Deep Learned Esophageal Contraction Vigor Classification on High-resolution Manometry Images
-
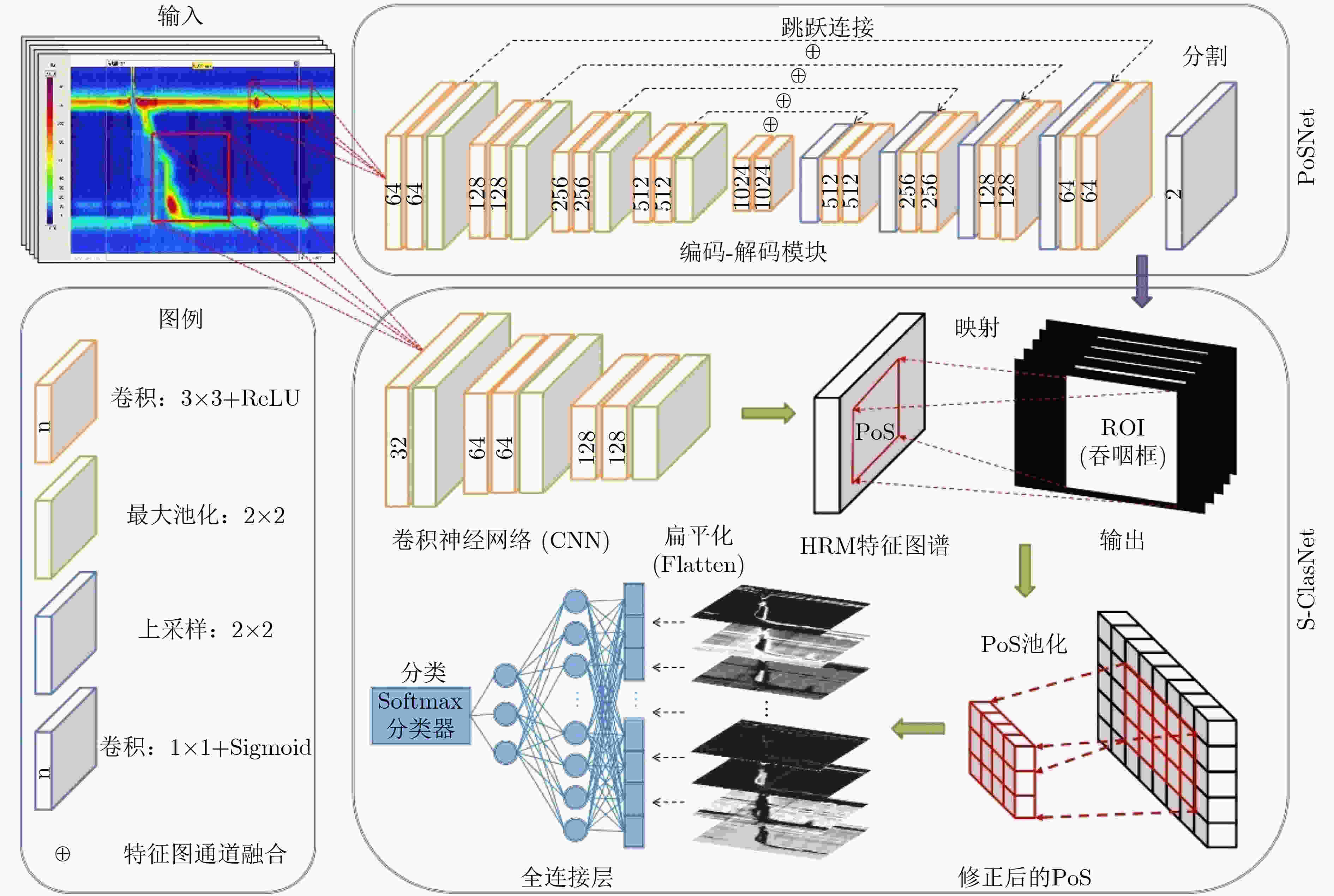
摘要: 高分辨率食管测压技术(HRM)作为检测食管动力障碍性疾病(EMD)的金标准,已广泛应用于临床试验以辅助医生进行诊断治疗。随着患病率的上升,HRM图像的数据量爆炸式增长,加之EMD的诊断流程较为复杂,临床上EMD误诊事件时有发生。为了提高EMD诊断的准确性,希望搭建一个计算机辅助诊断(Computer Aided Diagnosis, CAD)系统帮助医生对HRM图像进行自动分析。由于食管收缩活力的异常是诊断EMD的重要依据,该文提出了一个深度学习模型(PoS-ClasNet)以完成对HRM图像的食管收缩活力分类任务,为今后机器代替人工诊断EMD奠定基础。PoS-ClasNet作为一个多任务卷积神经网络(CNN)由PoSNet和S-ClasNet构成。前者用于HRM图像中吞咽框的检测和提取任务,后者根据食管吞咽特征鉴别收缩活力类型。实验使用了4000幅专家标记的HRM图像,用于训练、验证和测试的图像分别占比为70%, 20%和10%。在测试集上,食管收缩活力分类器PoS-ClasNet的分类准确率高达93.25%,精度和召回率分别为93.39%和93.60%。结果表明PoS-ClasNet能较好地适应HRM图像数据的特性,在智能诊断食管收缩活力的任务中表现出了不俗的准确性和稳健性。将它应用在临床上辅助医生诊疗,会带来巨大的社会效益。Abstract: As the gold standard for the detection of Esophageal Motility Disorder(EMD), High-Resolution Manometry(HRM) is widely used in clinical tests to assist doctors in diagnosis. The amount of HRM images explodes with an increase in the prevalence rate, and the diagnostic process of EMD is complicated, both of which may lead to misdiagnosis of EMD in clinic. To improve the accuracy of the diagnosis of EMD, we hope to build a Computer Aided Diagnosis(CAD) system to assist doctors in analyzing HRM images automatically. Since the abnormality of esophageal contraction vigor is an important basis for diagnosis of EMD, in this paper, a Deep Learning(DL) model(PoS-ClasNet) is proposed to classify esophageal contraction vigor, which lays the foundation for machine to diagnose EMD instead of manual in the future. PoS-ClasNet, as a multi-task Convolutional Neural Network(CNN), is formed by PoSNet and S-ClassNet. The former is used to detect and extract swallowing frames in HRM images, while the latter identifies the type of contraction vigor based on esophageal swallowing characteristics. 4,000 expert-labeled HRM images are used for the experiment, among which the images of training set, verification set and test set accounted for 70%, 20% and 10%. On the test set, the classification accuracy of esophageal contraction vigor classifier PoS-ClasNet is as high as 93.25%, meanwhile the precision rate and the recall rate are 93.39% and 93.60% respectively. The experimental results show PoS-ClasNet can well adapt to the features of HRM image, with the outstanding accuracy and robustness in the task of intelligent diagnosis of esophageal contraction vigor. If the proposed model is used to assist doctors in clinical prevention, diagnosis and treatment, it will bring enormous social benefits.
-
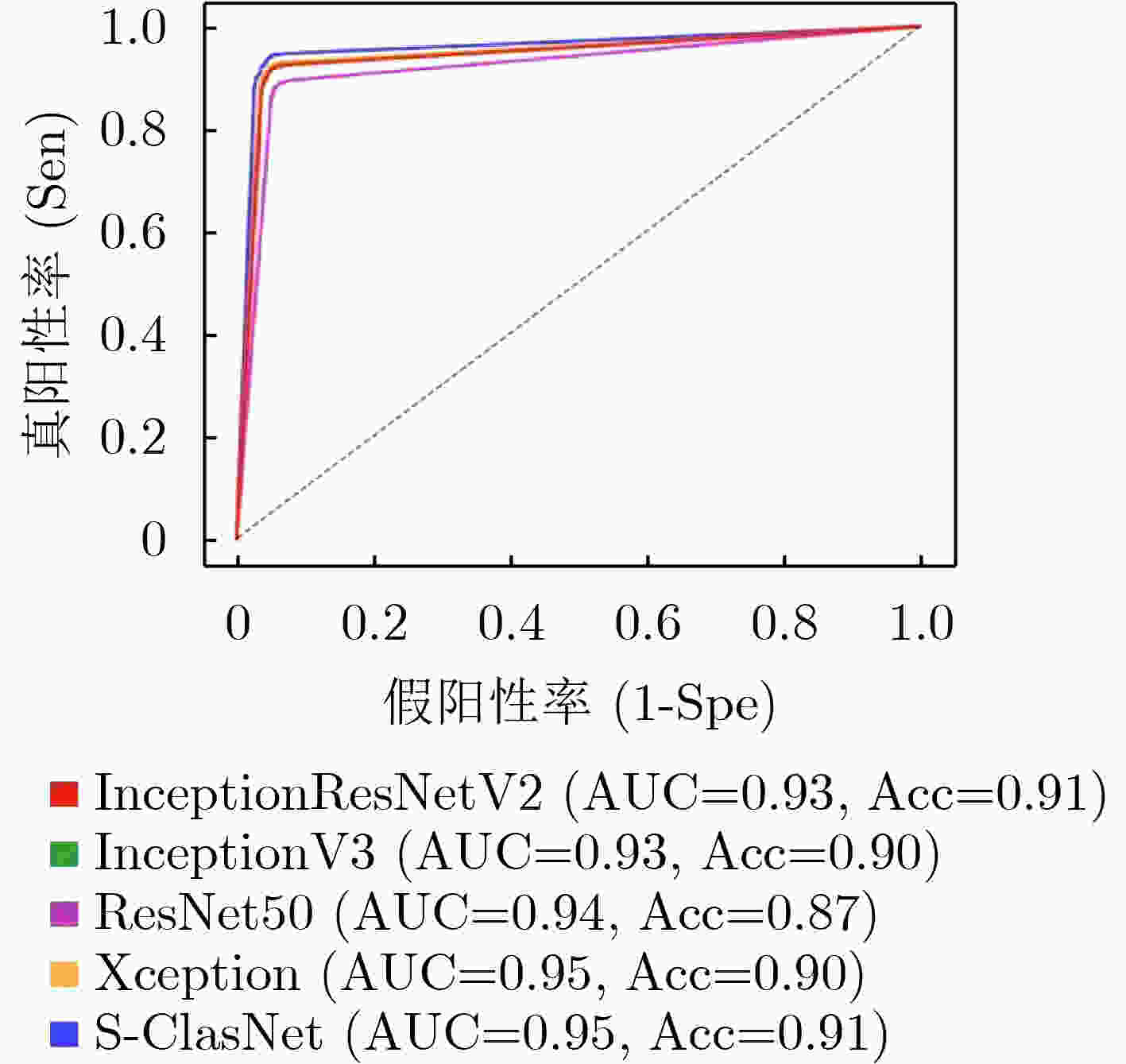
表 1 不同分类模型对食管收缩活力分类的结果比较(均值±标准差)
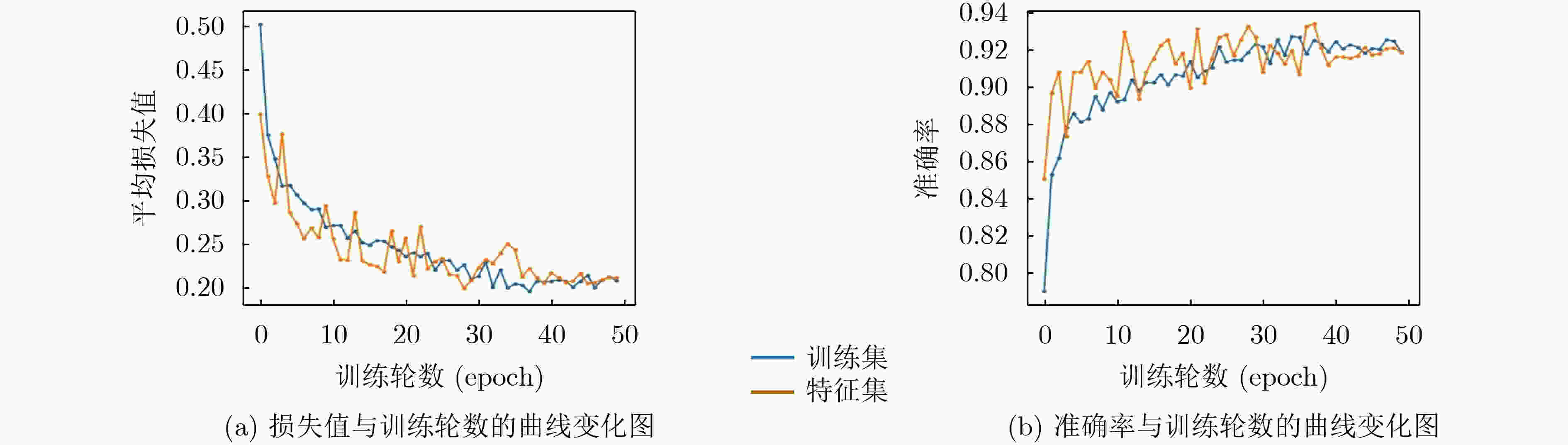
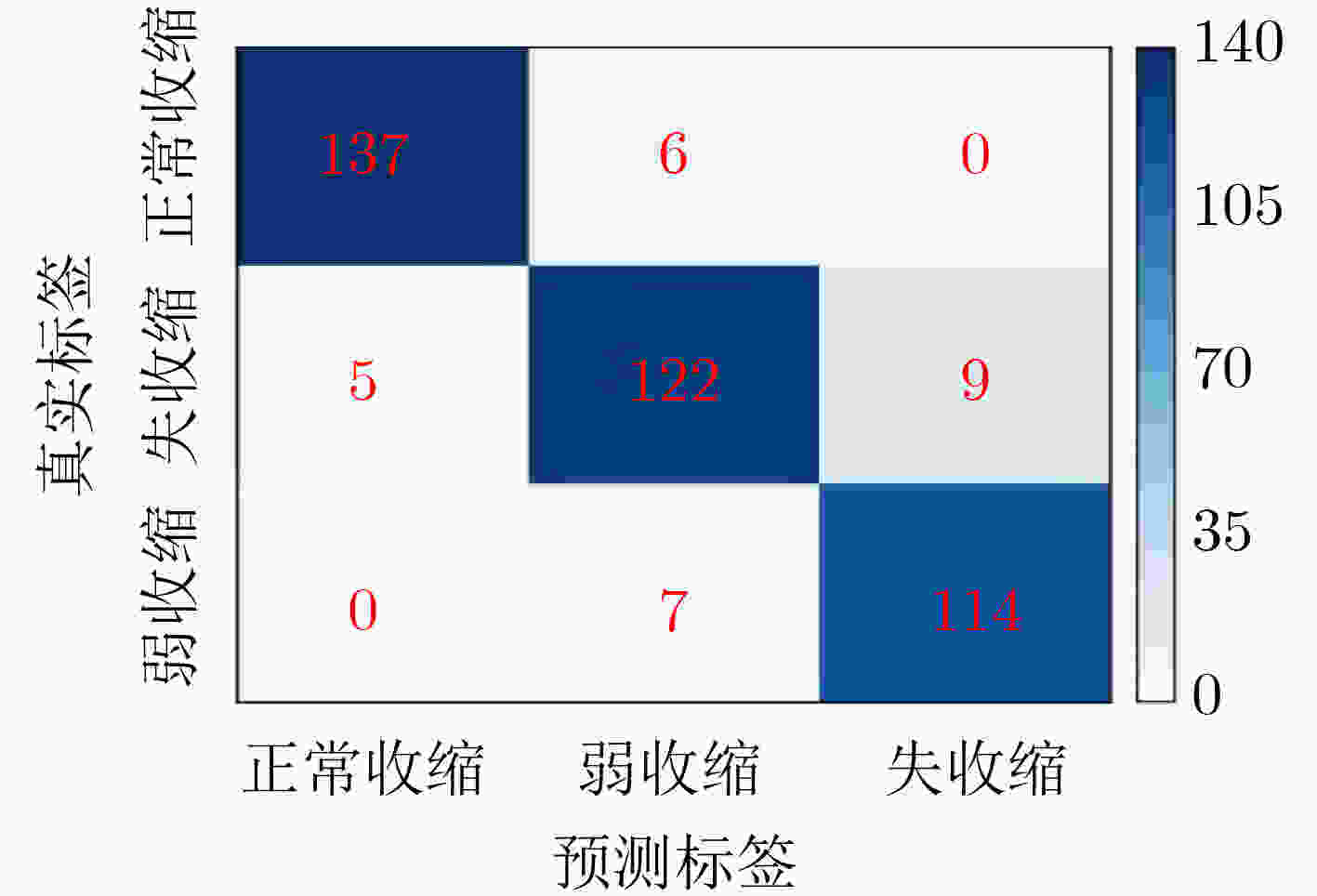
Inceptionresnetv2 Inceptionv3 Resnet50 Xception S-ClasNet 损失 训练集 0.2284±0.0830 0.2784±0.0890 0.3317±0.0806 0.2514±0.0641 0.2574±0.0574 验证集 0.2480±0.0535 0.2784±0.0940 0.3203±0.0825 0.2524±0.0421 0.2503±0.0429 准确率 训练集 0.9148±0.0339 0.8965±0.0376 0.8733±0.0318 0.9056±0.0278 0.9015±0.0249 验证集 0.9138±0.0247 0.8988±0.0524 0.8945±0.0248 0.9157±0.0169 0.9122±0.0162 精度 训练集 0.9185±0.0311 0.9009±0.0338 0.8776±0.0299 0.9093±0.0253 0.9040±0.0250 验证集 0.9162±0.0247 0.9023±0.0520 0.8990±0.0219 0.9191±0.0159 0.9143±0.0164 召回率/敏感性 训练集 0.9102±0.0391 0.8906±0.0440 0.8673±0.0346 0.9004±0.0332 0.8980±0.0294 验证集 0.9112±0.0246 0.8948±0.0542 0.8911±0.0278 0.9121±0.0175 0.9104±0.0167 F1得分 训练集 0.9137±0.0358 0.8949±0.0400 0.8717±0.0326 0.9041±0.0300 0.9005±0.0278 验证集 0.9133±0.0246 0.8980±0.0532 0.8944±0.0248 0.9151±0.0167 0.9121±0.0165 特异性 训练集 0.9599±0.0143 0.9515±0.0149 0.9397±0.0140 0.9554±0.0112 0.9527±0.0106 验证集 0.9584±0.0124 0.9516±0.0254 0.9500±0.0107 0.9599±0.0079 0.9573±0.0082 表 2 S-ClasNet在测试集上对食管收缩活力分类的结果比较
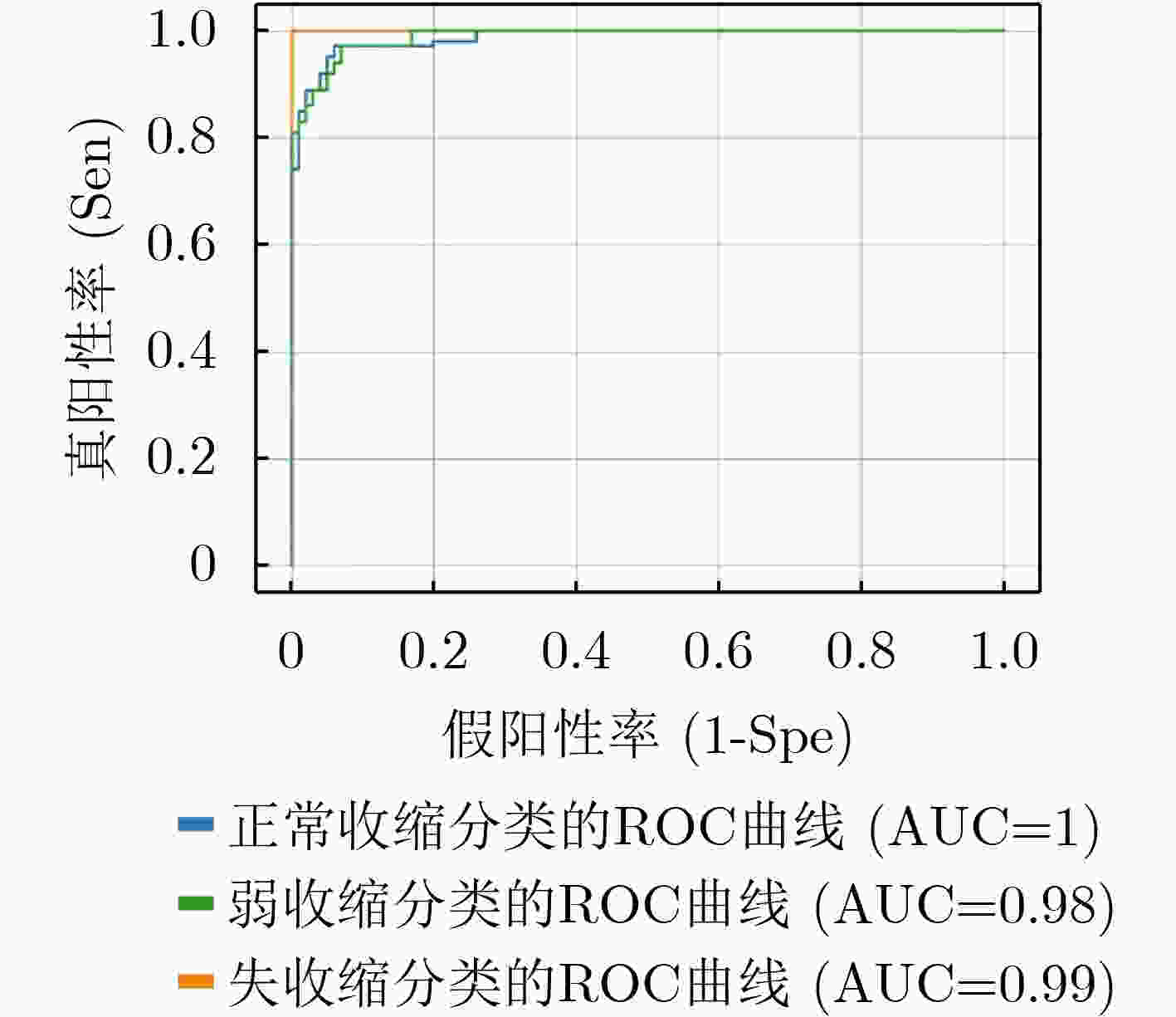
收缩活力分类 评判指标 准确率(%) 精度(%) 召回率(%) F1得分 正常收缩 97.25 96.48 95.80 0.9614 弱收缩 93.25 90.37 89.71 0.9004 失收缩 96.00 92.68 94.21 0.9344 S-ClasNet 93.25 93.18 93.24 0.9321 -
[1] BOWERS S P. Esophageal motility disorders[J]. Surgical Clinics of North America, 2015, 95(3): 467–482. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2015.02.003 [2] ZAMBITO G, ROETHER R, KERN B, et al. Is barium esophagram enough? Comparison of esophageal motility found on barium esophagram to high resolution manometry[J]. The American Journal of Surgery, 2021, 221(3): 575–577. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2020.11.028 [3] KUNIEDA K, FUJISHIMA I, WAKABAYASHI H, et al. Relationship between tongue pressure and pharyngeal function assessed using high-resolution manometry in older dysphagia patients with sarcopenia: A pilot study[J]. Dysphagia, 2021, 36(1): 33–40. doi: 10.1007/s00455-020-10095-1 [4] 李飞, 王美峰, 汤玉蓉, 等. 《食管动力障碍的测压(第4版芝加哥分类)》更新点解读[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2021, 41(7): 492–497. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311367-20210323-00173 [5] PANDOLFINO J E, FOX M R, BREDENOORD A J, et al. High-resolution manometry in clinical practice: Utilizing pressure topography to classify oesophageal motility abnormalities[J]. Neurogastroenterology & Motility, 2009, 21(8): 796–806. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2009.01311.x [6] SAWADA A, GUZMAN M, NIKAKI K, et al. Identification of different phenotypes of esophageal reflux hypersensitivity and implications for treatment[J]. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2021, 19(4): 690–698.E2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.063 [7] KAHRILAS P J, BREDENOORD A J, FOX M, et al. The Chicago Classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0[J]. Neurogastroenterology & Motility, 2015, 27(2): 160–174. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12477 [8] GYAWALI C P. High resolution manometry: The Ray Clouse legacy[J]. Neurogastroenterology & Motility, 2012, 24(S1): 2–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01836.x [9] SCHMIDHUBER J. Deep learning in neural networks[J]. Neural Networks, 2015, 61: 85–117. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2014.09.003 [10] LECUN Y, BENGIO Y, and HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [11] KOU Wenjun, CARLSON D A, BAUMANN A J, et al. A deep-learning-based unsupervised model on esophageal manometry using variational autoencoder[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2021, 112: 102006. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2020.102006 [12] CARLSON D A, KOU Wenjun, ROONEY K P, et al. Achalasia subtypes can be identified with functional luminal imaging probe (FLIP) panometry using a supervised machine learning process[J]. Neurogastroenterology & Motility, 2021, 33(3): e13932. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13932 [13] 侯晓华. 消化道高分辨率测压图谱[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.HOU Xiaohua. High Resolution Manometry in Digestive Tract[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. [14] RENA Y. High-resolution esophageal manometry: Interpretation in clinical practice[J]. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology, 2017, 33(4): 301–309. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000369 [15] BREDENOORD A J and SMOUT A J. High-resolution manometry of the esophagus: More than a colorful view on esophageal motility?[J]. Expert Review of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2007, 1(1): 61–69. doi: 10.1586/17474124.1.1.61 [16] LI Zewen, LIU Fan, YANG Wenjie, et al. A survey of convolutional neural networks: Analysis, applications, and prospects[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, To be published. [17] GU Jiuxiang, WANG Zhenhua, KUEN J, et al. Recent advances in convolutional neural networks[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 77: 534–377. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.10.013 [18] SARVAMANGALA D R and KULKARNI R V. Convolutional neural networks in medical image understanding: A survey[J]. Evolutionary Intelligence, 2021(4): 1–22. doi: 10.1007/s12065-020-00540-3 [19] MOHAPATRA S, SWARNKAR T, and DAS J. Deep Convolutional Neural Network in Medical Image Processing[M]. BALAS V E, MISHRA B K, and KUMAR R. Handbook of Deep Learning in Biomedical Engineering. Amsterdam: Academic Press, 2021: 25–60. [20] LITJENS G, KOOI T, BEJNORDI B E, et al. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2017, 42: 60–88. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.07.005 [21] GREENSPAN H, VAN GINNEKEN B, and SUMMERS R M. Guest editorial deep learning in medical imaging: Overview and future promise of an exciting new technique[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35(5): 1153–1159. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2016.2553401 [22] JANOWCZYK A and MADABHUSHI A. Deep learning for digital pathology image analysis: A comprehensive tutorial with selected use cases[J]. Journal of Pathology Informatics, 2016, 7: 29. doi: 10.4103/2153-3539.186902 [23] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [24] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. [25] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1440–1448. [26] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [27] ZHANG Ziang, WU Chengdong, COLEMAN S, et al. DENSE-INception U-net for medical image segmentation[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2020, 192: 105395. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105395 [28] WANG Zheng, MENG Yu, WENG Futian, et al. An effective CNN method for fully automated segmenting subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue on CT scans[J]. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 48(1): 312–328. doi: 10.1007/s10439-019-02349-3 [29] DROZDZAL M, VORONTSOV E, CHARTRAND G, et al. The importance of skip connections in biomedical image segmentation[C]. Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Large-Scale Annotation of Biomedical Data and Expert Label Synthesis, Athens, Greece, 2016: 179–187. [30] IOFFE S and SZEGEDY C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]. Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 448–456. [31] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers: Surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 2015: 1026–1034. [32] KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2014. -





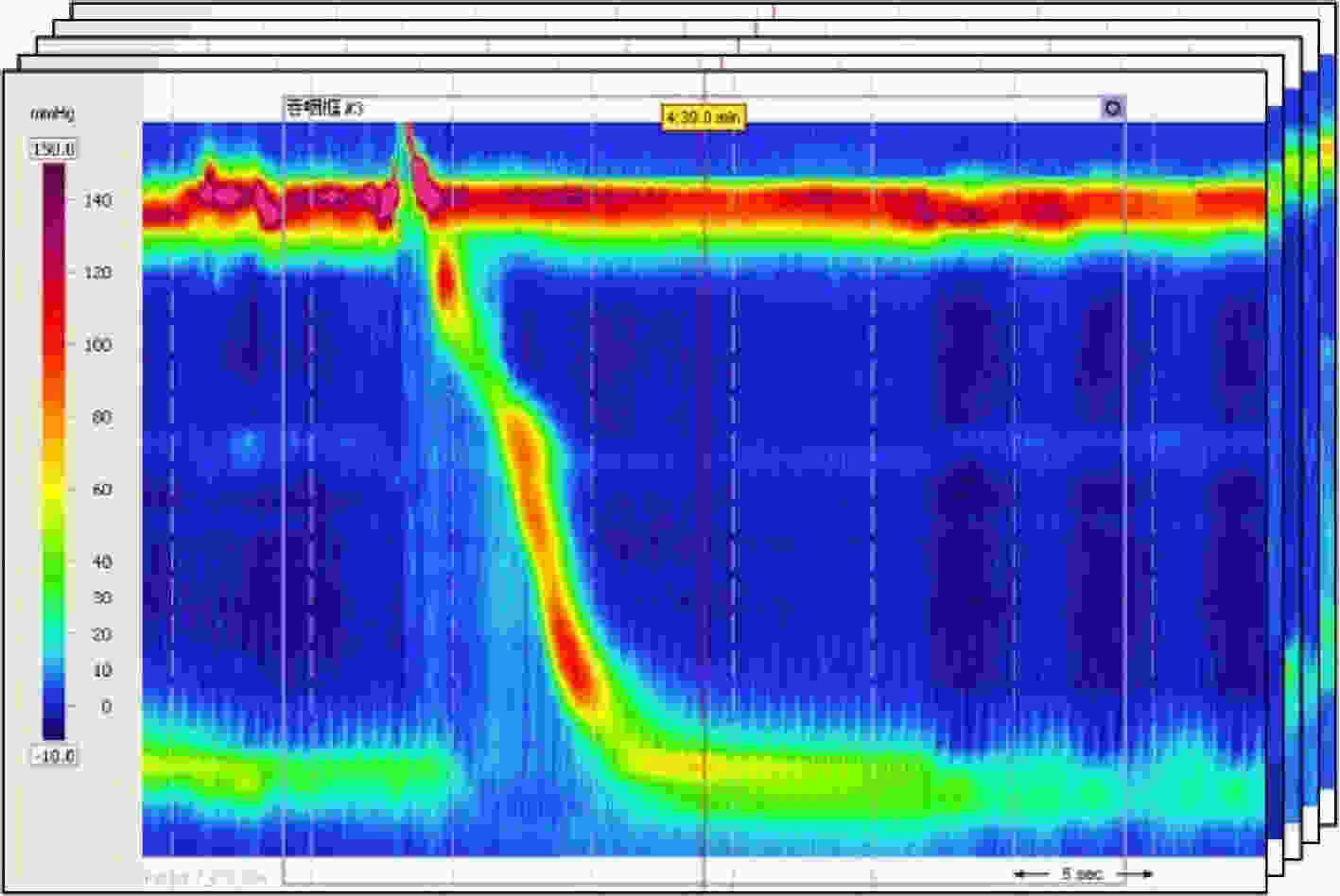
 下载:
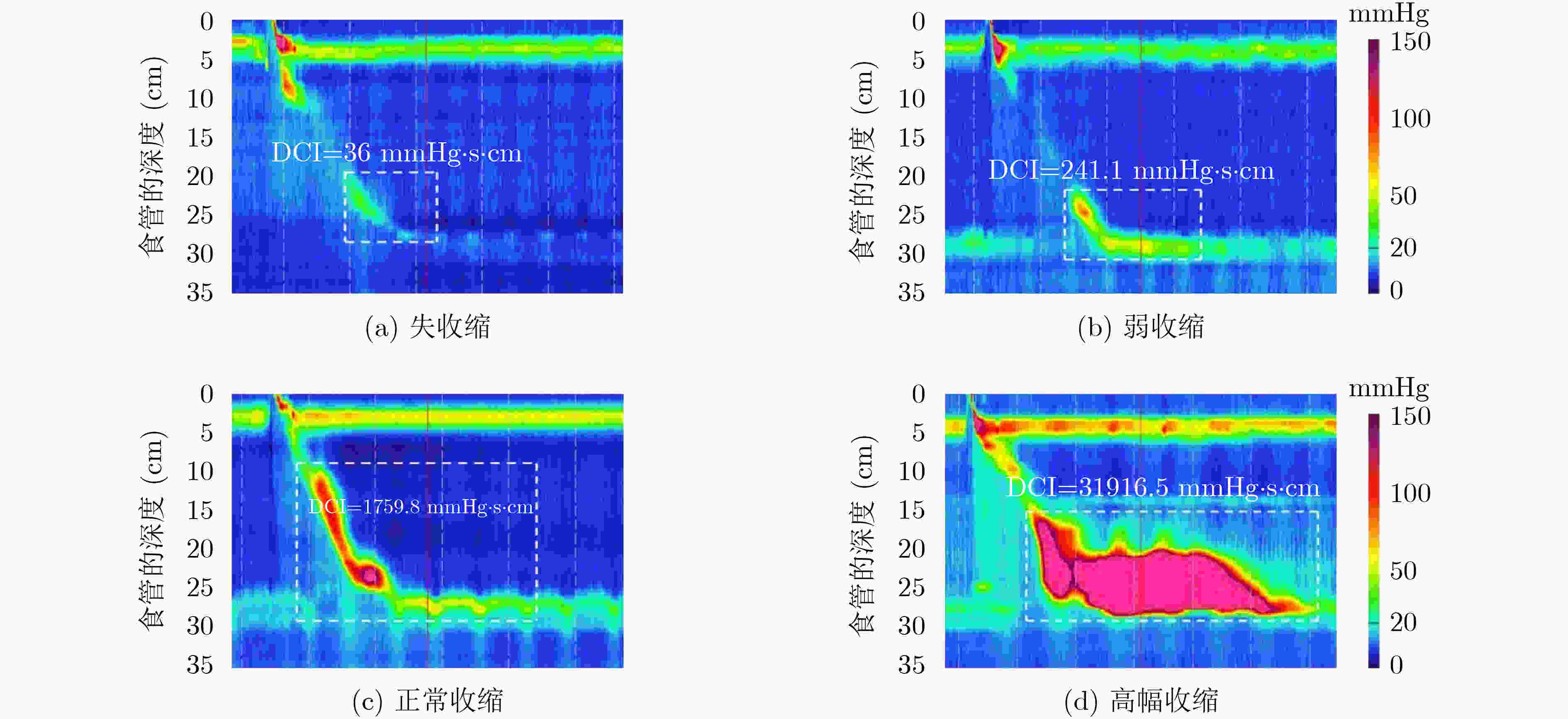
下载:
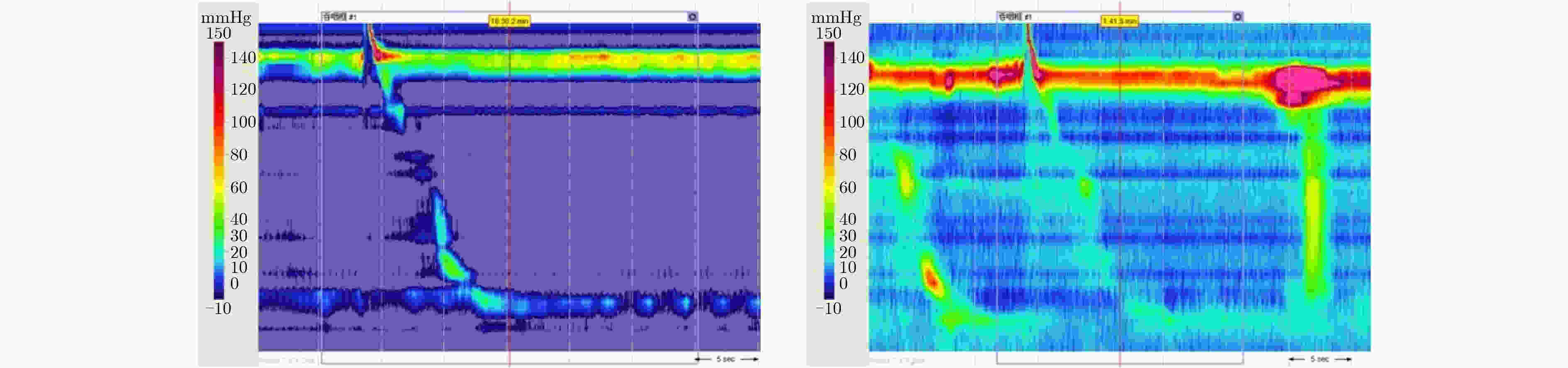



 下载:
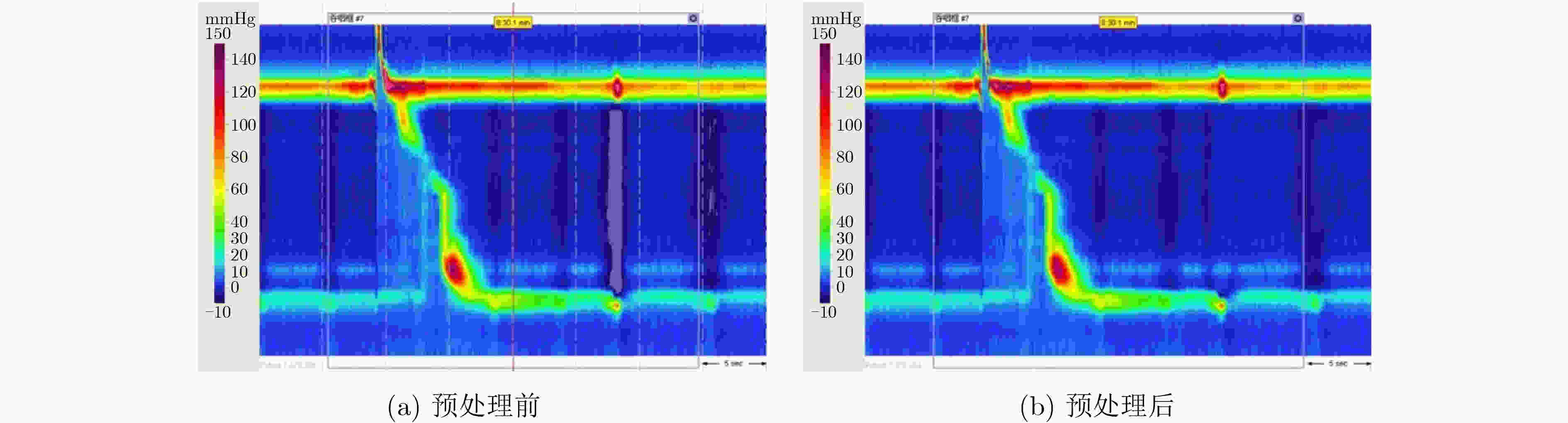
下载:
