Research on Optimization of Camera-based Visible Light Positioning System
-
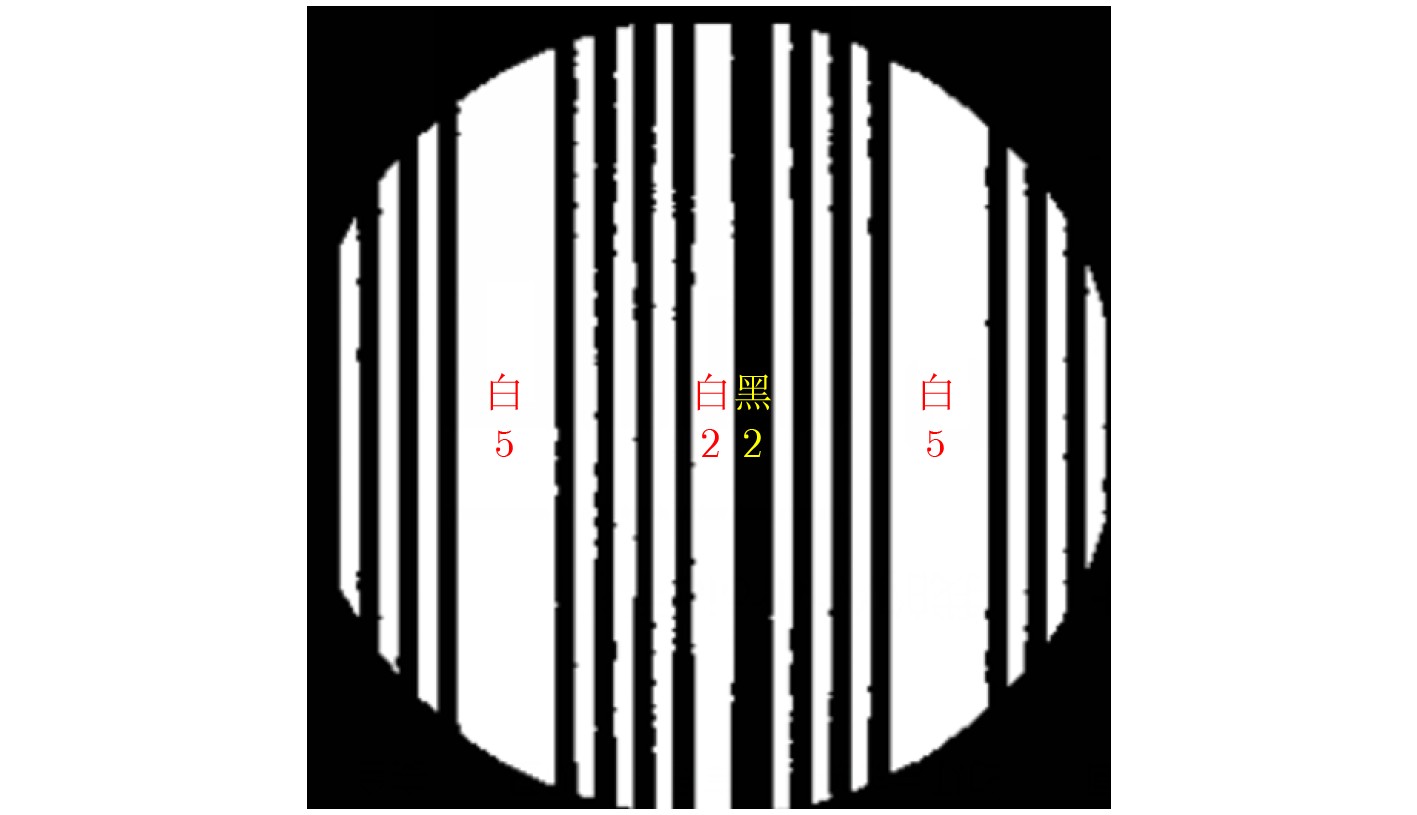
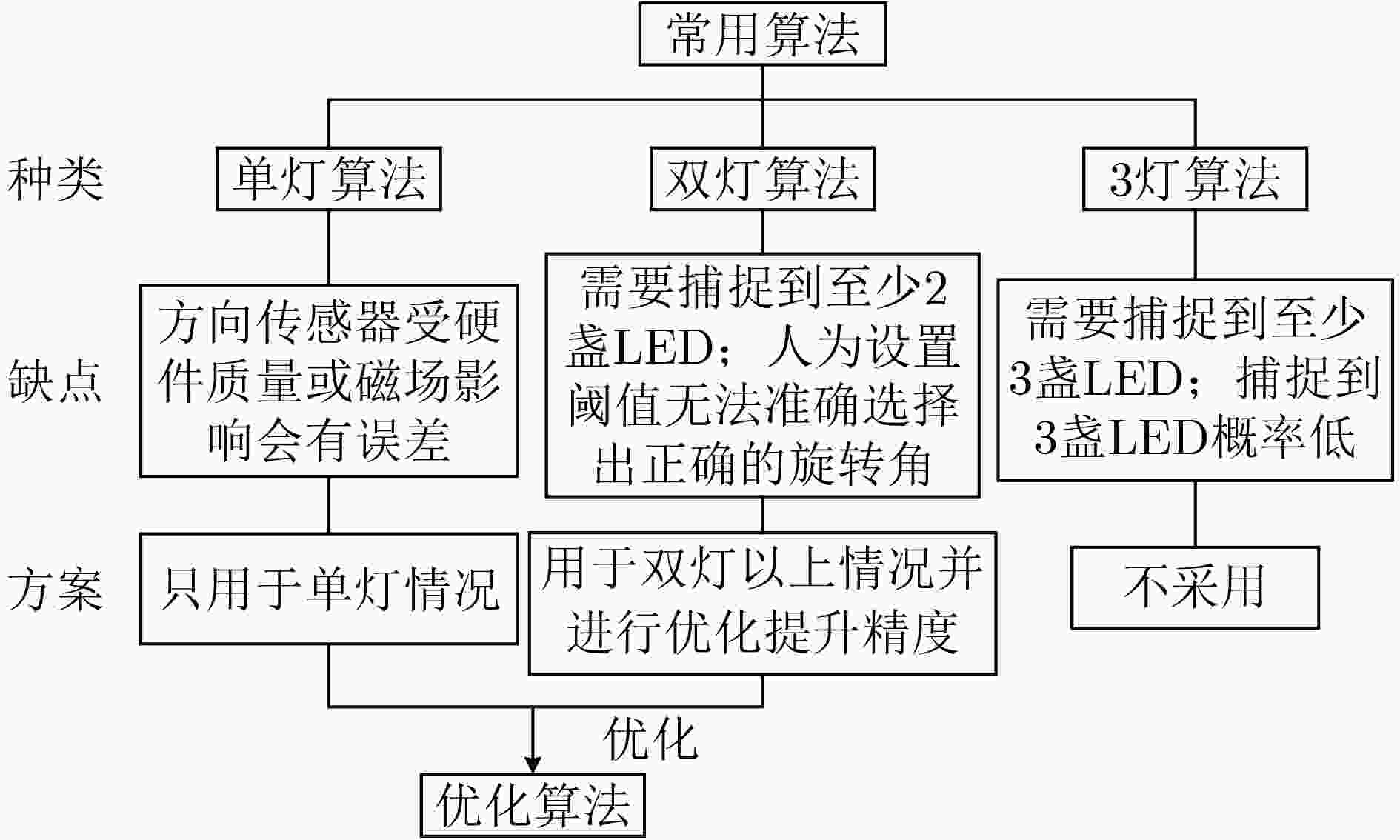
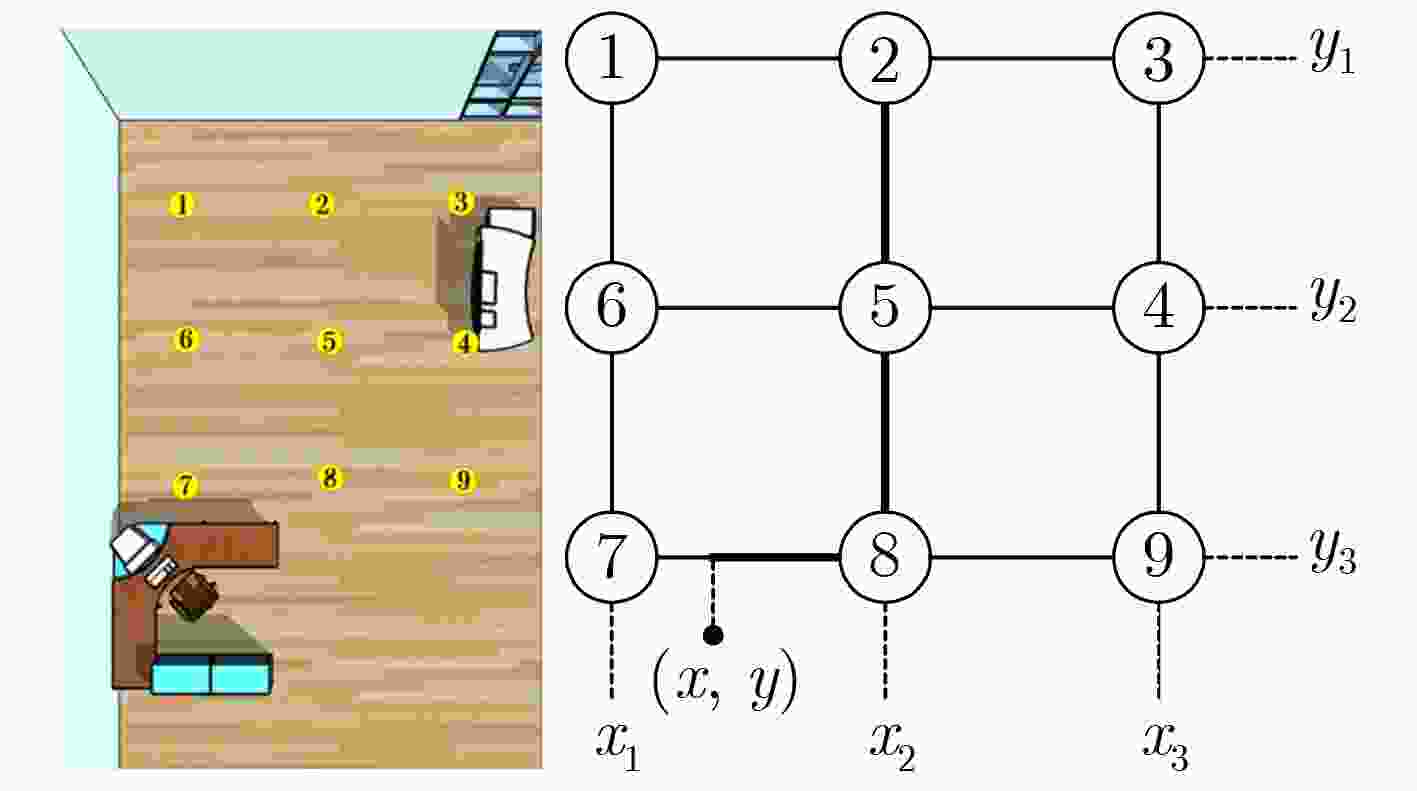
摘要: 现有室内成像型可见光定位系统多注重定位精度的提高,而忽略了系统的解码识别成功率和定位算法的适用性。表现在:(1)接收端捕获带有模糊效应的图像会导致解码识别率变低;(2)定位系统移动状态下采用单一算法定位,且双灯(dual-LED)算法的旋转角存在非确定性,导致定位精度大幅度变化,甚至定位系统失效。该文首先提出基于条纹宽度比的解码算法,消除人为设定硬阈值的缺陷;然后,提出基于旋转角优化的联合定位算法,利用方向传感器辅助确认旋转角并联合定位;此外,还设计了简易导航功能。实验结果表明,该算法使得解码识别率在1.5 m内可达99%,系统平均定位误差为3.998 cm。Abstract: The existing indoor visible light positioning systems focus more on the positioning accuracy improvement and ignores the system's decoding success rate and the applicability of the positioning algorithm. The specific aspects are as follows: (1) Captured images with the blurring effect result in a lower decoding recognition rate; (2) Most existing systems use a single algorithm to achieve the positioning, and the dual-Light Emitting Diode (dual-LED) positioning algorithm exists the uncertainty for the rotation angle. The above problems result in the positioning accuracy decreasing or even the positioning system failure. First, the decoding algorithm based on the fringe width ratio is proposed to remove the defect of the artificial hard-threshold. Then, the joint positioning algorithm based on optimized rotation angle is proposed, which uses the smartphone orientation sensor to calibrate the rotation angle. Furthermore, a simple navigation application is designed. Experimental results show that the designed algorithms raise the decoding recognition rate up to 99% within 1.5 m, and the average positioning error is 3.998 cm.
-
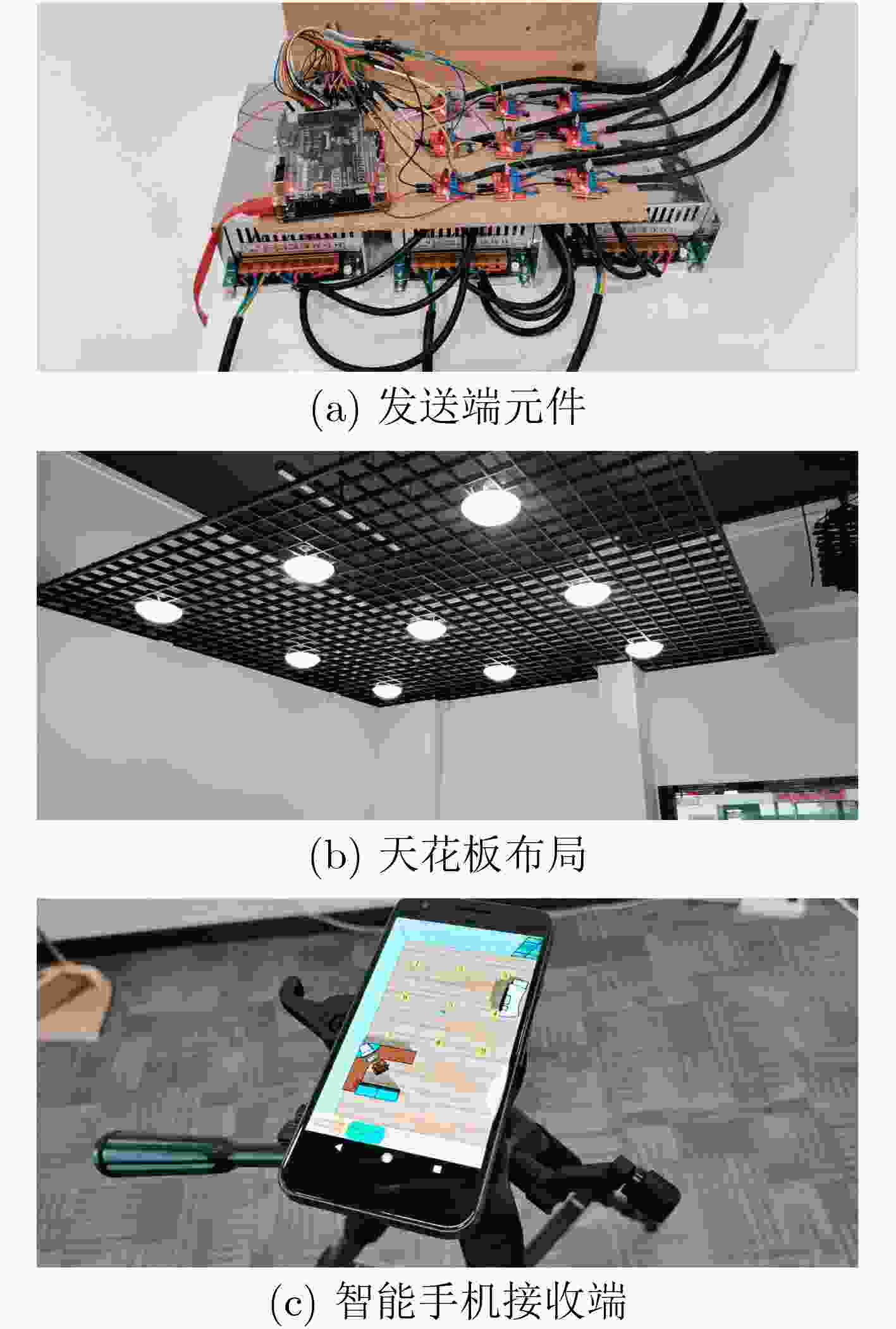
表 1 系统参数设置
参数 值 实验区域大小 3.2 m×3.0 m×2.65 m LED型号 CXA1512 LED最大功率 21.6 W 灯罩直径 20 cm 芯片型号 Cylone IV EP4CE6F 放大电路 LM324N MOS管型号 IRF520 电源 GPS-430C 智能手机型号 Google Pixel 屏幕分辨率 1920×1080 系统版本 Android 7.0/8.0 前置摄像头分辨率 2448×3264 相机曝光时间 100 µs 相机感光度 64 表 2 信标编码参数
参数 值(µs) 序列头宽度 400 序列尾宽度 80 时隙(单位编码)宽度 80 -
[1] WU Xiping, SOLTANI M D, ZHOU Lai, et al. Hybrid LiFi and WiFi networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 1398–1420. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3058296 [2] LIU Fen, LIU Jing, YIN Yuqing, et al. Survey on WiFi-based indoor positioning techniques[J]. IET Communications, 2020, 14(9): 1372–1383. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2019.1059 [3] BERNARDINI F, BUFFI A, FONTANELLI D, et al. Robot-based indoor positioning of UHF-RFID tags: The SAR method with multiple trajectories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 70: 8001415. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3033728 [4] SPACHOS P and PLATANIOTIS K N. BLE beacons for indoor positioning at an interactive IoT-based smart museum[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(3): 3483–3493. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.2969088 [5] YAO C Y and HSIA W C. An indoor positioning system based on the dual-channel passive RFID technology[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(11): 4654–4663. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2828044 [6] FENG Daquan, WANG Chunqi, HE Chunlong, et al. Kalman-filter-based integration of IMU and UWB for high-accuracy indoor positioning and navigation[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(4): 3133–3146. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2965115 [7] ZHOU Mu, LI Xinyue, WANG Ya, et al. 6G multisource-information-fusion-based indoor positioning via Gaussian kernel density estimation[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(20): 15117–15125. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3031639 [8] KOMINE T and NAKAGAWA M. Fundamental analysis for visible-light communication system using LED lights[J]. IEEE transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2004, 50(1): 100–107. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2004.1277847 [9] LUO Junhai, FAN Liying, and LI Husheng. Indoor positioning systems based on visible light communication: State of the art[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(4): 2871–2893. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2743228 [10] GU Wenjun, AMINIKASHANI M, DENG Peng, et al. Impact of multipath reflections on the performance of indoor visible light positioning systems[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2016, 34(10): 2578–2587. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2016.2541659 [11] KUO Yesheng, PANNUTO P, HSIAO K J, et al. Luxapose: Indoor positioning with mobile phones and visible light[C]. Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Maui, USA, 2014: 447–458. [12] LIU Xiangyu, WEI Xuetao, and GUO Lei. DIMLOC: Enabling high-precision visible light localization under dimmable LEDs in smart buildings[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 3912–3924. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2893251 [13] WANG Zeyu, YANG Zhice, HUANG Qianyi, et al. ALS-P: Light weight visible light positioning via ambient light sensor[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 2019: 1306–1314. [14] ZHANG Chi and ZHANG Xinyu. Pulsar: Towards ubiquitous visible light localization[C]. Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Snowbird, USA, 2017: 208–221. [15] ZHANG Chi, TABOR J, ZHANG Jialiang, et al. Extending mobile interaction through near-field visible light sensing[C]. The 21st Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Paris, France, 2015: 345–357. -






 下载:
下载:

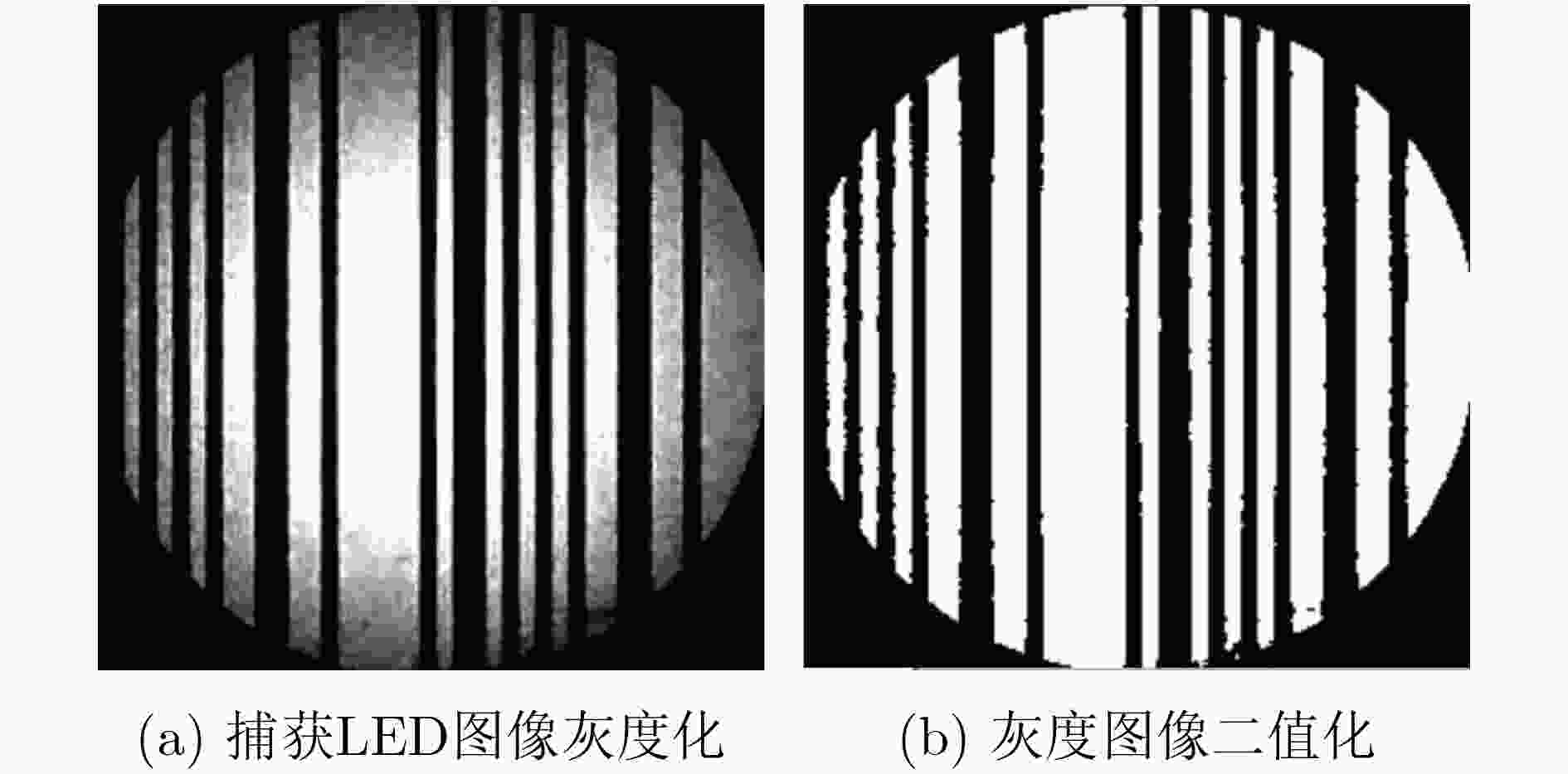
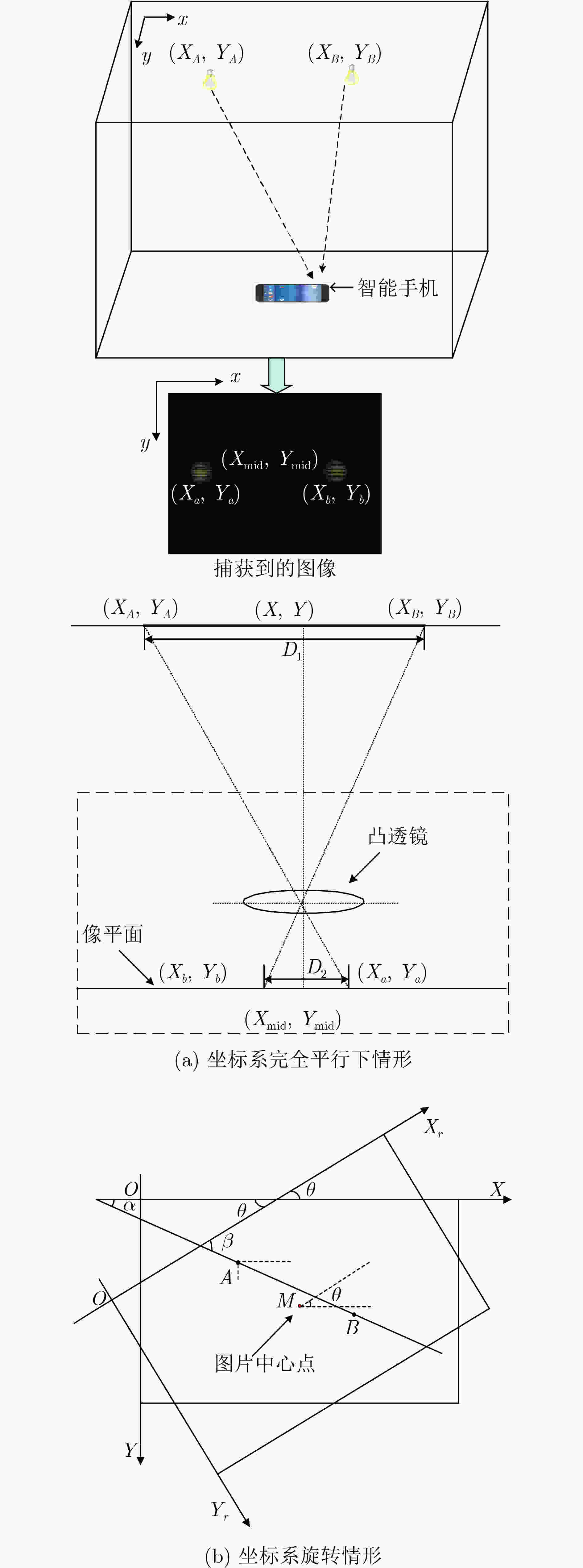
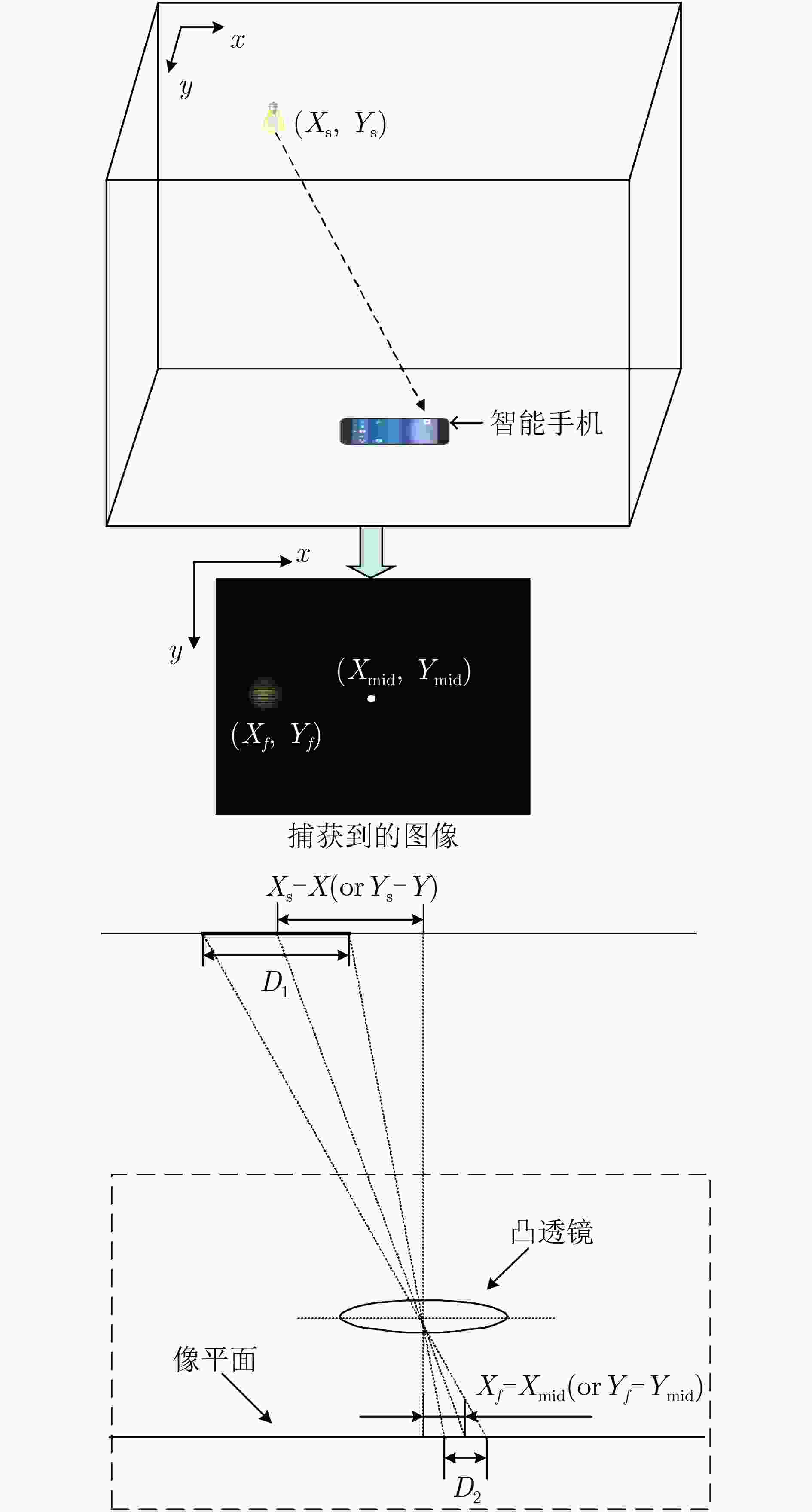
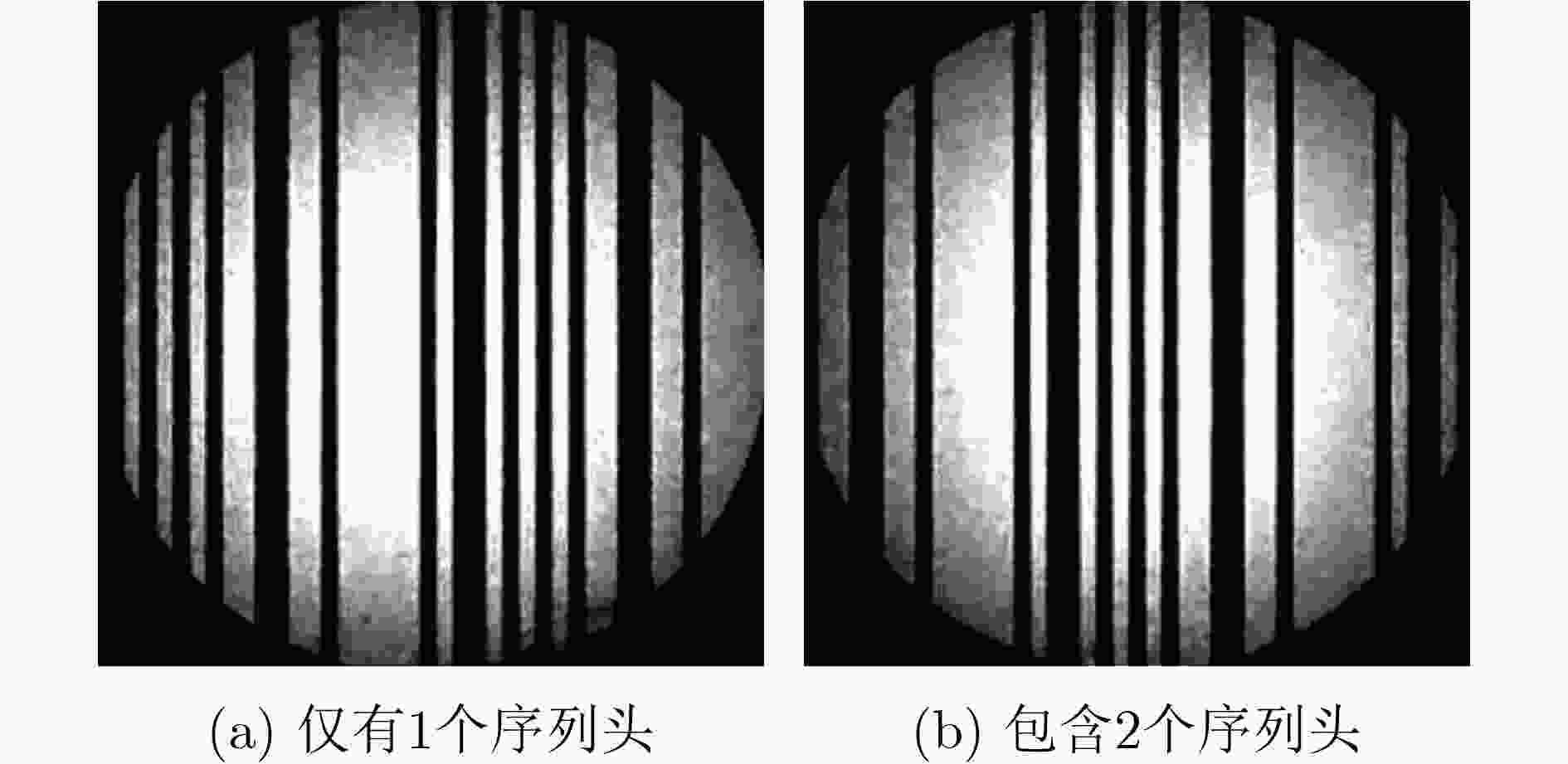

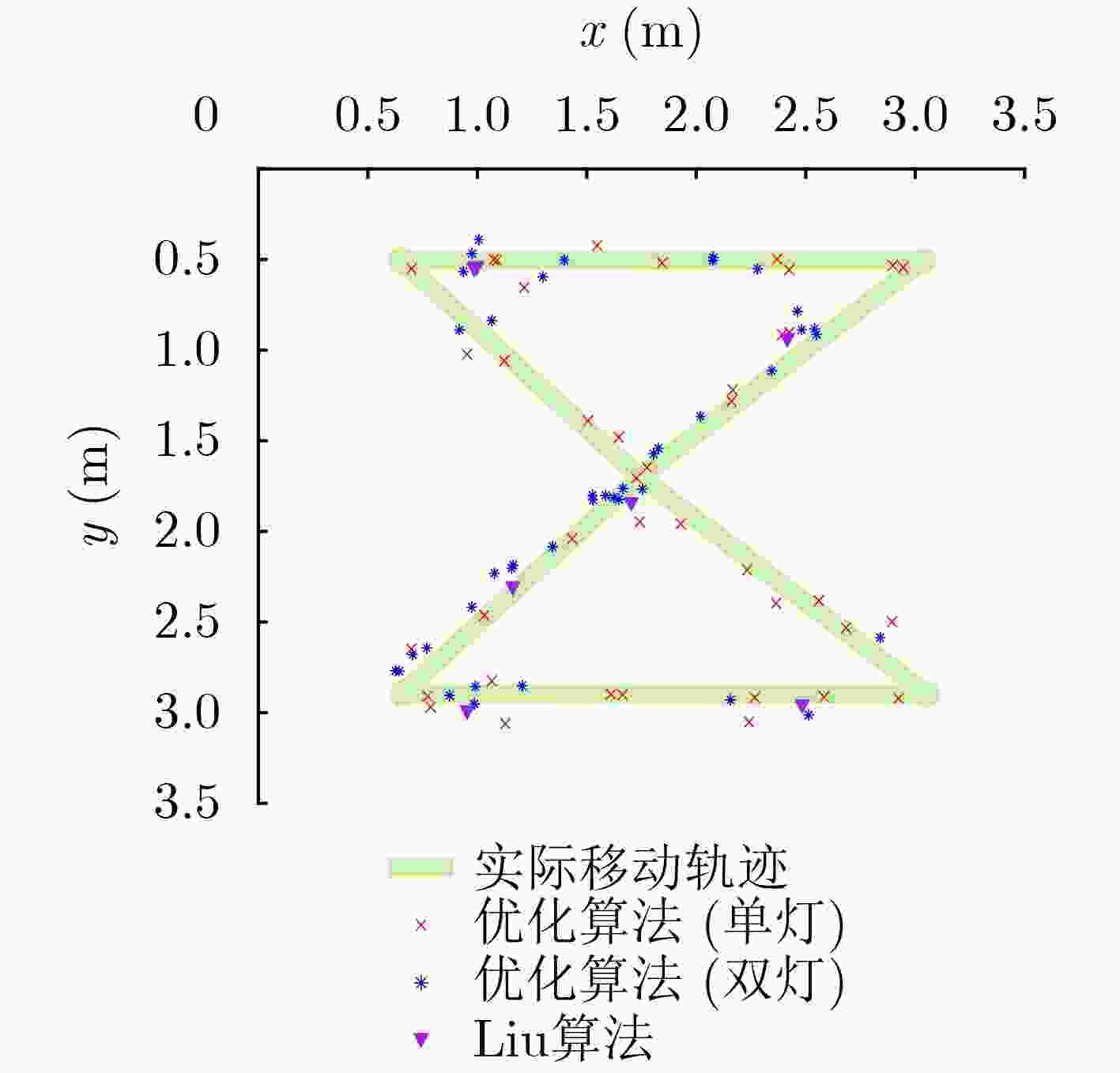
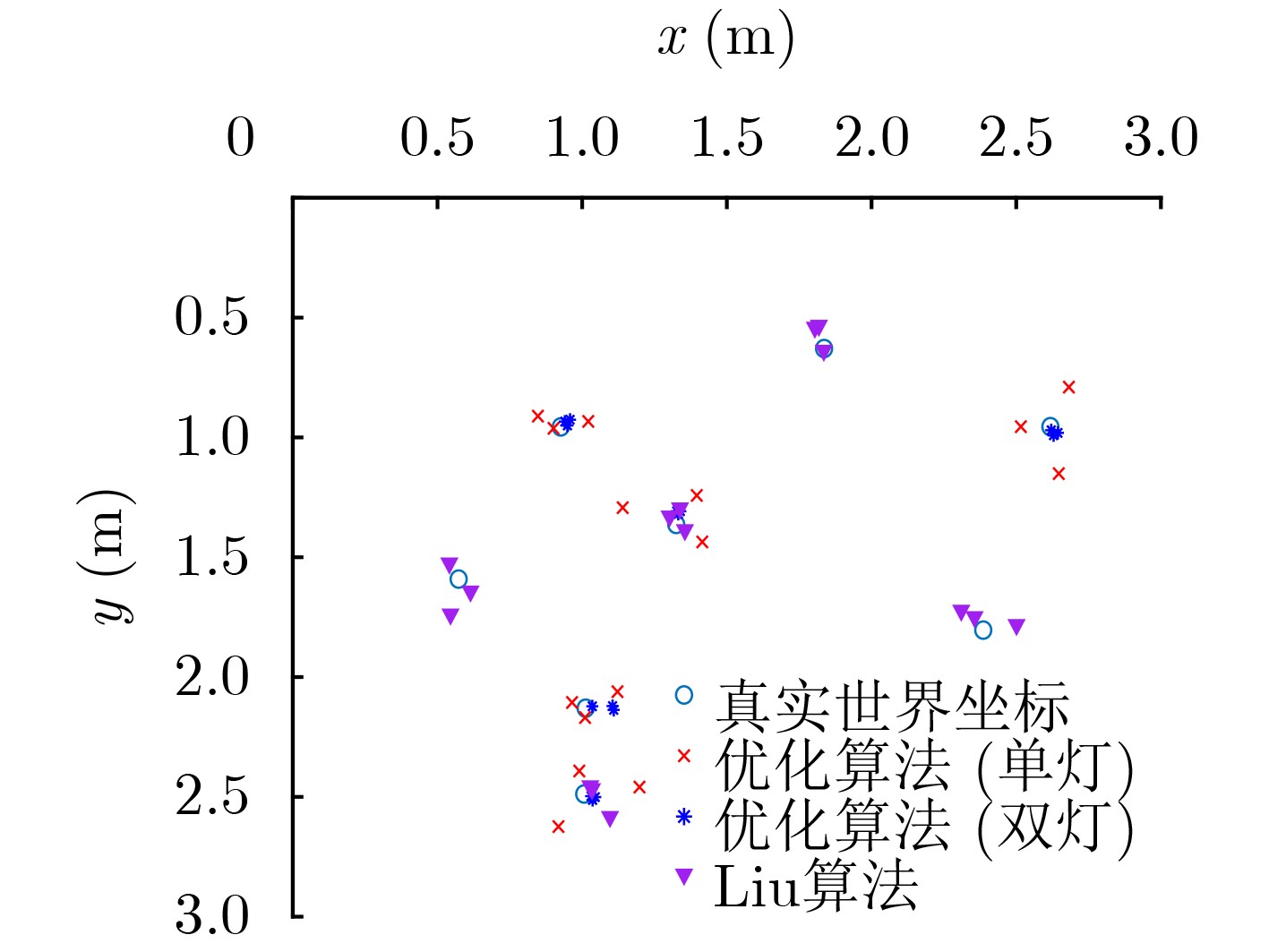
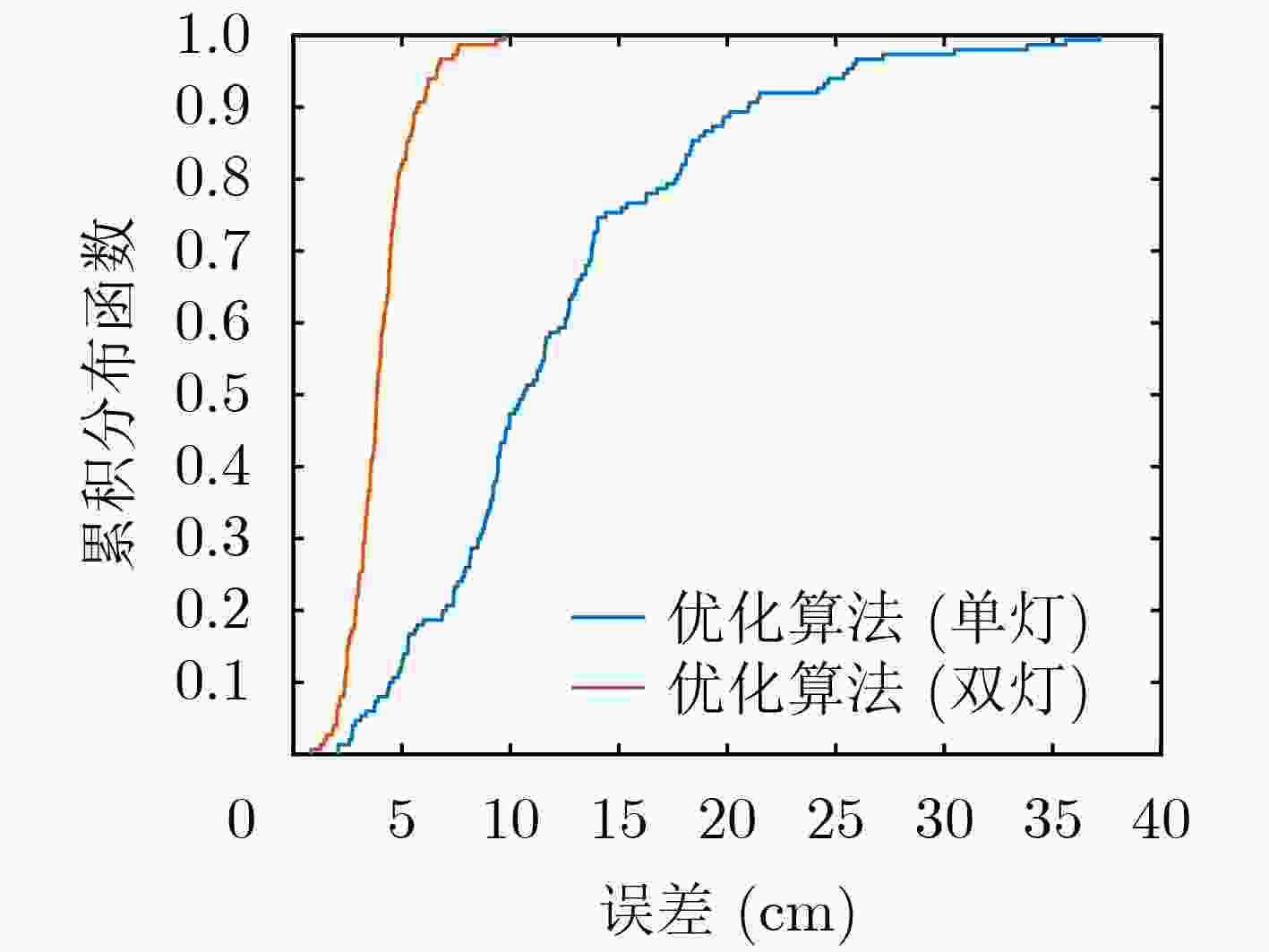
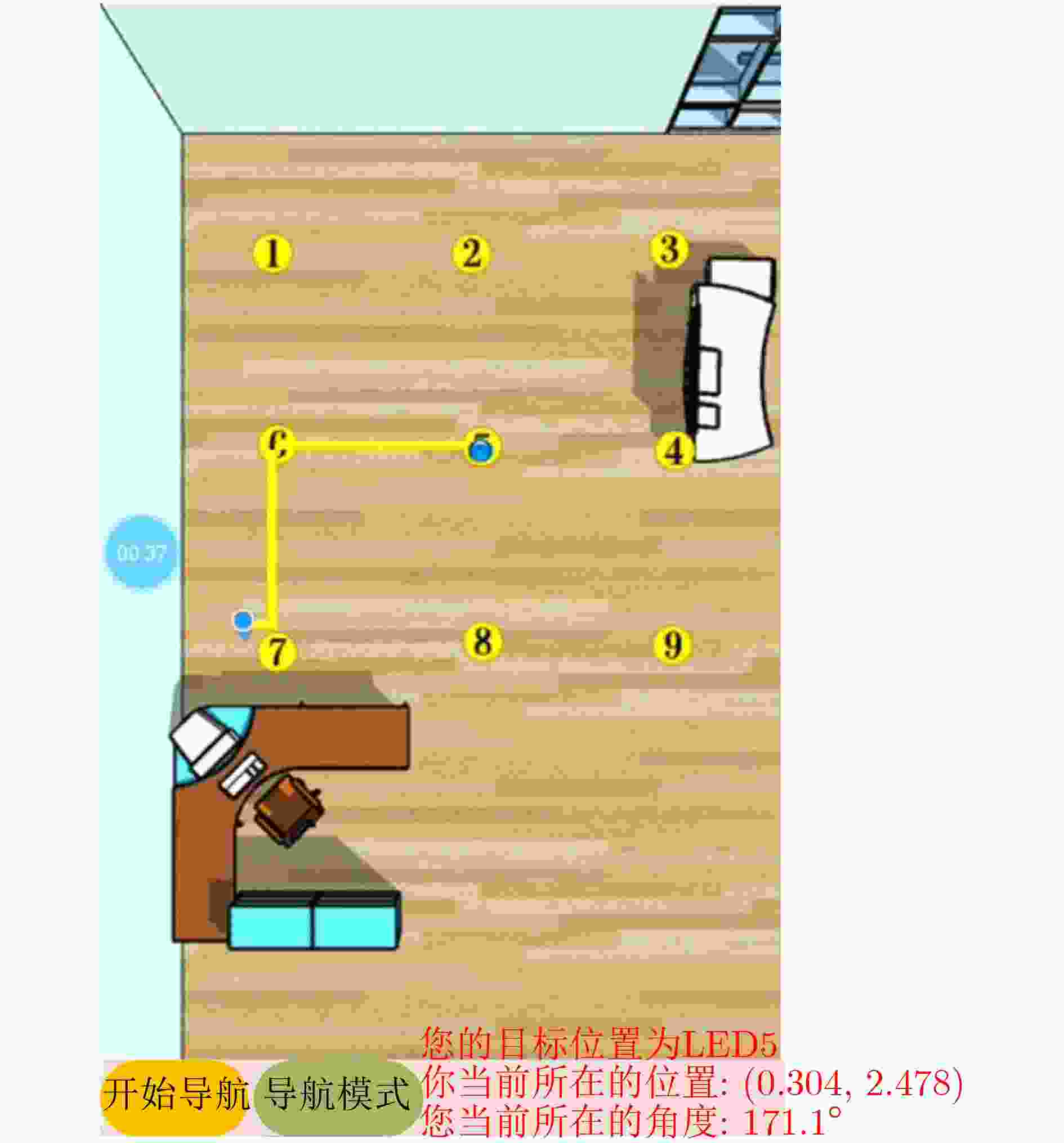


 下载:
下载:
