to see in the dark[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 3291–3300. [11] WANG Ruixing, ZHANG Qing, FU C, et al. Underexposed photo enhancement using deep illumination estimation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6842–6850. [12] JIANG Yifan, GONG Xinyu, LIU Ding, et al. EnlightenGAN: Deep light enhancement without paired supervision[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2340–2349. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3051462 [13] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [14] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [15] LAI Weisheng, HUANG Jiabin, AHUJA N, et al. Fast and accurate image super-resolution with deep laplacian pyramid networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(11): 2599–2613. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2865304 [16] WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [17] JOHNSON J, ALAHI A, and LI F F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 694–711. [18] LUO M R, CUI G, and RIGG B. The development of the CIE 2000 colour-difference formula: CIEDE2000[J]. Color Research and Application, 2001, 26(5): 340–350. doi: 10.1002/col.1049 [19] ZHANG R, ISOLA P, EFROS A A, et al. The unreasonable effectiveness of deep features as a perceptual metric[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 586–595. [20] LV Feifan, LU Feng, WU Jianhua, et al. MBLLEN: Low-light image/video enhancement using CNNs[C]. 2018 British Machine Vision Conference, Newcastle, UK, 2018: 1–13. [21] WANG Wenjing, WEI Chen, YANG Wenhan, et al. GLADNet: Low-light enhancement network with global awareness[C]. The 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2018), Xi'an, China, 2018: 751–755. [22] ZHANG Yu, DI Xiaoguang, ZHANG Bin, et al. Self-supervised image enhancement network: Training with low light images only[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.11300.pdf, 2020. [23] GUO Chunle, LI Chongyi, GUO Jichang, et al. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1777–1786. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
