An Adaptive EOG Removal Method Based on Local Density
-
摘要: 脑电信号幅值微弱且信噪比低易受到多种伪迹影响。其中,眼电伪迹幅值高、随机性强,常使脑电信号产生明显畸变,对信号的后续分析将产生极大的影响。传统伪迹去除方法难以精确定位伪迹成分,导致过多有效信息丢失。针对上述问题,该文提出一种基于数据驱动的自适应伪迹定位和去除方法。该方法将局部密度引入独立成分分析(ICA)并通过聚类分析自适应估计辨识脑电和噪声成分的阈值,最终实现了眼电伪迹的精准定位和去除。通过仿真和真实实验,该文对比了所提方法与传统伪迹去除方法在峰值信噪比、均方误差、互信息等量化指标下的性能差异,并通过统计检验揭示了所提方法相比于其他方法在信号恢复方面的显著性优势。Abstract: EEG (ElectroEncephaloGram) signal is susceptible to various of artifacts due to its low amplitude and poor SNR (Signal-Noise Ratio). Among this noise, the ocular artifacts usually hold higher amplitude and strong randomness which would cause serious distortion on EEG signal, and result in great influence on the subsequent analysis. However, traditional methods fail to locate the artifacts components accurately, leading to the loss of the efficient signal components. In order to solve the above problem, this paper proposes a data-driven based automatically artifact-localization-and-removement method. In this paper, the local density is firstly introduced into ICA (Independent Component Analysis) so as to estimate the adaptive threshold with clustering strategy. This adaptive threshold would be further used to noise localization and removal. Subsequently, this paper compared the performance differences between the proposed method and the traditional methods through simulation and the real resting-state EEG experiments. The results with indexes such as PSNR (Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio), MSE (Mean Square Error), and MI (Mutual Information) quantitatively verify the significant superiority of the proposed method to other ICA-based ocular artifacts removal strategies through statistical analysis.
-
表 1 仿真实验均值指标对比
Zeroing ICA wICA 本文ATICA SNR 3.96±0.41$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $ 4.70±0.53$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $ 5.73±0.40 MSE 5.46±0.25$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $ 3.56±0.95$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $ 2.69±0.25 PSNR 45.15±0.41$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $ 45.89±0.53$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $ 46.93±0.40 RMSE 1.80±0.06$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $ 1.56±0.13$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $ 1.37±0.06 RCE 0.80±0.02$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $ 0.52±0.03$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $ 0.87±0.03 表 2 真实实验PCC/MI均值对比
电极区域 指标 Zeroing
ICAwICA ATICA 额顶叶(FP) PCC
MI0.63±0.09$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
0.82±0.13$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.63±0.11$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
0.86±0.16$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.68±0.09
1.05±0.17前额叶(AF) PCC
MI0.69±0.09$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
0.88±0.14$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.71±0.11$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
0.98±0.18$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.74±0.09
1.15±0.17额叶(F) PCC
MI0.81±0.05$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
0.97"±0.16$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.85±0.06$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.17±0.24$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.88±0.04
1.35±0.23额颞叶(FT) PCC
MI0.85±0.04$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.01±0.16$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.85±0.05$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.24±0.31$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.88±0.04
1.35±0.28额中央(FC) PCC
MI0.84±0.05$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.02±0.16$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.88±0.05$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.26±0.26$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.91±0.04
1.45±0.23颞叶(T) PCC
MI0.87±0.04$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.09±0.17$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.91±0.04$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.31±0.32$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.94±0.03
1.55±0.32额叶中央沟(C) PCC
MI0.85±0.04$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.04±0.15$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.90±0.05$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.28±0.32$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.93±0.04
1.50±0.33颞顶叶(TP) PCC
MI0.88±0.04$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.07±0.15$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.91±0.03$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.28±0.27$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.94±0.02
1.53±0.27中央顶叶(CP) PCC
MI0.86±0.04$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.07±0.17$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.91±0.03$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.28±0.24$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.94±0.03
1.53±0.24顶叶(P) PCC
MI0.87±0.04$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.06±0.15$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.91±0.03$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.27±0.26$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.94±0.02
1.50±0.24枕叶(O) PCC
MI0.85±0.04$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.02±0.15$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.89±0.04$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.21±0.30$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.92±0.03
1.43±0.31通道指标均值 PCC
MI0.82±0.05$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.00±0.16$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.86±0.05$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $
1.20±0.26$ \boldsymbol{\psi } $0.89±0.04
1.41±0.26 -
[1] CHEN Xun, XU Xueyuan, LIU Aiping, et al. The use of multivariate EMD and CCA for denoising muscle artifacts from few-channel EEG recordings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2018, 67(2): 359–370. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2017.2759398 [2] QIU Yang, ZHOU Weidong, YU Nana, et al. Denoising sparse autoencoder-based ictal EEG classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2018, 26(9): 1717–1726. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2018.2864306. [3] JADAV G M, LERGA J, and ŠTAJDUHAR I. Adaptive filtering and analysis of EEG signals in the time-frequency domain based on the local entropy[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2020, 2020(1): 7. doi: 10.1186/s13634-020-00667-6 [4] SABA-SADIYA S, CHANTLAND E, ALHANAI T, et al. Unsupervised EEG artifact detection and correction[J]. Frontiers in Digital Health, 2021, 2: 608920. doi: 10.3389/fdgth.2020.608920 [5] JEBELLI H, HWANG S, and LEE S. EEG signal-processing framework to obtain high-quality brain waves from an off-the-shelf wearable EEG device[J]. Journal of Computing in Civil Engineering, 2018, 32(1): 04017070. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CP.1943-5487.0000719 [6] 杜晓燕, 李颖洁, 朱贻盛. 脑电信号伪迹去除的研究进展[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2008, 25(2): 464–467,671. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5515.2008.02.048DU Xiaoyan, LI Yingjie, and ZHU Yisheng. Removal of artifacts from EEG signal[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2008, 25(2): 464–467,671. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-5515.2008.02.048 [7] 刘长生, 唐艳, 汤井田. 基于独立分量分析的脑电中眼电伪迹消除[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2007, 43(17): 230–232. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.17.071LIU Changsheng, TANG Yan, and TANG Jingtian. Removal of ocular artifact from EEG based on ICA[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2007, 43(17): 230–232. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-8331.2007.17.071 [8] VISWANADHAM T and KUMAR P R. Artefacts removal from ECG signal: Dragonfly optimization-based learning algorithm for neural network-enhanced adaptive filtering[J]. Scalable Computing:Practice and Experience, 2020, 21(2): 247–263. doi: 10.12694/scpe.v21i2.1657 [9] KOSE M R, AHIRWAL M K, and KUMAR A. A new approach for emotions recognition through EOG and EMG signals[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2021, 15(8): 1863–1871. doi: 10.1007/s11760-021-01942-1 [10] 赵春煜, 邱天爽. 基于典型相关分析和小波变换的眼电伪迹去除[J]. 北京生物医学工程, 2011, 30(5): 474–479. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2011.05.08ZHAO Chunyu and QIU Tianshuang. Automatic removal of ocular artifacts in EEG signals by using CCA and wavelet transformation[J]. Beijing Biomedical Engineering, 2011, 30(5): 474–479. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2011.05.08 [11] 张莉, 何传红, 何为, 等. 基于典型相关分析与低通滤波的肌电伪迹去除[J]. 数据采集与处理, 2010, 25(2): 255–258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2010.02.023ZHANG Li, HE Chuanhong, HE Wei, et al. Method for removing EMG artifacts based on CCA and low-pass filtering[J]. Journal of Data Acquisition &Processing, 2010, 25(2): 255–258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9037.2010.02.023 [12] 张莉, 何传红, 何为. 典型相关分析去除脑电信号中眼电伪迹的研究[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2009, 45(31): 218–220. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2009.31.065ZHANG Li, HE Chuanhong, and HE Wei. Research on removing EOG artifacts from EEG based on CCA[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2009, 45(31): 218–220. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2009.31.065 [13] SHEORAN P and SAINI J S. A new method for automatic electrooculogram and eye blink artifacts correction of EEG signals using CCA and NAPCT[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2020, 167: 1761–1770. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2020.03.386 [14] DORA C and BISWAL P K. An improved algorithm for efficient ocular artifact suppression from frontal EEG electrodes using VMD[J]. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 40(1): 148–161. doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2019.03.002 [15] LIU Yizhi, HABIBNEZHAD M, SHAYESTEH S, et al. Paving the way for future eeg studies in construction: Dependent component analysis for automatic ocular artifact removal from brainwave signals[J]. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 2021, 147(8): 04021087. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0002097 [16] GU Yue, LI Xue, CHEN Shengyong, et al. AOAR: An automatic ocular artifact removal approach for multi-channel electroencephalogram data based on non-negative matrix factorization and empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2021, 18(5): 056012. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/abede0 [17] SUN Rui, CHAN C, HSIAO J, et al. Validation of SOB1-DANS method for automatic identification of horizontal and vertical eye movement components from EEG[J]. Psychophysiology, 2021, 58(2): e13731. doi: 10.1111/yp.13731 [18] KASTEN F H and HERRMANN C S. Recovering brain dynamics during concurrent tACS-M/EEG: An overview of analysis approaches and their methodological and interpretational pitfalls[J]. Brain Topography, 2019, 32(6): 1013–1019. doi: 10.1007/s10548-019-00727-7 [19] 李明爱, 刘帆. 脑电中眼电伪迹的自动识别与去除[J]. 北京生物医学工程, 2018, 37(6): 559–565. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2018.06.002LI Ming’ai and LIU Fan. The automatic identification and removal of ocular artifacts from EEG[J]. Beijing Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 37(6): 559–565. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3208.2018.06.002 [20] 刘志勇, 孙金玮, 卜宪庚. 单通道脑电信号眼电伪迹去除算法研究[J]. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(10): 1726–1735. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160191LIU Zhiyong, SUN Jinwei, and BU Xiangeng. EOG artifact removing method for single-channel EEG signal[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(10): 1726–1735. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160191 [21] 赵文瑞, 陈鑫源, 雷旭. 同步脑电-功能磁共振信号处理进展[J]. 信号处理, 2018, 34(8): 930–942. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.08.006ZHAO Wenrui, CHEN Xinyuan, and LEI Xu. Advances in signal processing of simultaneous EEG-fMRI[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2018, 34(8): 930–942. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2018.08.006 [22] 杨磊, 杨帆, 何艳. 采用样本熵自适应噪声完备经验模态分解的脑电信号眼电伪迹去除算法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2020, 54(8): 177–184. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202008023YANG Lei, YANG Fan, and HE Yan. An electroencephalogram artifacts removal algorithm for electroencephalogram signals based on sample entropy-complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise[J]. Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 2020, 54(8): 177–184. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202008023 [23] PEH W Y, THOMAS J, BAGHERI E, et al. Multi-center validation study of automated classification of pathological slowing in adult scalp electroencephalograms via frequency features[J]. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2021, 31(6): 2150016. doi: 10.1142/S0129065721500167 [24] DE BEER N A M, VAN DE VELDE M, and CLUITMANS P J M. Clinical evaluation of a method for automatic detection and removal of artifacts in auditory evoked potential monitoring[J]. Journal of Clinical Monitoring, 1995, 11(6): 381–391. doi: 10.1007/BF01616744 [25] PARADESHI K P and KOLEKAR U D. Ocular artifact suppression in multichannel EEG using dynamic segmentation and enhanced wICA[J]. IETE Journal of Research, 2020: 1–14. doi: 10.1080/03772063.2020.1725657. [26] RANJAN R, SAHANA B C, and BHANDARI A K. Ocular artifact elimination from electroencephalography signals: A systematic review[J]. Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, 2021, 41(3): 960–996. doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2021.06.007 [27] YADAV A and CHOUDHRY M S. A new approach for ocular artifact removal from EEG signal using EEMD and SCICA[J]. Cogent Engineering, 2020, 7(1): 1835146. doi: 10.1080/23311916.2020.1835146 [28] BARBATI G, PORCARO C, ZAPPASODI F, et al. Optimization of an independent component analysis approach for artifact identification and removal in magnetoencephalographic signals[J]. Clinical Neurophysiology, 2004, 115(5): 1220–1232. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2003.12.015 [29] RADÜNTZ T, SCOUTEN J, HOCHMUTH O, et al. Automated EEG artifact elimination by applying machine learning algorithms to ICA-based features[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2017, 14(4): 046004. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/aa69d1 [30] ISLAM S, EL-HAJJ A M, ALAWIEH H, et al. EEG mobility artifact removal for ambulatory epileptic seizure prediction applications[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2020, 55: 101638. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101638 [31] YASODA K, PONMAGAL R S, BHUVANESHWARI K S, et al. Automatic detection and classification of EEG artifacts using fuzzy kernel SVM and wavelet ICA (WICA)[J]. Soft Computing, 2020, 24(21): 16011–16019. doi: 10.1007/s00500-020-04920-w [32] DELORME A, SEJNOWSKI T, and MAKEIG S. Enhanced detection of artifacts in EEG data using higher-order statistics and independent component analysis[J]. Neuroimage, 2007, 34(4): 1443–1449. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.11.004 [33] ÇINAR S. Design of an automatic hybrid system for removal of eye-blink artifacts from EEG recordings[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 67: 102543. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102543 [34] MANOJPRABU M and DHULIPALA V R S. Power aware hessian multi-set canonical correlations based algorithm for wireless eeg sensor networks[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2021, 117(4): 2745–2756. doi: 10.1007/s11277-020-07045-3 [35] 吕健. 基于改进小波阈值函数的癫痫信号去噪算法[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2020, 48(10): 2348–2352. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2020.10.009LV Jian. An epileptic signal denoising algorithm based on improved wavelet threshold function[J]. Computer and Digital Engineering, 2020, 48(10): 2348–2352. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2020.10.009 [36] DEBNATH L and SHAH F A. Wavelet Transforms and Their Applications[M]. Boston: Birkhäuser, 2002. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-0097-0. [37] CASTELLANOS N P and MAKAROV V A. Recovering EEG brain signals: Artifact suppression with wavelet enhanced independent component analysis[J]. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2006, 158(2): 300–312. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2006.05.033 [38] MAHAJAN R and MORSHED B I. Unsupervised eye blink artifact denoising of EEG data with modified multiscale sample entropy, kurtosis, and wavelet-ICA[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2015, 19(1): 158–165. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2014.2333010 [39] MAHAJAN R and MORSHED B I. Sample entropy enhanced wavelet-ica denoising technique for eye blink artifact removal from scalp eeg dataset[C]. 2013 6th International IEEE/EMBS Conference on Neural Engineering (NER), San Diego, Ameriaca, 2013: 1394–1397. doi: 10.1109/NER.2013.6696203. [40] ZOU Ling, XU Soukun, MA Zhenghua, et al. Automatic removal of artifacts from attention deficit hyperactivity disorder electroencephalograms based on independent component analysis[J]. Cognitive Computation, 2013, 5(2): 225–233. doi: 10.1007/s12559-012-9199-3 [41] PION-TONACHINI L, HSU S H, CHANG C Y, et al. Online automatic artifact rejection using the real-time EEG source-mapping toolbox (REST)[C]. 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, USA, 2018: 106–109. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8512191. [42] SCHOEMAN D and FIELDING B C. Coronavirus envelope protein: Current knowledge[J]. Virology Journal, 2019, 16(1): 69. doi: 10.1186/s12985-019-1182-0 [43] 耿振伟, 粟毅, 郁文贤. 一种快速自适应的均值漂移聚类算法[J]. 信号处理, 2009, 25(1): 153–156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.01.032GENG Zhenwei, SU Yi, and YU Wenxian. A very fast adaptive mean shift clustering method[J]. Signal Processing, 2009, 25(1): 153–156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0530.2009.01.032 [44] 李乡儒, 吴福朝, 胡占义. 均值漂移算法的收敛性[J]. 软件学报, 2005, 16(3): 365–374.LI Xiangru, WU Fuchao, and HU Zhanyi. Convergence of a mean shift algorithm[J]. Journal of Software, 2005, 16(3): 365–374. [45] HUYNH-THU Q and GHANBARI M. Scope of validity of PSNR in image/video quality assessment[J]. Electronics Letters, 2008, 44(13): 800–801. doi: 10.1049/el:20080522 [46] KELTER R. Analysis of Bayesian posterior significance and effect size indices for the two-sample t-test to support reproducible medical research[J]. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 2020, 20(1): 88. doi: 10.1186/s12874-020-00968-2 [47] URBANO J, CORSI M, and HANJALIC A. How do metric score distributions affect the type I error rate of statistical significance tests in information retrieval?[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 ACM SIGIR International Conference on Theory of Information Retrieval, Virtual Event, Canada, 2021: 245–250. doi: 10.1145/3471158.3472242. [48] MAHADEVAN A S, TOOLEY U A, BERTOLERO M A, et al. Evaluating the sensitivity of functional connectivity measures to motion artifact in resting-state fMRI data[J]. NeuroImage, 2021, 241: 118408. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118408 [49] LILIENTHAL J and DARGIE W. Application of tensor decomposition in removing motion artifacts from the measurements of a wireless electrocardiogram[C]. 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Rustenburg, South Africa, 2020: 1–8. doi: 10.23919/FUSION45008.2020.9190621. [50] BENESTY J, CHEN Jingdong, HUANG Yiteng, et al. Pearson Correlation Coefficient[M]. COHEN I, HUANG Yiteng, CHEN Jingdong, et al. Noise Reduction in Speech Processing. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 2009: 1–4. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-00296-0_5. [51] 何海洋, 罗志增. 基于K近邻互信息估计的EEG伪迹消除方法[J]. 计算机工程, 2013, 39(6): 255–260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2013.06.057HE Haiyang and LUO Zhizeng. EEG artifacts removal method based on K-nearest neighbors mutual information estimation[J]. Computer Engineering, 2013, 39(6): 255–260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3428.2013.06.057 [52] ONTON J and MAKEIG S. Information-based modeling of event-related brain dynamics[J]. Progress in Brain Research, 2006, 159: 99–120. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)59007-7 -





 下载:
下载:
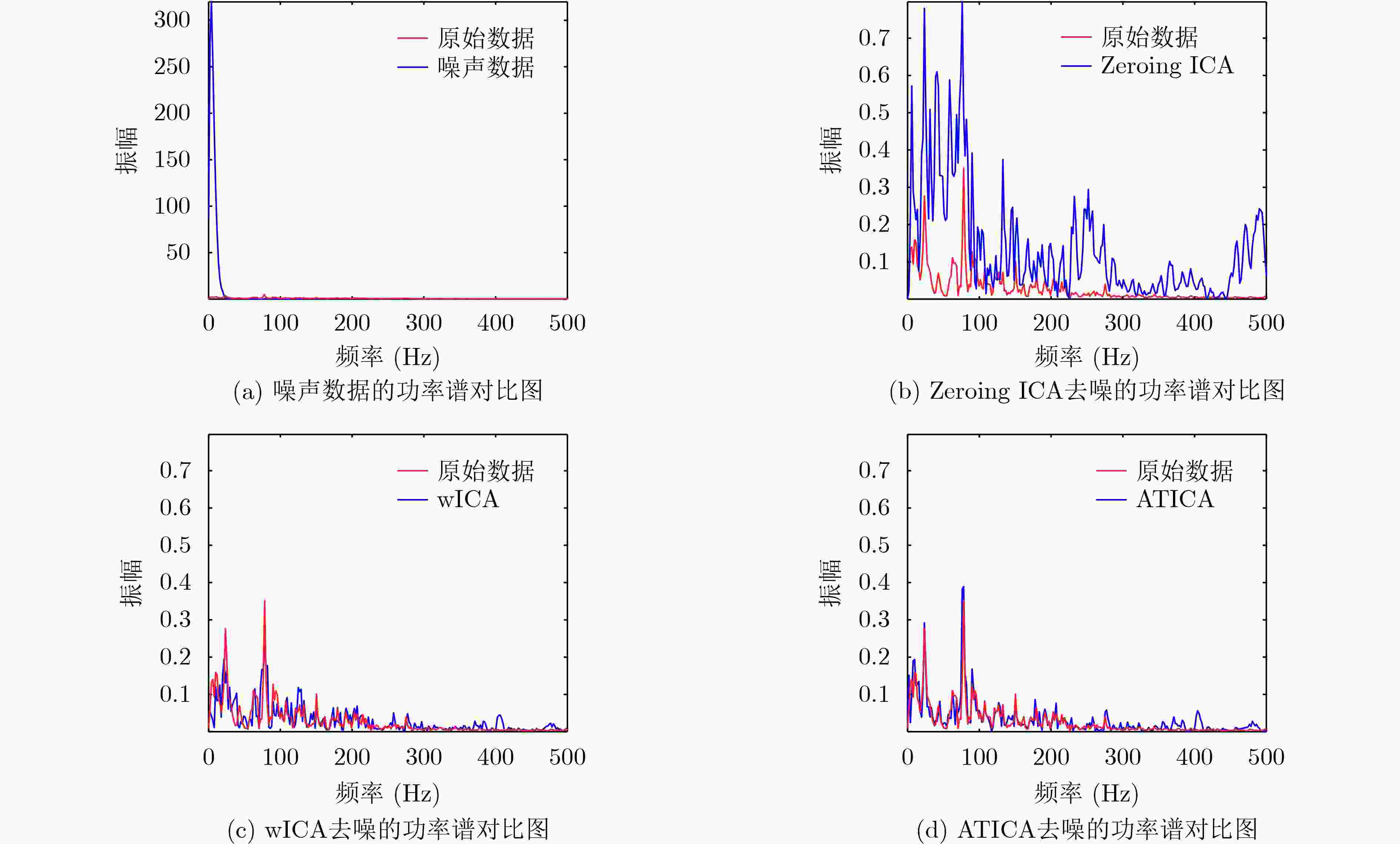
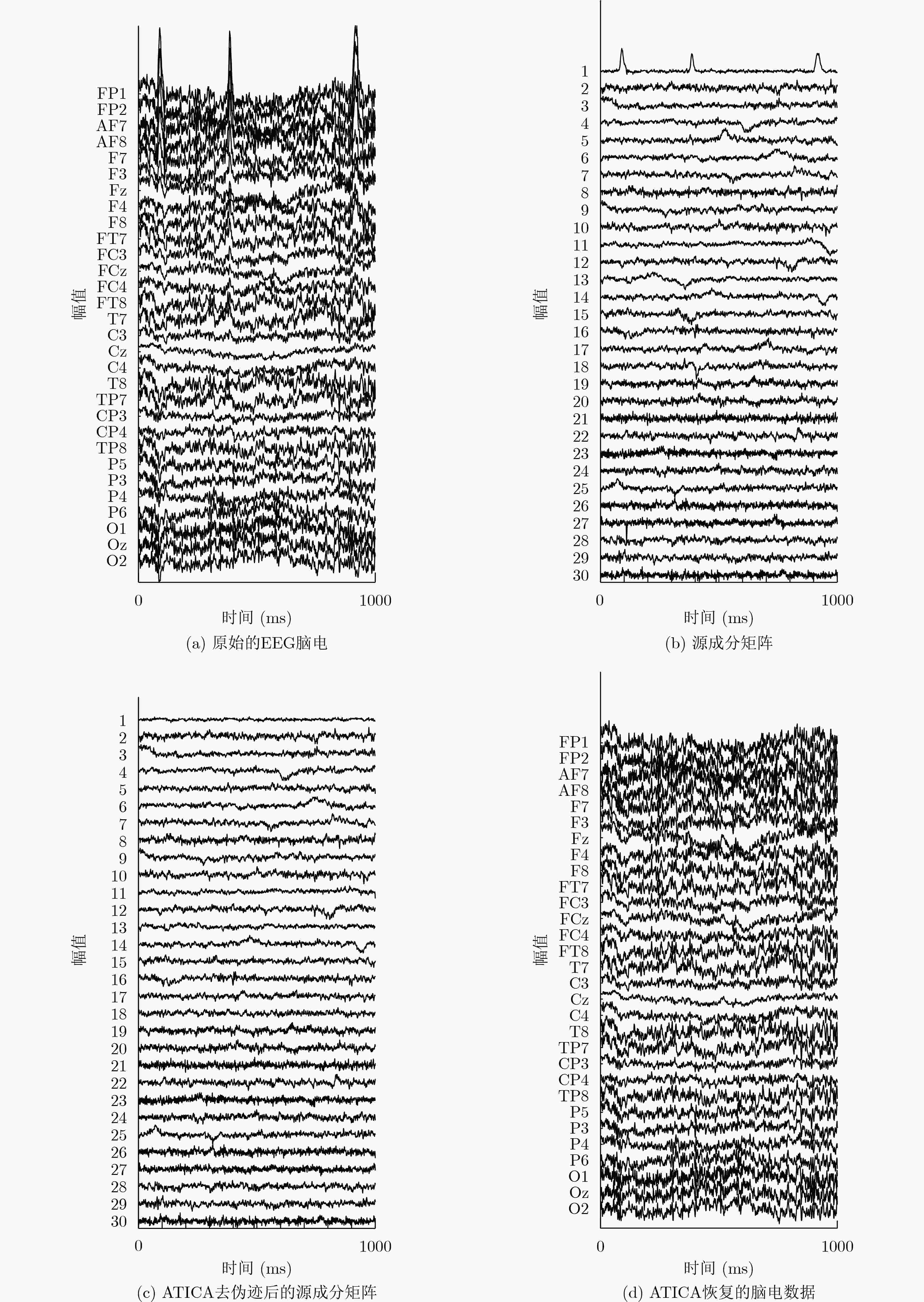
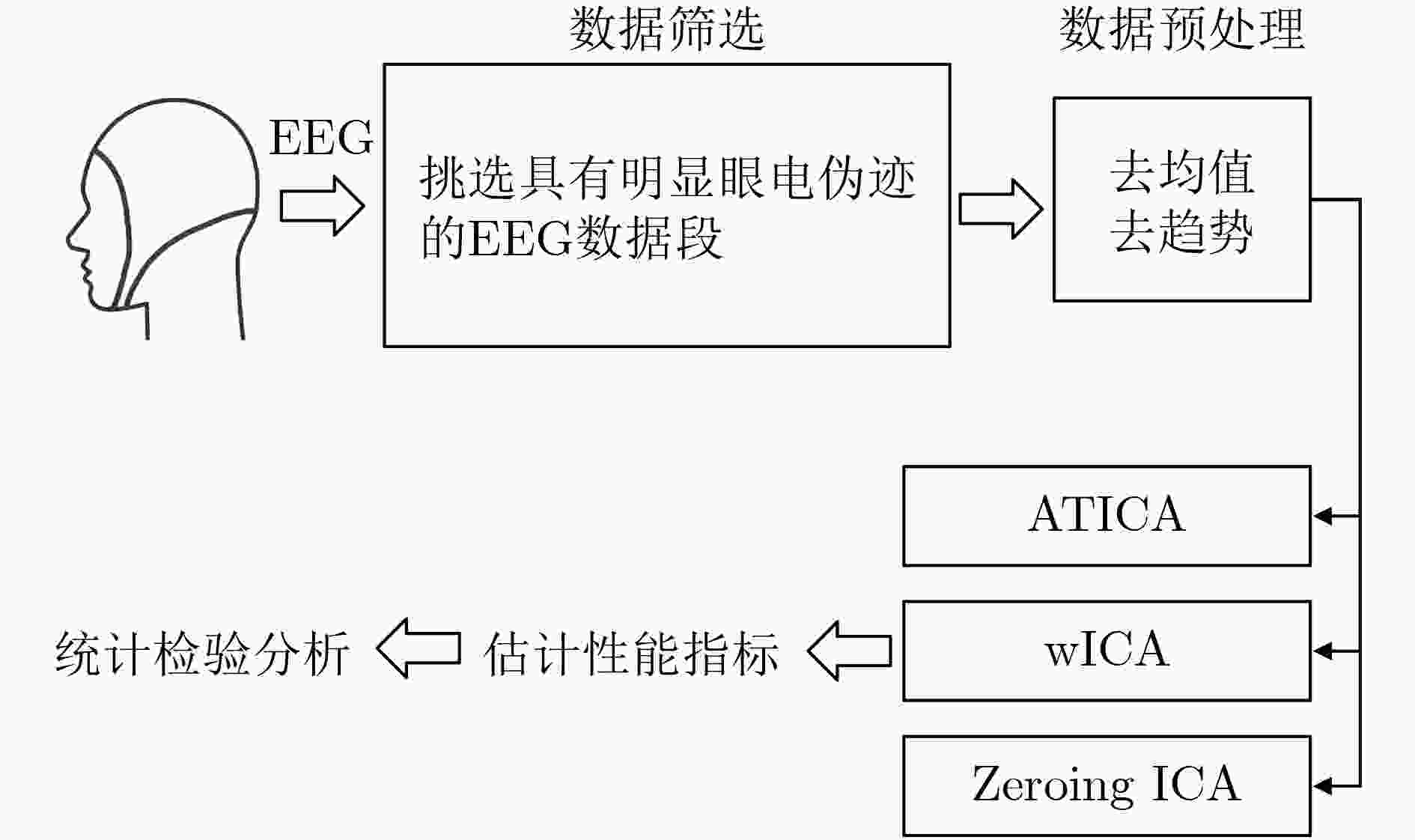
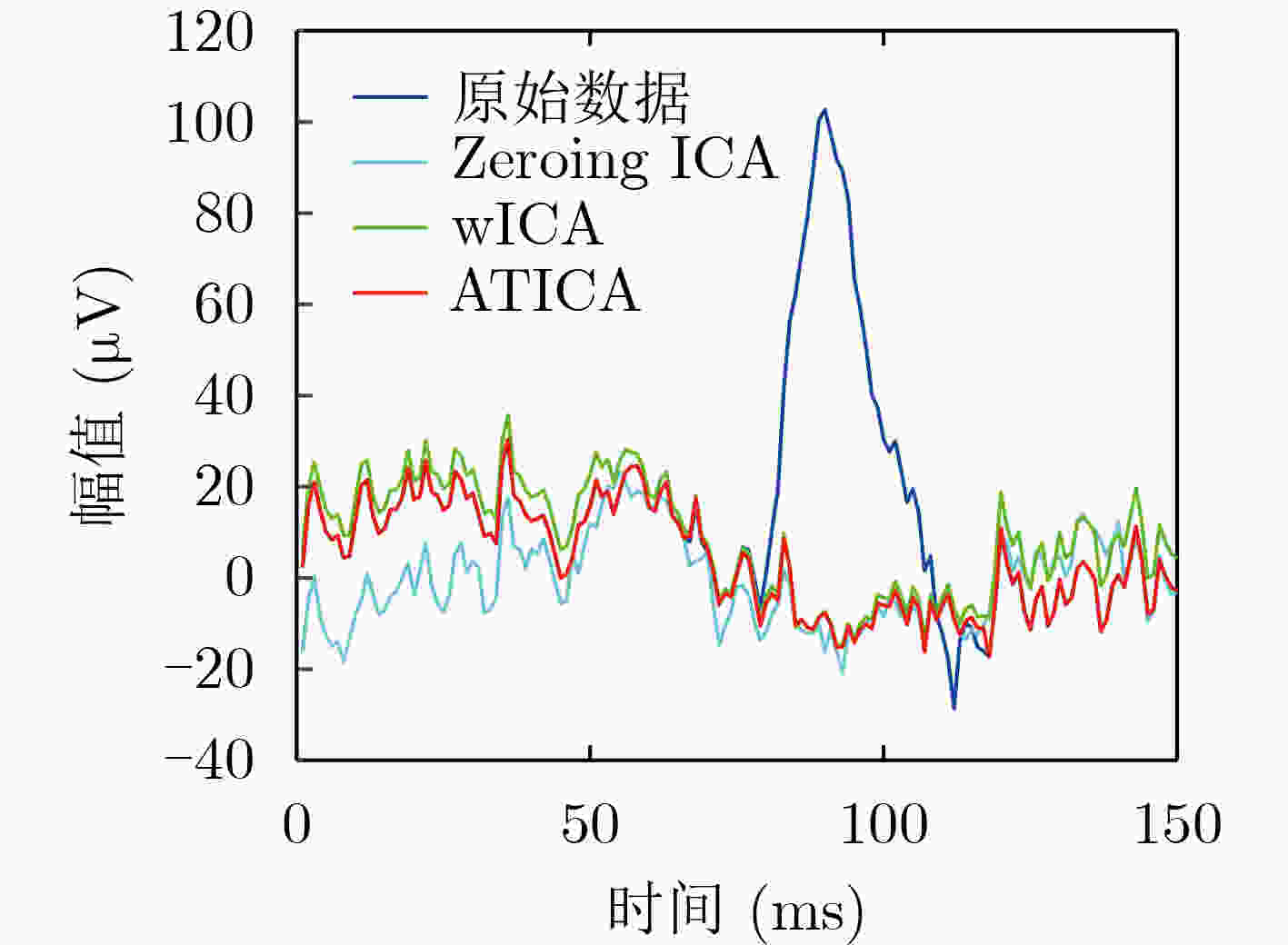


 下载:
下载:
