Energy-efficient Algorithm for Intelligent Reflecting Surface-aided Secure Communication Systems with Hardware Impairments
-
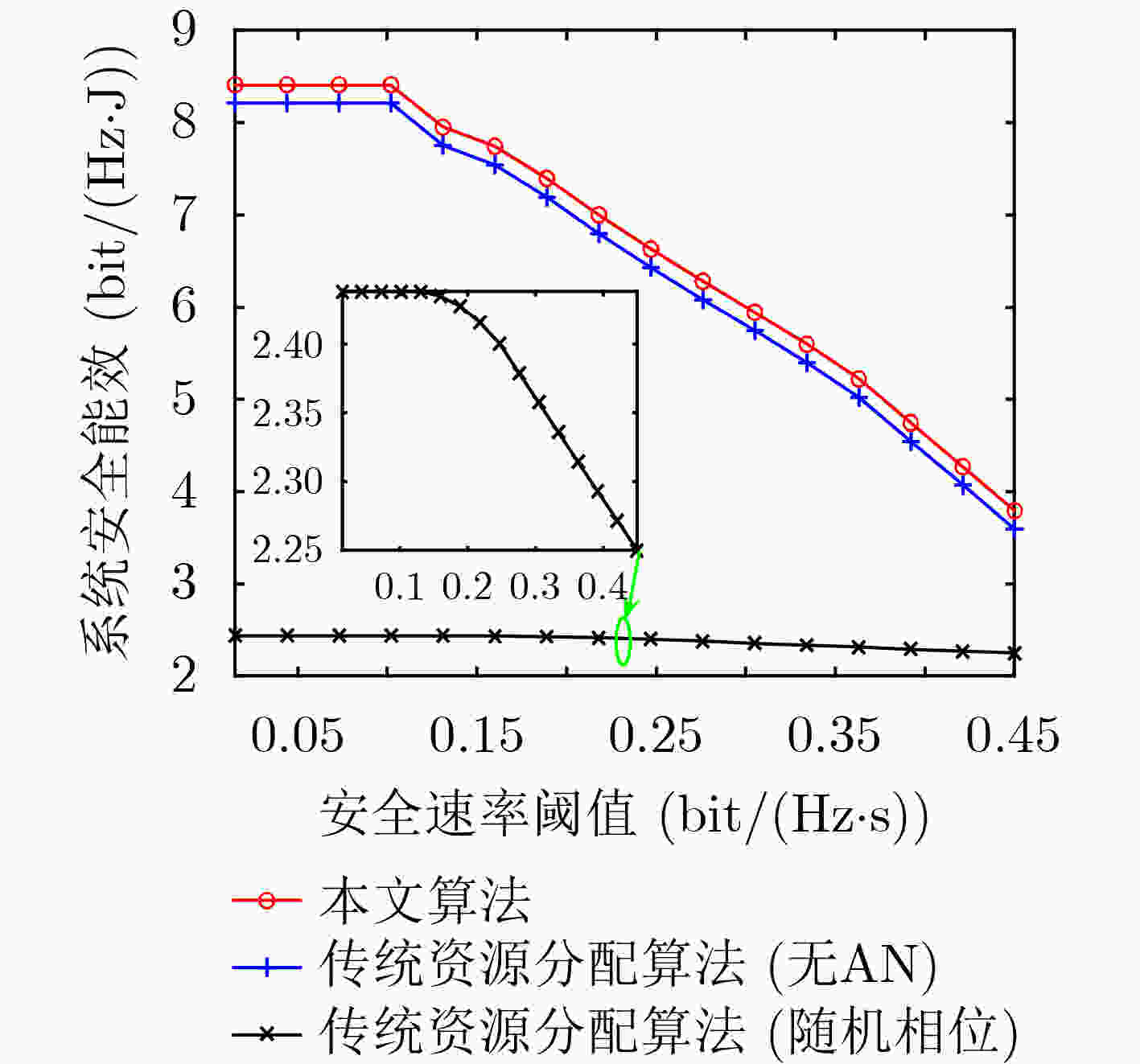
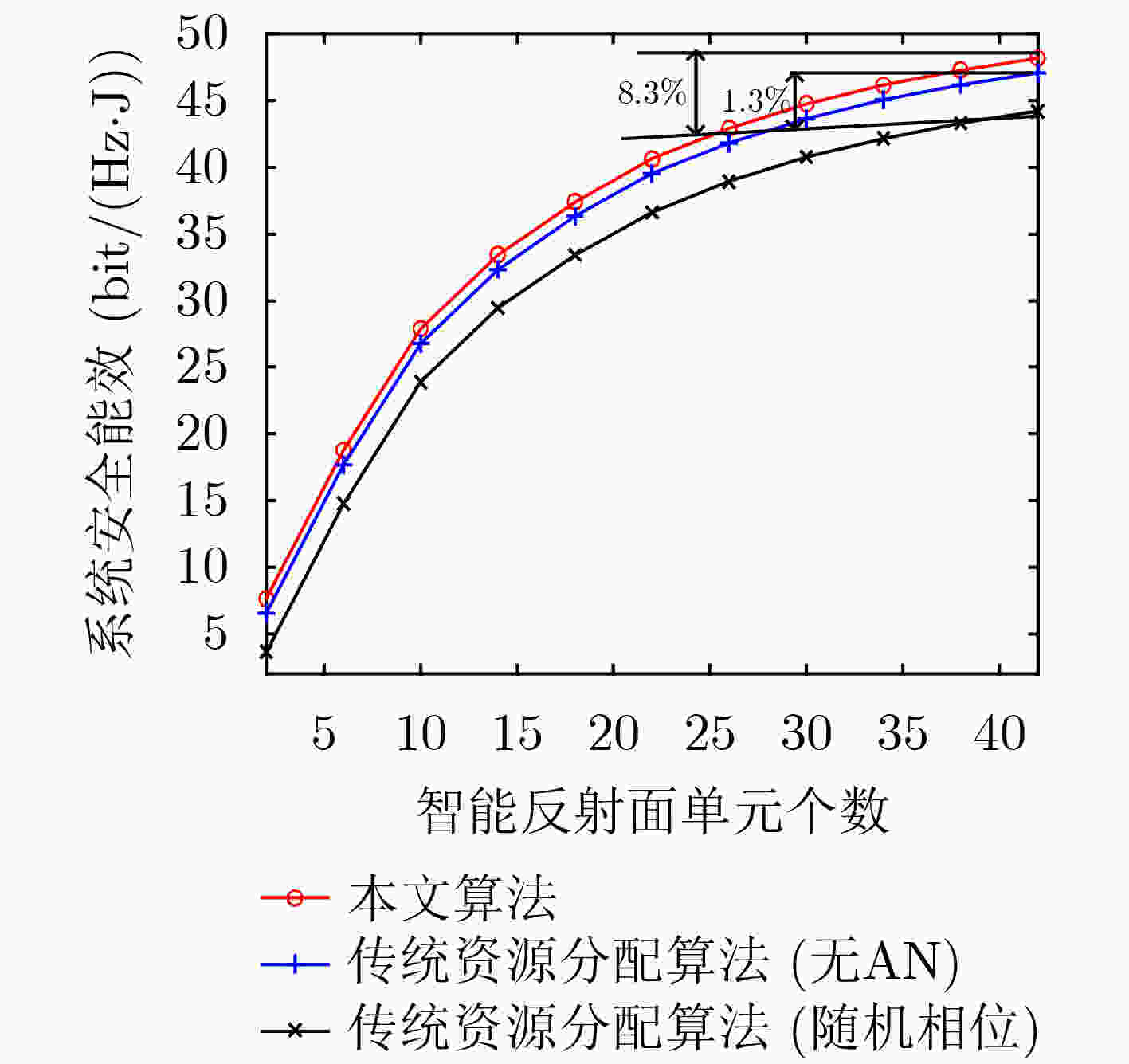
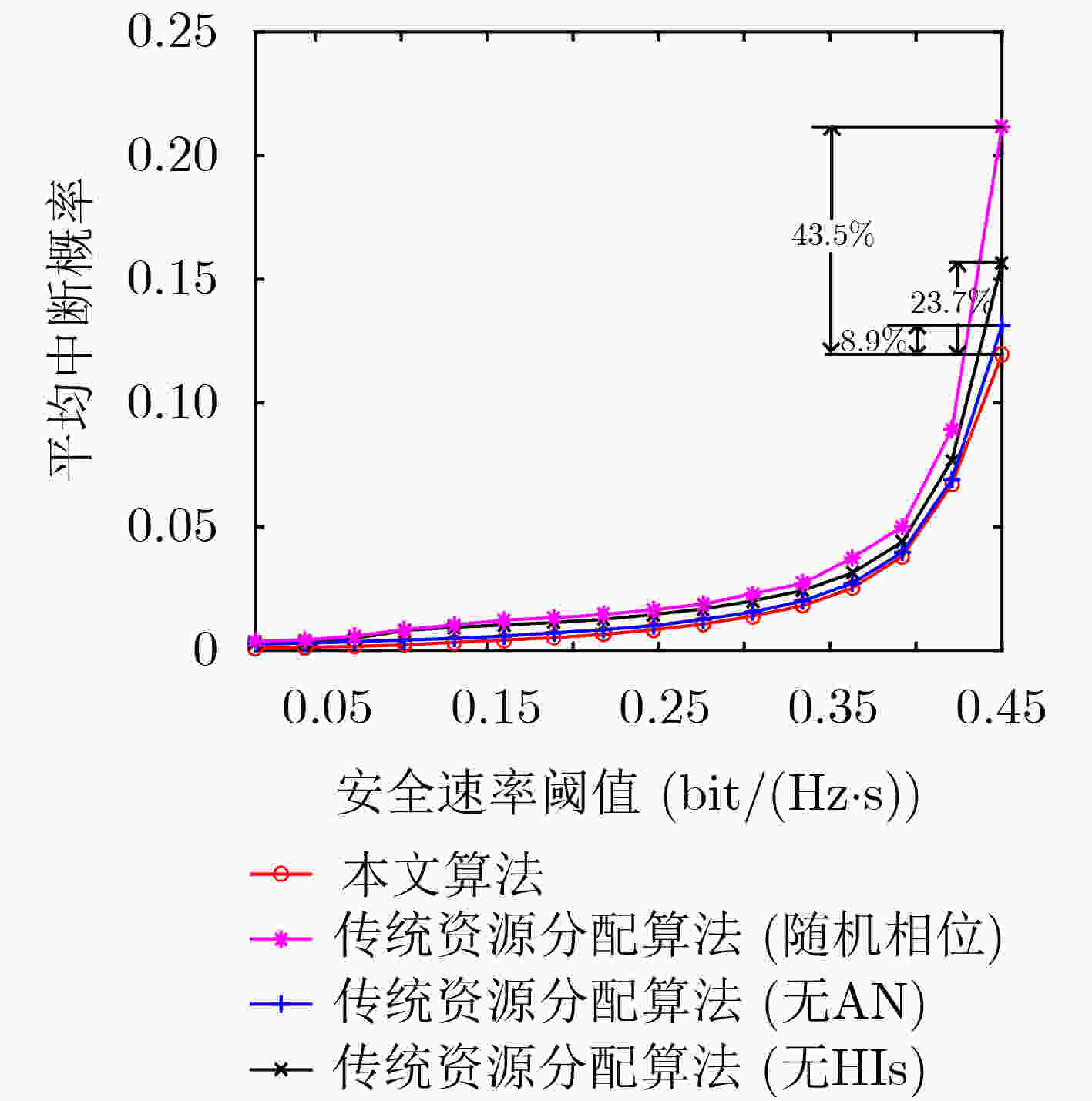
摘要: 为了克服阴影衰落和障碍物阻挡的影响,智能反射面(IRS)已经成为一种提高无线通信系统能量效率(EE)和降低硬件成本的有效技术。然而,传统无线资源分配(RA)算法忽略了系统收发机硬件损伤(HIs)的影响,由于放大器非线性、相位噪声的影响使得接收信号失真,从而使得这类算法的系统性能下降。为解决该问题,通过考虑收发机的硬件损伤和网络窃听者的影响,该文研究基于硬件损伤的IRS辅助安全通信系统能效优化问题。首先,基于基站的最大发射功率约束和用户的最小安全速率约束,建立一个含硬件损伤的能效最大资源优化问题。其次,采用辅助变量替换、半正定松弛以及Dinkelbach等方法,将原非凸问题转化为凸问题进行求解。最后,数值仿真结果表明,该算法与传统资源分配算法相比,合法用户的平均中断概率降低了43.5%,该算法中系统的安全能效提高了8.3%,因此,该算法具有较好的抗硬件损伤性和安全性。Abstract: To mitigate the effects of shadow fading and obstacle blocking, Intelligent Reflecting Surface (IRS) has become an effective technology to improve Energy Efficiency (EE) and reduce hardware cost of wireless communication systems. However, traditional radio Resource Allocation (RA) algorithms have ignored the impact of Hardware Impairments (HIs) of system’s transceivers. Since the distorted received signals are caused by the nonlinearity of amplifiers and the influence of phase noise. so that this type of algorithm can degrade system performance. To deal with this issue, Hardware Impairments of the transceiver and the influence of eavesdroppers is considered, and the problem of energy-saving optimization of hardware impairment in IRS-assisted secure communication systems is investigated. Firstly, an EE-based maximization resource optimization problem is formulated under the maximum transmit power constraint of the base station and the minimum secure rate constraints of users. Secondly, the original non-convex problem is transformed into a convex problem by using the auxiliary variable substitution, semidefinite relaxation and Dinkelbach’s method. Finally, simulation results show that the proposed algorithm is improved 8.3% in terms of security EE and is reduced by 43.5% in terms of the outage probability of legitimate users by comparing it with the traditional RA algorithms without HIs. Therefore, the proposed algorithm has better security and hardware damage resistance.
-
表 1 基于交替迭代的资源分配算法
初始化系统参数:初始化相移矩阵${{\boldsymbol{F}}^{(0)} }$,设置初始迭代次数${\rm{iter}} = 1$,最大迭代次数${{\rm{iter}}^{({\rm{max}})} }$,初始能效值$ {\lambda ^{(0)}} $,初始化松弛辅助变量$ \bar q_l^{(0)} $,
$\bar u_e^{(0)}$,收敛精度$\varepsilon = 1{0^{ - 4}}$。步骤1 for $ {\rm{iter }}= 1,2, \cdots ,{{\rm{iter}}^{({\rm{max}})}}$ do 步骤2 根据给定相移矩阵F,系统能效值$\lambda $以及松弛辅助变量$\overline q_l $, $\overline u_e $。求解问题式(15)得到波束向量矩阵${\boldsymbol{W}}_l^{({\rm{iter}})} $,AN协方差矩阵
${{\boldsymbol{Z}}^{({\rm{iter}})}} $,以及松弛辅助变量$p_l^{({\rm{iter}})},q_l^{({\rm{iter}})},u_e^{({\rm{iter}})},c_{e,l}^{({\rm{iter}})},c_{e,l}^{({\rm{iter}})} $。步骤3 更新松弛变量$\overline q _l^{({\rm{iter}})} = q_l^{({\rm{iter}})} $, $\overline u _e^{({\rm{iter}})} = u_e^{({\rm{iter}})} $。 步骤4 对${\boldsymbol{W}}_l^{({\rm{iter}})} $进行特征值分解${\boldsymbol{W}}_l^{({\rm{iter}})} = {\boldsymbol{U\varLambda}} {{\boldsymbol{U}}^{\rm{H}}} \$,以获得次优解${\boldsymbol{w}}_l^{({\rm{iter}})} = {\boldsymbol{U}}{{\boldsymbol{\varLambda}} ^{(1/2)}}{\boldsymbol{r}} $, ${\boldsymbol{r}} \sim {\rm{CN}}(0,{\boldsymbol{I}}) $。 步骤5 根据波束向量${\boldsymbol{W}}_l^{({\rm{iter}})} $, AN协方差矩阵${{\boldsymbol{Z}}^{({\rm{iter}})}} $,以及松弛辅助变量$p_l^{({\rm{iter}})},\bar q_l^{({\rm{iter}})},\bar u_e^{({\rm{iter}})},c_{e,l}^{({\rm{iter}})},{F^{({\rm{iter}})}} $。求解系统能效值
${\lambda ^{({\rm{iter} })} } = \displaystyle\sum\limits_l {\frac{ {p_l^{({\rm{iter} })} - q_l^{({\rm{iter} })} - (u_e^{({\rm{iter} })} - c_{e,l}^{({\rm{iter} })})} }{ {(\mu (B) + {P^c}){\rm{ln}}2} } }$,目标函数$E_2^{({\rm{iter}})} $。步骤6 对${{\boldsymbol{F}}^{({\rm{iter}})}} $采用步骤4中的方法来求解${{\boldsymbol{f}}^{({\rm{iter}})}} $。 步骤7 if $\frac{{|E_1^{({\rm{iter}} + 1)} - E_1^{({\rm{iter}})}|}}{{|E_1^{({\rm{iter}})}|}} \le \varepsilon $ and $\frac{ {|E_2^{({\rm{iter}} + 1)} - E_2^{({\rm{iter}})}|} }{ {|E_2^{({\rm{iter}})}|} } \le \varepsilon$ and $\frac{ {|{\lambda ^{({\rm{iter} } + 1)} } - {\lambda ^{({\rm{iter} })} }|} }{ {|{\lambda ^{({\rm{iter} })} }|} } \le\varepsilon$。 break else iter = iter + 1。 end 步骤8 end 步骤9 输出所需要的优化变量${\lambda ^*},{{\boldsymbol{f}}^*},{\boldsymbol{w}}_l^*,{{\boldsymbol{Z}}^*} $。 -
[1] 徐勇军, 刘子腱, 李国权, 等. 基于NOMA的无线携能D2D通信鲁棒能效优化算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1289–1297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200175XU Yongjun, LIU Zijian, LI Guoquan, et al. Robust energy efficiency optimization algorithm for NOMA-based D2D communication with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1289–1297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200175 [2] XU Yongjun, GUI Guan, GACANIN H, et al. A survey on resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous networks: Current research, future trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 668–695. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3059896 [3] 徐勇军, 谷博文, 杨洋, 等. 基于不完美CSI的D2D通信网络鲁棒能效资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2189–2198. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200587XU Yongjun, GU Bowen, YANG Yang, et al. Robust energy-efficient resource allocation algorithm in D2D communication networks with imperfect CSI[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2189–2198. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200587 [4] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107 [5] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Beamforming optimization for wireless network aided by intelligent reflecting surface with discrete phase shifts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(3): 1838–1851. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2958916 [6] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5394–5409. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2936025 [7] WU Qingqing, ZHANG Shuowen, ZHENG Beixiong, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless communications: A tutorial[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(5): 3313–3351. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3051897 [8] ZHOU Fuhui, CHU Zheng, SUN Haijian, et al. Artificial noise aided secure cognitive beamforming for cooperative MISO-NOMA using SWIPT[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(4): 918–931. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2824622 [9] GUI Miao, ZHANG Guangchi, and ZHANG Rui. Secure wireless communication via intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(5): 1410–1414. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2919685 [10] FENG Biqian, WU Yongpeng, and ZHENG Mengfan. Secure transmission strategy for intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless system[C]. 11th International Conference On Wireless Communications and Signal Processing, Xi’an, China, 2019: 1–6. [11] ZHANG Jiayi, DAI Linglong, ZAHNG Xinlin, et al. Achievable rate of rician large-scale MIMO channels with transceiver hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(10): 8800–8806. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2504428 [12] XING Zhe, WANG Rui, WU Jun, et al. Achievable rate analysis and phase shift optimization on intelligent reflecting surface with hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(9): 5514–5530. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3068225 [13] KHANSEFID A, Minn H, Zhan Qi, et al. Waveform parameter design and comparisons for millimeter-wave massive MIMO systems with RF distortions[C]. IEEE Globecom Workshops, Washington, USA, 2016: 1–6. [14] ZHANG Jiayi, XUE Xipeng, BJÖRNSON E, et al. Spectral efficiency of multipair massive MIMO two-way relaying with hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2018, 7(1): 14–17. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2017.2750162 [15] ZHOU Shaoqing, XU Wei, WANG Kezhi, et al. Spectral and energy efficiency of IRS-assisted MISO communication with hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(9): 1366–1369. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2990431 [16] SHEN Hong, XU Wei, GONG Shulei, et al. Beamforming optimization for IRS-aided communications with transceiver hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(2): 1214–1227. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3033575 [17] PAPAZAFEIROPOULOS A, PAN Cunhua, ELBIR A, et al. Asymptotic analysis of max-min weighted SINR for IRS-assisted MISO systems with hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, To be published. [18] YU Xianghao, XU Dongfang, SUN Ying, et al. Robust and secure wireless communications via intelligent reflecting surfaces[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(11): 2637–2652. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3007043 [19] XU Yongjun, XIE Hao, and HU R Q. Max-min beamforming design for heterogeneous networks with hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(4): 1328–1332. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3044936 [20] ZHOU Gui, PAN Cunhua, REN Hong, et al. Secure wireless communication in RIS-aided MISO system with hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(6): 1309–1313. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3064992 [21] DINKELBACH W. On nonlinear fractional programming[J]. Management Science, 1967, 13(7): 492–498. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.13.7.492 -





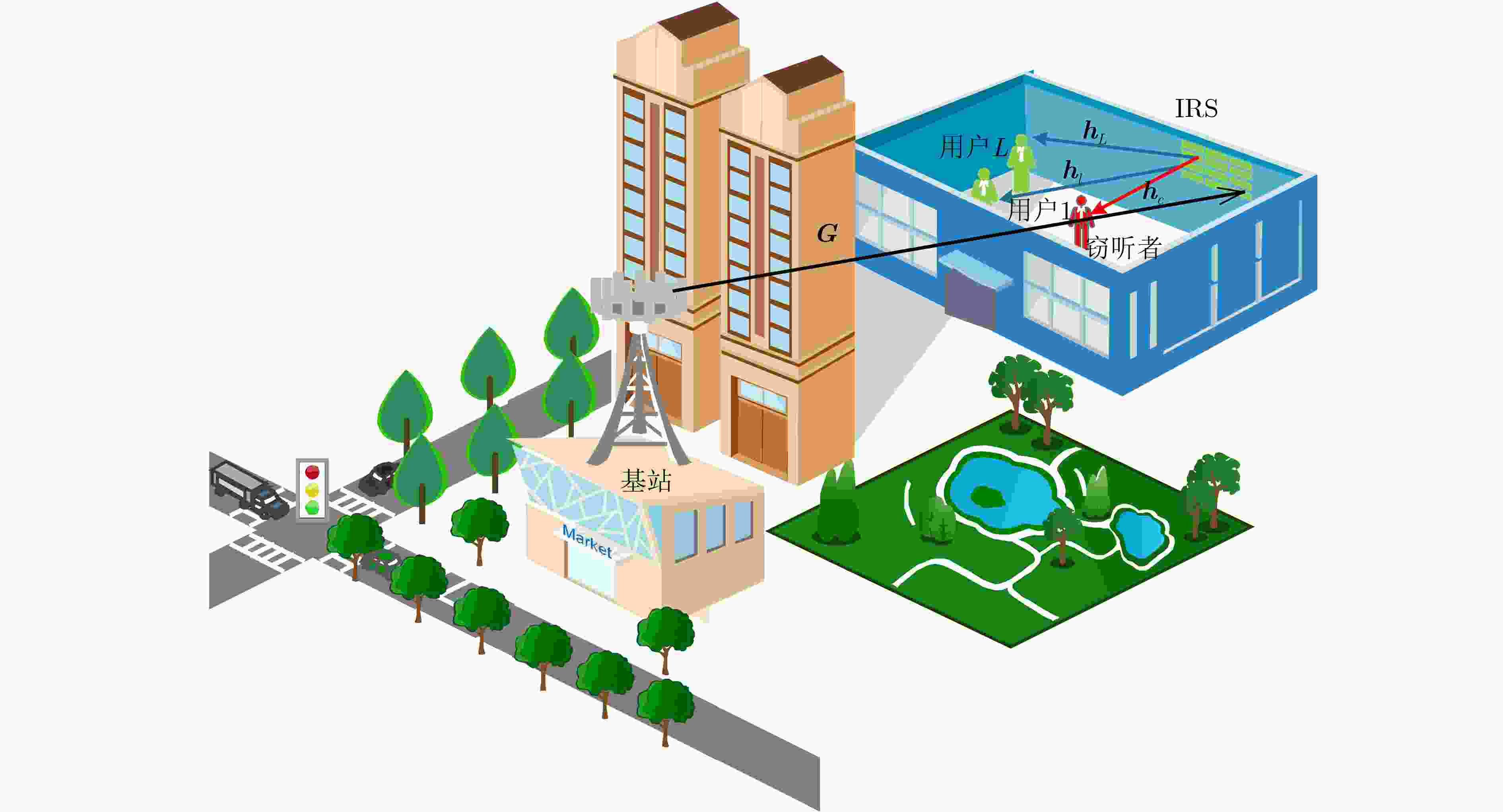
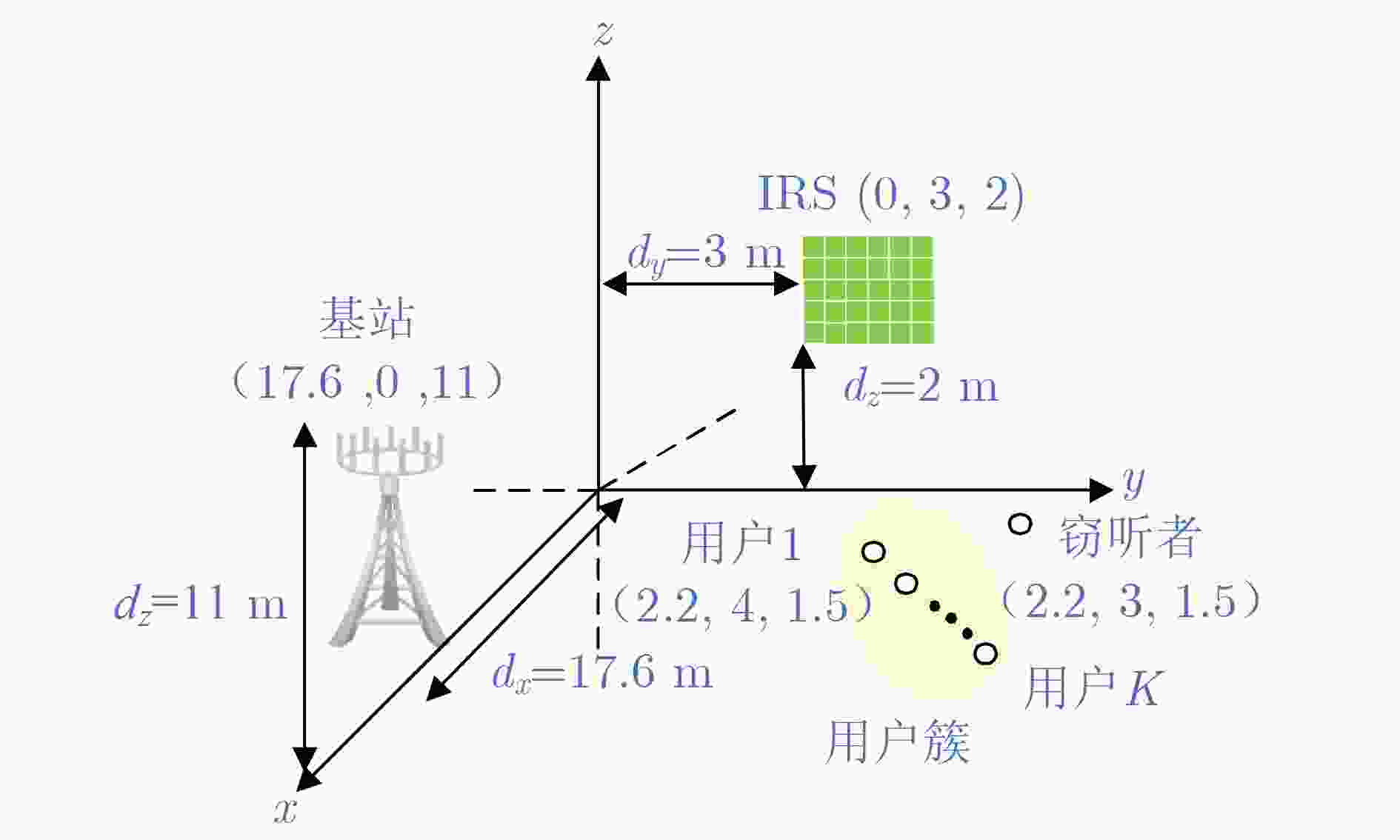
 下载:
下载:
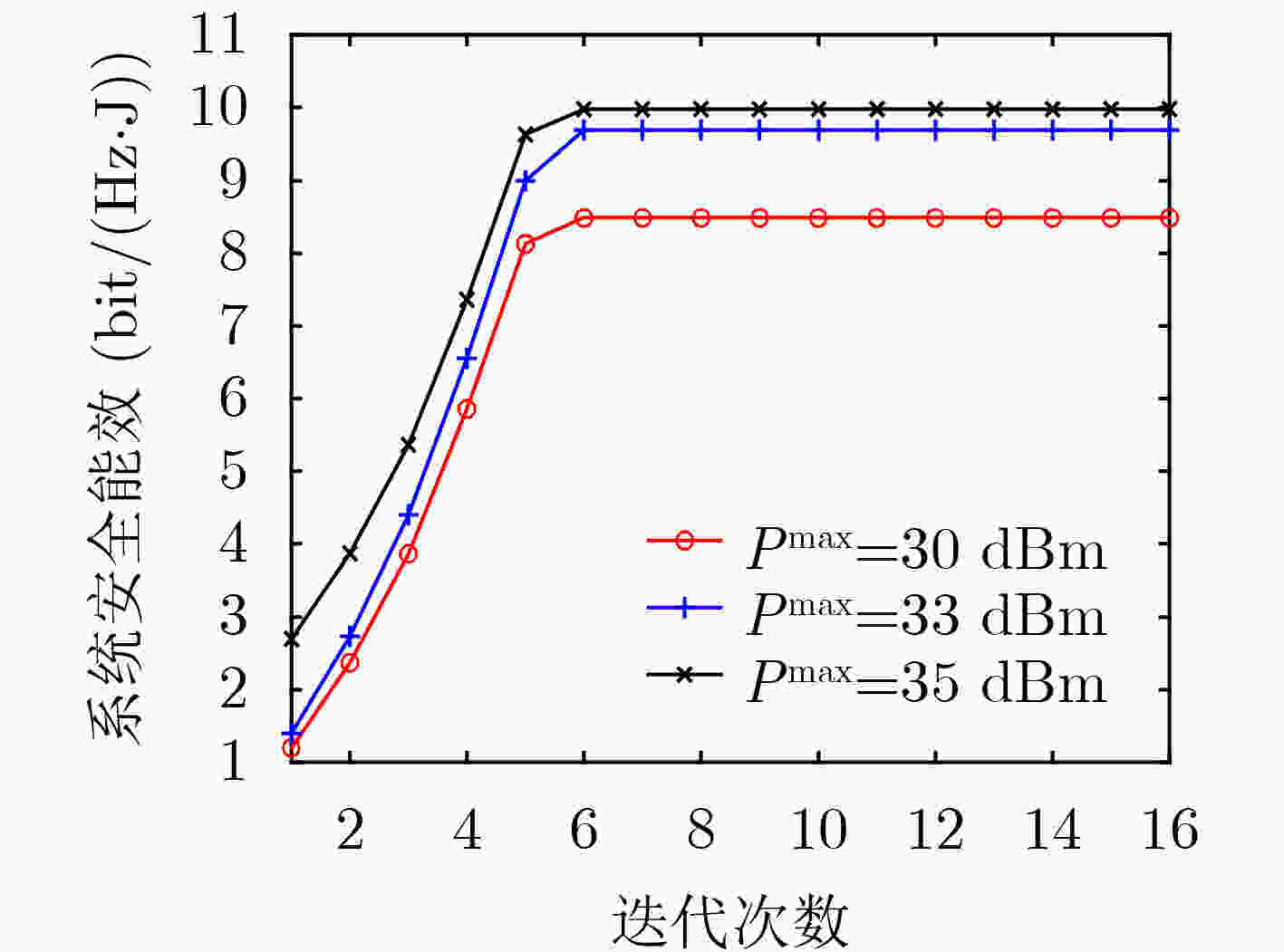
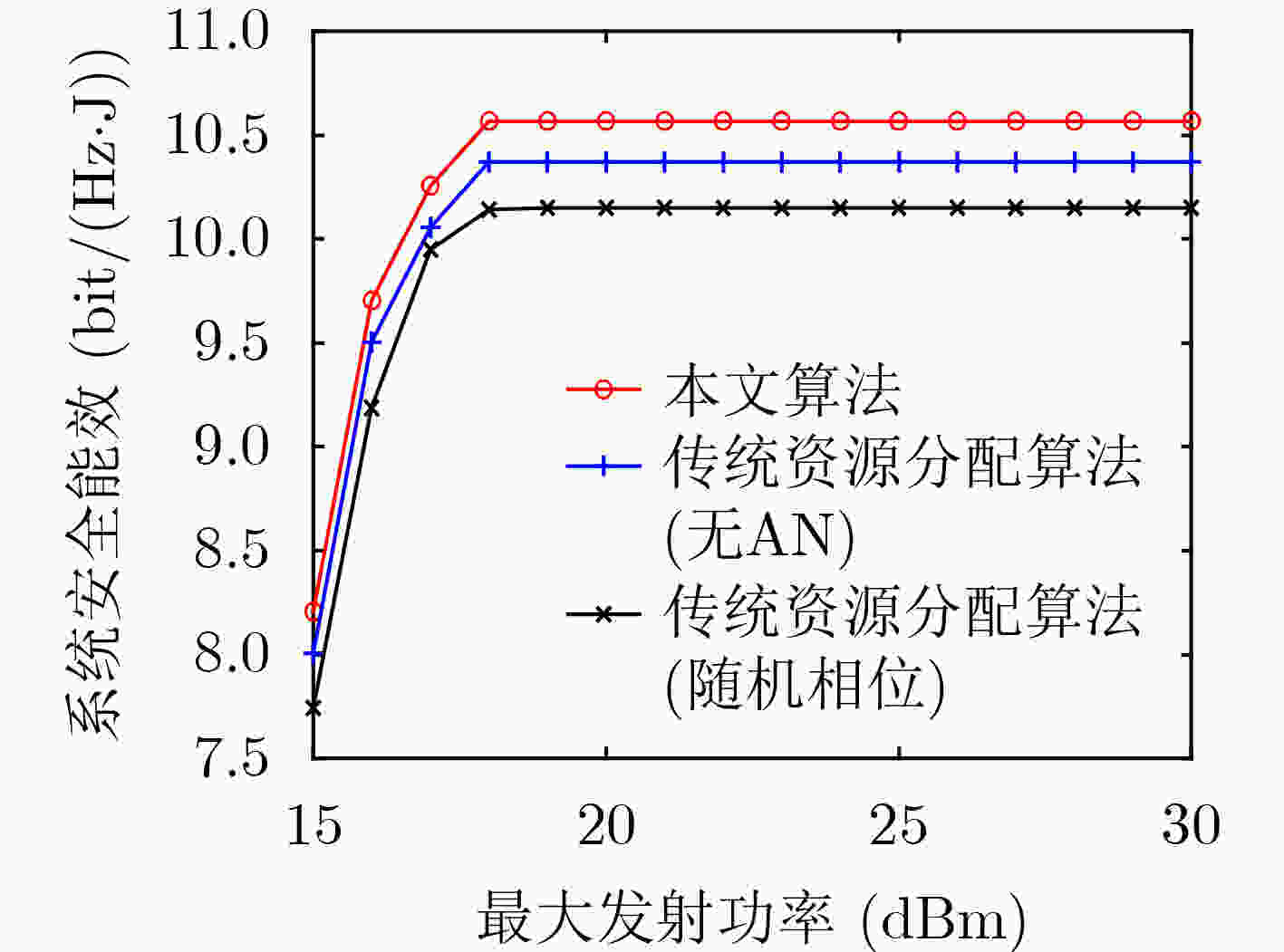



 下载:
下载:
