Vertical Handoff Algorithm Considering Load Balance and User Experience
-
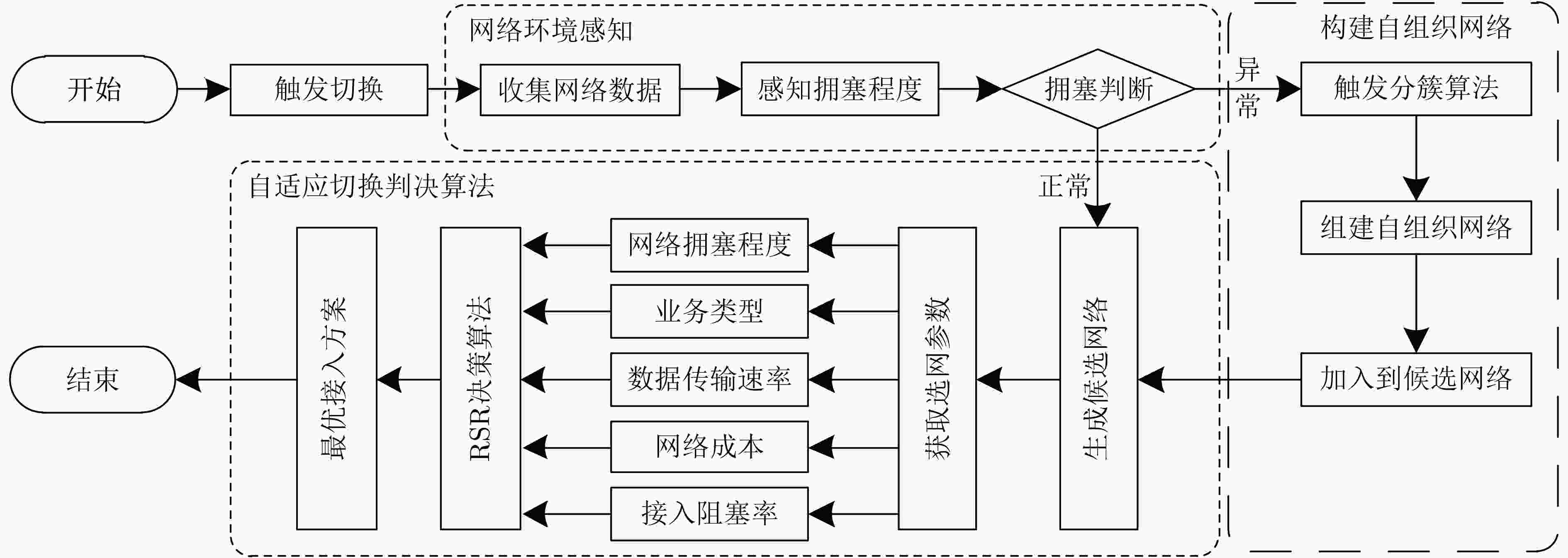
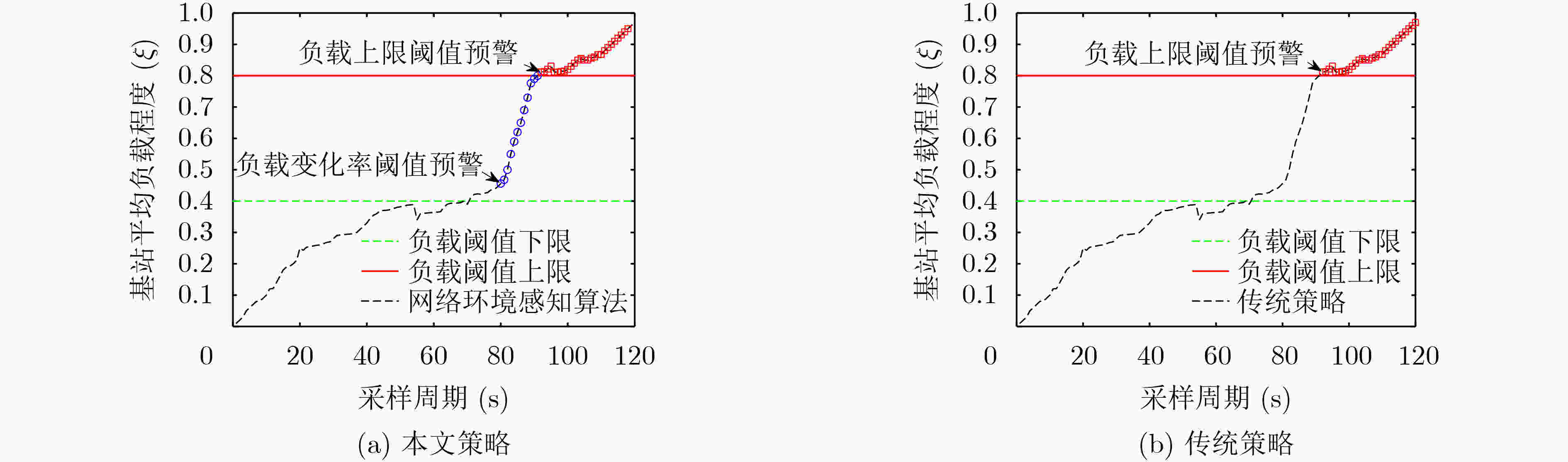
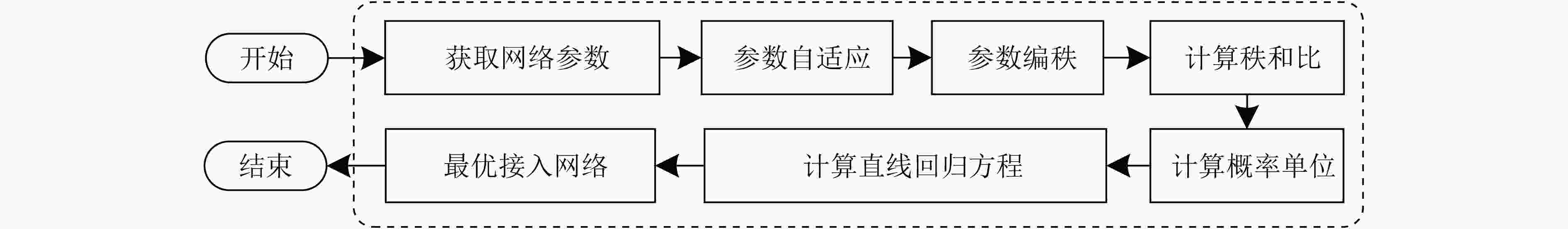
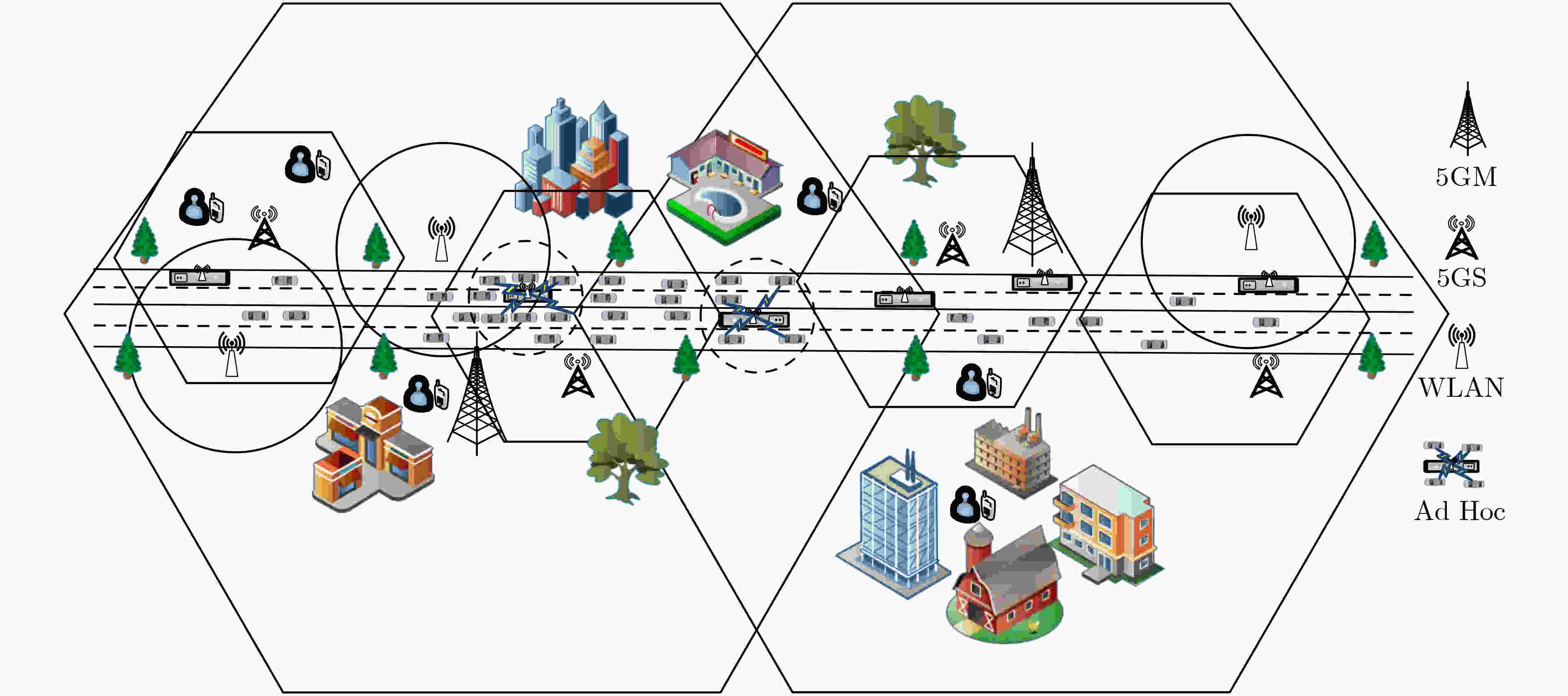
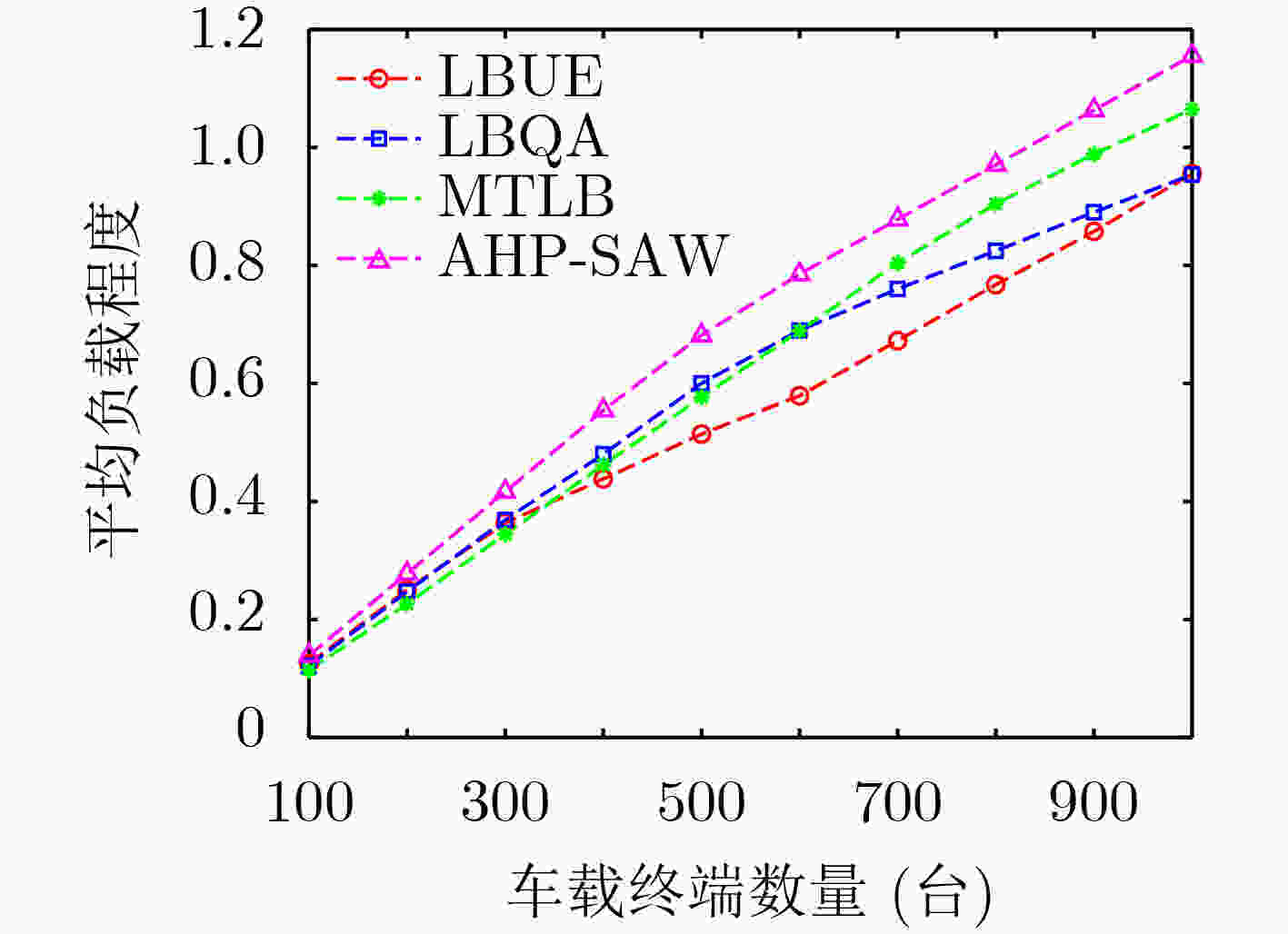
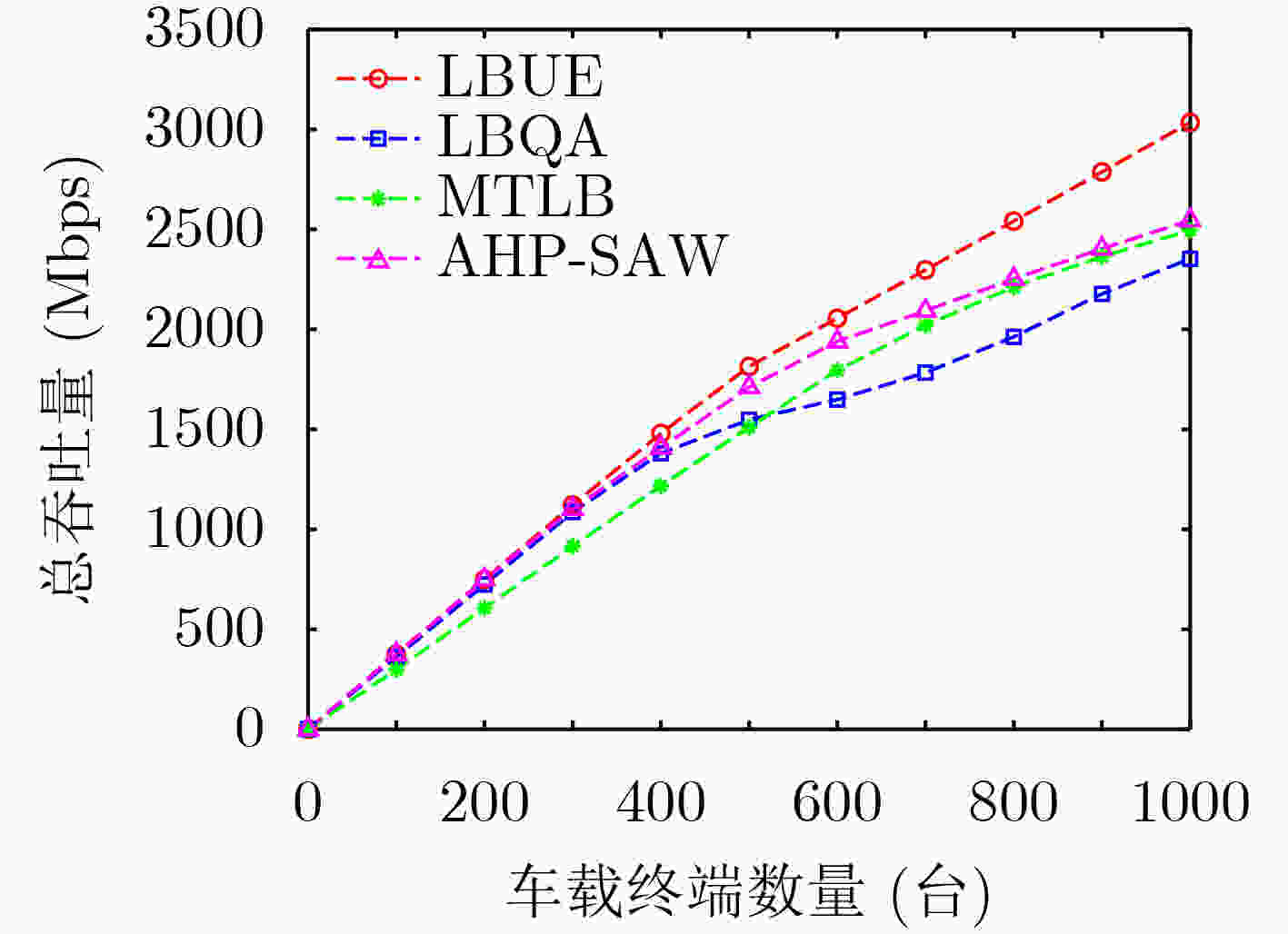
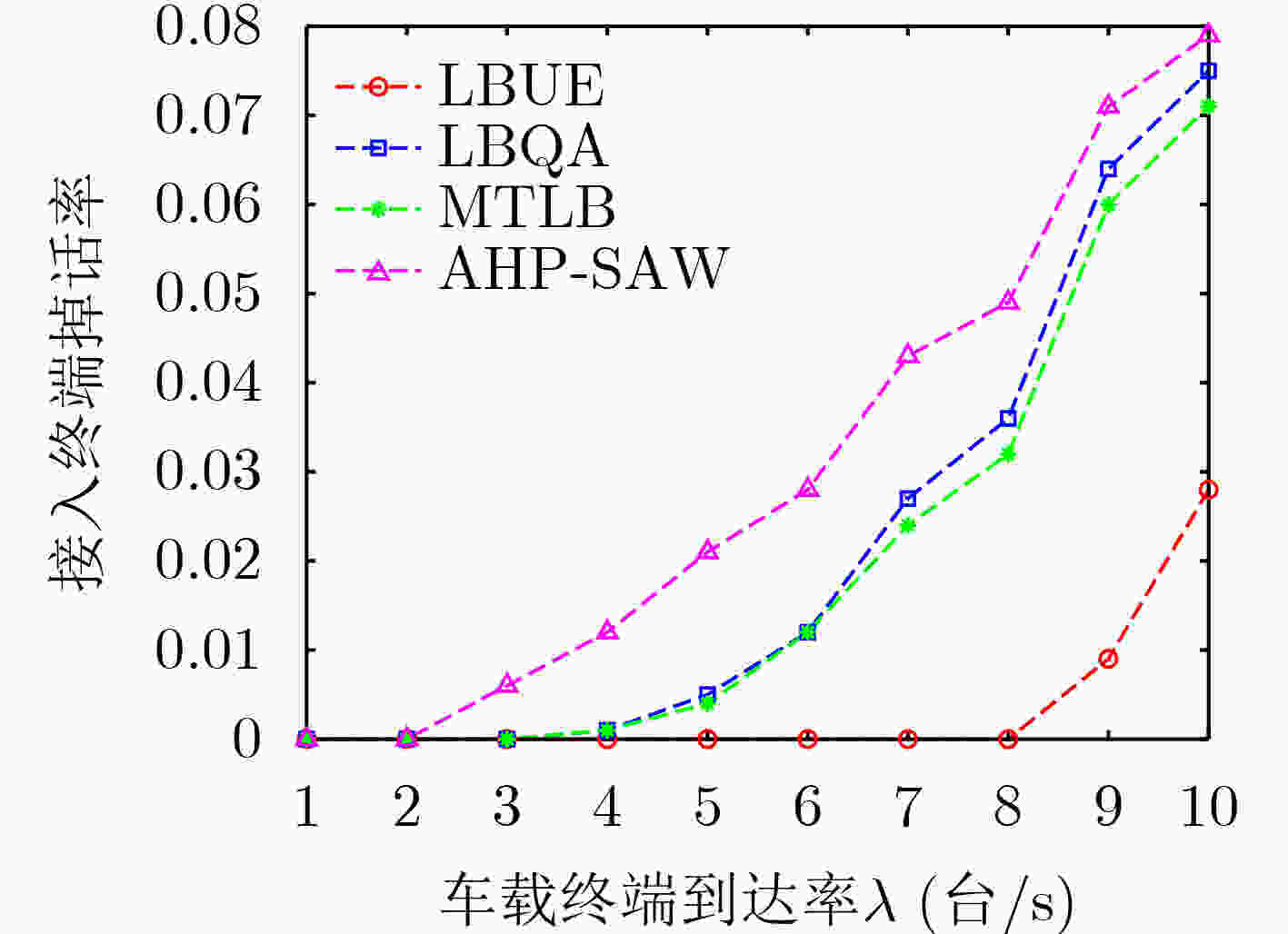
摘要: 在超密集异构无线网络中,针对城区交通高峰期,大规模车载终端短时间聚集性移动引起的网络拥塞问题,该文提出一种考虑负载均衡和用户体验(LBUE)的垂直切换算法。首先,引入网络环境感知模型预测网络未来的拥塞程度,并提出一个融合自组织网络的网络架构,缓解网络拥塞。其次,定义业务适应度和负收益因子,并提出一种基于秩和比(RSR)的自适应切换判决算法,为用户筛选出当前环境下满意度最高的目标网络。实验结果表明,该算法能够有效降低终端接入网络的阻塞率和掉话率,实现网络间负载均衡并提升用户体验。Abstract: In ultra dense heterogeneous wireless networks, a vertical handoff algorithm considering Load Balancing and User Experience (LBUE) is proposed to solve the problem of network congestion caused by large-scale mobile terminals clustering in short time in urban traffic peak. Firstly, the network environment perception model is introduced to predict the future congestion degree of the network, and a network architecture integrating self-organizing network is proposed to alleviate network congestion. Secondly, the business fitness and negative return factor are defined, and an adaptive handoff decision algorithm based on Rank Sum Ratio(RSR) is proposed to screen out the most satisfactory target network for users in the current environment. Experimental results show that the algorithm can effectively reduce the blocking rate and call drop rate of terminal access network, achieve load balancing between networks and improve user experience.
-
表 1 车辆自组织网络分簇算法
输入:簇头集合$ {\text{ch}} $、车载终端集合$ {\text{vt}} $ 输出:各个簇的簇信息表(CIT) 初始化:启动簇头上的无线信号收发器(RT); FOR ∀ h∈ $ {\text{ch}} $ 给每个簇头分配资源$ Rh $,并且簇头广播建簇的hello消息; FOR ∀ i ∈ $ {\text{vt}} $ 按式(5)计算终端i与各个簇头之间的$ \beta $值,终端i向$ \beta $值最大的簇头发送request消息; 该簇头解析出request消息携带的数据,并按照式(6)计算簇的剩余可用资源$ \psi h $; IF ($\xi i \lt \psi h$) 簇头向终端i发送ack消息,允许终端接入簇,并更新簇信息表; ELSE 簇头向终端i发送nack消息,拒绝终端接入簇; END END IF ($\psi h = 0$) 簇饱和,不允许接入新的簇节点; ELSE IF ($\psi h \equiv Rh$) 长时间没有簇节点接入簇,销毁簇,关闭RT; END END 表 2 网络仿真参数
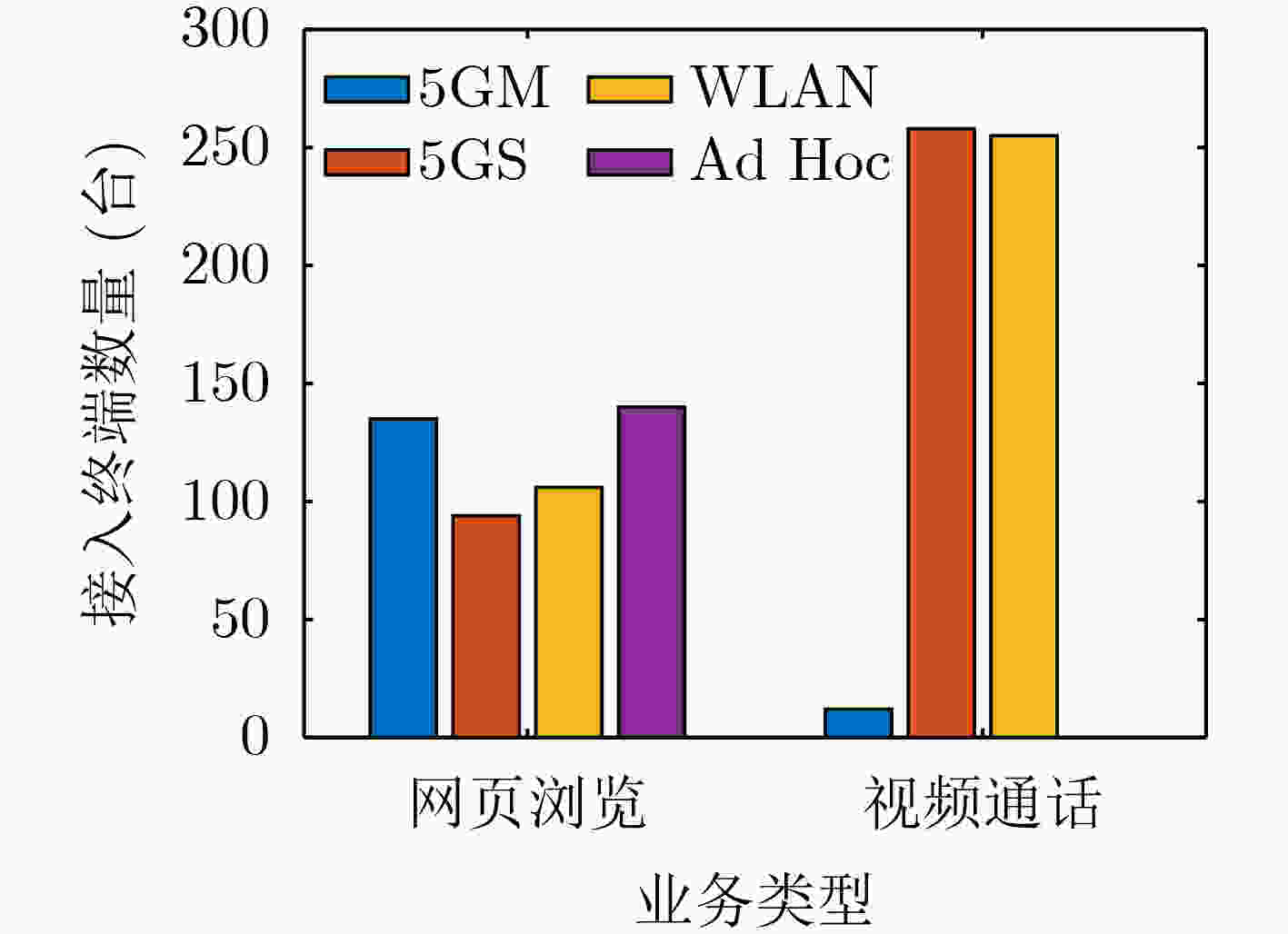
网络
类型发射功率
(dBm)损耗因子
(dBm)覆盖半径
(m)总带宽
(MHz)资源块带宽
(kHz)资源块价格
(元/块)最大容量
(台)5GM 32 46 1000 20 2 0.25 100 5GS 23 56 300 15 2 0.3 20 WLAN 17 58 200 10 2 0.2 15 Ad Hoc 17 58 100 4 2 0 10 其他 网络中的干扰信号强度:I = –130+æ(x),æ(x)为服从参数为(0, σ2)的正态分布,其中σ2为10 dBm。视频通话的
速率需求为300 kbps~2 Mbps,网页浏览的速率需求为20~400 kbps -
[1] CHAHAL M and HARIT S. Network selection and data dissemination in heterogeneous software-defined vehicular network[J]. Computer Networks, 2019, 161: 32–44. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2019.06.008 [2] NDASHIMYE E, RAY S K, SARKAR N I, et al. Vehicle-to-infrastructure communication over multi-tier heterogeneous networks: A survey[J]. Computer Networks, 2017, 112: 144–166. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2016.11.008 [3] ROY S D and REDDY S R V. Signal strength ratio based vertical handoff decision algorithms in integrated heterogeneous networks[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2014, 77(4): 2565–2585. doi: 10.1007/s11277-014-1655-9 [4] HAIDER A, GONDAL I, and KAMRUZZAMAN J. Dynamic dwell timer for hybrid vertical handover in 4G coupled networks[C]. The 73rd Vehicular Technology Conference, Budapest, Hungary, 2011: 1–5. [5] KUNARAK S and SULEESATHIRA R. Multi-criteria vertical handoff decision algorithm for overlaid heterogeneous mobile IP networks[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2020, 357(10): 6321–6351. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2020.03.025 [6] PALAS R, ISLAM R, ROY P, et al. Multi-criteria handover mobility management in 5G cellular network[J]. Computer Communications, 2021, 174: 81–91. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2021.04.020 [7] 马彬, 李尚儒, 谢显中. 异构无线网络中基于模糊逻辑的分级垂直切换算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 629–636. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190190MA Bin, LI Shangru, and XIE Xianzhong. A hierarchical vertical handover algorithm based on fuzzy logic in heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 629–636. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190190 [8] ZHU Anqi, GUO Songtao, LIU Bei, et al. Adaptive multiservice heterogeneous network selection scheme in mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(4): 6862–6875. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2912155 [9] ZINEB A B, AYADI M, and TABBANE S. QoE-based vertical handover decision management for cognitive networks using ANN[C]. The Sixth International Conference on Communications and Networking, Hammamet, Tunisia, 2017: 1–7. [10] LIANG Gen, YU Hewei, GUO Xiaoxue, et al. Joint access selection and bandwidth allocation algorithm supporting user requirements and preferences in heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 23914–23929. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2899405 [11] MOLLEL M S, ABUBAKAR A I, OZTURK M, et al. Intelligent handover decision scheme using double deep reinforcement learning[J]. Physical Communication, 2020, 42: 101133. doi: 10.1016/j.phycom.2020.101133 [12] YANG Feng, WU Wenjun, WANG Xiaoxi, et al. Deep reinforcement learning based handoff algorithm in end-to-end network slicing enabling HetNets[C]. 2021 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Nanjing, China, 2021: 1–7. [13] 朱豪, 彭艺, 张申, 等. 基于改进遗传算法的自适应越区切换方案[J]. 吉林大学学报:理学版, 2020, 58(1): 133–139. doi: 10.13413/j.cnki.jdxblxb.2019151ZHU Hao, PENG Yi, ZHANG Shen, et al. Adaptive handover scheme based on improved genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Science Edition, 2020, 58(1): 133–139. doi: 10.13413/j.cnki.jdxblxb.2019151 [14] AI Ning, WU Bin, LI Boyu, et al. 5G heterogeneous network selection and resource allocation optimization based on cuckoo search algorithm[J]. Computer Communications, 2021, 168: 170–177. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2020.12.026 [15] ABDULSHAKOOR A I, ANANY M G, and ELMESALAWY M M. Outage-aware matching game approach for cell selection in LTE/WLAN Multi-RAT HetNets[J]. Computer Networks, 2020, 183: 107596. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2020.107596 [16] ALHABO M, ZHANG Li, NAWAZ N, et al. Game theoretic handover optimisation for dense small cells heterogeneous networks[J]. IET Communications, 2019, 13(15): 2395–2402. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2019.0383 [17] WU Xiaoyan and DU Qinghe. Utility-function-based radio-access-technology selection for heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2016, 52: 171–182. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2015.06.010 [18] HAN Shen. Congestion-aware WiFi offload algorithm for 5G heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. Computer Communications, 2020, 164: 69–76. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2020.10.006 [19] FENG Bing, ZHANG Chi, LIU Jianqing, et al. D2D communications-assisted traffic offloading in integrated cellular-WiFi networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(5): 8670–8680. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2922550 [20] HASAN M and KWON S. Cluster-based load balancing algorithm for ultra-dense heterogeneous networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 8: 2153–2162. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2961949 [21] ZHANG Qi, XU Xiaodong, ZHANG Jingxuan, et al. Dynamic load adjustments for small cells in heterogeneous ultra-dense networks[C]. 2020 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Seoul, Korea (South), 2020: 1–6. [22] 潘甦, 张磊, 刘胜美. 基于未来负载预测的无线异构网络自适应负载均衡算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(6): 1384–1390. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.06.24PAN Su, ZHANG Lei, and LIU Shengmei. Adaptive load balancing algorithm based on future load predicting[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(6): 1384–1390. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2015.06.24 [23] 张振浩, 梁俊, 肖楠, 等. 空天异构网络中基于Q学习的切换判决优化算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2018, 44(5): 296–302,308. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0047111ZHANG Zhenhao, LIANG Jun, XIAO Nan, et al. Handoff decision optimized algorithm based on Q-learning approach for heterogeneous networks in aerospace[J]. Computer Engineering, 2018, 44(5): 296–302,308. doi: 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0047111 [24] WANG Lingxia, YANG Chungang, and HU R Q. Autonomous traffic offloading in heterogeneous ultra-dense networks using machine learning[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2019, 26(4): 102–109. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2019.1800034 [25] 肖清华. 基于负载匹配的LTE切换算法[J]. 邮电设计技术, 2017(6): 32–35. doi: 10.12045/j.issn.1007-3043.2017.06.007XIAO Qinghua. LTE handover algorithm based on matched cell load[J]. Designing Techniques of Posts and Telecommunications, 2017(6): 32–35. doi: 10.12045/j.issn.1007-3043.2017.06.007 [26] 马彬, 毛步绚, 谢显中. 自组织异构网络中降低阻塞的垂直切换算法[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2019, 42(2): 19–24. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2018-145MA Bin, MAO Buxuan, and XIE Xianzhong. Vertical handoff algorithm for reducing congestion in ad hoc heterogeneous network[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019, 42(2): 19–24. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2018-145 [27] JANGSHER S and LI V O K. Backhaul resource allocation for existing and newly arrived moving small cells[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(4): 3211–3219. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2590502 [28] 付学谦, 陈皓勇. 基于加权秩和比法的电能质量综合评估[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2015, 35(1): 128–132. doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2015.01.019FU Xueqian and CHEN Haoyong. Comprehensive power quality evaluation based on weighted rank sum ration method[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2015, 35(1): 128–132. doi: 10.16081/j.issn.1006-6047.2015.01.019 [29] YU Hewei and ZHANG Biao. A heterogeneous network selection algorithm based on network attribute and user preference[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2018, 72: 68–80. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2018.01.011 [30] BHOSALE S and DARUWALA R. Multi-criteria vertical handoff decision algorithm using hierarchy modeling and additive weighting in an integrated WiFi/WiMAX/UMTS environment– a case study[J]. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems, 2014, 8(1): 35–57. doi: 10.3837/tiis.2014.01.003 [31] HUANG Zhangpeng, LIU Jing, SHEN Qiang, et al. A threshold-based multi-traffic load balance mechanism in LTE-A networks[C]. 2015 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), New Orleans, USA, 2015: 1273–1278. [32] ALJERI N and BOUKERCHE A. Load balancing and QoS-aware network selection scheme in heterogeneous vehicular networks[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. -





 下载:
下载:

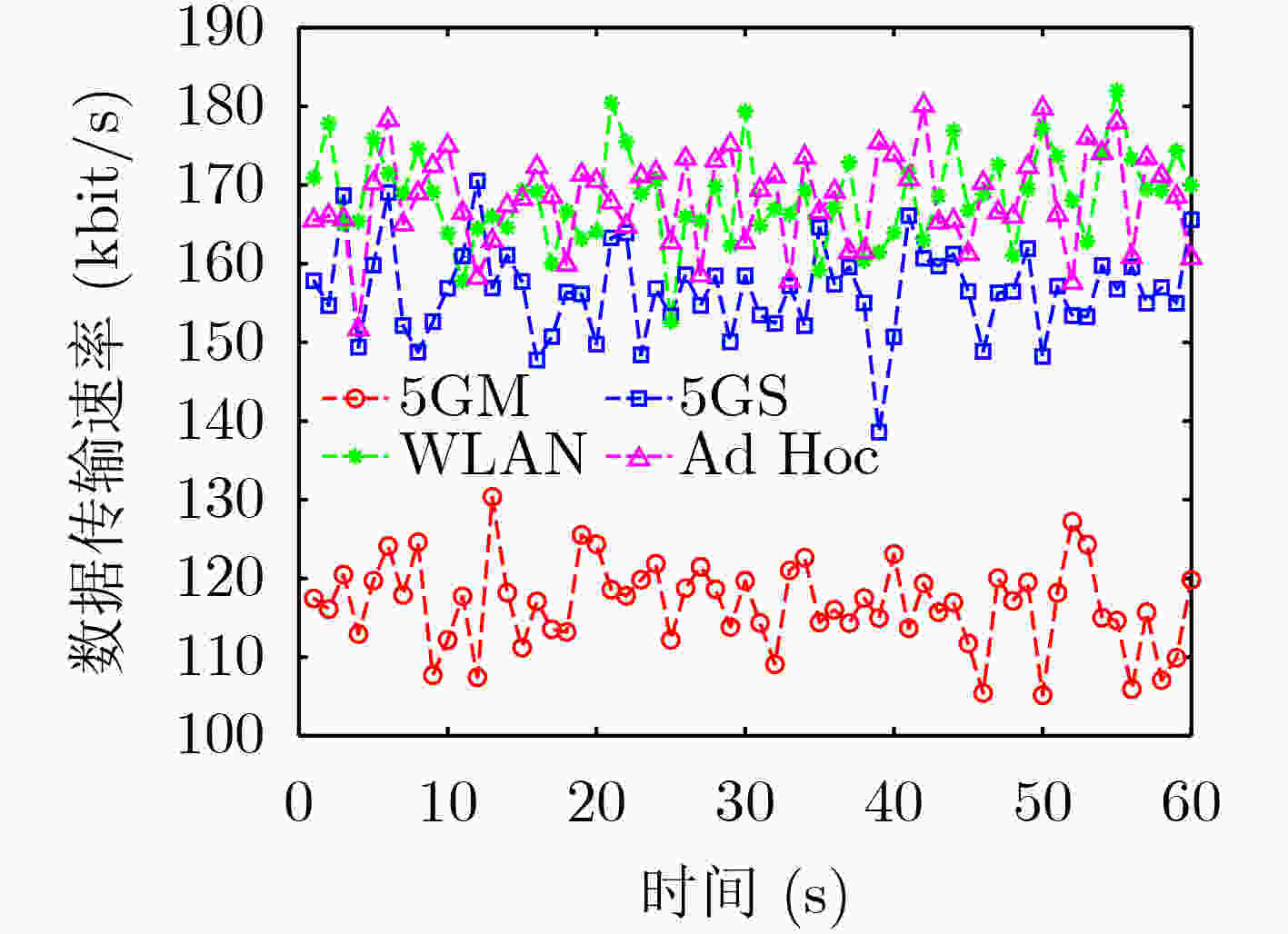
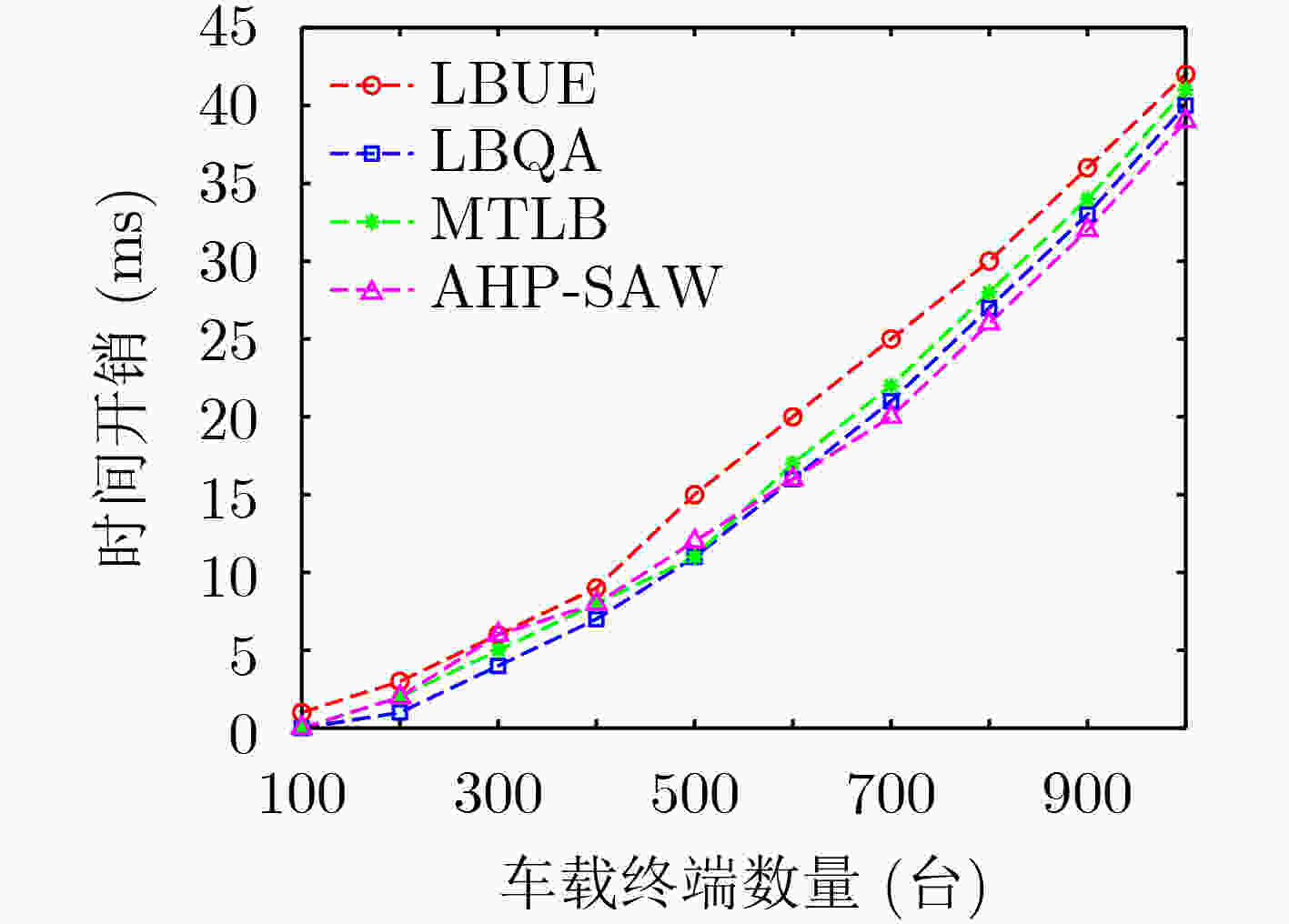
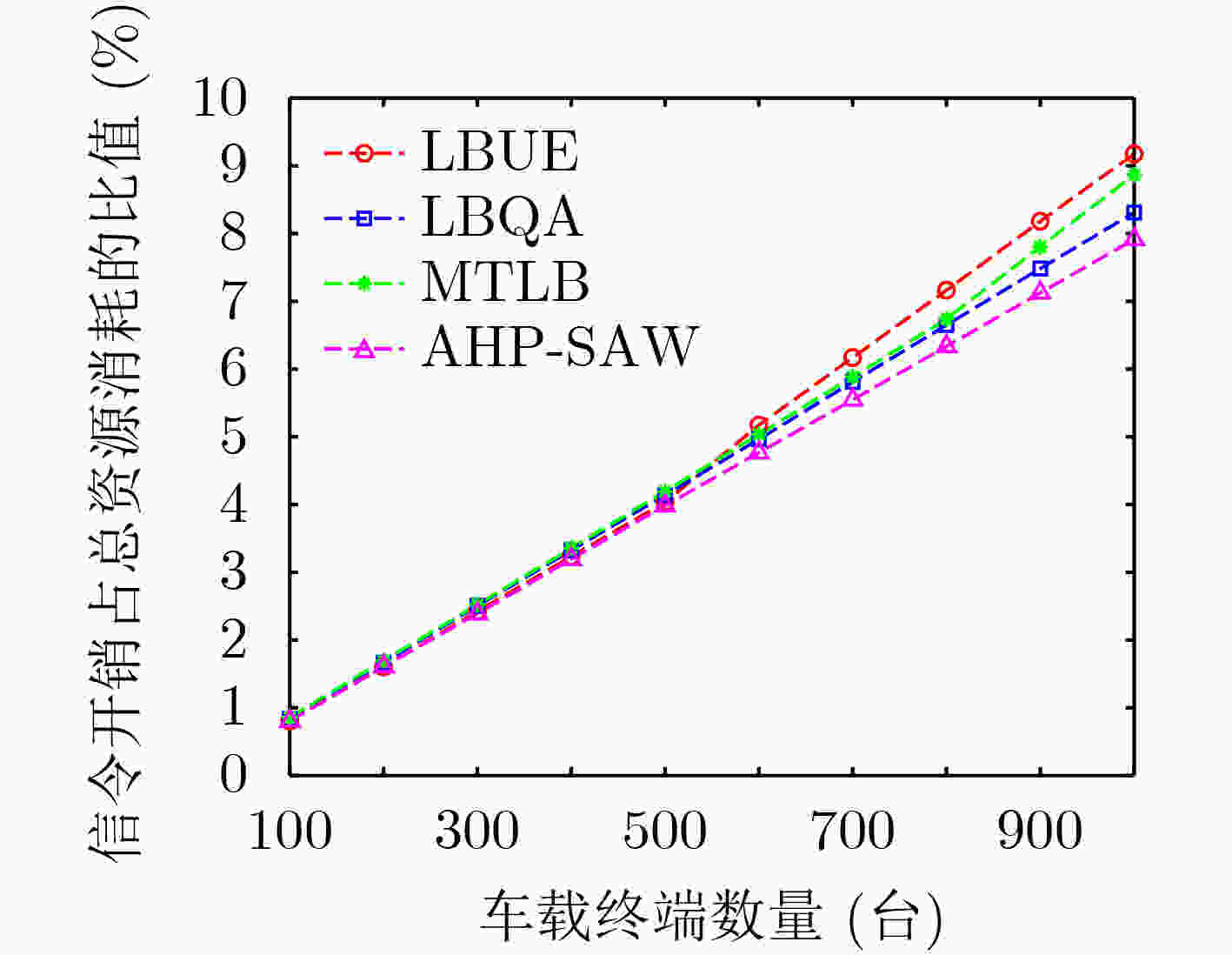


 下载:
下载:
