A Passive Ranging Method for Shallow Water Sound Sources Based on Large Aperture Horizontal Array
-
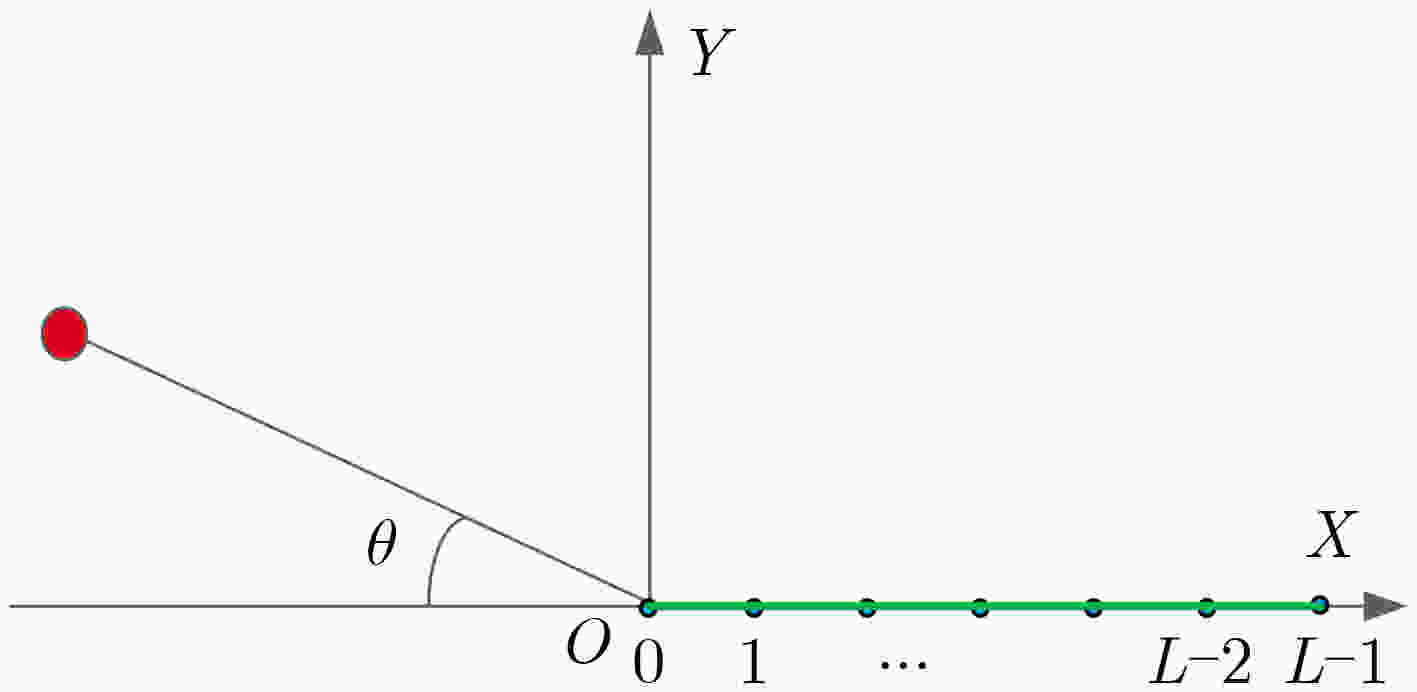
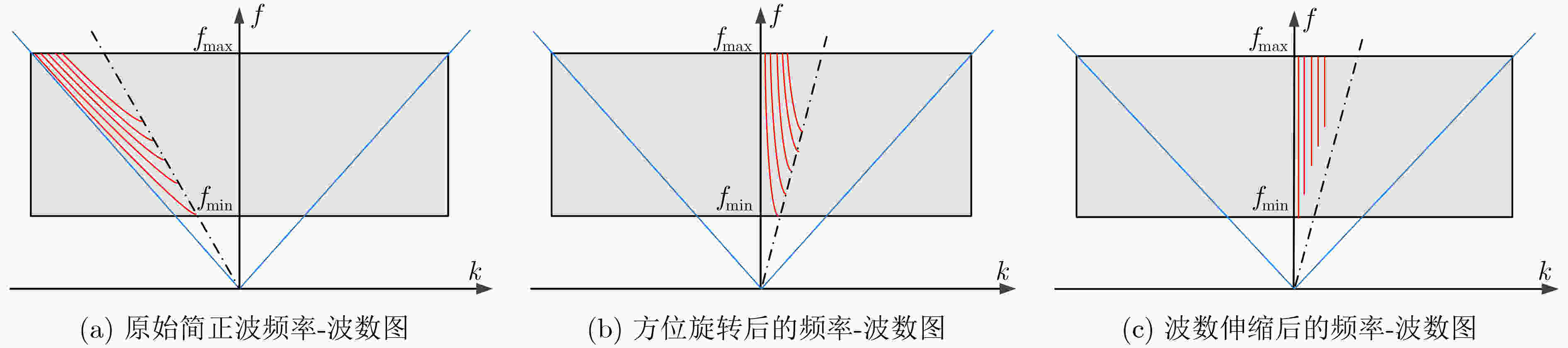
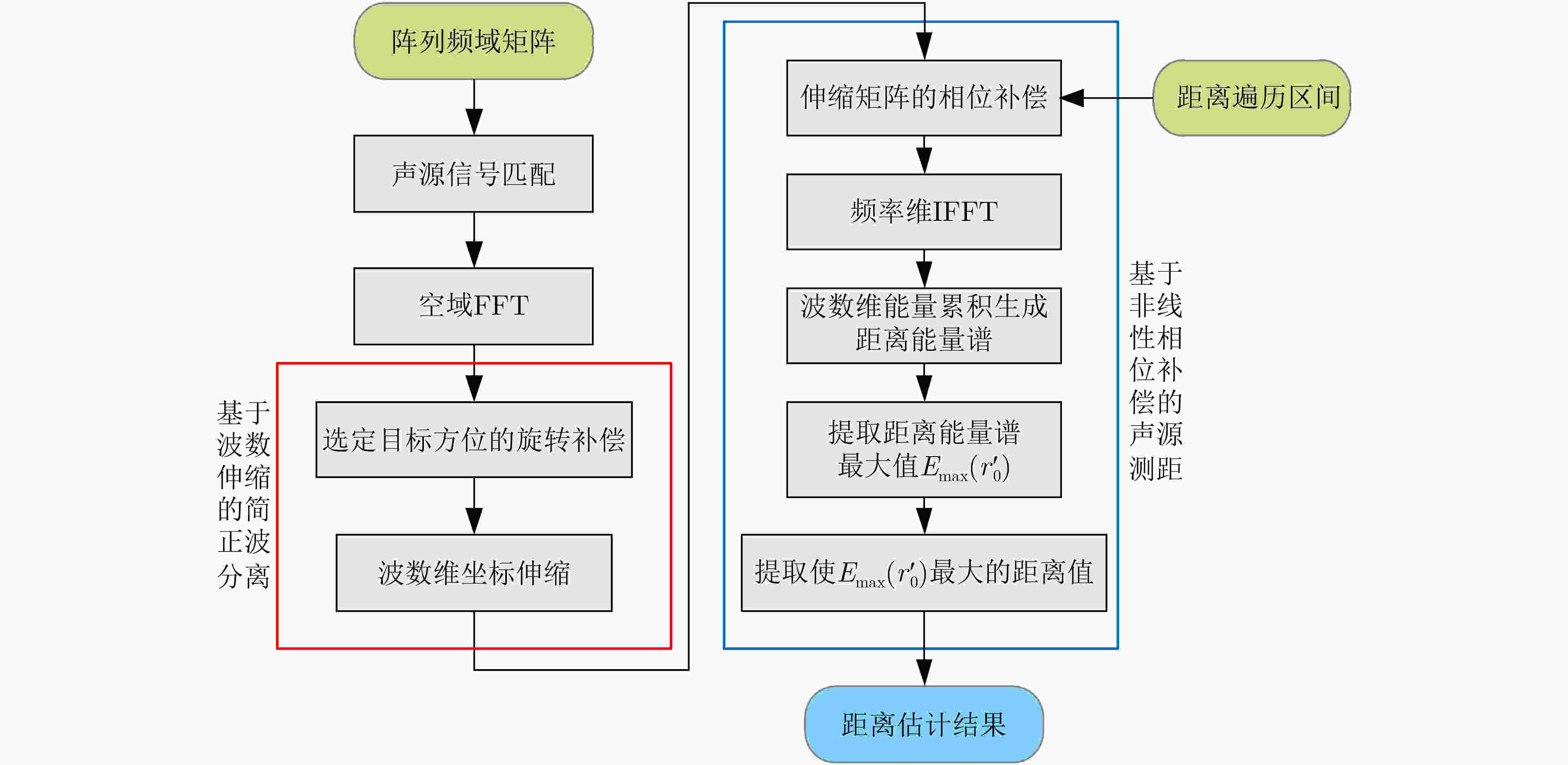
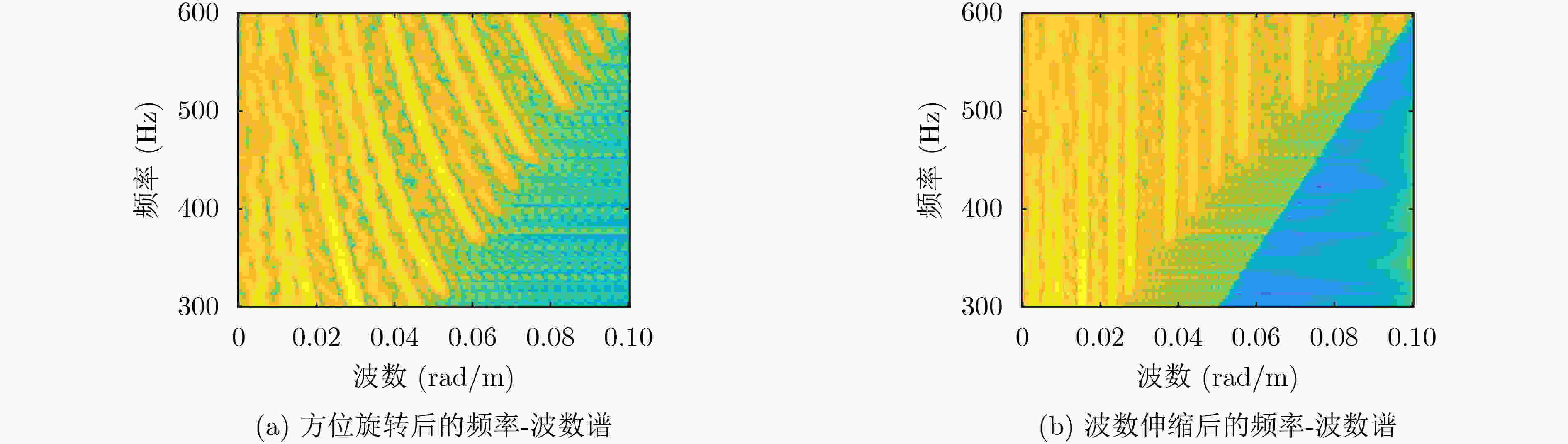
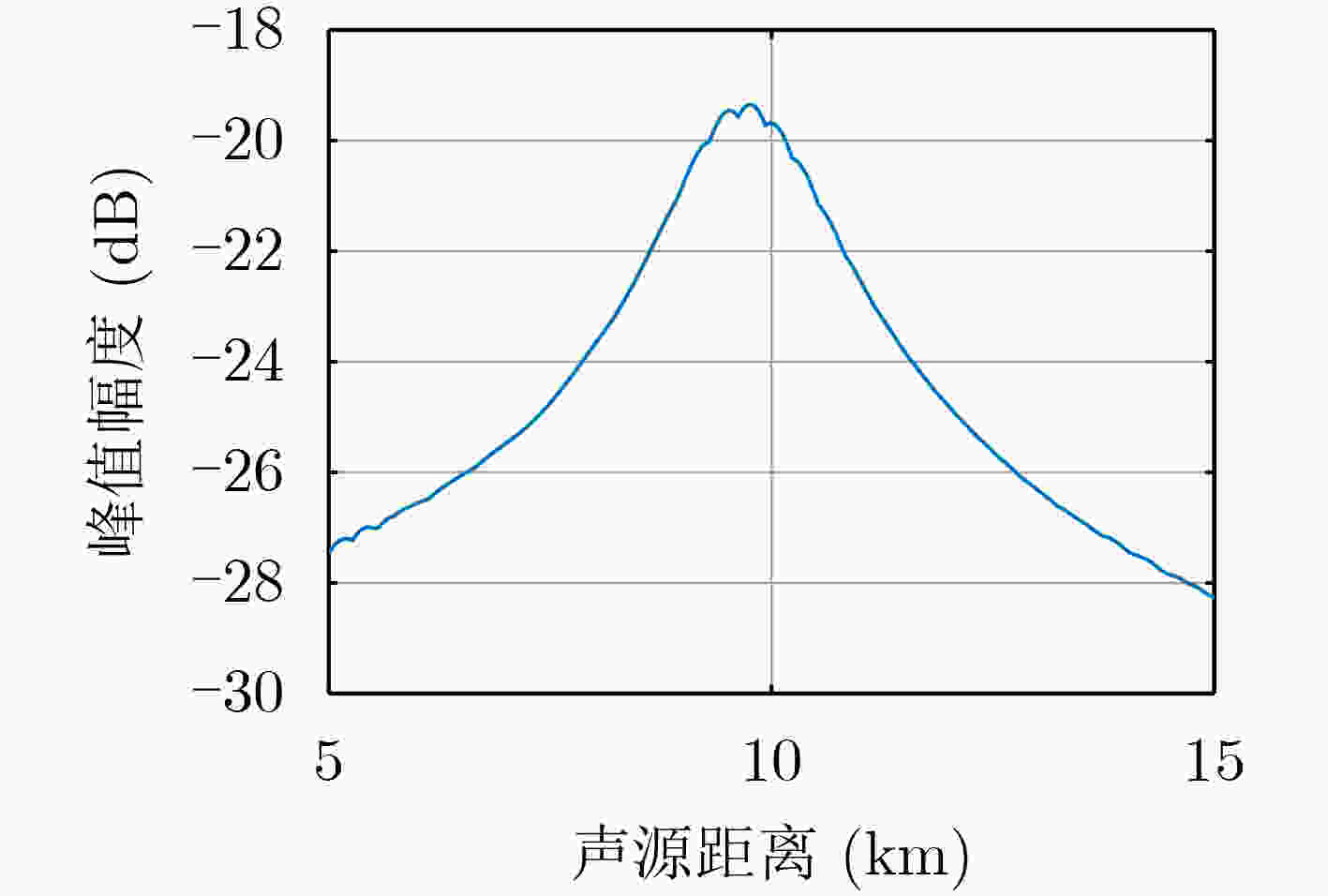
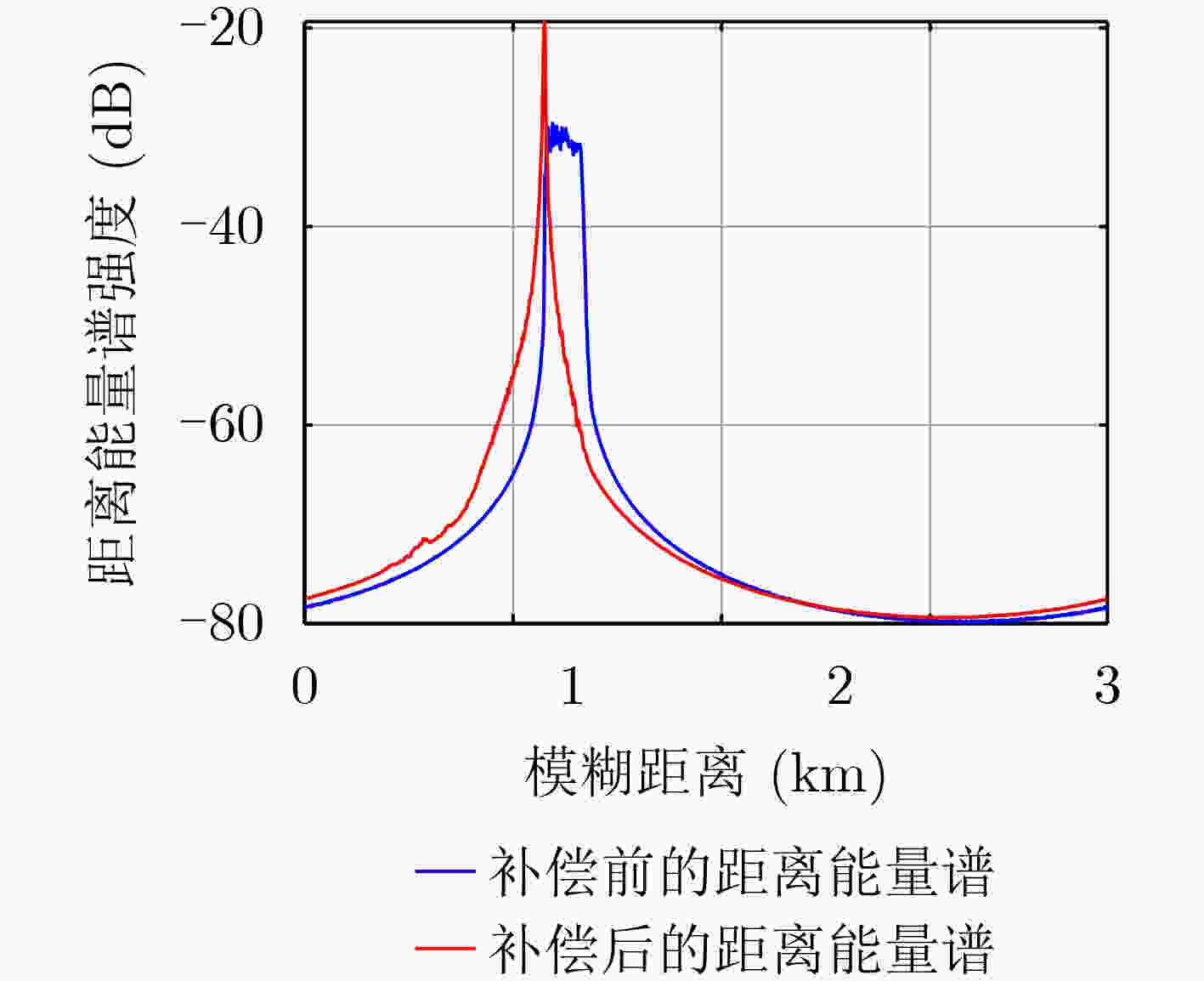
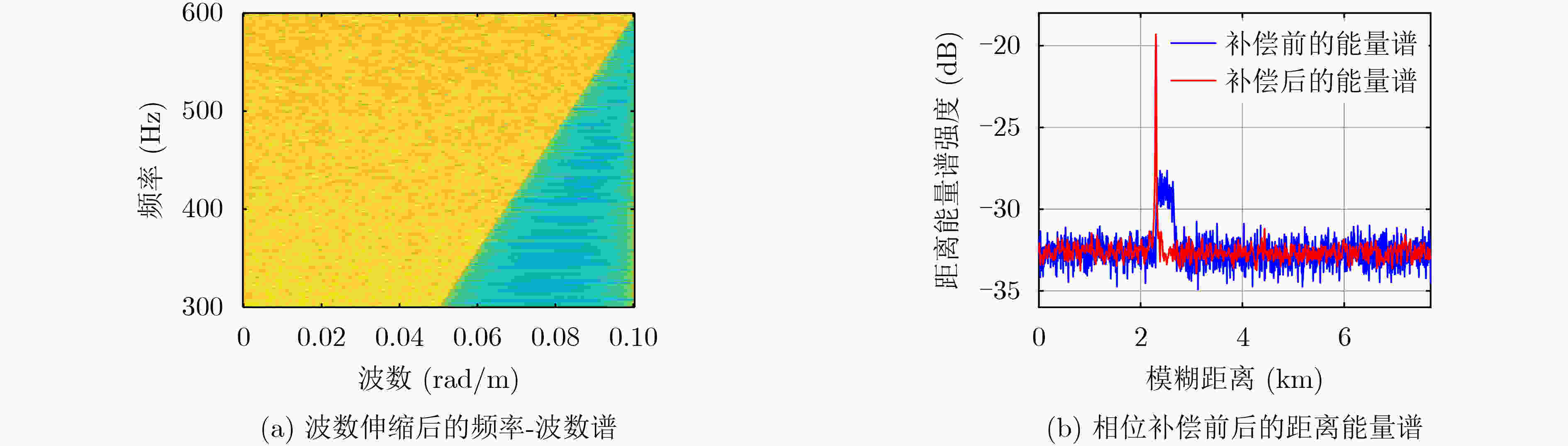
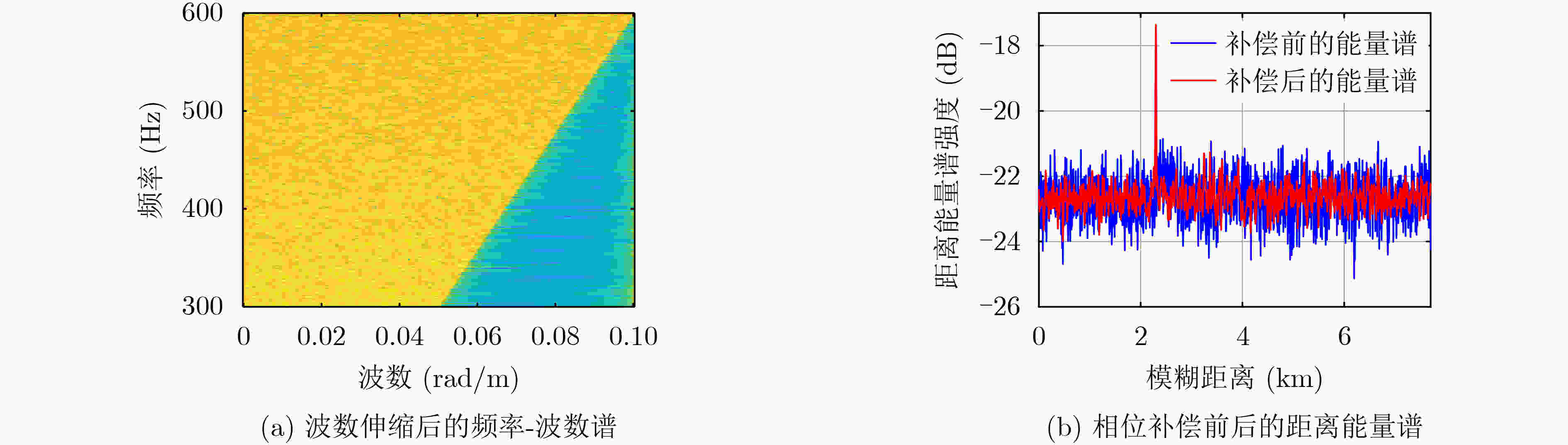
摘要: 面向浅海水下声源的被动测距需求,该文提出一种基于大孔径水平阵的简正波分离与测距方法。该方法针对频率波数域模态曲线弯曲导致的同阶简正波分离处理复杂的问题,在各阶简正波截止频率不随信号频率变化的条件下,提出基于波数伸缩的简正波模态对齐方法,实现不同阶简正波的有效分离。通过非线性相位补偿实现多阶简正波的能量聚焦,结合距离遍历、峰值提取实现声源距离的被动估计。该方法可获得空域、频域增益,实现多模态能量的累积,为微弱声源目标的距离估计提供了新的技术途径。最后,结合仿真数据验证了方法的有效性。Abstract: In order to meet the demand for passive ranging of sound sources in shallow water, a normal mode separation and ranging method based on a large-aperture horizontal array is proposed. This method deals with the problem of modal separation that caused by the bending of the modal curve in the frequency-wavenumber domain. Under the condition that the cut-off frequency of each order normal mode does not change with the signal frequency, a alignment method based on wavenumber scaling is presented to realize the effective separation of normal modes. The energy focusing of normal modes is realized by nonlinear phase compensation, and the passive ranging of the sound source is realized by combining distance traversal and peak extraction. This method can effectively achieve gains in space and frequency domains, and obtain multi-modal energy accumulation, which provides a new approach for the distance estimation of weak sound sources. The effectiveness of the method is verified by simulation data.
-
Key words:
- Large aperture array /
- Passive ranging /
- Wavenumber scaling /
- Normal mode separation
-
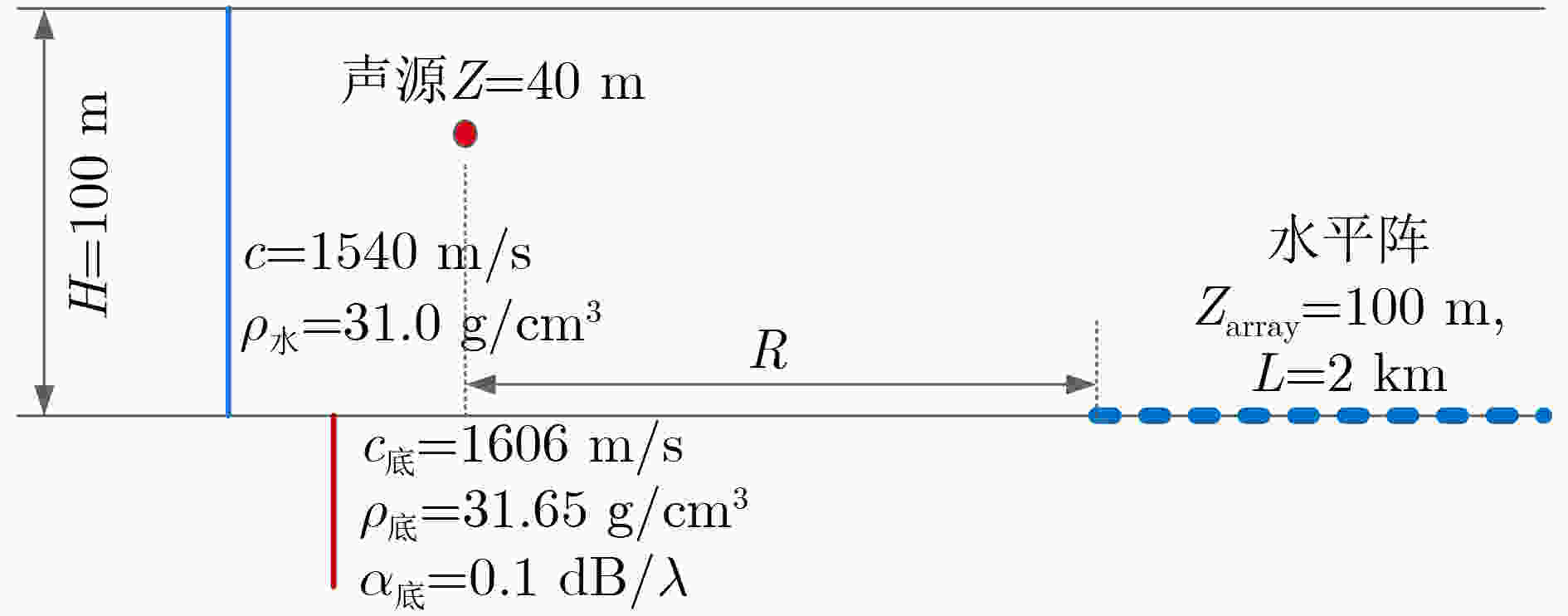
表 1 不同信噪比下的声源测距结果
输入信噪比(dB) 测距均值(km) 平均误差(m) 标准差(m) –20 9.7595 –240.50 3.29 –25 9.7590 –240.10 8.53 –30 9.7587 –241.30 10.36 –35 9.7592 –240.80 79.62 –40 9.7097 –290.27 112.74 表 2 不同阵列长度的声源测距结果
阵列长度(m) 测距结果(km) 相对误差 500 9.56 4.4%R 1000 9.62 3.8%R 1500 9.75 2.5%R 2000 9.76 2.4%R 表 3 不同频段LFM信号的声源测距结果
处理频段(Hz) 测距结果(km) 相对误差 100~400 17.59 12.05%R 200~500 17.96 10.20%R 300~600 19.25 3.75%R 400~700 19.74 1.30%R 表 4 不同距离的声源测距结果
声源距离(km) 测距结果(km) 相对误差 10 9.76 2.40%R 20 19.25 3.75%R 30 28.72 4.36%R 40 38.19 4.52%R 50 46.38 7.24%R -
[1] 李启虎. 水下目标被动测距的一种新方法: 利用波导不变量提取目标距离信息[J]. 声学学报, 2015, 40(2): 138–143. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2015.02.004LI Qihu. A new method of passive ranging for underwater target: Distance information extraction based on wave guide invariant[J]. Acta Acustica, 2015, 40(2): 138–143. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2015.02.004 [2] 戚聿波, 周士弘, 任云, 等. 浅海中利用单水听器的声源被动测距[J]. 声学学报, 2015, 40(2): 144–152. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2015.02.005QI Yubo, ZHOU Shihong, REN Yun, et al. Passive source range estimation with a single receiver in shallow water[J]. Acta Acustica, 2015, 40(2): 144–152. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2015.02.005 [3] 杨坤德, 段睿, 李辉, 等. 水下声源定位理论与技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版, 2019: 116–125.YANG Kunde, DUAN Rui, LI Hui, et al. Theory and Technology of Underwater Sound Source Location[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2019: 116–125. [4] 王宁, 高大治, 王好忠. 频散、声场干涉结构、波导不变量与消频散变换[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2010, 31(7): 825–831. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.2010.07.002WANG Ning, GAO Dazhi, and WANG Haozhong. Mode dispersion, interference, waveguide invariance and the dedispersion transform[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2010, 31(7): 825–831. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7043.2010.07.002 [5] WALKER S C, ROUX P, and KUPERMAN W A. Data-based mode extraction with a partial water column spanning array[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2005, 118(3): 1518–1525. doi: 10.1121/1.1993149 [6] NICOLAS B, MARS J I, and LACOUME J L. Source depth estimation using a horizontal array by matched-mode processing in the frequency-wavenumber domain[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2006, 2006: 065901. doi: 10.1155/ASP/2006/65901 [7] 梁玉权, 周士弘, 宫在晓, 等. 水平阵信号压缩感知用于简正波分离[J]. 声学学报, 2020, 45(5): 609–624. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2020.05.001LIANG Yuquan, ZHOU Shihong, GONG Zaixiao, et al. Normal mode separation based on compressive sensing with a horizontal array[J]. Acta Acustica, 2020, 45(5): 609–624. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2020.05.001 [8] 高伟. 浅海波导中简正波相干分量的奇异值分解提取方法[J]. 声学学报, 2016, 41(1): 41–48. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2016.01.005GAO Wei. Extracting the interference components of normal modes in shallow water waveguide using singular value decomposition method[J]. Acta Acustica, 2016, 41(1): 41–48. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2016.01.005 [9] 徐国军, 笪良龙, 李玉阳. 基于波导不变性的水平阵列测距研究[J]. 舰船科学技术, 2015, 37(10): 81–84. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2015.10.017XU Guojun, DA Lianglong, and LI Yuyang. Research on the source ranging with the horizontal array based on the waveguide invariant theory[J]. Ship Science and Technology, 2015, 37(10): 81–84. doi: 10.3404/j.issn.1672-7649.2015.10.017 [10] 余赟, 惠俊英, 赵智勇, 等. 基于声场干涉结构的双水平阵(元)被动测距[J]. 声学学报, 2012, 37(4): 440–447. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2012.04.002YU Yun, HUI Junying, ZHAO Zhiyong, et al. Passive ranging based on acoustic field interference structure using double arrays (elements)[J]. Acta Acustica, 2012, 37(4): 440–447. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2012.04.002 [11] TURGUT A, ORR M, and ROUSEFF D. Broadband source localization using horizontal-beam acoustic intensity striations[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2010, 127(1): 73–83. doi: 10.1121/1.3257211 [12] 宋雪晶, 赵安邦, 马骏, 等. 基于波导不变量的单水平阵被动测距技术[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2016, 38(10): 2252–2257. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1001-506X.2016.10.05SONG Xuejing, ZHAO Anbang, MA Jun, et al. Passive ranging with horizontal array based on waveguide invariant[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(10): 2252–2257. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1001-506X.2016.10.05 [13] YANG T C. Beam intensity striations and applications[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2003, 113(3): 1342–1352. doi: 10.1121/1.1534604 [14] 徐国军, 赵建昕, 笪良龙, 等. 频率自适应最优权重阵列干涉条纹处理技术[J]. 声学学报, 2017, 42(3): 257–266. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2017.03.001XU Guojun, ZHAO Jianxin, DA Lianglong, et al. A frequency adaptive optimal array weighted method of interference striations[J]. Acta Acustica, 2017, 42(3): 257–266. doi: 10.15949/j.cnki.0371-0025.2017.03.001 [15] NIU Haiqiang, OZANICH E, and GERSTOFT P. Ship localization in Santa Barbara Channel using machine learning classifiers[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2017, 142(5): EL455–EL460. doi: 10.1121/1.5010064 [16] NIU Haiqiang, REEVES E, and GERSTOFT P. Source localization in an ocean waveguide using supervised machine learning[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2017, 142(3): 1176–1188. doi: 10.1121/1.5000165 [17] 保铮, 邢孟道, 王彤. 雷达成像技术[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2005: 38–39.BAO Zheng, XING Mengdao, and WANG Tong. Radar Imaging Techniques[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2005: 38–39. -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
