A Calibration Method of 2D Lidar and a Camera Based on Effective Lower Bound Estimation of Observation Probability
-
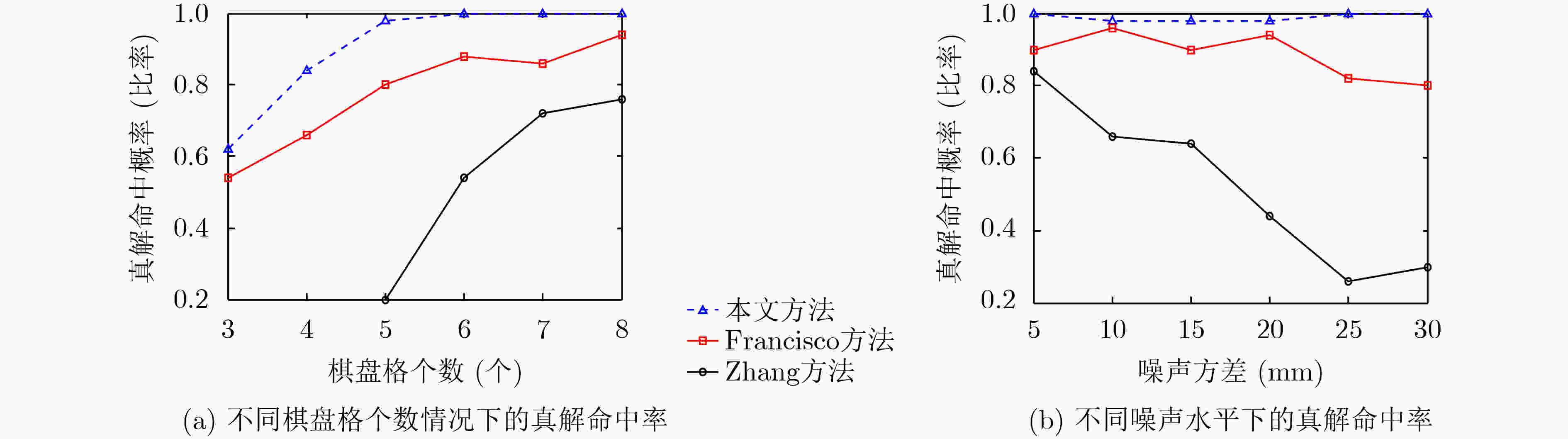
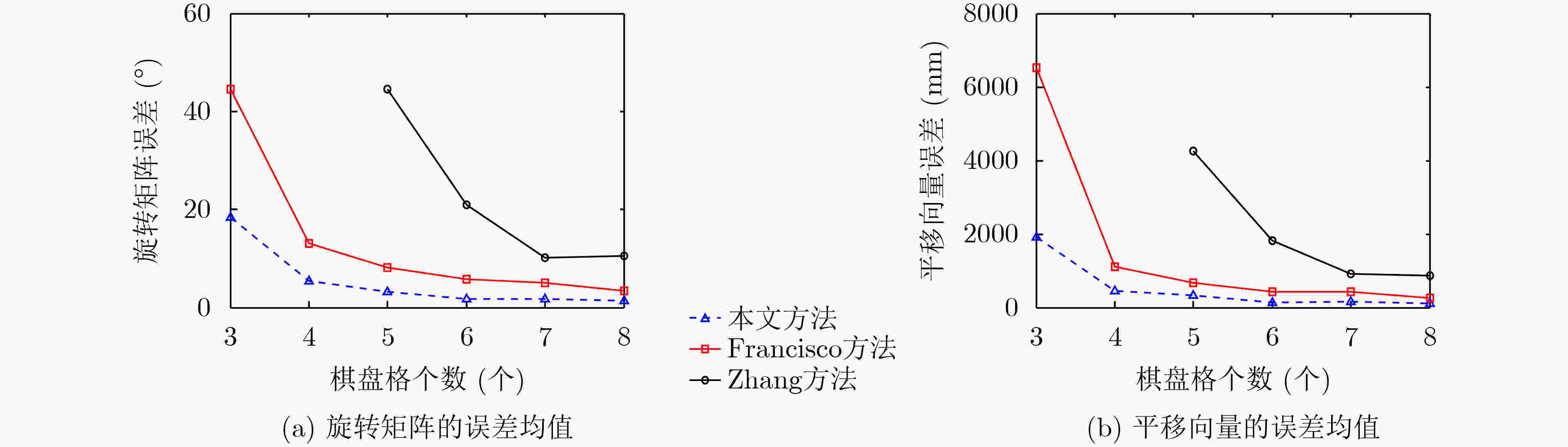
摘要: 针对2D激光雷达和摄像机最小解标定方法的多解问题,该文提出一种基于观测概率有效下界估计的标定方法。首先,提出一种最小解集合的分级聚类方法,将每类最优解替换原来的解集合,从而减少解集合样本个数。然后,提出一种基于激光误差的联合观测概率度量,对解集合元素的优劣进行度量。最后,利用聚类结果和观测概率度量结果,该文提出基于观测概率有效下界估计的有效解选取策略,将优化初始值从最优解转化为有效解候选集合,提高了标定结果的准确性。仿真实验结果表明,在真解命中率性能上相比于Francisco方法,该文方法在不同棋盘格个数情况下提升真解命中率16%~20%,在不同噪声水平下提升真解命中率6%~20%,有效提高真解比例。Abstract: Considering the multi solution problem of minimum solution method for calibration of 2D lidar and camera, a calibration method based on the estimation of the effective lower bound of observation probability is proposed. Firstly, a hierarchical clustering method with minimum solution set is proposed which should be used to replace the original solution set with each kind of optimal solution, so as to reduce the number of samples in the solution set. Then, a joint observation probability measure based on laser error is proposed to measure the quality of solutions. Finally, using the clustering results and the measurement results of observation probability, an effective solution selection strategy based on the estimation of the effective lower bound of observation probability is proposed, which transforms the optimized initial value from the optimal solution to the candidate set of effective solutions, and improves the accuracy of calibration results. Comparing with the existing methods, results of both simulation and real data experiment show that the proposed algorithm improves significantly the true solution hit rate by 16%~20% under different number of checkerboards and 6%~20% under different noise levels.
-
Key words:
- Extrinsic calibration /
- 2D lidar /
- Camera /
- Multi solution problem /
- Effective lower bound estimation
-
表 1 本文所提标定算法伪代码
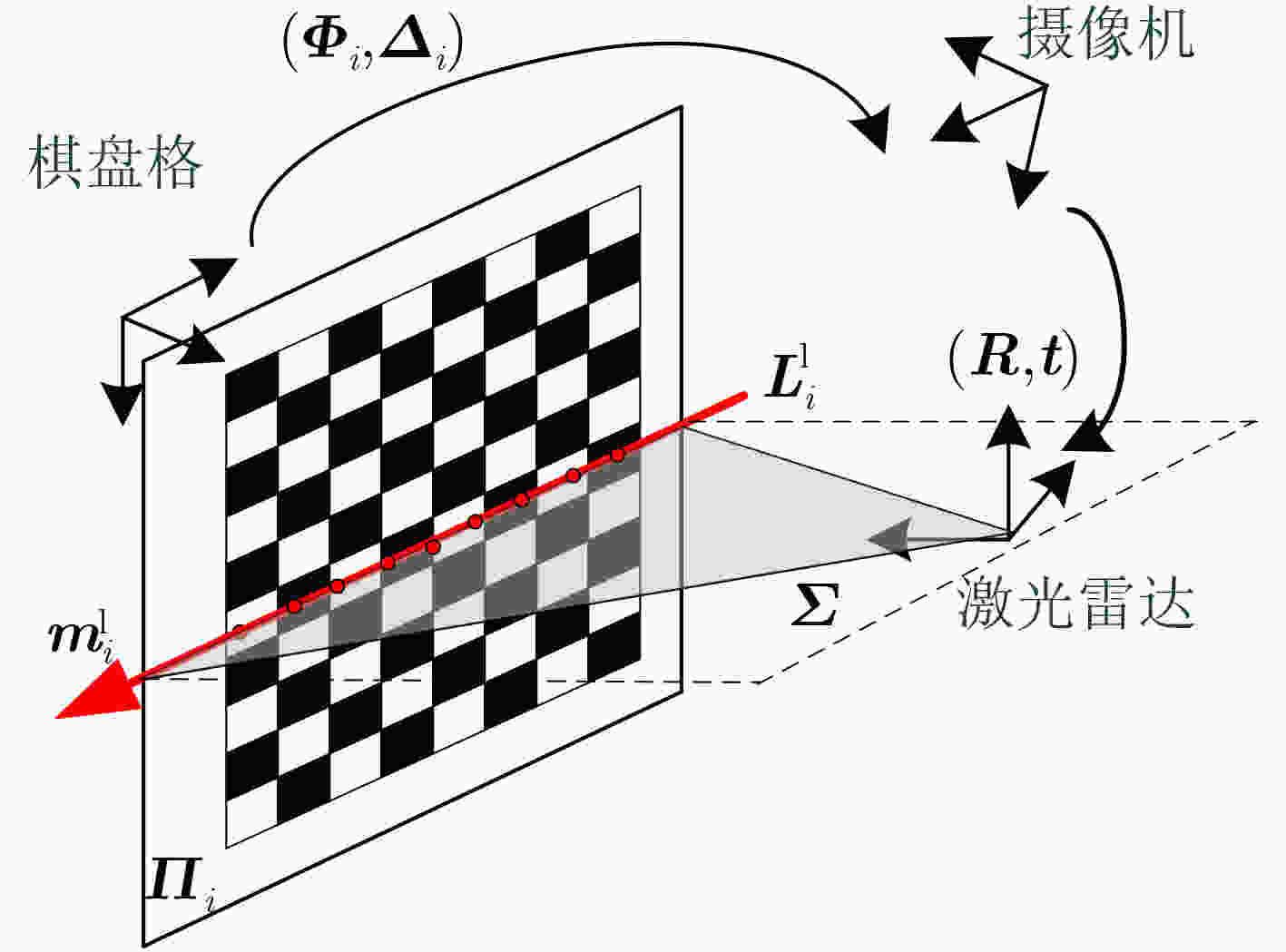
输入: 基于$ N $个棋盘格${{\boldsymbol{\varPi}} _i}$和对应的共面直线${\boldsymbol{L}}_i^{\rm{l}}$。 输出: 旋转矩阵${\boldsymbol{R}}$和平移向量$ t $。 (1) 构造一个集合${\boldsymbol{K} } = \left\{ {\left. { {k_1},{k_2}, \cdots ,{k_d} } \right\} } \right.\;\left( {d = C_N^3} \right)$,其中$ {k_i} \in {Z^3} $表示从$\left\{ {\left. {1,2, \cdots ,N} \right\} } \right.$的$ N $个数中选取3个数的一种可能组合,${\boldsymbol{K}}$表示所有
的可能组合。(2) 设置解集合${\boldsymbol{D}} = \phi$, ${\boldsymbol{S}} = \phi$。 (3) For t =1,2,···, d do (4) 选择和$ {k_t} $的各元素对应的3个棋盘格${{\boldsymbol{\varPi}} _{ {k_{t,1} } } }$, ${{\boldsymbol{\varPi}} _{ {k_{t,2} } } }$和${{\boldsymbol{\varPi}} _{ {k_{t,3} } } }$以及对应的共面直线${\boldsymbol{L} }_{ {k_{t,1} } }^{\text{l} }$, ${\boldsymbol{L}}_{ {k_{t,2} } }^l$和${\boldsymbol{L}}_{ {k_{t,3} } }^l$,使用文献[5]的算法计算一组最
小解$\left( {{\boldsymbol{R}}_t^{(m)},{\boldsymbol{t}}_t^{(m)} } \right)$, $ m \lt 8 $。(5) 将当前这组解合并到解集合${\boldsymbol{D}} = {\boldsymbol{D}} \cup \left( {{\boldsymbol{R}}_t^{(m)},{\boldsymbol{t}}_t^{(m)} } \right)$。 (6) End for (7) 利用式(3)和式(4)作为类之间的距离度量,对解集合${\boldsymbol{D}}$进行分级聚类,聚类结果为$ \left\{ {{C_i}} \right\}_{i = 1}^k $。 (8) 根据式(8)—式(11)计算基于激光误差的联合观测概率$ {\pi _j} $。 (9) 根据聚类结果$ \left\{ {{C_i}} \right\}_{i = i}^k $和联合观测概率$ {\pi _j} $,利用式(12)获取每类中局部最优观测概率的解$\left\{ {\left( { { {\tilde {\boldsymbol{R}}}_i},{ {\tilde {\boldsymbol{t}}}_i} } \right)} \right\}_{i = i}^k$,其对应的观测概率为
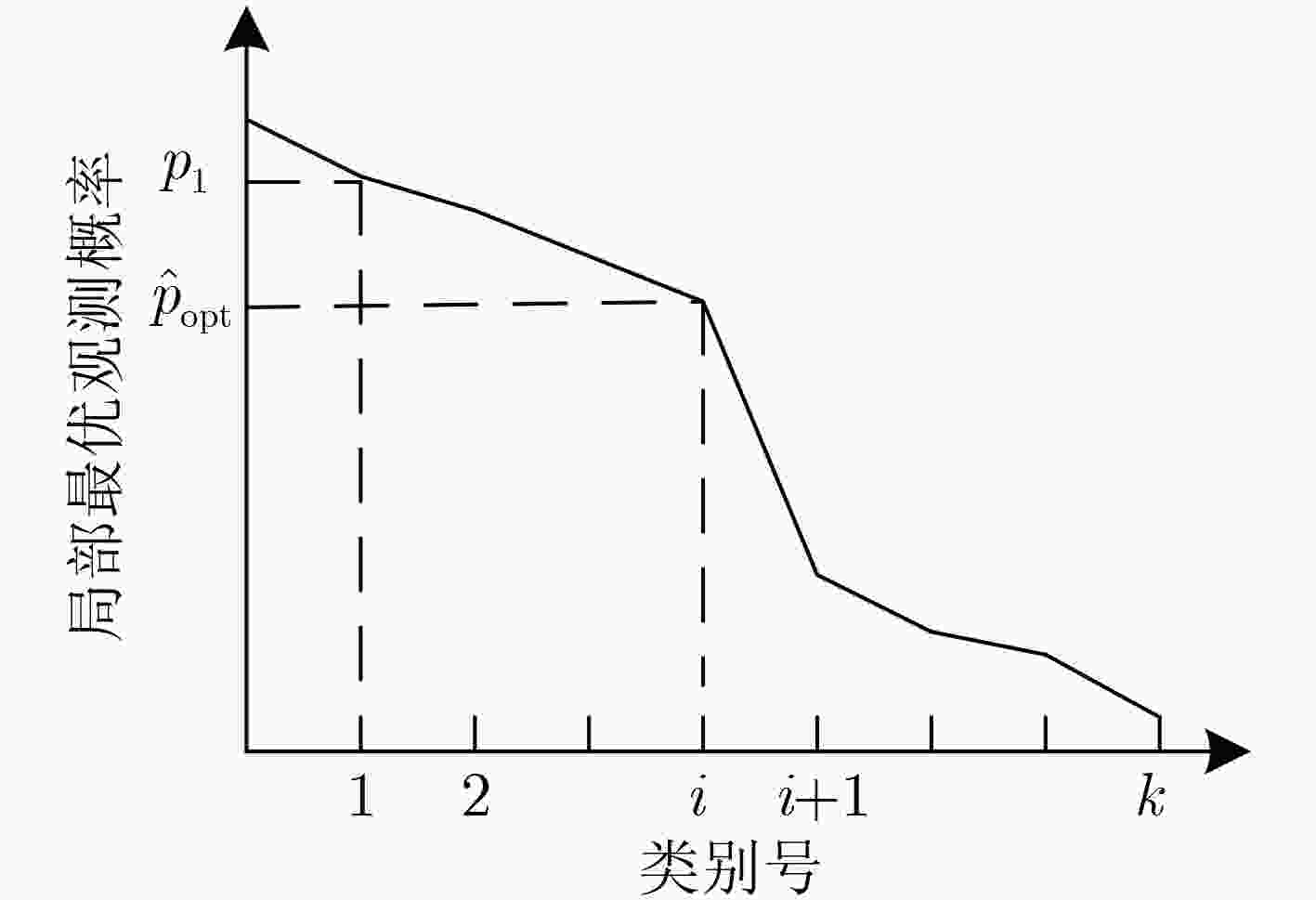
$ \left\{ {{p_i}} \right\}_{i = i}^k $。(10) 根据式(13)计算观测概率有效下界${\hat p_{{\rm{opt}}} }$,将${p_i} \gt {\hat p_{{\rm{opt}}} }$的局部最优解$\left( { { {\tilde {\boldsymbol{R}}}_i},{ {\tilde {\boldsymbol{t}}}_i} } \right)$加入到有效解候选集合$ S $,将$ S $作为标定参数优化的初始值。 表 2 本文方法的有效解个数以及运算时间的比较
棋盘格的个数 3 4 5 6 7 8 本文方法的有效解个数均值(个) 2.1 2.3 2.4 2.6 2.7 2.7 本文方法的运算时间(s) 1.351 1.725 2.437 2.650 3.896 4.682 Francisco方法的运算时间(s) 0.210 0.351 0.531 0.720 1.241 1.631 -
[1] SAKTHIVEL P and ANBARASU B. Integration of vision and LIDAR for navigation of micro aerial vehicle[C]. The 2020 Third International Conference on Multimedia Processing, Communication & Information Technology (MPCIT), Shivamogga, India, 2020: 14–18. [2] LI Zimo, GOGIA P C, and KAESS M. Dense surface reconstruction from monocular vision and LiDAR[C]. The 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, Canada, 2019: 6905–6911. [3] LI Yanhao and LI Hao. A collaborative relative localization method for vehicles using vision and LiDAR sensors[C]. The 2020 16th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV), Shenzhen, China, 2020: 281–286. [4] ZHANG Qilong and PLESS R. Extrinsic calibration of a camera and laser range finder (improves camera calibration)[C]. The IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Sendai, Japan, 2004: 2301−2306. [5] ASCONCELOS F, BARRETO J P, and NUNES U. A minimal solution for the extrinsic calibration of a camera and a laser-rangefinder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2097–2107. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.18 [6] 胡钊政, 赵斌, 李娜, 等. 基于虚拟三面体的摄像机与二维激光测距仪外参数最小解标定新算法[J]. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(11): 1951–1960. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c150108HU Zhaozheng, ZHAO Bin, LI Na, et al. Minimal solution to extrinsic calibration of camera and 2D laser rangefinder based on virtual trihedron[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(11): 1951–1960. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c150108 [7] 彭梦, 蔡自兴. 基于多约束误差函数的2维激光雷达和摄像机标定方法[J]. 机器人, 2014, 36(6): 662–667,675. doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.2014.0662PENG Meng and CAI Zixing. A calibration method of a camera and 2D laser radar based on multi-constraint error function[J]. Robot, 2014, 36(6): 662–667,675. doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.2014.0662 [8] HOANG V D, HERNÁNDEZ D C, and JO K H. Simple and efficient method for calibration of a camera and 2D laser rangefinder[C]. The 6th Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems, Bangkok, Thailand, 2014: 561–570. [9] SIM S, SOCK J, and KWAK K. Indirect correspondence-based robust extrinsic calibration of LiDAR and camera[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(6): 933. doi: 10.3390/s16060933 [10] DONG Wenbo and ISLER V. A novel method for the extrinsic calibration of a 2D laser rangefinder and a camera[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(10): 4200–4211. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2819082 [11] ITAMI F and YAMAZAKI T. A simple calibration procedure for a 2D LiDAR with respect to a camera[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 19(17): 7553–7564. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2915991 [12] FAN Jia, HUANG Yuchun, SHAN Jie, et al. Extrinsic calibration between a camera and a 2D laser rangefinder using a photogrammetric control field[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(9): 2030. doi: 10.3390/s19092030 [13] YE Quan, SHU Leizheng, and ZHANG Wei. Extrinsic calibration of a monocular camera and a single line scanning Lidar[C]. The 2019 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Tianjin, China, 2019: 1047–1054. [14] ZHOU Lipu and DENG Zhidong. A new algorithm for the establishing data association between a camera and a 2-D LIDAR[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2014, 19(3): 314–322. doi: 10.1109/TST.2014.6838203 [15] GOMEZ-OJEDA R, BRIALES J, FERNANDEZ-MORAL E, et al. Extrinsic calibration of a 2D laser-rangefinder and a camera based on scene corners[C]. The 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, USA, 2015: 3611–3616. [16] HU Zhaozheng, LI Yicheng, LI Na, et al. Extrinsic calibration of 2-D laser rangefinder and camera from single shot based on minimal solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2016, 65(4): 915–929. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2016.2518248 [17] ROYER E, SLADE M, and DHOME M. Easy auto-calibration of sensors on a vehicle equipped with multiple 2D-LIDARs and cameras[C]. The 2019 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Paris, France, 2019: 1296–1303. [18] 张学工. 模式识别[M]. 3版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2010: 203–205.ZHANG Xuegong. Pattern Recognition[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2010: 203–205. -





 下载:
下载:

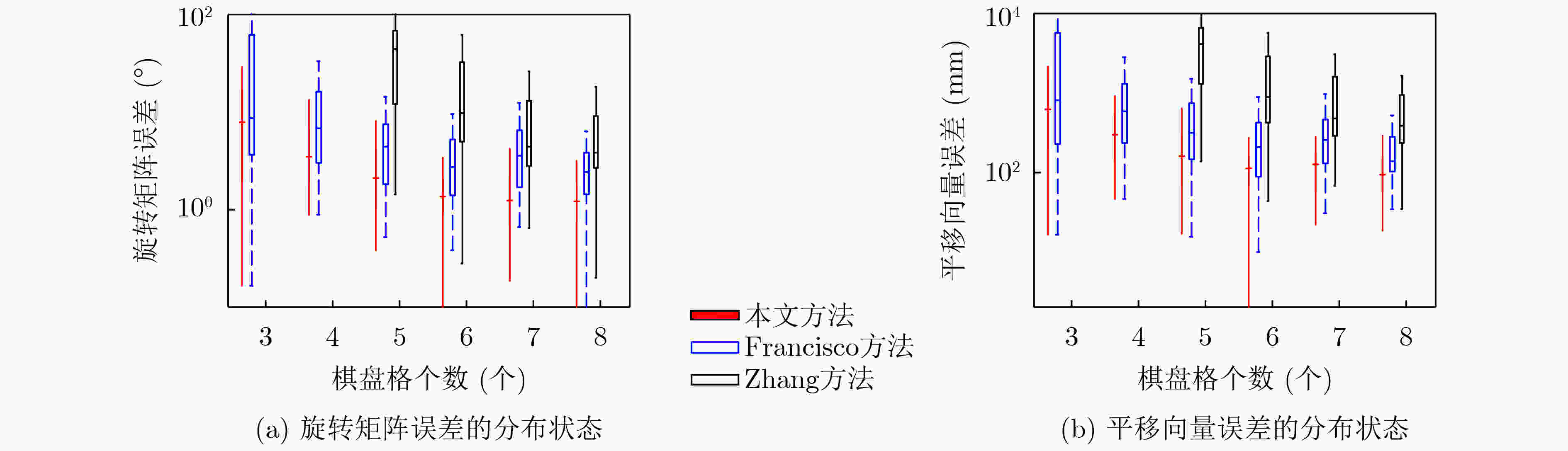
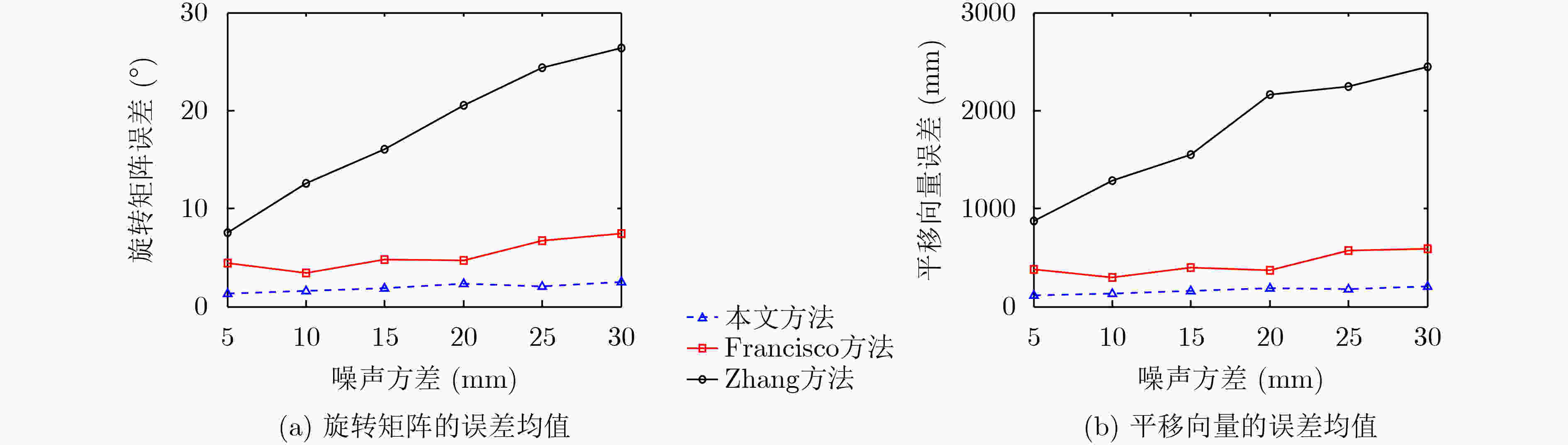
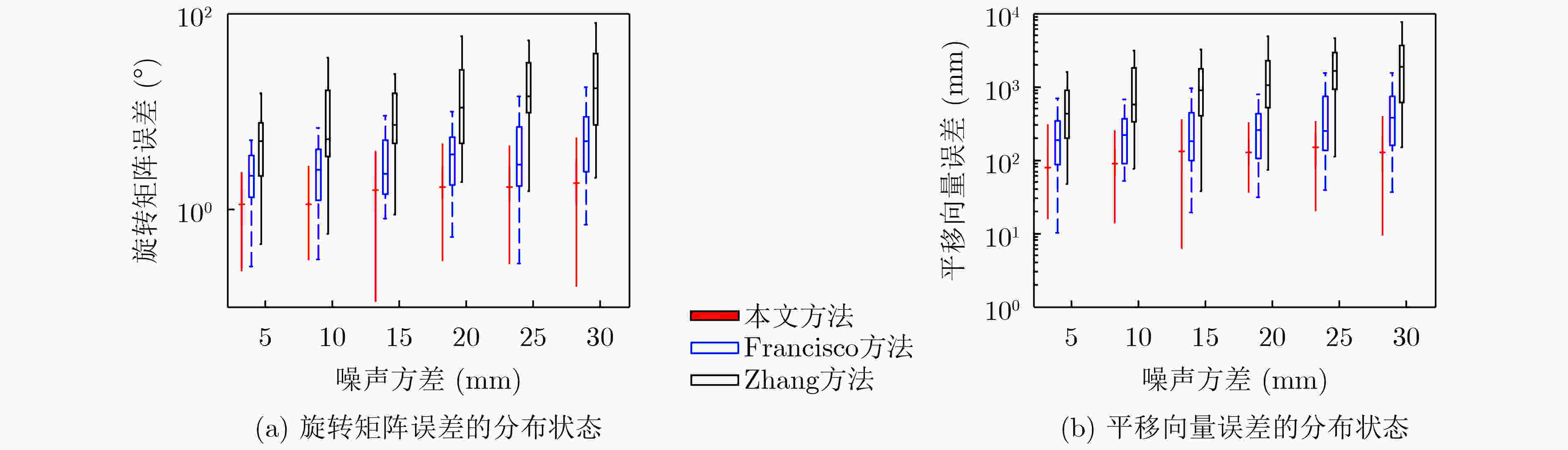

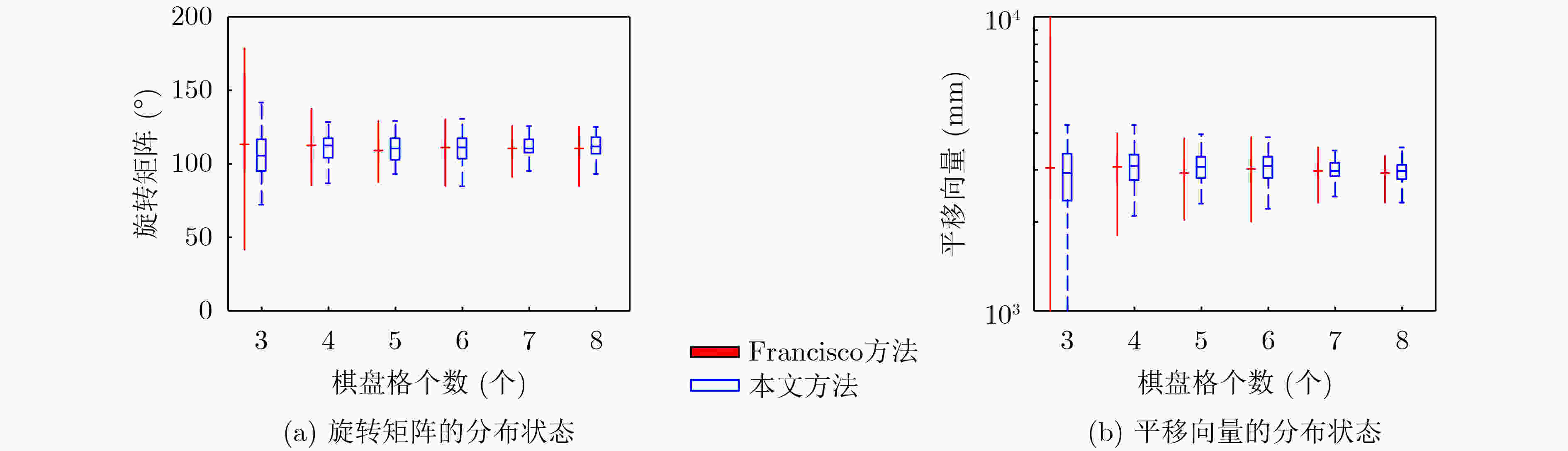


 下载:
下载:
