Small-Data Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Object Recognition Based on Gaussian Prototypical Network
-
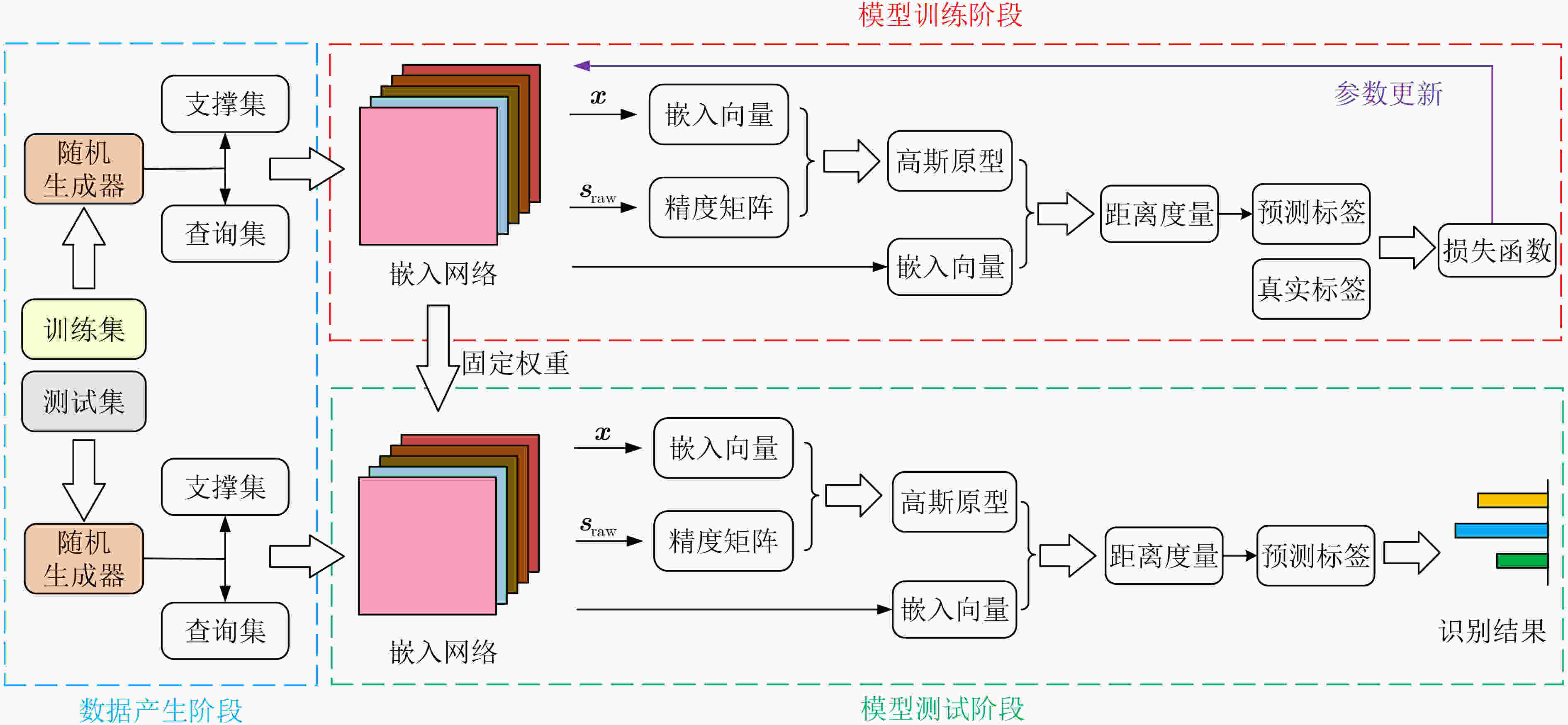
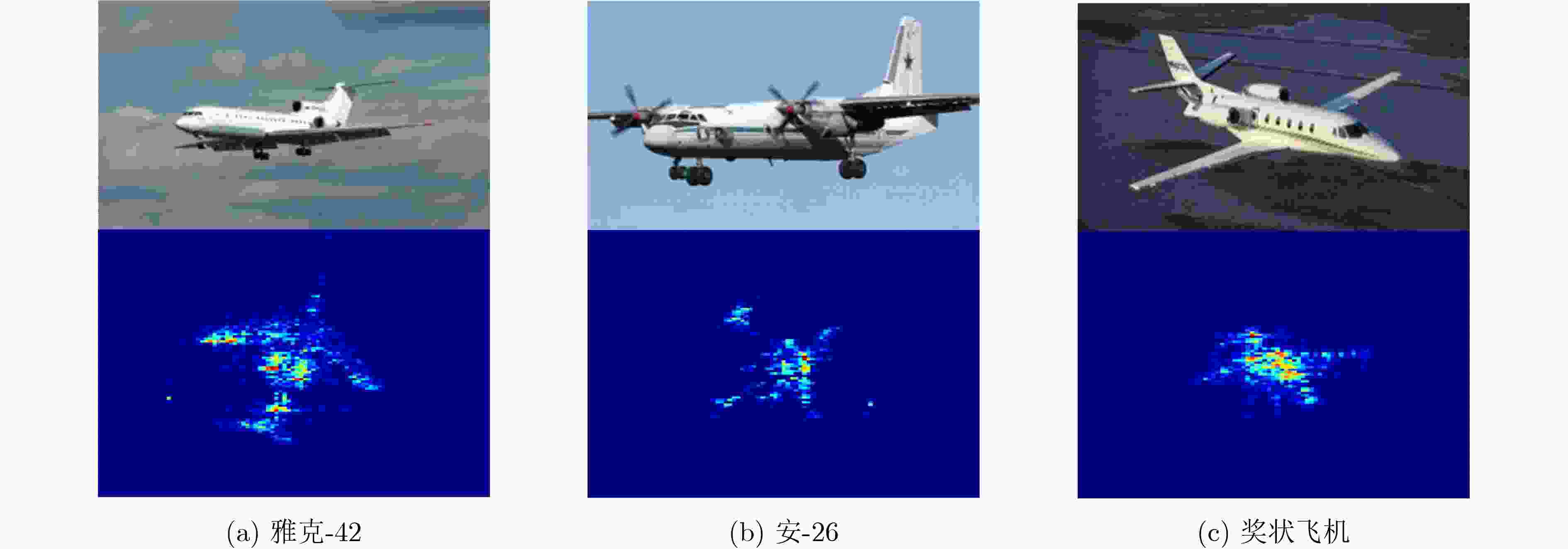
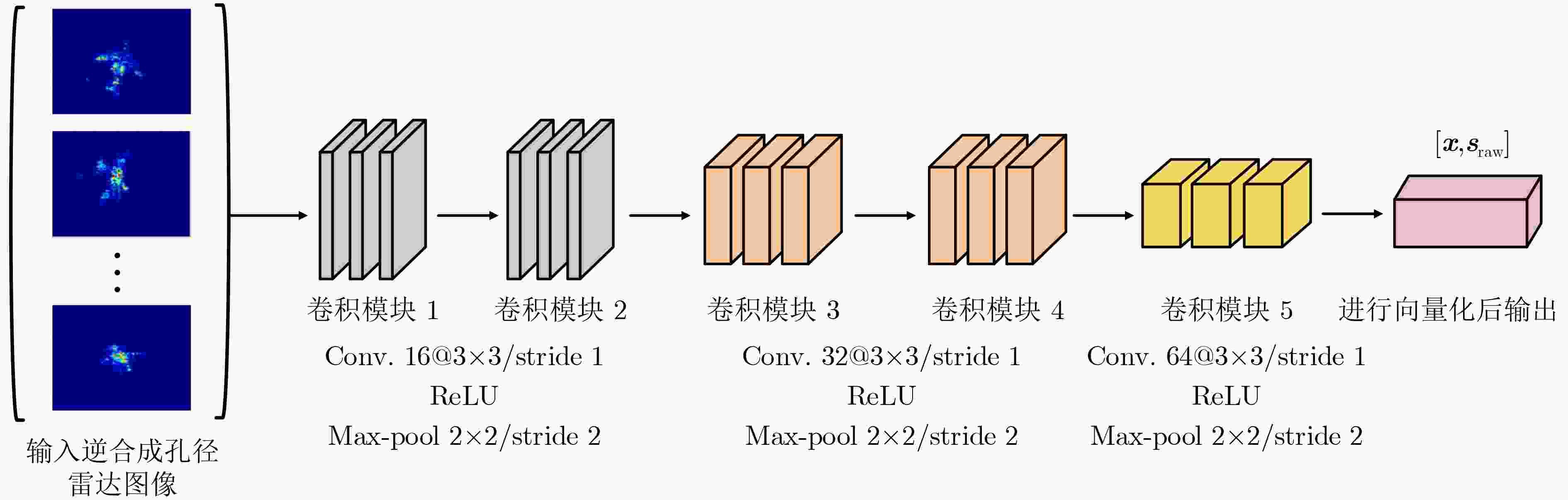
摘要: 针对现有基于深度卷积神经网络(DCNNs)的逆合成孔径雷达(ISAR)目标识别方法在训练样本不足时性能下降甚至失效等问题,该文提出基于高斯原型网络(GPN)的小样本ISAR目标识别方法。该方法通过嵌入网络将ISAR像映射为嵌入向量,进而根据加权嵌入向量构建高斯原型,最终根据测试样本到原型的马氏距离预测目标类别。3类飞机目标实测数据的识别结果表明,该方法在小样本条件下可获得更高的平均识别精度。Abstract: Considering the issue of performance degradation or even failure of the available Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar (ISAR) object recognition methods based on Deep Convolution Neural Networks (DCNNs) with insufficient training samples, a small- data ISAR object recognition method based on Gaussian Prototypical Network (GPN) is proposed. Firstly, ISAR images are maped into embedding vectors by the embedding network, and then Gaussian prototypes are constructed according to the weighted embedding vectors. Finally, the object category is output according to the Mahalanobis distance from the test samples to all prototypes. Recognition results of the three different types of aircraft show that the proposed method can obtain higher average recognition accuracy under small-data scenarios.
-
表 1 PN与GPN识别结果对比
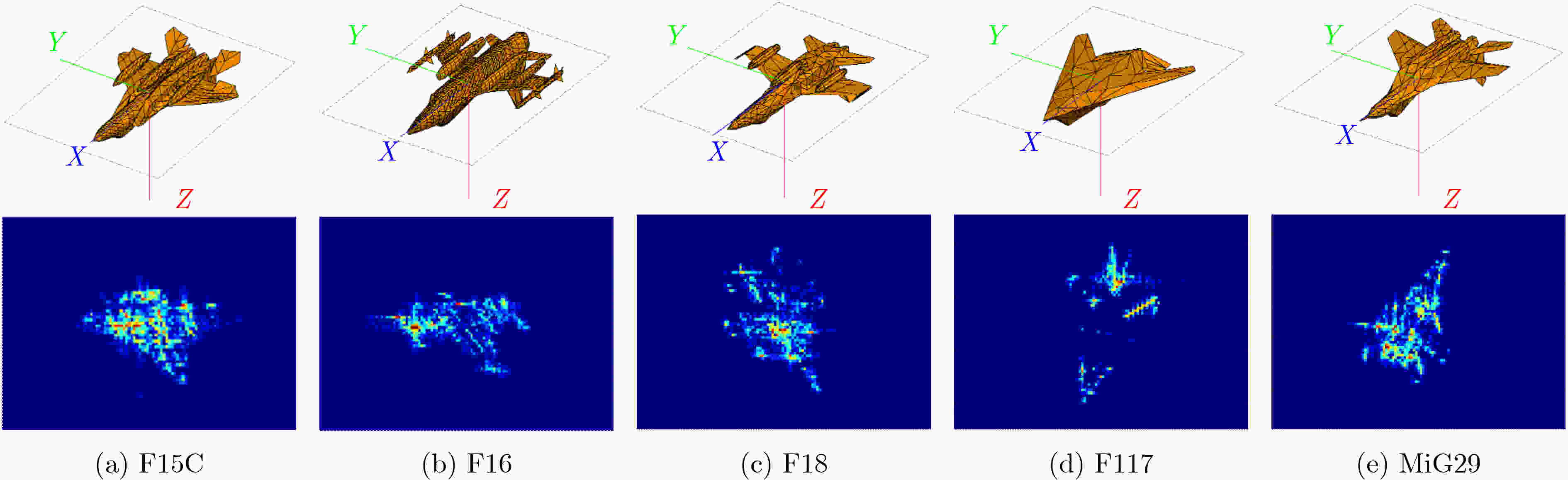
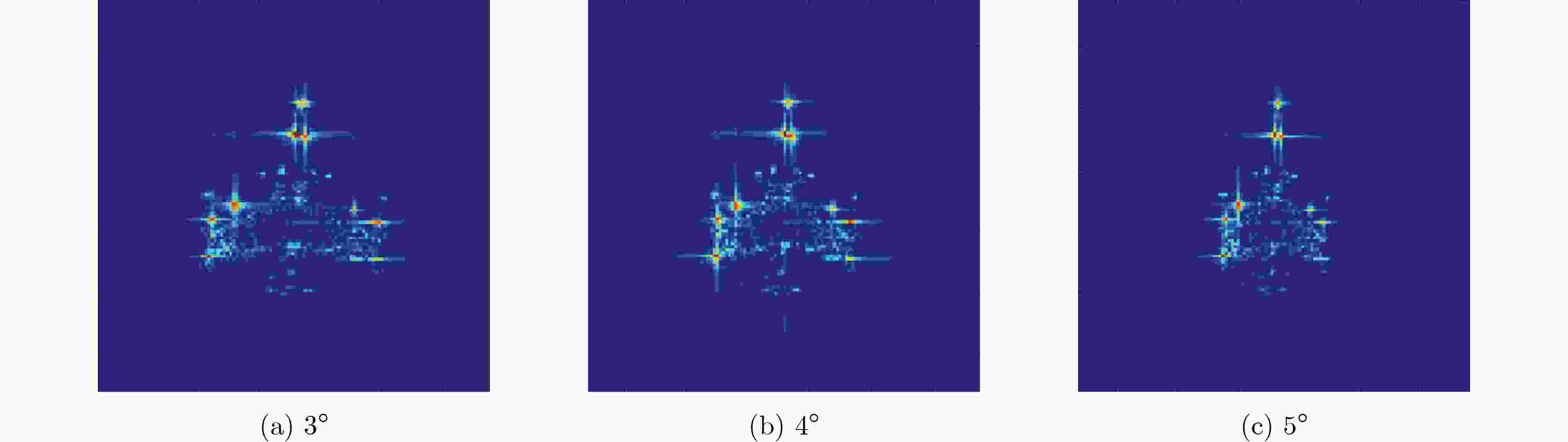
成像积累角 模型 类型 测试准确率(%) 标准差 均值 最大值 最小值 3° PN 1-shot 73.55 89.14 55.06 0.0772 5-shot 89.95 95.69 73.33 0.0299 GPN 1-shot 74.31 89.51 45.69 0.0894 5-shot 92.52 97.65 77.25 0.0219 4° PN 1-shot 75.74 91.01 49.81 0.0831 5-shot 90.56 98.43 72.55 0.0423 GPN 1-shot 77.05 89.89 55.81 0.0836 5-shot 92.82 98.43 83.14 0.0274 5° PN 1-shot 69.52 90.26 47.94 0.0819 5-shot 87.36 94.51 72.94 0.0343 GPN 1-shot 70.09 82.77 43.82 0.0801 5-shot 91.99 97.25 76.08 0.0295 表 2 小样本条件下传统DCNN与GPN识别结果对比(%)
模型 1-shot 5-shot DCNN (Layer=6) 45.69 68.24 GPN (3°) 74.31 92.52 GPN (4°) 77.05 92.82 GPN (5°) 70.09 91.99 -
[1] BAI Xueru, ZHOU Xuening, ZHANG Feng, et al. Robust Pol-ISAR target recognition based on ST-MC-DCNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(12): 9912–9927. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2930112 [2] KANG Le, LUO Ying, ZHANG Qun, et al. 3-D scattering image sparse reconstruction via radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, To be published. [3] ZHANG Shuanghui, LIU Yongxiang, LI Xiang, et al. Enhancing ISAR image efficiently via convolutional reweighted l1 minimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 4291–4304. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3070442 [4] 杨磊, 夏亚波, 毛欣瑶, 等. 基于分层贝叶斯Lasso的稀疏ISAR成像算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 623–631. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200292YANG Lei, XIA Yabo, MAO Xinyao, et al. Sparse ISAR imaging algorithm based on Bayesian-lasso[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 623–631. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200292 [5] LEE S J, LEE M J, KIM K T, et al. Classification of ISAR images using variable cross-range resolutions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(5): 2291–2303. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2814211 [6] BENEDEK C and MARTORELLA M. Moving target analysis in ISAR image sequences with a multiframe marked point process model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(4): 2234–2246. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2258927 [7] PALADINI R, MARTORELLA M, and BERIZZI F. Classification of man-made targets via invariant coherency-matrix eigenvector decomposition of polarimetric SAR/ISAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2011, 49(8): 3022–3034. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2116121 [8] PARK S H, JUNG J H, KIM S H, et al. Efficient classification of ISAR images using 2D fourier transform and polar mapping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(3): 1726–1736. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2015.140184 [9] MARTORELLA M, GIUSTI E, CAPRIA A, et al. Automatic target recognition by means of polarimetric ISAR images and neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(11): 3786–3794. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2025371 [10] TOUMI A, HOUSSEINI A E, and KHENCHAF A. Aircrafts recognition using convolutional neurons network[C]. International Conference on Radar Systems, Belfast, UK, 2017: 1–4. [11] LIN Zhao, JI Kefeng, KANG Miao, et al. Deep convolutional highway unit network for SAR target classification with limited labeled training data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(7): 1091–1095. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2698213 [12] WANG Li, BAI Xueru, GONG Chen, et al. Hybrid inference network for few-shot SAR automatic target recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(11): 9257–9269. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3051024 [13] WANG Yaqing, YAO Quanming, KWOK J T, et al. Generalizing from a few examples: A survey on few-shot learning[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 2020, 53(3): 63. [14] KOCH G, ZEMEL R, SALAKHUTDINOV R, et al. Siamese neural networks for one-shot image recognition[C]. 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 2015: 1–27. [15] VINYALS O, BLUNDELL C, LILLICRAP T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]. 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing System, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 3637–3645. [16] SNELL J, SWERSKY K, and ZEMEL R S. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]. 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing System, Long Beach, USA, 2017: 4080–4090. [17] FORT S. Gaussian prototypical networks for few-shot learning on omniglot[C]. Second workshop on Bayesian Deep Learning (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, USA, 2017: 1–10. [18] GLOROT X, BORDES A, and BENGIO Y. Deep sparse rectifier neural networks[C]. Fourteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 2011: 315–323. [19] VAN DER MAATEN L and HINTON G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9(86): 2579–2605. [20] WILK M B and GNANADESIKAN R. Probability plotting methods for the analysis of data[J]. Biometrika, 1968, 55(1): 1–17. [21] KINGMA D P and BA J L. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representation, San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–15. -





 下载:
下载:


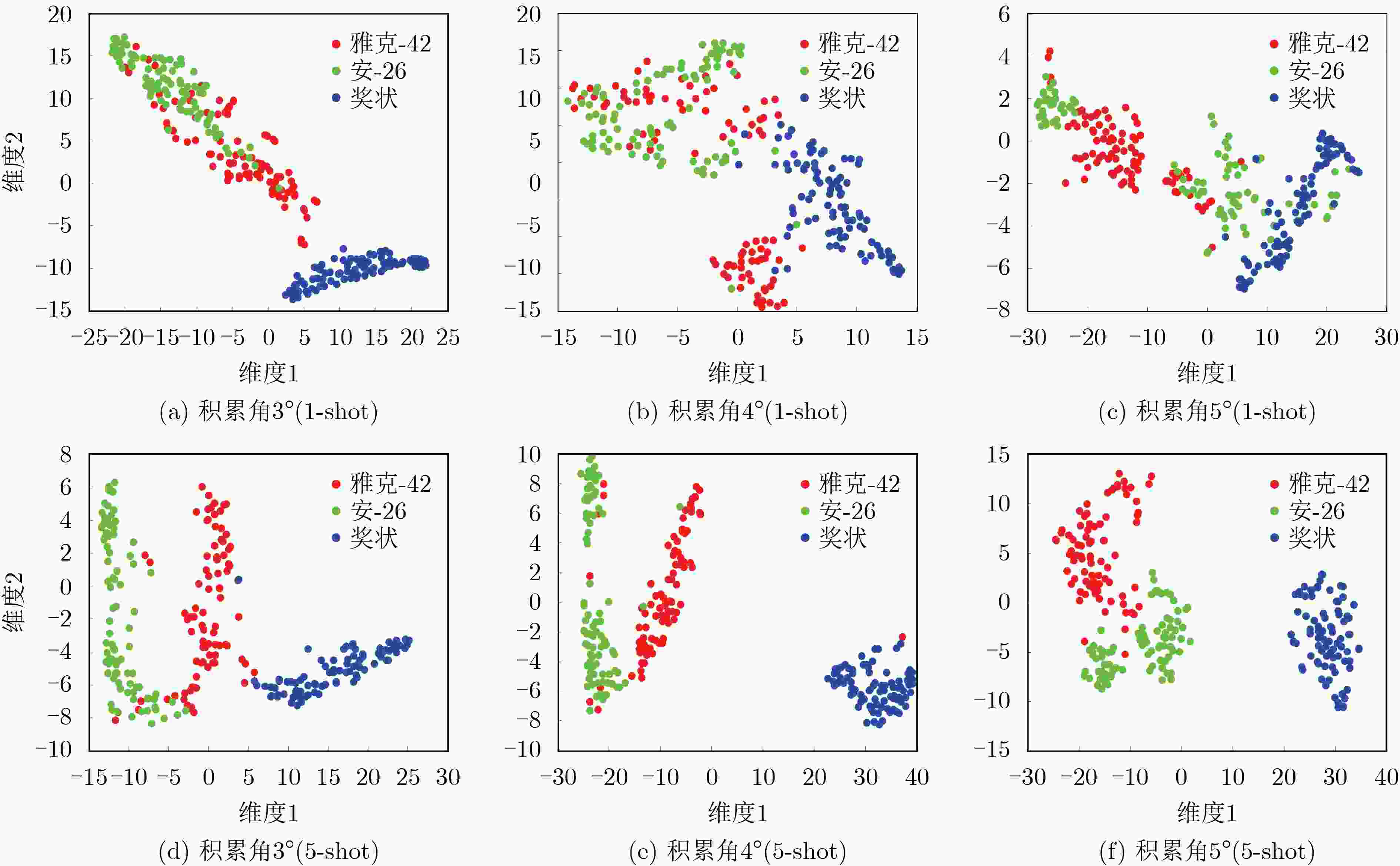
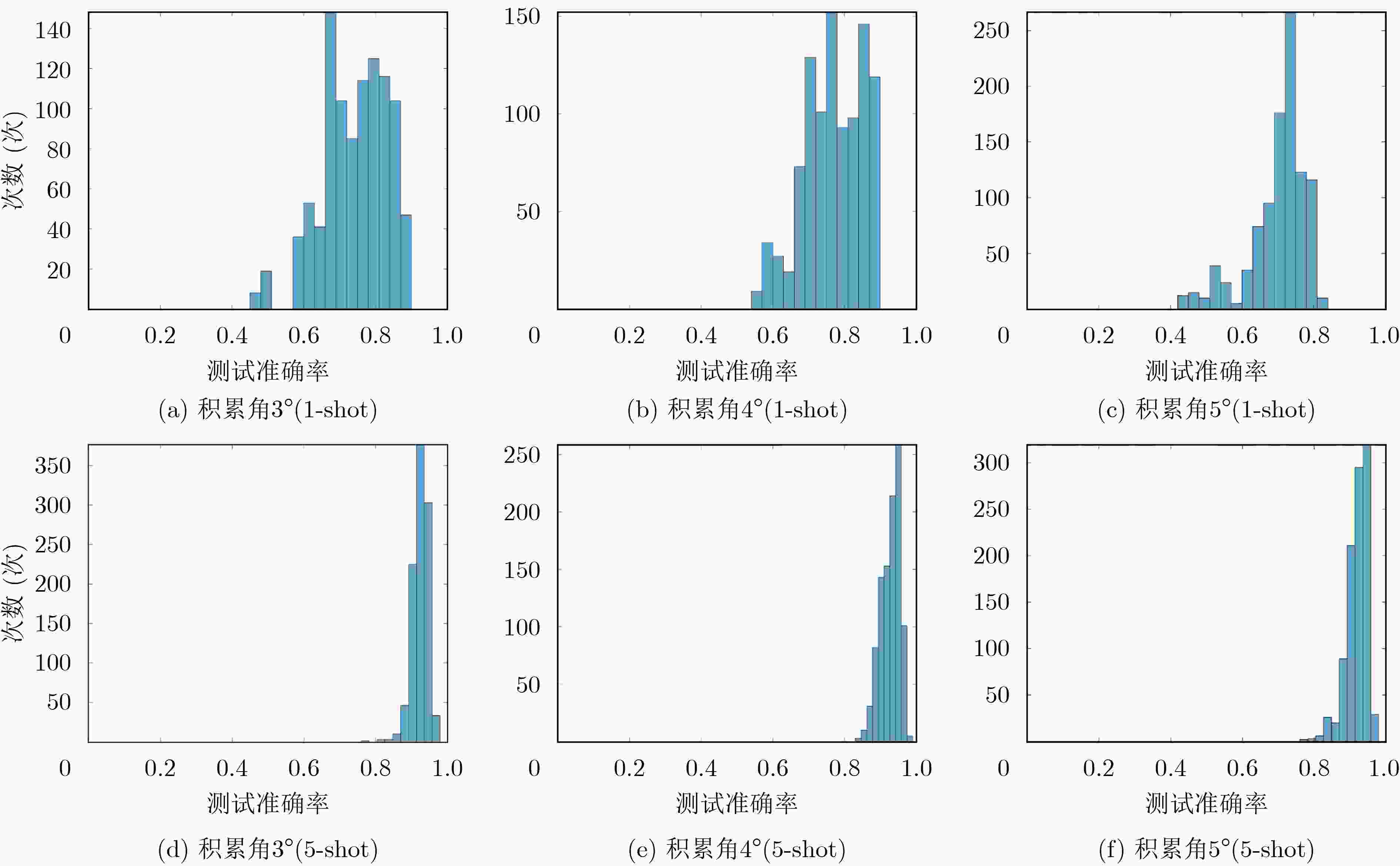


 下载:
下载:
