Underwater Image Restoration Based on Background Light Corrected Image Formation Model
-
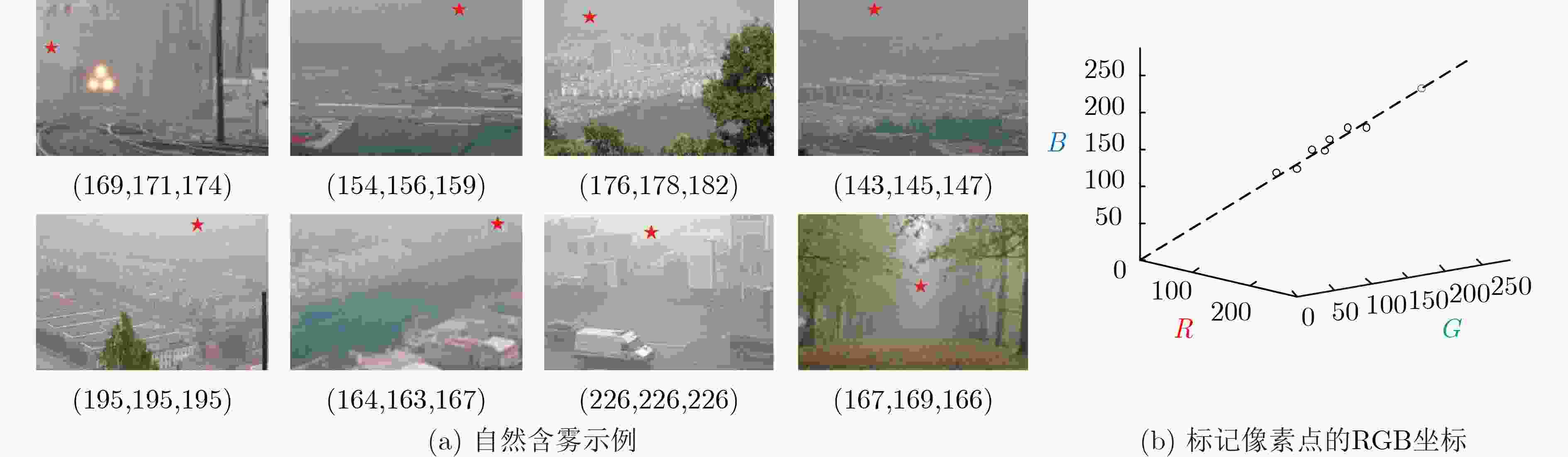
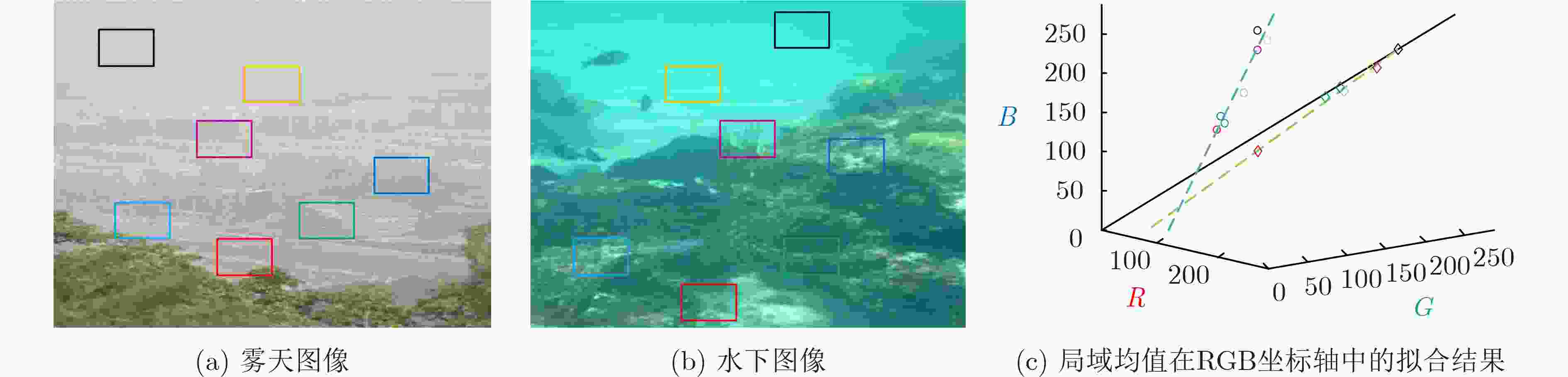
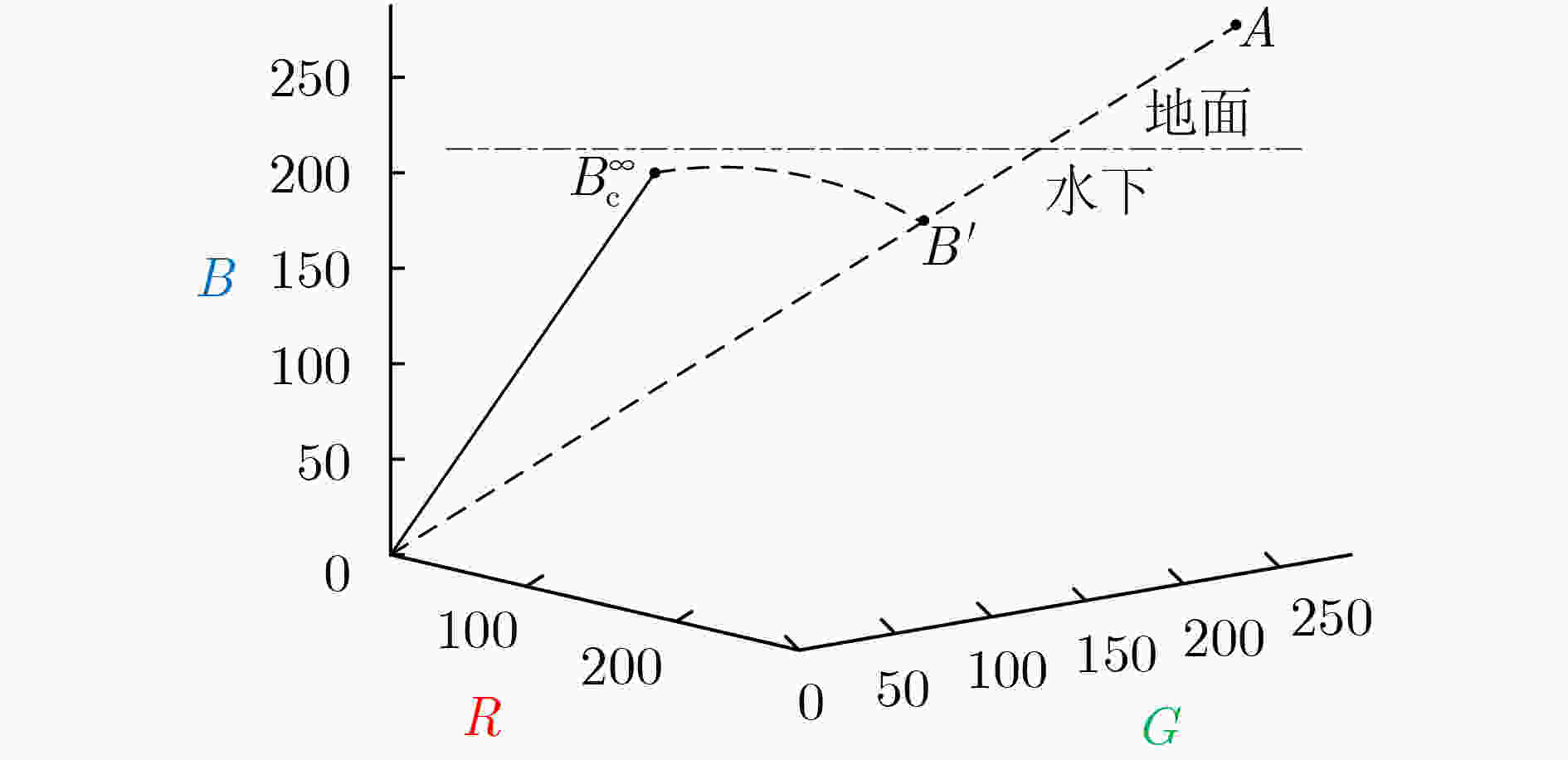
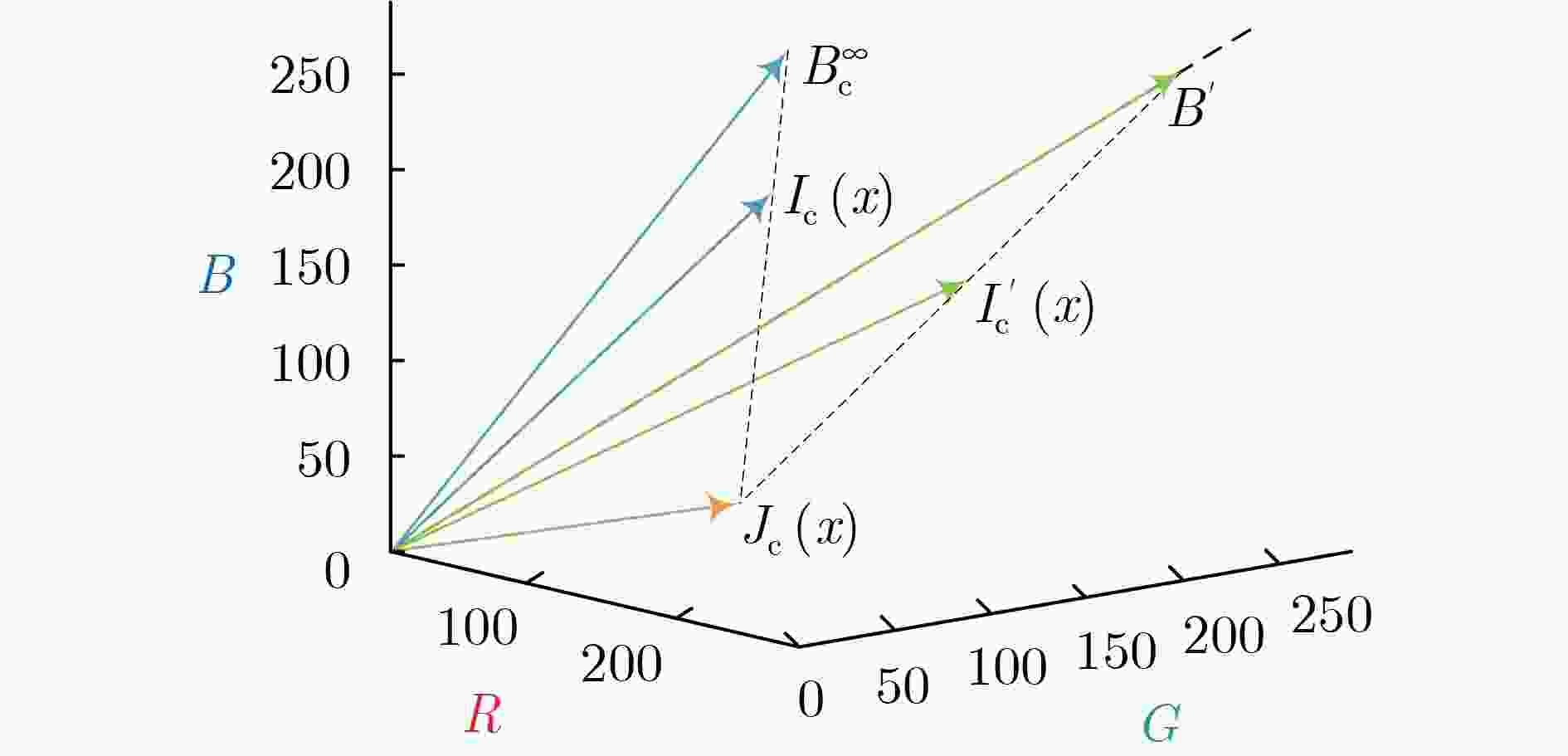
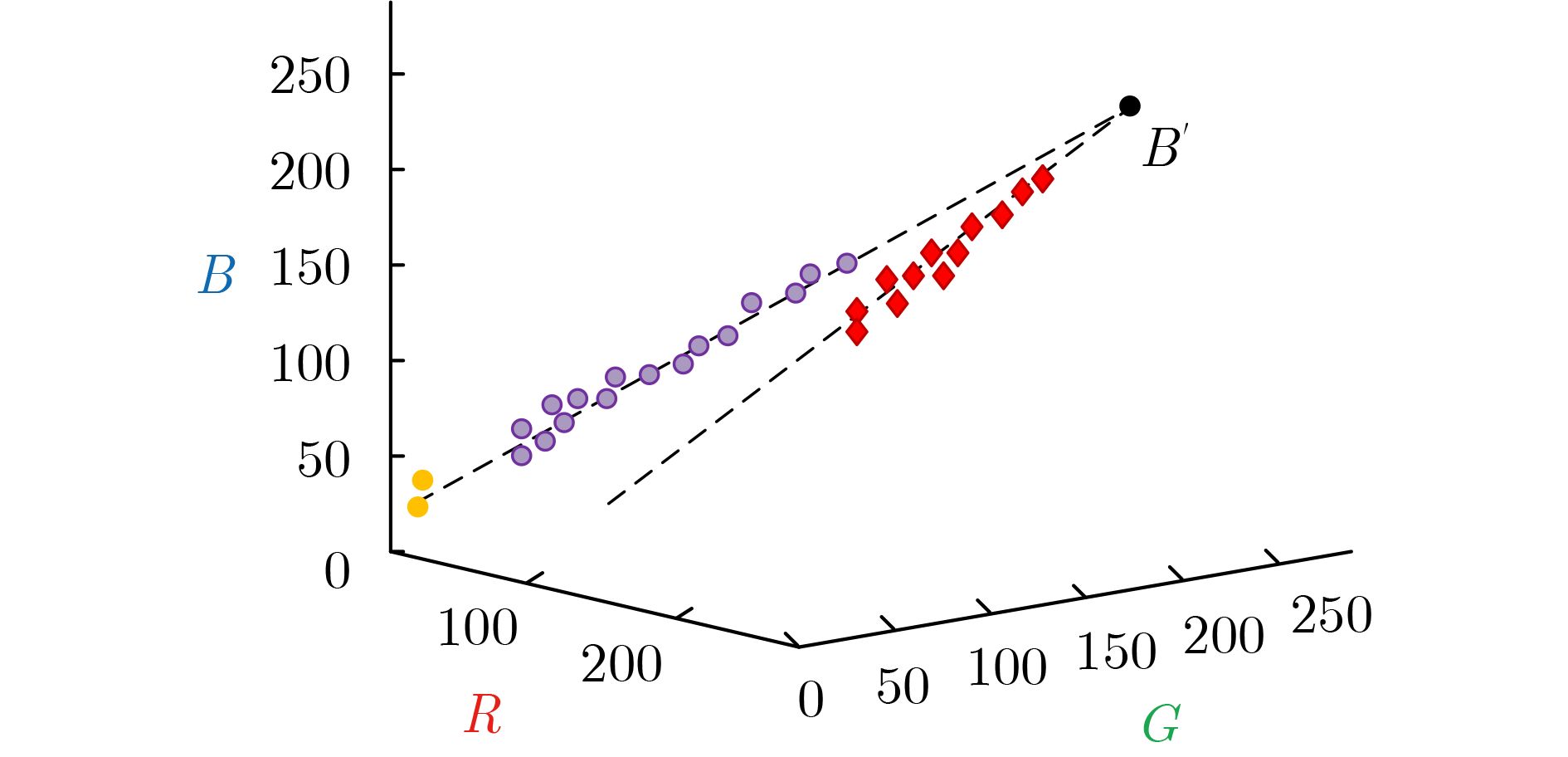
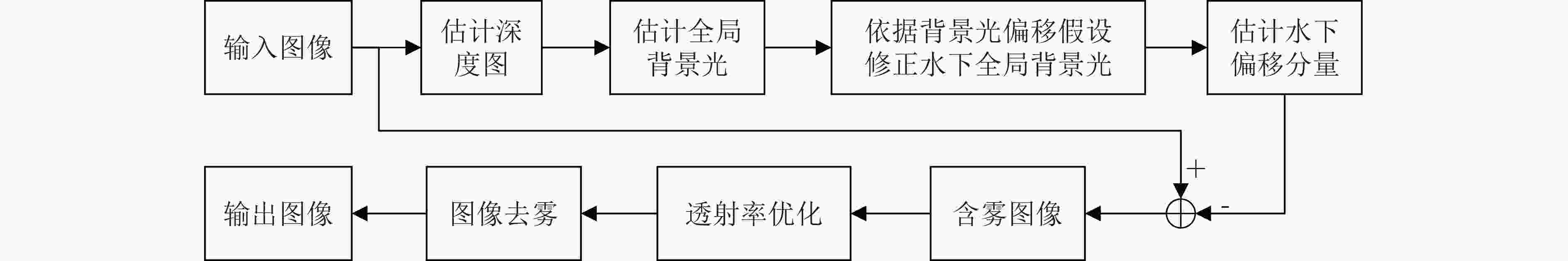
摘要: 光在水下传播时由于受到水体吸收和散射作用的影响,导致水下图像质量严重退化。为了有效去除色偏和模糊,改善水下图像质量,该文提出一种基于背景光修正成像模型的水下图像复原方法。该方法基于对雾天图像的观察,提出了水下图像背景光偏移假设,并基于此建立背景光修正成像模型;随后使用单目深度估计网络获得场景深度的估计,并结合背景光修正的水下成像模型,利用非线性最小二乘拟合获得水下偏移分量的估计值从而实现水下图像去水;最后优化去水后的含雾图像的透射率,并结合修正后的背景光实现图像复原。实验结果表明,该文方法在恢复水下图像颜色和去除散射光方面效果良好。Abstract: The underwater image quality is seriously degraded due to the effects of absorption and scattering when light propagates underwater. In order to remove color distortion and blur, and improve the quality of underwater image effectively, an underwater image restoration method based on background light corrected image formation model is proposed in this paper. Based on the observation of ground hazy images, the assumption of background light offset for underwater images is put forward, which is the cornerstone of the background light corrected image formation model. Then, a monocular depth estimation network is used to obtain the estimate of the scene depth. Combined with the background light corrected image formation model, the underwater offset component is obtained by non-linear least square fitting, so as to remove water from underwater images. Finally, the transmittance of hazy image after water removed is optimized and combined with the corrected background light to achieve image recovery. Experimental results show that the method works well in restoring the original color of underwater scenes and removing scattered light.
-
表 1 不同水体中各算法复原结果的CIEDE2000色差指标对比
表 2 各方法客观评价指标平均值比较
方法 低质量水下图像 低照度水下图像 AG IE UCIQE UIQM AG IE UCIQE UIQM 原图 6.4231 2.1744 0.4030 3.5151 6.0967 1.3027 0.4421 2.3293 文献[16] 6.9084 4.7642 0.5957 4.3580 6.8364 3.7480 0.5592 2.5836 文献[17] 7.3189 5.1387 0.6098 4.7196 7.2517 3.9023 0.5806 3.0269 文献[18] 7.2730 5.0059 0.5737 4.6711 6.4905 2.6523 0.5755 2.6256 文献[19] 7.0860 5.0510 0.5847 4.4900 6.9061 3.4108 0.5766 2.9130 本文算法 7.3238 5.1482 0.6280 4.6647 7.5311 4.2754 0.5724 3.0785 -
[1] LI Changli, TANG Shiqing, KWAN H K, et al. Color correction based on CFA and enhancement based on Retinex with dense pixels for underwater images[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 155732–155741. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3019354 [2] 郭银景, 吴琪, 苑娇娇, 等. 水下光学图像处理研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(2): 426–435. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190803GUO Yinjing, WU Qi, YUAN Jiaojiao, et al. Research progress on underwater optical image processing[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(2): 426–435. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190803 [3] LIMARE N, LISANI J L, MOREL J M, et al. Simplest color balance[J]. Image Processing on Line, 2011, 1: 297–315. doi: 10.5201/ipol.2011.llmps-scb [4] JOBSON D J, RAHMAN Z, and WOODELL G A. A multiscale Retinex for bridging the gap between color images and the human observation of scenes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 1997, 6(7): 965–976. doi: 10.1109/83.597272 [5] GIBSON J. Improving sea-thru with monocular depth estimation methods[EB/OL]. https://github.com/hainh/sea-thru/blob/master/report.tex, 2020. [6] HE Kaiming, SUN Jian, and TANG Xiaoou. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(12): 2341–2353. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [7] BERMAN D, LEVY D, AVIDAN S, et al. Underwater single image color restoration using haze-lines and a new quantitative dataset[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(8): 2822–2837. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2977624 [8] AKKAYNAK D and TREIBITZ T. Sea-thru: A method for removing water from underwater images[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Los Angeles, USA, 2019: 1682–1691. [9] PENG Y T, ZHAO Xiangyun, and COSMAN P C. Single underwater image enhancement using depth estimation based on blurriness[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Quebec City, Canada, 2015: 4952–4956. [10] AKKAYNAK D and TREIBITZ T. A revised underwater image formation model[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6723–6732. [11] GODARD C, AODHA O M, FIRMAN M, et al. Digging into self-supervised monocular depth estimation[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 3827–3837. [12] ZHAO Chaoqiang, SUN Qiyu, ZHANG Chongzhen, et al. Monocular depth estimation based on deep learning: An overview[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2020, 63(9): 1612–1627. doi: 10.1007/s11431-020-1582-8 [13] 蔡晨东, 霍冠英, 周妍, 等. 基于场景深度估计和白平衡的水下图像复原[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(3): 031008.CAI Chendong, HUO Guanying, ZHOU Yan, et al. Underwater image restoration method based on scene depth estimation and white balance[J]. Laser &Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(3): 031008. [14] BERMAN D, TREIBITZ T, and AVIDAN S. Single image dehazing using haze-lines[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(3): 720–734. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2882478 [15] BERMAN D, TREIBITZ T, and AVIDAN S. Non-local image dehazing[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 1674–1682. [16] ANCUTI C O, ANCUTI C, DE VLEESCHOUWER C, et al. Color channel transfer for image dehazing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(9): 1413–1417. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2932189 [17] ANCUTI C O, ANCUTI C, DE VLEESCHOUWER C, et al. Color balance and fusion for underwater image enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(1): 379–393. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2759252 [18] LI Chongyi, GUO Jichang, CONG Runmin, et al. Underwater image enhancement by dehazing with minimum information loss and histogram distribution prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(12): 5664–5677. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2612882 [19] 王丹, 张子玉, 赵金宝, 等. 基于场景深度估计的自然光照水下图像增强方法[J]. 机器人, 2021, 43(3): 364–372. doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.200275WANG Dan, ZHANG Ziyu, ZHAO Jinbao, et al. An enhancement method for underwater images under natural illumination based on scene depth estimation[J]. Robot, 2021, 43(3): 364–372. doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.200275 -






 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
