ECG Reconstruction Based on Improved Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks
-
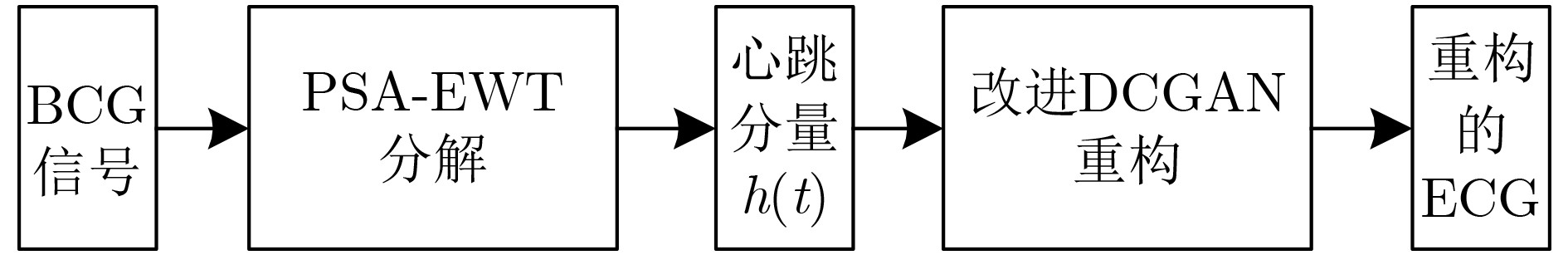
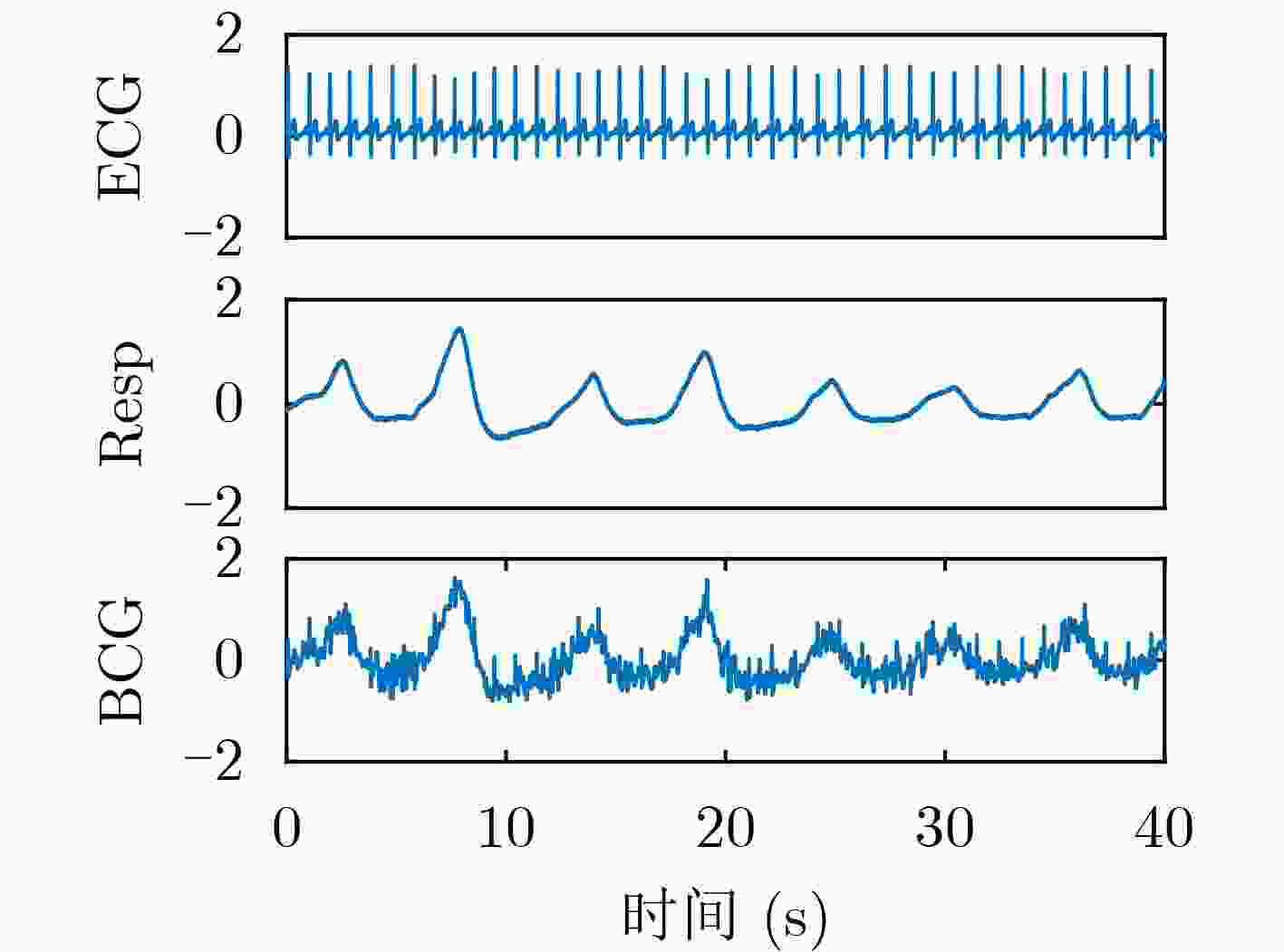
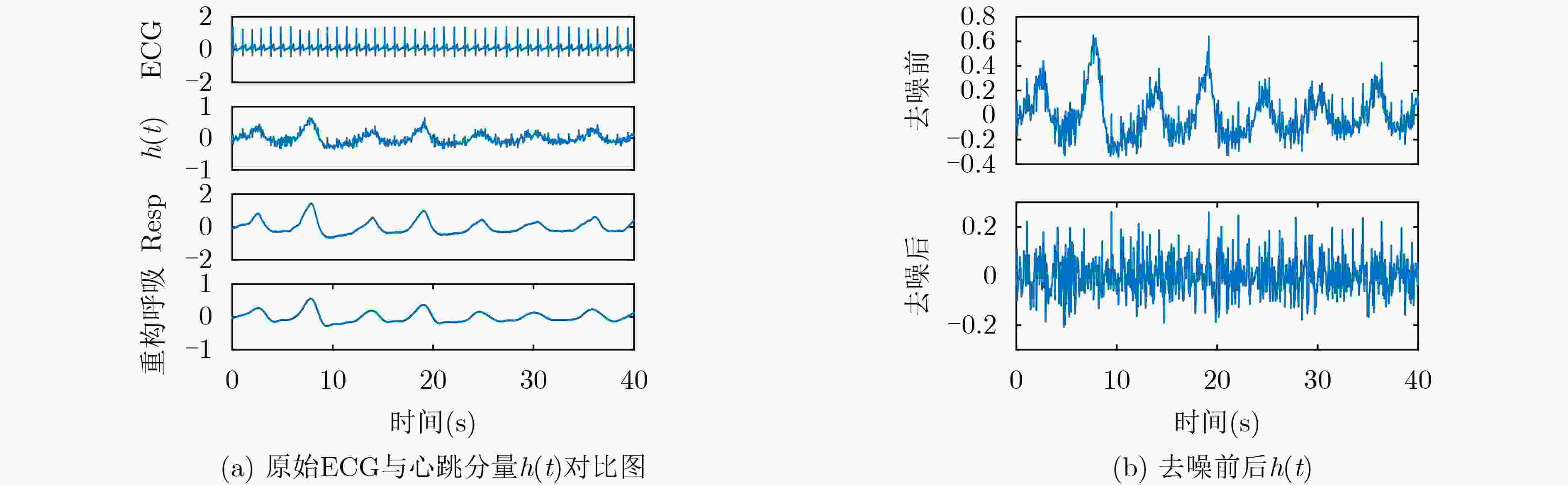
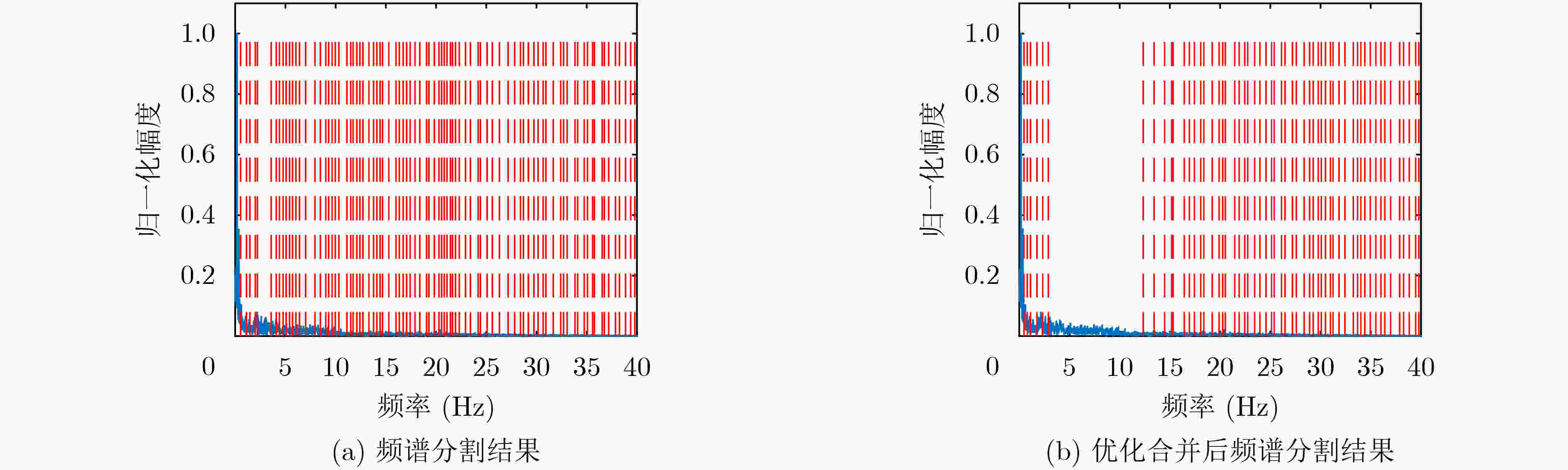
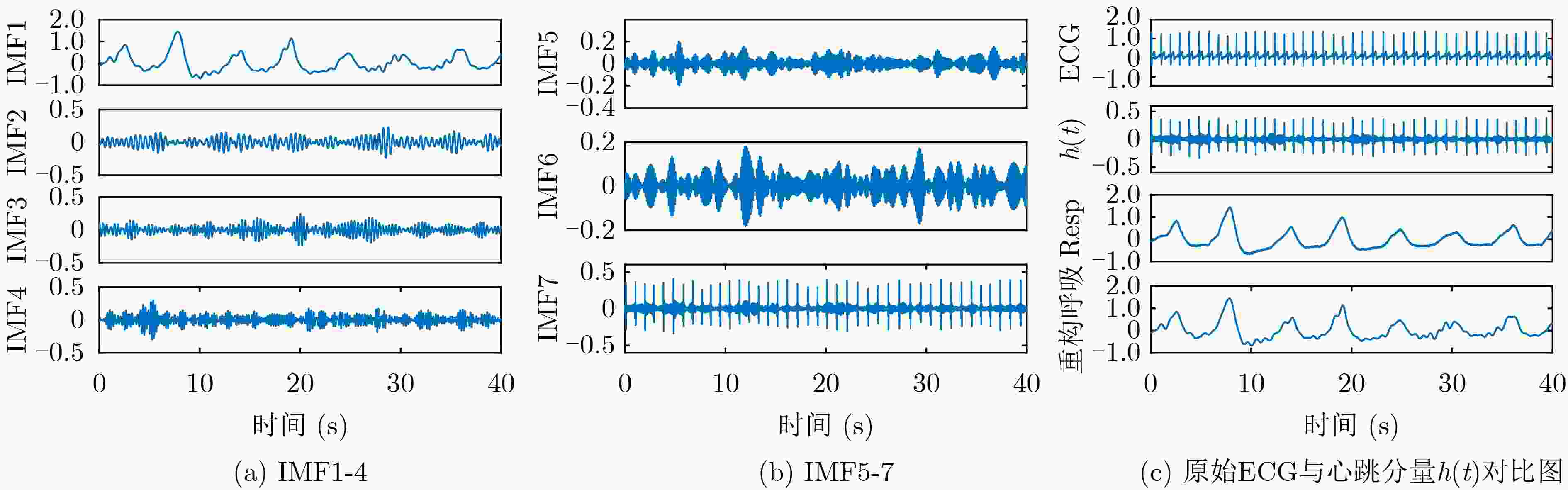
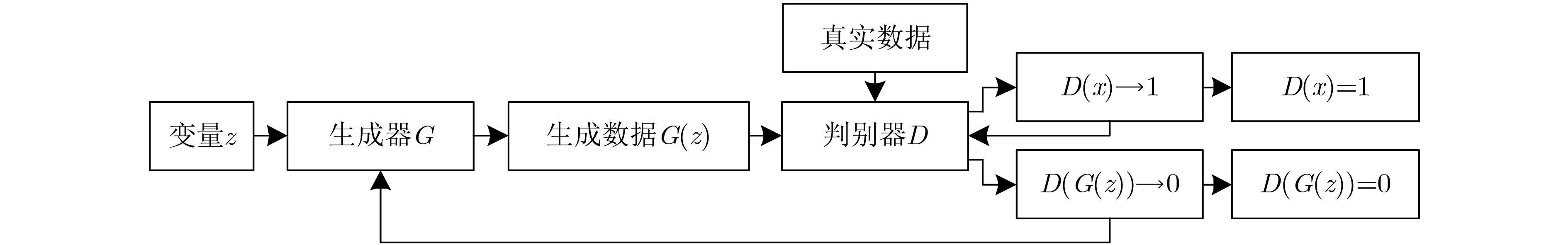
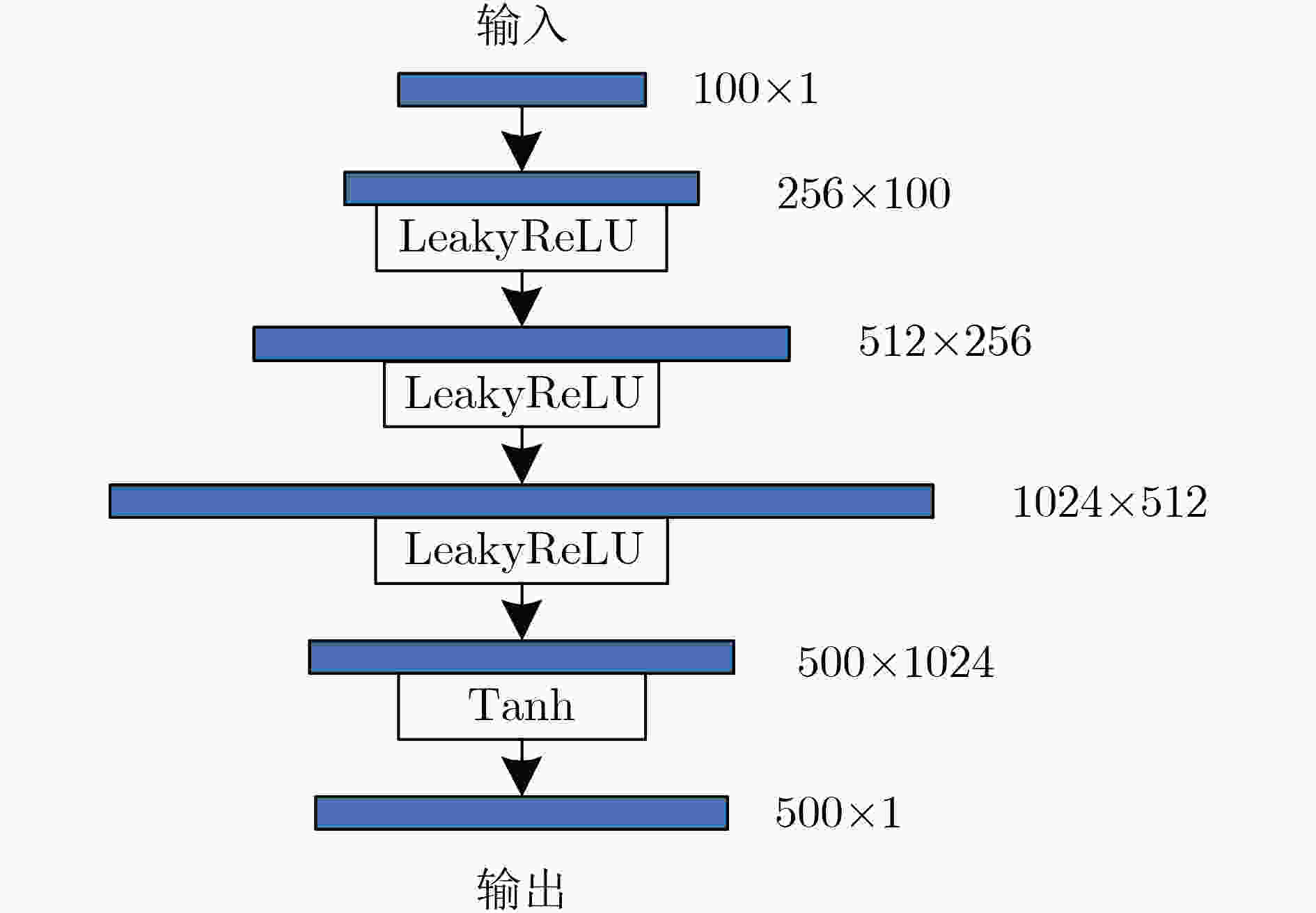
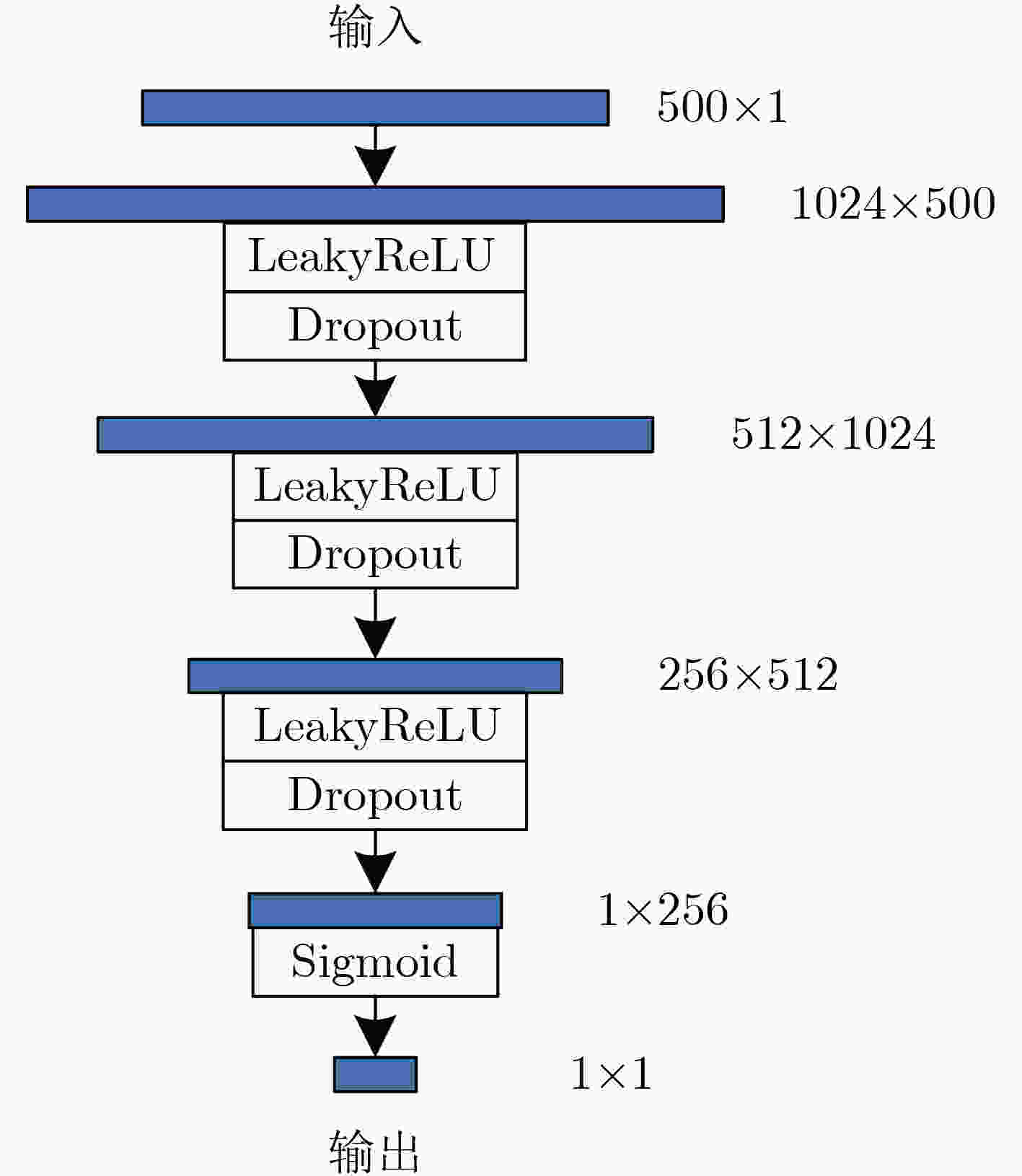
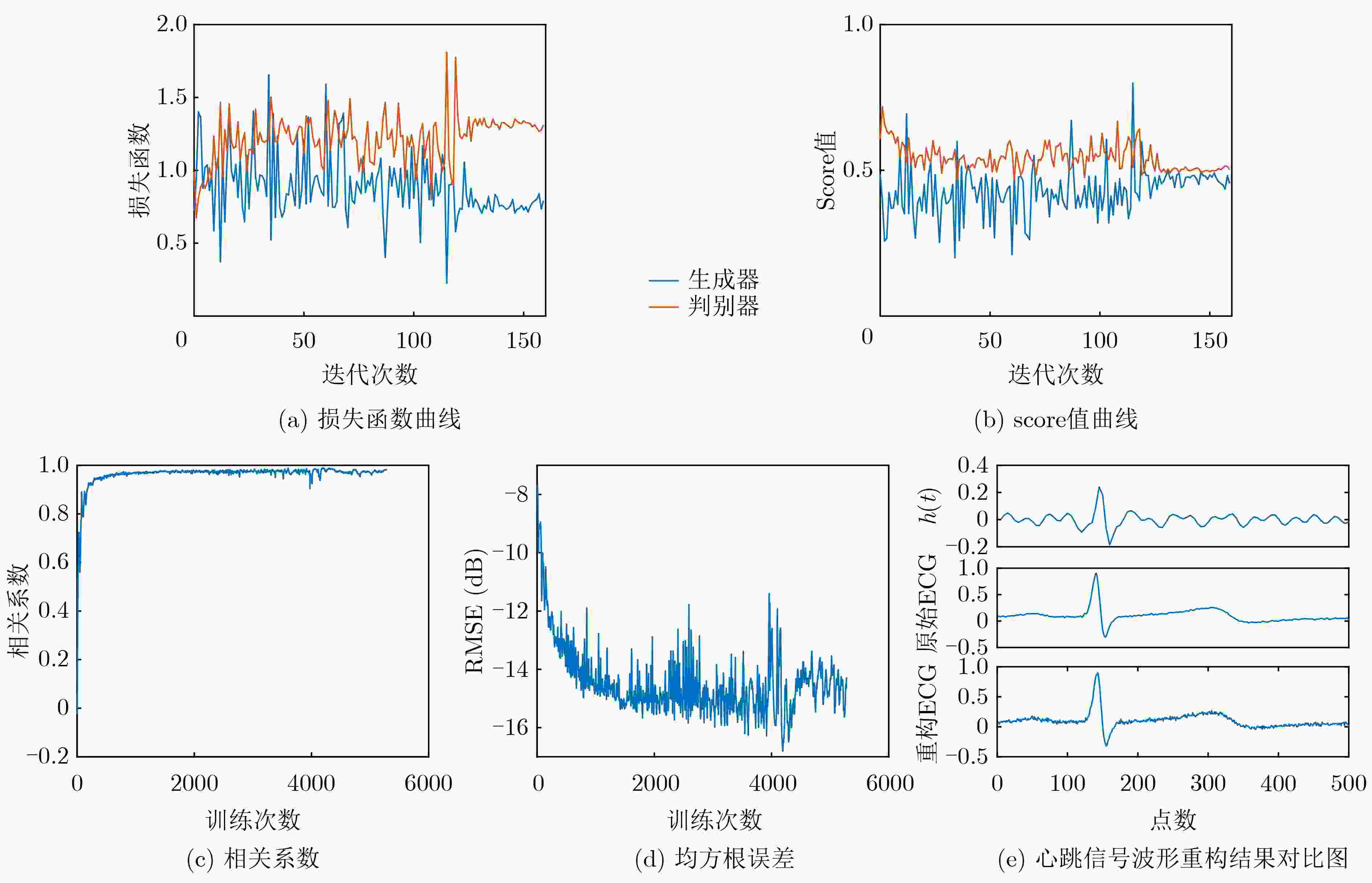
摘要: 心冲击图(BCG)信号中含有睡眠时期的心跳等生理参数,采用非接触式测量,但易受干扰影响应用受限;心电图(ECG)信号应用很广,但采用接触式测量,操作不便。为了实现非接触式测量并监测心电信号,该文将无参数尺度空间法(PSA)引入并与经验小波变换(EWT)算法结合,从BCG信号中分解得到心跳分量,结果表明所提分解方法能有效地从BCG信号中最大限度地分解出心跳信号;并在此基础上通过改进的深度卷积生成对抗网络(DCGAN)重构出ECG信号。实验结果表明,该文所提信号重构算法能从心跳分量重构恢复出ECG信号,均方根误差为–16.8422 dB。Abstract: BallistoCardioGraphy (BCG) signal contains physiological parameters during sleep for example heartbeat. It is measured by non-contact method, therefore its application is limited due to interference. ElectroCardioGram (ECG) signals are widely used, but it is difficult to operate using contact measure. In order to realize the non-contact measurement and monitoring of ECG signals, this paper introduces the Parameterless Scale space Approach (PSA) and improves the Empirical Wavelet Transform (EWT) algorithm to decompose the heartbeat component from BCG signal. The results show that the proposed method can effectively decompose the heartbeat signal from BCG signal to the maximum extent. On this basis, ECG signals are reconstructed by improved Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks (DCGAN). The results show that the ECG signals can be reconstructed from heartbeat components by the proposed algorithm, and the root mean square error is –16.8422 dB.
-
表 1 不同分解方法下的心跳分量评价指标
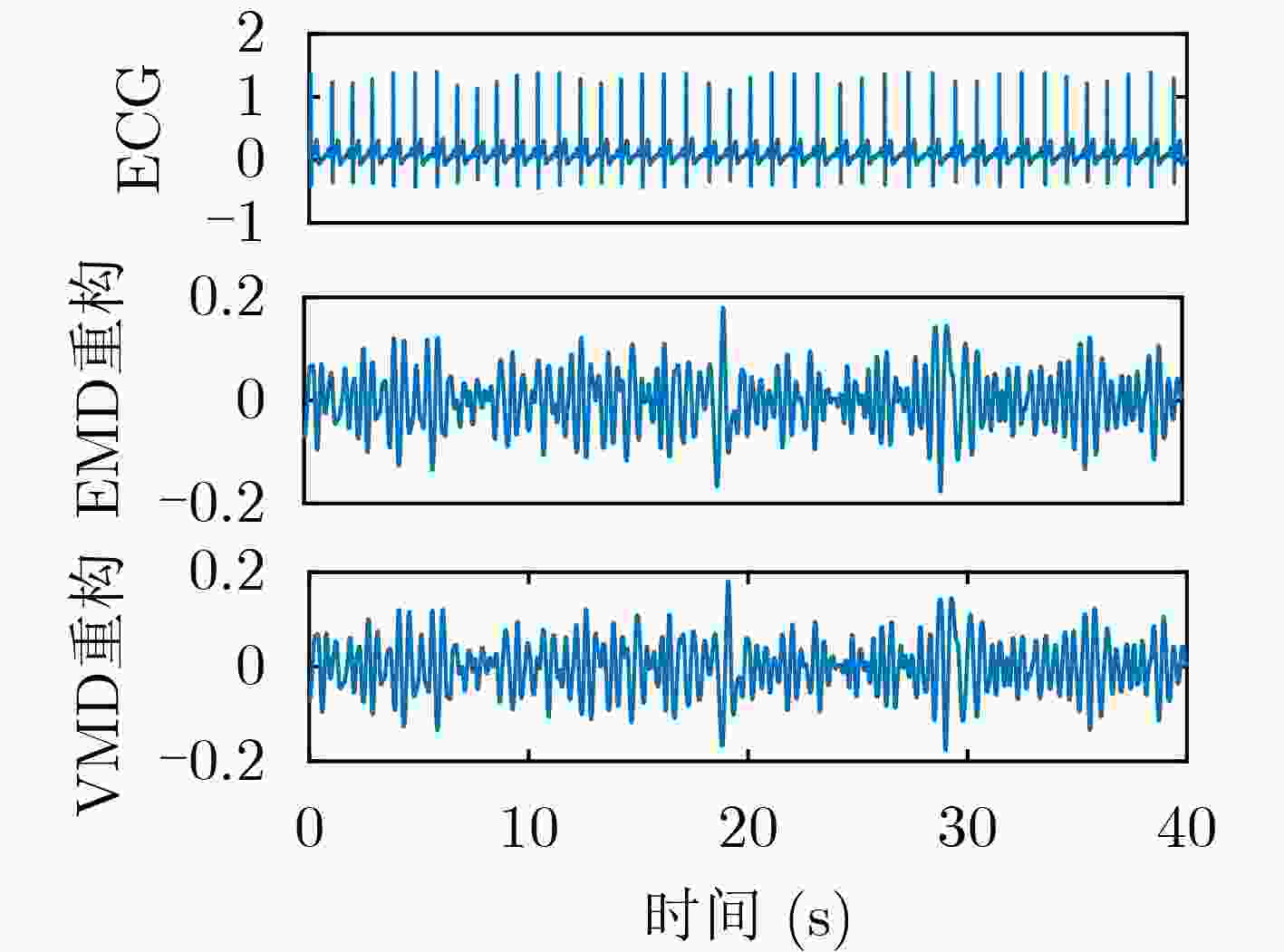
方法 EMD VMD 小波 PSA-EWT 相关系数 0.1594 0.1187 0.3947 0.6590 峭度 3.5634 3.3030 3.4048 15.3154 查全率 0.0476 0.0000 0.5526 0.9512 查准率 0.0476 0.0000 0.8750 1.0000 表 2 不同方法下ECG信号重构结果对比
GAN DCGAN 改进DCGAN 相关系数 0.9788 0.9135 0.9885 均方根误差(dB) –15.5248 –12.1443 –16.8422 -
[1] CHO J W and DUFFY J F. Sleep, sleep disorders, and sexual dysfunction[J]. The World Journal of Men’s Health, 2019, 37(3): 261–275. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.180045 [2] HIROTSU C, TUFIK S, and ANDERSEN M L. Interactions between sleep, stress, and metabolism: From physiological to pathological conditions[J]. Sleep Science, 2015, 8(3): 143–152. doi: 10.1016/j.slsci.2015.09.002 [3] HUNGIN A and CLOSE H. Sleep disturbances and health problems: Sleep matters[J]. British Journal of General Practice, 2010, 60(574): 319–320. doi: 10.3399/bjgp10X484147 [4] ANKER S D, VON HAEHLING S, and GERMANY R. Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease[J]. Indian Heart Journal, 2016, 68(S1): S69–S76. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2015.11.018 [5] KRIEGER A C. Social and economic dimensions of sleep disorders[J]. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 2017, 12(1): i. doi: 10.1016/S1556-407X(16)30117-5 [6] MOHSENIN V. Obstructive sleep apnea and hypertension: A critical review[J]. Current Hypertension Reports, 2014, 16(10): 482. doi: 10.1007/s11906-014-0482-4 [7] PINHEIRO E, POSTOLACHE O, and GIRÃO P. Theory and developments in an unobtrusive cardiovascular system representation: Ballistocardiography[J]. The Open Biomedical Engineering Journal, 2010, 4(1): 201–216. doi: 10.2174/1874120701004010201 [8] PAALASMAA J, TOIVONEN H, and PARTINEN M. Adaptive heartbeat modeling for beat-to-beat heart rate measurement in ballistocardiograms[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2015, 19(6): 1945–1952. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2014.2314144 [9] 方震, 白忠瑞, 陈贤祥, 等. 基于压电陶瓷传感器的非接触式精准逐拍心率提取方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1472–1479. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200045FANG Zhen, BAI Zhongrui, CHEN Xianxiang, et al. Unconstrained accurate beat-to-beat heart rate extraction based on piezoelectric ceramics sensor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1472–1479. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200045 [10] PAALASMAA J and RANTA M. Detecting heartbeats in the ballistocardiogram with clustering[C]. The ICML/UAI/COLT 2008 Workshop on Machine Learning Health-Care Applications. Helsinki, Finland, 2008. [11] NAGURA M, MITSUKURA Y, KISHIMOTO T, et al. A practical BCG measuring system with bed sensors and algorithm for heartbeat detection[C]. 2018 IEEE 15th International Workshop on Advanced Motion Control (AMC), Tokyo, Japan, 2018: 317–321. [12] SADEK I and BISWAS J. Nonintrusive heart rate measurement using ballistocardiogram signals: a comparative study[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2019, 13(3): 475–482. doi: 10.1007/s11760-018-1372-z [13] WANG Feng, TANAKA M, and CHONAN S. Development of a PVDF piezopolymer sensor for unconstrained in-sleep cardiorespiratory monitoring[J]. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2003, 14(3): 185–190. doi: 10.1177/1045389X03014003006 [14] 冯久超, 潘水洋. 基于经验模态分解的生命信号提取算法[J]. 华南理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 30(10): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-565X.2010.10.001FENG Jiuchao and PAN Shuiyang. Extraction algorithm of vital signals based on empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2010, 30(10): 1–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-565X.2010.10.001 [15] CAO Xinrong, GUO Hong, and TANG Jintian. Heart rate extraction of ballistocardiogram based on hilbert-huang transformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2019, 28(3): 118–124. [16] 王春武, 程礼邦, 丁煜, 等. 基于脉搏的心冲击信号特征提取方法研究[J]. 微型机与应用, 2016, 35(22): 36–39. doi: 10.19358/j.issn.1674-7720.2016.22.010WANG Chunwu, CHENG Libang, DING Yu, et al. Ballistocardiogram signals feature extraction method based on pulse signals[J]. Microcomputers &Its Applications, 2016, 35(22): 36–39. doi: 10.19358/j.issn.1674-7720.2016.22.010 [17] SADEK I, BISWAS J, ABDULRAZAK B, et al. Continuous and unconstrained vital signs monitoring with ballistocardiogram sensors in headrest position[C]. 2017 IEEE EMBS International Conference on Biomedical & Health Informatics (BHI), Orlando, USA, 2017: 289–292. [18] 沈劲鹏, 王新安. 适用于床垫式生理信号监测系统的信号处理方法[J]. 北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 54(5): 921–926. doi: 10.13209/j.0479-8023.2018.012SHEN Jinpeng and WANG Xin’an. Signal processing method for mattress-type physiological monitoring[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2018, 54(5): 921–926. doi: 10.13209/j.0479-8023.2018.012 [19] 姜星, 耿读艳, 张园园, 等. 基于EMD-ICA的心冲击信号降噪研究[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 2019, 38(2): 138–145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2019.02.002JIANG Xing, GENG Duyan, ZHANG Yuanyuan, et al. BCG signal de-noising method research based on EMD-ICA[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2019, 38(2): 138–145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2019.02.002 [20] 李倩, 王飞, 刘芊, 等. 心冲击图信号的采集和特征分析及其应用[J]. 中国医学物理学杂志, 2020, 37(198): 83–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-202X.2020.01.017LI Qian, WANG Fei, LIU Qian, et al. Acquisition, feature analysis and application of ballistocardiogram signals[J]. Chinese Journal of Medical Physics, 2020, 37(198): 83–89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-202X.2020.01.017 [21] 熊鹏, 刘学朋, 杜海曼, 等. 基于平稳和连续小波变换融合算法的心电信号P, T波检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1441–1447. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200049XIONG Peng, LIU Xuepeng, DU Haiman, et al. Detection of ECG Signal P and T wave based on stationary and continuous wavelet transform fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1441–1447. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200049 [22] 林金朝, 李必禄, 李国权, 等. 基于集合经验模态分解和信号结构分析的心电信号R波识别算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2352–2360. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200915LIN Jinzhao, LI Bilu, LI Guoquan, et al. ElectroCardioGram R-wave recognition algorithm based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition and signal structure analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2352–2360. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200915 [23] GILLES J and HEAL K. A parameterless scale-space approach to find meaningful modes in histograms — Application to image and spectrum segmentation[J]. International Journal of Wavelets, Multiresolution and Information Processing, 2014, 12(6): 1450044. doi: 10.1142/S0219691314500441 [24] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139–144. doi: 10.1145/3422622 [25] RADFORD A, METZ L, and CHINTALA S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[J]. arXiv: 1511.06434, 2015. -





 下载:
下载:
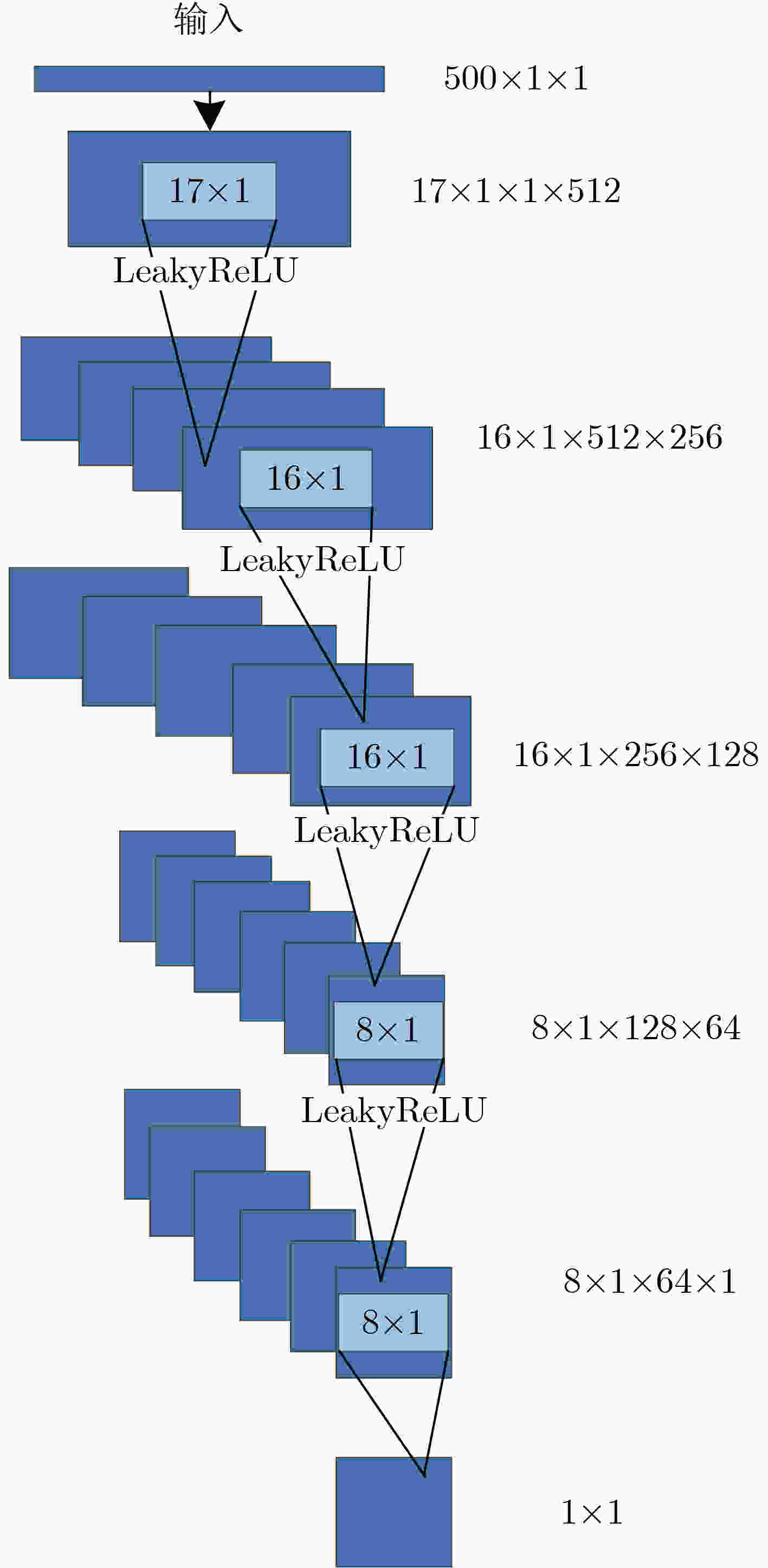
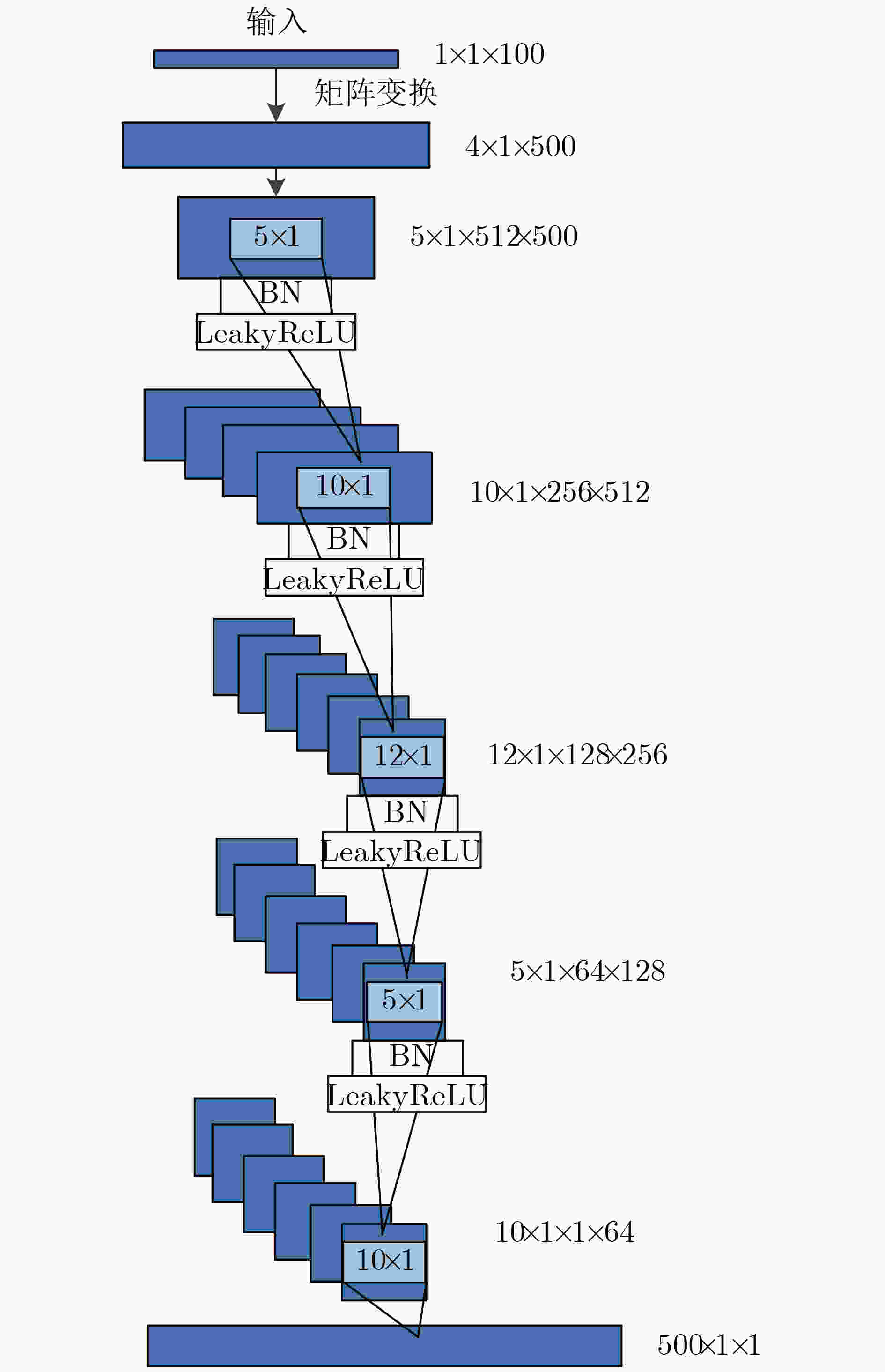
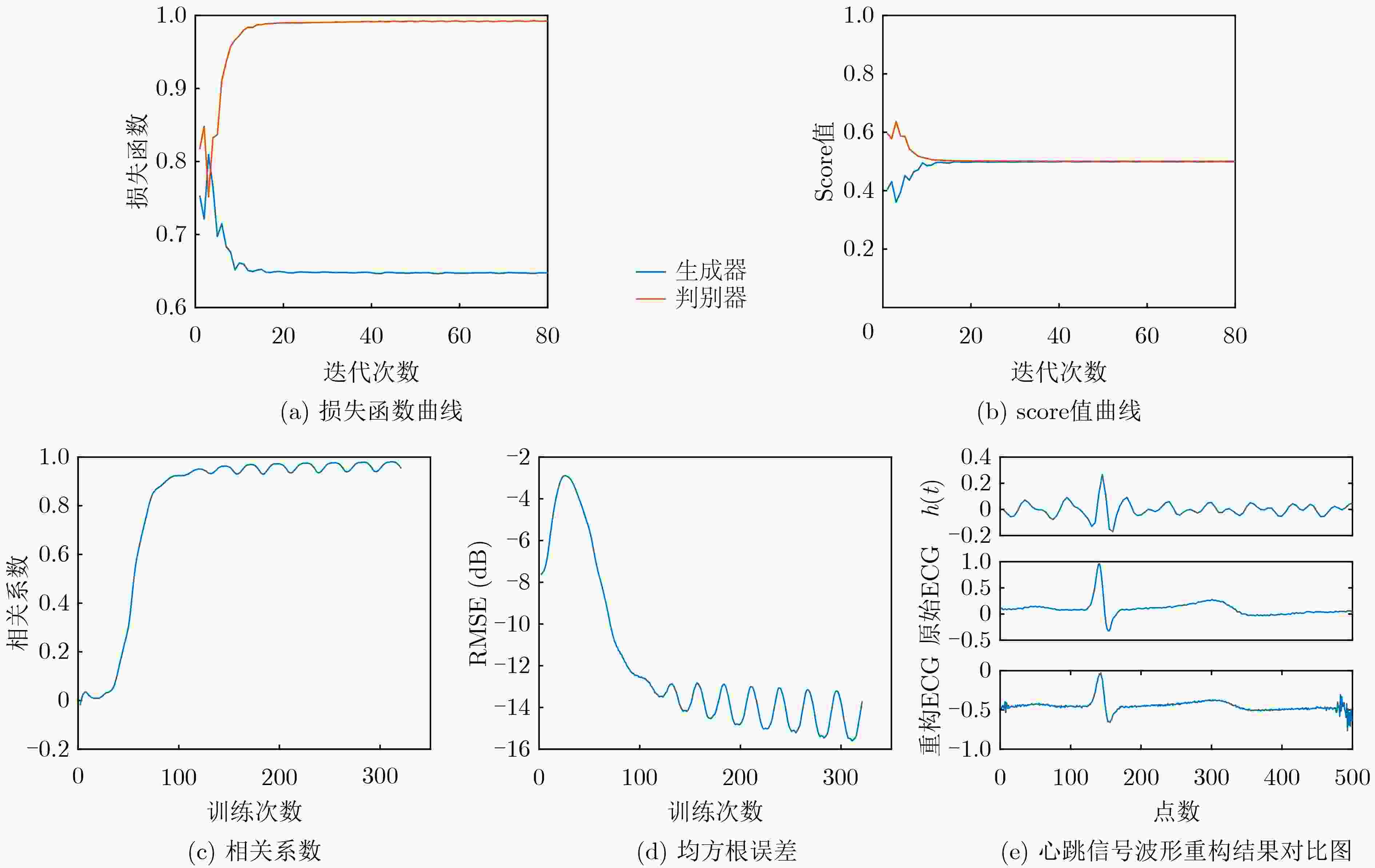

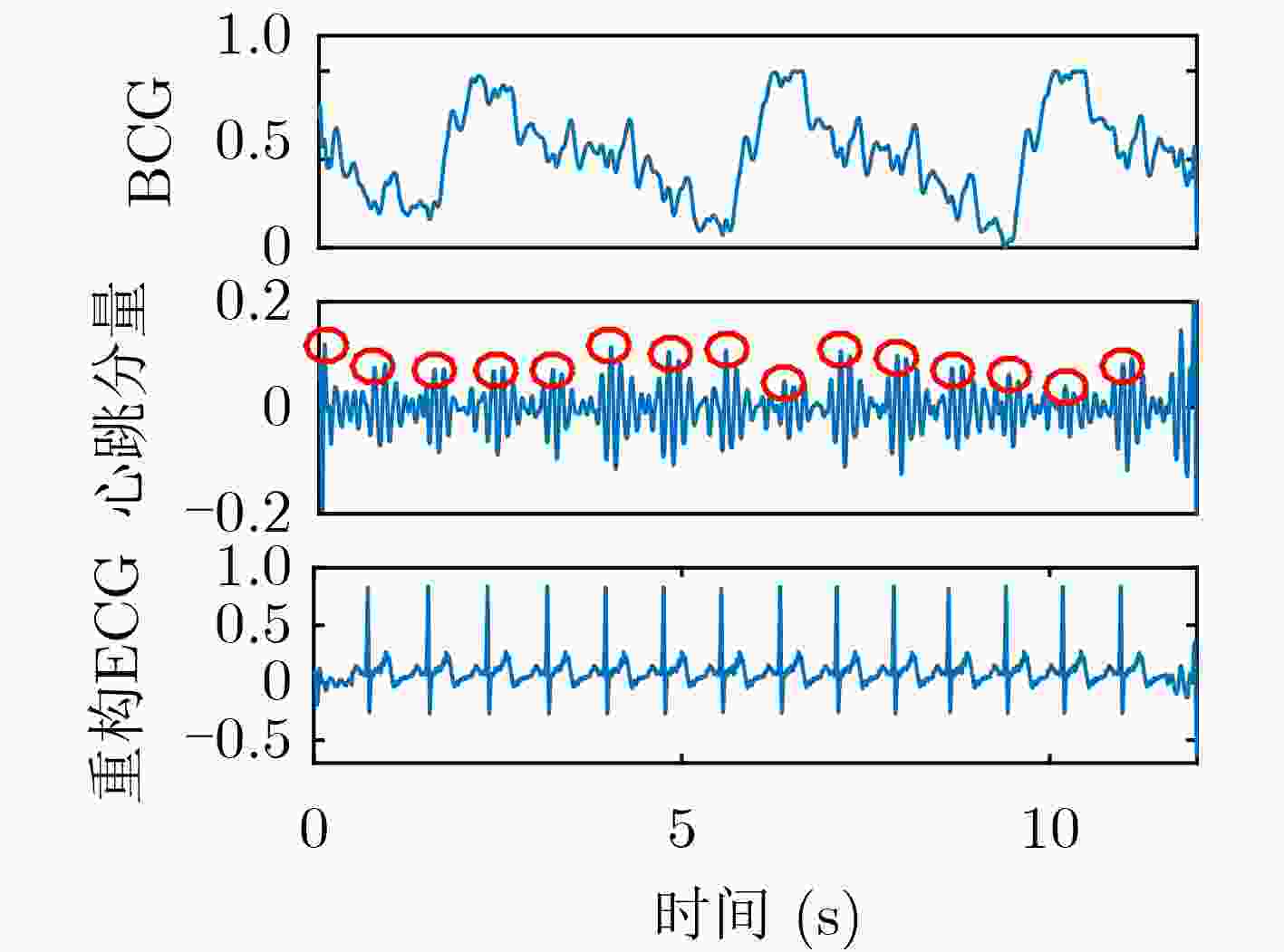


 下载:
下载:
