Robust Energy Efficiency Maximization Algorithm for Intelligent Reflecting Surface-aided Wireless Powered-communication Networks
-
摘要: 为了解决能量收集效率易受到障碍物阻挡和信道不确定性影响的问题,该文提出一种基于智能反射面(IRS)辅助的无线供电通信网络鲁棒能效(EE)最大化算法。首先,考虑最小收集能量、IRS相移、最小吞吐量等约束,基于有界信道不确定性,建立一个联合优化能量波束、相移、传输时间的多变量耦合非线性资源分配模型。然后,利用最坏准则、变量替换和S-Procedure等方法,将原非凸问题转换为确定性凸优化问题,同时,提出一种基于迭代的鲁棒能效最大化算法进行求解。仿真结果表明,与现有算法比较,该文算法具有较好的能效和鲁棒性。Abstract: To resolve the effect of channel uncertainties and low energy transfer efficiency caused by obstacles, a robust Energy Efficiency (EE) maximization algorithm for an Intelligent Reflecting Surface (IRS)-assisted Wireless-Powered Communication Network (WOCN) is proposed. Firstly, considering the constraint of the minimum energy harvesting, the constraint of the phase-shift, and the constraint of the minimum throughput, a multi-variable coupling nonlinear resource allocation model that jointly optimizing the energy beamforming, the phase shifts, and the transmission time is established based on the bounded channel uncertainties. Then, the original non-convex problem is transformed into a deterministic convex optimization problem by using the worst-case approach, the variable substitution and S-Procedure methods. At the same time, a robust EE maximization algorithm based on iteration is proposed to solve the problem. The simulation results show that the proposed algorithm has better EE and robustness by comparing it with the existing algorithms.
-
表 1 基于迭代的鲁棒能效最大化算法
初始化系统参数:$ M $, $ N $, $ K $, $ T $, $ P_{\text{B}}^{\text{C}} $, $ P_{\text{e}}^{\text{C}} $, $ p_k^{\text{C}} $, $ P_{\text{D}}^{\text{C}} $, $ {\bar {\boldsymbol{G}}_k} $, $ {\bar g_k} $, $ {\omega _k} $, $ {\sigma _k} $, $ R_k^{\min } $, $ \eta $, $ {P^{\max }} $, $ {q^{(0)}} $, $ {{\boldsymbol{v}}^{(0)}} $;设置收敛精度$ \varepsilon \ge 0 $,最大迭代次数$ {L_{\max }} $,
初始化$ l \ge 0 $;(1) While $ \left| {{q^{(l)}} - {q^{(l - 1)}}} \right| \ge \varepsilon $或$l \le {L_{\max } }$ do (2) 设置迭代次数$ l = l + 1 $; (3) 固定$ {{\boldsymbol{v}}^{(l - 1)}} $,根据式(18)计算$ \left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{W}}^{(l)}},t_0^{(l)},t_k^{(l)},p_k^{(l)}} \right\} $; (4) 固定$ \left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{W}}^{(l)}},t_0^{(l)},t_k^{(l)},p_k^{(l)}} \right\} $,根据式(20)计算$ {{\boldsymbol{V}}^{(l)}} $; (5) 特征值分解$ {{\boldsymbol{V}}^{(l)}} = {\boldsymbol{U}}{\boldsymbol{\varLambda}} {\boldsymbol{U}} $, $ {{\boldsymbol{v}}^{(l)}} = {\boldsymbol{U}}{{\boldsymbol{\varLambda}} ^{(1/2)}}{\boldsymbol{r}} $;
(6) 更新能效$ {q^{(l)}} = \frac{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{k = 1}^K {{t_k}{{\log }_2}} \left( {1 + \frac{{{p_k}{{\tilde g}_k}}}{{{\delta ^2}}}} \right)}}{{{t_0}(P_{\text{B}}^{\text{C}} + NP_{\text{e}}^{\text{C}}) + \displaystyle\sum\limits_{k = 1}^K {({t_0} + {t_k})} p_k^{\text{C}} + {t_0}{\text{Tr(}}{\boldsymbol{W}}{\text{)}} - \displaystyle\sum\limits_{k = 1}^K {{\chi _k}} + \displaystyle\sum\limits_{k = 1}^K {{t_k}{p_k}} + \displaystyle\sum\limits_{k = 1}^K {{t_k}P_{\text{D}}^{\text{C}}} }} $;(7) End While -
[1] 徐勇军, 刘子腱, 李国权, 等. 基于NOMA的无线携能D2D通信鲁棒能效优化算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1289–1297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200175XU Yongjun, LIU Zijian, LI Guoquan, et al. Robust energy efficiency optimization algorithm for NOMA-based D2D communication with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1289–1297. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200175 [2] XU Yongjun, GAO Zhengnian, WANG Zhengqiang, et al. RIS-enhanced WPCNs: Joint radio resource allocation and passive beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(8): 7980–7991. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3096603 [3] 李国权, 徐勇军, 陈前斌. 基于干扰效率多蜂窝异构无线网络最优基站选择及功率分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 957–964. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190419LI Guoquan, XU Yongjun, and CHEN Qianbin. Interference efficiency-based base station selection and power allocation algorithm for multi-cell heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 957–964. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190419 [4] XU Yongjun, GUI Guan, GACANIN H, et al. A survey on resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous networks: Current research, future trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 668–695. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3059896 [5] XIE Lifeng, XU Jie, and ZHANG Rui. Throughput maximization for UAV-enabled wireless powered communication networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 1690–1703. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2018.2875446 [6] DI Xiaofei, XIONG Ke, FAN Pingyi, et al. Optimal resource allocation in wireless powered communication networks with user cooperation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(12): 7936–7949. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2754494 [7] CHU Zheng, ZHOU Fuhui, ZHU Zhengyu, et al. Energy beamforming design and user cooperation for wireless powered communication networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2017, 6(6): 750–753. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2017.2739148 [8] WU Qingqing, TAO Meixia, NG D W K, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation for wireless powered communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(3): 2312–2327. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2502590 [9] BOSHKOVSKA E, NG D W K, ZLATANOV N, et al. Robust resource allocation for MIMO wireless powered communication networks based on a non-linear EH model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2017, 65(5): 1984–1999. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2017.2664860 [10] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107 [11] GONG Shimin, LU Xiao, HOANG D T, et al. Toward smart wireless communications via intelligent reflecting surfaces: A contemporary survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(4): 2283–2314. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2020.3004197 [12] WU Qingqing, ZHOU Xiaobo, and SCHOBER R. IRS-assisted wireless powered NOMA: Do we really need different phase shifts in DL and UL?[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(7): 1493–1497. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3072502 [13] ZHENG Yuan, BI Suzhi, ZHANG Yingjun, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced user cooperation in wireless powered communication networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(6): 901–905. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2974721 [14] ZHENG Yuan, BI Suzhi, ZHANG Y J A, et al. Joint beamforming and power control for throughput maximization in IRS-assisted MISO WPCNs[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(10): 8399–8410. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3045703 [15] HUANG Chongwen, ZAPPONE A, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(8): 4157–4170. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922609 [16] XU Yongjun, ZHAO Xiaohui, and LIANG Yingchang. Robust power control and beamforming in cognitive radio networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(4): 1834–1857. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2425040 [17] XU Yongjun, LI Guoquan, YANG Yang, et al. Robust resource allocation and power splitting in SWIPT enabled heterogeneous networks: A robust minimax approach[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(6): 10799–10811. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2941897 [18] XU Yongjun, XIE Hao, LIANG Chengchao, et al. Robust secure energy efficiency optimization in SWIPT-aided heterogeneous networks with a non-linear energy harvesting model[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 19(8): 14908–14919. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3072965 -





 下载:
下载:
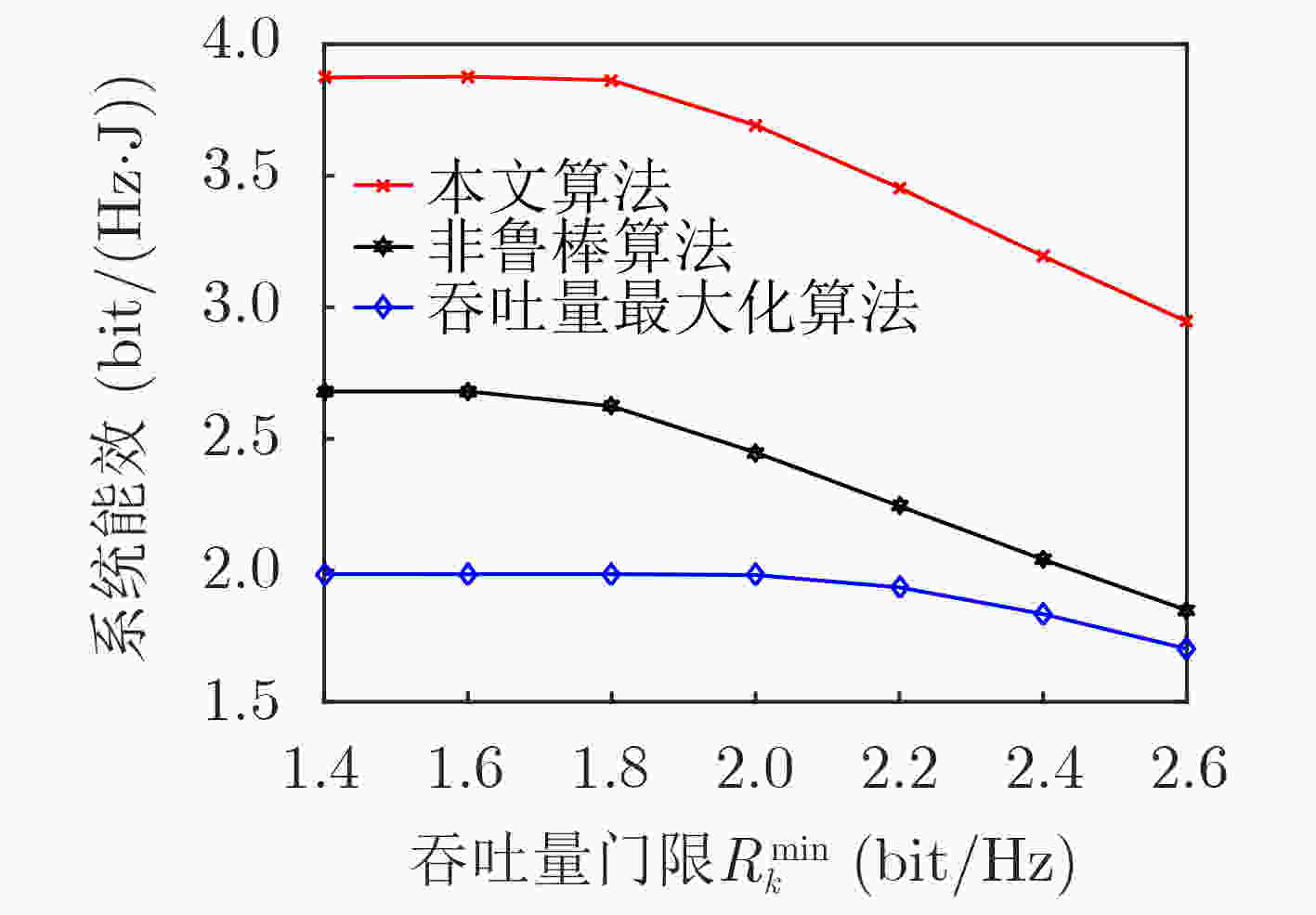
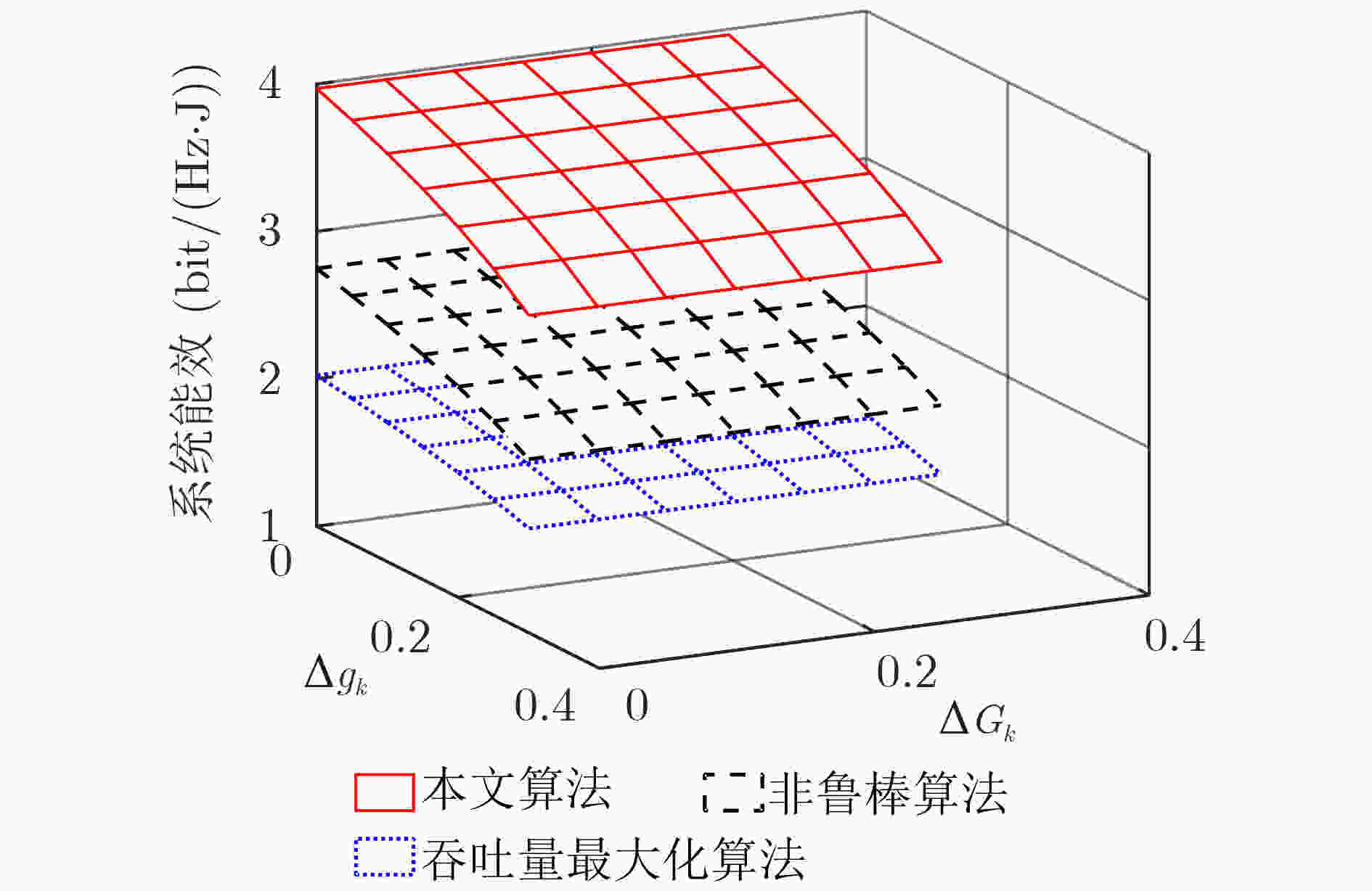
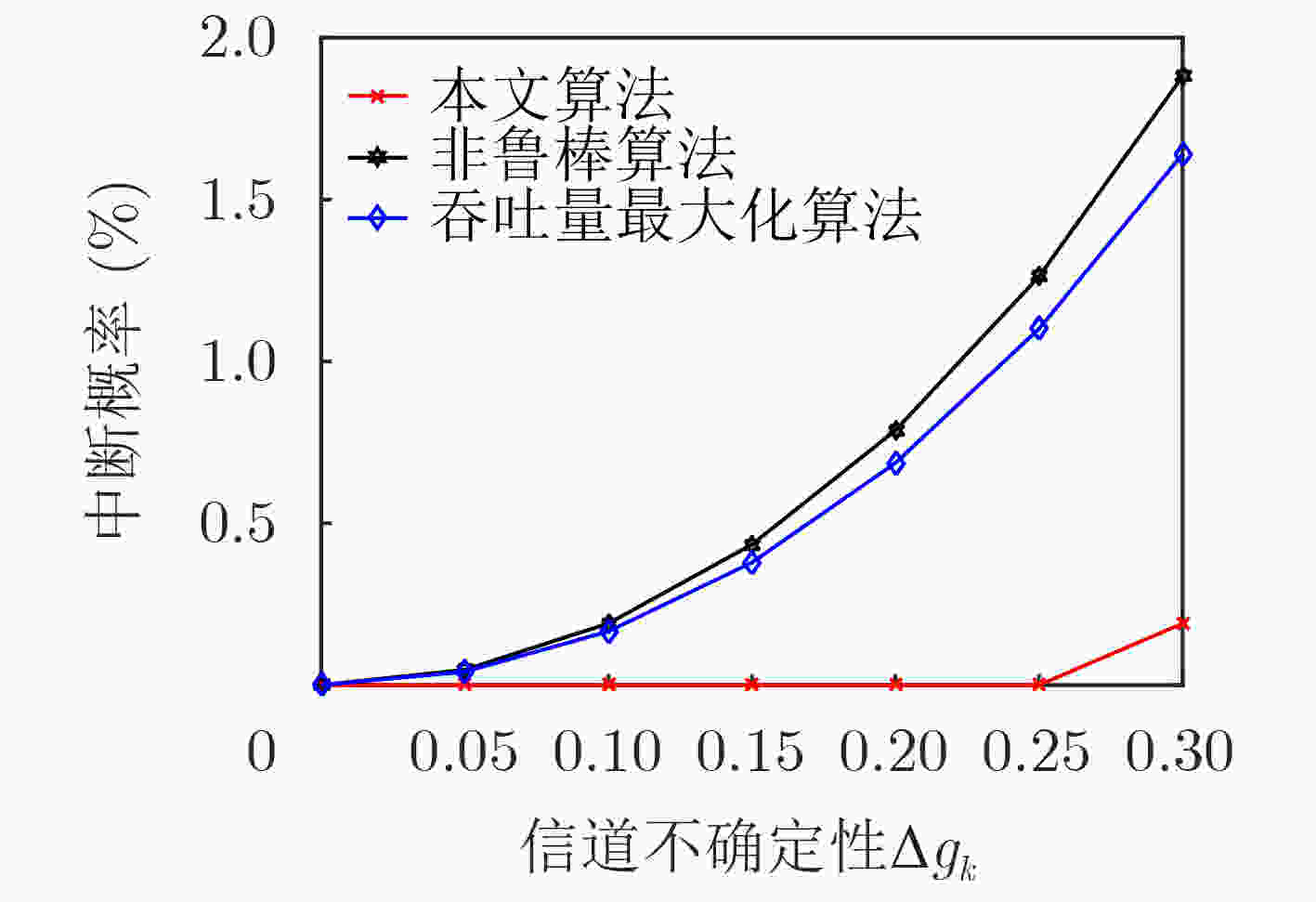


 下载:
下载:
