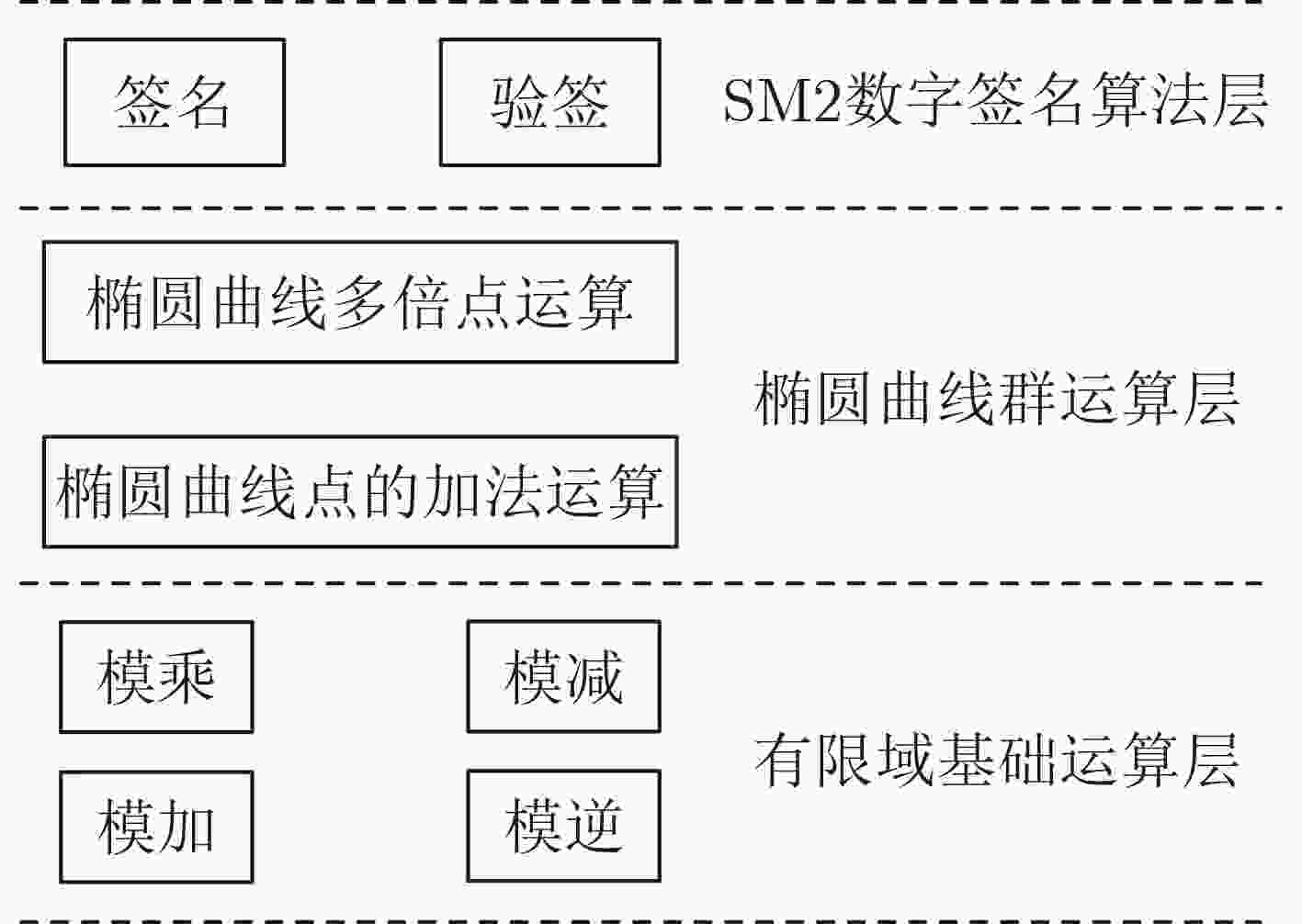
A High Throughput SM2 Digital Signature Computing Scheme Based on Graphics Processing Unit Platform
-
摘要: 随着数据传输安全的普及和认证信息细粒化程度的提高,基于公钥密码学的签名运算使用越来越频繁,其处理速度逐渐成为制约各种高并发安全应用的瓶颈问题。为此,该文提出一种基于图形处理器(GPU)的高吞吐量SM2数字签名计算方案。首先,通过GPU底层指令优化基础运算的计算过程,构建高效的基础运算模块;进而,结合GPU的平台特性,优化基于费马小定理的模逆算法,缩短SM2推荐素数的加法链,大幅提升模逆处理速度;同时,按需使用倍点运算和重复倍点算法,避免线程束分化现象,并有效减少未知点乘运算的计算量。理论分析和实验测试结果表明该方案可有效地提升SM2签名和验签算法的处理速度,在RTX3090单卡上实现了7.609
$ \times {10^7}$ 次/s的签名吞吐量和3.46$ \times {10^6}$ 次/s的验签吞吐量。Abstract: With the pervasiveness of secure data transmission techniques and increasing requirements of information authentication, the public key-based digital signature scheme has been extensively used in various fields. However, the process speed of digital signature has gradually become the bottleneck of various security and high-concurrency applications. In this paper, a high-throughput SM2 digital signature computing scheme based on Graphics Processing Unit(GPU) platform is proposed. Firstly, the basic operations are optimized by low-level instructions of GPU. Then, according to the characteristics of GPU platform, the addition chain of SM2 recommended prime number is reduced and the speed of modular inverse operation based on Fermat's theorem is improved. Furthermore, a pre-computing table is constructed and the repeated doubling algorithm is introduced to accelerate the unknown point multiplication. Due to the construction of pre-computing table, divergence of threads can be successfully avoided. The experiments show that the proposed scheme can effectively speed up SM2 algorithm, and the throughput of signing and verification can respectively reach 76.09 million ops and 3.46 million ops on RTX3090.-
Key words:
- Digital signature /
- SM2 /
- High throughput /
- Graphics Processing Unit(GPU)
-
表 1 针对素数SCA-256的快速模约算法
输入:大整数c以${2^{32}}$进制表示为 $c = ({c_{15} },\cdots,{c_1},{c_0}),0 \le c < {P^2}_{ {\text{SCA-256} } }$ 输出:$Z = c{\text{ } }(\bmod {P_{ {\text{SCA-256} } } })$ (1) 定义大整数 ${s_1} = ({c_7},{c_6},{c_5},{c_4},{c_3},{c_2},{c_1},{c_0})$ ${s_2} = ({c_{15}},{c_{14}},{c_{13}},{c_{12}},{c_{11}},0,{c_9},{c_8})$ ${s_3} = ({c_{14}},0,{c_{15}},{c_{14}},{c_{13}},0,{c_{14}},{c_{13}})$ ${s_4} = ({c_{13}},0,0,0,0,0,{c_{15}},{c_{14}})$ $ {s_5} = ({c_{12}},0,0,0,0,0,0,{c_{15}}) $ ${s_6} = ({c_{11}},{c_{11}},{c_{10}},{c_{15}},{c_{14}},0,{c_{13}},{c_{12}})$ ${s_7} = ({c_{10}},{c_{15}},{c_{14}},{c_{13}},{c_{12}},0,{c_{11}},{c_{10}})$ ${s_8} = ({c_9},0,0,{c_9},{c_8},0,{c_{10}},{c_9})$ $ {s_9} = ({c_8},0,0,0,{c_{15}},0,{c_{12}},{c_{11}}) $ ${s_{10}} = ({c_{15}},0,0,0,0,0,0,0)$ ${s_{11}} = (0,0,0,0,0,{c_{14}},0,0)$ ${s_{12}} = (0,0,0,0,0,{c_{13}},0,0)$ ${s_{13}} = (0,0,0,0,0,{c_9},0,0)$ ${s_{14}} = (0,0,0,0,0,{c_8},0,0)$ (2) 计算
$\begin{gathered} Z = ({s_1} + {s_2} + 2{s_3} + 2{s_4} + 2{s_5} + {s_6} + {s_7} + {s_8} + {s_9} \\ \qquad + 2{s_{10} } - {s_{11} } - {s_{12} } - {s_{13} } - {s_{14} }){\text{ } } \\ \end{gathered}$(3) 进一步约减$Z = Z{\text{ }}\bmod {P_{{\text{SCA-256}}}}$ 表 2 PTX ISA指令及其含义
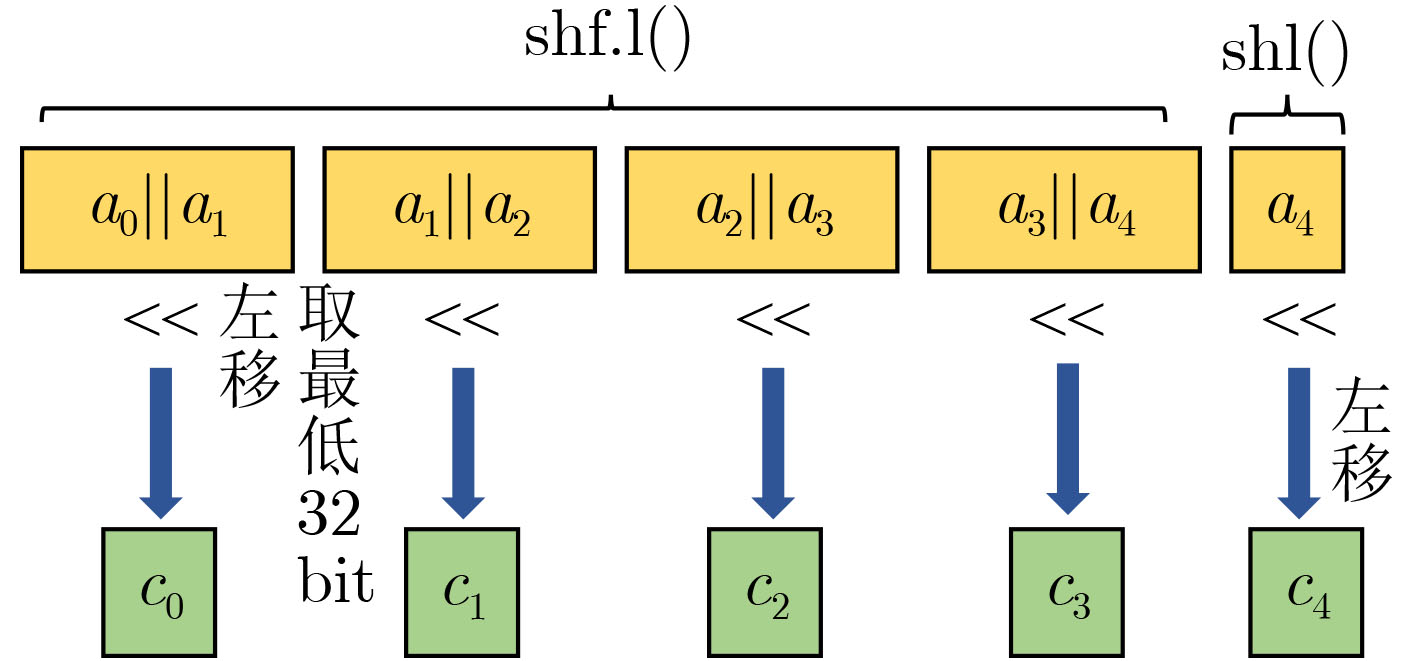
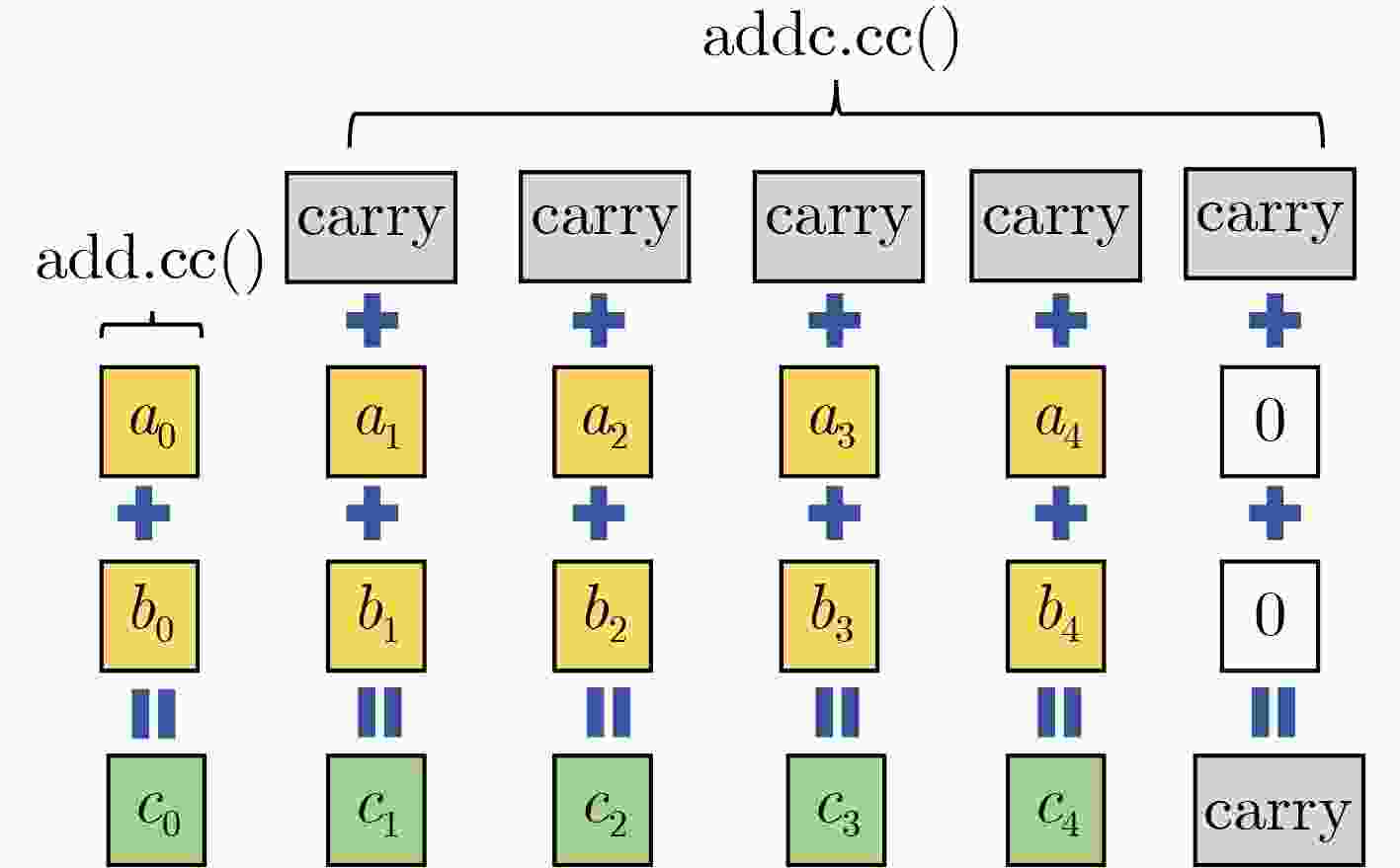
指令 指令描述 含义 ${\text{add}}(c,a,b)$ 加法 $c = a + b$ ${\text{addc}}(c,a,b)$ 进位加法 $c = a + b + {\text{CC}}{\text{.CF}}$ ${\text{sub}}(c,a,b)$ 减法 $c = a - b$ ${\text{subc}}(c,a,b)$ 借位减法 $c = a - (b + {\text{CC}}{\text{.CF}})$ ${\text{shf}}{\text{.r}}(c,a,b,n)$ 漏斗左移 $c = ((a||b) > > n)[0:32]$ ${\text{shf}}{\text{.l}}(c,a,b,n)$ 漏斗右移 $c = ((a||b) < < n)[32:63]$ ${\text{shl}}(c,a,n)$ 左移 $c = a < < n$ ${\text{shr}}(c,a,n)$ 右移 $c = a > > n$ 表 3 进一步约减算法
输入:$Z = ({Z_8},\cdots,{Z_1},{Z_0}),Z \in [0,14{P_{ {\text{SCA-256} } } })$ 输出:$Z = ({Z_7},\cdots,{Z_1},{Z_0}),Z \in [0,{P_{ {\text{SCA-256} } } })$ (1) ${\text{carry}} = {\text{ADD}}(Z,Z,T[{Z_8}])$ (2) ${\text{if} }({\text{carry} } > 0){\text{ SUB} }(Z,Z,{P_{ {\text{SCA-256} } } })$ 表 4 针对素数
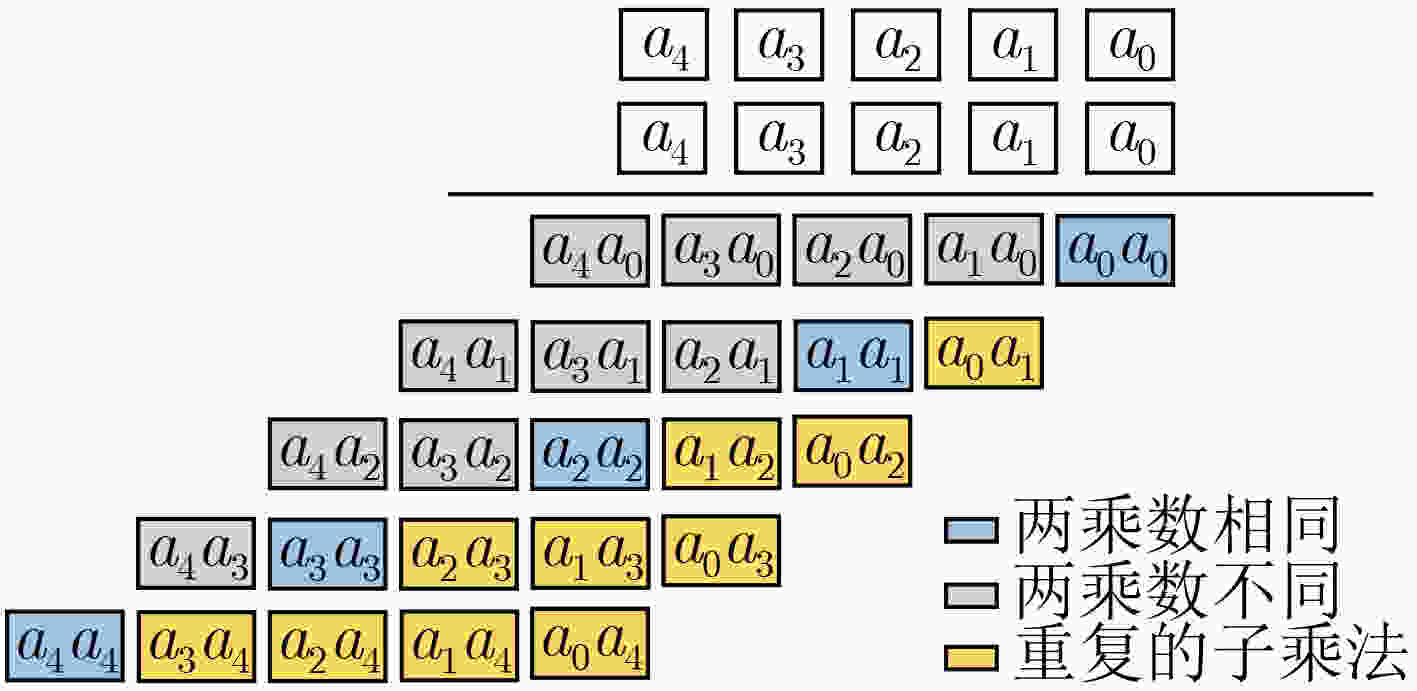
${P_{{\text{SCA-256}}}}$ 的快速模逆算法输入:大整数$z$满足$1 \le z \le p - 1,p = {P_{ {\text{SCA-256} } } }$ 输出:$z$模$p$的逆$t$, $t = {z^{ - 1}}\bmod p = {z^{p - 2}}\bmod p$ (1) ${t_0} = {z^2} \cdot z$ $\{ 1S + 1M\} $ (2) ${t_1} = {t_0}^2 \cdot z$ $\{ 1S + 1M\} $ (3) $ {t_2} = {t_1}^{{2^3}} \cdot {t_1} $ $\{ 3S + 1M\} $ (4) ${t_1} = {t_2}^2$ $\{ 1S\} $ (5) $ {t_3} = {t_1} \cdot z $ $\{ 1M\} $ (6) $ {t_1} = {t_1}^{{2^5}} \cdot {t_2} $ $\{ 5S + 1M\} $ (7) $ {t_2} = {t_1}^{{2^{12}}} \cdot {t_1} $ $\{ 12S + 1M\} $ (8) $ {t_1} = {t_2}^{{2^7}} \cdot {t_3} $ $\{ 7S + 1M\} $ (9) $ {t_2} = {t_1}^{{2^2}} $ $\{ 2S\} $ (10) $ {t_3} = {t_2}^{{2^{29}}} $ $\{ 29S\} $ (11) ${t_1} = {t_1} \cdot {t_3}$ $\{ 1M\} $ (12) $ {t_3} = {t_3}^{{2^2}} $ $\{ { 2S } \}$ (13) ${t_0} = {t_0} \cdot {t_3} \cdot {t_2}$ ${ {\{ 2{{M} }\} } }$ (14) $ {t_2} = {({({t_3}^{{2^{32}}} \cdot {t_0})^{{2^{64}}}} \cdot {t_0})^{{2^{94}}}} $ ${ {\{ 190{{S} } + 2{{M} }\} } }$ (15) $ {t_0} = {({t_1} \cdot {t_2})^{{2^2}}} \cdot z $ ${ {\{ 2{{S} } + 2{{M} }\} } }$ 表 5 优化的窗口未知点乘法
输入:$n$比特标量$k$,椭圆曲线点$P$ 输出:椭圆曲线点$[k]P$ 设窗口长度为$w,l = \left\lceil {{n}/{w} } \right\rceil$ 预计算: (1)${P_0} = O,{P_1} = P,{P_2} = [2]P,Q = O$ (2)$i$从3~${2^w} - 1$计算${P_i} = {P_{i - 2}} + {P_2};{\text{ }}i = i + 2;$ (3)$i$从2~${2^{w - 1}}$计算${P_{2i}} = [2]{P_i};{\text{ }}i = i + 1;$ (4)计算$k$的${2^w}$进制表示形式
$ k = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 0}^{l - 1} {{k_j}{2^{wj}}} ,{k_j} \in \{ 0,1,\cdots,{2^w} - 1\} $主循环: (5)$i$从$l - 1$下降到0执行: (a)$Q = [{2^w}]Q$ (b)$Q = Q + {P_{{k_{\text{j}}}}}$ (6)输出$Q$ 表 6 GPU高负载运行时不同算法的吞吐量结果
算法 总线程数
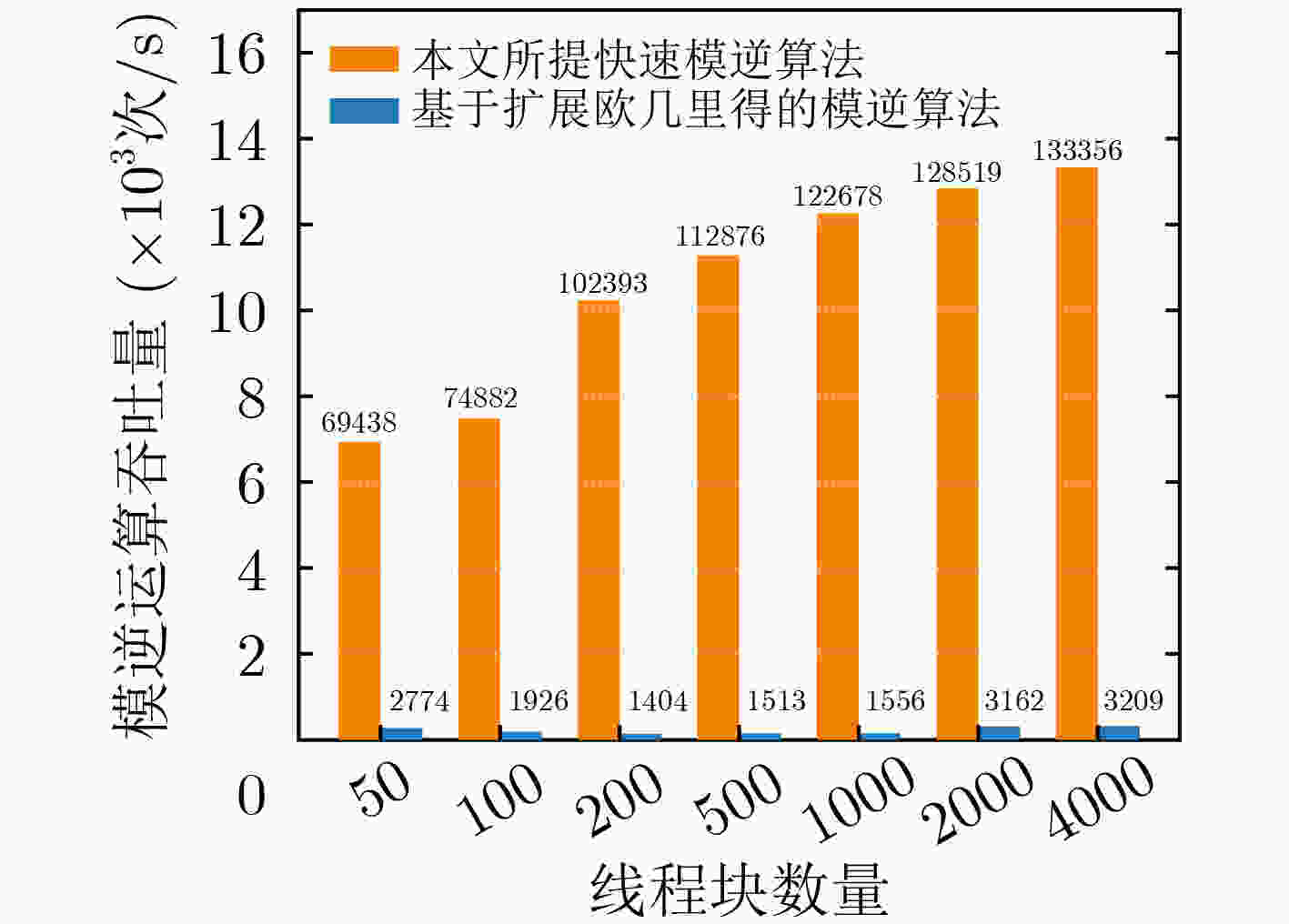
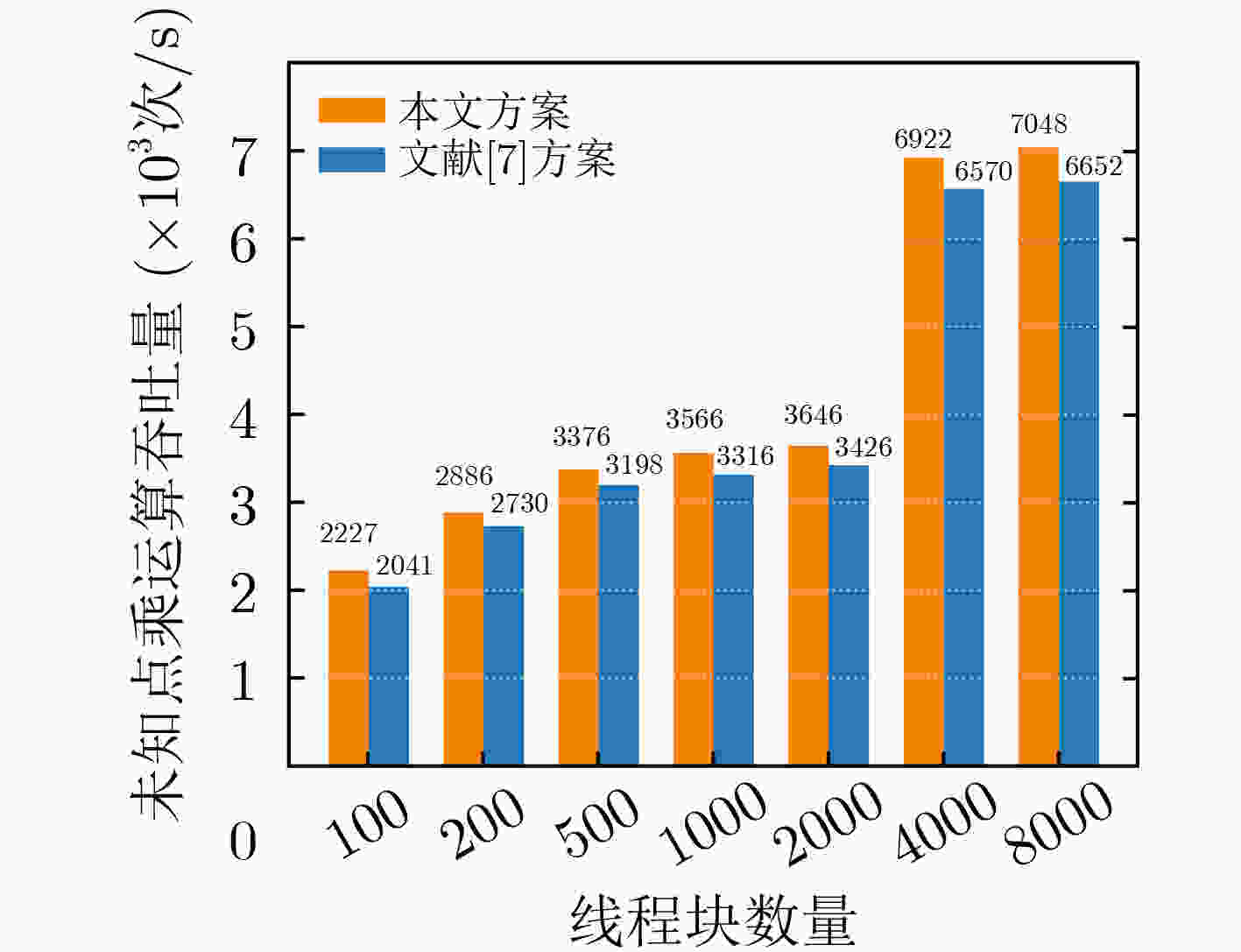
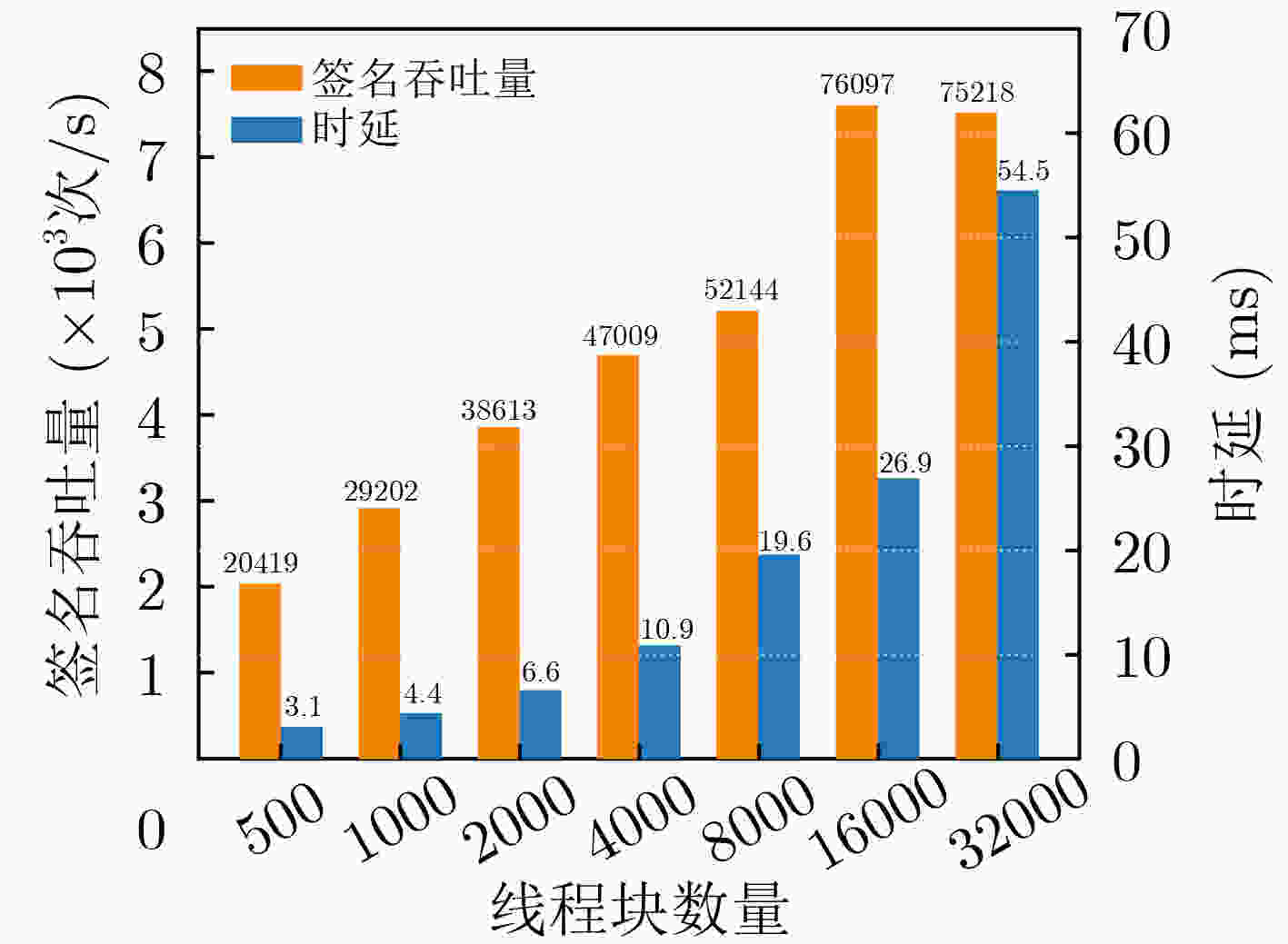
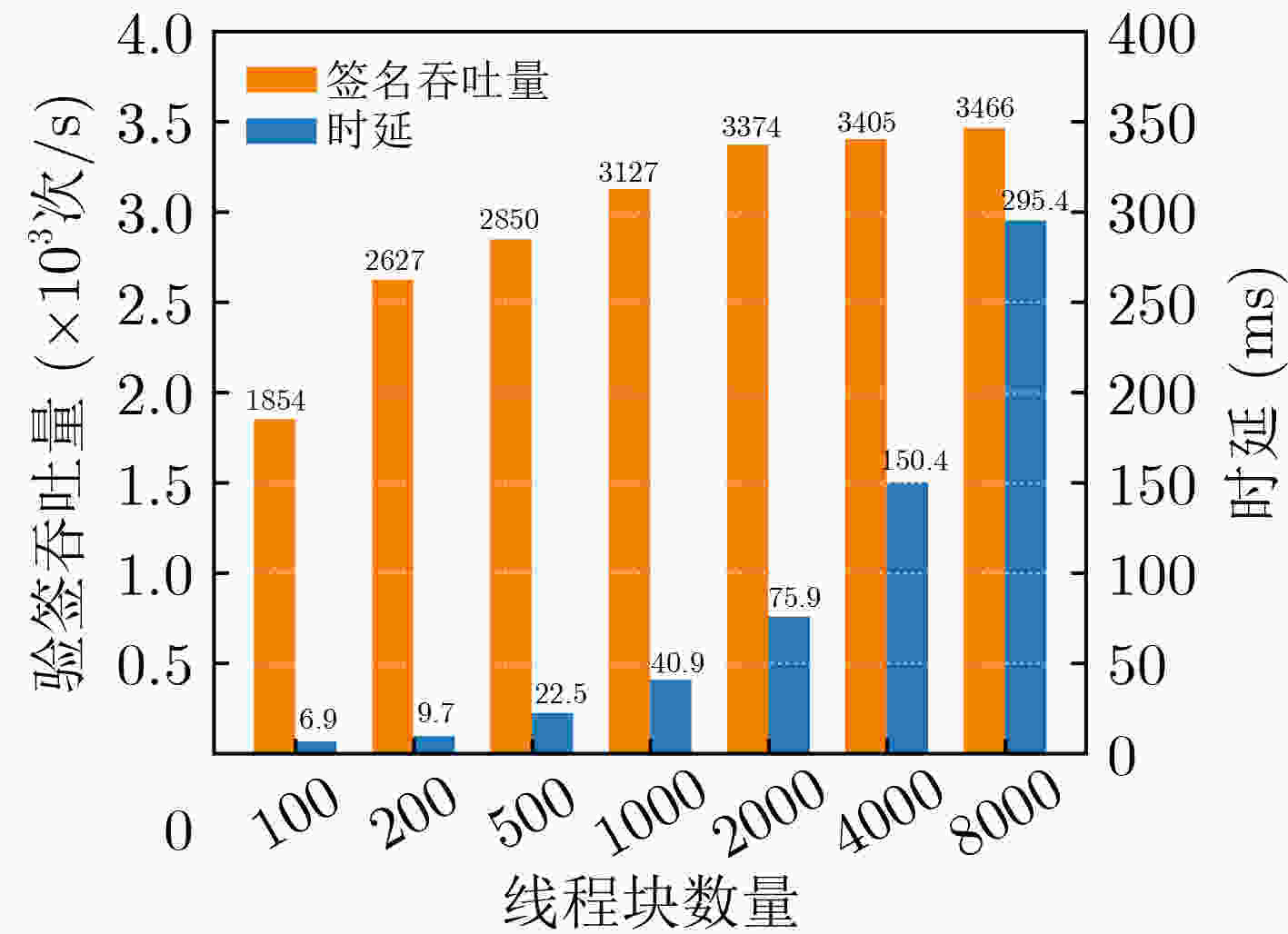
(个)吞吐量(×103次/s) 最优线程块大小 size=64 size=128 size=256 size=512 本文所提快速模逆算法 3072,000 135400 134749 133860 132787 64 基于扩展欧几里得的模逆算法 3072,000 2164 1208 1449 3223 512 本文所提快速未知点乘算法 2048,000 3078 3219 3786 7008 512 SM2签名算法 2048,000 73759 76097 71663 69449 128 SM2验签算法 1024,000 3410 3449 3438 3392 128 *${\text{size}}$为线程块大小 表 7 GPU平台各个ECC优化方案性能对比
算法 GPU GPU架构 GPU整数/浮点性能 ECC曲线 吞吐量1(×103次/s) 吞吐量2(×103次/s) 本文方案 RTX 3090 Ampere 17800 GIOPS SCA 256 76097(签名) 3405(验签) Pan等人[7] GTX 780Ti Kepler 5345 GIOPS NIST P-256 8710(签名) 929(验签) Dong等人[21] GTX 1080 Pascal 8873 GIOPS Curve25519 – 2860(未知点乘) Gao等人[22] TITAN V Volta 14899 GFLOPS Edwards25519 77301(固定点乘) 7216(未知点乘) Lee等人[23] GTX1060 Pascal 4375 GIOPS NIST P-256 60(签名) – * GIOPS(Giga Integer Operations Per Second)为GPU整数性能单位,表示单位时间内GPU最高可进行的整数操作次数。GFLOPS(Giga FLoat-point Operations Per Second)为GPU浮点性能单位,表示单位时间内GPU最高可进行的浮点操作次数。文献[22]基于浮点运算实现密码算法,因此给出GPU的浮点性能作为参考,其他方案基于整型运算实现密码算法,因此给出GPU整数性能作为参考 表 8 T1000上各个算法的性能表现
算法 总线程数 最优线程块大小 吞吐量(次/s) 时延(ms) 本文所提模逆优化算法 5120000 128 19400301 265 基于扩展欧几里得的模逆算法 51200 128 235921 873 本文所提未知点乘优化算法 102400 256 390154 263 文献[7]所提未知点乘算法 102400 256 367293 281 签名算法 1024000 128 6348632 162 验签算法 51200 128 345248 157 -
[1] 国家密码管理局. GM/T 0003.2-2012 SM2椭圆曲线公钥密码算法 第2部分: 数字签名算法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2012.State Cryptography Administration of China. GM/T 0003.2-2012 Public key cryptographic algorithm SM2 based on elliptic curves-Part 2: Digital signature algorithm[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2012. [2] International Organization for Standardization. ISO/IEC 14888-3: 2018 IT security techniques - Digital signatures with appendix - Part 3: Discrete logarithm based mechanisms[S]. Geneva: ISO, 2018. [3] 新浪科技. 阿里首席技术官程立: “双十一”的技术挑战进入新的历史阶段[EB/OL].https://tech.sina.com.cn/roll/2020-11-11/doc-iiznctke0933662.shtml, 2020.Sina Technology. Cheng Li, CTO of Alibaba: The technical challenges of "the Double Eleventh" have entered a new historical stage[EB/OL]. https://tech.sina.com.cn/roll/2020-11-11/doc-iiznctke0933662.shtml, 2020. [4] KOPPERMANN P, DE SANTIS F, HEYSZL J, et al. Low-latency X25519 hardware implementation: Breaking the 100 microseconds barrier[J]. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 2017, 52: 491–497. doi: 10.1016/j.micpro.2017.07.001 [5] HUANG Junhao, LIU Zhe, HU Zhi, et al. Parallel implementation of SM2 elliptic curve cryptography on Intel processors with AVX2[C]. 25th Australasian Conference on Information Security and Privacy, Perth, Australia, 2020: 204–224. [6] OWENS J D, HOUSTON M, LUEBKE D, et al. GPU computing[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2008, 96(5): 879–899. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2008.917757 [7] PAN Wuqiong, ZHENG Fangyu, ZHAO Yuan, et al. An efficient elliptic curve cryptography signature server with GPU acceleration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2017, 12(1): 111–122. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2603974 [8] SOLINAS J A. An improved algorithm for arithmetic on a family of elliptic curves[C]. 17th Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 1997: 357–371. [9] YAROM Y and BENGER N. Recovering OpenSSL ECDSA nonces using the FLUSH+RELOAD cache side-channel attack[J]. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2014, 2014: 140. [10] VAN DE POL J, SMART N P, and YAROM Y. Just a little bit more[C]. The Cryptographer’s Track at the RSA Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2015: 3–21. [11] ZHOU Lu, SU Chunhua, HU Zhi, et al. Lightweight implementations of NIST P-256 and SM2 ECC on 8-bit resource-constraint embedded device[J]. ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems, 2019, 18(3): 23. doi: 10.1145/3236010 [12] 国家密码管理局. GM/T 0004-2012 SM3密码杂凑算法[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2012.State Cryptography Administration of China. GM/T 0004-2012 SM3 cryptographic hash algorithm[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2012. [13] 国家密码管理局. GM/T 0004-2012 SM2椭圆曲线公钥密码算法 第5部分: 参数定义[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2012.State Cryptography Administration of China. GM/T 0003.5-2012 Public key cryptographic algorithm SM2 based on elliptic curves-Part 5: Parameter definition[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2012. [14] ZHAO Zhenwei and BAI Guoqiang. Ultra high-speed SM2 ASIC implementation[C]. The 2014 IEEE 13th International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications, Beijing, China, 2014: 182–188. [15] HU Xianghong, ZHENG Xin, ZHANG Shengshi, et al. A High-performance elliptic curve cryptographic processor of SM2 over GF(p)[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(4): 431. doi: 10.3390/electronics8040431 [16] RIVAIN M. Fast and regular algorithms for scalar multiplication over elliptic curves[J/OL]. IACR Cryptology ePrint Archive, 2011, 338. [17] Nvidia. Parallel thread execution ISA version 7.3[EB/OL]. https://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/parallel-thread-execution/index.html#ptx-machine-mode, 2022. [18] SZERWINSKI R and GÜNEYSU T. Exploiting the power of GPUs for asymmetric cryptography[C]. 10th International Workshop on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, Washington, USA, 2008: 79–99. [19] KOC C K, ACAR T, and KALISKI B S. Analyzing and comparing Montgomery multiplication algorithms[J]. IEEE Micro, 1996, 16(3): 26–33. doi: 10.1109/40.502403 [20] HANKERSON D, VANSTONE S, and MENEZES A. Guide to Elliptic Curve Cryptography[M]. New York: Springer, 2004: 110–111. [21] DONG Jiankuo, ZHENG Fangyu, CHENG Juanjuan, et al. Towards high-performance X25519/448 key agreement in general purpose GPUs[C]. 2018 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security, Beijing, China, 2018: 1–9. [22] GAO Lili, ZHENG Fangyu, EMMART N, et al. DPF-ECC: Accelerating elliptic curve cryptography with floating-point computing power of GPUs[C]. 2020 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium, New Orleans, USA, 2020: 494–504. [23] LEE S, SEO H, KWON H, et al. Hybrid approach of parallel implementation on CPU–GPU for high-speed ECDSA verification[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2019, 75(8): 4329–4349. doi: 10.1007/s11227-019-02744-6 -







 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
