Research on Progress of Computing In-Memory Based on Static Random-Access Memory
-
摘要: 随着“算力时代”到来,大规模数据需要在存储器和处理器之间往返,然而传统冯·诺依曼架构中计算与存储分离,无法满足频繁访问的需求。存内计算(CIM)技术的诞生突破了冯·诺依曼瓶颈,打破了传统计算架构中的“存储墙”,因此对于“算力时代”具有革命性意义。由于静态随机存取存储器(SRAM)读取数据的速度快且与先进逻辑工艺具有较好的兼容性,因此基于SRAM的存内计算技术受到国内外学者的关注。该文主要概述了基于SRAM的存内计算技术在机器学习、编码、加解密算法等方面的应用;回顾了实现运算功能的各种电路结构,比较了各类以模数转换器(ADC)为核心的量化技术;之后分析了现有存内计算架构面临的挑战并且给出了现有的解决策略,最后从不同方面展望存内计算技术。Abstract: With the arrival of the “computing power era”, large-scale data need to go back and forth between the memory and the processor. However, the demand for frequent access can not be achieved in the traditional Von Neumann architecture which separates the computing and storage. The Von Neumann bottleneck and the “storage wall” in the traditional computing architecture have been broken with the birth of Computing In-Memory (CIM) Static Random-Access Memory technique. Thereby, for the “computing power era” it has revolutionary significance. Due to Static Random-Access Memory (SRAM) reads data fast and has better compatibility with advanced logic technology. Therefore, the attention of scholars at domestic and international has been attracted by SRAM-based CIM technology. The application of SRAM-based CIM technology is summarized, including machine learning, coding, encryption and decryption algorithm. The various circuit structures to realize the operation function and various quantization techniques based on Analog-to-Digital Conversion (ADC) are summarized and compared in this paper. In addition, the problems and challenges of the existing CIM architectures are analyzed. Then some existing solution strategies for those issues also are presented. Finally, the technique of SRAM-based CIM is prospected from different aspects.
-
表 1 CIM实现布尔运算的相关设计参数以及性能指标
文献[2] 文献[26] 文献[29] 文献[31] 文献[33] 传输管
工艺
阵列大小8T/8T+ 8T 8T 6T 8T 45 nm PTM 180 nm 22 nm FD-SOI 28 nm 65 nm NA NA 4 kB 16 kb 16 kb 功耗每bit(fJ) 8T:17.25
8T+:29.6721.84 248 (0.9 V) 23.8 16.6 (0.8 V)
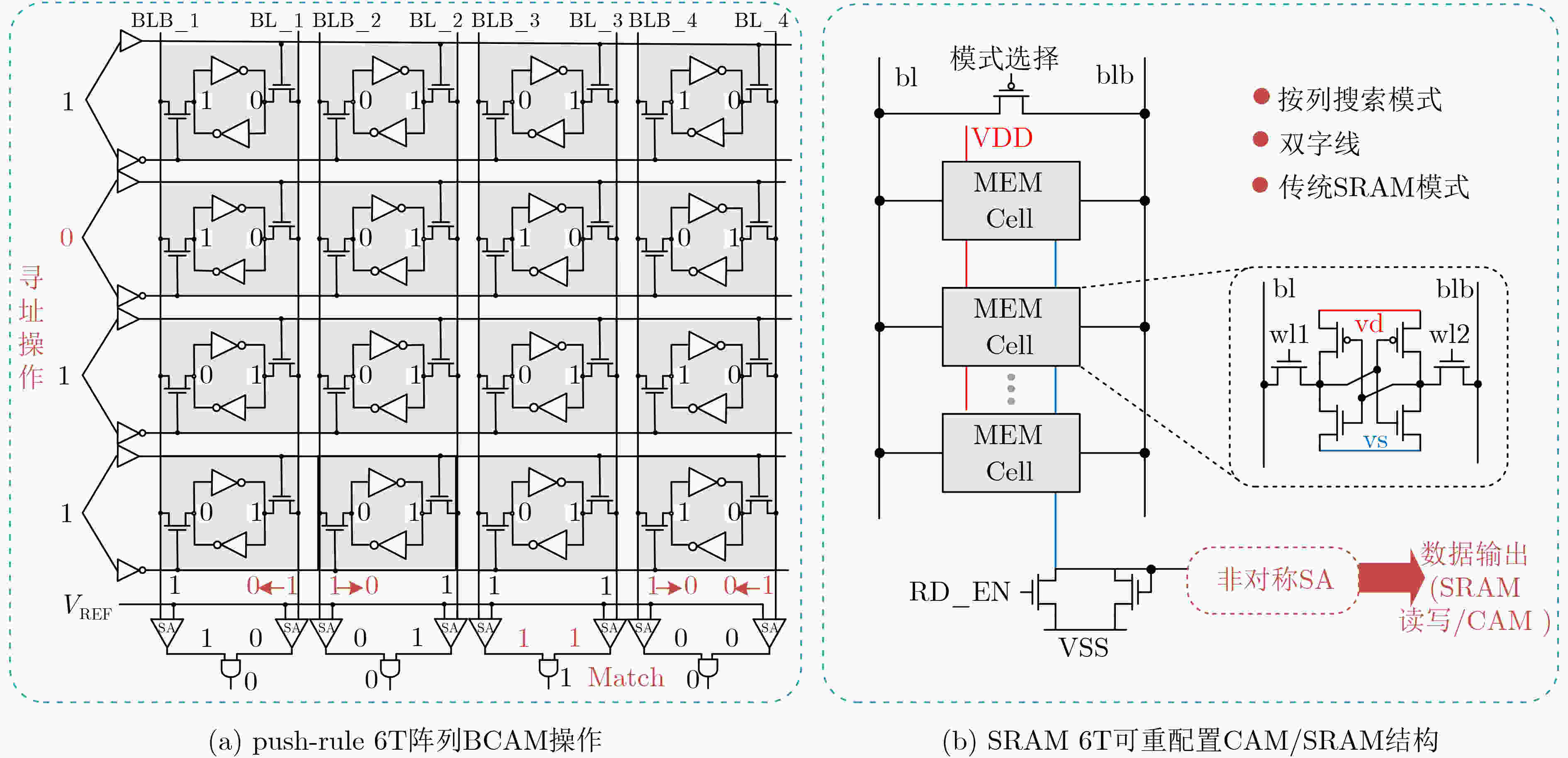
13.2 (0.6 V)功能 NAND/XOR/
NOR/RCSNAND/AND/NOR/
OR/XORAND/OR (multi_row selsction) NOR/AND/XOR AND/NAND /NOR/OR/ XOR/XNOR 特点 8T:读写分离
8T+:读写分离,非对称SA检测读写分离 读写分离 局部位线 4输入的布尔逻辑运算 表 2 存内实现乘法运算的参数以及性能指标
文献[3] 文献[4] 文献[12] 文献[11,13] 文献[14] 文献[37] 文献[18,19] 文献[40] 单元类型 6T 8T1C 10T 8T 10T Twin-8T 6T 6T 工艺(nm) 65 65 65 7 45 55 130 55 阵列大小(Kb) 64 2 16 4 8 3.75 16 4 输入(bit) 5 1 6 4 1 1, 2, 4 5 1, 2, 7, 8 权重(bit) 5 1 1 4 1 2, 5 1 1, 2, 8 能效TOPS/W NA 671.5 40.3(1 V) 351(0.8 V) NA singles channel:18.4-72.0 NA 0.6~40.2(0.9 V) 面积(μm2) NA 8.1×104 6.3×104 3.2×103 NA 4.69×104 2.67×105 5.94×106 精确度(%) MINST 99.05 98.31 >98 >99 NA 90.02~99.52 >90 >98 CIFAR10 88.83 83.50 NA >88 约89 85.56~90.42 NA >85 表 3 存内CAM芯片参数以及性能指标总结
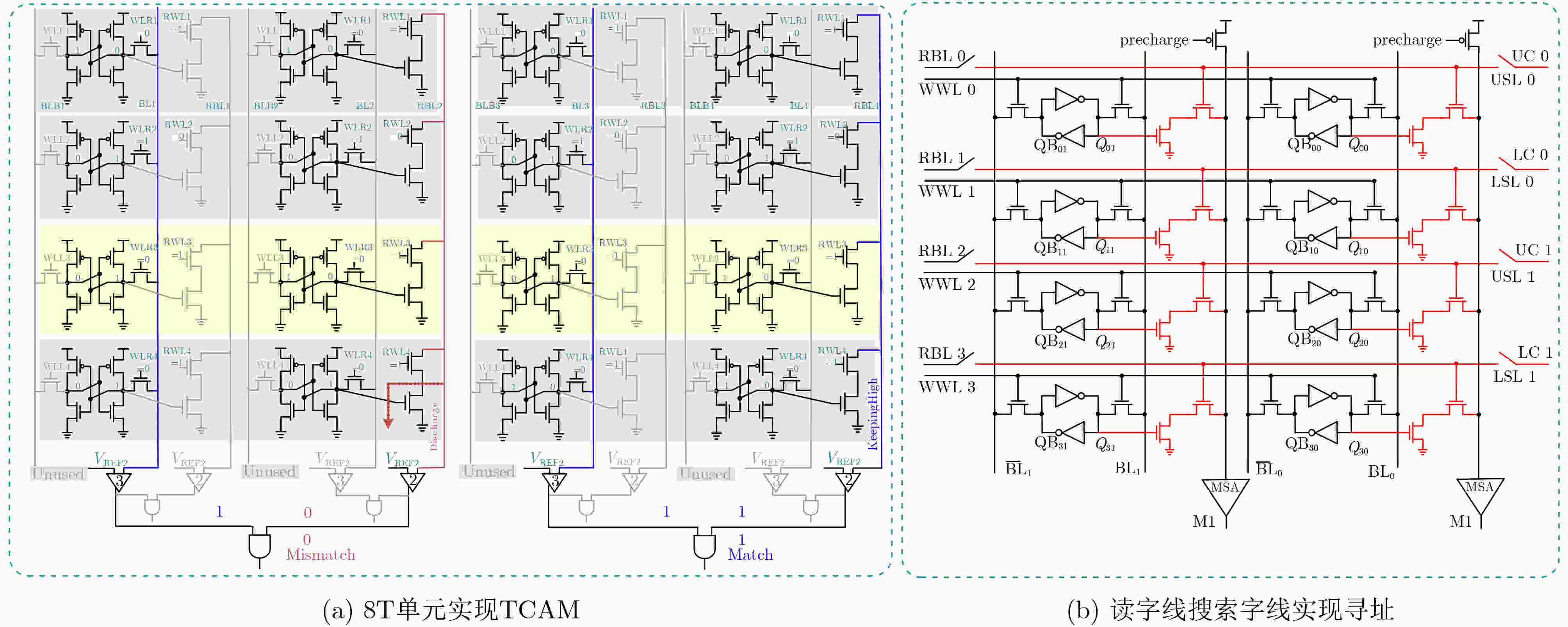
文献[9] 文献[10] 文献[33] 文献[41] 文献[42] 阵列大小 BCAM:4 kb 16 kb 16 kb 8 kb 16 kb TCAM:2 kb 单元类型 6T 4+2T 8T 6T 9T 工艺(nm) 28 55 65 28 65 功能 BCAM/TCAM/
SRAM/LogicBCAM/TCAM/Logic BCAM/TCAM/
SRAM/LogicBCAM/SRA/
Pseudo-TCAMBCAM 功耗每bit(fJ) BCAM:0.6 (1 V) BCAM:0.45 (0.8 V) BCAM:0.24 (0.6 V) 0.13(0.9 V) BCAM:2.07 (0.4 V) TCAM:0.74 TCAM:0.41 -
[1] JAISWAL A, CHAKRABORTY I, AGRAWAL A, et al. 8T SRAM cell as a multibit dot-product engine for beyond von neumann computin[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VlSI) Systems, 2019, 27(11): 2556–2567. doi: 10.1109/tvlsi.2019.2929245 [2] AGRAWAL A, JAISWAL A, LEE C, et al. X-SRAM: Enabling in-memory boolean computations in CMOS static random access memories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2018, 65(12): 4219–4232. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2018.2848999 [3] ALI M, JAISWAL A, KODGE S, et al. IMAC: In-memory multi-bit multiplication and ACcumulation in 6T SRAM array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2020, 67(8): 2521–2531. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2020.2981901 [4] JIANG Zhewei, YIN Shihui, SEO J S, et al. C3SRAM: In-memory-computing SRAM macro based on capacitive-coupling computing[J]. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Letters, 2019, 2(9): 131–134. doi: 10.1109/LSSC.2019.2934831 [5] JIANG Zhewei, YIN Shihui, SEO J S, et al. C3SRAM: An in-memory-computing SRAM macro based on robust capacitive coupling computing mechanism[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(7): 1888–1897. doi: 10.1109/Jssc.2020.2992886 [6] ZENG Jianmin, ZHANG Zhang, CHEN Runhao, et al. DM-IMCA: A dual-mode in-memory computing architecture for general purpose processing[J]. IEICE Electronics Express, 2020, 17(4): 20200005. doi: 10.1587/elex.17.20200005 [7] ZHANG Hongtu, SHU Yuhao, JIANG Weixiong, et al. A 55nm, 0.4V 5526-TOPS/W compute-in-memory binarized CNN accelerator for AIoT applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2021, 68(5): 1695–1699. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2021.3066520 [8] WANG Jingcheng, WANG Xiaowei, ECKERT C, et al. A 28-nm compute SRAM with bit-serial logic/arithmetic operations for programmable in-memory vector computing[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(1): 76–86. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2939682 [9] JELOKA S, AKESH N B, SYLVESTER D, et al. A 28 nm configurable memory (TCAM/BCAM/SRAM) using push-rule 6T bit cell enabling logic-in-memory[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2016, 51(4): 1009–1021. doi: 10.1109/jssc.2016.2515510 [10] DONG Qing, JELOKA S, SALIGANE M, et al. A 4 + 2T SRAM for searching and in-memory computing with 0.3-V VDDmin[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2018, 53(4): 1006–1015. doi: 10.1109/jssc.2017.2776309 [11] DONG Qing, SINANGIL M E, ERBAGCI B, et al. 15.3 A 351TOPS/W and 372.4GOPS compute-in-memory SRAM macro in 7nm FinFET CMOS for machine-learning applications[C]. The 2020 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference - (ISSCC), San Francisco, USA, 2020: 242–244. [12] BISWAS A and CHANDRAKASAN A P. CONV-SRAM: An energy-efficient SRAM with in-memory dot-product computation for low-power convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2019, 54(1): 217–230. doi: 10.1109/jssc.2018.2880918 [13] SINANGIL M E, ERBAGCI B, NAOUS R, et al. A 7-nm compute-in-memory SRAM macro supporting multi-bit input, weight and output and achieving 351 TOPS/W and 372.4 GOPS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2021, 56(1): 188–189. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.3031290 [14] AGRAWAL A, JAISWAL A, ROY D, et al. Xcel-RAM: Accelerating binary neural networks in high-throughput SRAM compute arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2019, 66(8): 3064–3076. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2019.2907488 [15] SI Xin, KHWA W S, CHEN Jiajing, et al. A dual-split 6T SRAM-based computing-in-memory unit-macro with fully parallel product-sum operation for binarized DNN edge processors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2019, 66(11): 4172–4185. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2019.2928043 [16] KHWA W S, CHEN Jiajing, LI Jiafang, et al. A 65nm 4Kb algorithm-dependent computing-in-memory SRAM unit-macro with 2.3ns and 55.8TOPS/W fully parallel product-sum operation for binary DNN edge processors[C]. The 2018 IEEE International Solid - State Circuits Conference - (ISSCC), San Francisco, USA, 2018: 496–498. [17] CHIH Y D, LEE P H, FUJIWARA H, et al. 16.4 An 89TOPS/W and 16.3TOPS/mm2 all-digital SRAM-based full-precision compute-in memory macro in 22nm for machine-learning edge applications[C]. The 2021 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, USA, 2021: 252–254. [18] ZHANG Jintao, WANG Zhuo, and VERMA N. A machine-learning classifier implemented in a standard 6T SRAM array[C]. The 2016 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits (VLSI-Circuits), Honolulu, USA, 2016: 1–2. [19] ZHANG Jintao, WANG Zhuo, and VERMA N. In-memory computation of a machine-learning classifier in a standard 6T SRAM array[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2017, 52(4): 915–924. doi: 10.1109/Jssc.2016.2642198 [20] KANG M, GONUGONDLA S K, and SHANBHAG N R. A 19.4 nJ/decision 364K decisions/s in-memory random forest classifier in 6T SRAM array[C]. The ESSCIRC 2017 - 43rd IEEE European Solid State Circuits Conference, Leuven, Belgium, 2017: 263–266. [21] KANG M and SHANBHAG N R. In-memory computing architectures for sparse distributed memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2016, 10(4): 855–863. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2016.2545402 [22] ALI M, AGRAWAL A, and ROY K. RAMANN: In-SRAM differentiable memory computations for memory-augmented neural networks[C]. The ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design, Massachusetts, USA, 2020: 61–66. [23] WANG Yuhao, NI Leibin, CHANG C H, et al. DW-AES: A domain-wall nanowire-based AES for high throughput and energy-efficient data encryption in non-volatile memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(11): 2426–2440. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2576903 [24] WANG Yuhao, YU Hao, SYLVESTER D, et al. Energy efficient in-memory AES encryption based on nonvolatile domain-wall nanowire[C]. The 2014 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Dresden, Germany, 2014: 1–4. [25] HUANG Shanshi, JIANG Hongwu, PENG Xiaochen, et al. XOR-CIM: Compute-in-memory SRAM architecture with embedded XOR encryption[C]. The 39th International Conference On Computer-Aided Design, San Diego, CA, USA, 2020: 77. [26] RAJPUT A K and PATTANAIK M. Implementation of boolean and arithmetic functions with 8T SRAM cell for in-memory computation[C]. The 2020 International Conference for Emerging Technology (INCET), Belgaum, India, 2020: 1–5. [27] CHEN Jian, ZHAO Wenfeng, and HA Yajun. Area-efficient distributed arithmetic optimization via heuristic decomposition and in-memroy computing[C]. The 2019 IEEE 13th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), Chongqing, China, 2019: 1–4. [28] KIM H, CHEN Qian, and KIM B. A 16K SRAM-based mixed-signal in-memory computing macro featuring voltage-mode accumulator and row-by-row ADC[C]. The 2019 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), Macao, China, 2019: 35–36. [29] NOEL J P, PEZZIN M, GAUCHI R, et al. A 35.6 TOPS/W/mm² 3-stage pipelined computational SRAM with adjustable form factor for highly data-centric applications[J]. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Letters, 2020, 3: 286–289. doi: 10.1109/lssc.2020.3010377 [30] SIMON W A, QURESHI Y M, RIOS M, et al. BLADE: An in-cache computing architecture for edge devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2020, 69(9): 1349–1363. doi: 10.1109/TC.2020.2972528 [31] SIMON W, GALICIA J, LEVISSE A, et al. A fast, reliable and wide-voltage-range in-memory computing architecture[C]. The 56th Annual Design Automation Conference 2019, San Francisco, USA, 2019: 83. [32] SURANA N, LAVANIA M, BARMA A, et al. Robust and high-performance 12-T interlocked SRAM for in-memory computing[C]. The 2020 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 2020: 1323–1326. [33] LIN Zhiting, ZHAN Honglan, LI Xuan, et al. In-memory computing with double word lines and three read ports for four operands[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2020, 28(5): 1316–1320. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2020.2976099 [34] SUN Xiaoyu, LIU Rui, PENG Xiaochen, et al. Computing-in-memory with SRAM and RRAM for binary neural networks[C]. The 2018 14th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), Qingdao, China, 2018: 1–4. [35] JIANG Hongwu, LIU Rui, and YU Shimeng. 8T XNOR-SRAM based parallel compute-in-memory for deep neural network accelerator[C]. The 2020 IEEE 63rd International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Springfield, USA, 2020: 257–260. [36] LIU Rui, PENG Xiaochen, SUN Xiaoyu, et al. Parallelizing SRAM arrays with customized bit-cell for binary neural networks[C]. The 55th Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2018: 21. [37] SI Xin, CHEN Jiajing, TU Y N, et al. A Twin-8T SRAM computation-in-memory unit-macro for multibit CNN-based AI edge processors[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(1): 189–202. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2952773 [38] SU Jianwei, SI Xin, CHOU Y C, et al. 15.2 A 28nm 64Kb inference-training two-way transpose multibit 6T SRAM compute-in-memory macro for AI edge chips[C]. The 2020 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference - (ISSCC), San Francisco, USA, 2020: 240–242. [39] KNEIP A and BOL D. Impact of analog non-idealities on the design space of 6T-SRAM current-domain dot-product operators for in-memory computing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2021, 68(5): 1931–1944. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2021.3058510 [40] CHIU Y C, ZHANG Zhixiao, CHEN Jiajing, et al. A 4-Kb 1-to-8-bit configurable 6T SRAM-based computation-in-memory unit-macro for CNN-based AI edge processors[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(10): 2790–2801. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.3005754 [41] GUPTA N, MAKOSIEJ A, VLADIMIRESCU A, et al. 1.56GHz/0.9V energy-efficient reconfigurable CAM/SRAM using 6T-CMOS bitcell[C]. The ESSCIRC 2017 - 43rd IEEE European Solid State Circuits Conference, Leuven, Belgium, 2017: 316–319. [42] WANG Bo, NGUYEN T Q, DO A T, et al. Design of an ultra-low voltage 9T SRAM with equalized bitline leakage and CAM-assisted energy efficiency improvement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2015, 62(2): 441–448. doi: 10.1109/tcsi.2014.2360760 [43] SRINIVASA S, CHEN Weihao, TU Y N, et al. Monolithic-3D integration augmented design techniques for computing in SRAMs[C]. The 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Sapporo, Japan, 2019: 1–5. [44] CHEN Hanchun, LI Jinfu, HSU C L, et al. Configurable 8T SRAM for enbling in-memory computing[C]. The 2019 2nd International Conference on Communication Engineering and Technology (ICCET), Nagoya, Japan, 2019: 139–142. [45] LIN Zhiting, ZHU Zhiyong, ZHAN Honglan, et al. Two-direction in-memory computing based on 10T SRAM with horizontal and vertical decoupled read ports[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2021, 56(9): 2832–2844. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2021.3061260 [46] XUE Chengxin, ZHAO Weicheng, YANG T H, et al. A 28-nm 320-Kb TCAM macro using split-controlled single-load 14T cell and triple-margin voltage sense amplifier[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2019, 54(10): 2743–2753. doi: 10.1109/jssc.2019.2915577 [47] BISWAS A and CHANDRAKASAN A P. Conv-RAM: An energy-efficient SRAM with embedded convolution computation for low-power CNN-based machine learning applications[C]. The 2018 IEEE International Solid - State Circuits Conference - (ISSCC), San Francisco, USA, 2018: 488–490. [48] KHADDAM-ALJAMEH R, FRANCESE P A, BENINI L, et al. An SRAM-based multibit in-memory matrix-vector multiplier with a precision that scales linearly in area, time, and power[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2021, 29(2): 372–385. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2020.3037871 [49] JIA Hongyang, VALAVI H, TANG Yinqi, et al. A programmable heterogeneous microprocessor based on bit-scalable in-memory computing[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(9): 2609–2621. doi: 10.1109/jssc.2020.2987714 [50] GONG Minxiang, CAO Ningyuan, CHANG Muya, et al. A 65nm thermometer-encoded time/charge-based compute-in-memory neural network accelerator at 0.735pJ/MAC and 0.41pJ/Update[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2021, 68(4): 1408–1412. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2020.3027801 [51] JIANG Hongwu, PENG Xiaochen, HUANG Shanshi, et al. CIMAT: A compute-in-memory architecture for on-chip training based on transpose SRAM arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2020, 69(7): 944–954. doi: 10.1109/tc.2020.2980533 [52] JIANG Hongwu, PENG Xiaochen, HUANG Shanshi, et al. CIMAT: A transpose SRAM-based compute-in-memory architecture for deep neural network on-chip training[C]. The International Symposium on Memory Systems, Columbia, 2019: 490–496. [53] YIN Shihui, JIANG Zhewei, SEO J S, et al. XNOR-SRAM: In-memory computing SRAM macro for binary/ternary deep neural networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55(6): 1733–1743. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2963616 [54] SU Jianwei, CHOU Y C, LIU Ruhui, et al. 16.3 a 28nm 384kb 6T-SRAM computation-in-memory macro with 8b precision for AI edge chips[C]. The 2021 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, USA, 2021: 250–252. [55] GONUGONDLA S K, KANG M, and SHANBHAG N R. A variation-tolerant in-memory machine learning classifier via on-chip training[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2018, 53(11): 3163–3173. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2018.2867275 [56] GONUGONDLA S K, KANG M, and SHANBHAG N. A 42pJ/decision 3.12TOPS/W robust in-memory machine learning classifier with on-chip training[C]. The 2018 IEEE International Solid - State Circuits Conference - (ISSCC), San Francisco, USA, 2018: 490–492. [57] ZHANG Jin, LIN Zhiting, WU Xiulong, et al. An 8T SRAM array with configurable word lines for in-memory computing operation[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(3): 300. doi: 10.3390/electronics10030300 [58] LIN Zhiting, ZHANG Honglan, CHEN Zhongwei, et al. Cascade current mirror to improve linearity and consistency in SRAM in-memory computing[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2021, 56(8): 2550–2562. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2021.3063719 [59] KIM H, YOO T, KIM T T H, et al. Colonnade: A reconfigurable SRAM-based digital bit-serial compute-in-memory macro for processing neural networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2021, 56(7): 2221–2233. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2021.3061508 [60] KANG M, GONUGONDLA S K, PATIL A, et al. A multi-functional in-memory inference processor using a standard 6T SRAM array[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2018, 53(2): 642–655. doi: 10.1109/jssc.2017.2782087 -





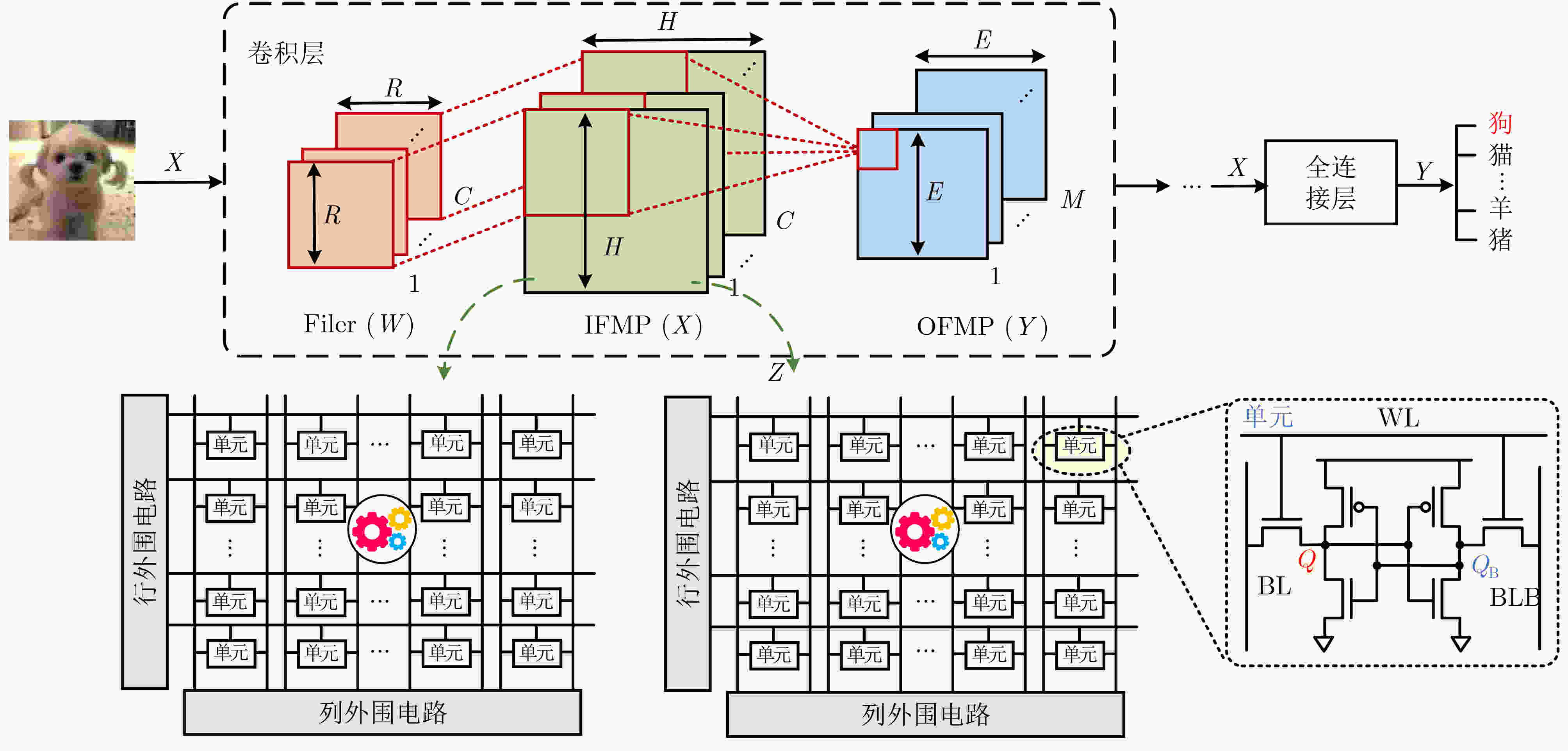
 下载:
下载:
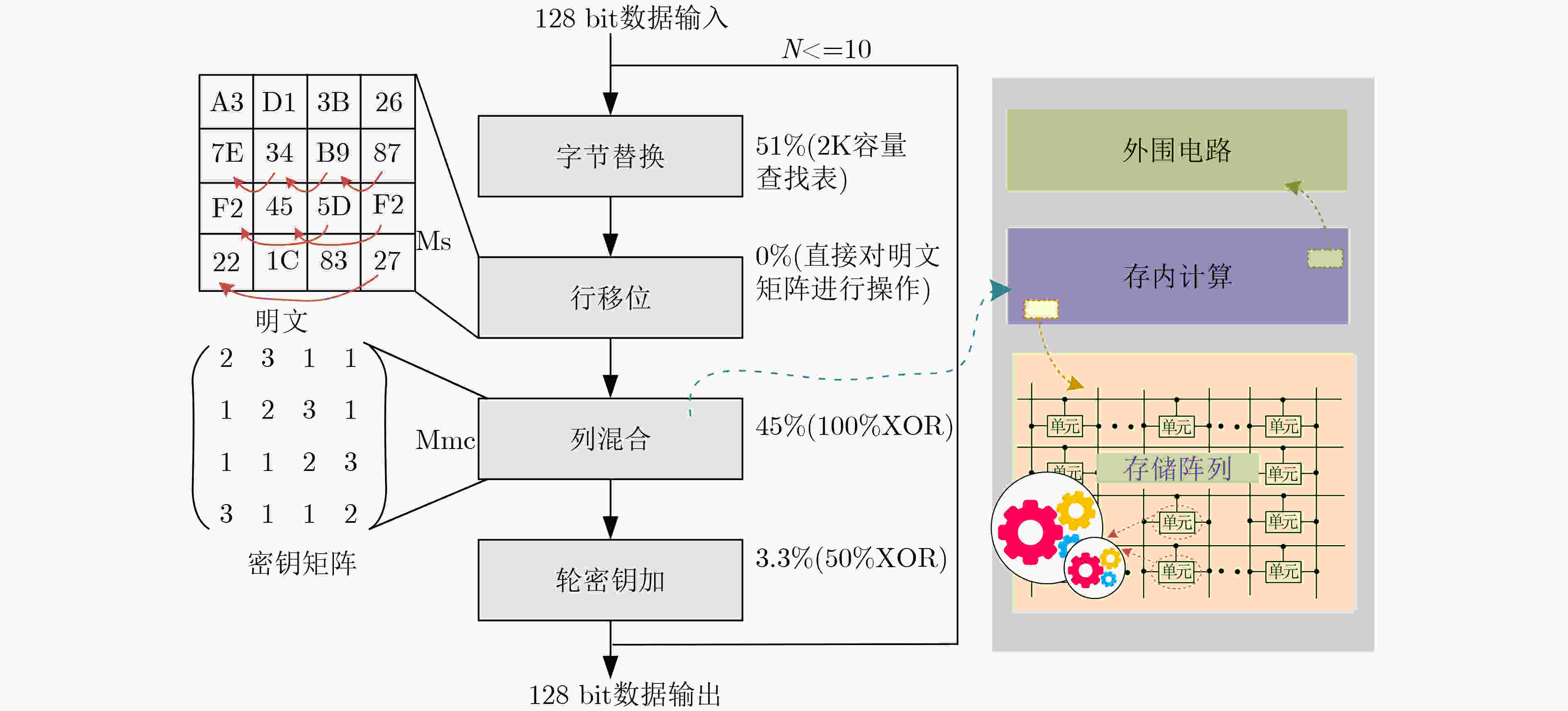
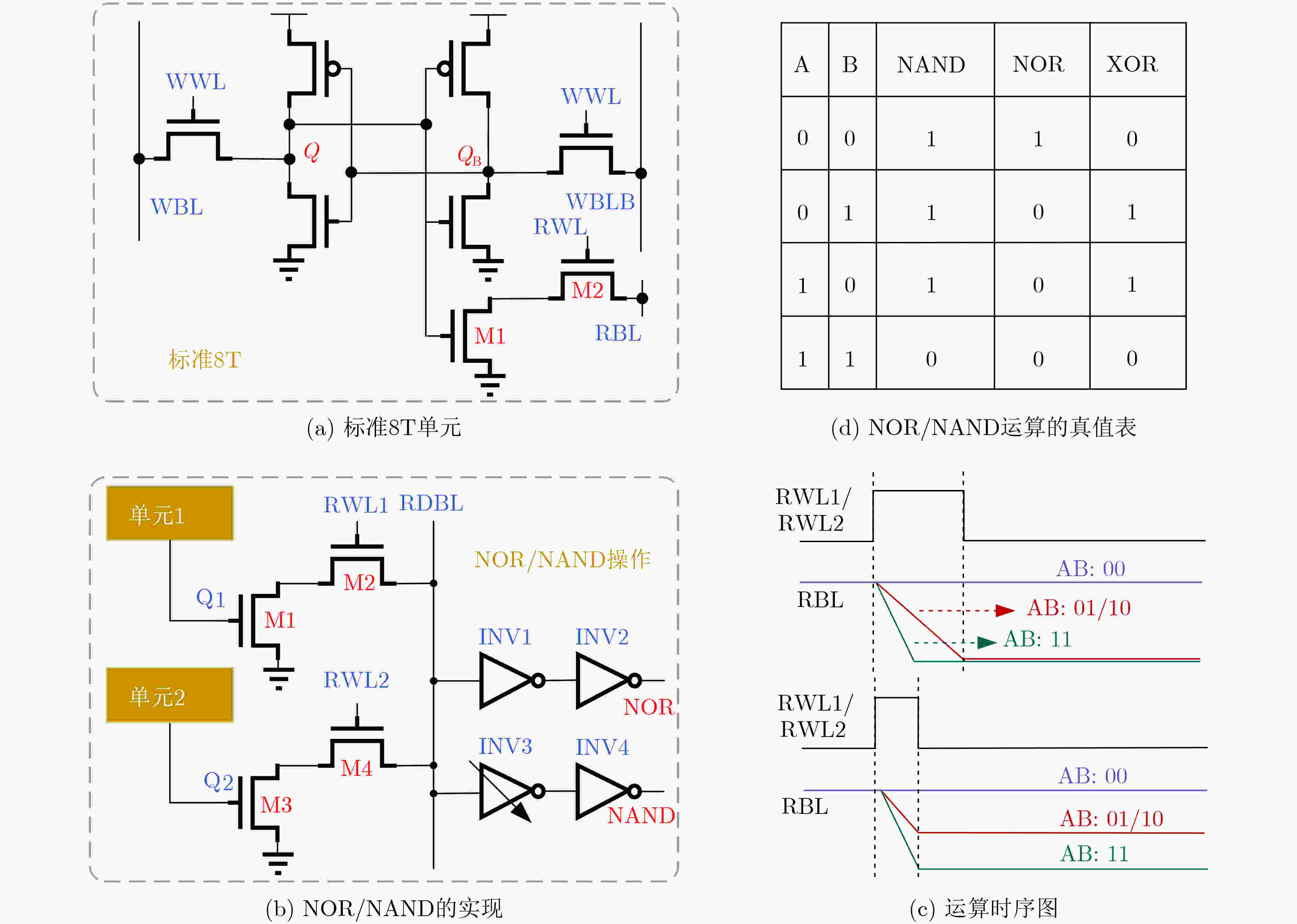

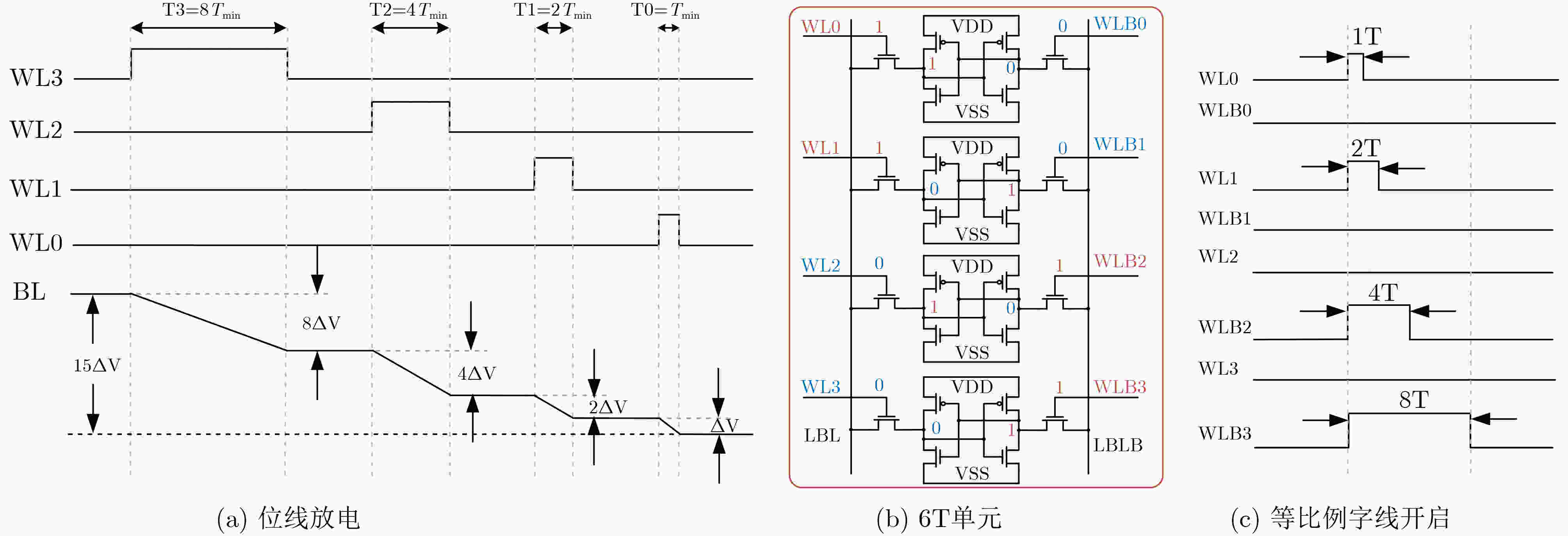
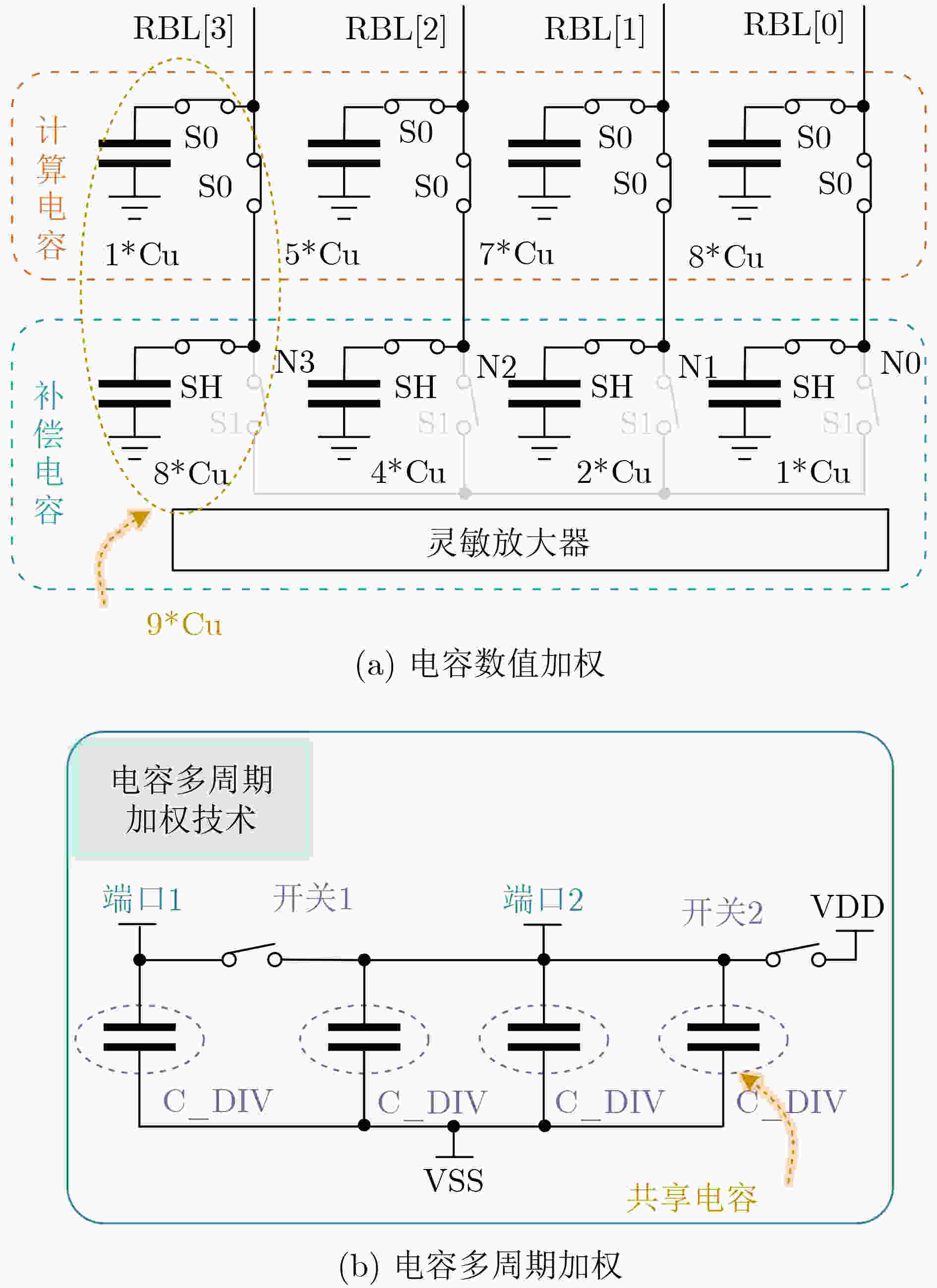
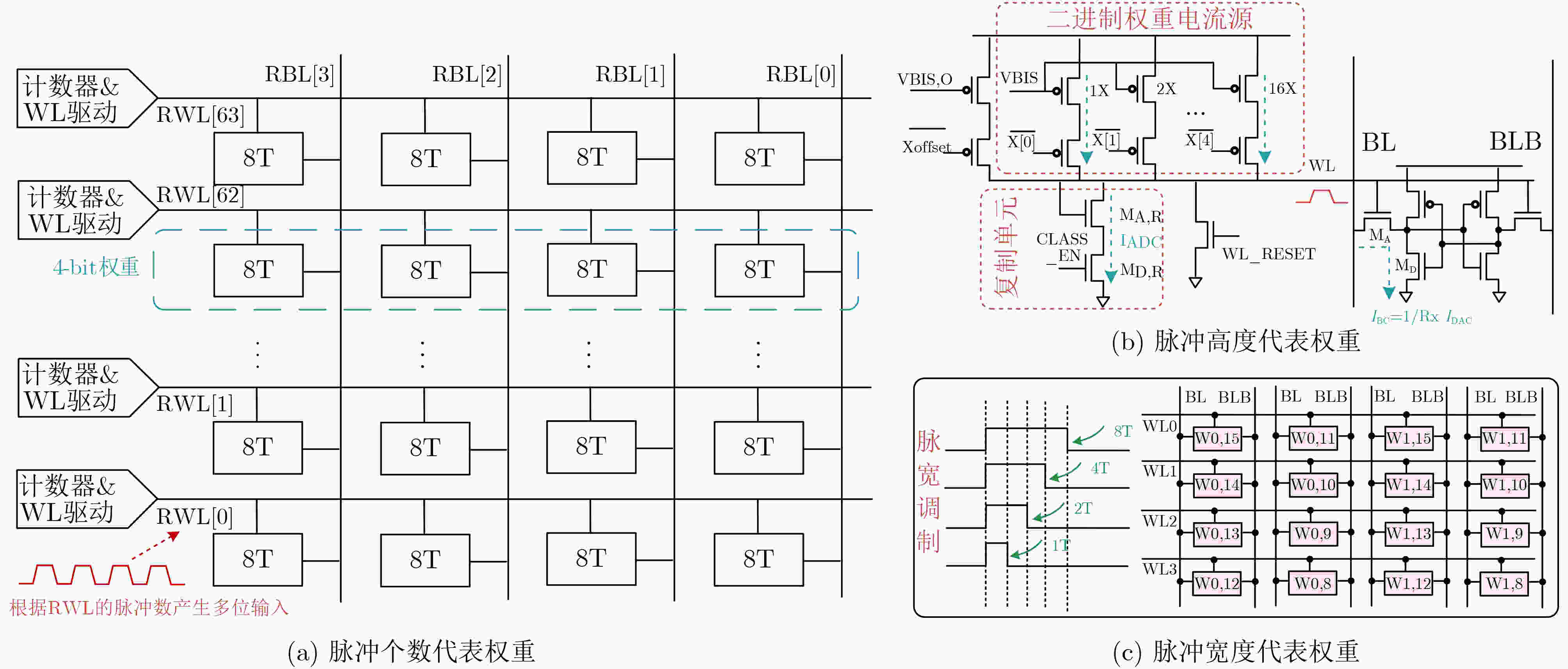
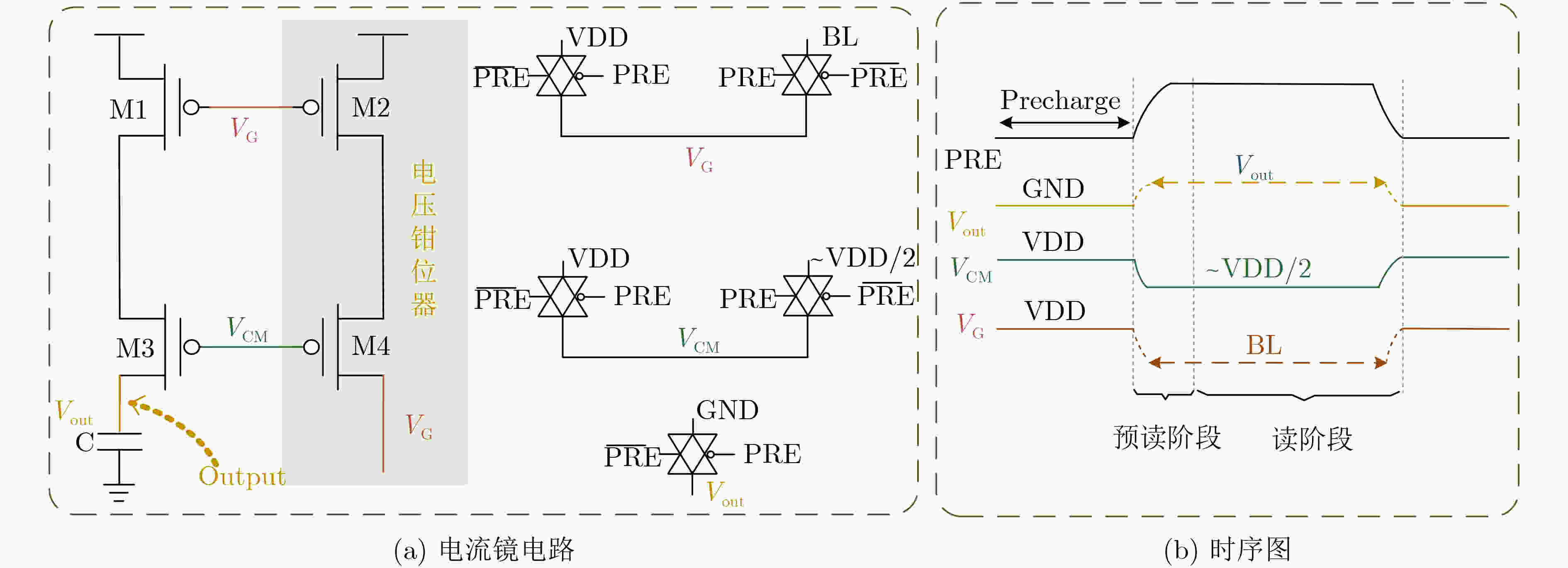
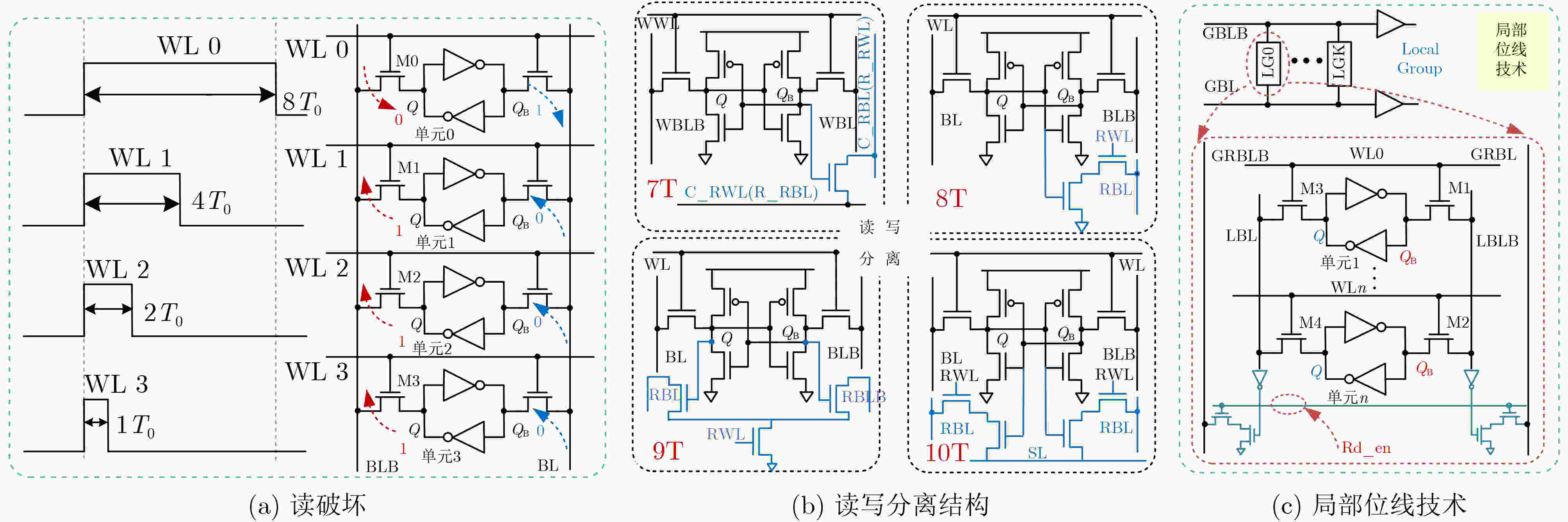
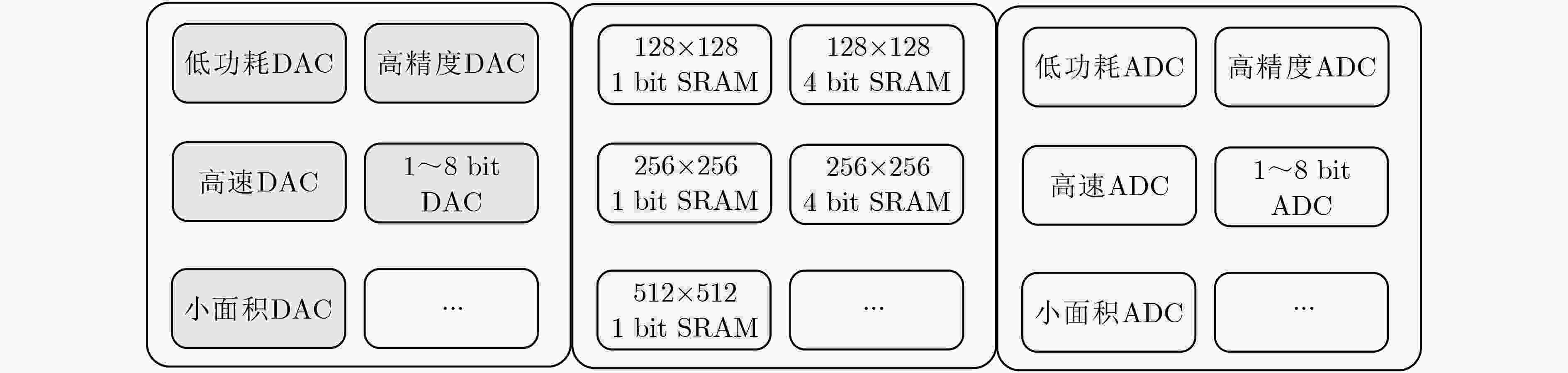
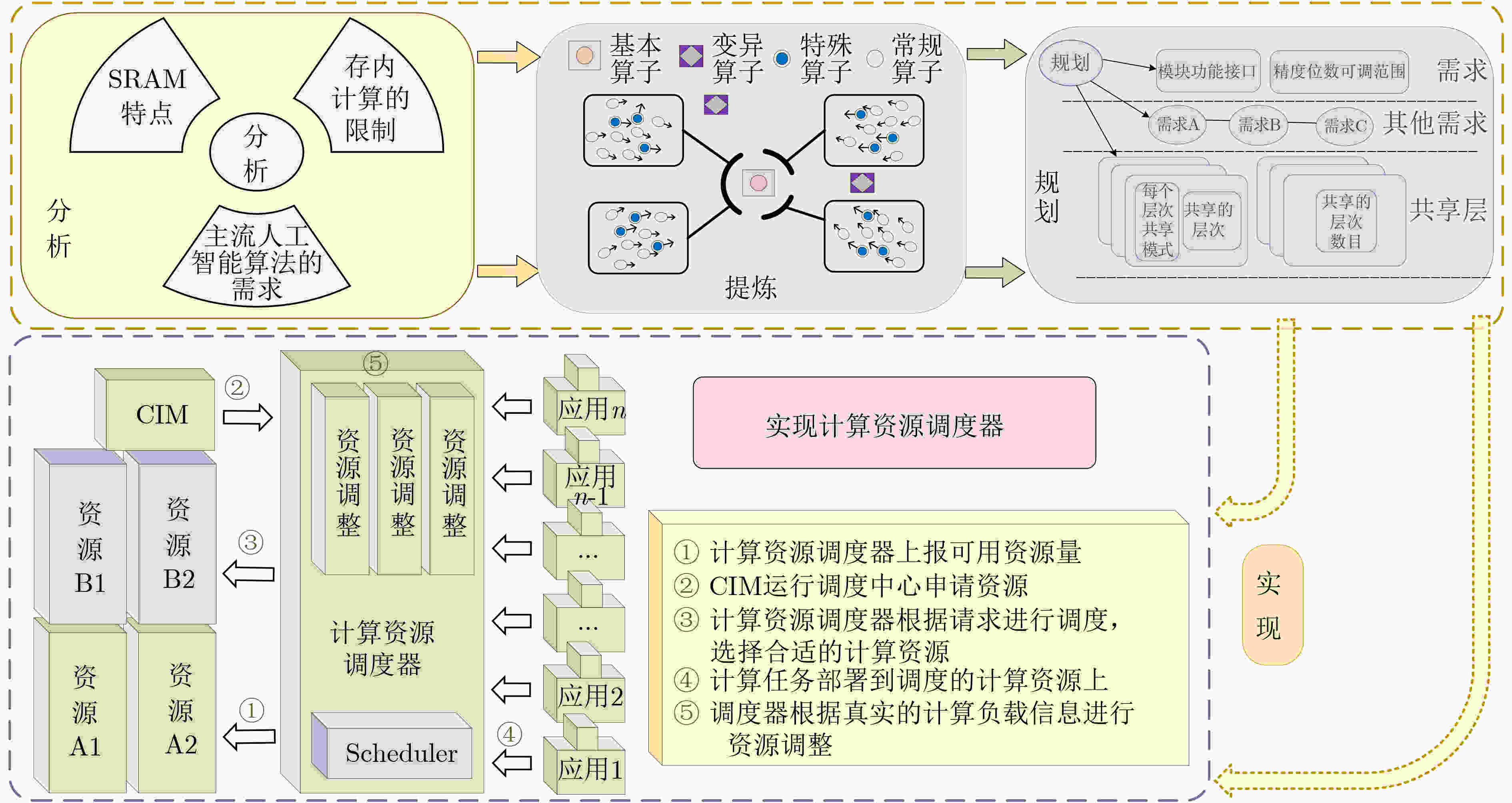
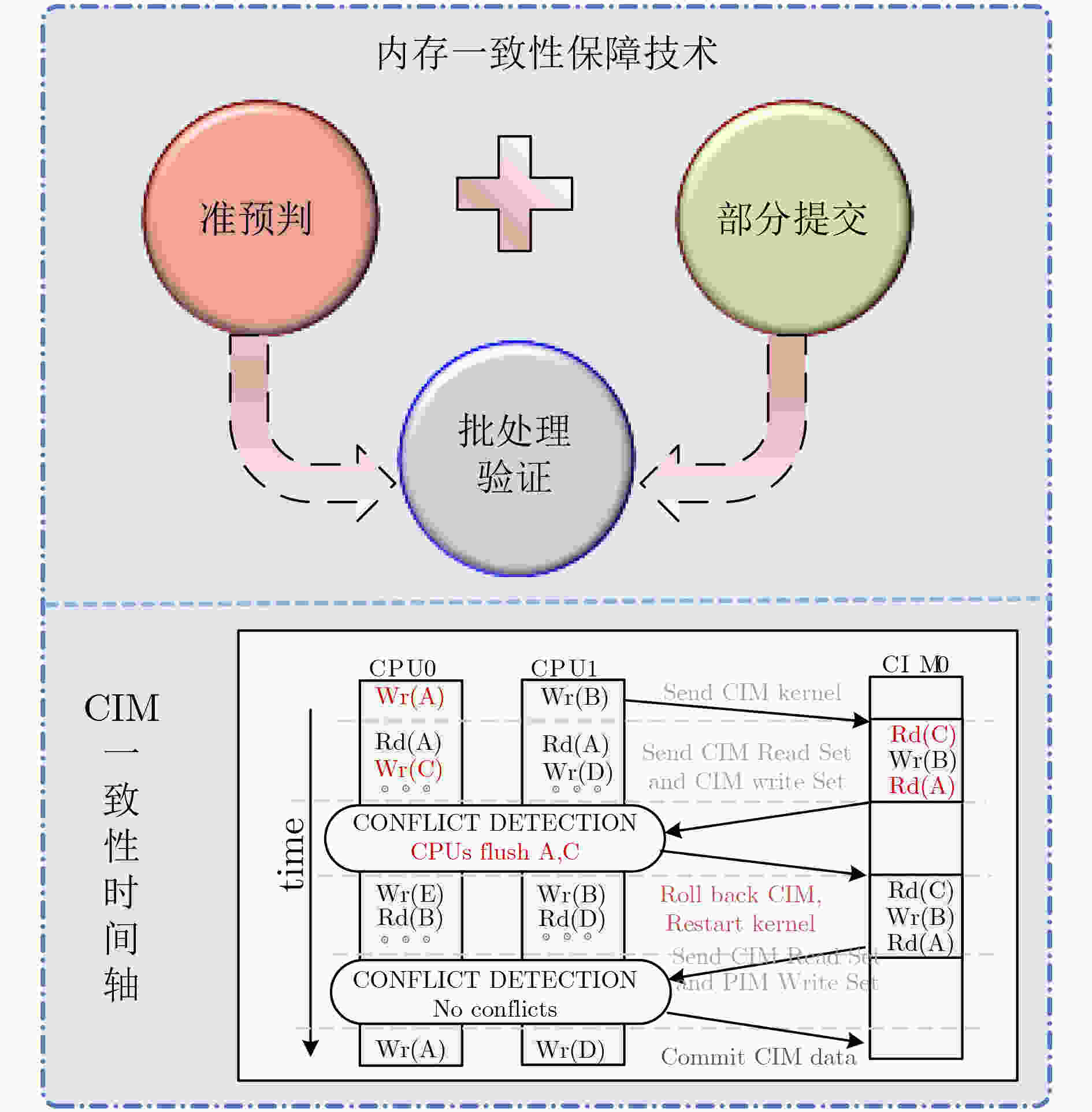


 下载:
下载:
