TCM Tongue Color Classification Method under Noisy Labeling
-
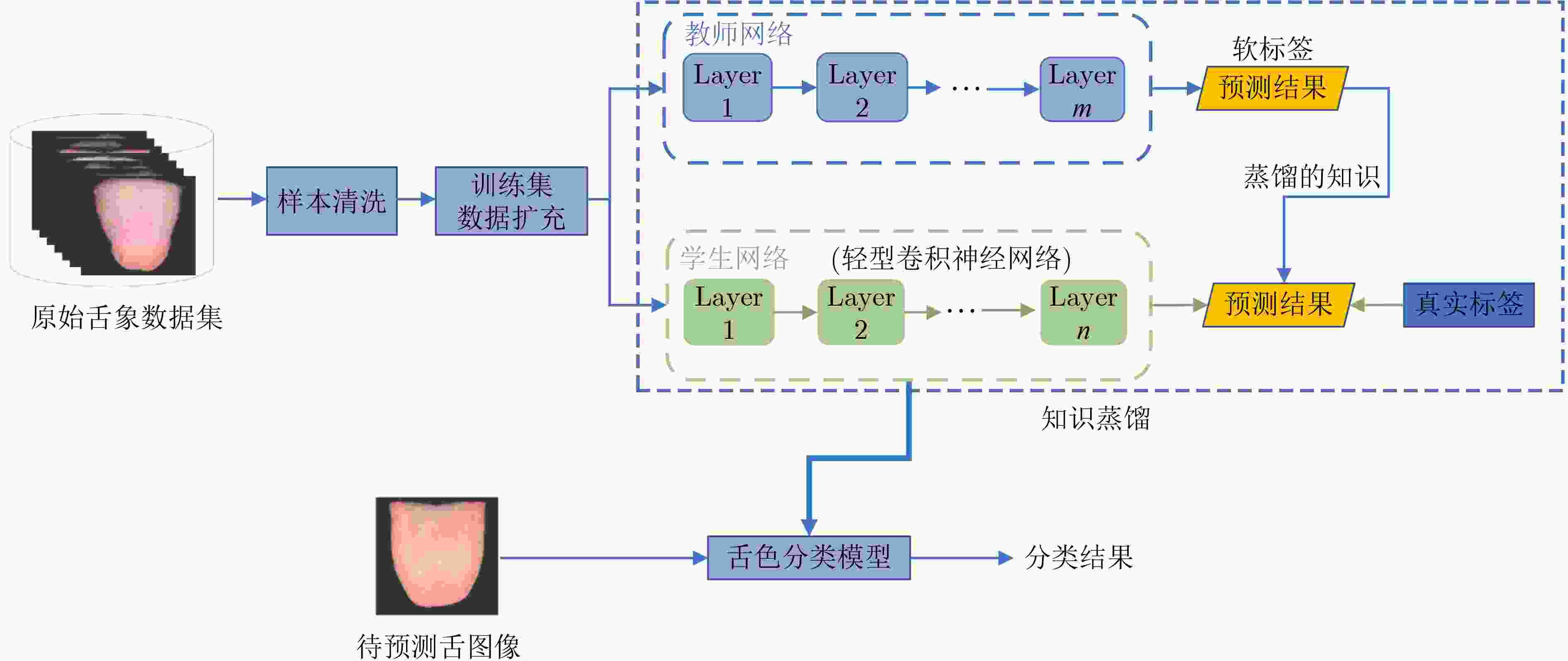
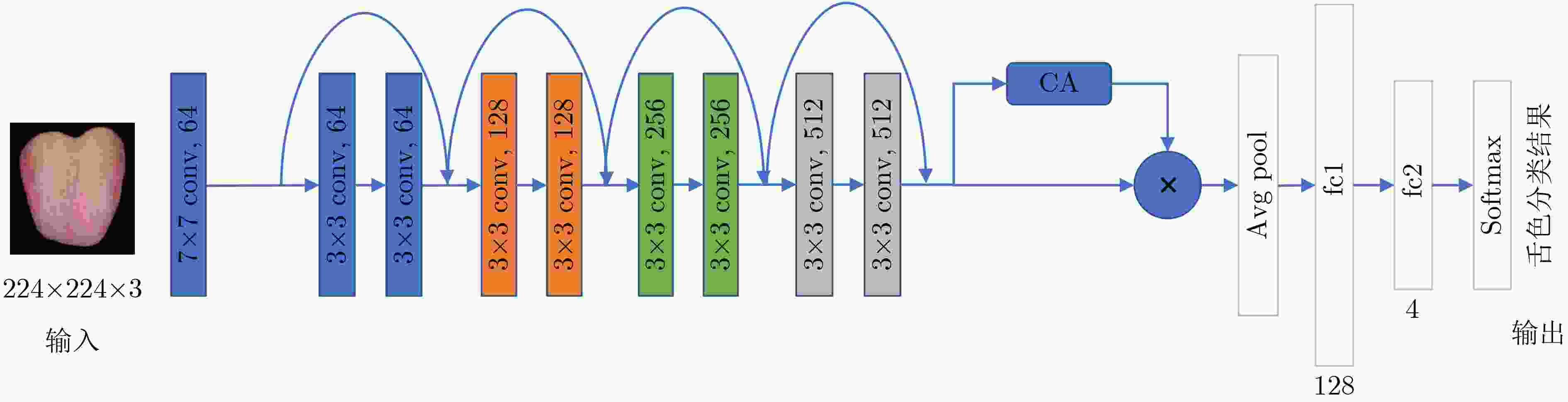
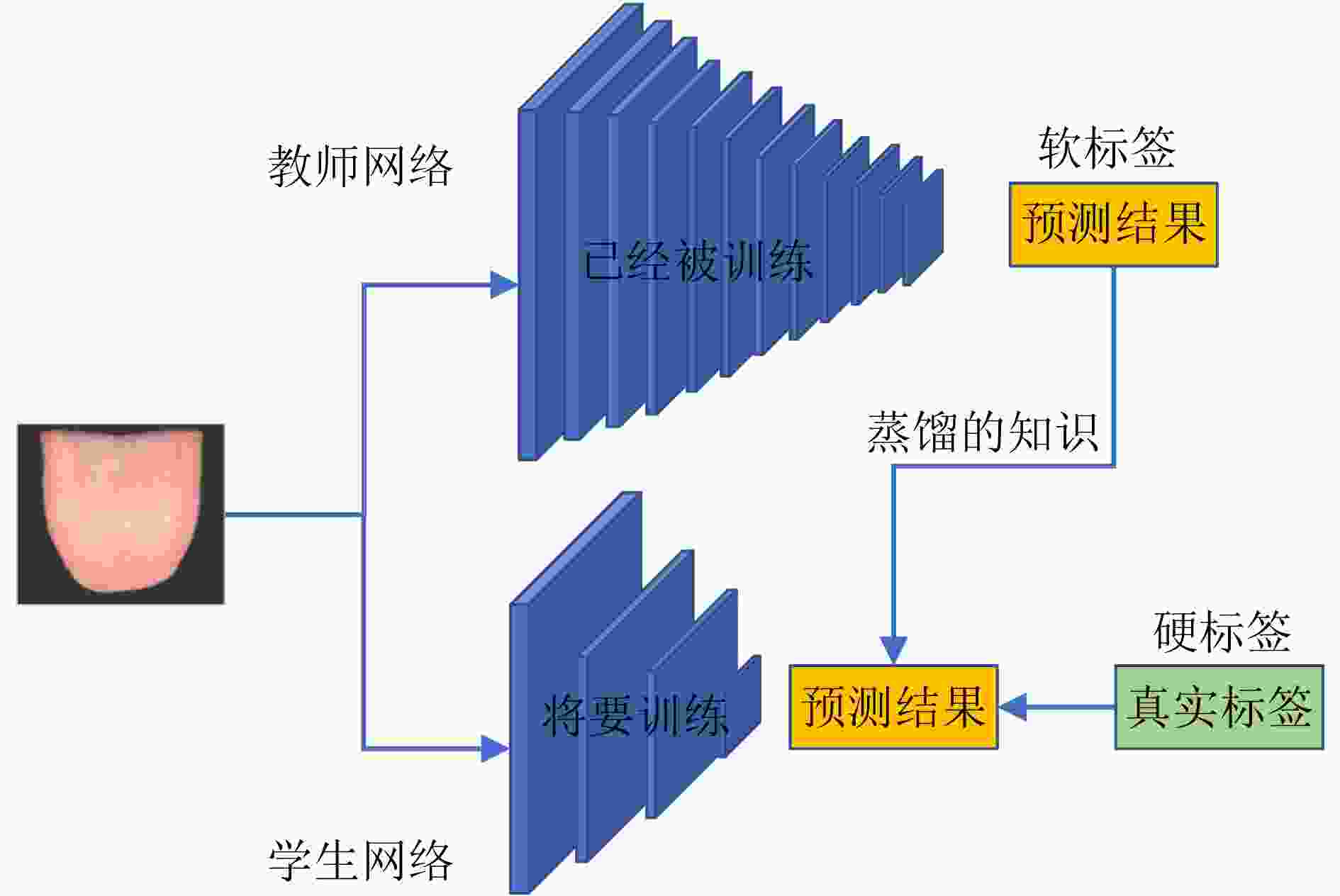
摘要: 舌色是中医(TCM)望诊最关注的诊察特征之一,自动准确的舌色分类是舌诊客观化研究的重要内容。由于不同类别舌色之间的视觉界限存在模糊性以及医生标注者的主观性等,标注的舌象数据中常含有噪声,影响舌色分类模型的训练。为此,该文提出一种有噪声标注情况下的中医舌色分类方法:首先,提出一种两阶段的数据清洗方法,对含有噪声的标注样本进行识别,并进行清洗;其次,设计一种基于通道注意力机制的轻型卷积神经网络,通过增强特征的表达能力,实现舌色的准确分类;最后,提出一种带有噪声样本过滤机制的知识蒸馏策略,该策略中加入了由教师网络主导的噪声样本过滤机制,进一步剔除噪声样本,同时利用教师网络指导轻型卷积神经网络的训练,提升了分类性能。在自建的中医舌色分类数据集上的实验结果表明,该文提出的舌色分类方法能以较低的计算复杂度,显著提升分类的准确率,达到了93.88%。Abstract: Tongue color is one of the most concerned diagnostic features of tongue diagnosis in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Automatic and accurate tongue color classification is an important content of the objectification of tongue diagnosis. Due to the vagueness of the visual boundaries between different types of tongue colors and the subjectivity of the doctors, the annotated tongue image data samples often contain noises, which has a negative effect on the training of the tongue color classification model. Therefore, in this paper, a tongue color classification method in TCM with noisy labels is proposed. Firstly, a two-stage data cleaning method is proposed to identify and clean noisy labeled samples. Secondly, a lightweight Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) based on the channel attention mechanism is designed in this paper to achieve accurate classification of tongue color by enhancing the expressiveness of features. Finally, a knowledge distillation strategy with a noise sample filtering mechanism is proposed. This strategy adds a noise sample filtering mechanism led by the teacher network to eliminate further noise samples. At the same time, the teacher network is used to guide the training of the light convolutional neural network to improve the classification performance.The experimental results on the self-established TCM tongue color classification dataset show that the proposed method in this paper can significantly improve the classification accuracy with lower computational complexity, reaching 93.88%.
-
表 1 有噪声标准舌图像的数据清洗流程
输入: 原始数据集${D_o} = \{ ({x_1},{y_1}),({x_2},{y_2}) \cdots ({x_n},{y_n})\}$; 准确率阈值${\text{Ac} }{ {\text{c} }_{{\rm{th}}} } = 0.9$; 变量$ a = 0 $; 过程: 第1阶段: (1) 将${D_{\rm{o}}}$按照4:1随机划分为训练集和测试集; ${D_{ {\text{train} } } } = \{ ({x_{r + 1} },{y_{r + 1} }),({x_{r + 2} },{y_{r + 2} }), \cdots, ({x_{r + {\text{len} }({D_{ {\text{train} } } })} },{y_{r + {\text{len} }({D_{ {\text{train} } } })} })\}$ ${D_{ {\text{test} } } } = \{ ({x_{e + 1} },{y_{e + 1} }),({x_{e + 2} },{y_{e + 2} }) ,\cdots , ({x_{e + {\text{len} }({D_{ {\text{test} } } })} },{y_{e + {\text{len} }({D_{ {\text{test} } } })} })\}$ (2) 用$ {D_{{\text{train}}}} $训练ResNet18网络; (3) 用训练好的ResNet18模型对$ {D_{{\text{test}}}} $中样本进行预测得到
$\hat y = ({\hat y_{e + 1} }\; \cdots \;{\hat y_{e + {\text{len} }({D_{ {\text{test} } } })} })$;(4) for i in range ($ {\text{len}}({D_{{\text{test}}}}) $): if $ {\hat y_{e + i}}! = y{}_{e + i} $: $ {D_{{\text{test}}}} $.remove($ {x_{e + i}} $) ; $ {D_{{\text{detele}}}} $add($ {x_{e + i}} $) ; // 将删除的数据放在一起组成$ {D_{{\text{detele}}}} $ $ {\text{Acc}} = {\text{len}}({D_{{\text{test}}}})/({\text{len}}({D_{{\text{test}}}}) + {\text{len}}({D_{{\text{detele}}}}) - a) $; $ a = a + {\text{len}}({D_{{\text{detele}}}}) $; (5) while ${\text{Acc} } \le {\text{Ac} }{ {\text{c} }_{ {\text{th} } } }$ do $ {D_{{\text{onew}}}} \leftarrow {D_{{\text{train}}}} + {D_{{\text{test}}}} $;// 将去除噪声样本的
$ {D_{{\text{train}}}} $与$ {D_{{\text{test}}}} $组合形成$ {D_{{\text{onew}}}} $将步骤(1)中的${D_{\rm{o}}}$换成$ {D_{{\text{onew}}}} $,repeat 步骤(1)—步骤
(4)操作;end while 第2阶段: (6) 将最终的$ {D_{{\text{onew}}}} $训练ResNet18和VGG16; (7) 利用各个网络训练的最优网络模型对$ {D_{{\text{detele}}}} $中的样本进行
预测得到:$ {\hat y_r} = ({\hat y_{r + 1}},{\hat y_{r + 2}}, \cdots ,{\hat y_{r + {\text{len}}({D_{{\text{detele}}}})}}) $ // ResNet18模
型的预测值$ {\hat y_v} = ({\hat y_{v + 1}},{\hat y_{v + 2}}, \cdots ,{\hat y_{v + {\text{len}}({D_{{\text{detele}}}})}}) $ // VGG16模型
预测值for i in range ($ {\text{len}}({D_{{\text{detele}}}}) $): if $ {\hat y_{r + i}} = = {\hat y_{v + i}} $: // 当三者一致时,将预测结果作
为样本新的标注$ {y_i} = {\hat y_{v + i}} $ $ {D_{{\text{onew}}}} $.add($ {x_{r + i}} $) 输出:经过清洗后的舌象数据$ {D_{{\text{onew}}}} $ 表 2 噪声样本过滤流程
输入:训练集$ {D_t} = \{ ({x_1},{y_1}),({x_2},{y_2}), \cdots ,({x_n},{y_n})\} $; 教师网络$ {\text{Mode}}{{\text{l}}_t} $和已经训练好的模型参数$ \theta $以及损失函数
Loss;remember_rate=0.95; 单次送入网络的样本数量为batch_size; 过程: (1) 将训练集中的样本按照batch_size大小送入教师网络中; (2) 利用教师网络$ {\text{Mode}}{{\text{l}}_t} $和训练好的模型参数$ \theta $得到batch_size个
样本的预测结果;(3) 利用损失函数Loss计算样本的损失值,将batch_size个样本
的损失值按照升序方式排序;(4) 设置remember_rate将样本按照排序的结果保留前
batch_size×remember_rate个样本,清除掉剩余的样本;(5) 将步骤(4)保留的样本更新送入学生网络样本。 输出:干净的数据样本,并将数据送入学生网络 表 3 数据清洗前后分类准确率(%)对比结果
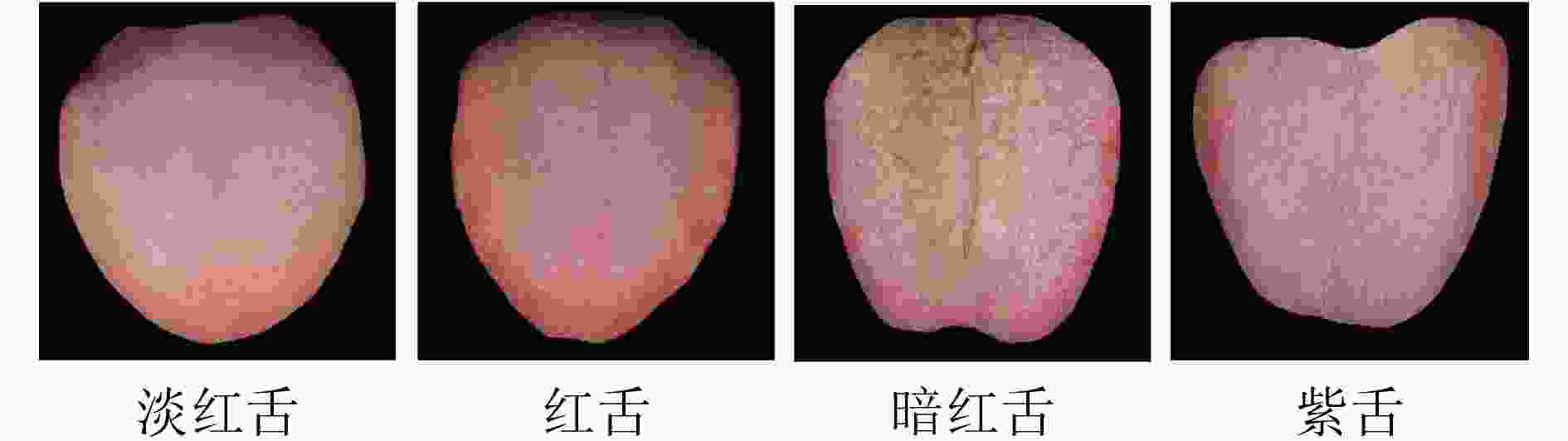
淡红舌 红舌 暗红舌 紫舌 整体精度 清洗前 75 76.92 91.30 88.89 82.34 清洗后 88 88.46 95.65 100 91.81 表 4 各种CNN网络结构的参数量(MB)
AlexNet VGG16 ResNet18 MobileNet V2 轻型CNN网络 参数量 61.1 138.4 11.2 4.2 5.2 表 5 采用知识蒸馏前后的对比实验结果
教师网络 学生网络 名称 精度 参数量(MB) 名称 精度 参数量(MB) × × × 轻型卷积
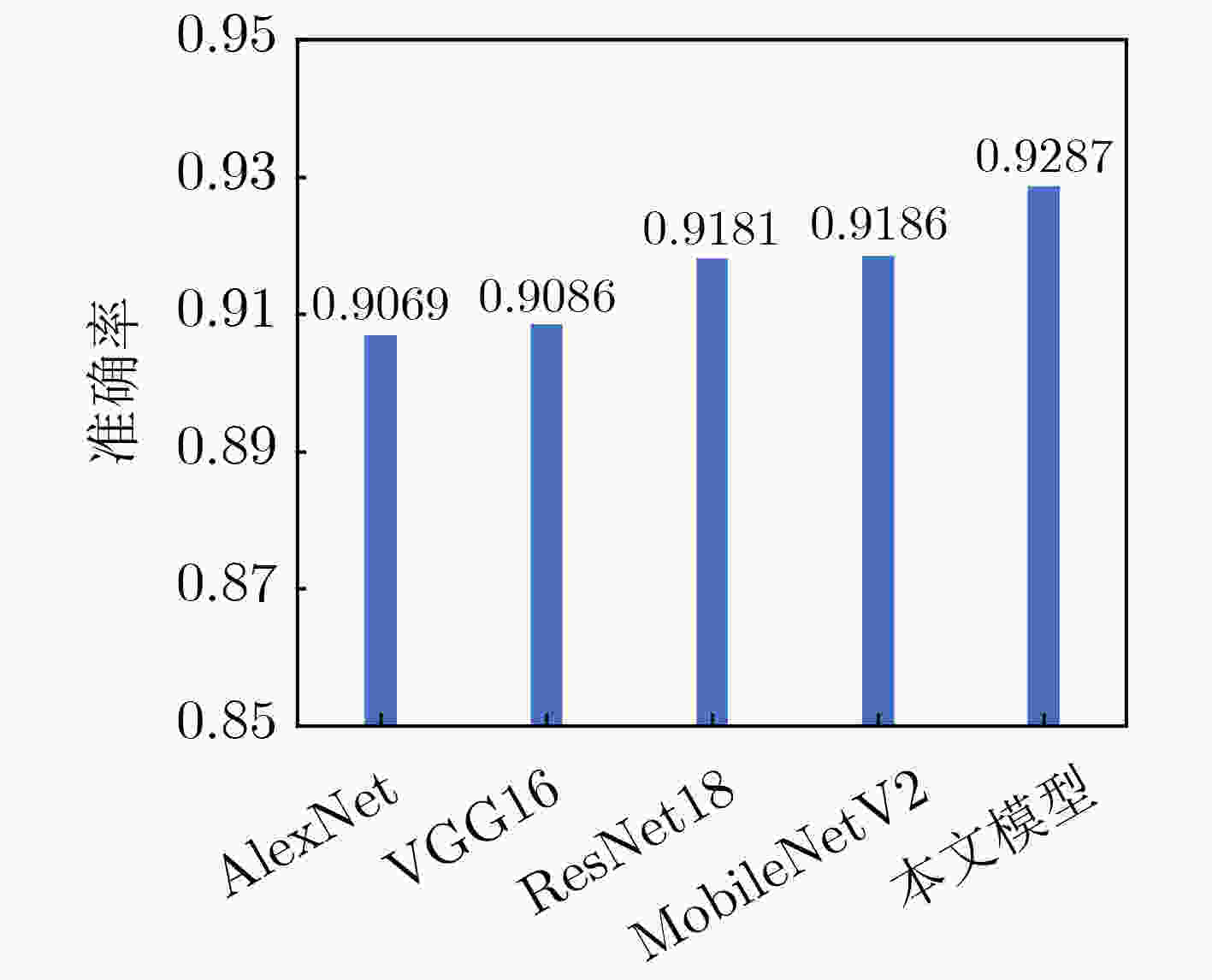
神经网络0.9287 5.2 ResNet18+CBAM 0.9418 11.8 0.9345 ResNet50 0.9415 25.6 0.9356 ResNext50 0.9423 25.1 0.9345 ResNet101 0.9435 44.6 0.9352 ResNet50+SeNet 0.9447 28.1 0.9388 表 6 不同分类网络的比较结果(%)
淡红舌 红舌 暗红舌 紫舌 整体精度 DenseNet121 82.60 68.00 84.61 88.89 82.92 ResNet18 75.00 76.92 91.30 88.89 82.34 ResNext50 78.26 84.00 80.76 77.78 80.72 ShuffleNetV2 86.95 76.00 76.92 88.89 81.14 MobileNetV2 86.95 80.00 76.92 77.78 81.32 EfficientNet-b4 86.95 64.00 84.61 77.78 81.45 本文方法 91.30 92.00 96.15 100.00 93.88 表 7 基于两阶段数据清洗方法的消融实验结果
原始数据集 第1阶段 第2阶段 准确率(%) 方式1 √ × × 82.34 方式2 √ √ × 90.02 方式3 √ √ √ 91.81 表 8 轻型CNN网络的消融实验结果
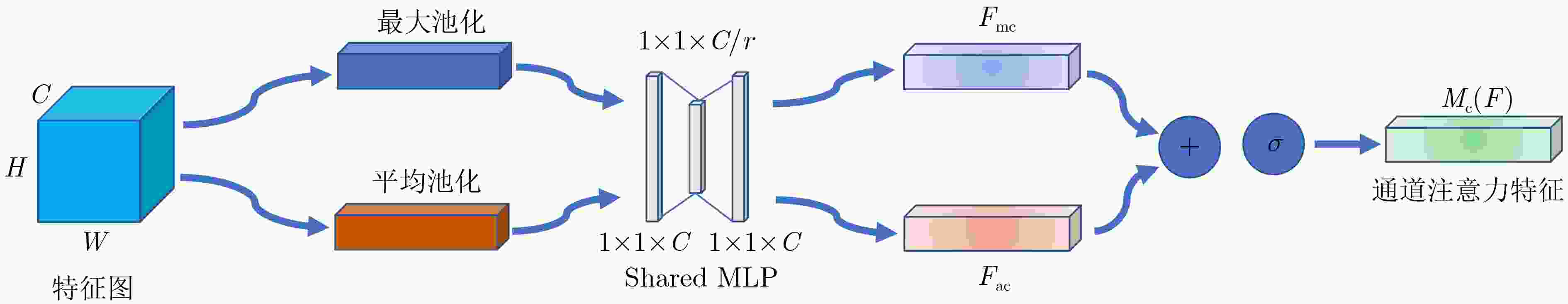
知识蒸馏 基线模型 通道注意力 准确率(%) √ √ × 92.78 √ √ √ 93.88 -
[1] 李乃民. 中国舌诊大全[M]. 北京: 学苑出版社, 1994: 30–170.LI Naimin. Complete Collection of Tongue Diagnosis of Traditional Chinese Medicine[M]. Beijing: Academy Press, 1994: 30–170. [2] WANG Xingyuan and WANG Zongyu. A novel method for image retrieval based on structure elements’ descriptor[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2013, 24(1): 63–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2012.10.003 [3] WANG Xingyuan, CHEN Zhifeng, and YUN Jiaojiao. An effective method for color image retrieval based on texture[J]. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 2012, 34(1): 31–35. doi: 10.1016/j.csi.2011.05.001 [4] WANG Chunpeng, WANG Xingyuan, XIA Zhiqiu, et al. Image description with polar harmonic Fourier moments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2020, 30(12): 4440–4452. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2019.2960507 [5] XIA Zhiqiu, WANG Xingyuan, ZHOU Wenjie, et al. Color medical image lossless watermarking using chaotic system and accurate quaternion polar harmonic transforms[J]. Signal Processing, 2019, 157: 108–118. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.11.011 [6] WANG Xingyuan and WANG Zongyu. The method for image retrieval based on multi-factors correlation utilizing block truncation coding[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2014, 47(10): 3293–3303. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2014.04.020 [7] 王奕然, 张新峰. 基于AdaBoost级联框架的舌色分类[J]. 北京生物医学工程, 2020, 39(1): 8–14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2020.01.002WANG Yiran and ZHANG Xinfeng. Tongue color classification based on AdaBoost cascade framework[J]. Beijing Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 39(1): 8–14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2020.01.002 [8] 张艺凡, 胡广芹, 张新峰. 基于支持向量机的痤疮患者舌色苔色识别算法研究[J]. 北京生物医学工程, 2016, 35(1): 7–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2016.01.02ZHANG Yifan, HU Guangqin, and ZHANG Xinfeng. An algorithm study on tongue color recognition of patients with acne based on support vector machine[J]. Beijing Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 35(1): 7–11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2016.01.02 [9] 张静, 张新峰, 王亚真, 等. 多标记学习在中医舌象分类中的研究[J]. 北京生物医学工程, 2016, 35(2): 111–116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2016.02.01ZHANG Jing, ZHANG Xinfeng, WANG Yazhen, et al. Research on multi-label learning in the classification of tongue images in TCM[J]. Beijing Biomedical Engineering, 2016, 35(2): 111–116. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2016.02.01 [10] 王永刚, 杨杰, 周越. 中医舌象颜色识别的研究[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2005, 22(6): 1116–1120. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5515.2005.06.008WANG Yonggang, YANG Jie, and ZHOU Yue. Tongue image color recognition in traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2005, 22(6): 1116–1120. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5515.2005.06.008 [11] 王爱民, 赵忠旭, 沈兰荪. 中医舌象自动分析中舌色、苔色分类方法的研究[J]. 北京生物医学工程, 2000, 19(3): 136–142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2000.03.002WANG Aimin, ZHAO Zhongxu, and SHEN Lansun. Research on the tongue color classification in automatic tongue analysis of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Beijing Biomedical Engineering, 2000, 19(3): 136–142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2000.03.002 [12] Hou Jun, Su Hongyi, Yan Bo, et al. Classification of tongue color based on CNN[C]. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data Analysis, Beijing, China, 2017: 725–729. [13] FU Shengyu, ZHENG Hong, YANG Zijiang, et al. Computerized tongue coating nature diagnosis using convolutional neural network[C]. The 2017 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Big Data Analysis, Beijing, China, 2017: 730–734. [14] 肖庆新. 基于深度学习的中医舌象特征分类技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京工业大学, 2019.XIAO Qingxin. Research on TCM tongue feature classification technology based on deep learning[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Technology, 2019. [15] UNAR S, WANG Xingyuan, and ZHANG Chuan. Visual and textual information fusion using Kernel method for content based image retrieval[J]. Information Fusion, 2018, 44: 176–187. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.03.006 [16] UNAR S, WANG Xingyuan, WANG Chunpeng, et al. A decisive content based image retrieval approach for feature fusion in visual and textual images[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2019, 179: 8–20. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.05.001 [17] PENG Xiaojiang, WANG Kai, ZENG Zhaoyang, et al. Suppressing mislabeled data via grouping and self-attention[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 786–802. [18] NORTHCUTT C G, JIANG Lu, and CHUANG I L. Confident learning: Estimating uncertainty in dataset labels[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2021, 70: 1373–1411. doi: 10.1613/jair.1.12125 [19] MA Xingjun, HUANG Hanxun, WANG Yisen, et al. Normalized loss functions for deep learning with noisy labels[C]. The 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 2020: 6543–6553. [20] ZHENG Songzhu, WU Pengxiang, GOSWAMI A, et al. Error-bounded correction of noisy labels[C]. The 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 2020: 11447–11457. [21] YI Kun and WU Jianxin. Probabilistic end-to-end noise correction for learning with noisy labels[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 7010–7018. [22] WANG Kai, PENG Xiaojiang, YANG Jianfei, et al. Suppressing uncertainties for large-scale facial expression recognition[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 6896–6905. [23] ZENG Jiabei, SHAN Shiguang, and CHEN Xilin. Facial expression recognition with inconsistently annotated datasets[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 227–243. [24] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. [25] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [26] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. [27] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [28] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]. The 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1409–1556. [29] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU Menglong, et al. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4510–4520. [30] XIE Saining, GIRSHICK R, DOLLÁR P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5987–5995. [31] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. [32] MA Ningning, ZHANG Xiangyu, ZHENG Haitao, et al. ShuffleNet V2: Practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 122–138. [33] TAN Mingxing and LE Q V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6105–6114. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
